Child–Adult Transition in Sarcoidosis: A Series of 52 Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Patients
2.2. Collected Data
2.3. Statistics
2.4. Legal Dispositions
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
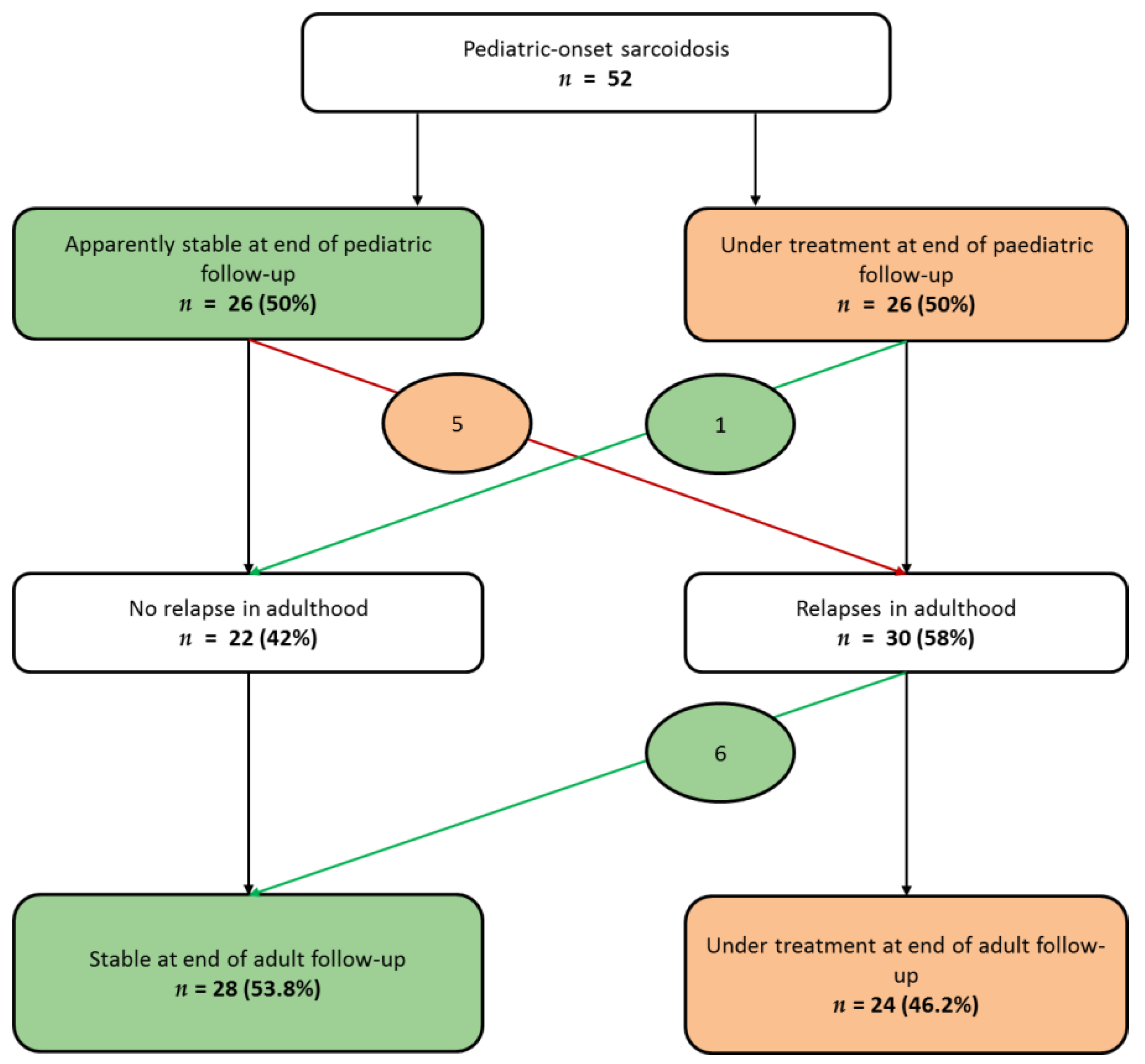
3.2. Evolution from Childhood to Adulthood
3.2.1. Disease Activity During Follow-Up
3.2.2. Organ Involvement
3.2.3. Relapse During Follow up
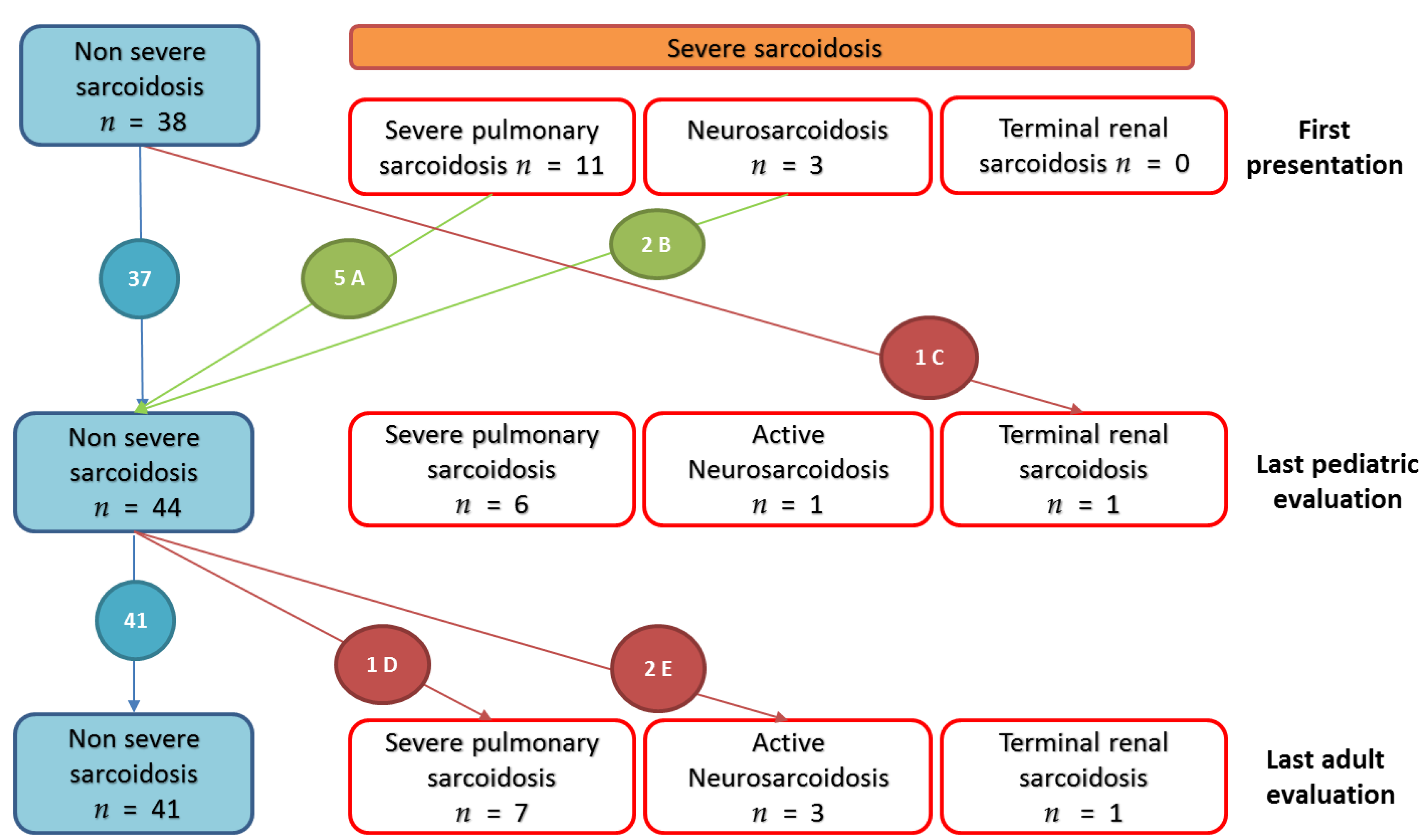
3.2.4. Evolution of Severe Sarcoidosis during Follow-Up
3.3. Treatment and Adverse Events
3.4. Prognostic Factors for Severe Sarcoidosis in Adulthood
4. Discussion
4.1. Pediatric Sarcoidosis: A Multiorganic Disease
4.2. Unexpected Tolerance of Intensive and Prolonged Treatment
4.3. Severe Pediatric-Onset Sarcoidosis at Adulthood
4.4. Risk Factors for a Severe Evolution of the Disease
4.5. Extreme Severe Evolution May Be Underestimated
4.6. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costabel, U.; Hunninghake, G.W. ATS/ERS/WASOG statement on sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Statement Committee. American Thoracic Society. European Respiratory Society. World Association for Sarcoidosis and Other Granulomatous Disorders. Eur. Respir. J. 1999, 14, 735–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannuzzi, M.C.; Rybicki, B.A.; Teirstein, A.S. Sarcoidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2153–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito-Zerón, P.; Kostov, B.; Superville, D.; Baughman, R.P.; Ramos-Casals, M. Autoimmune Big Data Study Group Geoepidemiological big data approach to sarcoidosis: Geographical and ethnic determinants. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2019, 37, 1052–1064. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sawahata, M.; Sugiyama, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Nakayama, M.; Mato, N.; Yamasawa, H.; Bando, M. Age-related and historical changes in the clinical characteristics of sarcoidosis in Japan. Respir. Med. 2015, 109, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchemann, B.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; de Naurois, C.J.; Sanyal, S.; Brillet, P.-Y.; Brauner, M.; Kambouchner, M.; Huynh, S.; Naccache, J.M.; Borie, R.; et al. Prevalence and incidence of interstitial lung diseases in a multi-ethnic county of Greater Paris. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, N.; Marcelo, P.; Houdouin, V.; Epaud, R.; de Blic, J.; Valeyre, D.; Houzel, A.; Busson, P.-F.; Corvol, H.; Deschildre, A.; et al. Lung sarcoidosis in children: Update on disease expression and management. Thorax 2015, 70, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, R.P.; Teirstein, A.S.; Judson, M.A.; Rossman, M.D.; Yeager, H., Jr.; Bresnitz, E.A.; De Palo, L.; Hunninghake, G.; Iannuzzi, M.C.; Johns, C.J.; et al. Clinical characteristics of patients in a case control study of sarcoidosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 1885–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, A.K.; Gedalia, A. Sarcoidosis in children. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. 2000, 30, 149–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, A.K.; Gedalia, A. Childhood sarcoidosis: A rare but fascinating disorder. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2008, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A.L.; Milman, N.; Byg, K.E. Childhood sarcoidosis in Denmark 1979-1994: Incidence, clinical features and laboratory results at presentation in 48 children. Acta Paediatr. 2004, 93, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milman, N.; Svendsen, C.B.; Hoffmann, A.L. Health-related quality of life in adult survivors of childhood sarcoidosis. Respir. Med. 2009, 103, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gedalia, A.; Khan, T.A.; Shetty, A.K.; Dimitriades, V.R.; Espinoza, L.R. Childhood sarcoidosis: Louisiana experience. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 1879–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, N.; Sileo, C.; Calender, A.; Pacheco, Y.; Rosental, P.-A.; Cavalin, C.; Macchi, O.; Valeyre, D.; Clement, A.; French Sarcoidosis Group (GSF); et al. Paediatric sarcoidosis. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2019, 29, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, N.; Taam, R.A.; Epaud, R.; Delacourt, C.; Deschildre, A.; Reix, P.; Chiron, R.; de Pontbriand, U.; Brouard, J.; Fayon, M.; et al. A national internet-linked based database for pediatric interstitial lung diseases: The French network. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2012, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, S.L.; Wells, A.U.; Sverzellati, N.; Keir, G.J.; Calandriello, L.; Antoniou, K.M.; Copley, S.J.; Devaraj, A.; Maher, T.M.; Renzoni, E.; et al. An integrated clinicoradiological staging system for pulmonary sarcoidosis: A case-cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marruchella, A.; Tondini, M. Reliability of bronchoalveolar lavage in the routine clinical assessment of patients with sarcoidosis. A retrospective analysis. Panminerva Med. 2002, 44, 257–260. [Google Scholar]
- Mañá, J.; Rubio-Rivas, M.; Villalba, N.; Marcoval, J.; Iriarte, A.; Molina-Molina, M.; Llatjos, R.; García, O.; Martínez-Yélamos, S.; Vicens-Zygmunt, V.; et al. Multidisciplinary approach and long-term follow-up in a series of 640 consecutive patients with sarcoidosis: Cohort study of a 40-year clinical experience at a tertiary referral center in Barcelona, Spain. Medicine 2017, 96, e7595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzato, G.; Montemurro, L.; Colombo, P. The late follow-up of chronic sarcoid patients previously treated with corticosteroids. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 1998, 15, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Kurland, G.; Deterding, R.R.; Hagood, J.S.; Young, L.R.; Brody, A.S.; Castile, R.G.; Dell, S.; Fan, L.L.; Hamvas, A.; Hilman, B.C.; et al. An Official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice Guideline: Classification, Evaluation, and Management of Childhood Interstitial Lung Disease in Infancy. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 376–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, N.; Borensztajn, K.; Clement, A. Genetic causes and clinical management of pediatric interstitial lung diseases. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, A.; Cunningham, S.; de Blic, J.; Barbato, A.; Clement, A.; Epaud, R.; Hengst, M.; Kiper, N.; Nicholson, A.G.; Wetzke, M.; et al. European protocols for the diagnosis and initial treatment of interstitial lung disease in children. Thorax 2015, 70, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, R.P.; Nagai, S.; Balter, M.; Costabel, U.; Drent, M.; du Bois, R.; Grutters, J.C.; Judson, M.A.; Lambiri, I.; Lower, E.E.; et al. Defining the clinical outcome status (COS) in sarcoidosis: Results of WASOG Task Force. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2011, 28, 56–64. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, N.A.; Donatelli, C.V.; Tonelli, A.R.; Wiesen, J.; Ribeiro Neto, M.L.; Sahoo, D.; Culver, D.A. Toxicity risk from glucocorticoids in sarcoidosis patients. Respir. Med. 2017, 132, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnolo, P.; Rossi, G.; Trisolini, R.; Sverzellati, N.; Baughman, R.P.; Wells, A.U. Pulmonary sarcoidosis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossier, C.; Delbet, J.-D.; Boyer, O.; Daoud, P.; Mesples, B.; Pellegrino, B.; See, H.; Benoist, G.; Chace, A.; Larakeb, A.; et al. Five-year outcome of children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: The NEPHROVIR population-based cohort study. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 34, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bast, T.; Richter, S.; Ebinger, F.; Rating, D.; Wiemer-Kruel, A.; Schubert-Bast, S. Efficacy and tolerability of methylprednisolone pulse therapy in childhood epilepsies other than infantile spasms. Neuropediatrics 2014, 45, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judson, M.A.; Chaudhry, H.; Louis, A.; Lee, K.; Yucel, R. The effect of corticosteroids on quality of life in a sarcoidosis clinic: The results of a propensity analysis. Respir. Med. 2015, 109, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, G.H.; Young, L.R.; Deterding, R.R.; Fan, L.L.; Dell, S.D.; Bean, J.A.; Brody, A.S.; Nogee, L.M.; Trapnell, B.C.; Langston, C.; et al. Diffuse lung disease in young children: Application of a novel classification scheme. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, A.; Tran-Dang, M.-A.; Bush, A.; Nicholson, A.G. Diffuse lung disease in infancy and childhood: Expanding the chILD classification. Histopathology 2013, 63, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dishop, M.K. Paediatric interstitial lung disease: Classification and definitions. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2011, 12, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sileo, C.; Epaud, R.; Mahloul, M.; Beydon, N.; Elia, D.; Clement, A.; Le Pointe, H.D. Sarcoidosis in children: HRCT findings and correlation with pulmonary function tests. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2014, 49, 1223–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, J.M.; Johnson, R.E. Course and prognosis of sarcoidosis in a nonreferral setting. Analysis of 86 patients observed for 10 years. Am. J. Med. 1985, 78, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, A.; Brillet, P.-Y.; Letoumelin, P.; Girard, F.; Brauner, M.; Uzunhan, Y.; Naccache, J.-M.; Valeyre, D.; Nunes, H. Stage IV sarcoidosis: Comparison of survival with the general population and causes of death. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38, 1368–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkil, G.; Lower, E.E.; Baughman, R.P. Predictors of Mortality in Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. Chest 2018, 153, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthropométrie, Adultes: Tableaux de Distribution ENNS. 2020. Available online: https://www.santepubliquefrance.fr/determinants-de-sante/nutrition-et-activite-physique/articles/enns-etude-nationale-nutrition-sante/anthropometrie-adultes-tableaux-de-distribution-enns (accessed on 20 May 2020).


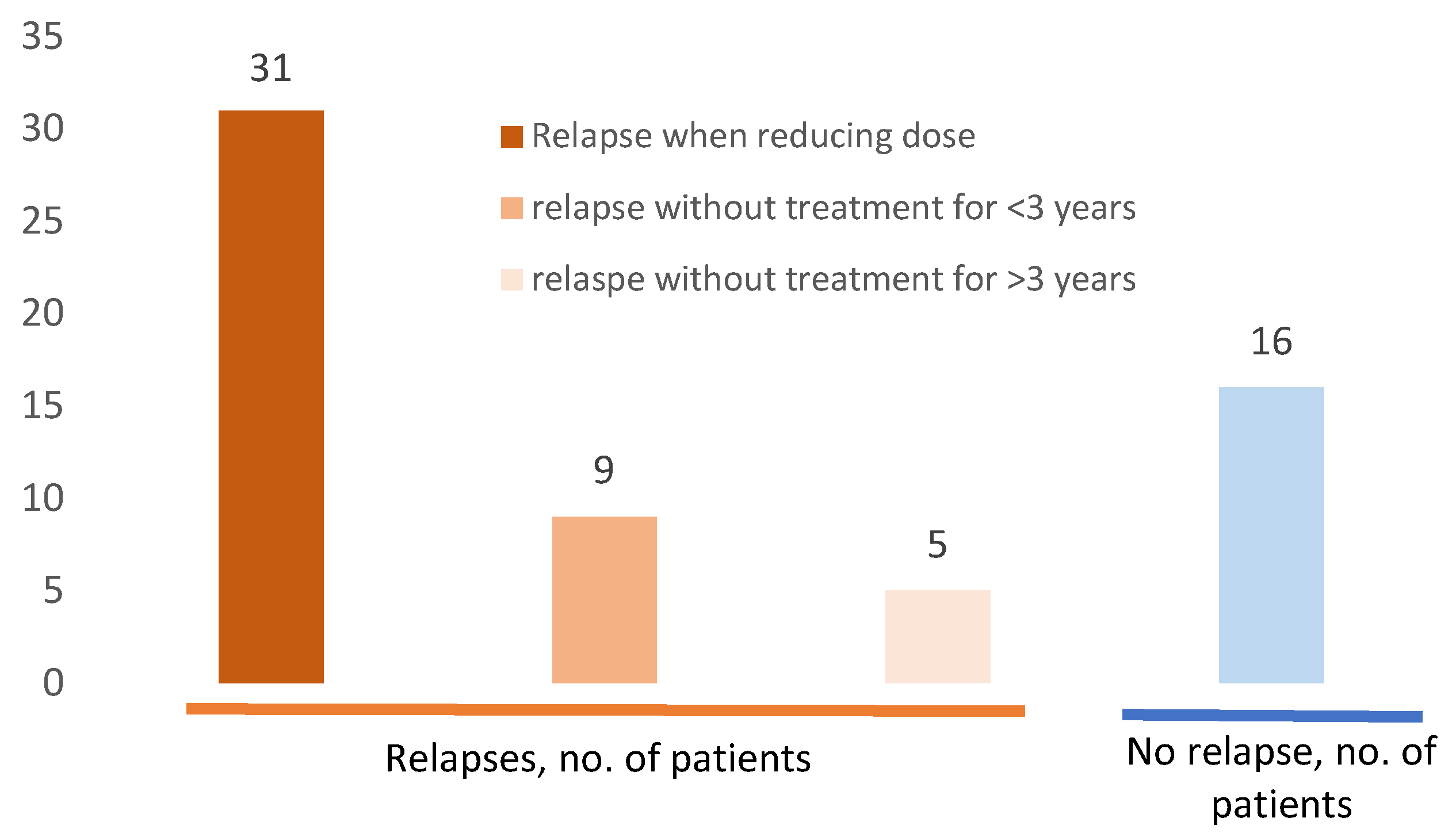
| Clinical Characteristics | Study Population (n = 52) |
|---|---|
| Female, n (%) | 29 (56%) |
| Ancestry, n (%) | |
| European | 5 (9.6%) |
| Sub-Saharan Africa/Caribbean | 37 (71.15%) |
| North African | 9 (17.3%) |
| India | 1 (1.9%) |
| Age at diagnosis, in years, mean ± SD (rv) | 12.03 ± 2.715 (5; 15) |
| Age at the last evaluation, in years, median (Q1–Q3) | 23.6 (19.25–26.48) |
| Length of follow-up, in years, median (Q1–Q3) | 11.48 (6.48;14.5) |
| Delayed diagnosed comorbidity, n (%) | |
| Crohn disease | 2 (3.8%) |
| Acquired hemophilia | 1 (1.9%) |
| Immune thrombocytopenia | 1 (1.9%) |
| Hemochromatosis | 1 (1.9%) |
| Idiopathic hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis | 1 (1.9%) |
| First Presentation * | Adulthood ** | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organ involvement, median, (Q1–Q3) | 4 (2.7–4) | 1.5 (1–2) | <0.0001 1 |
| Lung, n (%) | 27 (90%) | 14 (47%) | 0.0006 2 |
| Eye, n (%) | 15 (50%) | 11 (36.6%) | ns 2 |
| Kidney, n (%) | 4 (13.3%) | 2 (6.6%) | ns 2 |
| Liver, n (%) | 17 (56.3%) | 7 (23.3%) | 0.017 2 |
| Peripheral lymph node, n (%) | 13 (43%) | 3 (10%) | 0.007 2 |
| Joints, n (%) | 5 (17%) | 1 (3.3%) | ns 2 |
| Skin, n (%) | 5 (17%) | 3 (10%) | ns 2 |
| Spleen, n (%) | 6 (20%) | 1 (3.3%) | ns 2 |
| Central neurologic, n (%) | 3 (10%) | 3(10%) | ns 2 |
| General signs, n (%) | 11 (36.7%) | 2 (6.6%) | <0.05 2 |
| Fever, n (%) | 8 (26%) | 0 (0%) | 0.01 2 |
| Fatigue, n (%) | 11 (36%) | 2 (6.6%) | <0.002 2 |
| Study Population (n = 52) | |
|---|---|
| Treatment during pediatric and adult follow-up | |
| Corticosteroids therapy, n (%) | 49 (94.2%) |
| Cumulative dose, in mg, median (Q1–Q3) | 17,900 (9900-35,200) |
| Duration of treatment, in years, median (Q1–Q3) | 5 (1.38-10.3) |
| Intravenous pulse, n (%) | 25 (48.1%) |
| Other immunosuppressive treatment, n (%) | 25 (48.1%) |
| Duration of treatment, in years, median (Q1–Q3) | 3 (1.1-5) |
| Reason for the treatment | |
| Corticosteroid dependence | 11 (21.1%) |
| Resistance to corticosteroid therapy | 9 (17.3%) |
| Biotherapy | 5 (9.6%) |
| Adverse events of treatment, n patients (%) | 18 (35.3%) |
| Obesity (BMI > 30 kg/m2) | 8 (15.4%) |
| Overweight (BMI > 25 kg/m2) | 4 (7.7%) |
| Insulin-dependent diabetes | 2 (3.8%) |
| Arterial hypertension | 1 (1.9%) |
| Dyslipidemia | 1 (1.9%) |
| Chronic glaucoma | 2 (3.8%) |
| Posterior cataract | 3 (5.8%) |
| Depression | 2 (3.8%) |
| Septic shock | 1 (1.9%) |
| Pneumonia | 1 (1.9%) |
| Corticotrope deficiency 1 | 1 (4%) |
| Reversible amenorrhea 2 | 1 (1.9%) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chauveau, S.; Jeny, F.; Montagne, M.-E.; Abou Taam, R.; Houdouin, V.; Meinzer, U.; Delacourt, C.; Epaud, R.; Cohen Aubart, F.; Chapelon-Abric, C.; et al. Child–Adult Transition in Sarcoidosis: A Series of 52 Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072097
Chauveau S, Jeny F, Montagne M-E, Abou Taam R, Houdouin V, Meinzer U, Delacourt C, Epaud R, Cohen Aubart F, Chapelon-Abric C, et al. Child–Adult Transition in Sarcoidosis: A Series of 52 Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(7):2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072097
Chicago/Turabian StyleChauveau, Simon, Florence Jeny, Marie-Emeline Montagne, Rola Abou Taam, Véronique Houdouin, Ulrich Meinzer, Christophe Delacourt, Ralph Epaud, Fleur Cohen Aubart, Catherine Chapelon-Abric, and et al. 2020. "Child–Adult Transition in Sarcoidosis: A Series of 52 Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 7: 2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072097
APA StyleChauveau, S., Jeny, F., Montagne, M.-E., Abou Taam, R., Houdouin, V., Meinzer, U., Delacourt, C., Epaud, R., Cohen Aubart, F., Chapelon-Abric, C., Israël-Biet, D., Juvin, K., Dossier, A., Bodaghi, B., Prévot, G., Naccache, J.-M., Mattioni, S., Deschildre, A., Brouard, J., ... for the French Sarcoidosis Group (GSF). (2020). Child–Adult Transition in Sarcoidosis: A Series of 52 Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(7), 2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072097





