Impulsivity, Emotional Dysregulation and Executive Function Deficits Could Be Associated with Alcohol and Drug Abuse in Eating Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure and Assessment
2.2.1. Psychopathological/Personality Measures
2.2.2. Neuropsychological Measures
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Sample
3.2. Prevalence of A/DA in ED Patients
3.3. Comparison of the Clinical and Neuropsychological Profile of Patients with and without A/DA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bahji, A.; Mazhar, M.N.; Hudson, C.C.; Nadkarni, P.; MacNeil, B.A.; Hawken, E. Prevalence of substance use disorder comorbidity among individuals with eating disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 273, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, J.I.; Hiripi, E.; Pope, H.G.; Kessler, R.C. The Prevalence and Correlates of Eating Disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 61, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouladi, F.; Mitchell, J.E.; Crosby, R.D.; Engel, S.G.; Crow, S.; Hill, L.; Le Grange, D.; Powers, P.; Steffen, K.J. Prevalence of Alcohol and Other Substance Use in Patients with Eating Disorders. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2015, 23, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, A.B.; Pryor, T. The Complex Relationship between Eating Disorders and Substance Use Disorders. In Clinical Handbook of Complex and Atypical Eating Disorders; Anderson, L.K., Murray, S.B., Kaye, W.H., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 60–78. [Google Scholar]
- Harrop, E.N.; Marlatt, G.A. The comorbidity of substance use disorders and eating disorders in women: Prevalence, etiology, and treatment. Addict. Behav. 2010, 35, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munn-Chernoff, M.A.; Baker, J.H. A Primer on the Genetics of Comorbid Eating Disorders and Substance Use Disorders. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2016, 24, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munn-Chernoff, M.A.; Johnson, E.C.; Chou, Y.L.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Thornton, L.M.; Walters, R.K.; Yilmaz, Z.; Baker, J.H.; Hübel, C.; Gordon, S.; et al. Shared genetic risk between eating disorder- and substance-use-related phenotypes: Evidence from genome-wide association studies. Addict. Biol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, I.; Pinheiro, A.P.; Bulik, C.; Jiménez-Murcia, S.; Granero, R.; Penelo, E.; Masuet, C.; Agüera, Z.; Fernández-Aranda, F. Lifetime substance abuse, family history of alcohol abuse/dependence and novelty seeking in eating disorders: Comparison study of eating disorder subgroups. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2009, 63, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Mondragón, S.; Adan, A. Personality in male patients with substance use disorder and/or severe mental illness. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 228, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingo, T.; Nesil, T.; Choi, J.S.; Li, M.D. Novelty Seeking and Drug Addiction in Humans and Animals: From Behavior to Molecules. J. Neuroimmune Pharmcol. 2016, 11, 456–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilenfeld, L.R.; Kaye, W.H.; Greeno, C.G.; Merikangas, K.R.; Plotnicov, K.; Pollice, C.; Rao, R.; Strober, M.; Bulik, C.M.; Nagy, L. Psychiatric disorders in women with bulimia nervosa and their first-degree relatives: Effects of comorbid substance dependence. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1997, 22, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, E.; Hall, K.; Moulding, R.; Bryce, S.; Mildred, H.; Staiger, P.K. Emotion regulation as a transdiagnostic treatment construct across anxiety, depression, substance, eating and borderline personality disorders: A systematic review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2017, 57, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldao, A.; Nolen-Hoeksema, S. Specificity of cognitive emotion regulation strategies: A transdiagnostic examination. Behav. Res. Ther. 2010, 48, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Hartmann, M.; Skunde, M.; Herzog, W.; Friederich, H.-C. Inhibitory Control in Bulimic-Type Eating Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavagnino, L.; Arnone, D.; Cao, B.; Soares, J.C.; Selvaraj, S. Inhibitory control in obesity and binge eating disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis of neurocognitive and neuroimaging studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 68, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.E.; Tchanturia, K.; Treasure, J.L. Overlapping neurocognitive inefficiencies in anorexia nervosa: A preliminary investigation of women with both poor set-shifting and weak central coherence. Eat. Weight Disord. Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2016, 21, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aloi, M.; Rania, M.; Caroleo, M.; Bruni, A.; Palmieri, A.; Cauteruccio, M.A.; De Fazio, P.; Segura-García, C. Decision making, central coherence and set-shifting: A comparison between Binge Eating Disorder, Anorexia Nervosa and Healthy Controls. BMC Psychiatry 2015, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagundo, A.B.; de la Torre, R.; Jiménez-Murcia, S.; Agüera, Z.; Granero, R.; Tárrega, S.; Botella, C.; Baños, R.; Fernández-Real, J.M.; Rodríguez, R.; et al. Executive Functions Profile in Extreme Eating/Weight Conditions: From Anorexia Nervosa to Obesity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, S.; Gorwood, P.; Jollant, F.; Van den Eynde, F.; Courtet, P.; Richard-Devantoy, S. Impaired decision-making in symptomatic anorexia and bulimia nervosa patients: A meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 2015, 45, 3377–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luijten, M.; Machielsen, M.W.J.; Veltman, D.J.; Hester, R.; de Haan, L.; Franken, I.H.A. Systematic review of ERP and fMRI studies investigating inhibitory control and error processing in people with substance dependence and behavioural addictions. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2014, 39, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.N.; Woods, S.P. Neuropsychological Aspects of Substance Use Disorders: Evidence-Based Perspectives; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; ISBN 9780199930838. [Google Scholar]
- Ersche, K.D.; Turton, A.J.; Chamberlain, S.R.; Müller, U.; Bullmore, E.T.; Robbins, T.W. Cognitive dysfunction and anxious-impulsive personality traits are endophenotypes for drug dependence. Am. J. Psychiatry 2012, 169, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Serrano, M.J.; Pérez-García, M.; Verdejo-García, A. What are the specific vs. generalized effects of drugs of abuse on neuropsychological performance? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2011, 35, 377–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, B.L.; Minassian, A.; Perry, W. Effect of methamphetamine dependence on everyday functional ability. Addict. Behav. 2010, 35, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersche, K.D.; Sahakian, B.J. The neuropsychology of amphetamine and opiate dependence: Implications for treatment. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2007, 17, 317–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Serrano, M.J.; Perales, J.C.; Moreno-López, L.; Pérez-García, M.; Verdejo-García, A. Neuropsychological profiling of impulsivity and compulsivity in cocaine dependent individuals. Psychopharmacology 2012, 219, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezak, M.D.; Howieson, D.B.; Bigler, E.D.; Tranel, D. Neuropsychological Assessment, 5th ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; ISBN 9780195395525. [Google Scholar]
- First, M.; Williams, J.; Karg, R.; Spitzer, R. Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5 Disorders, Clinician Version (SCID-5-CV); American Psychiatric Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cloninger, C.R.; Przybeck, T.R.; Svrakic, D.M.; Wetzel, R.D. The Temperament and Character Inventory (TCI): A Guide to Its Development and Use; Center for Psychobiology of Personality, Washington University: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1994; ISBN 0-9642917-03. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez-Zotes, J.A.; Bayón, C.; Montserrat, C.; Valero, J.; Labad, A.; Cloninger, C.; Fernández-Aranda, F. Temperament and Character Inventory-Revised (TCI-R). Standardization and normative data in a general population sample. Actas Esp Psiquiatr 2004, 32, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Derogatis, L.R. Symptom Checklist-90-R (SCL-90-R): Administration, scoring, and procedures manual, 3rd ed.; NCS Pearson: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 1994; ISBN 2090-6684 (Print) 2090-6692. [Google Scholar]
- González de Rivera, J.L.; de las Cuevas, C.; Rodríguez-Abuín, M.; y Rodríguez-Pulido, F. SCL-90-R. Cuestionario de 90 Síntomas. Manual; TEA Ediciones: Madrid, Spain, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Garner, D.M. Eating Disorder Inventory-2; Psychological Assessment Resources: Odessa, Ukraine, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Garner, D.M. Inventario de Trastornos de la Conducta Alimentaria (EDI-2)-Manual; TEA: Madrid, Spain, 1998.
- Golden, C.J. Stroop colour and word test. Age 1978, 15, 90. [Google Scholar]
- Golden, C.J. Stroop: Test de Colores y Palabras: Manual; TEA Ediciones: Madrid, Spain, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Heaton, R.K. PAR Staff Wisconsin Card Sorting TestTM: Computer Version 4, Research Edition; Psychological Assessment Resources: Lutz, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bechara, A.; Damasio, A.R.; Damasio, H.; Anderson, S.W. Insensitivity to future consequences following damage to human prefrontal cortex. Cognition 1994, 50, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisinger, A.; Magi, A.; Gyurkovics, M.; Szabo, E.; Demetrovics, Z.; Kokonyei, G. Iowa Gambling Task: Illustration of a behavioral measurement. Neuropsychopharmacol. Hung. 2016, 18, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- StataCorp Stata Statistical Software: Release 16; StataCorp LLC.: College Station, TX, USA, 2019.
- Kelley, K.; Preacher, K.J. On effect size. Psychol. Methods 2012, 17, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for Behavioural Sciences; Lawrence Earlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1998; ISBN 0805802835. [Google Scholar]
- Finner, H. On a Monotonicity Problem in Step-Down Multiple Test Procedures. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1993, 88, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Root, T.L.; Pinheiro, A.P.; Thornton, L.; Strober, M.; Fernandez-Aranda, F.; Brandt, H.; Crawford, S.; Fichter, M.M.; Halmi, K.A.; Johnson, C.; et al. Substance use disorders in women with anorexia nervosa. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2010, 43, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongers, P.; Jansen, A.; Houben, K.; Roefs, A. Happy eating: The single target implicit association test predicts overeating after positive emotions. Eat. Behav. 2013, 14, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leehr, E.J.; Krohmer, K.; Schag, K.; Dresler, T.; Zipfel, S.; Giel, K.E. Emotion regulation model in binge eating disorder and obesity-a systematic review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 49, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassino, S.; Pierò, A.; Gramaglia, C.; Abbate-Daga, G. Clinical, psychopathological and personality correlates of interoceptive awareness in anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa and obesity. Psychopathology 2004, 37, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasin, D.; Katz, H. Somatoform and substance use disorders. Psychosom. Med. 2007, 69, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanner, R. Substance Abuse, Somatization, and Personality Disorders. In Emergency Neurology; Roos, K.L., Ed.; Elseiver: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 375–384. ISBN 9780387885858. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Aranda, F.; Jiménez-Murcia, S.; Álvarez-Moya, E.M.; Granero, R.; Vallejo, J.; Bulik, C.M. Impulse control disorders in eating disorders: Clinical and therapeutic implications. Compr. Psychiatry 2006, 47, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Murcia, S.; Granero, R.; Moragas, L.; Steiger, H.; Israel, M.; Aymamí, N.; Gómez-Peña, M.; Sauchelli, S.; Agüera, Z.; Sánchez, I.; et al. Differences and similarities between bulimia nervosa, compulsive buying and gambling disorder. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2015, 23, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.E. Impulse control disorders, a clinician’s guide to understanding and treating behavi oral addictions. Psicoter. Cogn. E Comport. 2011, 17, 130–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, L.; Odlaug, B.L.; Grant, J.E. Impulse control disorders: Updated review of clinical characteristics and pharmacological management. Front. Psychiatry 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schag, K.; Schönleber, J.; Teufel, M.; Zipfel, S.; Giel, K.E. Food-related impulsivity in obesity and Binge Eating Disorder-a systematic review. Obes. Rev. 2013, 14, 477–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrege, J.; Schmidt, A.; Walter, A.; Smieskova, R.; Bendfeldt, K.; Radue, E.-W.; Lang, U.; Borgwardt, S. Effects of Cannabis on Impulsivity: A Systematic Review of Neuroimaging Findings. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 2126–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdejo-Garcia, A.; Benbrook, A.; Funderburk, F.; David, P.; Cadet, J.L.; Bolla, K.I. The differential relationship between cocaine use and marijuana use on decision-making performance over repeat testing with the Iowa Gambling Task. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2007, 90, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechara, A.; Tranel, D.; Damasio, H. Characterization of the decision-making deficit of patients with ventromedial prefrontal cortex lesions. Brain 2000, 123, 2189–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechara, A.; Damasio, H.; Damasio, A.R.; Lee, G.P. Different contributions of the human amygdala and ventromedial prefrontal cortex to decision-making. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 5473–5481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turton, R.; Nazar, B.P.; Burgess, E.E.; Lawrence, N.S.; Cardi, V.; Treasure, J.; Hirsch, C.R. To Go or Not to Go: A Proof of Concept Study Testing Food-Specific Inhibition Training for Women with Eating and Weight Disorders. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2018, 26, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claudat, K.; Brown, T.A.; Anderson, L.; Bongiorno, G.; Berner, L.A.; Reilly, E.; Luo, T.; Orloff, N.; Kaye, W.H. Correlates of co-occurring eating disorders and substance use disorders: A case for dialectical behavior therapy. Eat. Disord. 2020, 28, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, K.E.; Christensen, K.A.; Forbush, K.T. A preliminary systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials of cognitive remediation therapy for anorexia nervosa. Eat. Behav. 2020, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Without A/DA | With A/DA | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 118 | n = 27 | |||||
| n | % | n | % | |||
| Sex | Women | 88 | 74.6% | 20 | 74.1% | 0.957 |
| Men | 30 | 25.4% | 7 | 25.9% | ||
| ED subtype | Anorexia restrictive | 49 | 41.5% | 8 | 29.6% | 0.751 |
| Anorexia binge/purge | 20 | 16.9% | 6 | 22.2% | ||
| Bulimia | 21 | 17.8% | 7 | 25.9% | ||
| Binge eating disorder | 18 | 15.3% | 4 | 14.8% | ||
| Other specified feeding eating dis. | 10 | 8.5% | 2 | 7.4% | ||
| Education | Primary | 30 | 25.4% | 10 | 37.0% | 0.438 |
| Secondary | 52 | 44.1% | 11 | 40.7% | ||
| University | 36 | 30.5% | 6 | 22.2% | ||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | p | ||
| Age (years-old) | 30.30 | 10.13 | 30.56 | 11.22 | 0.907 | |
| Onset of the ED (years-old) | 22.94 | 8.99 | 21.59 | 9.83 | 0.491 | |
| Duration of the ED (years) | 7.36 | 7.58 | 8.96 | 6.72 | 0.312 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 21.70 | 8.47 | 22.50 | 8.87 | 0.663 | |
| Other impulsive behaviours | n | % | n | % | p | |
| Binges episodes | 46 | 39.3% | 16 | 59.3% | 0.049 * | |
| Theft | 18 | 15.3% | 9 | 33.3% | 0.029 * | |
| Kleptomania | 2 | 1.7% | 3 | 11.1% | 0.045 * | |
| Compulsive buying | 10 | 8.5% | 6 | 22.2% | 0.040 * | |
| Total | AN-R | AN-BP | BN | BED | OSFED | Women | Men | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 145 | n = 57 | n = 26 | n = 28 | n = 22 | n = 12 | n = 108 | n = 37 | ||||||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % |
| 27 | 18.6% | 8 | 14.0% | 6 | 23.1% | 7 | 25.0% | 4 | 18.2% | 2 | 16.7% | 20 | 18.5% | 7 | 18.9% |
| χ2 | 1.92 | (df = 4) | 0.01 | (df = 1) | |||||||||||
| p | 0.751 | 0.957 | |||||||||||||
| α | Without A/DA | With A/DA | p | |d| | η2 | Power | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 118 | n = 27 | ||||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||||||
| EDI Drive for thinness | 0.846 | 11.24 | 6.65 | 12.10 | 6.50 | 0.544 | 0.13 | 0.003 | 0.093 |
| EDI Body dissatisfaction | 0.922 | 13.35 | 8.86 | 15.66 | 7.70 | 0.213 | 0.28 | 0.011 | 0.237 |
| EDI Interoceptive awareness | 0.868 | 8.98 | 7.13 | 12.10 | 5.95 | 0.036 * | 0.52 † | 0.030 | 0.556 |
| EDI Bulimia | 0.791 | 4.92 | 5.20 | 6.51 | 4.83 | 0.148 | 0.32 | 0.015 | 0.303 |
| EDI Interpersonal distrust | 0.824 | 5.59 | 4.84 | 5.92 | 4.47 | 0.752 | 0.07 | 0.001 | 0.061 |
| EDI Ineffectiveness | 0.905 | 8.61 | 6.89 | 10.78 | 6.91 | 0.142 | 0.32 | 0.015 | 0.312 |
| EDI Maturity fears | 0.841 | 7.54 | 5.08 | 7.58 | 5.89 | 0.975 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.050 |
| EDI Perfectionism | 0.842 | 5.31 | 4.40 | 5.16 | 4.54 | 0.878 | 0.03 | 0.001 | 0.053 |
| EDI Impulse regulation | 0.850 | 5.43 | 5.85 | 5.60 | 4.43 | 0.886 | 0.03 | 0.001 | 0.052 |
| EDI Ascetic | 0.703 | 5.99 | 4.37 | 6.92 | 3.76 | 0.307 | 0.23 | 0.007 | 0.175 |
| EDI Social insecurity | 0.825 | 6.37 | 5.17 | 7.28 | 5.72 | 0.417 | 0.17 | 0.005 | 0.127 |
| EDI Total score | 0.974 | 83.33 | 48.73 | 95.62 | 42.19 | 0.228 | 0.27 | 0.010 | 0.225 |
| SCL-90R Somatization | 0.857 | 1.45 | 0.90 | 1.82 | 0.77 | 0.049 * | 0.44 | 0.026 | 0.497 |
| SCL-90-R Obsessive-compulsive | 0.909 | 1.57 | 0.98 | 1.78 | 0.89 | 0.308 | 0.22 | 0.007 | 0.174 |
| SCL-90-R Interpersonal sensitive | 0.912 | 1.76 | 1.04 | 1.94 | 0.91 | 0.416 | 0.18 | 0.005 | 0.128 |
| SCL-90-R Depression | 0.946 | 2.00 | 1.05 | 2.21 | 0.82 | 0.329 | 0.22 | 0.007 | 0.164 |
| SCL-90-R Anxiety | 0.911 | 1.38 | 0.95 | 1.66 | 0.74 | 0.145 | 0.34 | 0.015 | 0.307 |
| SCL-90-R Hostility | 0.774 | 1.17 | 0.88 | 1.25 | 0.97 | 0.672 | 0.09 | 0.001 | 0.071 |
| SCL-90-R Phobic anxiety | 0.854 | 0.78 | 0.87 | 0.86 | 0.73 | 0.667 | 0.10 | 0.001 | 0.072 |
| SCL-90-R Paranoia | 0.875 | 1.27 | 0.89 | 1.32 | 0.81 | 0.821 | 0.05 | 0.001 | 0.056 |
| SCL-90-R Psychotic | 0.893 | 1.17 | 0.77 | 1.28 | 0.67 | 0.529 | 0.14 | 0.003 | 0.096 |
| SCL-90-R GSI | 0.980 | 1.50 | 0.82 | 1.69 | 0.68 | 0.257 | 0.26 | 0.009 | 0.204 |
| SCL-90-R PST | 0.980 | 56.61 | 19.91 | 63.15 | 17.64 | 0.119 | 0.35 | 0.017 | 0.345 |
| SCL-90-R PSDI | 0.980 | 2.20 | 0.66 | 2.32 | 0.42 | 0.383 | 0.21 | 0.005 | 0.140 |
| TCI-R Novelty seeking | 0.797 | 94.68 | 13.80 | 103.37 | 13.83 | 0.004 * | 0.63 † | 0.057 | 0.834 |
| TCI-R Harm avoidance | 0.925 | 112.31 | 20.84 | 116.07 | 21.50 | 0.402 | 0.18 | 0.005 | 0.133 |
| TCI-R Reward dependence | 0.700 | 101.21 | 15.47 | 102.56 | 17.33 | 0.691 | 0.08 | 0.001 | 0.068 |
| TCI-R Persistence | 0.860 | 114.12 | 20.30 | 107.33 | 24.13 | 0.133 | 0.30 | 0.016 | 0.323 |
| TCI-R Self-directedness | 0.908 | 125.72 | 21.84 | 119.33 | 24.19 | 0.181 | 0.28 | 0.012 | 0.266 |
| TCI-R Cooperativeness | 0.831 | 136.66 | 17.28 | 135.89 | 15.97 | 0.832 | 0.05 | 0.001 | 0.055 |
| TCI-R Self-transcendence | 0.893 | 63.16 | 15.28 | 63.37 | 18.91 | 0.951 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.050 |
| Without A/DA | With A/DA | p | |d| | η2 | Power | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 118 | n = 27 | |||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||||
| Stroop Words | 104.43 | 19.39 | 95.61 | 24.53 | 0.045 * | 0.40 | 0.028 | 0.521 |
| Stroop Colour | 75.84 | 16.06 | 80.24 | 19.74 | 0.221 | 0.24 | 0.010 | 0.231 |
| Stroop Words-colour | 48.27 | 11.75 | 46.50 | 9.33 | 0.467 | 0.17 | 0.004 | 0.112 |
| Stroop Interference | 5.09 | 8.99 | 4.42 | 7.92 | 0.725 | 0.08 | 0.001 | 0.064 |
| WCST Total trials | 94.42 | 20.72 | 100.55 | 20.70 | 0.168 | 0.30 | 0.013 | 0.280 |
| WCST Correct | 67.83 | 10.87 | 68.06 | 14.02 | 0.924 | 0.02 | 0.001 | 0.051 |
| WCST Perseverative errors | 12.40 | 10.33 | 18.54 | 19.41 | 0.023 * | 0.39 | 0.036 | 0.629 |
| WCST Non-perseverative errors | 14.20 | 15.25 | 14.22 | 11.91 | 0.993 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.050 |
| WCST Conceptual | 60.64 | 16.54 | 59.18 | 19.97 | 0.692 | 0.08 | 0.001 | 0.068 |
| WCST Categories completed | 5.10 | 1.80 | 4.88 | 1.98 | 0.577 | 0.12 | 0.002 | 0.086 |
| WCST Trials completed 1st categ. | 20.36 | 24.17 | 26.73 | 31.78 | 0.248 | 0.23 | 0.009 | 0.210 |
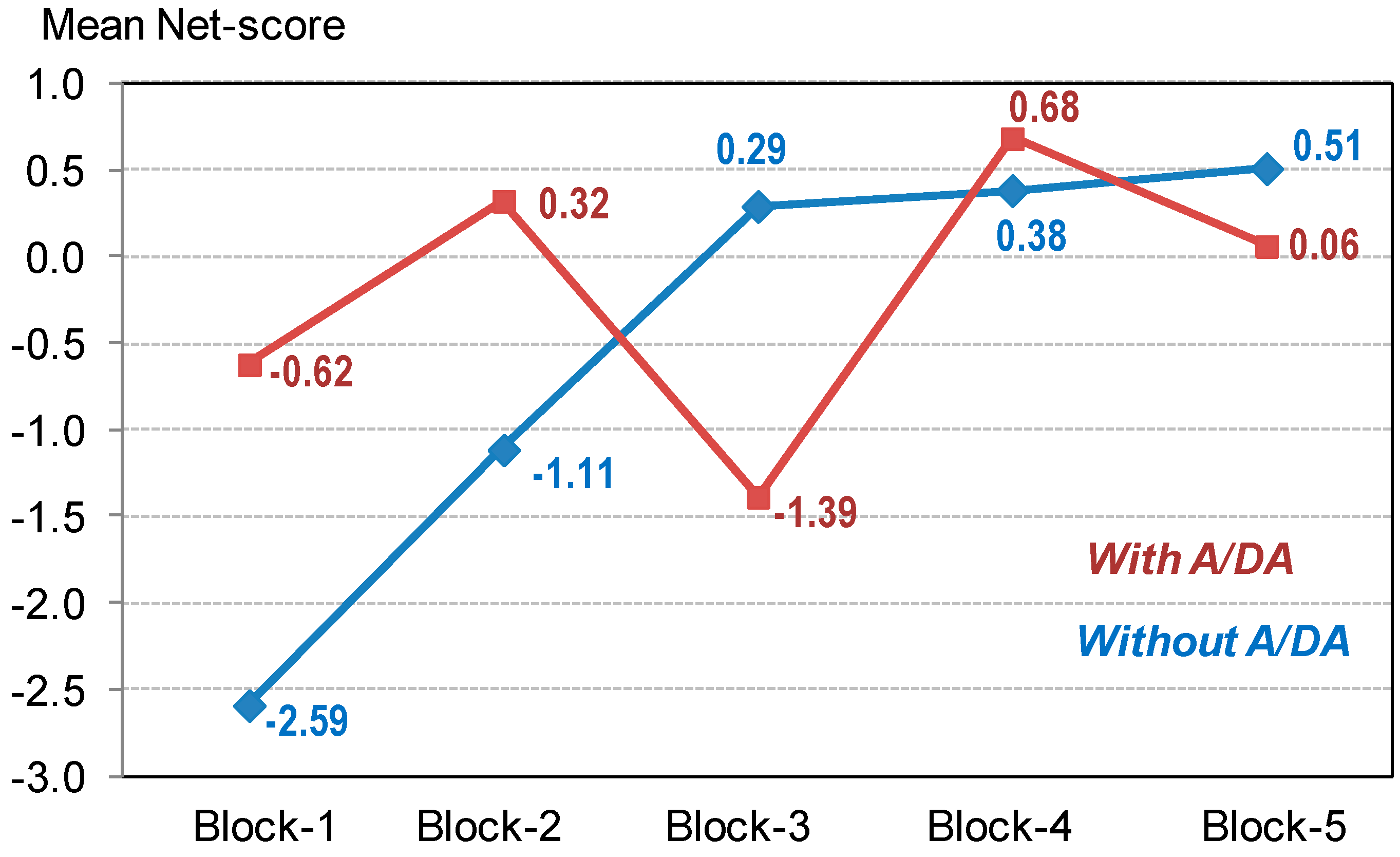
| IGT Block 1 | −2.59 | 4.21 | −0.62 | 2.84 | 0.023 * | 0.55 † | 0.036 | 0.629 |
| IGT Block 2 | −1.11 | 4.91 | 0.32 | 4.41 | 0.165 | 0.31 | 0.013 | 0.284 |
| IGT Block 3 | 0.29 | 5.80 | −1.39 | 3.55 | 0.152 | 0.35 | 0.014 | 0.298 |
| IGT Block 4 | 0.38 | 6.69 | 0.68 | 6.67 | 0.834 | 0.04 | 0.001 | 0.055 |
| IGT Block 5 | 0.51 | 7.78 | 0.06 | 5.42 | 0.777 | 0.07 | 0.001 | 0.059 |
| IGT Total | −2.52 | 20.79 | −0.95 | 11.51 | 0.704 | 0.09 | 0.001 | 0.067 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lozano-Madrid, M.; Clark Bryan, D.; Granero, R.; Sánchez, I.; Riesco, N.; Mallorquí-Bagué, N.; Jiménez-Murcia, S.; Treasure, J.; Fernández-Aranda, F. Impulsivity, Emotional Dysregulation and Executive Function Deficits Could Be Associated with Alcohol and Drug Abuse in Eating Disorders. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1936. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061936
Lozano-Madrid M, Clark Bryan D, Granero R, Sánchez I, Riesco N, Mallorquí-Bagué N, Jiménez-Murcia S, Treasure J, Fernández-Aranda F. Impulsivity, Emotional Dysregulation and Executive Function Deficits Could Be Associated with Alcohol and Drug Abuse in Eating Disorders. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(6):1936. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061936
Chicago/Turabian StyleLozano-Madrid, María, Danielle Clark Bryan, Roser Granero, Isabel Sánchez, Nadine Riesco, Núria Mallorquí-Bagué, Susana Jiménez-Murcia, Janet Treasure, and Fernando Fernández-Aranda. 2020. "Impulsivity, Emotional Dysregulation and Executive Function Deficits Could Be Associated with Alcohol and Drug Abuse in Eating Disorders" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 6: 1936. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061936
APA StyleLozano-Madrid, M., Clark Bryan, D., Granero, R., Sánchez, I., Riesco, N., Mallorquí-Bagué, N., Jiménez-Murcia, S., Treasure, J., & Fernández-Aranda, F. (2020). Impulsivity, Emotional Dysregulation and Executive Function Deficits Could Be Associated with Alcohol and Drug Abuse in Eating Disorders. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(6), 1936. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061936









