Associations of Sedentary Behaviour, Physical Activity, Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Body Composition with Risk of Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders in Children with Overweight/Obesity: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Procedures and Measurements
2.2.1. Sedentary Behaviour and Physical Activity
2.2.2. Cardiorespiratory Fitness
2.2.3. Body Composition Parameters
2.2.4. Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders
2.2.5. Covariates
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine. International Classification of Sleep Disorders, 3rd ed.; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Darien, IL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sateia, M.J. International classification of sleep disorders: Third edition: Highlights and Modifications. Chest 2014, 146, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsara, V.; Amfilochiou, A.; Papagrigorakis, J.; Georgopoulos, D.; Liolios, E.; Kadiths, A.; Koudoumnakis, E.; Aulonitou, E.; Emporiadou, M.; Tsakanikos, M.; et al. Guidelines for Diagnosing and Treating Sleep related Breathing Disorders in Adults and Children (Part 3: Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children, Diagnosis and Treatment). Hippokratia 2010, 14, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Peng, L.; Kou, C.; Hua, S.; Yuan, H. Associations of Overweight, Obesity and Related Factors with Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders and Snoring in Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Survey. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalzitti, N.J.; Sarber, K.M. Diagnosis and perioperative management in pediatric sleep-Disordered breathing. Pediatr. Anesth. 2018, 28, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikävalko, T.; Tuomilehto, H.; Pahkala, R.; Tompuri, T.; Laitinen, T.; Myllykangas, R.; Vierola, A.; Lindi, V.; Närhi, M.; Lakka, T.A. Craniofacial morphology but not excess body fat is associated with risk of having sleep-disordered breathing-The PANIC Study (a questionnaire-based inquiry in 6-8-year-olds). Eur. J. Pediatr. 2012, 171, 1747–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehlink, E.; Tan, H. Update on paediatric obstructive sleep apnoea. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, 224–235. [Google Scholar]
- Urquhart, D.S.; Hill, E.A.; Morley, A. Sleep-Disordered breathing in children. Paediatr. Child Health (Oxford) 2017, 27, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, C.L.; Brooks, L.J.; Ward, S.D.; Draper, K.A.; Gozal, D.; Halbower, A.C.; Jones, J.; Lehmann, C.; Schechter, M.S.; Sheldon, S.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Childhood Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. Am. Acad. Pediatr. 2012, 130, e714–e755. [Google Scholar]
- Lumeng, J.C.; Chervin, R.D. Epidemiology of Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2008, 5, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaditis, A.G.; Alvarez, M.L.A.; Boudewyns, A.; Alexopoulos, E.I.; Ersu, R.; Joosten, K.; Larramona, H.; Miano, S.; Narang, I.; Trang, H.; et al. Obstructive sleep disordered breathing in 2-To 18-Year-Old children: Diagnosis and management. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsan, Z.; Ishman, S.L.; Kimball, T.R.; Zhang, N.; Zou, Y.; Amin, R.S. Longitudinal Cardiovascular Outcomes of Sleep Disordered Breathing in Children: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Sleep 2017, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, W.; Dong, H.; Xue, X.; Ding, J.; Xing, W.; Wang, W. Association of obstructive sleep apnea with hypertension: A systematic review and meta-Analysis. J. Glob. Health 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wan, Y.; Xu, M.; Ming, J.; Xing, Y.; An, F.; Ji, Q. The association between obstructive sleep apnea and metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-Analysis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2015, 15, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galland, B.; Spruyt, K.; Dawes, P.; McDowall, P.S.; Elder, D.; Schaughency, E. Sleep disordered breathing and academic performance: A meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2015, 136, e934–e946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beebe, D.W.; Ris, M.D.; Kramer, M.E.; Long, E.; Amin, R. The association between sleep disordered breathing, academic grades, and cognitive and behavioral functioning among overweight subjects during middle to late childhood. Sleep 2010, 33, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guh, D.P.; Zhang, W.; Bansback, N.; Amarsi, Z.; Birmingham, C.L.; Anis, A.H. The incidence of co-morbidities related to obesity and overweight: A systematic review and meta-Analysis. BMC Public Health 2009, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators; Afshin, A.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Reitsma, M.B.; Sur, P.; Estep, K.; Lee, A.; Marczak, L.; Mokdad, A.H.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; et al. Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries over 25 years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Reilly, J.J.; Kelly, J. Long-Term impact of overweight and obesity in childhood and adolescence on morbidity and premature mortality in adulthood: Systematic review. Int. J. Obes. 2011, 35, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, L.M.; Tamanyan, K.; Limawan, A.P.; Biggs, S.N.; Weichard, A.J.; Davey, M.J.; Nixon, G.M.; Horne, R.S.C. Overweight and obese children with sleep disordered breathing have elevated arterial stiffness. Sleep Med. 2018, 48, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, Y.K.; Hui, S.H.; Pak, W.M.; Ho, C.K.; Cheung, A.; Li, A.M.; Fok, T.F. A controlled study of sleep related disordered breathing in obese children. Arch. Dis. Child. 2003, 88, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, R.; Hakim, F.; Gozal, D. Sleep, sleep-Disordered breathing and lipid homeostasis: Translational evidence from murine models and children. Clin. Lipidol. 2012, 7, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhulst, S.L.; Van Gaal, L.; De Backer, W.; Desager, K. The prevalence, anatomical correlates and treatment of sleep-disordered breathing in obese children and adolescents. Sleep Med. Rev. 2008, 12, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhulst, S.L.; Schrauwen, N.; Haentjens, D.; Suys, B.; Rooman, R.P.; Van Goal, L.; De Backer, W.A.; Desager, K.N. Sleep-Disordered breathing in overweight and obese children and adolescents: Prevalence, characteristics and the role of fat distribution. Arch. Dis. Child. 2007, 92, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bixler, E.O.; Vgontzas, A.N.; Lin, H.-M.; Liao, D.; Calhoun, S.; Vela-Bueno, A.; Fedok, F.; Vlasic, V.; Graff, G. Sleep Disordered Breathing in Children in a General Population Sample: Prevalence and Risk Factors. Sleep 2009, 32, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaoussoglou, M.; Bixler, E.O.; Calhoun, S.; Chrousos, G.P.; Sauder, K.; Vgontzas, A.N. Sleep-Disordered Breathing in Obese Children Is Associated with Prevalent Excessive Daytime Sleepiness, Inflammation, and Metabolic Abnormalities. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, L.; Tesse, R.; Miniello, V.L.; Colella, I.; Delvecchio, M.; Logrillo, V.P.; Francavilla, R.; Armenio, L. Sleep-Disordered breathing in obese children: The Southern Italy experience. Chest 2010, 137, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, I.G.; Holm, J.C.; Homøe, P. Obstructive sleep apnea in obese children and adolescents, treatment methods and outcome of treatment-A systematic review. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 87, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, I.G.; Holm, J.C.; Homøe, P. Obstructive sleep apnea in children and adolescents with and without obesity. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2019, 276, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, J.L.; Narang, I. Sleeping too Close Together: Obesity and Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Childhood and Adolescence. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2014, 15, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, C.E.; Krafty, R.T.; Mulukutla, S.; Hall, M.H. Associations of sedentary time and moderate-Vigorous physical activity with sleep-Disordered breathing and polysomnographic sleep in community-Dwelling adults. Sleep Breath 2017, 21, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shin, J.C.; Li, D.; An, R. Sedentary Behavior and Sleep Problems: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Behav. Med. 2017, 24, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelson, M.; Bailly, S.; Marillier, M.; Flore, P.; Borel, J.C.; Vivodtzev, I.; Doutreleau, S.; Verges, S.; Tamisier, R.; Pépin, J.L. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, objectively measured physical activity and exercise training interventions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beitler, J.R.; Awad, K.M.; Bakker, J.P.; Edwards, B.A.; DeYoung, P.; Djonlagic, I.; Forman, D.E.; Quan, S.F.; Malhotra, A. Obstructive sleep apnea is associated with impaired exercise capacity: A cross-Sectional study. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2014, 10, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhecke, T.E.; Franklin, B.A.; Ajluni, S.C.; Sangal, R.B.; McCullough, P.A. Cardiorespiratory fitness and sleep-related breathing disorders. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2008, 6, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadenas-Sánchez, C.; Mora-González, J.; Migueles, J.H.; Martín-Matillas, M.; Gómez-Vida, J.; Escolano-Margarit, M.V.; Maldonado, J.; Enriquez, G.M.; Pastor-Villaescusa, B.; de Teresa, C.; et al. An exercise-Based randomized controlled trial on brain, cognition, physical health and mental health in overweight/obese children (ActiveBrains project): Rationale, design and methods. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2016, 47, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keadle, S.K.; Arem, H.; Moore, S.C.; Sampson, J.N.; Matthews, C.E. Impact of changes in television viewing time and physical activity on longevity: A prospective cohort study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2015, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, M.S.; LeBlanc, A.G.; Kho, M.E.; Saunders, T.J.; Larouche, R.; Colley, R.C.; Goldfield, G.; Gorber, S.C. Systematic review of sedentary behaviour and health indicators in school-Aged children and youth. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Maurice, P.F.; Welk, G.J. Web-Based assessments of physical activity in youth: Considerations for design and scale calibration. J. Med. Internet Res. 2014, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Maurice, P.F.; Welk, G.J. Validity and calibration of the youth activity profile. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairclough, S.J.; Christian, D.L.; Saint-Maurice, P.F.; Hibbing, P.R.; Noonan, R.J.; Welk, G.J.; Dixon, P.M.; Boddy, L.M. Calibration and validation of the youth activity profile as a physical activity and sedentary behaviour surveillance tool for english youth. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hees, V.T.; Renström, F.; Wright, A.; Gradmark, A.; Catt, M.; Chen, K.Y.; Löf, M.; Bluck, L.; Pomeroy, J.; Wareham, N.J.; et al. Estimation of daily energy expenditure in pregnant and Non-Pregnant women using a Wrist-Worn Tri-Axial accelerometer. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hees, V.T.; Sabia, S.; Anderson, K.N.; Denton, S.J.; Oliver, J.; Catt, M.; Abell, J.G.; Kivimäki, M.; Trenell, M.I.; Singh-Manoux, A. A novel, open access method to assess sleep duration using a wrist-Worn accelerometer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hees, V.T.; Gorzelniak, L.; Dean León, E.C.; Eder, M.; Pias, M.; Taherian, S.; Ekelund, U.; Renström, F.; Franks, P.W.; Horsch, A.; et al. Separating Movement and Gravity Components in an Acceleration Signal and Implications for the Assessment of Human Daily Physical Activity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hees, V.T.; Fang, Z.; Langford, J.; Assah, F.; Mohammad, A.; da Silva, I.C.M.; Trenell, M.I.; White, T.; Wareham, N.J.; Brage, S. Autocalibration of accelerometer data for free-living physical activity assessment using local gravity and temperature: An evaluation on four continents. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 117, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, M.; Van Hees, V.T.; Hansen, B.H.; Ekelund, U. Age group comparability of raw accelerometer output from wrist-And hip-Worn monitors. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2014, 46, 1816–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.R.; Castro-Piñero, J.; España-Romero, V.; Artero, E.G.; Ortega, F.B.; Cuenca, M.A.M.; Enez-Pavón, D.J.; Chillón, P.; Girela-Rejón, M.J.; Mora, J.; et al. Field-Based fitness assessment in young people: The ALPHA health-Related fitness test battery for children and adolescents. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artero, E.G.; España-Romero, V.; Castro-Piero, J.; Ortega, F.B.; Suni, J.; Castillo-Garzon, M.J.; Ruiz, J.R. Reliability of field-Based fitness tests in youth. Int. J. Sports Med. 2011, 32, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Piñero, J.; Artero, E.G.; España-Romero, V.; Ortega, F.B.; Sjostrom, M.; Suni, J.; Ruiz, J.R. Criterion-Related validity of field-Based fitness tests in youth: A systematic review. Br. J. Sport. Med. 2010, 44, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.R.; Castro-Piñero, J.; Artero, E.G.; Ortega, F.B.; Sjöström, M.; Suni, J.; Castillo, M.J. Predictive validity of health-related fitness in youth: A systematic review. Br. J. Sports Med. 2009, 43, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léger, L.A.; Mercier, D.; Gadoury, C.; Lambert, J. The multistage 20 metre shuttle run test for aerobic fitness. J. Sports Sci. 1988, 6, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, T.J.; Lobstein, T. Extended international (IOTF) body mass index cut-Offs for thinness, overweight and obesity. Pediatr. Obes. 2012, 7, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bervoets, L.; Massa, G. Defining morbid obesity in children based on BMI 40 at age 18 using the extended international (IOTF) cut-offs. Pediatr. Obes. 2014, 9, e94–e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracia-Marco, L.; Moreno, L.A.; Ortega, F.B.; Len, F.; Sioen, I.; Kafatos, A.; Martinez-Gomez, D.; Widhalm, K.; Castillo, M.J.; Vicente-Rodrguez, G. Levels of physical activity that predict optimal bone mass in adolescents: The HELENA study. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2011, 40, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracia-Marco, L.; Ortega, F.B.; Jiménez-Pavón, D.; Rodríguez, G.; Castillo, M.J.; Vicente-Rodríguez, G.; Moreno, L.A. Adiposity and bone health in Spanish adolescents. the HELENA study. Osteoporos. Int. 2012, 23, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vila, M.T.; Torres, A.M.; Soto, B.B. Spanish Version of the Pediatric Sleep Questionnaire (PSQ). A useful instrument in investigation of sleep disturbances in childhood. Reliability analysis. An. Pediatr. 2007, 66, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Chervin, R.D.; Weatherly, R.A.; Garetz, S.L.; Ruzicka, D.L.; Giordani, B.J.; Hodges, E.K.; Dillon, J.E.; Guire, K.E. Pediatric sleep questionnaire. Prediction of sleep apnea and outcomes. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2007, 133, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosiek, A.; Maciejewska, N.F.; Leksowski, K.; Rosiek-Kryszewska, A.; Leksowski, Ł. Effect of television on obesity and excess of weight and consequences of health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 9408–9426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, V.; Hunter, S.; Kuzik, N.; Gray, C.E.; Poitras, V.J.; Chaput, J.; Saunders, T.J.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Okely, A.D.; Gorber, S.C.; et al. Systematic review of sedentary behaviour and health indicators in school-Aged children and youth: An update. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, S240–S265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paavonen, E.J.; Pennonen, M.; Roine, M.; Valkonen, S.; Lahikainen, A.R. TV exposure associated with sleep disturbances in 5- to 6-year-old children. J. Sleep Res. 2006, 15, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.L.; Tkacz, J.; Gregoski, M.; Boyle, C.A.; Lovrekovic, G. Aerobic Exercise and Snoring in Overweight Children: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2006, 14, 1985–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, F.; Ruiz, J.; Castillo, M.; Sjöström, M. Physical fitness in childhood and adolescence: A powerful marker of health. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojek, M.M.K.; Montoya, A.K.; Drescher, C.F.; Newberry, A.; Sultan, Z.; Williams, C.F.; Pollock, N.K.; Davis, C.L. Fitness, Sleep-Disordered Breathing, Symptoms of Depression, and Cognition in Inactive Overweight Children: Mediation Models. Public Health Rep. 2017, 132, 65S–73S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twig, G.; Afek, A.; Derazne, E.; Tzur, D.; Cukierman-Yaffe, T.; Gerstein, H.C.; Tirosh, A. Diabetes risk among overweight and obese metabolically healthy young adults. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2989–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikävalko, T.; Närhi, M.; Eloranta, A.M.; Lintu, N.; Myllykangas, R.; Vierola, A.; Tuomilehto, H.; Lakka, T.; Pahkala, R. Predictors of sleep disordered breathing in children: The PANIC study. Eur. J. Orthod. 2018, 40, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carotenuto, M.; Bruni, O.; Santoro, N.; del Giudice, E.M.; Perrone, L.; Pascotto, A. Waist circumference predicts the occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing in obese children and adolescents: A questionnaire-Based study. Sleep Med. 2006, 7, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bixler, E.O.; Fernandez-Mendoza, J.; Liao, D.; Calhoun, S.; Rodriguez-Colon, S.M.; Gaines, J.; He, F.; Vgontzas, A.N. Natural history of sleep disordered breathing in prepubertal children transitioning to adolescence. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 1402–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, R.; Lesser, D.J.; Oliveira, F.G.S.A.; Tran, W.H.; Keens, T.G.; Khoo, M.C.K.; Ward, S.L.D. Body fat composition: A predictive factor for sleep related breathing disorder in obese children. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2015, 11, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Piovezan, R.D.; Hirotsu, C.; Moizinho, R.; de Sá Souza, H.; D’Almeida, V.; Tufik, S.; Poyares, D. Associations between sleep conditions and body composition states: Results of the EPISONO study. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 962–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovin, S.; Bercea, R.; Cojocaru, C.; Rusu, G.; Mihãescu, T. Body composition in obstructive sleep apneahypopnea syndrome: Bio-impedance reflects the severity of sleep apnea. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2010, 5, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuźnar-Kamińska, B.; Grabicki, M.; Trafas, T.; Szulińska, M.; Cofta, S.; Piorunek, T.; Brajer-Luftmann, B.; Nowicka, A.; Bromińska, B.; Batura-Gabryel, H. Body composition, anthropometric indices and hydration status of obstructive sleep apnea patients: Can cachexia coexist with obesity? Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1020, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega, F.B.; Sui, X.; Lavie, C.J.; Blair, S.N. Body Mass Index, the Most Widely Used but also Widely Criticized Index: Would a Gold-Standard Measure of Total Body Fat be a Better Predictor of Cardiovascular Disease Mortality? Mayo Clin. Proc. 2016, 91, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| All | Boys | Girls | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | 109 (100) | 64 (59) | 45 (41) |
| Age (years) | 10.0 ± 1.1 | 10.2 ± 1.1 | 9.9 ± 1.1 |
| Sedentary behaviour | |||
| Television viewing time, n (%) (n = 107) | |||
| None | 1 (1) | 0 (0) | 1 (2) |
| <1 h/day | 41 (38) | 24 (38) | 17 (39) |
| 1–2 h/day | 42 (39) | 22 (34) | 20 (47) |
| <2–3 h/day | 13 (12) | 8 (12) | 5 (12) |
| >3 h/day | 10 (9) | 10 (16) | 0 (0) |
| Sedentary time (min/day) (n = 103) | 520.1 ± 54.7 | 521.3 ± 52.0 | 518.4 ± 58.9 |
| Physical activity | |||
| Moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (min/day) (n = 103) | 51.4 ± 20.1 | 59.1 ± 21.0 | 40.2 ± 11.7 |
| Cardiorespiratory fitness | |||
| 20 m shuttle run test (laps) | 16.0 ± 7.7 | 17.2 ± 8.1 | 14.4 ± 6.9 |
| 20 m shuttle run test (VO2max, mL/kg/min) a | 40.7 ± 2.7 | 40.8 ± 2.7 | 40.6 ± 2.7 |
| Body composition parameters | |||
| Weight (kg) | 56.2 ± 11.2 | 57.1 ± 11.2 | 54.9 ± 11.3 |
| Height (cm) | 144.2 ± 8.4 | 145.0 ± 8.0 | 143.1 ± 9.0 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 26.8 ± 3.6 | 27.0 ± 3.7 | 26.6 ± 3.5 |
| Fat mass index (kg/m2) | 11.8 ± 2.9 | 11.5 ± 2.9 | 12.1 ± 2.8 |
| Lean mass index (kg/m2) | 14.0 ± 1.4 | 14.3 ±1.3 | 13.5 ± 1.4 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 90.2 ± 9.9 | 91.3 ± 9.4 | 88.7 ± 10.5 |
| Sleep-related breathing disorders | |||
| SRBD scale (0 to 1) | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 |
| Presence of SRBD, n (%) | 17(16) | 10 (16) | 7 (16) |
| SRBD Scale (0 to 1) | ||
|---|---|---|
| r | p | |
| Sedentary behaviour | ||
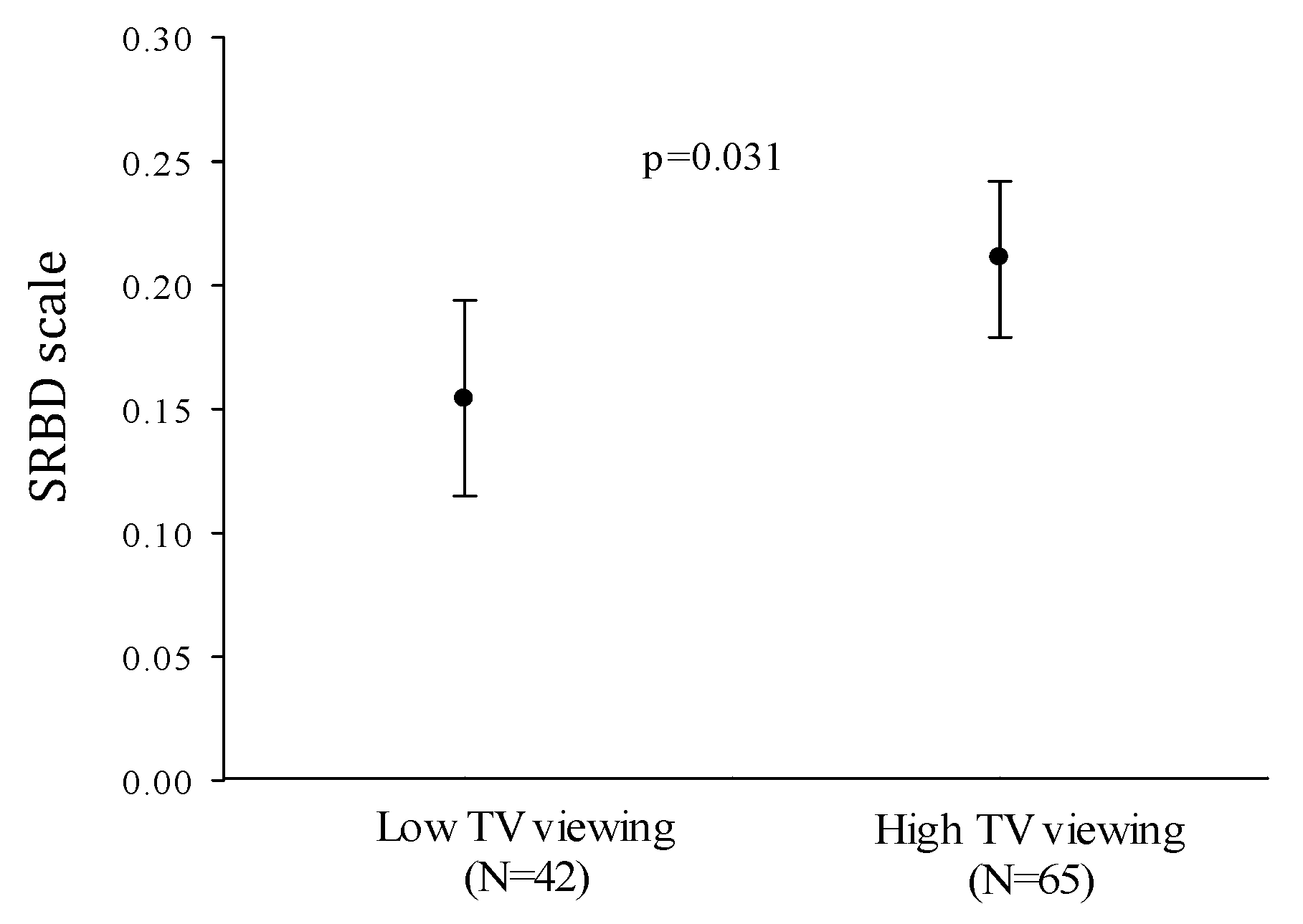
| Television viewing time (h/day) | 0.222 | 0.021 |
| Sedentary time (min/day) | 0.129 | 0.193 |
| Physical activity | ||
| Moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (min/day) | 0.054 | 0.585 |
| Cardiorespiratory fitness (VO2max mL/kg/min) a | −0.210 | 0.030 |
| Body composition parameters | ||
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 0.209 | 0.029 |
| Fat mass index (kg/m2) | 0.153 | 0.114 |
| Lean mass index (kg/m2) | 0.223 | 0.020 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 0.191 | 0.047 |
| β | p-Value | Change R2 | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | 0.063 | 0.063 | ||
| Body mass index | 0.251 | 0.011 | ||
| Model 2 | 0.048 | 0.111 | ||
| Body mass index | 0.249 | 0.010 | ||
| Television viewing time | 0.220 | 0.022 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torres-Lopez, L.V.; Cadenas-Sanchez, C.; Migueles, J.H.; Adelantado-Renau, M.; Plaza-Florido, A.; Solis-Urra, P.; Molina-Garcia, P.; Ortega, F.B. Associations of Sedentary Behaviour, Physical Activity, Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Body Composition with Risk of Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders in Children with Overweight/Obesity: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051544
Torres-Lopez LV, Cadenas-Sanchez C, Migueles JH, Adelantado-Renau M, Plaza-Florido A, Solis-Urra P, Molina-Garcia P, Ortega FB. Associations of Sedentary Behaviour, Physical Activity, Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Body Composition with Risk of Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders in Children with Overweight/Obesity: A Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(5):1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051544
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorres-Lopez, Lucia V., Cristina Cadenas-Sanchez, Jairo H. Migueles, Mireia Adelantado-Renau, Abel Plaza-Florido, Patricio Solis-Urra, Pablo Molina-Garcia, and Francisco B. Ortega. 2020. "Associations of Sedentary Behaviour, Physical Activity, Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Body Composition with Risk of Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders in Children with Overweight/Obesity: A Cross-Sectional Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 5: 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051544
APA StyleTorres-Lopez, L. V., Cadenas-Sanchez, C., Migueles, J. H., Adelantado-Renau, M., Plaza-Florido, A., Solis-Urra, P., Molina-Garcia, P., & Ortega, F. B. (2020). Associations of Sedentary Behaviour, Physical Activity, Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Body Composition with Risk of Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders in Children with Overweight/Obesity: A Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(5), 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051544








