Urinary Tract Infection in Febrile Children with Sickle Cell Disease Who Present to the Emergency Room with Fever
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Study Setting
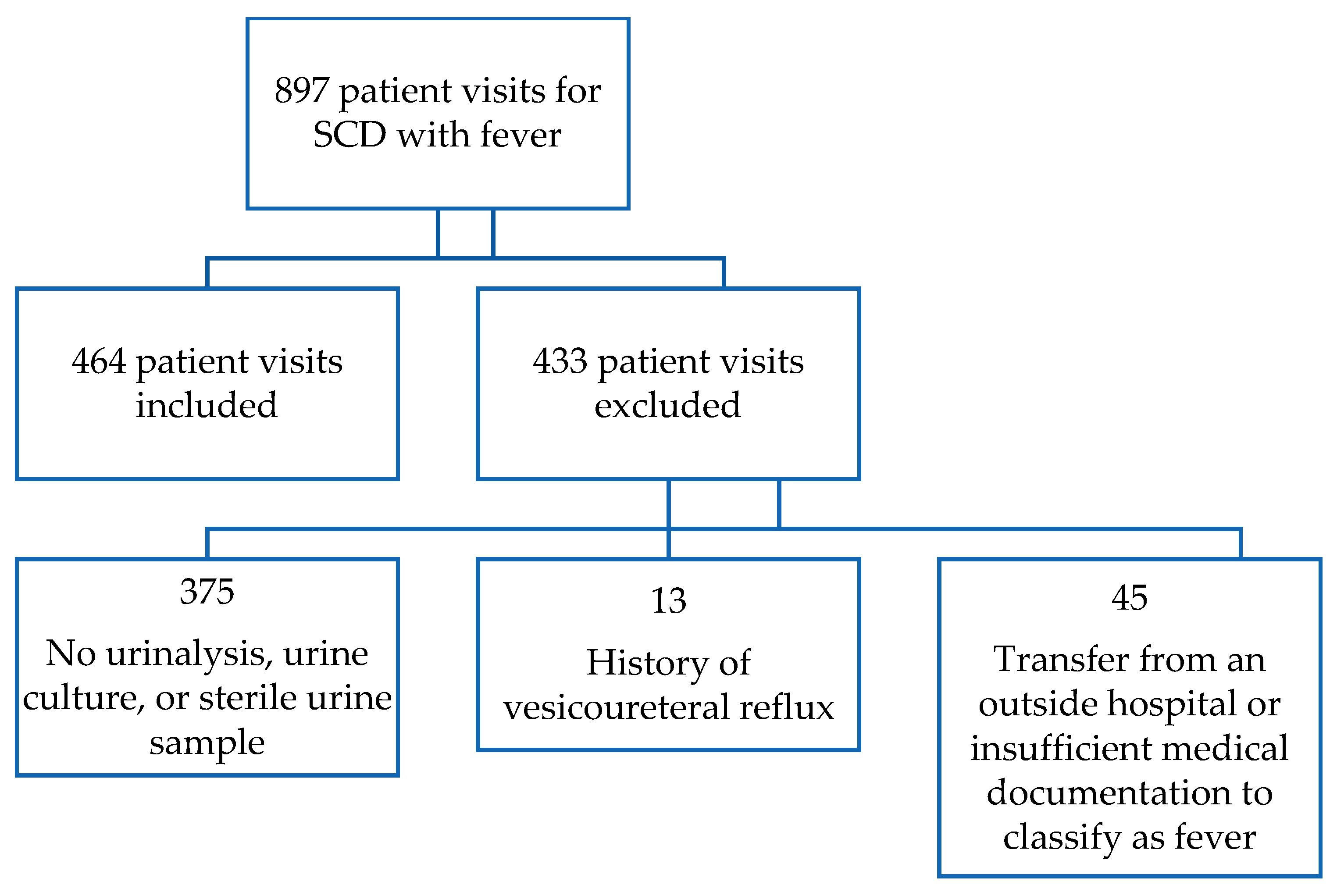
2.2. Study Sample
2.3. Definitions
2.4. Outcomes
2.5. Data Collection
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Costs of Intimate Partner Violence Against Women in the United States; National Center for Injury Prevention and Control: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chukwu, B.F.; Okafor, H.U.; Ikefuna, A.N. Asymptomatic bacteriuria in children with sickle cell anemia at The University of Nigeria teaching hospital, Enugu, South East, Nigeria. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2011, 37, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, K.A.; Hebbel, R.P. Sickle cell disease: Renal manifestations and mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2015, 11, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, D.; Wigfall, D.R.; Zimmerman, S.A.; Rosoff, P.M.; Wiener, J.S. Genitourinary Complications of Sickle Cell Disease. J. Urol. 2001, 166, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarry, W.; Duckett, J.W.; Snyder, H.M. Urological Complications of Sickle Cell Disease in a Pediatric Population. J. Urol. 1987, 138, 592–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asinobi, A.O.; Fatunde, O.J.; Brown, B.; Osinusi, K.; Fasina, N.A. Urinary tract infection in febrile children with sickle cell anaemia in Ibadan, Nigeria. Ann. Trop. Paediatr. 2003, 23, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansil, N.H.; Kim, T.Y.; Tieu, L.; Barcega, B. Incidence of Serious Bacterial Infections in Febrile Children with Sickle Cell Disease. Clin. Pediatr. 2013, 52, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiya, N.; Ibitoye, P.; Jiya, F. Urinary tract infection and malaria co-morbidity in febrile children with sickle-cell anaemia in Sokoto, Nigeria. Internat. J. Med. Med. Sci. 2012, 2, 154–157. [Google Scholar]
- Mava, Y.; Ambe, J.P.; Bello, M.; Watila, I.; Pius, S. Evaluation of the Nitrite Test in Screening for Urinary Tract Infection in Febrile Children with Sickle Cell Anaemia in Maiduguri-Nigeria. Niger. Med. J. 2011, 52, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yauba, M.; Aikhionbare, H.; Ogunrinde, G.; Bugaje, M. Significant bacteriuria in children with sickle cell anaemia in a Nigerian tertiary hospital. Niger. J. Paediatr. 2014, 41, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Heart Lung and Blood Institute; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Evidence-Based Management of Sickle Cell Disease: Expert Panel Report. Available online: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/evidence-based-management-sickle-cell-disease (accessed on 6 November 2019).
- Al-Orifi, F.; McGillivray, D.; Tange, S.; Kramer, M.S. Urine culture from bag specimens in young children: Are the risks too high? J. Pediatr. 2000, 137, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subcommittee on Urinary Tract Infection. Reaffirmation of aap clinical practice guideline: The diagnosis and management of the initial urinary tract infection in febrile infants and young children 2–24 months of age. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20163026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Thielke, R.; Payne, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Conde, J.G. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—A metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J. Biomed. Inform. 2008, 42, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, N.; Morone, N.E.; Bost, J.E.; Farrell, M.H. Prevalence of Urinary Tract Infection in Childhood. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2008, 27, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, P.-T.T.; Wilkinson, A.H.; Lew, S.Q.; Pham, P.-C.T. Renal abnormalities in sickle cell disease. Kidney Int. 2000, 57, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrissey, B.J.; Bycroft, T.P.; Almossawi, O.; Wilkey, O.B.; Daniels, J.G. Incidence and Predictors of Bacterial infection in Febrile Children with Sickle Cell Disease. Hemoglobin 2015, 39, 316–319. [Google Scholar]
- Das, P.; Baker, K.K.; Dutta, A.; Swain, T.; Sahoo, S.; Das, B.S.; Panda, B.; Nayak, A.; Bara, M.; Bilung, B.; et al. Menstrual Hygiene Practices, WASH Access and the Risk of Urogenital Infection in Women from Odisha, India. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, K.N.; Gorelick, M.; McGowan, K.L.; Yakscoe, N.M.; Schwartz, J.S. Prevalence of urinary tract infection in febrile young children in the emergency department. Pediatrics 1998, 102, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavelle, J.M.; Blackstone, M.M.; Funari, M.K.; Roper, C.; López, P.; Schast, A.; Taylor, A.M.; Voorhis, C.B.; Henien, M.; Shaw, K.N. Two-Step Process for ED UTI Screening in Febrile Young Children: Reducing Catheterization Rates. Pediatrics 2016, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | n = 167 (%) |
|---|---|
| Female | 98 (58.7) |
| African American | 159 (95.2) |
| Type of Sickle Cell Disease | |
| SS | 109 (65.3) |
| SC | 50 (29.9) |
| S-Beta Thalassemia | 6 (3.6) |
| Other | 2 (1.2) |
| Variables | Median (IQR) |
| Age (Months) | 11 (7–20) |
| Maximum Temperature (°C) | 39.3 (38.7–39.5) |
| White Blood Cell Count (k/mm3) | 12.3 (8.9–18.1) |
| Hemoglobin (gm/dL) | 9.5 (8.2–10.4) |
| Platelets (k/mm3) | 310.5 (238–378) |
| Length of Stay (days) | 2 (2–3) |
| Characteristic | UTI n = 19 | No UTI n = 445 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Sickle Cell Disease | n (%) | n (%) | |
| SS | 12 (63.2) | 291 (65.4) | 0.6 |
| SC | 6 (31.6) | 139 (31.2) | |
| S-Beta Thalassemia | 1 (5.3) | 12 (2.7) | |
| Variables | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | |
| Age in Months | 19 (12–30) | 17 (10–28) | 0.42 |
| Maximum Temperature (°C) | 39.5 (39.2–40.0) | 39.3 (38.7–39.6) | 0.13 |
| White Blood Cell Count | 13.8 (8.2–20.4) | 13.6 (9.2–18.8) | 0.82 |
| Urine Results Variables | n (%) | n (%) | |
| White Blood Cell Count >5 | 12 (63.2) | 38 (8.5) | <0.001 |
| Leukocyte Positive | 12 (63.2) | 48 (10.7) | <0.001 |
| Nitrite Positive | 6 (31.6) | 4 (0.9) | <0.001 |
| Patient Visit | Age in Months | Type of SCD | Name of First Urine Pathogen | Name of Second Urine Pathogen |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11 | S-beta thal | Candida albicans | Enterococcus faecium |
| 2 | 31 | SS | Escherichia coli | |
| 3 | 14 | SS | Escherichia coli | |
| 4 | 19 | SC | Escherichia coli | |
| 5 | 26 | SS | Escherichia coli | |
| 6 | 30 | SS | Escherichia coli | |
| 7 | 11 | SS | Escherichia coli | |
| 8 | 16 | SC | Escherichia coli | |
| 9 | 22 | SS | Escherichia coli | |
| 10 | 17 | SS | Escherichia coli | |
| 11 | 38 | SS | Escherichia coli | Enterococcus faecalis |
| 12 | 45 | SC | Escherichia coli | |
| 13 | 15 | SC | Escherichia coli | |
| 14 | 11 | SC | Escherichia coli | |
| 15 | 12 | SS | Escherichia coli | |
| 16 | 25 | SS | Klebsiella pneumonia | |
| 17 | 3 | SS | Klebsiella pneumonia | |
| 18 | 47 | SC | Morganella moganii | Enterococcus faecalis |
| 19 | 22 | SS | Proteus mirabilis |
| Parameter | Estimates | Standard Error | 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age in Months | 1.01 | 0.03 | 0.95–1.07 |
| Maximum Temperature (°C) | 1.6 | 0.57 | 0.78–3.2 |
| White Blood Cell Count | 0.99 | 0.03 | 0.94–1.05 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patel, N.; Farooqi, A.; Callaghan, M.; Sethuraman, U. Urinary Tract Infection in Febrile Children with Sickle Cell Disease Who Present to the Emergency Room with Fever. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051531
Patel N, Farooqi A, Callaghan M, Sethuraman U. Urinary Tract Infection in Febrile Children with Sickle Cell Disease Who Present to the Emergency Room with Fever. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(5):1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051531
Chicago/Turabian StylePatel, Nehal, Ahmad Farooqi, Michael Callaghan, and Usha Sethuraman. 2020. "Urinary Tract Infection in Febrile Children with Sickle Cell Disease Who Present to the Emergency Room with Fever" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 5: 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051531
APA StylePatel, N., Farooqi, A., Callaghan, M., & Sethuraman, U. (2020). Urinary Tract Infection in Febrile Children with Sickle Cell Disease Who Present to the Emergency Room with Fever. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(5), 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051531





