Lower Activity and Function Scores Are Associated with a Higher Risk of Preoperative Deep Venous Thrombosis in Patients Undergoing Total Hip Arthroplasty
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Samama, C.M. Fast-Track Procedures in Major Orthopaedic Surgery: Is Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Still Mandatory? Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 119, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Chan, N.C.; Ibrahim, Q.; Kruger, P.; Sinha, S.; Bhagirath, V.; Ginsberg, J.; Bangdiwala, S.; Guyatt, G.; Eikelboom, J.; et al. Reduction in Mortality following Elective Major Hip and Knee Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 119, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falck-Ytter, Y.; Francis, C.W.; Johanson, N.A.; Curley, C.; Dahl, O.E.; Schulman, S.; Ortel, T.L.; Pauker, S.G.; Colwell, C.W. Prevention of VTE in orthopedic surgery patients: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 2012, 141 (Suppl. 2), e278S–e325S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, H.; Hasegawa, M.; Niimi, R.; Sudo, A. Clinical analysis of preoperative deep vein thrombosis risk factors in patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty. Thromb. Res. 2015, 136, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, N.; Miyasaka, D.; Shimada, H.; Suda, K.; Ito, T.; Endo, N. Usefulness of a novel method for the screening of deep vein thrombosis by using a combined D-dimer- and age-based index before total hip arthroplasty. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beksac, B.; Gonzalez Della Valle, A.; Salvati, E.A. Thromboembolic disease after total hip arthroplasty: Who is at risk? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2006, 453, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baser, O.; Supina, D.; Sengupta, N.; Wang, L.; Kwong, L. Impact of postoperative venous thromboembolism on Medicare recipients undergoing total hip replacement or total knee replacement surgery. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2010, 67, 1438–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, A.B.; Mehnert, F.; Sorensen, H.T.; Emmeluth, C.; Overgaard, S.; Johnsen, S.P. The risk of venous thromboembolism, myocardial infarction, stroke, major bleeding and death in patients undergoing total hip and knee replacement: A 15-year retrospective cohort study of routine clinical practice. Bone Jt. J. 2014, 96, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-K.; Chen, C.-F.; Chung, L.-H.; Liu, C.-L.; Chen, W.-M. Population-based epidemiology of postoperative venous thromboembolism in Taiwanese patients receiving hip or knee arthroplasty without pharmacological thromboprophylaxis. Thromb. Res. 2014, 133, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, A.B.; Mehnert, F.; Johnsen, S.P.; Husted, S.; Sorensen, H.T. Venous thromboembolism in patients having knee replacement and receiving thromboprophylaxis: A Danish population-based follow-up study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2011, 93, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guijarro, R.; Montes, J.; Roman, C.S.; Arcelus, J.I.; Barillari, G.; Granero, X.; Monreal, M. Venous thromboembolism and bleeding after total knee and hip arthroplasty. Findings from the Spanish National Discharge Database. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 105, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.; Eriksson, B.I.; Puskas, D.; Shi, M.; Bocanegra, T.; Weitz, J.; Raskob, G.E. Oral direct factor Xa inhibition with edoxaban for thromboprophylaxis after elective total hip replacement. A randomised double-blind dose-response study. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 104, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, A.; Labonte, A.J.; Winter, M.R.; Segal, J.B.; Silliman, R.A.; Katz, J.N.; Losina, E.; Berlowitz, D. Risk of venous thromboembolism after total hip and knee replacement in older adults with comorbidity and co-occurring comorbidities in the Nationwide Inpatient Sample (2003–2006). BMC Geriatr. 2010, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.E.; Low, J.; Courtenay, B.; Neil, M.J.; McGrath, M.; Ma, D. A single-centre prospective study of clinical and haemostatic risk factors for venous thromboembolism following lower limb arthroplasty. Br. J. Haematol. 2005, 129, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.J.; Lee, Y.-K.; Kim, H.J.; Ha, Y.-C.; Koo, K.-H. Deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism are uncommon in East Asian patients after total hip arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 3423–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baser, O.; Supina, D.; Sengupta, N.; Wang, L.; Kwong, L. Clinical and cost outcomes of venous thromboembolism in Medicare patients undergoing total hip replacement or total knee replacement surgery. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2011, 27, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, R.J.; Hess, S.; Berkowitz, S.D.; Homering, M. Complication rates after hip or knee arthroplasty in morbidly obese patients. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2013, 471, 3358–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, N.M. Venous thrombosis of the lower limbs with particular reference to bed-rest. Br. J. Surg. 1957, 45, 209–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, P.S.; Warming, T.; Hansen, K.; Paltved, C.; Berg, H.V.; Jensen, R.; Kirchhoff-Jensen, R.; Kjaer, L.; Kerbouche, N.; Leth-Espensen, P.; et al. Low molecular weight heparin (Innohep) as thromboprophylaxis in outpatients with a plaster cast: A venografic controlled study. Thromb. Res. 2002, 105, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassen, M.R.; Borris, L.C.; Nakov, R.L. Use of the low-molecular-weight heparin reviparin to prevent deep-vein thrombosis after leg injury requiring immobilization. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 726–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, D.W.; Fitzpatrick, R.; Rogers, K.; Pandit, H.G.; Beard, D.J.; Carr, A.J.; Dawson, J. The use of the Oxford hip and knee scores. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2007, 89, 1010–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, R.E.; Cronin, M.D.; Singh, P.J. The Oxford hip scores for primary and revision hip replacement. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2005, 87, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amstutz, H.C.; Thomas, B.J.; Jinnah, R.; Kim, W.; Grogan, T.; Yale, C. Treatment of primary osteoarthritis of the hip. A comparison of total joint and surface replacement arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1984, 66, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naal, F.D.; Impellizzeri, F.M.; Leunig, M. Which is the best activity rating scale for patients undergoing total joint arthroplasty? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2009, 467, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weel, H.; Lindeboom, R.; Kuipers, S.E.; Vervest, T.M.J.S. Comparison between the Harris- and Oxford Hip Score to evaluate outcomes one-year after total hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2017, 83, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parsons, N.R.; De Souza, R.-M.; Oni, T.; Achten, J.; Krikler, S.J.; Costa, M.L. A comparison of Harris and Oxford hip scores for assessing outcome after resurfacing arthroplasty of the hip: Can the patient tell us everything we need to know. HIP Int. 2010, 20, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaule, P.E.; Dorey, F.J.; Hoke, R.; Le Duff, M.; Amstutz, H.C. The value of patient activity level in the outcome of total hip arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2006, 21, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sechriest, V.F., 2nd; Kyle, R.F.; Marek, D.J.; Spates, J.D.; Saleh, K.J.; Kuskowski, M. Activity level in young patients with primary total hip arthroplasty: A 5-year minimum follow-up. J. Arthroplast. 2007, 22, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Kataoka, M.; Goto, K.; Kuroda, Y.; So, K.; Matsuda, S. Patient- and Surgery-Related Factors that Affect Patient-Reported Outcomes after Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heit, J.A.; Silverstein, M.D.; Mohr, D.N.; Petterson, T.M.; O’Fallon, W.M.; Melton, L.J., 3rd. Risk factors for deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: A population-based case-control study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2000, 160, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akeda, K.; Matsunaga, H.; Imanishi, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Sakakibara, T.; Kasai, Y.; Sudo, A. Prevalence and countermeasures for venous thromboembolic diseases associated with spinal surgery: A follow-up study of an institutional protocol in 209 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2014, 39, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiozaki, T.; Tabata, T.; Motohashi, T.; Kondo, E.; Tanida, K.; Okugawa, T.; Ikeda, T. Preoperative management of patients with gynecologic malignancy complicated by existing venous thromboembolism. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2012, 164, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloan, M.; Sheth, N.; Lee, G.-C. Is Obesity Associated with Increased Risk of Deep Vein Thrombosis or Pulmonary Embolism After Hip and Knee Arthroplasty? A Large Database Study. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2019, 477, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieber, B.; Han, J.; Appelboom, G.; Taylor, B.E.; Han, B.; Agarwal, N.; Connolly, E.S. Association of Steroid Use with Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Neurosurgical Patients: A National Database Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2016, 89, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, I.A.; Lin, M.; Donoho, D.A.; Ding, L.; Giannotta, S.L.; Attenello, F.; Mack, W.J.; Liu, J.C. Venous Thromboembolism After Degenerative Spine Surgery: A Nationwide Readmissions Database Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019, 125, e165–e174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Cutrera, N.J.; Dodd, A.C.; Wallace, C.; Avilucea, F.R.; Melbourne, C.; Jahangir, A.A.; Mir, H.H.; Obremskey, W.T.; Sethi, M.K. The risk of deep vein thrombosis in total joint patients compared to orthopaedic trauma patients: Need for new prevention guidelines. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2017, 8 (Suppl. 2), S52–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, J.; Breusch, S.J.; Tian, J. Risk factors for venous thromboembolism after total hip and total knee arthroplasty: A meta-analysis. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2015, 135, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enga, K.F.; Rye-Holmboe, I.; Hald, E.M.; Mathiesen, E.B.; Njølstad, I.; Wilsgaard, T.; Braekkan, S.K.; Løchen, M.-L.; Hansen, J.-B. Atrial fibrillation and future risk of venous thromboembolism:the Tromso study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, P.; Gregoire, F.; Capon, A.; Lehert, P. Atrial fibrillation as a risk factor for deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary emboli in stroke patients. Stroke 1991, 22, 760–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Overall | DVT | No DVT | p Value # | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 500 | 26 | 474 | ||
| Sex | Male | 91 | 2 | 89 | 0.12 |
| Female | 409 | 24 | 385 | ||
| Age, years | 64.79 ± 12.7 (22–89) | 70.0 ± 14.6 (35–87) | 64.5 ± 12.5 (22–89) | 0.0083 | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 24.0 ± 4.0 (12.2–41.7) | 23.6 ± 3.9 (18.2–32.2) | 24.3 ± 4.2 (12.2–41.8) | 0.63 | |
| Current steroid use | 54 | 10/26 | 44/474 | <0.0001 | |
| Previous DVT history | 11/500 | 6/26 | 5/474 | <0.0001 | |
| Current anticoagulant use | 51/500 | 6/26 | 45/474 | 0.026 | |
| Atrial fibrillation | 15/500 | 1/26 | 14/474 | 0.80 | |
| Congestive heart failure | 16/500 | 1/26 | 15/474 | 0.85 | |
| Major surgery | 347/500 | 20/26 | 327/474 | 0.22 | |
| Major surgery within last 12 months | 70/500 | 7/26 | 63/474 | 0.053 | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 54/500 | 3/26 | 51/474 | 0.9 | |
| Collagen disease | 55/500 | 7/26 | 48/474 | 0.023 | |
| Malignancy | 78/500 | 3/26 | 75/474 | 0.55 | |
| Current smoking | 36/500 | 1/26 | 35/474/ | 0.50 |
| Type of Collagen Disease | Overall (n = 500) | DVT (n = 26) | No DVT (n = 474) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 23 | 2 | 21 |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | 15 | 2 | 13 |
| Dermatomyositis | 8 | 1 | 7 |
| Systemic sclerosis | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| Sjögren syndrome | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| Polymyalgia rheumatica | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Polyarteritis nodosa | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Adult Still’s disease | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Behçet’s disease | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Variables | Overall | DVT | No DVT | p Value # |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxford Hip Score | 29.4 ± 10.2 | 22.5 ± 12.3 | 29.7 ± 10.0 | 0.0060 |
| Harris Hip Score | 52.6 ± 16.1 | 50.9 ± 17.8 | 52.7 ± 16.0 | 0.55 |
| UCLA activity score | 3.69 ± 1.34 | 2.64 ± 0.91 | 3.75 ± 1.33 | <0.0001 |
| VAS | 6.08 ± 2.81 | 6.88 ± 2.50 | 6.04 ± 2.82 | 0.21 |
| UCLA | OHS | HHS | VAS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UCLA | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0039 |
| OHS | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| HHS | <0.0001 | 0.0032 | ||
| VAS | <0.0001 |
| UCLA | OHS | HHS | VAS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UCLA | 1.0 | 0.34 | 0.43 | −0.14 |
| OHS | 1.0 | 0.42 | −0.60 | |
| HHS | 1.0 | −0.31 | ||
| VAS | 1.0 |
| Variables | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p Value | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OHS | 0.95 | 0.91–0.99 | 0.031 | 1.02 |
| Age | 1.07 | 1.03–1.12 | 0.00056 | 1.12 |
| Previous history of DVT | 27.15 | 3.31–222.53 | 0.0021 | 1.18 |
| Current anticoagulant use | 0.48 | 0.09–2.63 | 0.39 | 1.20 |
| Collagen disease | 0.93 | 0.19–4.64 | 0.93 | 1.60 |
| Current steroid use | 10.45 | 2.31–47.34 | 0.0023 | 1.67 |
| Variables | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p Value | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UCLA activity score | 0.49 | 0.28–0.84 | 0.0099 | 1.16 |
| Age | 1.07 | 1.02–1.12 | 0.0027 | 1.27 |
| Previous history of DVT | 74.98 | 8.54–658.18 | <0.0001 | 1.17 |
| Current anticoagulant use | 0.34 | 0.056–2.06 | 0.24 | 1.20 |
| Collagen disease | 1.03 | 0.23–4.68 | 0.97 | 1.55 |
| Current steroid use | 9.32 | 2.14–40.68 | 0.0030 | 1.69 |
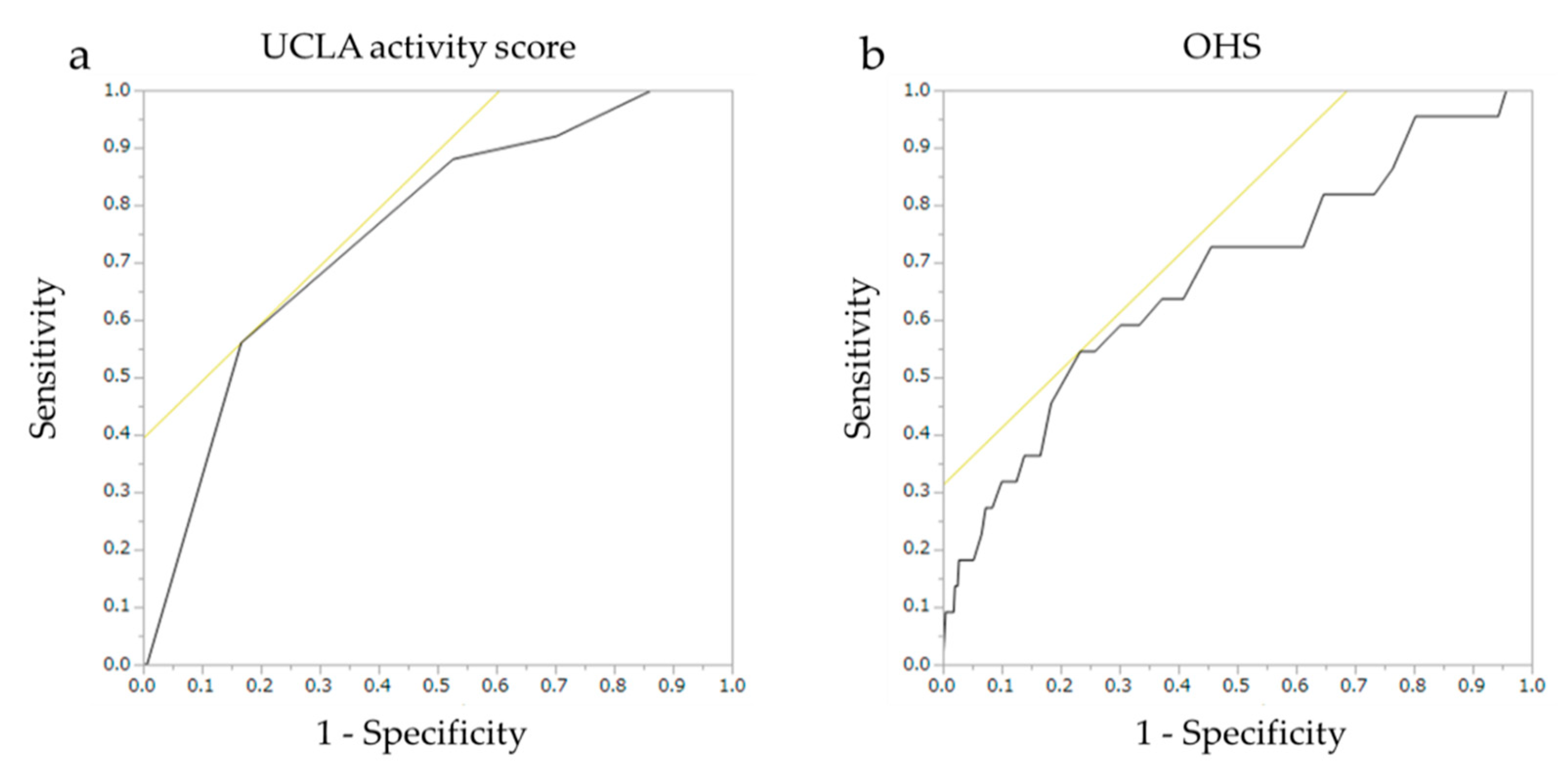
| Variables | AUC | Youden Index | Predictive Cutoff | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV (%) | NPV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UCLA activity score | 0.755 | 0.393 | 2 | 56.0 | 83.3 | 15.7 | 94.7 |
| OHS | 0.673 | 0.312 | 22 | 54.5 | 76.6 | 10.4 | 97.1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kawai, T.; Goto, K.; Kuroda, Y.; Matsuda, S. Lower Activity and Function Scores Are Associated with a Higher Risk of Preoperative Deep Venous Thrombosis in Patients Undergoing Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051257
Kawai T, Goto K, Kuroda Y, Matsuda S. Lower Activity and Function Scores Are Associated with a Higher Risk of Preoperative Deep Venous Thrombosis in Patients Undergoing Total Hip Arthroplasty. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(5):1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051257
Chicago/Turabian StyleKawai, Toshiyuki, Koji Goto, Yutaka Kuroda, and Shuichi Matsuda. 2020. "Lower Activity and Function Scores Are Associated with a Higher Risk of Preoperative Deep Venous Thrombosis in Patients Undergoing Total Hip Arthroplasty" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 5: 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051257
APA StyleKawai, T., Goto, K., Kuroda, Y., & Matsuda, S. (2020). Lower Activity and Function Scores Are Associated with a Higher Risk of Preoperative Deep Venous Thrombosis in Patients Undergoing Total Hip Arthroplasty. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(5), 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051257






