Tuberculosis in HIV-Associated Cryptococcal Meningitis is Associated with an Increased Risk of Death
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Study Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
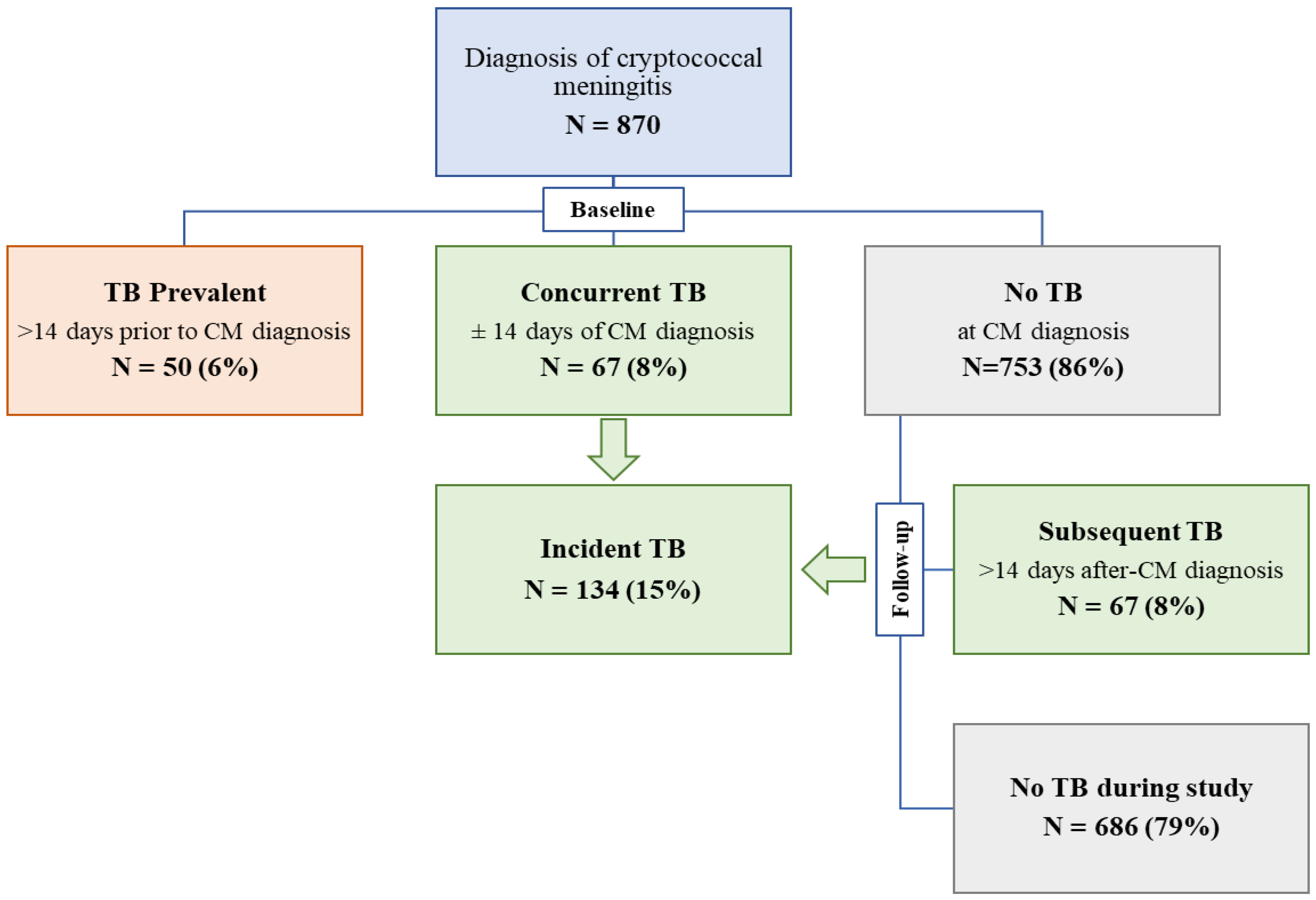
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rajasingham, R.; Smith, R.M.; Park, B.J.; Jarvis, J.N.; Govender, N.P.; Chiller, T.M.; Denning, D.W.; Loyse, A.; Boulware, D.R. Global burden of disease of HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis: an updated analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV and AIDS. Global HIV & AIDS Statistics-2019 Fact Sheet. Available online: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet (accessed on 10 August 2019).
- Cox, J.A.; Lukande, R.L.; Nelson, A.M.; Mayanja-Kizza, H.; Colebunders, R.; Van Marck, E.; Manabe, Y.C. An autopsy study describing causes of death and comparing clinico-pathological findings among hospitalized patients in Kampala, Uganda. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karat, A.S.; Omar, T.; von Gottberg, A.; Tlali, M.; Chihota, V.N.; Churchyard, G.J.; Fielding, K.L.; Johnson, S.; Martinson, N.A.; McCarthy, K.; et al. Autopsy Prevalence of Tuberculosis and Other Potentially Treatable Infections among Adults with Advanced HIV Enrolled in Out-Patient Care in South Africa. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.B.; Omar, T.; Setlhako, G.J.; Osih, R.; Feldman, C.; Murdoch, D.M.; Martinson, N.A.; Bangsberg, D.R.; Venter, W.D. Causes of death on antiretroviral therapy: a post-mortem study from South Africa. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.; Cresswell, F.V.; Rhein, J.; Ssebambulidde, K.; Boulware, D.R. Cryptococcal Meningitis and Tuberculous Meningitis Co-infection in HIV-Infected Ugandan Adults. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018, 5, ofy193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.T.; Tsai, Y.J.; Fan, J.Y.; Ku, S.C.; Yu, C.J. Cryptococcosis and tuberculosis co-infection at a university hospital in Taiwan, 1993-2006. Infection 2010, 38, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Al-Hatmi, A.M.; Chen, Y.; Ying, Y.; Fang, W.; Xu, J.; Hagen, F.; Hong, N.; Boekhout, T.; Liao, W.; et al. Cryptococcosis and tuberculosis co-infection in mainland China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2016, 5, e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Denning, D.W.; Hagen, F.; Jiang, W.; Hong, N.; Deng, S.; Lei, X.; Deng, D.; et al. Tuberculosis/cryptococcosis co-infection in China between 1965 and 2016. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2017, 6, e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelson, M. Diagnosing tuberculosis in HIV-infected patients: challenges and future prospects. Br. Med. Bull. 2007, 81–82, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabanda, T.; Siedner, M.J.; Klausner, J.D.; Muzoora, C.; Boulware, D.R. Point-of-care diagnosis and prognostication of cryptococcal meningitis with the cryptococcal antigen lateral flow assay on cerebrospinal fluid. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2014, 58, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J.E.; Toniolo, C.; Paulino, A.; Colombo, A.L.; Martins, M.D.A.; Meira, C.D.S.; Azevedo, R.G.S.; Pereira-Chioccola, V.L.; Gomes, H.R.; Lazera, M.D.S.; et al. Performance of cryptococcal antigen lateral flow assay in serum, cerebrospinal fluid, whole blood, and urine in HIV-infected patients with culture-proven cryptococcal meningitis admitted at a Brazilian referral center. Rev. Inst Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2018, 60, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulware, D.R.; Rolfes, M.A.; Rajasingham, R.; von Hohenberg, M.; Qin, Z.; Taseera, K.; Schutz, C.; Kwizera, R.; Butler, E.K.; Meintjes, G.; et al. Multisite validation of cryptococcal antigen lateral flow assay and quantification by laser thermal contrast. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwizera, R.; Nguna, J.; Kiragga, A.; Nakavuma, J.; Rajasingham, R.; Boulware, D.R.; Meya, D.B. Performance of cryptococcal antigen lateral flow assay using saliva in Ugandans with CD4 < 100. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolfes, M.; Butler, E.; von Hohenberg, M.; Nabeta, H.; Kwizera, R.; Rajasingham, R.; Bahr, N.; Bohjanen, P.; Meya, D.; Boulware, D. Evaluation of a novel point-of-care lateral flow assay to detect cryptococcal antigen in plasma and CSF. In Proceedings of the 19th Conference on Retrovirus and Opportunistic Infections, Seattle, WA, USA, 8 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, D.A.; Kiiza, T.; Kwizera, R.; Kiggundu, R.; Velamakanni, S.; Meya, D.B.; Rhein, J.; Boulware, D.R. Evaluation of fingerstick cryptococcal antigen lateral flow assay in HIV-infected persons: a diagnostic accuracy study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulware, D.R.; Meya, D.B.; Muzoora, C.; Rolfes, M.A.; Huppler Hullsiek, K.; Musubire, A.; Taseera, K.; Nabeta, H.W.; Schutz, C.; Williams, D.A.; et al. Timing of antiretroviral therapy after diagnosis of cryptococcal meningitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2487–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhein, J.; Huppler Hullsiek, K.; Tugume, L.; Nuwagira, E.; Mpoza, E.; Evans, E.E.; Kiggundu, R.; Pastick, K.A.; Ssebambulidde, K.; Akampurira, A.; et al. Adjunctive sertraline for HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis: a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind phase 3 trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhein, J.; Morawski, B.M.; Hullsiek, K.H.; Nabeta, H.W.; Kiggundu, R.; Tugume, L.; Musubire, A.; Akampurira, A.; Smith, K.D.; Alhadab, A.; et al. Efficacy of adjunctive sertraline for the treatment of HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis: an open-label dose-ranging study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tugume, L.; Morawski, B.M.; Abassi, M.; Bahr, N.C.; Kiggundu, R.; Nabeta, H.W.; Hullsiek, K.H.; Taseera, K.; Musubire, A.K.; Schutz, C.; et al. Prognostic implications of baseline anaemia and changes in haemoglobin concentrations with amphotericin B therapy for cryptococcal meningitis. HIV Med. 2017, 18, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tugume, L.; Rhein, J.; Hullsiek, K.H.; Mpoza, E.; Kiggundu, R.; Ssebambulidde, K.; Schutz, C.; Taseera, K.; Williams, D.A.; Abassi, M.; et al. HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis occurring at relatively higher CD4 counts. J. Infect Dis. 2019, 219, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerga, H.; Mathabire Rucker, S.C.; Cossa, L.; Bastard, M.; Amoros, I.; Manhica, I.; Mbendera, K.; Telnov, A.; Szumilin, E.; Sanchez-Padilla, E.; et al. Diagnostic value of the urine lipoarabinomannan assay in HIV-positive, ambulatory patients with CD4 below 200 cells/mul in 2 low-resource settings: A prospective observational study. PLoS Med. 2019, 16, e1002792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, J.G.; Theron, G.; van Zyl-Smit, R.; Haripersad, A.; Mottay, L.; Kraus, S.; Binder, A.; Meldau, R.; Hardy, A.; Dheda, K. Diagnostic accuracy of a urine lipoarabinomannan strip-test for TB detection in HIV-infected hospitalised patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 40, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geppert, E.F.; Leff, A. The pathogenesis of pulmonary and miliary tuberculosis. Arch. Intern. Med. 1979, 139, 1381–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.B.; Perlin, D.S.; Xue, C. Molecular mechanisms of cryptococcal meningitis. Virulence 2012, 3, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Ji, X.; Gao, B.; Liang, S.; Bai, J.; Lu, H.; Gu, S.; Xu, J.; Li, H. Diagnostic Analysis of Pulmonary Cryptococcosis in 134 Serum CRAG-Negative Cases. Chest J. 2016, 149, A86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidelines for Managing Advanced HIV Disease and Rapid Initiation of Antiretroviral Therapy, July 2017; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- WHO Guidelines on Tuberculosis Infection Prevention and Control, 2019 Update; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Araujo-Mariz, C.; Lopes, E.P.; Acioli-Santos, B.; Maruza, M.; Montarroyos, U.R.; Ximenes, R.A.; Lacerda, H.R.; Miranda-Filho Dde, B.; Albuquerque Mde, F. Hepatotoxicity during Treatment for Tuberculosis in People Living with HIV/AIDS. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panomvana Na Ayudhya, D.; Thanompuangseree, N.; Tansuphaswadikul, S. Effect of rifampicin on the pharmacokinetics of fluconazole in patients with AIDS. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2004, 43, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assebe, L.F.; Reda, H.L.; Wubeneh, A.D.; Lerebo, W.T.; Lambert, S.M. The effect of isoniazid preventive therapy on incidence of tuberculosis among HIV-infected clients under pre-ART care, Jimma, Ethiopia: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
| Characteristic | TB Prevalent | Concurrent TB | No TB | p value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (>14 days Prior) | (Days −14 to +14) | (By day +14) | ||
| (n = 50) | (n = 67) | (n = 753) | ||
| Demographics | ||||
| Age, years | 35 (29, 40) | 35 (30, 40) | 35 (30, 41) | 0.88 |
| Women | 22 (44%) | 21 (31%) | 312 (41%) | 0.24 |
| Clinical characteristics | ||||
| Weight, kg | 50 (45, 55) | 58 (50, 60) | 52 (48, 60) | <0.001 |
| Glasgow Coma Score < 15 | 14 (28%) | 23 (34%) | 303 (40%) | 0.16 |
| Receiving HIV therapy | 30 (60%) | 18 (27%) | 298 (40%) | <0.01 |
| Duration of HIV, months | 3.0 (1.5, 22.3) | 6.0 (0.4, 55.1) | 4.1 (0.2, 37.0) | 0.55 |
| CD4 T cells/mm3 | 26 (11, 54) | 21 (6, 65) | 17 (7, 51) | 0.25 |
| Confirmed TB | 23 (46%) | 12 (18%) | ||
| Baseline CSF parameters | ||||
| Cryptococcus culture, log10 CFU/mL | 4.2 (2.4, 5.3) | 4.4 (2.7, 5.5) | 4.7 (3.3, 5.4) | 0.17 |
| Sterile CSF culture | 3 (6%) | 4 (6%) | 51 (7%) | 0.95 |
| CSF opening pressure, mm H2O | 210 (155, 305) | 260 (180, 360) | 280 (180, 420) | <0.01 |
| CSF white cell ≥5 cells/mm3 | 19 (42%) | 28 (44%) | 287 (40%) | 0.71 |
| CSF protein, mg/dL | 54 (30, 110) | 71.5 (24, 164) | 60 (25, 120) | 0.61 |
| Days on TB Medications | TB Prevalent | Concurrent TB | No TB |
|---|---|---|---|
| (>14 days Prior) | (Days −14 to +14) | (By day +14) | |
| (n = 50) | (n = 67) | (n = 753) | |
| Prior to Cryptococcal Diagnosis | |||
| Max | 180 | 12 | |
| Median (IQR) | 41 (29, 72) | 4 (0, 11) | |
| Min | 17 | 0 | |
| N | 50 | 15 | |
| After Cryptococcal Diagnosis 1 | |||
| Max | 15 | 126 | |
| Median (IQR) | 7 (2, 11) | 41 (22, 69) | |
| Min | 1 | 12 | |
| N | 52 | 67 | |
| Unadjusted Model | Adjusted Model * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Event | HR (95% CI) | p value | HR (95% CI) | p value |
| Including TB prevalent † (n = 870 | ||||
| Death by day 30 | 1.33 (0.90, 1.97) | 0.15 | 1.47 (1.00, 2.17) | 0.05 |
| Any death | 1.62 (1.23, 2.14) | <0.001 | 1.75 (1.33, 2.32) | <0.001 |
| Excluding TB prevalent (n = 805) | ||||
| Death by day 30 | 1.30 (0.80, 2.11) | 0.29 | 1.34 (0.83, 2.19) | 0.23 |
| Any death | 1.72 (1.25, 2.36) | <0.001 | 1.77 (1.28, 2.43) | <0.001 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rutakingirwa, M.K.; Cresswell, F.V.; Kwizera, R.; Ssebambulidde, K.; Kagimu, E.; Nuwagira, E.; Tugume, L.; Mpoza, E.; Dobbin, J.; Williams, D.A.; et al. Tuberculosis in HIV-Associated Cryptococcal Meningitis is Associated with an Increased Risk of Death. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030781
Rutakingirwa MK, Cresswell FV, Kwizera R, Ssebambulidde K, Kagimu E, Nuwagira E, Tugume L, Mpoza E, Dobbin J, Williams DA, et al. Tuberculosis in HIV-Associated Cryptococcal Meningitis is Associated with an Increased Risk of Death. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(3):781. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030781
Chicago/Turabian StyleRutakingirwa, Morris K., Fiona V. Cresswell, Richard Kwizera, Kenneth Ssebambulidde, Enock Kagimu, Edwin Nuwagira, Lillian Tugume, Edward Mpoza, Joanna Dobbin, Darlisha A. Williams, and et al. 2020. "Tuberculosis in HIV-Associated Cryptococcal Meningitis is Associated with an Increased Risk of Death" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 3: 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030781
APA StyleRutakingirwa, M. K., Cresswell, F. V., Kwizera, R., Ssebambulidde, K., Kagimu, E., Nuwagira, E., Tugume, L., Mpoza, E., Dobbin, J., Williams, D. A., Muzoora, C., Meya, D. B., Boulware, D. R., Hullsiek, K. H., & Rhein, J. (2020). Tuberculosis in HIV-Associated Cryptococcal Meningitis is Associated with an Increased Risk of Death. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(3), 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030781





