Dosimetric Comparison of Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy, Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy and Hybrid Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy/Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy Techniques for Right Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Treatment Planning Selection
2.2. Mould Fabrication and Computed Tomography (CT) Simulation
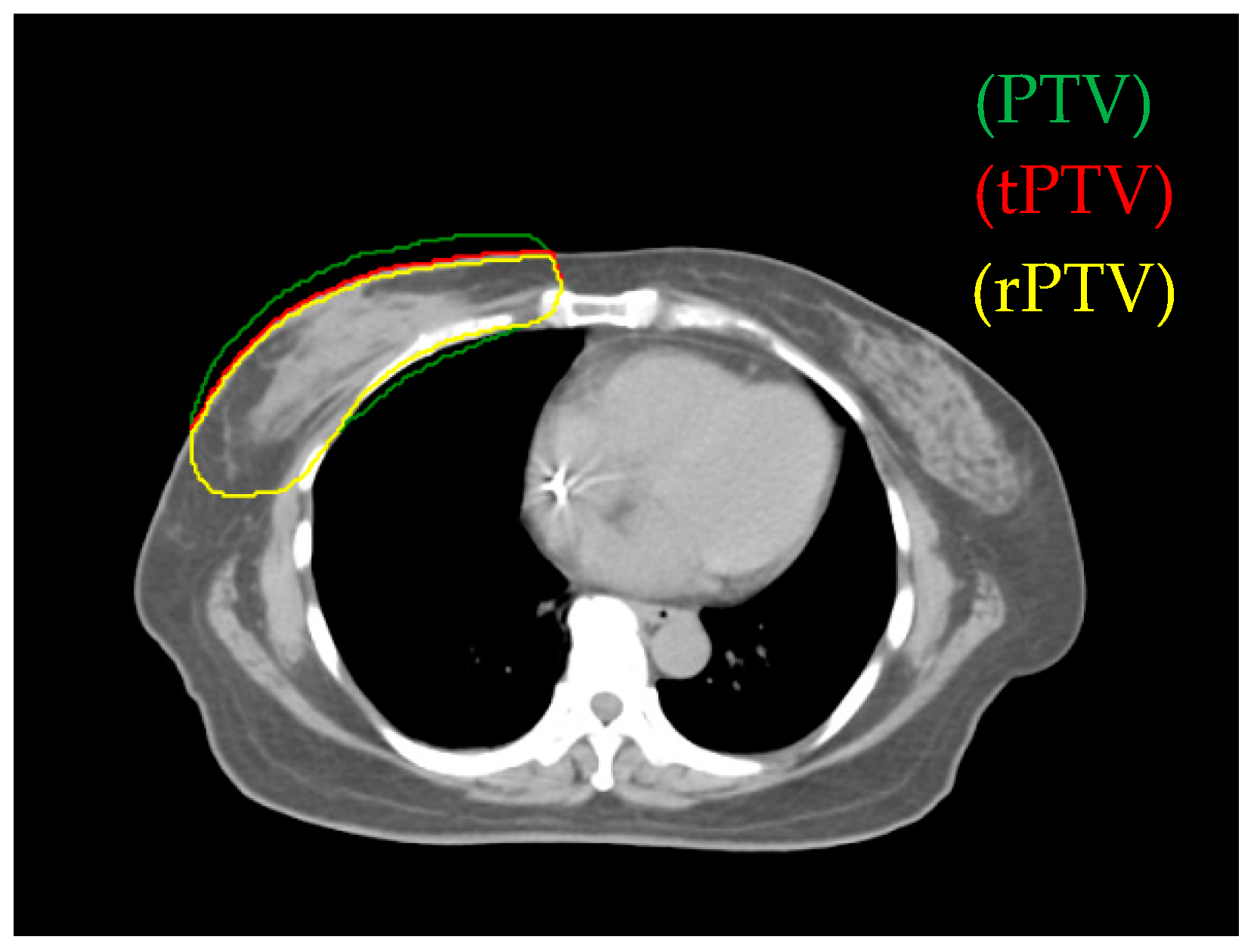
2.3. Target Volume and Planning Organs-at-Risk Definition
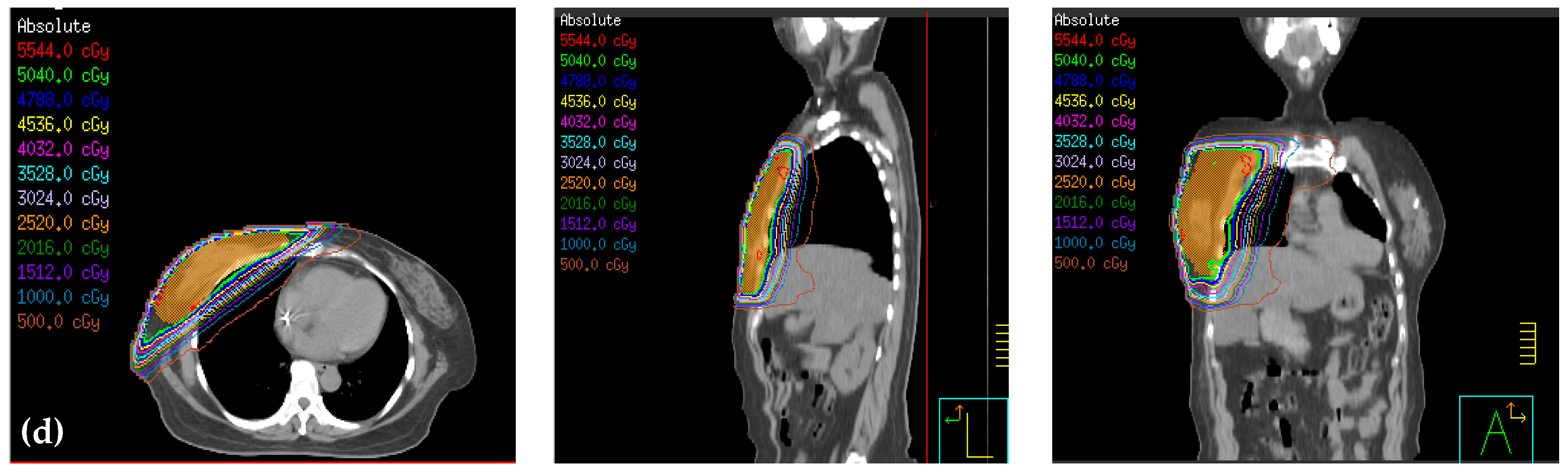
2.4. Design of the Treatment Plan
2.5. IMRT Treatment Planning
2.6. Hybrid 3D-CRT/IMRT Treatment Planning
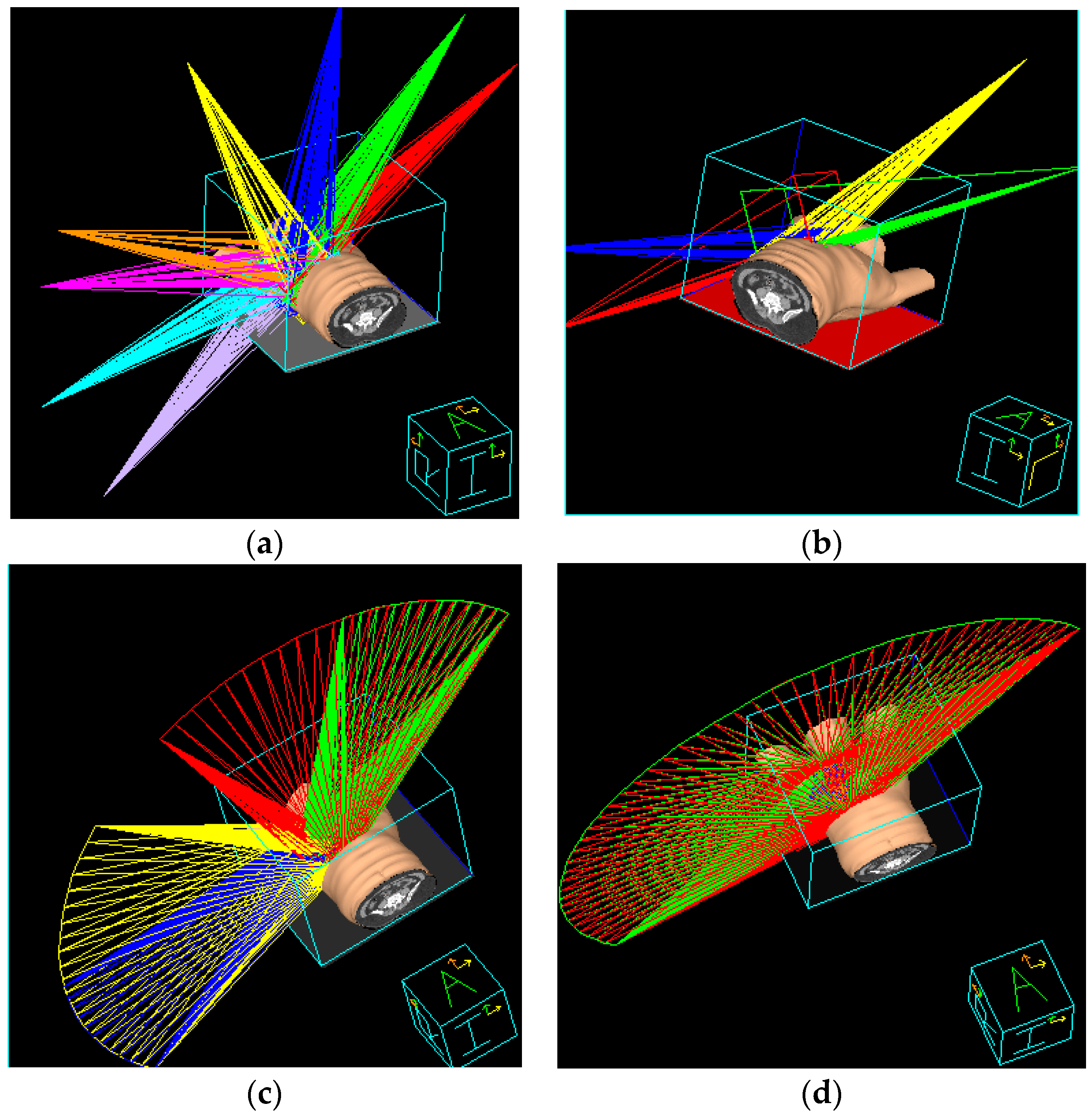
2.7. Non-Continuous Partial Arc Treatment Planning
2.8. Continuous Partial Arc Treatment Planning
2.9. Organ Absorbed Dose and Whole-Body Effective Dose Measurement
2.10. Dosimetry Parameters Comparison among Treatment Plans
- TVRI: PTV in 95% prescription dose;
- TV: PTV;
- VRI: whole volume in 95% prescription dose;
- CI ranged from 0 to 1, and the plan is more conformal as CI gets closer to 1.
- VPTV,95%dose: Volume reaching 95% prescription dose in target volume;
- VPTV,105% dose: Volume reaching 105% prescription dose in target volume;
- VPTV: PTV.
- D2%: Maximum absorbed dose in 2% PTV;
- D98%: Minimum absorbed dose in 98% PTV;
- DP: Prescription dose.
3. Results
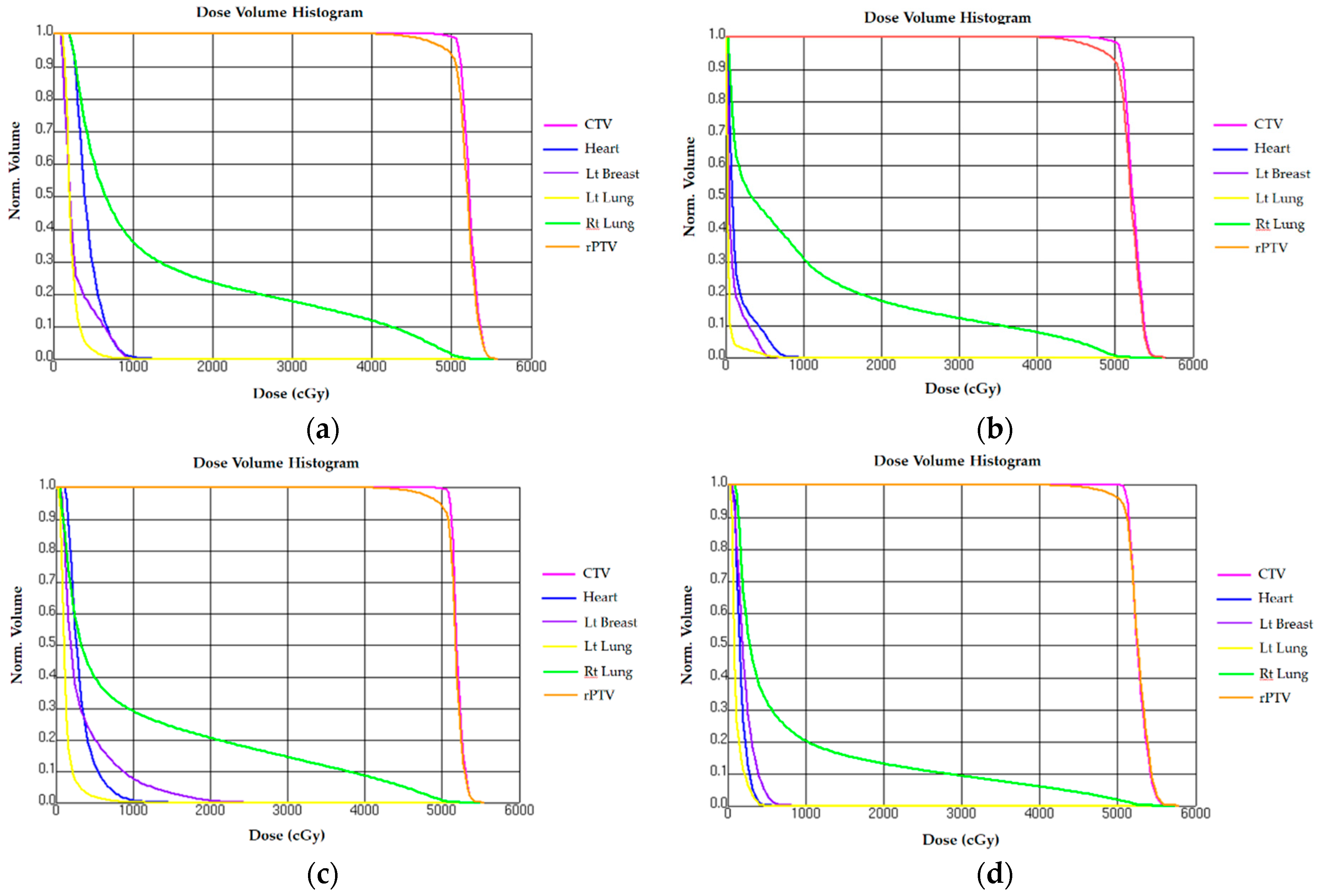
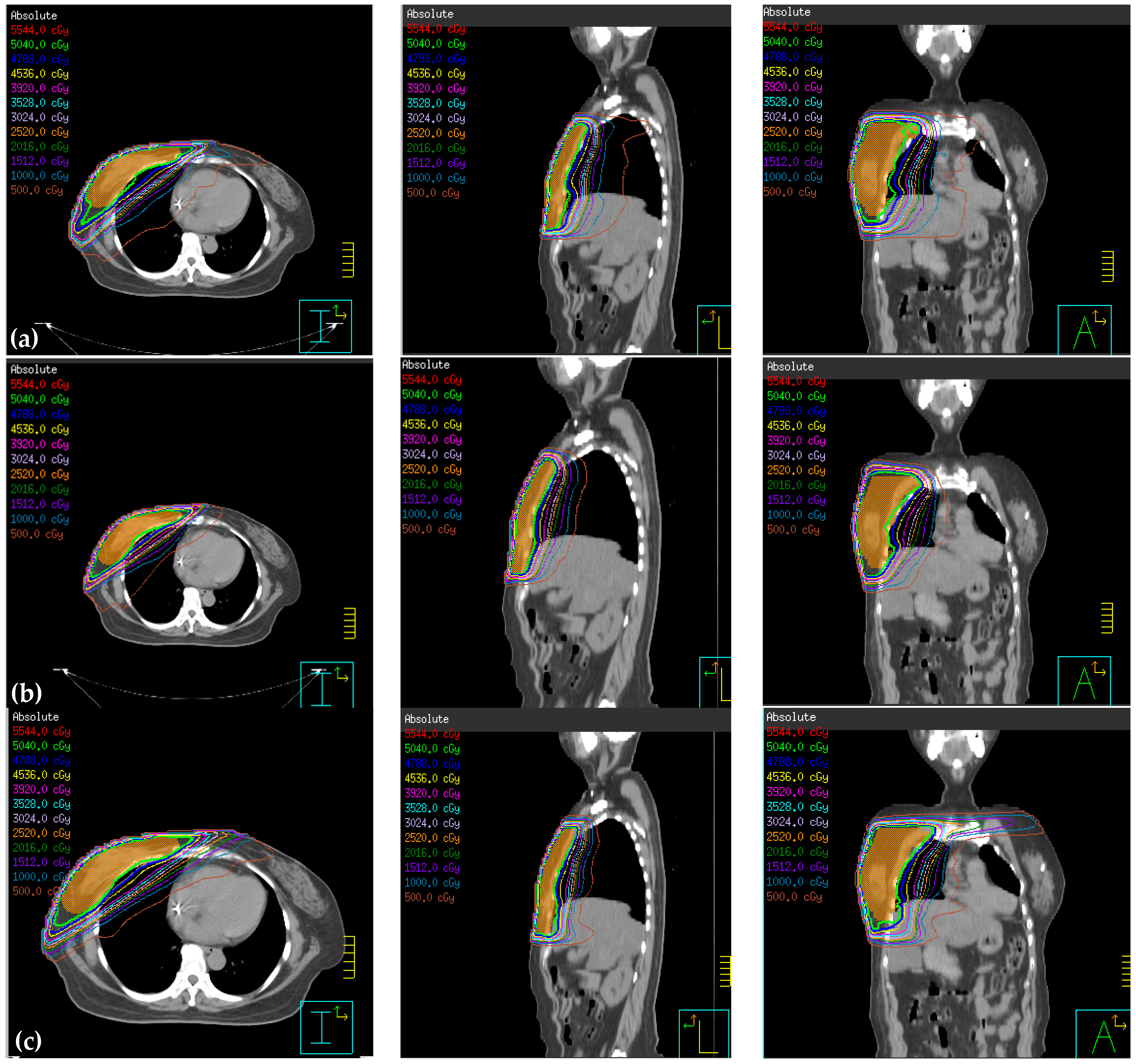
3.1. Comparison of Reduced PTV (rPTV) in Four Techniques on Dosimetry
3.2. Normal Tissue Comparison on Dosimetry
3.2.1. Heart
3.2.2. Ipsilateral Lung
3.2.3. Contralateral Lung
3.2.4. Contralateral Breast
3.2.5. Comparison of Planning Parameter Optimization
3.2.6. Comparison between Organ Absorbed Dose and Whole-Body Effective Dose
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vaidya, J.S.; Joseph, D.J.; Tobias, J.S.; Bulsara, M.; Wenz, F.; Saunders, C.; Keshtgar, M. Targeted intraoperative radiotherapy versus whole breast radiotherapy for breast cancer (TARGIT-A trial): An international, prospective, randomised, non-inferiority phase 3 trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Dongen, J.A.; Voogd, A.C.; Fentiman, I.S.; Legrand, C.; Sylvester, R.J.; Tong, D.; Bartelink, H. Long-term results of a randomized trial comparing breast-conserving therapy with mastectomy: European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer 10801 trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Veronesi, U.; Orecchia, R.; Luini, A.; Galimberti, V.; Zurrida, S.; Intra, M.; Veronesi, P.; Arnone, P.; Leonardi, M.C.; Ciocca, M.; et al. Intraoperative radiotherapy during breast conserving surgery: A study on 1,822 cases treated with electrons. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 124, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fiorentino, A.; Gregucci, F.; Mazzola, R.; Figlia, V.; Ricchetti, F.; Sicignano, G.; Massocco, A. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy and hypofractionated volumetric modulated arc therapy for elderly patients with breast cancer: Comparison of acute and late toxicities. Radiol. Med. 2019, 124, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.C.; Wang, F.N.; Lin, H.H.; Hsu, C.H.; Lin, J.P.; Lai, L.H. Dosimetric measurement of testicular dose for colorectal cancer using optically-stimulated luminescent dosimeters in radiotherapy. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 172, 108792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onal, C.; Efe, E.; Guler, O.C.; Yildirim, B.A. Dosimetric Comparison of Sequential Versus Simultaneous-integrated Boost in Early-stage Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Breast-conserving Surgery. In Vivo 2019, 33, 2181–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.F.; Chen, P.H.; Shueng, P.W.; Lin, H.H.; Lai, L.H. Evaluation of various head flexion angles in hippocampal-avoidance whole-brain radiotherapy using volumetric modulated arc therapy. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 173, 108884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, L.; Lohr, F.; Fogliata, A.; Franceschini, D.; De Rose, F.; Filippi, A.R.; Scorsetti, M. Critical appraisal of the role of volumetric modulated arc therapy in the radiation therapy management of breast cancer. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sethi, R.A.; No, H.S.; Jozsef, G.; Ko, J.P.; Formenti, S.C. Comparison of three-dimensional versus intensity-modulated radiotherapy techniques to treat breast and axillary level III and supraclavicular nodes in a prone versus supine position. Radiother. Oncol. 2012, 102, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, M.Y.B.; Castilla, P.J.L.; Bautista, A.A.Q. Hypofractionation with concomitant boost using intensity-modulated radiation therapy in early-stage breast cancer in Mexico. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2018, 23, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghian, A.G.; Assaad, S.I.; Niemierko, A.; Kuter, I.; Younger, J.; Schoenthaler, R.; Roche, M.; Powell, S.N. Risk of pneumonitis in breast cancer patients treated with radiation therapy and combination chemotherapy with paclitaxel. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 1806–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das, S.K.; Baydush, A.H.; Zhou, S.; Miften, M.; Yu, X.; Craciunescu, O.; Oldham, M.; Light, K.; Wong, T.; Blazing, M.; et al. Predicting radiotherapy-induced cardiac perfusion defects. Med. Phys. 2005, 32, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, M.; Collins, R.; Darby, S.; Davies, C.; Elphinstone, P.; Evans, V.; Godwin, J.; Gray, R.; Hicks, C.; James, S.; et al. Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG). Effects of radiotherapy and of differences in the extent of surgery for early breast cancer on local recurrence and 15-year survival: An overview of the randomised trials. Lancet 2005, 366, 2087–2106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De la Torre, N.; Figureueroa, C.T.; Martinez, K.; Riley, S.; Chapman, J. A comparative study of surface dose and dose distribution for intact breast following irradiation with field-in-field technique vs. the use of conventional wedges. Med. Dosim. 2004, 29, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennberg, B.; Gagliardi, G.; Sundbom, L.; Svane, G.; Lind, P. Early response of lung in breast cancer irradiation: Radiologic density changes measured by CT and symptomatic radiation pneumonitis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2002, 52, 1196–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, L.B.; Yu, X.; Prosnitz, R.G.; Zhou, S.M.; Hardenbergh, P.H.; Blazing, M.; Hollis, D.; Lind, P.; Tisch, A.; Wong, T.Z.; et al. The incidence and functional consequences of RT-associated cardiac. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2005, 63, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kestin, L.L.; Sharpe, M.B.; Frazier, R.C.; Vicini, F.A.; Yan, D.; Matter, R.C.; Wong, J.W. Intensity modulation to improve dose uniformity with tangential breast radiotherapy: Initial clinical experience. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2000, 48, 1559–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicini, F.A.; Sharpe, M.; Kestin, L.; Martinez, A.; Mitchell, C.K.; Wallace, M.F.; Wong, J. Optimizing breast cancer treatment efficacy with intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2002, 54, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, Y.C.; Yasuda, G.; Fitzgerald, T.J.; Urie, M.M. Intensity modulation for breast treatment using static multi-leaf collimators. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2000, 46, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, E.M.; Yarnold, J.R.; Adams, E.J.; Morgan, A.; Warrington, A.P.; Evans, P.M. An investigation into methods of IMRT planning applied to breast radiotherapy. Br. J. Radiol. 2008, 81, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckham, W.A.; Popescu, C.C.; Patenaude, V.V.; Wai, E.S.; Olivotto, I.A. Is multibeam IMRT better than standard treatment for patients with left-sided breast cancer? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 69, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolini, G.; Clivio, A.; Fogliata, A.; Vanetti, E.; Cozzi, L. Simultaneous integrated boost radiotherapy for bilateral breast: A treatment planning and dosimetric comparison for volumetric modulated arc and fixed field intensity modulated therapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2009, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abo-Madyan, Y.; Aziz, M.H.; Aly, M.M.; Schneider, F.; Sperk, E.; Clausen, S.; Glatting, G. Second cancer risk after 3D-CRT, IMRT and VMAT for breast cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2014, 110, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, D.A.; Verbakel, W.F.; Otto, K.; Senan, S. New developments in arc radiation therapy: A review. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2010, 36, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, P.F.; Lin, S.M.; Lee, S.H.; Yeh, C.Y.; Huang, Y.T.; Lee, C.C.; Hong, J.H. The feasibility study of using multiple partial volumetric-modulated arcs therapy in early stage left-sided breast cancer patients. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2012, 13, 2085–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popescu, C.C.; Olivotto, I.A.; Beckham, W.A.; Ansbacher, W.; Zavgorodni, S.; Shaffer, R.; Wai, E.S.; Otto, K. Volumetric modulated arc therapy improves dosimetry and reduces treatment time compared to conventional intensity-modulated radiotherapy for locoregional radiotherapy of left-sided breast cancer and internal mammary nodes. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 76, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goody, R.B.; O’Hare, J.; McKenna, K.; Dearey, L.; Robinson, J.; Bell, P.; Hanna, G.G. Unintended cardiac irradiation during left-sided breast cancer radiotherapy. Br. J. Radiol. 2013, 86, 20120434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemanski, C.; Thariat, J.; Ampil, F.L.; Bose, S.; Vock, J.; Davis, R.; Godinez, J. Image-guided radiotherapy for cardiac sparing in patients with left-sided breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karpf, D.; Sakka, M.; Metzger, M.; Grabenbauer, G.G. Left breast irradiation with tangential intensity modulated radiotherapy (t-IMRT) versus tangential volumetric modulated arc therapy (t-VMAT): Trade-offs between secondary cancer induction risk and optimal target coverage. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakka, M.; Kunzelmann, L.; Metzger, M.; Grabenbauer, G.G. Cardiac dose-sparing effects of deep-inspiration breath-hold in left breast irradiation. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2017, 193, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AAPM TG-21. A protocol for the determination of absorbed dose from high-energy photon and electron beams. Med. Phys. 1983, 10, 741–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection. Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. In ICRP Publication 60, International Commission on Radiological Protection; ICRP: Stockholm, Sweden, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection. Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. In ICRP Publication 103, International Commission on Radiological Protection; ICRP: Stockholm, Sweden, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Feuvret, L.; Noël, G.; Mazeron, J.J.; Bey, P. Conformity index: A review. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 64, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Mohan, R.; Morris, M.; Lauve, A.; Schmidt-Ullrich, R. Simultaneous integrated boost intensity-modulated radiotherapy for locally advanced head-and-neck squamous cell carcinomas. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2003, 56, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, C.S.; Urie, M.M.; Fitzgerald, T.J. Hybrid IMRT plan-concurrently treating conventional and IMRT beams for improved irradiation and reduced planning time. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. 2005, 61, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, W.; Menon, G.; Wolfe, N.; Ploquin, N.; Trotter, T.; Pudney, D. IMRT for the breast: A comparison of tangential planning techniques. Phys. Med. Biol. 2010, 55, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darby, S.C.; Ewertz, M.; McGale, P.; Bennet, A.M.; Blom-Goldman, U.; Brønnum, D.; Correa, C.; Cutter, D.; Gagliardi, G.; Gigante, B.; et al. Risk of ischemic heart disease in women after radiotherapy for breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, X.; Liu, H.H.; Tucker, S.L.; Wang, S.; Mohan, R.; Cox, J.D.; Komaki, R.; Liao, Z. Risk factors for pericardial effusion in inoperable esophageal cancer patients treated with definitive chemoradiation therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2008, 70, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.H.; Chen, L.X.; Deng, X.W.; Liu, X.W.; Huang, Y.; Huang, X.B. A comparative dosimetric study for treating left-sided breast cancer for small breast size using five different radiotherapy techniques: Conventional tangential field, filed-in-filed, tangential-IMRT, multi-beam IMRT and VMAT. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 15, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graham, M.V.; Purdy, J.A.; Emami, B.; Harms, W.; Bosch, W.; Lockett, M.A.; Perez, C.A. Clinical dose-volume histogram analysis for pneumonitis after 3D treatment for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1999, 45, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujino, K.; Hirota, S.; Endo, M.; Obayashi, K.; Kotani, Y.; Satouchi, M.; Kado, T.; Takada, Y. Predictive value of dose-volume histogram parameters for predicting radiation pneumonitis after concurrent chemoradiation for lung cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2003, 55, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haciislamoglu, E.; Colak, F.; Canyilmaz, E.; Dirican, B.; Gurdalli, S.; Yilmaz, A.H.; Yoney, A.; Bahat, Z. Dosimetric comparison of left-sided whole-breast irradiation with 3DCRT, forward-planned IMRT, inverse-planned IMRT, helical tomotherapy, and volumetric arc therapy. Phys. Med. 2015, 31, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernando, M.L.; Marks, L.B.; Bentel, G.C.; Zhou, S.M.; Hollis, D.; Das, S.K.; Fan, M.; Munley, M.T.; Shafman, T.D.; Anscher, M.S.; et al. Radiation-induced pulmonary toxicity: A dose-volume histogram analysis in 201 patients with lung cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2001, 51, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boice, J.D., Jr.; Harvey, E.B.; Blettner, M.; Stovall, M.; Flannery, J.T. Cancer in the contralateral breast after radiotherapy for breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 12, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Target | Dose (cGy) | Volume (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTV | Max dose | <5544 | |
| Max DVH | 4788 | 100% | |
| Heart | Max dose | <5292 | |
| Max DVH | 1765 | <35% | |
| Ipsilateral lung | Max dose | <5544 | |
| Max DVH | 2000 | <25% | |
| Contralateral lung | Max dose | <5292 | |
| Max DVH | 1764 | <20% | |
| Structures | Continuous Partial Arc | Non-Continuous Partial Arc | Hybrid 3D-CRT/IMRT | IMRT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean dose (Gy) | 52.05 ± 0.09 | 51.61 ± 1.33 | 51.82 ± 1.52 | 51.81 ± 1.45 |
| Maximum dose (Gy) | 55.88 ± 0.16 | 55.07 ± 0.08 | 56.15 ± 0.07 | 55.52 ± 0.08 |
| minimal dose (Gy) | 25.60 ± 0.16 | 23.69 ± 1.23 | 21.67 ± 0.15 | 23.00 ± 0.04 |
| V100 (%) | 97.42 ± 0.09 | 92.39 ± 0.23 | 87.61 ± 1.23 | 89.12 ± 1.43 |
| V95 (%) | 97.42 ± 0.07 | 97.41 ± 0.9 | 95.77 ± 1.18 | 96.62 ± 2.01 |
| V105 (%) | 18.59 ± 0.14 | 18.81 ± 0.11 | 15.31 ± 1.01 | 14.39 ± 1.54 |
| V107 (%) | 2.05 ± 0.06 | 0.78 ± 0.04 | 2.44 ± 0.10 | 2.38 ± 0.07 |
| V110 (%) | 0.10 ± 0.11 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.01 |
| D2 (Gy) | 53.93 ± 1.45 | 53.60 ± 2.73 | 54.25 ± 1.61 | 54.25 ± 1.48 |
| D98 (Gy) | 47.21 ± 0.98 | 47.15 ± 1.44 | 45.67 ± 1.77 | 46.4 ± 1.22 |
| CI | 0.74 ± 0.01 | 0.74 ± 0.01 | 0.68 ± 0.03 | 0.64 ± 0.05 |
| HI1 | 0.79 ± 0.02 | 0.89 ± 0.11 | 0.71 ± 0.21 | 0.78 ± 0.11 |
| HI2 | 13.33 ± 0.01 | 12.79 ± 0.03 | 17.02 ± 0.03 | 15.57 ± 0.04 |
| Structures | Continuous Partial Arc | Non-Continuous Partial Arc | Hybrid 3D-CRT/IMRT | IMRT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heart | ||||
| Mean dose (Gy) | 1.73 ± 0.07 | 3.15 ± 0.03 | 1.47 ± 0.02 | 4.35 ± 0.01 |
| minimal dose (Gy) | 0.71 ± 0.04 | 1.04 ± 0.04 | 0.30 ± 0.01 | 1.93 ± 0.03 |
| Maximum dose (Gy) | 5.82 ± 0.02 | 1.47 ± 0.07 | 9.52 ± 0.08 | 12.38 ± 0.06 |
| V5Gy (%) | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.27 ± 0.03 |
| V10Gy (%) | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.70 ± 0.03 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.005 ± 0.01 |
| V50.40Gy (%) | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| Right lung (ipsilateral) | ||||
| Mean dose (Gy) | 8.32 ± 1.61 | 10.71 ± 0.09 | 10.14 ± 1.47 | 12.76 ± 1.23 |
| minimal dose (Gy) | 0.80 ± 0.04 | 0.50 ± 0.03 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | 1.65 ± 0.01 |
| Maximum dose (Gy) | 54.06 ± 1.08 | 52.32 ± 0.06 | 51.88 ± 0.09 | 52.37 ± 0.05 |
| V5Gy (%) | 32.56 ± 0.91 | 39.69 ± 0.02 | 45.12 ± 0.77 | 60.82 ± 0.32 |
| V10Gy (%) | 20.02 ± 0.13 | 8.96 ± 0.10 | 30.97 ± 0.58 | 35.80 ± 0.18 |
| V20Gy (%) | 12.96 ± 0.34 | 20.43 ± 1.00 | 17.55 ± 1.69 | 23.33 ± 1.91 |
| V30Gy (%) | 9.16 ± 0.45 | 14.30 ± 0.09 | 12.09 ± 1.01 | 17.54 ± 0.09 |
| V40Gy (%) | 5.80 ± 0.69 | 8.38 ± 0.45 | 7.69 ± 0.33 | 11.60 ± 0.17 |
| V50.40Gy (%) | 1.01 ± 0.09 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 0.19 ± 0.04 | 0.79 ± 0.01 |
| Left lung (contralateral) | ||||
| Mean dose (Gy) | 1.19 ± 0.56 | 1.31 ± 0.71 | 0.42 ± 0.23 | 2.25 ± 0.05 |
| minimal dose (Gy) | 0.43 ± 0.05 | 0.21 ± 0.07 | 1.02 ± 0.02 | 0.83 ± 0.01 |
| Maximum dose (Gy) | 5.27 ± 0.03 | 11.65 ± 0.17 | 6.89 ± 0.09 | 10.09 ± 0.12 |
| V5Gy (%) | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 1.79 ± 0.04 | 0.67 ± 0.05 | 2.57 ± 0.03 |
| V10Gy (%) | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| V50.40Gy (%) | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| Left breast | ||||
| Mean dose (Gy) | 2.26 ± 0.13 | 3.51 ± 1.25 | 0.98 ± 0.15 | 2.78 ± 0.17 |
| minimal dose (Gy) | 0.41 ± 0.08 | 0.19 ± 0.09 | 0.22 ± 0.09 | 0.36 ± 0.04 |
| Maximum dose (Gy) | 8.39 ± 0.32 | 24.49 ± 1.33 | 6.60 ± 1.12 | 9.60 ± 1.66 |
| V5Gy (%) | 3.44 ± 0.13 | 20.13 ± 0.07 | 1.25 ± 0.08 | 14.90 ± 0.09 |
| V10Gy (%) | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 7.53 ± 0.09 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| V50.40Gy (%) | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| Machine Parameters | Continuous Partial Arc | Non-Continuous Partial Arc | Hybrid 3D-CRT/IMRT | IMRT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calculation mode | SmartArc | SmartArc | DMPO | DMPO |
| Maximum number of segments | 40 | 40 | 25 | 25 |
| Gantry angle | Beam 1: 55 ± 10°–235 ± 10° Beam 2: 235 ± 10°–55 ± 10° | Beam 1: 55 ± 10°–335 ± 10° Beam 2: 275 ± 10°–235 ± 10° Beam 3: 235 ± 10°–315 ± 10° Beam 4: 15 ± 10°–55 ± 10° | Beam 1: 3D–235 ± 10° Beam 2: 3D–55 ± 10° Beam 3: IMRT–250 ± 10° Beam 4: IMRT–35° | Beam 1: 56° Beam 2: 37° Beam 3: 7° Beam 4: 333° Beam 5: 284° Beam 6: 257° Beam 7: 229° Beam 8: 295° |
| Collimator angle | 10° | 10° | 3D: 10° 3D: 350° | × |
| Wedge | × | × | × | × |
| Delivery time (s) | 234 ± 15 | 146 ± 11 | 245 ± 20 | 300 ± 35 |
| Delivery MU | 687 ± 15 | 519.4 ± 17 | 319.1 ± 19 | 427.1 ± 25 |
| Dose | Continuous Partial Arc | Non-Continuous Partial Arc | Hybrid 3D-CRT/IMRT | IMRT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organ dose (Gy) | ||||
| Lens | 4.7 ± 0.03 | 0.38 ± 0.01 | 0.46 ± 0.02 | 4.32 ± 0.04 |
| Skin | 2.34 ± 0.13 | 0.8 ± 0.09 | 1.65 ± 0.05 | 2.41 ± 0.01 |
| Effective dose (Sv) | ||||
| ICRP-60 | 2.01 ± 0.23 | 0.72 ± 0.08 | 0.9 ± 0.03 | 1.88 ± 1.1 |
| ICRP-103 | 2.89 ± 0.15 | 1.25 ± 0.1 | 1.48 ± 0.18 | 2.71 ± 0.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.-C.; Chang, H.-M.; Lin, H.-H.; Lu, C.-C.; Lai, L.-H. Dosimetric Comparison of Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy, Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy and Hybrid Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy/Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy Techniques for Right Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3884. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9123884
Liu Y-C, Chang H-M, Lin H-H, Lu C-C, Lai L-H. Dosimetric Comparison of Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy, Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy and Hybrid Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy/Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy Techniques for Right Breast Cancer. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(12):3884. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9123884
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yi-Chi, Hung-Ming Chang, Hsin-Hon Lin, Chia-Chun Lu, and Lu-Han Lai. 2020. "Dosimetric Comparison of Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy, Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy and Hybrid Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy/Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy Techniques for Right Breast Cancer" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 12: 3884. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9123884
APA StyleLiu, Y.-C., Chang, H.-M., Lin, H.-H., Lu, C.-C., & Lai, L.-H. (2020). Dosimetric Comparison of Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy, Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy and Hybrid Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy/Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy Techniques for Right Breast Cancer. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(12), 3884. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9123884





