Unknown Subclinical Hypothyroidism and In-Hospital Outcomes and Short- and Long-Term All-Cause Mortality among ST Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Design
2.2. Definitions of SCH, Overt Hypothyroidism and the Euthyroid State
2.3. Definition of STEMI Diagnosis
2.4. Definition of Time to Mortality Following PCI
2.5. Definitions of Chronic Kidney Disease and Acute Kidney Injury
2.6. Data Collection and Clinical Follow-Up
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. In-Hospital Outcomes
3.3. Short-Term Since PCI Mortality
3.4. Long-Term Mortality
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cooper, D.S.; Biondi, B. Subclinical thyroid disease. Lancet 2012, 379, 1142–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugge, J.B.; Bougatsos, C.; Chou, R. Screening and Treatment of Thyroid Dysfunction: An Evidence Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boelaert, K. Thyroid dysfunction in the elderly. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabatabaie, V.; Surks, M.I. The aging thyroid. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2013, 20, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappola, A.R.; Fried, L.P.; Arnold, A.M.; Danese, M.D.; Kuller, L.H.; Burke, G.L.; Tracy, R.P.; Ladenson, P.W. Thyroid Status, Cardiovascular Risk, and Mortality in Older Adults. JAMA 2006, 295, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grais, I.M.; Sowers, J.R. Thyroid and the Heart. Am. J. Med. 2014, 127, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Sara, J.D.S.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Gharib, H.; Bell, M.R.; Gulati, R.; Lerman, L.O.; Lerman, A. Clinical outcomes of patients with hypothyroidism undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2055–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodondi, N.; Elzen, W.P.J.D.; Bauer, D.C.; Cappola, A.R.; Razvi, S.; Walsh, J.P.; Åsvold, B.O.; Iervasi, G.; Imaizumi, M.; Collet, T.-H.; et al. Subclinical Hypothyroidism and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease and Mortality. JAMA 2010, 304, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collet, T.-H.; Gussekloo, J.; Bauer, D.C.; Elzen, W.P.J.D.; Cappola, A.R.; Balmer, P.; Iervasi, G.; Åsvold, B.O.; Sgarbi, J.A.; Voelzke, H.; et al. Subclinical Hyperthyroidism and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease and Mortality. Arch. Intern. Med. 2012, 172, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencer, B.; Collet, T.H.; Virgini, V.; Virgini, V.; Bauer, D.C.; Gussekloo, J.; Cappola, A.R.; Nanchen, D.; den Elzen, W.P.J.; Balmer, P.; et al. Subclinical thyroid dysfunction and the risk of heart failure events: An individual participant data analysis from 6 prospective cohorts. Circulation 2014, 126, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yao, L.; Fang, Y.; Yang, R.; Chen, Y.; Yang, K.; Tian, L. Relationship between Subclinical Thyroid Dysfunction and the Risk of Cardiovascular Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 2017, 8130796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, H.I.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.N.; Kim, S.; Kim, M.-J.; Jin, S.-M.; Hur, K.Y.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Subclinical thyroid dysfunction and risk of carotid atherosclerosis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shacham, Y.; Leshem-Rubinow, E.; Gal-Oz, A.; Arbel, Y.; Keren, G.; Roth, A.; Steinvil, A. Relation of Time to Coronary Reperfusion and the Development of Acute Kidney Injury After ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Am. J. Cardiol. 2014, 114, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shacham, Y.; Leshem-Rubinow, E.; Steinvil, A.; Keren, G.; Roth, A.; Arbel, Y. High sensitive C-reactive protein and the risk of acute kidney injury among ST elevation myocardial infarction patients undergoing primary percutaneous intervention. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2015, 19, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Gara, P.T.; Kushner, F.G.; Ascheim, D.D.; Casey, D.E.; Chung, M.K.; De Lemos, J.A.; Ettinger, S.M.; Fang, J.C.; Fesmire, F.M.; Franklin, B.A.; et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA Guideline for the Management of ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2013, 127, e362–e425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y. (Lucy); Castro, A.F.; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A New Equation to Estimate Glomerular Filtration Rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellum, J.A.; Lameire, N.; KDIGO AKI Guideline Work Group. Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of acute kidney injury: A KDIGO summary (Part 1). Crit. Care 2013, 17, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Yoshihisa, A.; Kimishima, Y.; Kiko, T.; Watanabe, S.; Kanno, Y.; Abe, S.; Miyata, M.; Sato, T.; Suzuki, S.; et al. Subclinical Hypothyroidism Is Associated With Adverse Prognosis in Heart Failure Patients. Can. J. Cardiol. 2018, 34, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Kong, S.H.; Choi, H.S.; Hwangbo, Y.; Lee, M.-K.; Moon, J.H.; Jang, H.C.; Cho, N.H.; Park, Y.J. Relation of Subclinical Hypothyroidism is Associated With Cardiovascular Events and All-Cause Mortality in Adults With High Cardiovascular Risk. Am. J. Cardiol. 2018, 122, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.H.; Yoon, J.W.; Kim, S.-Y.; Oh, T.J.; Park, K.-H.; Choh, J.H.; Park, Y.J.; Lim, C. Subclinical Hypothyroidism and Coronary Revascularization After Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting. Am. J. Cardiol. 2018, 122, 1862–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Kim, M.J.; Yu, J.M.; Yoo, H.J.; Park, Y.J. Subclinical Hypothyroidism and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Thyroid 2018, 28, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Lim, Y.-H.; Shin, J.-H.; Park, J.; Shin, J. Impact of subclinical hypothyroidism on clinical outcomes following percutaneous coronary intervention. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 253, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oner, F.A.; Yurdakul, S.; Oner, E.; Uzum, A.K.; Ergüney, M. Evaluation of the effect of l-thyroxin therapy on endothelial functions in patients with subclinical hypothyroidism. Endocrine 2011, 40, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razvi, S.; Ingoe, L.; Keeka, G.; Oates, C.; McMillan, C.; Weaver, J.U. The Beneficial Effect ofl-Thyroxine on Cardiovascular Risk Factors, Endothelial Function, and Quality of Life in Subclinical Hypothyroidism: Randomized, Crossover Trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, E.N. Update in Lipid Alterations in Subclinical Hypothyroidism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niafar, M.; Toufan, M.; Ghafoori, S.; Aghamohamm, N.; Aghamohammadzadeh, N. Subclinical hypothyroidism effects on cardiac function. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2009, 12, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, S.; Kim, D.K. Subclinical Hypothyroidism and Cardiovascular Disease. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 30, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Yang, Q.; Chen, S.-H. Carotid intima-media thickness in patients with subclinical hypothyroidism: A meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis 2013, 227, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahaly, G.J. Cardiovascular and Atherogenic Aspects of Subclinical Hypothyroidism. Thyroid 2000, 10, 665–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, P.; Bajo, M.A.; Selgas, R.; Díez, J.J. Thyroid dysfunction and kidney disease: An update. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2017, 18, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, V.P.; Shilpasree, A.S.; Patil, V.S.; Pravinchandra, K.R.; Ingleshwar, D.G.; Vani, A.C. Evaluation of renal function in subclinical hypothyroidism. J. Lab. Physicians 2018, 10, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turhan, S.; Tulunay, C.; Cin, M.O.; Gursoy, A.; Kilickap, M.; Dincer, I.; Candemir, B.; Gullu, S.; Erol, C. Effects of Thyroxine Therapy on Right Ventricular Systolic and Diastolic Function in Patients with Subclinical Hypothyroidism: A Study by Pulsed Wave Tissue Doppler Imaging. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 3490–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Wang, Y.; Ma, A.; Wang, T. Subclinical thyroid dysfunction is associated with adverse prognosis in heart failure patients with reduced ejection fraction. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2019, 19, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Datta, S.; Mandal, S.C. Prevalence of Subclinical Hypothyroidism in Acute Coronary Syndrome in Nondiabetics: Detailed Analysis from Consecutive 1100 Patients from Eastern India. J. Thyroid. Res. 2018, 2018, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calsolaro, V.; Niccolai, F.; Pasqualetti, G.; Calabrese, A.M.; Polini, A.; Okoye, C.; Magno, S.; Caraccio, N.; Monzani, F. Overt and Subclinical Hypothyroidism in the Elderly: When to Treat? Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calsolaro, V.; Niccolai, F.; Pasqualetti, G.; Tognini, S.; Magno, S.; Riccioni, T.; Bottari, M.; Caraccio, N.; Monzani, F. Hypothyroidism in the Elderly: Who Should Be Treated and How? J. Endocr. Soc. 2018, 3, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, D.; Rodondi, N.; Kearney, P.M.; Ford, I.; Westendorp, R.G.J.; Mooijaart, S.P.; Sattar, N.; Aubert, C.E.; Aujesky, D.; Bauer, D.C.; et al. Thyroid Hormone Therapy for Older Adults with Subclinical Hypothyroidism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2534–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razvi, S.; Weaver, J.U.; Butler, T.J.; Pearce, S.H.S. Levothyroxine Treatment of Subclinical Hypothyroidism, Fatal and Nonfatal Cardiovascular Events, and Mortality. Arch. Intern. Med. 2012, 172, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, I.M.; Lau, E.; Sousa-Pinto, B.; Carvalho, D. Subclinical hypothyroidism: To treat or not to treat, that is the question! A systematic review with meta-analysis on lipid profile. Endocr. Connect. 2017, 6, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekkering, G.E.; Agoritsas, T.; Lytvyn, L.; Heen, A.F.; Feller, M.; Moutzouri, E.; Abdulazeem, H.; Aertgeerts, B.; Beecher, D.; Brito, J.P.; et al. Thyroid hormones treatment for subclinical hypothyroidism: A clinical practice guideline. BMJ 2019, 365, l2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, A.; Ingoe, L.; Pearce, S.; Zaman, A.; Razvi, S. Thyroxine in acute myocardial infarction (ThyrAMI)—levothyroxine in subclinical hypothyroidism post-acute myocardial infarction: Study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials 2015, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Euthyroid Patients (n = 1525) | Patients with SCH (n = 68) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years, mean ± SD | 61 ± 7 | 62 ± 8 | 0.41 |
| Age > 60 years, n (%) | 772 (51) | 36 (53) | 0.71 |
| Male sex, n (%) | 1258 (83) | 40 (59) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 367 (24) | 20 (29) | 0.31 |
| Hyperlipidemia, n (%) | 745 (49) | 40 (59) | 0.11 |
| Family history of CAD, n (%) | 325 (21) | 16 (24) | 0.67 |
| Smoking, n (%) | 748 (49) | 44 (65) | 0.012 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 668 (44) | 33 (49) | 0.45 |
| Chronic kidney disease (eGFR ≤ 60), n (%) | 378(25) | 22(32) | 0.16 |
| Multivessel coronary disease, n (%) | 862(57) | 39(59) | 0.73 |
| Past myocardial infarction, n (%) | 193 (13) | 12 (18) | 0.23 |
| Time to ER, minutes, median (IQR 25–75) | 120 (60–360) | 120 (60–280) | 0.81 |
| Admission CRP, mg/dl, median (IQR 25–75) | 4.4 (1.5–10.9) | 6.6 (1.7–13.3) | 0.34 |
| Duration of hospitalization, days, mean ± SD | 6 ± 5 | 7 ± 11 | 0.27 |
| Variable | Euthyroid Patients (n = 1525) | Patients with SCH (n = 68) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heart failure, n | 153 (10%) | 7 (10%) | 0.95 |
| Acute kidney injury, n | 146 (10%) | 14 (20%) | 0.003 |
| LVEF, mean ± SD | 47 ± 8 | 44 ± 9 | 0.014 |
| LVEF ≤ 40%, n | 452 (30%) | 29 (43%) | 0.03 |
| Bleeding, n | 62 (4%) | 5 (7%) | 0.20 |
| Ventricular tachycardia/fibrillation, n | 116 (8%) | 8 (12%) | 0.21 |
| Bradycardia, n (%) | 66 (4%) | 3 (4%) | 0.99 |
| Intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation, n | 64 (4%) | 5 (7%) | 0.21 |
| New-onset atrial fibrillation, n | 79 (5%) | 0 (0) | 0.05 |
| In-hospital CABG, n | 26 (2%) | 2 (3%) | 0.34 |
| Mechanical ventilation, n | 74 (5%) | 6 (9%) | 0.15 |
| 30-day mortality, n | 45 (3%) | 6 (9%) | 0.02 |
| Variable | Univariate | Multivariate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95%CI) | p Value | OR (95%CI) | p Value | |
| TSH ≥ 5 mU/mL | 3.2 (1.3–7.7) | 0.01 | 3.2 (1.2–8.6) | 0.02 |
| Female sex | 3.2 (1.8–5.8) | <0.001 | 1.8 (0.9–3.4) | 0.09 |
| Age > 60 years | 5.4 (2.5–11.6) | <0.001 | 2.9 (1.2–6.9) | 0.02 |
| Hypertension | 2.2 (1.2–3.9) | 0.01 | 1.4 (0.7–2.4) | 0.29 |
| LVEF ≤ 40% | 9.7 (4.6–20.4) | <0.001 | 4.3 (1.9–9.8) | 0.001 |
| Family history of CAD | 0.2 (0.1–0.7) | 0.01 | 0.3 (0.7–1.34) | 0.12 |
| Smoking | 0.4 (0.2–0.7) | 0.002 | 0.6 (0.3–1.3) | 0.23 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 1.4 (0.8–2.6) | 0.23 | ND | ND |
| Hyperlipidemia | 0.8 (0.4–1.4) | 0.37 | ND | ND |
| Variable | Univariate | Multivariate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95%CI) | p Value | HR (95%CI) | p Value | |
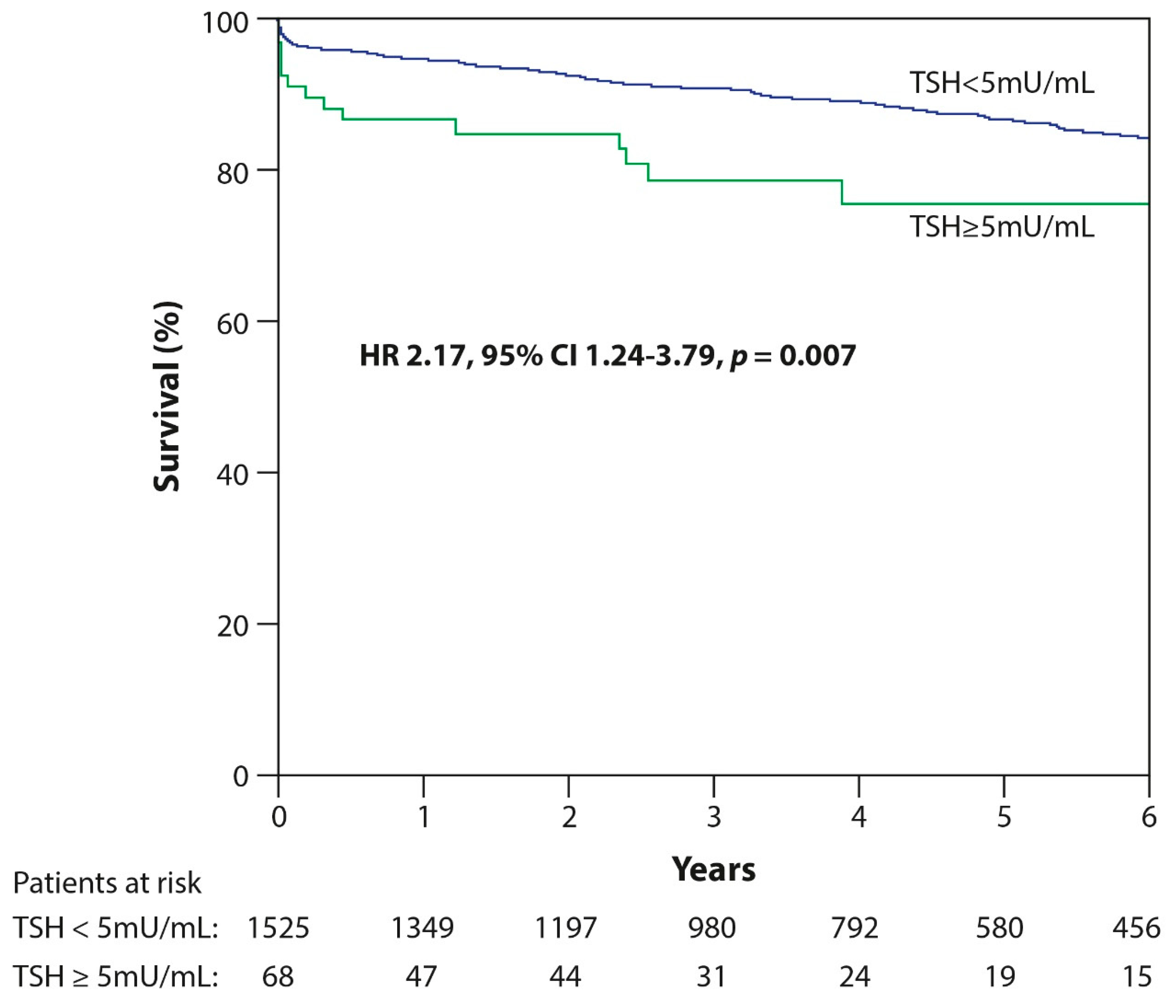
| TSH ≥ 5 mU/mL | 2.2 (1.3–3.6) | 0.003 | 2.2 (1.2–3.8) | 0.007 |
| Female sex | 2.1 (1.5–2.8) | <0.001 | 1.2 (0.8–1.5) | 0.36 |
| Age > 60 years | 7.0 (4.8–10.3) | <0.001 | 4.5 (2.9–6.8) | 0.001 |
| Hypertension | 2.8 (2.1–3.7) | <0.001 | 1.8 (1.3–2.4) | 0.001 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 1.7 (1.3–2.2) | <0.001 | 1.2 (0.8–1.6) | 0.35 |
| LVEF ≤ 40% | 2.2 (1.7–2.9) | <0.001 | 1.4 (1.1–1.9) | 0.02 |
| Past myocardial infarction | 2.0 (1.4–2.8) | <0.001 | 1.6 (1.1–2.3) | 0.01 |
| Family history of CAD | 0.2 (0.1–0.3) | <0.001 | 0.3 (0.1–0.6) | 0.001 |
| Smoking | 0.5 (0.4–0.7) | <0.001 | 0.9 (0.7–1.3) | 0.86 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 1.1 (0.8–1.4) | 0.48 | ND | ND |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Izkhakov, E.; Zahler, D.; Rozenfeld, K.-L.; Ravid, D.; Banai, S.; Topilsky, Y.; Stern, N.; Greenman, Y.; Shacham, Y. Unknown Subclinical Hypothyroidism and In-Hospital Outcomes and Short- and Long-Term All-Cause Mortality among ST Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3829. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9123829
Izkhakov E, Zahler D, Rozenfeld K-L, Ravid D, Banai S, Topilsky Y, Stern N, Greenman Y, Shacham Y. Unknown Subclinical Hypothyroidism and In-Hospital Outcomes and Short- and Long-Term All-Cause Mortality among ST Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(12):3829. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9123829
Chicago/Turabian StyleIzkhakov, Elena, David Zahler, Keren-Lee Rozenfeld, Dor Ravid, Shmuel Banai, Yan Topilsky, Naftali Stern, Yona Greenman, and Yacov Shacham. 2020. "Unknown Subclinical Hypothyroidism and In-Hospital Outcomes and Short- and Long-Term All-Cause Mortality among ST Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 12: 3829. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9123829
APA StyleIzkhakov, E., Zahler, D., Rozenfeld, K.-L., Ravid, D., Banai, S., Topilsky, Y., Stern, N., Greenman, Y., & Shacham, Y. (2020). Unknown Subclinical Hypothyroidism and In-Hospital Outcomes and Short- and Long-Term All-Cause Mortality among ST Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(12), 3829. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9123829




