Serum Zinc Level and non-Protein Respiratory Quotient in Patients with Chronic Liver Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Measurement of npRQ by IC
2.3. SMI and ECW to TBW Ratio using BIA
2.4. Statistical Considerations
3. Results
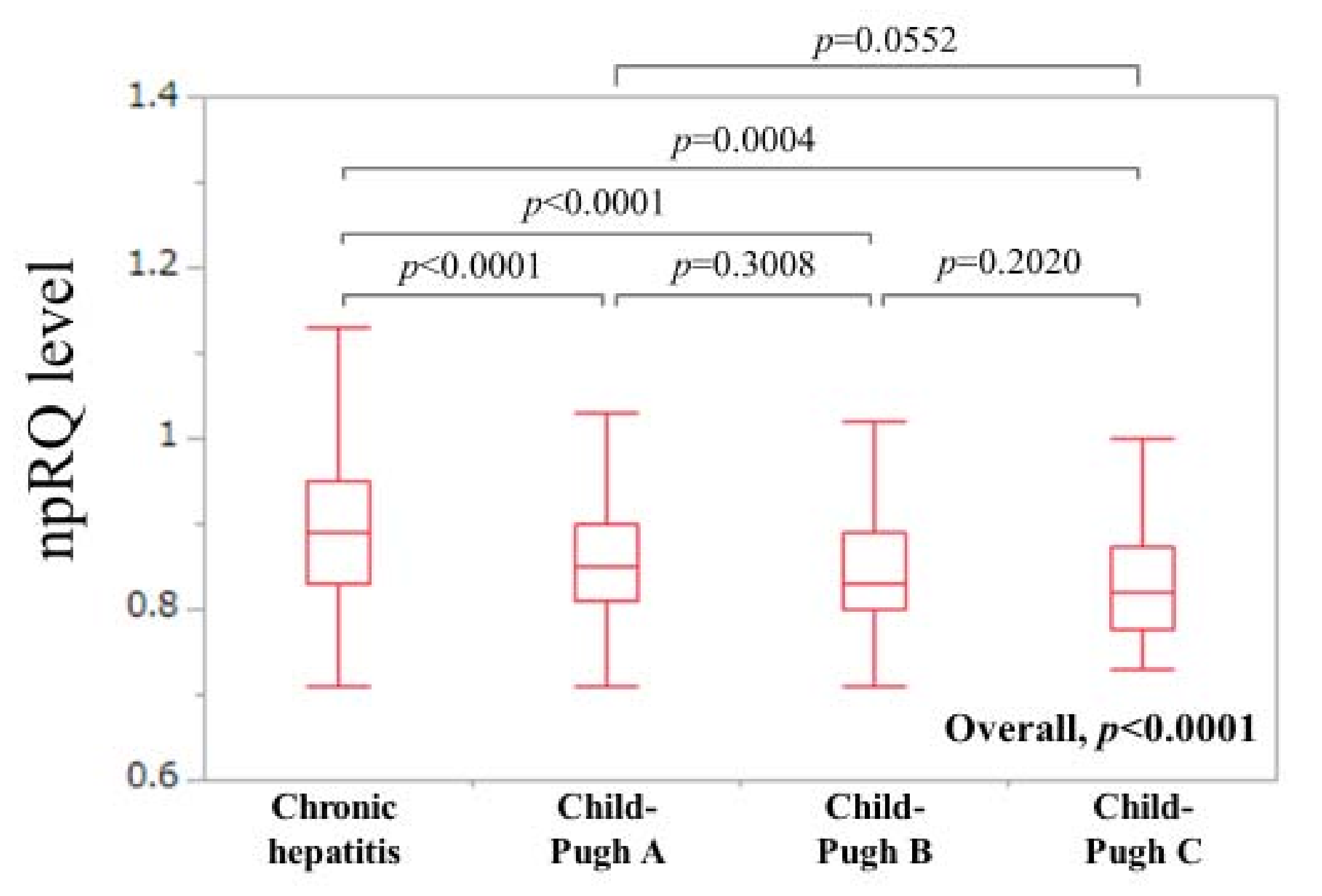
3.1. Patient Baseline Backgrounds
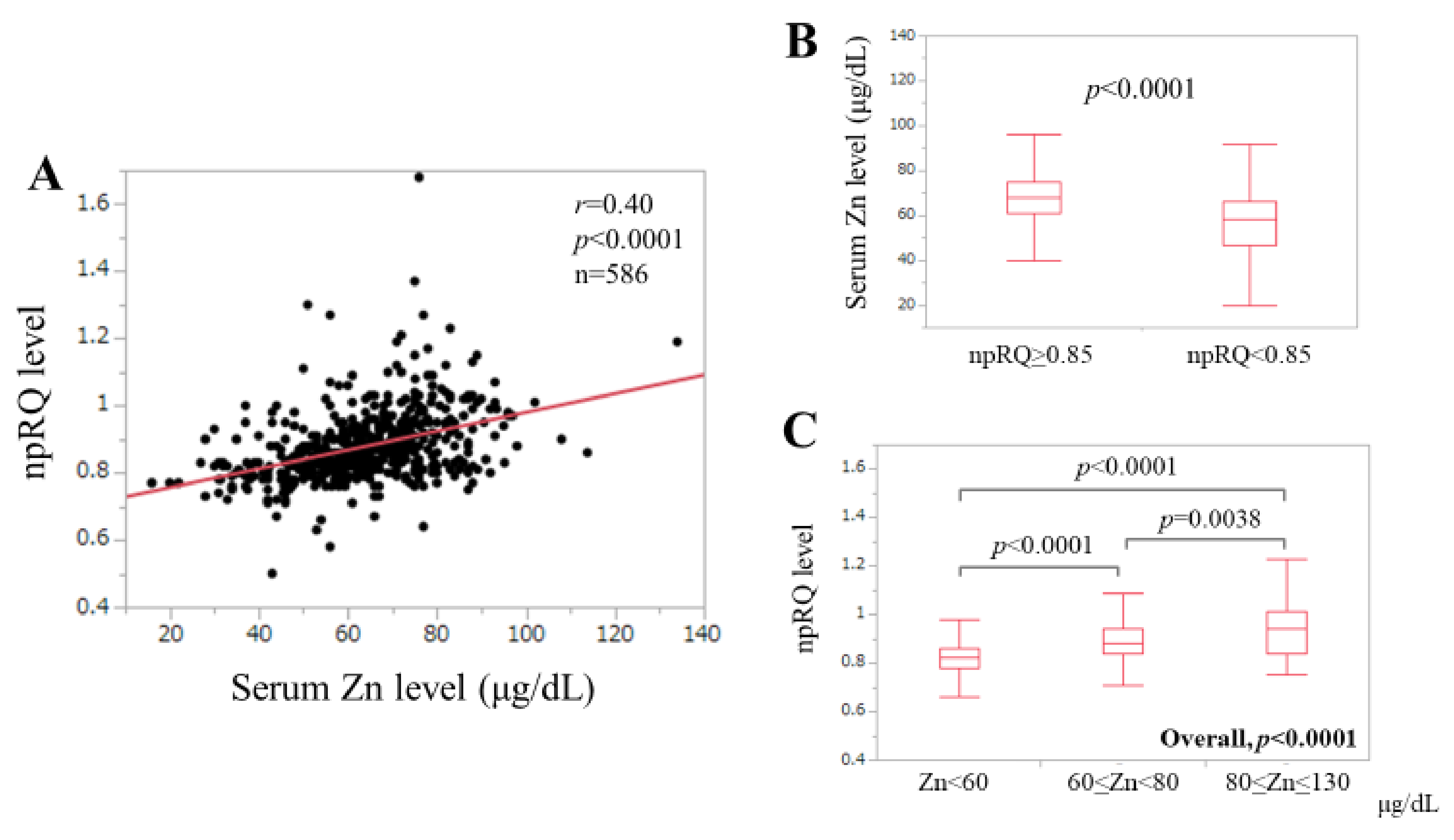
3.2. Correlation between npRQ Level and Serum Zn Level for All Cases
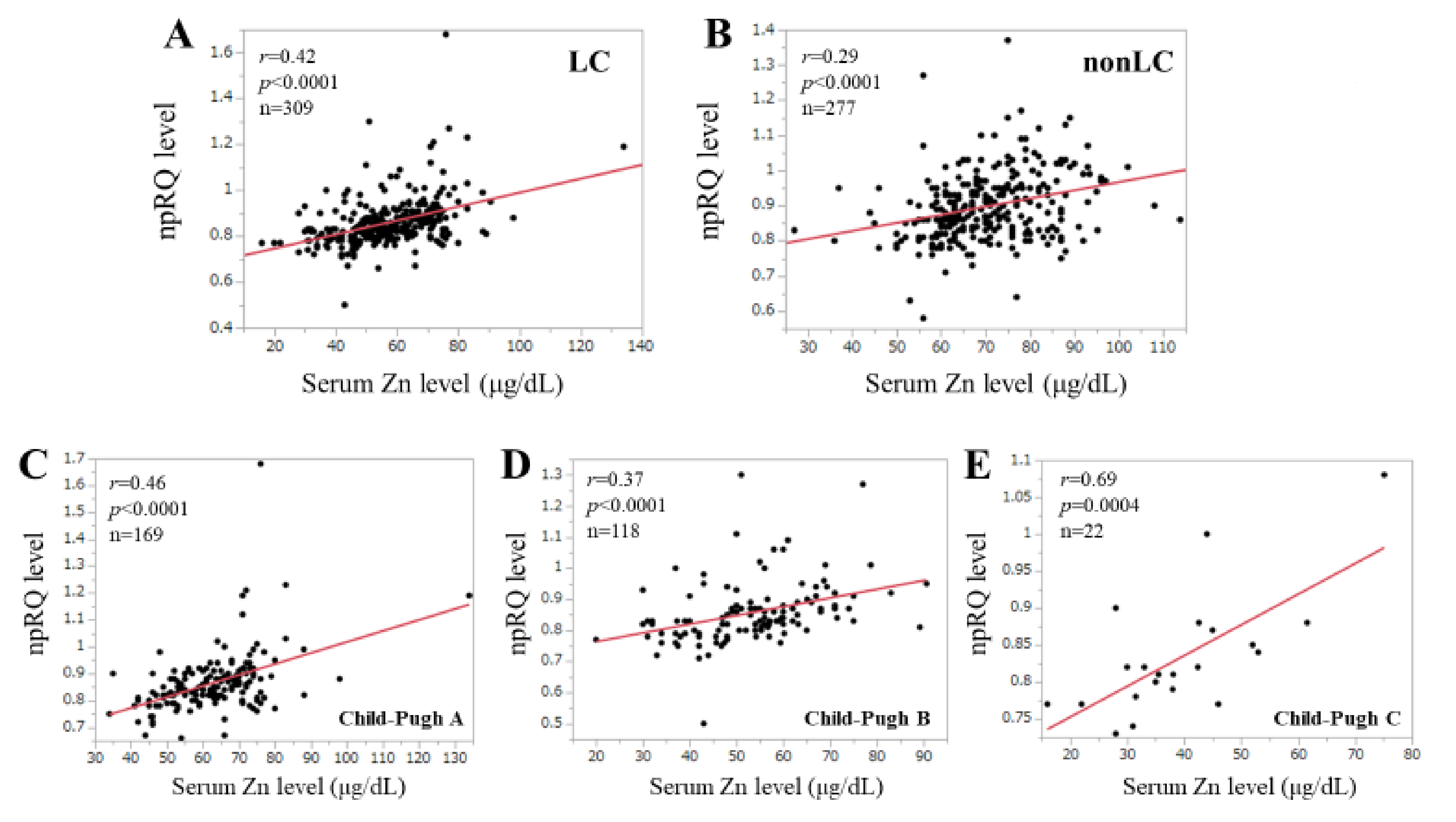
3.3. Correlation npRQ Level and Serum Zn Level According to the LC Status and the Child–Pugh Classification
3.4. Correlation npRQ Level and Serum Zn Level According to the Body Mass Index (BMI) Value
3.5. Correlation npRQ Level and Serum Zn Level According to the SMI Value
3.6. Correlation npRQ Level and Serum Zn Level According to the ECW/TBW
3.7. Correlation npRQ Level and Serum Zn Level According to the Presence or Absence of HCC
3.8. Correlation npRQ Level and Serum Zn Level According to the Liver Disease Etiologies
3.9. ROC Analyses for the npRQ < 0.85
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Charlton, M.R. Branched-chain amino acid enriched supplements as therapy for liver disease. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 295S–298S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriwaki, H.; Miwa, Y.; Tajika, M.; Kato, M.; Fukushima, H.; Shiraki, M. Branched-chain amino acids as a protein- and energy-source in liver cirrhosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 313, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirnimann, J.; Stirnimann, G. Nutritional Challenges in Patients with Advanced Liver Cirrhosis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, H.; Osaki, Y. Clinical significance of therapy using branched-chain amino acid granules in patients with liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2014, 44, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, T.; Shiraki, M.; Nishimura, K.; Ohnishi, S.; Imai, K.; Suetsugu, A.; Takai, K.; Shimizu, M.; Moriwaki, H. Sarcopenia impairs prognosis of patients with liver cirrhosis. Nutrition 2015, 31, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plauth, M. Nutritional Intervention in Chronic Liver Failure. Visc. Med. 2019, 35, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamparast, T.; Vandermeer, B.; Raman, M.; Gramlich, L.; Den, H.V.; Belland, D.; Ma, M.; Tandon, P. Are Predictive Energy Expenditure Equations Accurate in Cirrhosis? Nutrients 2019, 11, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajika, M.; Kato, M.; Mohri, H.; Miwa, Y.; Kato, T.; Ohnishi, H.; Moriwaki, H. Prognostic value of energy metabolism in patients with viral liver cirrhosis. Nutrition 2002, 18, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Plank, L.D.; McCall, J.L.; Gillanders, L.K.; McIlroy, K.; Gane, E.J. Body composition, muscle function, and energy expenditure in patients with liver cirrhosis: A comprehensive study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, Y.; Iwata, Y.; Enomoto, H.; Saito, M.; Yoh, K.; Ishii, A.; Takashima, T.; Aizawa, N.; Ikeda, N.; Tanaka, H.; et al. Two randomized controlled studies comparing the nutritional benefits of branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) granules and a BCAA-enriched nutrient mixture for patients with esophageal varices after endoscopic treatment. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraki, M.; Nishiguchi, S.; Saito, M.; Fukuzawa, Y.; Mizuta, T.; Kaibori, M.; Hanai, T.; Nishimura, K.; Shimizu, M.; Tsurumi, H.; et al. Nutritional status and quality of life in current patients with liver cirrhosis as assessed in 2007–2011. Hepatol. Res. 2013, 43, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takata, R.; Nishikawa, H.; Enomoto, H.; Yoh, K.; Iwata, Y.; Sakai, Y.; Kishino, K.; Ikeda, N.; Takashima, T.; Aizawa, N.; et al. Association between Albumin-Bilirubin Grade and Non-Protein Respiratory Quotient in Patients with Chronic Liver Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, H.; Enomoto, H.; Yoh, K.; Iwata, Y.; Sakai, Y.; Kishino, K.; Ikeda, N.; Takashima, T.; Aizawa, N.; Takata, R.; et al. Combined Albumin-Bilirubin Grade and Skeletal Muscle Mass as a Predictor in Liver Cirrhosis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grüngreiff, K. Zinc in liver disease. J. Trace Elem. Exp. Med. 2002, 15, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.A.; Overton, J.M.; Alshingiti, A.; Levenson, C.W. Regulation of metabolic rate and substrate utilization by zinc deficiency. Metabolism 2004, 53, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, C. Zinc: Physiology, deficiency, and parenteral nutrition. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2015, 30, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, H.O.; Teixeira, F.J.; Schoenfeld, B.J. Dietary vs. pharmacological doses of zinc: A clinical review. Clin. Nutr. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrajnowska, D.; Bobrowska-Korczak, B. Role of Zinc in Immune System and Anti-Cancer Defense Mechanisms. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glutsch, V.; Hamm, H.; Goebeler, M. Zinc and skin: An update. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2019, 17, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koop, A.H.; Mousa, O.Y.; Pham, L.E.; Corral-Hurtado, J.E.; Pungpapong, S.; Keaveny, A.P. An Argument for Vitamin D, A, and Zinc Monitoring in Cirrhosis. Ann. Hepatol. 2018, 17, 920–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Peinado, M.; Rueda-Robles, A.; Nogueras-López, F.; Villalón-Mir, M.; Oliveras-López, M.J.; Navarro-Alarcón, M. Serum zinc and copper concentrations and ratios in cirrhotic patients: Correlation with severity index. Nutr. Hosp. 2018, 35, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skalny, A.V.; Skalnaya, M.G.; Grabeklis, A.R.; Skalnaya, A.A.; Tinkov, A.A. Zinc deficiency as a mediator of toxic effects of alcohol abuse. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 2313–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, K.; Saito, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Endo, R.; Sawara, K.; Nishiguchi, S.; Kato, A.; Kohgo, H.; Suzuki, K.; Sakaida, I.; et al. Effect of zinc on liver cirrhosis with hyperammonemia: A preliminary randomized, placebo-controlled double-blind trial. Nutrition 2014, 30, 1409–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazunari, I.; Hirayuki, E.; Shuhei, N.; Nobuhiro, A.; Yoshiyuki, S.; Yoshinori, I.; Hironori, T.; Naoto, I.; Tomoyuki, T.; Masaki, S.; et al. Serum zinc value in patients with hepatitis virus-related chronic liver disease: Association with the histological degree of liver fibrosis and with the severity of varices in compensated cirrhosis. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2014, 55, 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Grüngreiff, K.; Reinhold, D.; Wedemeyer, H. The role of zinc in liver cirrhosis. Ann. Hepatol. 2016, 15, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, H.; Enomoto, H.; Yoh, K.; Iwata, Y.; Sakai, Y.; Kishino, K.; Ikeda, N.; Takashima, T.; Aizawa, N.; Takata, R.; et al. Serum Zinc Concentration and Sarcopenia: A Close Linkage in Chronic Liver Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, H.; Shiraki, M.; Hiramatsu, A.; Moriya, K.; Hino, K.; Nishiguchi, S. Japan Society of Hepatology guidelines for sarcopenia in liver disease (1st edition): Recommendation from the working group for creation of sarcopenia assessment criteria. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, H.; Enomoto, H.; Iwata, Y.; Kishino, K.; Shimono, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Nakano, C.; Takata, R.; Ishii, A.; Nishimura, T.; et al. Prognostic significance of nonprotein respiratory quotient in patients with liver cirrhosis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2017, 96, e5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, H.; Enomoto, H.; Yoh, K.; Iwata, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Nakano, C.; Takata, R.; Kishino, K.; Shimono, Y.; Sakai, Y.; et al. Serum hyaluronic acid predicts protein-energy malnutrition in chronic hepatitis C. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016, 95, e3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, R.N.; Tidwell, A.C.; Minard, G.; Croce, M.A.; Brown, R.O. Predicting total urinary nitrogen excretion from urinary urea nitrogen excretion in multiple-trauma patients receiving specialized nutritional support. Nutrition 2005, 21, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malbrain, M.L.; Huygh, J.; Dabrowski, W.; De Waele, J.J.; Staelens, A.; Wauters, J. The use of bio-electrical impedance analysis (BIA) to guide fluid management, resuscitation and deresuscitation in critically ill patients: A bench-to-bedside review. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2014, 46, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, H.; Saito, H.; Ueno, Y.; Uto, H.; Obara, K.; Sakaida, I.; Shibuya, A.; Seike, M.; Nagoshi, S.; Segawa, M.; et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for liver cirrhosis 2015. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 629–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, H.; Enomoto, H.; Yoh, K.; Iwata, Y.; Sakai, Y.; Kishino, K.; Ikeda, N.; Takashima, T.; Aizawa, N.; Takata, R.; et al. Serum Zinc Level Classification System: Usefulness in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.J.; Tian, Z.B.; Jiang, N.; Ding, X.L.; Mao, T.; Jing, X. Effects of Late Evening Snack on Cirrhotic Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 9189062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.B.; Pu, S.B.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z.F.; Niu, M.; Yan, X.Z.; Zhao, Y.L.; Wang, L.F.; Qin, X.M.; Ma, Z.J.; et al. Metabolomic Profiling of Autoimmune Hepatitis: The Diagnostic Utility of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 3792–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignoli, A.; Orlandini, B.; Tenori, L.; Biagini, M.R.; Milani, S.; Renzi, D.; Luchinat, C.; Calabrò, A.S. Metabolic Signature of Primary Biliary Cholangitis and Its Comparison with Celiac Disease. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohm, M.; Zeigerer, A.; Machado, J.; Herzig, S. Energy metabolism in cachexia. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e47258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | Number or Median (Interquartile Range) |
|---|---|
| Gender, male/female | 290/296 |
| Age (years) | 63 (54, 71) |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 22.2 (20.2, 24.9) |
| Presence of LC, yes/no | 309/277 |
| Child–Pugh A, B and C (LC patients) | 169/118/22 |
| Presence of HCC, yes/no/unknown | 161/422/3 |
| Ascites, yes/no/unknown | 50/533/3 |
| Skeletal muscle mass index (kg/m2), male | 7.3 (6.8, 8.0) |
| Skeletal muscle mass index (kg/m2), female | 5.8 (5.3, 6.3) |
| ECW to TBW ratio | 0.385 (0.376, 0.393) |
| Causes of liver disease Hepatitis B/Hepatitis C/alcohol/NAFLD or NASH/AIH or PBC/others | 62/309/44/71/71/29 |
| Liver histology F0/F1/F2/F3/F4 | 12/113/77/75/309 |
| npRQ | 0.86 (0.82, 0.93) |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.9 (0.7, 1.3) |
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 3.8 (3.3, 4.1) |
| Prothrombin time (%) | 86.0 (72, 95.4) |
| Platelets (×104/mm3) | 12.3 (7.8, 19.0) |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dl) | 160 (135, 188) |
| AST (IU/L) | 39.5 (28, 62) |
| ALT (IU/L) | 35.5 (23, 62) |
| Serum zinc (μg/dL) | 64 (55, 73) |
| HbA1c (NGSP) | 5.2 (4.9, 5.7) |
| Branched-chain amino acid to tyrosine ratio | 5.04 (3.73, 6.335) |
| AUC | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Cutoff Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.57 | 49.2 | 65.4 | 66.5 |
| Body mass index | 0.56 | 48.4 | 66.5 | 23.1 |
| Serum zinc | 0.69 | 62.2 | 60.7 | 60 |
| Serum albumin | 0.63 | 61.2 | 61.6 | 3.7 |
| BTR | 0.60 | 60.0 | 59.0 | 4.92 |
| PT | 0.65 | 56.3 | 68.5 | 81 |
| Platelet count | 0.60 | 47.9 | 53.9 | 9.3 |
| Total bilirubin | 0.59 | 41.7 | 73.8 | 1.2 |
| Total cholesterol | 0.58 | 63.7 | 52.3 | 164 |
| HbA1c | 0.53 | 26.0 | 87.5 | 4.7 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nishikawa, H.; Takata, R.; Enomoto, H.; Yoh, K.; Iwata, Y.; Sakai, Y.; Kishino, K.; Shimono, Y.; Ikeda, N.; Takashima, T.; et al. Serum Zinc Level and non-Protein Respiratory Quotient in Patients with Chronic Liver Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010255
Nishikawa H, Takata R, Enomoto H, Yoh K, Iwata Y, Sakai Y, Kishino K, Shimono Y, Ikeda N, Takashima T, et al. Serum Zinc Level and non-Protein Respiratory Quotient in Patients with Chronic Liver Diseases. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(1):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010255
Chicago/Turabian StyleNishikawa, Hiroki, Ryo Takata, Hirayuki Enomoto, Kazunori Yoh, Yoshinori Iwata, Yoshiyuki Sakai, Kyohei Kishino, Yoshihiro Shimono, Naoto Ikeda, Tomoyuki Takashima, and et al. 2020. "Serum Zinc Level and non-Protein Respiratory Quotient in Patients with Chronic Liver Diseases" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 1: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010255
APA StyleNishikawa, H., Takata, R., Enomoto, H., Yoh, K., Iwata, Y., Sakai, Y., Kishino, K., Shimono, Y., Ikeda, N., Takashima, T., Aizawa, N., Hasegawa, K., Ishii, N., Yuri, Y., Nishimura, T., Iijima, H., & Nishiguchi, S. (2020). Serum Zinc Level and non-Protein Respiratory Quotient in Patients with Chronic Liver Diseases. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(1), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010255




