Histological Scores Validate the Accuracy of Hepatic Iron Load Measured by Signal Intensity Ratio and R2* Relaxometry MRI in Dialysis Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Dialysis
2.2. Quantification of Hepatic Iron Stores by MRI
2.3. Quantitative Liver Histology
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Correlations between Quantitative MRI Methods and Histological Scoring Systems
3.3. Evaluation of the Accuracy of the Three Quantitative MRI Methods for the Diagnosis of Iron Overload in Haemodialysis Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hörl, W.H. Clinical aspects of iron use in the anemia of kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eschbach, J.W.; Egrie, J.C.; Downing, M.R.; Browne, J.K.; Adamson, J.W. Correction of the anemia of end-stage renal disease with recombinant human erythropoietin. Results of a combined phase I and II clinical trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 1987, 316, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaziri, N.D. Epidemic of iron overload in dialysis population caused by intravenous iron products: A plea for moderation. Am. J. Med. 2012, 125, 951–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostoker, G.; Vaziri, N.D.; Fishbane, S. Iatrogenic iron overload in dialysis patients at the beginning of the 21st century. Drugs 2016, 76, 741–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ali, M.; Rigolosi, R.; Fayemi, A.O.; Braun, E.V.; Franscino, J.; Singer, R. Failure of serum ferritin levels to predict bone-marrow iron content after intravenous iron-dextran therapy. Lancet 1982, 1, 652–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschbach, J.W.; Adamson, J.W. Iron overload in renal failure patients: Changes since the introduction of erythropoietin therapy. Kidney Int. 1999, 69, S35–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Canavese, C.; Bergamo, D.; Ciccone, G.; Longo, F.; Fop, F.; Thea, A.; Martina, G.; Piga, A. Validation of serum ferritin values by magnetic susceptometry in predicting iron overload in dialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrari, P.; Kulkarni, H.; Dheda, S.; Betti, S.; Harrison, C.; St Pierre, T.G.; Olunyk, J.K. Serum iron markers are inadequate for guiding iron repletion in chronic kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghoti, H.; Rachmilewitz, E.A.; Simon-Lopez, R.; Gaber, R.; Katzir, Z.; Konen, E.; Kushnir, T.; Girelli, D.; Campostrini, N.; Fibach, E.; et al. Evidence for tissue iron overload in long-term hemodialysis patients and the impact of withdrawing parenteral iron. Eur. J. Haematol. 2012, 89, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostoker, G.; Griuncelli, M.; Loridon, C.; Couprie, R.; Benmaadi, A.; Bounhiol, C.; Roy, M.; Machado, G.; Janklewicz, P.; Drahi, G.; et al. Hemodialysis-associated hemosiderosis in the era of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents: A MRI study. Am. J. Med. 2012, 125, 991–999.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostoker, G.; Vaziri, N.D. Risk of iron overload with chronic indiscriminate use of intravenous iron products in ESRD and IBD populations. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barton, J.C.; Edwards, C.Q.; Phatak, P.D.; Britton, R.S.; Bacon, B.R. Handbook of Iron Overload Disorders; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-0-521-87343-7. [Google Scholar]
- Brissot, P.; Troadec, M.B.; Bardou-Jacquet, E.; Le Lan, C.; Jouanolle, A.M.; Deugnier, Y.; Loreal, O. Current approach to hemochromatosis. Blood Rev. 2008, 22, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelucci, E.; Barosi, G.; Camaschella, C.; Cappellini, M.D.; Cazzola, M.; Galanello, R.; Marchetti, M.; Piga, A.; Tura, S. Italian Society of Hematology practice guidelines for the management of iron overload in thalassemia major and related disorders. Haematologica 2008, 93, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paisant, A.; d’Assignies, G.; Bannier, E.; Bardou-Jacquet, E.; Gandon, Y. MRI for the measurement of liver iron content, and for the diagnosis and follow-up of iron overload disorders. Presse Med. 2017, 46, e279–e287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandon, Y.; Olivié, D.; Guyader, D.; Aubé, C.; Oberti, F.; Sebille, V.; Deugnier, Y. Non-invasive assessment of hepatic iron stores by MRI. Lancet 2004, 363, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St Pierre, T.G.; Clark, P.R.; Chua-anusorn, W.; Fleming, A.J.; Jeffrey, G.P.; Olynyk, J.K.; Pootrakul, P.; Robins, E.; Lindeman, R. Noninvasive measurement and imaging of liver iron concentrations using proton magnetic resonance. Blood 2005, 105, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.C.; Enriquez, C.; Ghugre, N.; Tyzka, M.; Carson, S.; Nelson, M.D.; Coates, T.D. MRI R2 and R2* mapping accurately estimates hepatic iron concentration in transfusion-dependent thalassemia and sickle cell disease patients. Blood 2005, 106, 1460–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kühn, J.P.; Hernando, D.; Muñoz del Rio, A.; Evert, M.; Kannengiesser, S.; Völzke, H.; Mensel, B.; Puls, R.; Hosten, N.; Reeder, S.B. Effect of multipeak spectral modeling of fat for liver iron and fat quantification: Correlation of biopsy with MR imaging results. Radiology 2012, 265, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macdougall, I.C.; White, C.; Anker, S.D.; Bhandari, S.; Farrington, K.; Kalra, P.A.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Murray, H.; Tomson, C.R.V.; Wheeler, D.C.; et al. PIVOTAL Investigators and Committees. Intravenous iron in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnadurai, R.; Macdougall, I.C.; Kalra, P.A. Treatment of anaemia in end-stage renal disease: A double-edged iron sword? EBioMedicine 2019, 40, 31–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Weerd, N.C.; Grooteman, M.P.C.; Bots, M.L.; van den Dorpel, M.A.; den Hoedt, C.H.; Mazairac, A.H.; Nube, M.J.; Lars Penne, E.; Wetzels, J.F.M.; Wiegerinck, E.T.; et al. Hepcidin-25 is related to cardiovascular events in chronic haemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 3062–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rostoker, G.; Loridon, C.; Griuncelli, M.; Rabaté, C.; Lepeytre, F.; Ureña-Torres, P.; Issad, B.; Ghali, N.; Cohen, Y. Liver iron load influences hepatic fat fraction in end-stage renal disease patients on dialysis: A proof of concept study. EBioMedicine 2019, 39, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bailie, G.R.; Larkina, M.; Goodkin, D.A.; Li, Y.; Pisoni, R.L.; Bieber, B.; Mason, N.; Tong, L.; Locatelli, F.; Marshall, M.R.; et al. Data from the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study validate an association between high intravenous iron doses and mortality. Kidney Int. 2015, 87, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdougall, I.C.; Bircher, A.J.; Eckardt, K.U.; Obrador, G.T.; Pollock, C.A.; Stenvinkel, P.; Swinkels, D.W.; Wanner, C.; Weiss, G.; Chertow, G.M. Conference participants. Iron management in chronic kidney disease: Conclusions from a “Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes” (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deugnier, Y.; Turlin, B. Pathology of hepatic iron overload. Semin. Liver Dis. 2011, 31, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheuer, P.J.; Williams, R.; Muir, A.R. Hepatic pathology in relatives of patients with haemochromatosis. J. Pathol. Bacteriol. 1962, 84, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, F.; Bárány, P.; Covic, A.; De Francisco, A.; Del Veccio, L.; Goldsmith, D.; Horl, W.; London, G.; Vanholder, R.; Biesen, W.V.; et al. Kidney disease: Improving global outcomes guidelines on anaemia management in chronic kidney disease: A European Renal Best Practice position statement. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 1346–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idilman, I.S.; Aniktar, H.; Idilman, R.; Kabacam, G.; Savas, B.; Elhan, A.; Celik, A.; Bahar, K.; Karcaaltincaba, M. Hepatic steatosis: Quantification by proton density fat fraction with MR imaging versus liver biopsy. Radiology 2013, 267, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deugnier, Y.M.; Loréal, O.; Turlin, B.; Guyader, D.; Jouanolle, H.; Moirand, R.; Jacquelinet, C.; Brissot, P. Liver pathology in genetic hemochromatosis: A review of 135 homozygous cases and their bioclinical correlations. Gastroenterology 1992, 102, 2050–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turlin, B.; Deugnier, Y. Histological assessment of liver siderosis. J. Clin. Pathol. 1997, 50, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butensky, E.; Fisher, R.; Hudes, M.; Schumacher, L.; Williams, R.; Moyer, T.P.; Vichinsky, E.; Harmatz, P. Variability in hepatic iron concentration in percutaneous needle biopsy specimens from patients with transfusional hemosiderosis. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 123, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deugnier, Y.M.; Turlin, B.; Powell, L.W.; Summers, K.M.; Moirand, R.; Fletcher, L.; Halliday, J.W.; Olivier, L.; Brissot, P. Differentiation between heterozygotes and homozygotes in genetic hemochromatosis by means of a histological hepatic iron index: A study of 192 cases. Hepatology 1993, 17, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbert-Bismut, F.; Charlotte, F.; Turlin, B.; Khalil, L.; Piton, A.; Brissot, P.; Le Charpentier, Y.; Delattre, J.; Opolon, P.; Deugnier, Y.; et al. Low hepatic iron concentration: Evaluation of two complementary methods, colorimetric assay and iron histological scoring. J. Clin. Pathol. 1999, 52, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brissot, P.; Bourel, M.; Herry, D.; Verger, J.P.; Messner, M.; Beaumont, C.; Regnouard, F.; Ferrand, B.; Simon, M. Assessment of liver iron content in 271 patients: A reevaluation of direct and indirect methods. Gastroenterology 1981, 80, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, L.W.; Hopwood, D.; Shepherd, A.N.; Stewart, W.K. Hepatic iron in dialysed patients given intravenous iron dextran. J. Clin. Pathol. 1990, 43, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheskin, D.J. Handbook of Parametric and Nonparametric Statistical Procedures, 4th ed.; Chapman and Hall, Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Motulsky, H. Intuitive Biostatistics: A Nonmathematical Guide to Statistical Thinking, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: New-York, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN-13: 978-0199730063, ISBN-10: 0199730067. [Google Scholar]
- Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Diagnostic tests 4: Likelihood ratios. BMJ 2004, 329, 168–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fagan, T.J. Nomogram for Baye’s theorem. N. Engl. J. Med. 1975, 293, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diagnostic Test Calculator. Available online: http://araw.mede.uic.edu/cgi-bin/testcalc.pl (accessed on 29 November 2019).
- Villeneuve, J.P.; Bilodeau, M.; Lepage, R.; Côté, J.; Lefebvre, M. Variability in hepatic iron concentration measurement from needle-biopsy specimens. J. Hepatology. 1996, 25, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostoker, G.; Laroudie, M.; Blanc, R.; Galet, B.; Rabaté, C.; Griuncelli, M.; Cohen, Y. Signal-intensity-ratio MRI accurately estimates hepatic iron load in hemodialysis patients. Heliyon 2017, 3, e000226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wish, J.B.; Aronoff, G.R.; Bacon, B.R.; Brugnara, C.; Eckardt, K.U.; Ganz, T.; Macdougall, I.C.; Nunez, J.; Perahia, A.J.; Wood, J.C. Positive iron balance in chronic kidney disease: How much is too much and how to tell? Am. J. Nephrol. 2018, 47, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, J.P.; He, T.; Kirk, P.; Roughton, M.; Anderson, L.J.; De Noronha, S.V.; Sheppard, M.N.; Porter, J.B.; Walker, J.M.; Wood, J.C.; et al. On T2* magnetic resonance and cardiac iron. Circulation 2011, 123, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meloni, A.; Rienhoff, H.Y.; Jones, A.; Pepe, A.; Lombardi, M.; Wood, J.C. The use of appropriate calibration curves corrects for systematic differences in liver R2* values measured using different software packages. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 161, 888–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhaveri, K.; Kannengiesser, S.A.R.; Ward, R.; Kuo, K.; Sussman, M.S. Prospective evaluation of an R2* method for assessing liver iron concentration (LIC) against FerriScan: Derivation of the calibration curve and characterization of the nature and source of uncertainty in the relationship. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 49, 1467–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labranche, R.; Gilbert, G.; Cerny, M.; Vu, K.N.; Soulières, D.; Olivié, D.; Billiard, J.S.; Yokoo, T. Liver iron quantification with MR imaging: A primer for radiologists. RadioGraphics 2018, 38, 392–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinnadurai, R.; Ritchie, J.; Green, D.; Kalra, P.A. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and clinical outcomes in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 34, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Site | Scoring | Final Score |
|---|---|---|
| Hepatocytic iron score (HIS) | 0, 3, 6, 9, or 12 according to granule size in each Rappaport area | 0–36 |
| Sinusoidal iron score (SIS) | 0, 3, 6, 9, or 12 according to granule size in each Rappaport area | 0–12 |
| Portal iron score (PIS) | 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4 according to the percentage of iron overloaded macrophages, biliary cells and vascular walls | 0–12 |
| Total iron score (TIS) | 0–60 |
| Grade | Histology |
|---|---|
| Grade 0 | Granules absent or barely discernible at ×400 magnification |
| Grade 1 | Granules barely discernible at ×250 magnification and easily confirmed at ×100 |
| Grade 2 | Discrete granules resolved at ×100 magnification |
| Grade 3 | Discrete granules resolved at ×25 magnification |
| Grade 4 | Masses visible at ×10 magnification or by naked eye |
| Histological Scoring of LIC | SIR According to Rennes University | R2* Relaxometry (Classical) | R2* Relaxometry (IDEAL-IQ®) |
|---|---|---|---|
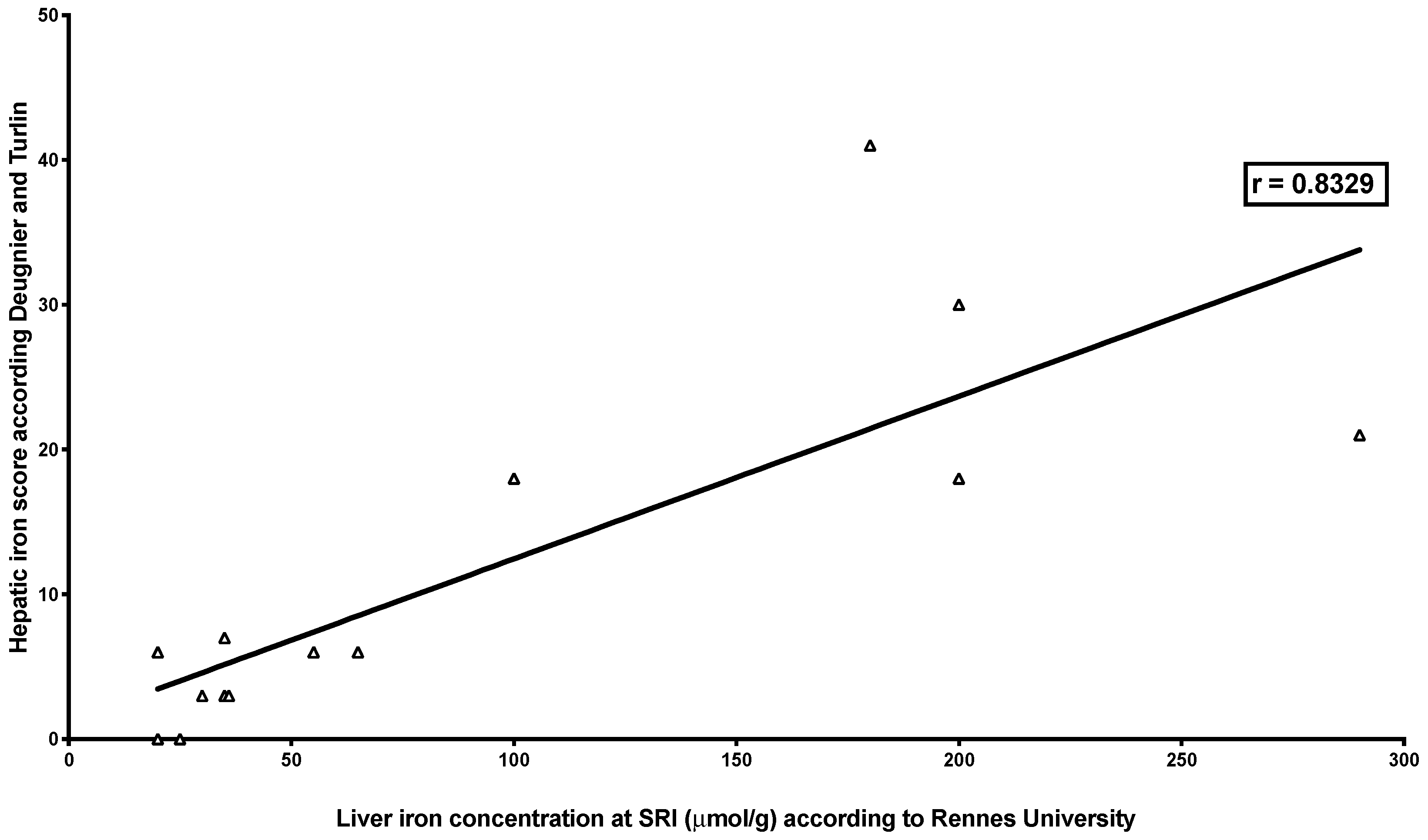
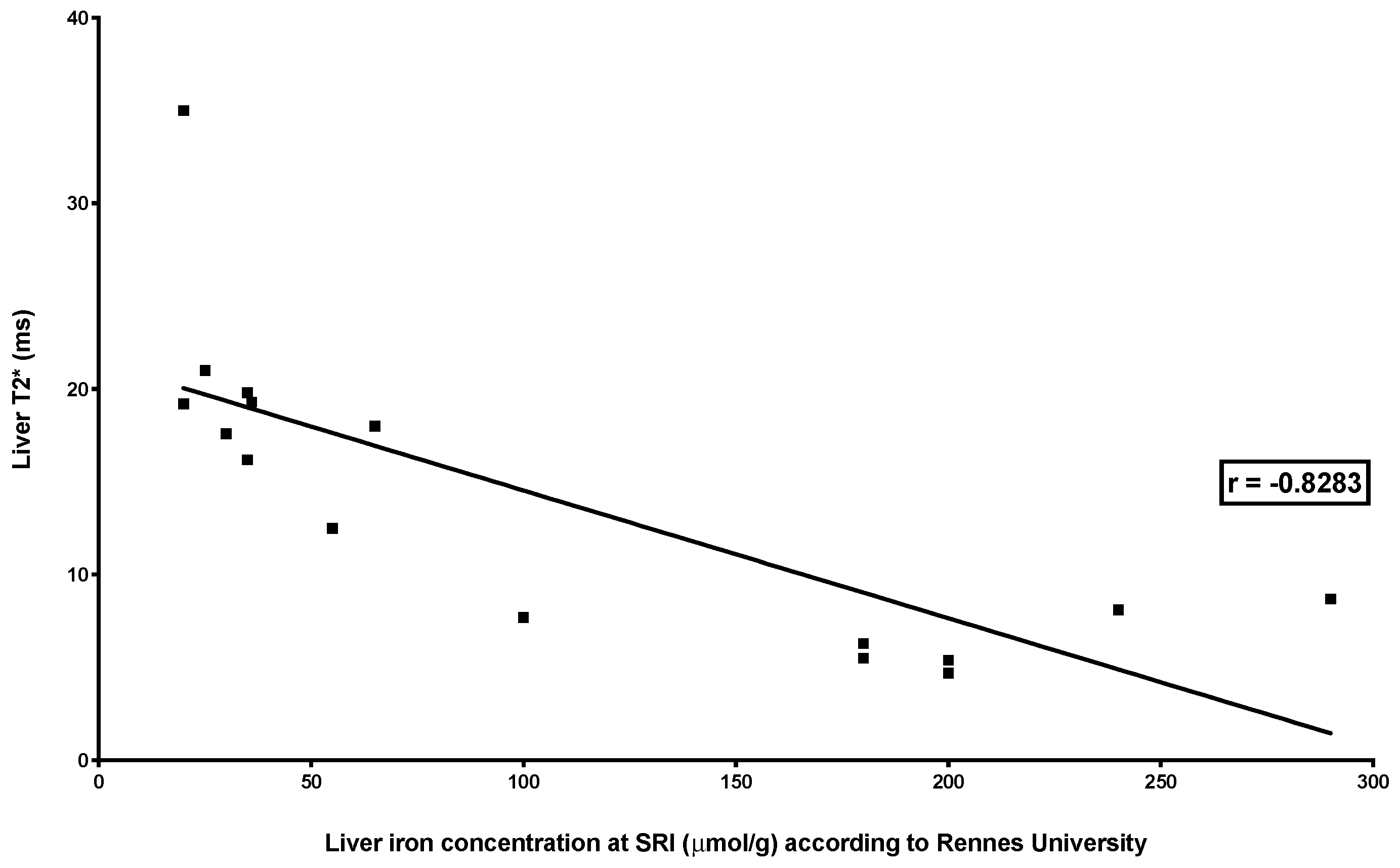
| Deugnier’s and Turlin’s histological scoring | r = 0.8329 p = 0.0002 | r = −0.9099 p < 0.0001 | r = −0.872 p = 0.0018 |
| Scheuer’s classification | r = 0.7106 p = 0.0009 | r = −0.7453 p = 0.0004 | r = −0.7142 p = 0.0120 |
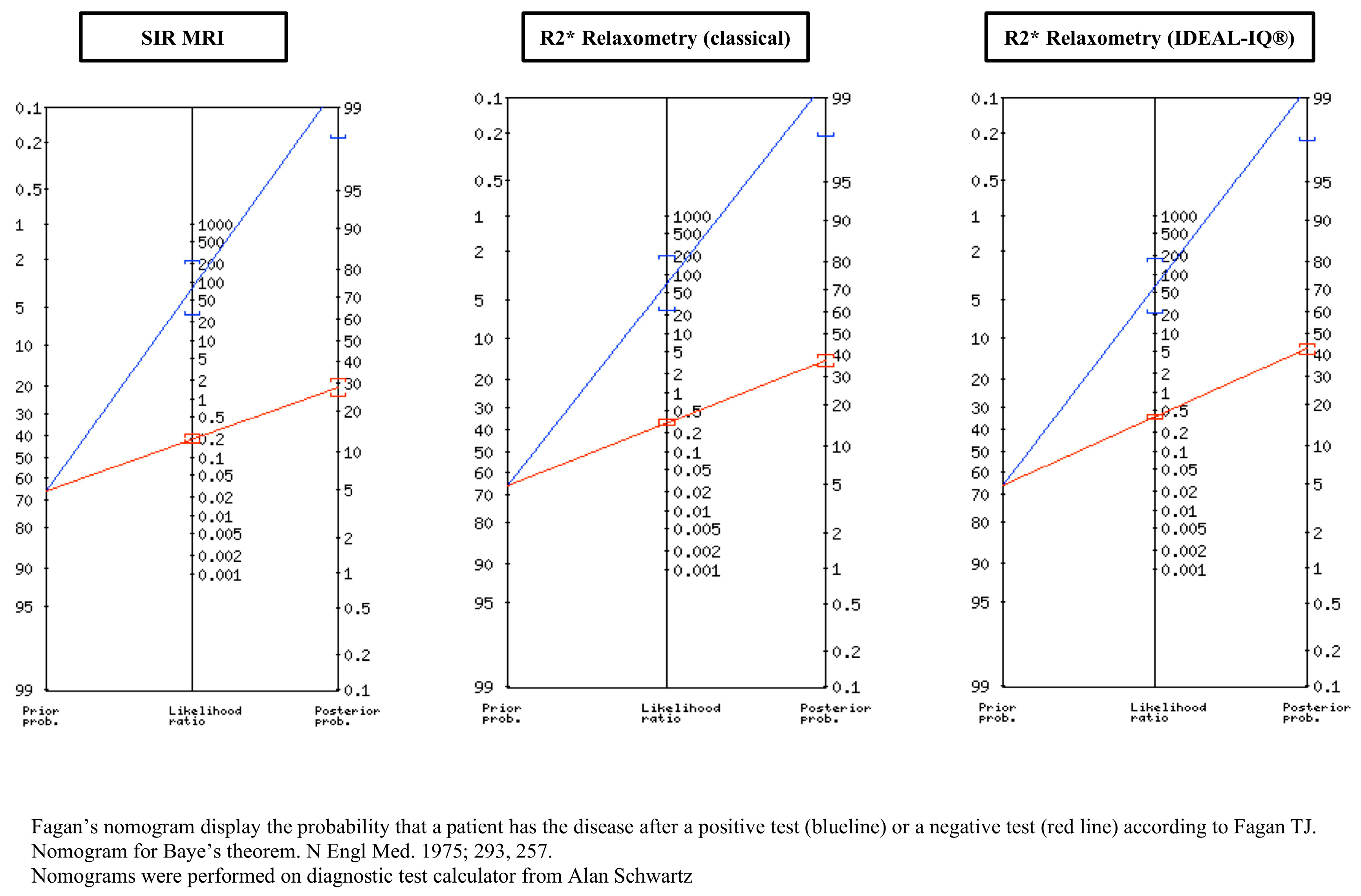
| SIR MRI According to Rennes University | R2* Relaxometry (Classical) | R2* Relaxometry (IDEAL-IQ®) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity (%) | 80 | 70 | 62.5 |
| Specificity (%) | 99 | 99 | 99 |
| Positive predictive value (%) | 99.36 | 99.27 | 99.18 |
| Negative predictive value (%) | 71.83 | 62.96 | 57.63 |
| Positive likelihood ratio | 80 | 70 | 62.5 |
| Posterior probability (%) | 99.36 | 99.27 | 99.18 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rostoker, G.; Laroudie, M.; Blanc, R.; Griuncelli, M.; Loridon, C.; Lepeytre, F.; Rabaté, C.; Cohen, Y. Histological Scores Validate the Accuracy of Hepatic Iron Load Measured by Signal Intensity Ratio and R2* Relaxometry MRI in Dialysis Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010017
Rostoker G, Laroudie M, Blanc R, Griuncelli M, Loridon C, Lepeytre F, Rabaté C, Cohen Y. Histological Scores Validate the Accuracy of Hepatic Iron Load Measured by Signal Intensity Ratio and R2* Relaxometry MRI in Dialysis Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleRostoker, Guy, Mireille Laroudie, Raphaël Blanc, Mireille Griuncelli, Christelle Loridon, Fanny Lepeytre, Clémentine Rabaté, and Yves Cohen. 2020. "Histological Scores Validate the Accuracy of Hepatic Iron Load Measured by Signal Intensity Ratio and R2* Relaxometry MRI in Dialysis Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010017
APA StyleRostoker, G., Laroudie, M., Blanc, R., Griuncelli, M., Loridon, C., Lepeytre, F., Rabaté, C., & Cohen, Y. (2020). Histological Scores Validate the Accuracy of Hepatic Iron Load Measured by Signal Intensity Ratio and R2* Relaxometry MRI in Dialysis Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010017






