Clinical Characteristics of and Risk Factors for Fever after Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration: A Retrospective Study Involving 6336 Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Definition and Inclusion Criteria
2.2. Patient Characteristics and Measure
2.3. EBUS-TBNA Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethics Approval
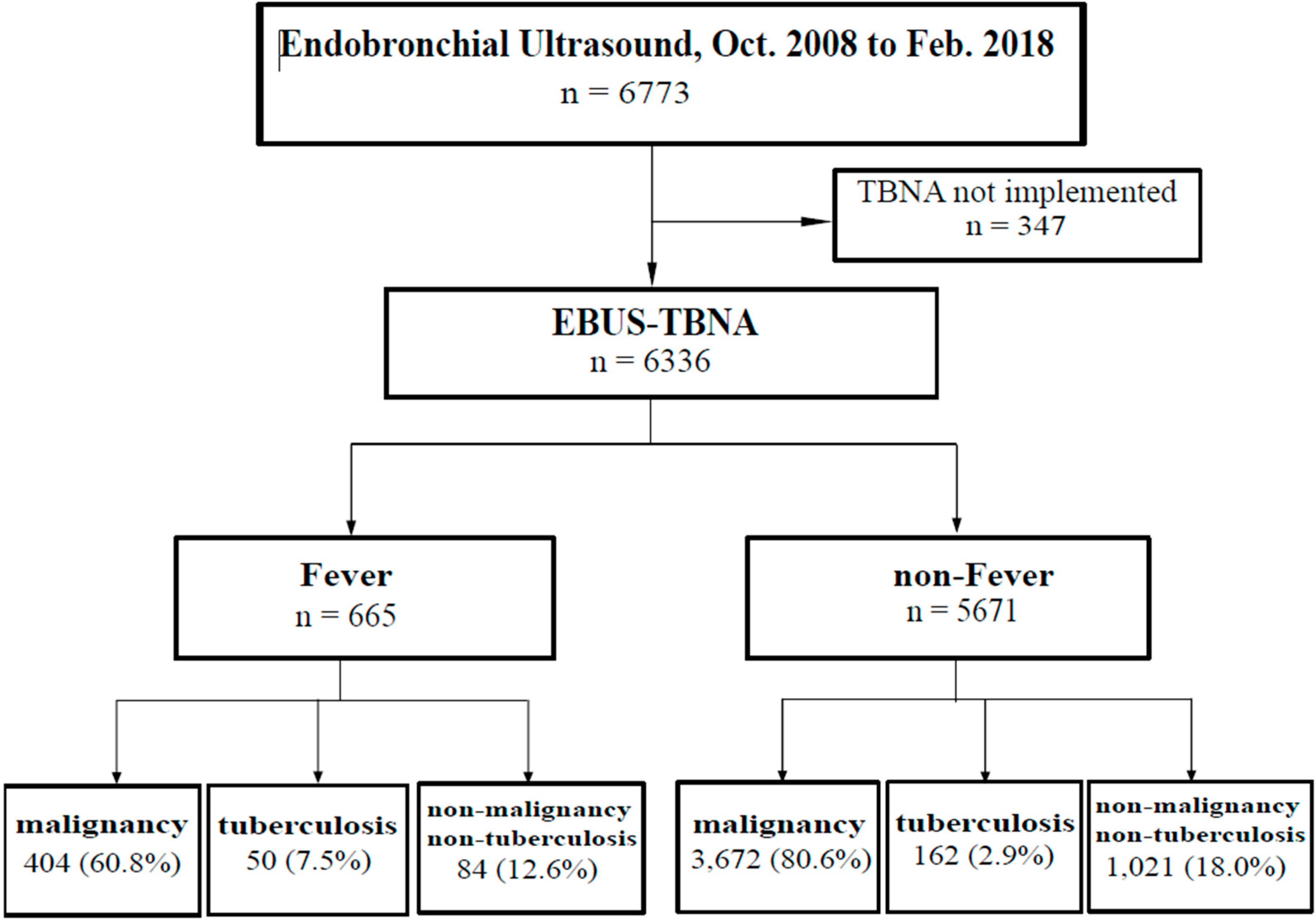
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Associations of Fever after EBUS-TBNA with Clinical and Laboratory Findings
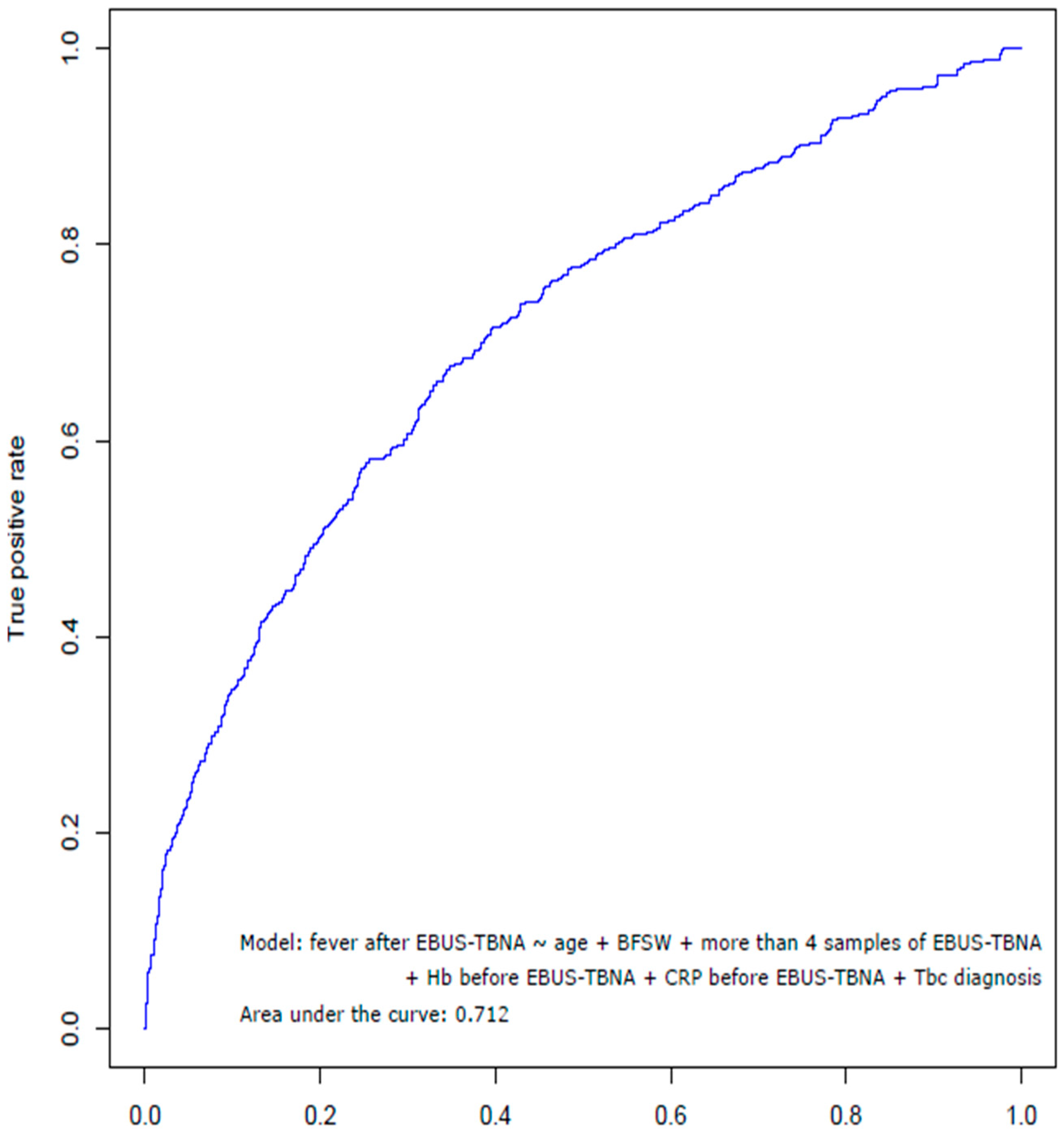
3.3. Risk Factors Associated with Fever after EBUS-TBNA
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ernst, A.; Anantham, D.; Eberhardt, R.; Krasnik, M.; Herth, F.J. Diagnosis of mediastinal adenopathy—Real-time endobronchial ultrasound guided needle aspiration versus mediastinoscopy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2008, 3, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasufuku, K.; Chiyo, M.; Sekine, Y.; Chhajed, P.N.; Shibuya, K.; Iizasa, T.; Fujisawa, T. Real-time endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration of mediastinal and hilar lymph nodes. Chest 2004, 126, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela-Lema, L.; Fernandez-Villar, A.; Ruano-Ravina, A. Effectiveness and safety of endobronchial ultrasound-transbronchial needle aspiration: A systematic review. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 33, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, I.S.; Agarwal, R.; Dhooria, S.; Prasad, K.T.; Aggarwal, A.N. Role of EBUS TBNA in Staging of Lung Cancer: A Clinician’s Perspective. J. Cytol. 2019, 36, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, K.; Shah, P.L.; Edmonds, L.; Lim, E. Test performance of endobronchial ultrasound and transbronchial needle aspiration biopsy for mediastinal staging in patients with lung cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Thorax 2009, 64, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, P.; Zhao, Y.Z.; Jiang, L.Y.; Zhang, W.; Xin, Y.; Han, B.H. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration for staging of lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trisolini, R.; Baughman, R.P.; Spagnolo, P.; Culver, D.A. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in sarcoidosis: Beyond the diagnostic yield. Respirology 2019, 24, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhooria, S.; Agarwal, R.; Aggarwal, A.N.; Bal, A.; Gupta, N.; Gupta, D. Differentiating tuberculosis from sarcoidosis by sonographic characteristics of lymph nodes on endobronchial ultrasonography: A study of 165 patients. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 148, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.; Ozturk, A. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration is useful in the diagnosis of lymphoma: Don’t give up! Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2018, 119, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.T.; Chen, C.Y.; Ho, C.C.; Yu, C.J. A rare constellation of empyema, lung abscess, and mediastinal abscess as a complication of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2011, 40, 264–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, A.R. Infectious complications from full extension endobronchial ultrasound transbronchial needle aspiration. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 33, 935–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffatt-Bruce, S.D.; Ross, P. Mediastinal abscess after endobronchial ultrasound with transbronchial needle aspiration: A case report. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2010, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, K.L.; Bizekis, C.S.; Zervos, M.D. Severe mediastinal infection with abscess formation after endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbrochial needle aspiration. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 89, 1271–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botana-Rial, M.; Nunez-Delgado, M.; Pallares-Sanmartin, A.; Leiro-Fernandez, V.; Represas Represas, C.; Gonzalez Silva, A.I.; Fernandez-Villar, A. Intramural hematoma of the pulmonary artery and hemopneumomediastinum after endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration. Respiration 2012, 83, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchimura, K.; Yamasaki, K.; Hirano, Y.; Sakagami, K.; Kido, T.; Mukae, H.; Yatera, K. The Successful Removal of a Broken Needle as an Unusual Complication of Endobronchial Ultrasound-guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration (EBUS-TBNA): A Case Report and Literature Review. J. UOEH 2019, 41, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Kim, J.; Jo, Y.S.; Park, Y.S. Bacterial pericarditis as a fatal complication after endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration. Eur. J. Cardio Thorac. Surg. 2014, 48, 630–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, M.; Magalhaes, A.; Hespanhol, V. Transient fever after fiberoptic bronchoscopy—A prospective study. Rev. Port. Pneumol. 2004, 10, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, S.-W.; Choi, C.-M.; Lee, C.-T.; Kim, Y.W.; Han, S.K.; Shim, Y.-S.; Yoo, C.-G.J.C. Prospective analysis of clinical characteristics and risk factors of postbronchoscopy fever. Chest 2004, 125, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif-Kashani, B.; Shahabi, P.; Behzadnia, N.; Mohammad-Taheri, Z.; Mansouri, D.; Masjedi, M.R.; Zargari, L.; Negad, L.S.J.A.M.I. Incidence of fever and bacteriemia following flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy: A prospective study. Acta Med. Iran. 2010, 48, 385–388. [Google Scholar]
- Kanemoto, K.; Satoh, H.; Ishikawa, H.; Ishikawa, S.; Ohtsuka, M.; Sekizawa, K.J.J.A.G.S. Prospective study of fever and pneumonia after flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy in older people. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2006, 54, 827–830. [Google Scholar]
- Carlens, J.; Fuge, J.; Price, T.; DeLuca, D.S.; Price, M.; Hansen, G.; Schwerk, N. Complications and risk factors in pediatric bronchoscopy in a tertiary pediatric respiratory center. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2018, 53, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oguri, T.; Imai, N.; Imaizumi, K.; Elshazley, M.; Hashimoto, I.; Hashimoto, N.; Hasegawa, Y. Febrile complications after endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration for intra-pulmonary mass lesions of lung cancer—A series of 3 cases. Respir. Investig. 2012, 50, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Lee, J.W.; Park, Y.S.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, S.M.; Yim, J.J.; Kim, Y.W.; Han, S.K.; Yoo, C.G. Incidence of Fever Following Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2017, 80, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, F.; Aoe, M.; Ohsaki, Y.; Okada, Y.; Sasada, S.; Sato, S.; Suzuki, E.; Semba, H.; Fukuoka, K.; Fujino, S.J.R.r. Complications associated with endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration: A nationwide survey by the Japan Society for Respiratory Endoscopy. Respir. Res. 2013, 14, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caglayan, B.; Yilmaz, A.; Bilaceroglu, S.; Comert, S.S.; Demirci, N.Y.; Salepci, B. Complications of Convex-Probe Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration: A Multi-Center Retrospective Study. Respir. Care 2016, 61, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinfort, D.; Johnson, D.; Irving, L. Incidence of bacteraemia following endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 36, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.C.; Prakash, U.B.; Garland, R.; Haponik, E.; Moses, L.; Schaffner, W.; Silvestri, G. American College of Chest Physicians and American Association for Bronchology Consensus Statement: Prevention of flexible bronchoscopy-associated infection. Chest 2005, 128, 1742–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee, B.T.S.B.G. British Thoracic Society guidelines on diagnostic flexible bronchoscopy. Thorax 2001, 56, i1–i21. [Google Scholar]
- Takagi, H.; Nagaoka, T.; Ando, K.; Tsutsumi, T.; Ichikawa, M.; Koyama, R.; Shimada, N.; Tobin, K.; Takahashi, K. Efficacy of Antibiotic Prophylaxis after Endobronchial Ultrasound-guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration: A Preliminary Prospective Study. J. Pulm. Respir. Med. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, F.; Aoe, M.; Ohsaki, Y.; Okada, Y.; Sasada, S.; Sato, S.; Suzuki, E.; Senba, H.; Fujino, S.; Ohmori, K. Deaths and complications associated with respiratory endoscopy: A survey by the Japan Society for Respiratory Endoscopy in 2010. Respirology 2012, 17, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Bartheld, M.B.; van Breda, A.; Annema, J.T. Complication rate of endosonography (endobronchial and endoscopic ultrasound): A systematic review. Respiration 2014, 87, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Fever (N = 665) | Non-Fever (N = 5671) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical manifestation | |||
| Age, year, median (range) | 65.0 (14–96) | 66.0 (14–90) | |
| Sex, male, n (%) | 456 (68.6) | 3,868 (68.2) | 0.848 1 |
| Height, cm | 162.1 ± 12.8 | 162.4 ± 11.8 | 0.547 2 |
| Weight, kg | 61.2 ± 23.0 | 62.5 ± 15.3 | 0.051 2 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 23.3 ± 10.4 | 23.8 ± 12.3 | 0.297 2 |
| FEV1, % | 76.9 ± 17.9 | 80.6 ± 18.5 | 0.127 2 |
| Comorbidity, n (%) | |||
| Hypertension | 245 (36.8) | 2037 (35.9) | 0.477 1 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 64 (9.6) | 509 (9.0) | 0.581 1 |
| Hepatitis | 24 (3.6) | 179 (3.2) | 0.682 1 |
| Smoking History, n (%) | 0.477 1 | ||
| Never smoker | 237 (35.6) | 2073 (36.6) | |
| Ex-smoker | 336 (50.5) | 2713 (47.8) | |
| pack-year | 35.4 ± 24.1 | 35.0 ± 23.6 | 0.763 2 |
| Current smoker | 72 (10.8) | 711 (12.5) | |
| pack-year | 32.2 ± 20.9 | 36.1 ± 23.8 | 0.183 2 |
| Past medical history, n (%) | |||
| Malignancy | 514 (77.3) | 4,431 (78.1) | 0.620 1 |
| Tuberculosis | 52 (7.8) | 225 (4.0) | <0.001 1 |
| Mortality, n (%) | |||
| 30 days mortality | 14 (2.1) | 88 (1.6) | 0.283 1 |
| 60 days mortality | 30 (4.5) | 185 (3.3) | 0.092 1 |
| 90 days mortality | 52 (7.8) | 280 (4.9) | 0.002 1 |
| Day from EBUS to death, median (range) | 51.5 (3–89) | 47.0 (3–90) |
| Parameters | Fever (N = 665) | Non-Fever (N = 5671) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample number of EBUS-TBNA, mean | 2.14 | 2.03 | 0.004 2 |
| ≥2, n (%) | 424 (63.8) | 3599 (63.5) | 0.898 1 |
| ≥3, n (%) | 172 (25.9) | 1372 (24.2) | 0.340 1 |
| ≥4, n (%) | 38 (5.7) | 214 (3.8) | 0.021 1 |
| 5, n (%) | 1 (0.2) | 21 (0.4) | 0.723 1 |
| Final diagnosis of EBUS-TBNA, n (%) | |||
| Malignancy | 404 (60.8) | 3672 (64.8) | 0.042 |
| Tuberculosis | 50 (7.5) | 162 (2.9) | <0.001 |
| Non-malignancy & Non-tuberculosis | 84 (12.6) | 1021 (18.0) | 0.001 |
| Follow-up | 1 (0.2) | 10 (0.2) | 1.000 |
| Loss of follow-up | 1 (0.2) | 0 | 0.105 |
| Parameters | Fever (N = 665) | Non-Fever (N = 5671) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Additional procedure, n (%) | |||
| Bronchoscopic washing | 419 (63.0) | 3080 (54.3) | <0.001 1 |
| Bronchoscopic biopsy | 140 (21.1) | 1000 (17.6) | 0.030 1 |
| Core needle biopsy | 40 (6.0) | 287 (5.1) | 0.293 1 |
| Transbronchial lung biopsy | 10 (1.5) | 42 (0.7) | 0.039 1 |
| Number of additional procedures, mean | 1.99 | 1.84 | <0.001 2 |
| Only EBUS-TBNA, n (%) | 198 (29.8) | 2180 (38.4) | <0.001 1 |
| ≥1 type, n (%) | 467 (70.2) | 3491 (61.1) | <0.001 1 |
| ≥2 types, n (%) | 172 (25.9) | 1208 (21.3) | 0.008 1 |
| ≥3 types, n (%) | 16 (2.4) | 84 (1.5) | 0.097 1 |
| 4 types, n (%) | 1 (0.2) | 7 (0.1) | 0.588 1 |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | Crude OR (95% CI) | p-Value | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | |
| Age | 0.202 | 0.996 (0.989–1.002) | 0.015 | 0.983 (0.969–0.997) |
| Sex | 0.848 | 1.017 (0.855–1.209) | NA | NA |
| Body mass index | 0.317 | 0.991 (0.975–1.008) | NA | NA |
| Bronchoscopic washing | <0.001 | 1.433 (1.214–1.691) | 0.012 | 1.624 (1.114–2.368) |
| More than four samples of EBUS-TBNA | 0.016 | 1.545 (1.084–2.204) | 0.007 | 2.472 (1.288–4.745) |
| Hemoglobin 1 | <0.001 | 0.750 (0.715–0.786) | <0.001 | 0.876 (0.822–0.933) |
| C-reactive protein 1 | <0.001 | 1.150 (1.128–1.173) | <0.001 | 1.115 (1.075–1.157) |
| White blood cells 1 | <0.001 | 1.104 (1.080–1.128) | NA | NA |
| Platelets 1 | <0.001 | 1.003 (1.002–1.004) | NA | NA |
| ALP 1 | <0.001 | 1.002 (1.001–1.003) | NA | NA |
| GGT 1 | 0.009 | 1.002 (1.000–1.003) | NA | NA |
| Cholesterol 1 | <0.001 | 0.991 (0.989–0.993) | NA | NA |
| Tuberculosis of EBUS-TBNA diagnosis | <0.001 | 2.765 (1.992–3.837) | <0.001 | 3.409 (1.870–6.217) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moon, K.M.; Choi, C.-M.; Ji, W.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.W.; Jo, K.-W.; Song, J.W.; Lee, J.C. Clinical Characteristics of and Risk Factors for Fever after Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration: A Retrospective Study Involving 6336 Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010152
Moon KM, Choi C-M, Ji W, Lee JS, Lee SW, Jo K-W, Song JW, Lee JC. Clinical Characteristics of and Risk Factors for Fever after Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration: A Retrospective Study Involving 6336 Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(1):152. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010152
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoon, Kyoung Min, Chang-Min Choi, Wonjun Ji, Jae Seung Lee, Sei Won Lee, Kyung-Wook Jo, Jin Woo Song, and Jae Cheol Lee. 2020. "Clinical Characteristics of and Risk Factors for Fever after Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration: A Retrospective Study Involving 6336 Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 1: 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010152
APA StyleMoon, K. M., Choi, C.-M., Ji, W., Lee, J. S., Lee, S. W., Jo, K.-W., Song, J. W., & Lee, J. C. (2020). Clinical Characteristics of and Risk Factors for Fever after Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration: A Retrospective Study Involving 6336 Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(1), 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010152






