Machine Perfusion for Abdominal Organ Preservation: A Systematic Review of Kidney and Liver Human Grafts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Inclusion Criteria
2.2. Primary Objectives
- Compare DGF in transplanted kidneys (defined as the need for dialysis within 7 days post-transplantation) and EAD (defined using Olthoff [3] criteria) in transplanted livers preserved by MP to SCS.
- Compare PNF in kidneys and livers preserved by machine perfusion and simple cold storage.
- Compare post-transplantation estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and serum creatinine levels in kidneys preserved via HMP and SCS.
- Compare post-transplantation bilirubin and AST levels in serum in livers preserved via MP and SCS.
2.3. Secondary Objectives
- Where sufficient data existed, to compare one-year graft survival of organs perfused by MP and SCS.
- Compare acute organ rejection of organs preserved via MP and SCS.
- Indirectly compare the effectiveness of preserving liver grafts with HMP and NMP through evaluating studies that compared HMP to SCS and NMP to SCS.
2.4. Data Extraction and Review
2.5. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.6. Data Analysis
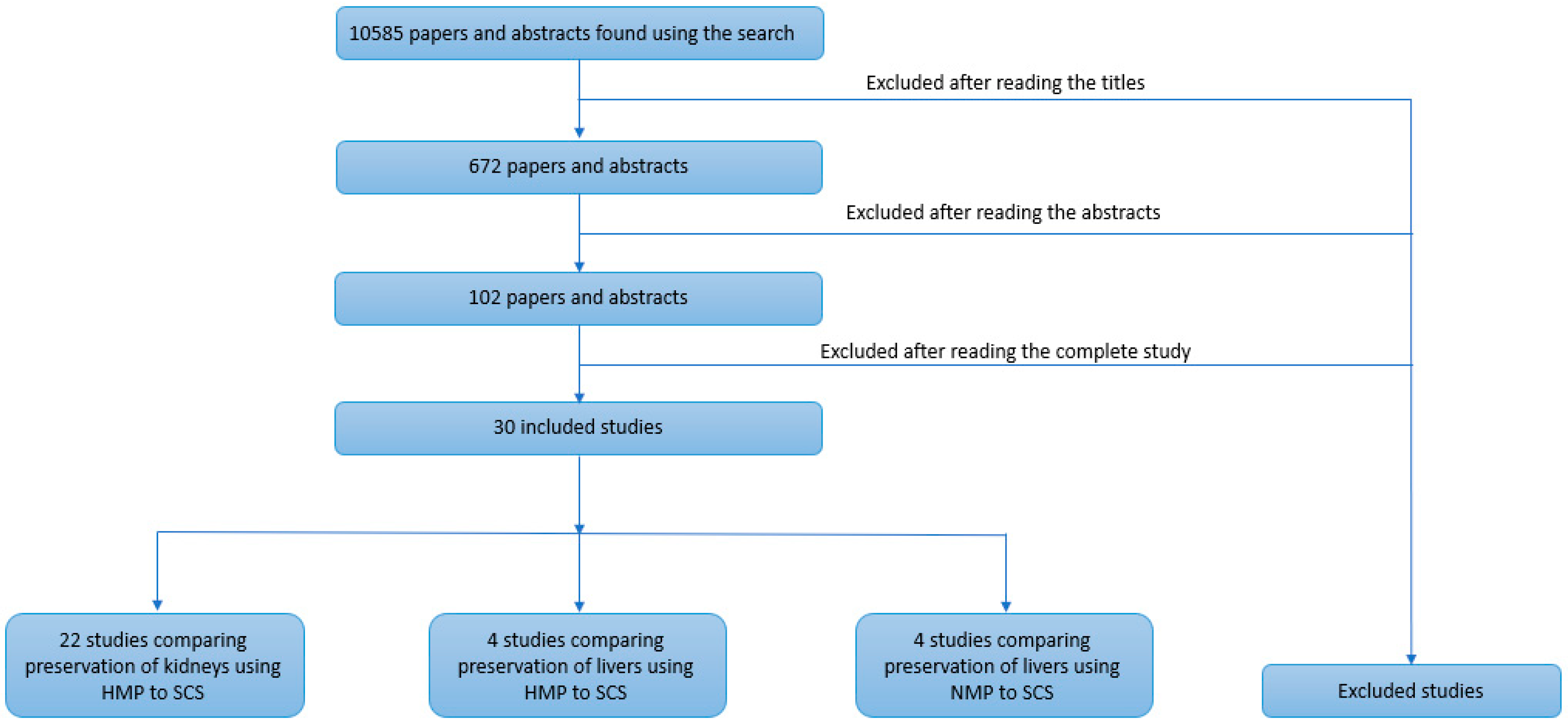
3. Results
3.1. Selected Study Characteristics
3.2. Risk of Bias Assessment
3.3. Kidney Transplant Outcomes
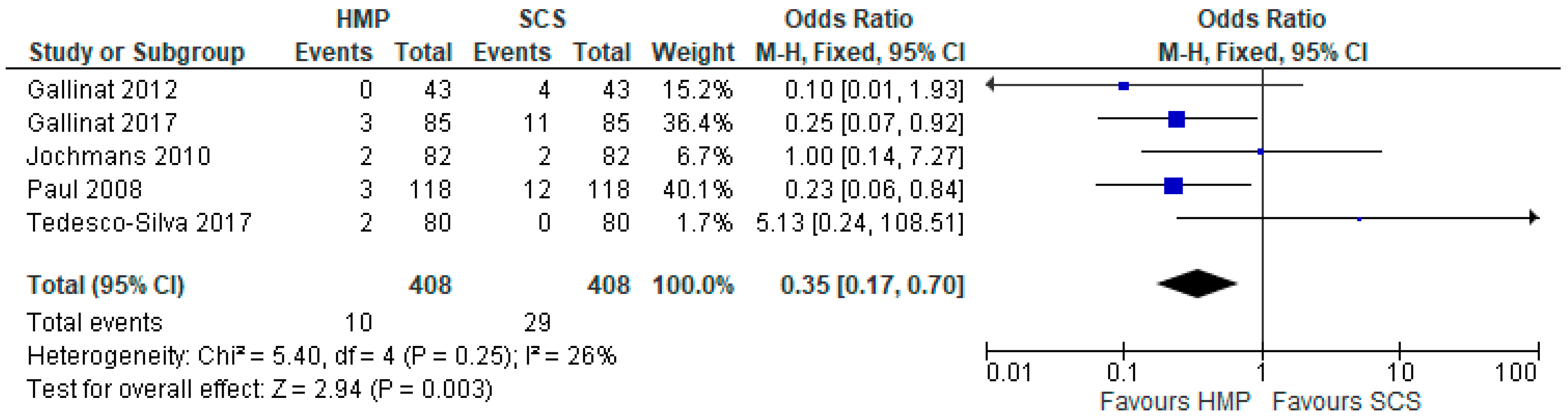
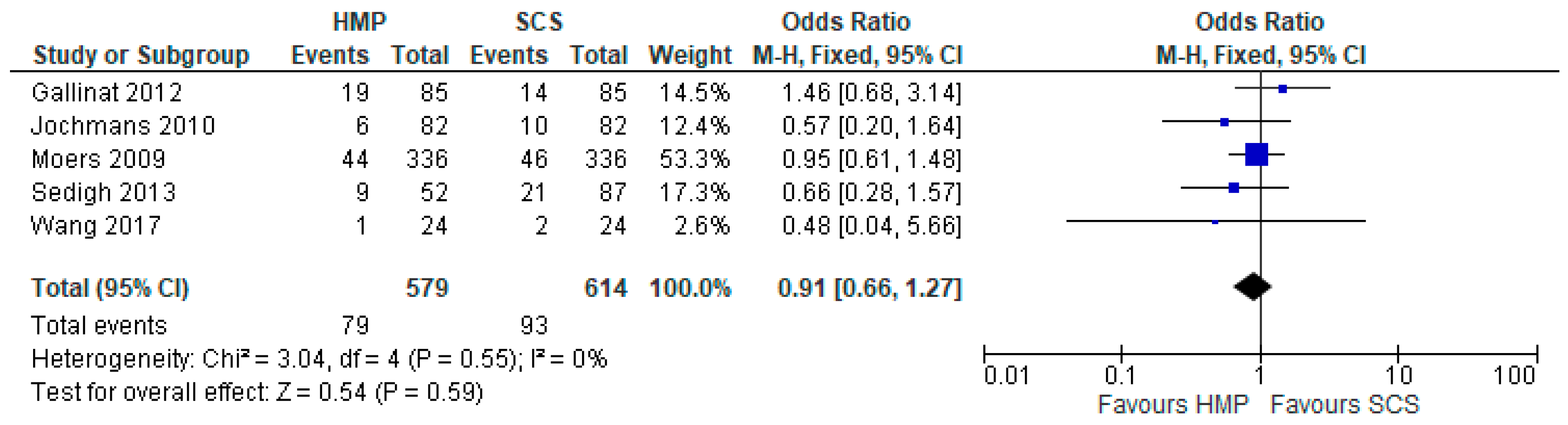
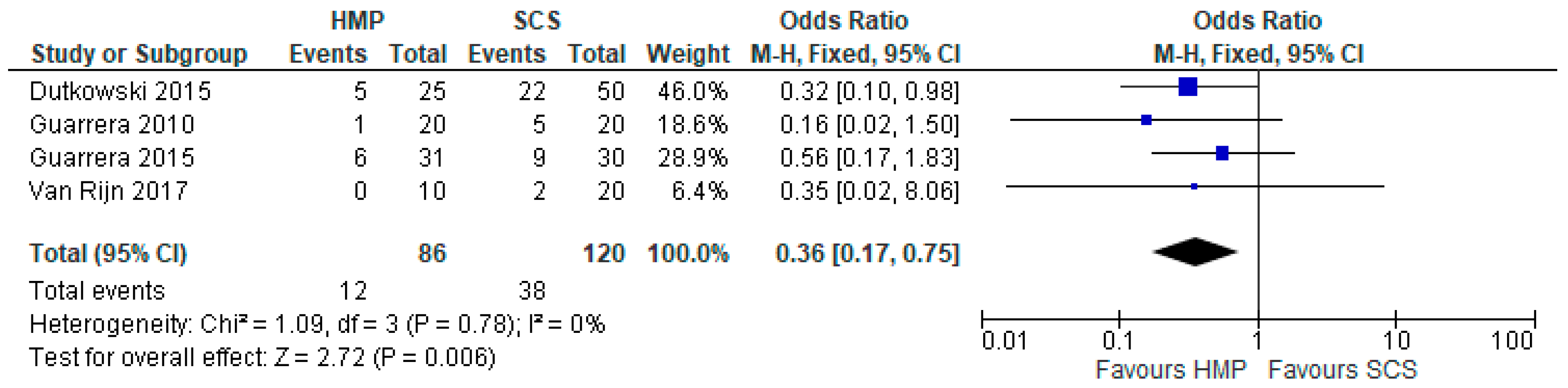
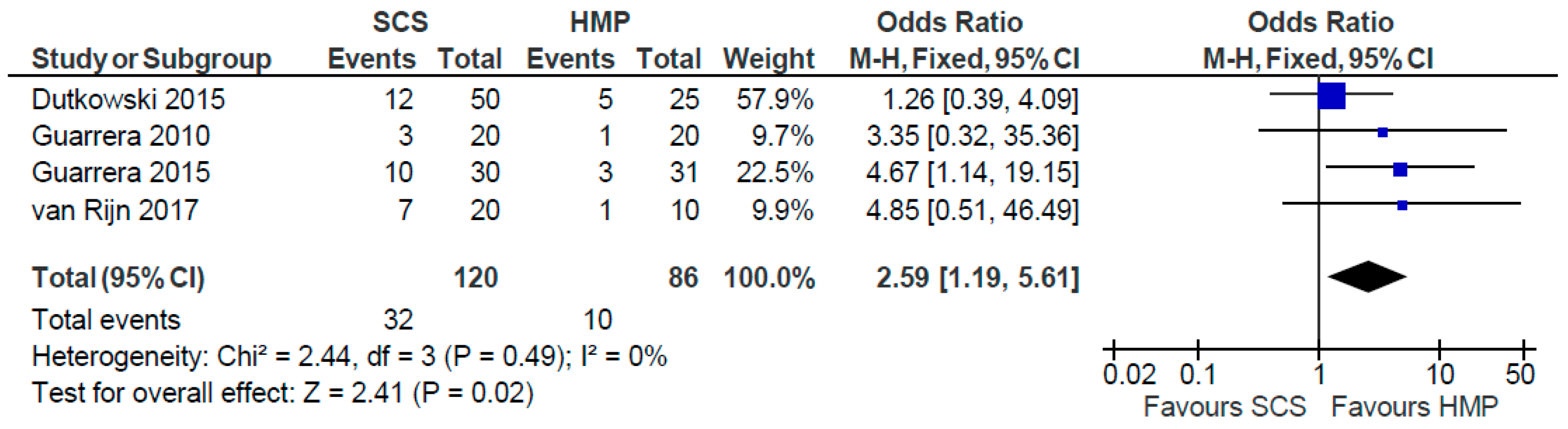
3.4. Primary Non-Function
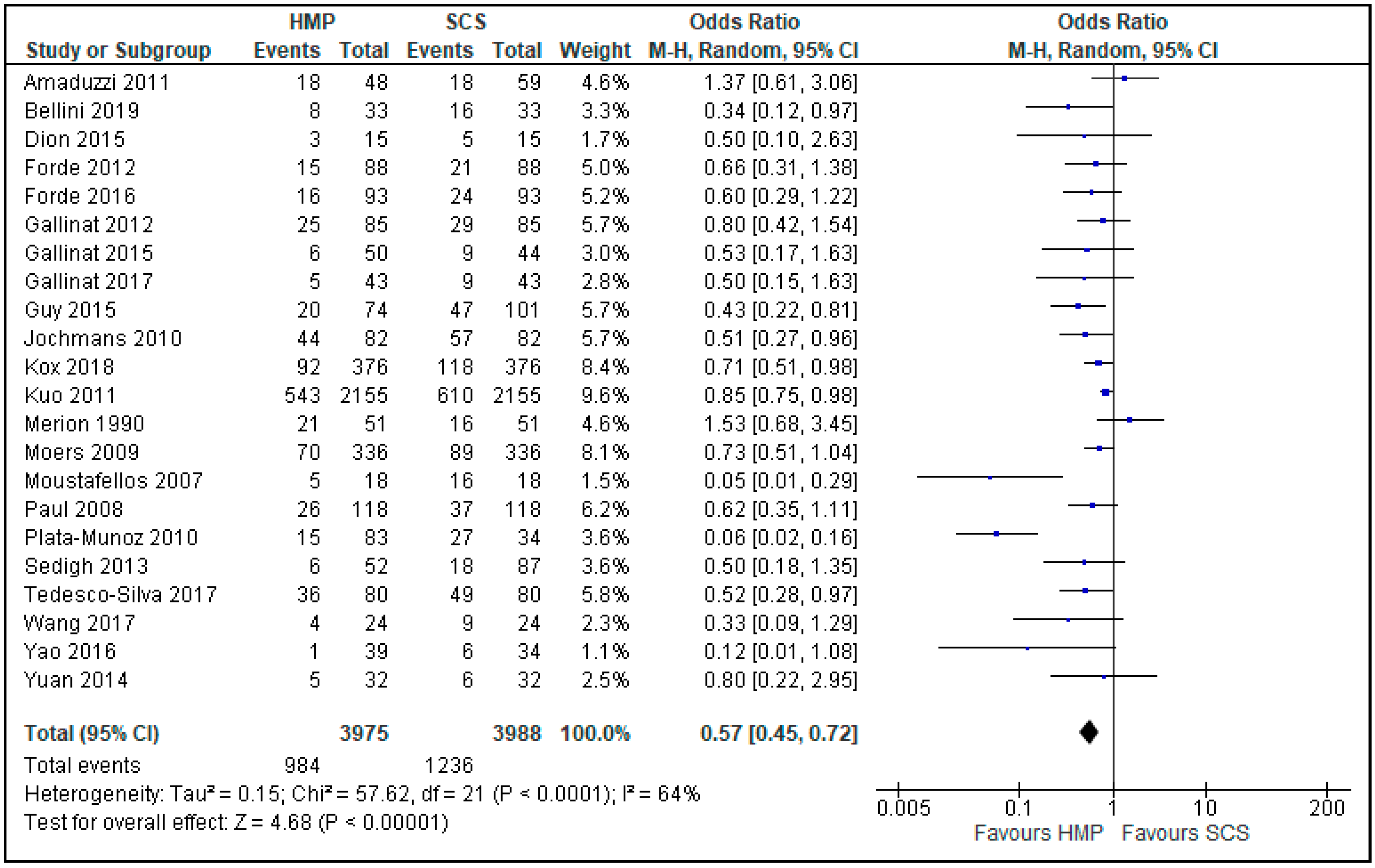
3.5. Delayed Graft Function
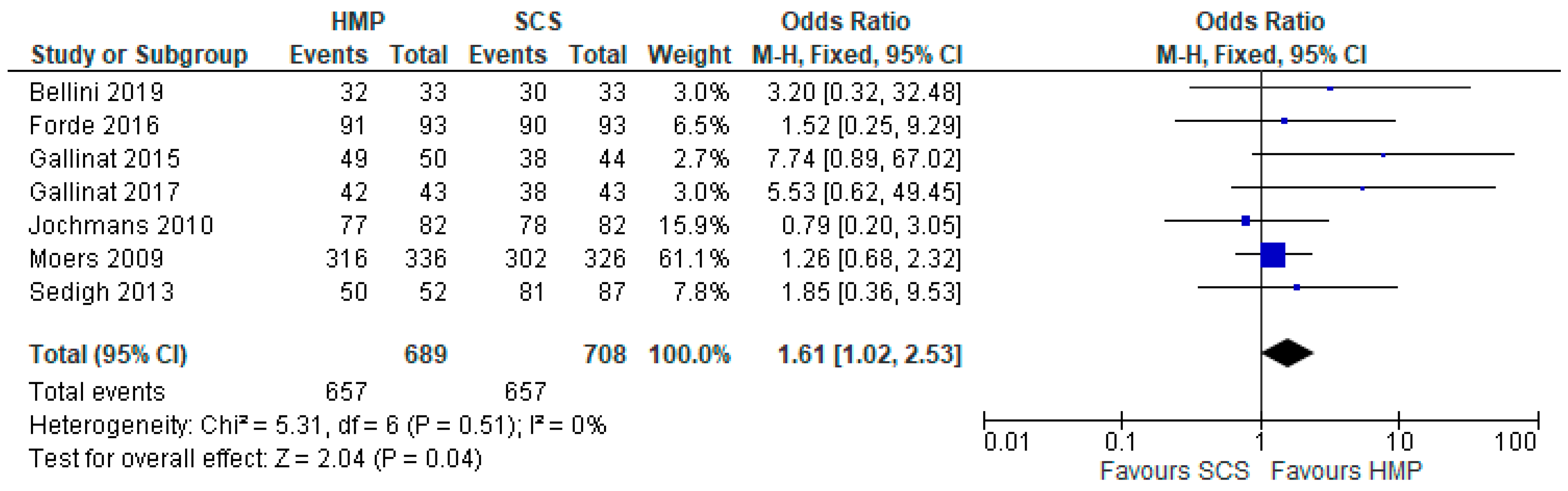
3.6. Acute Rejection
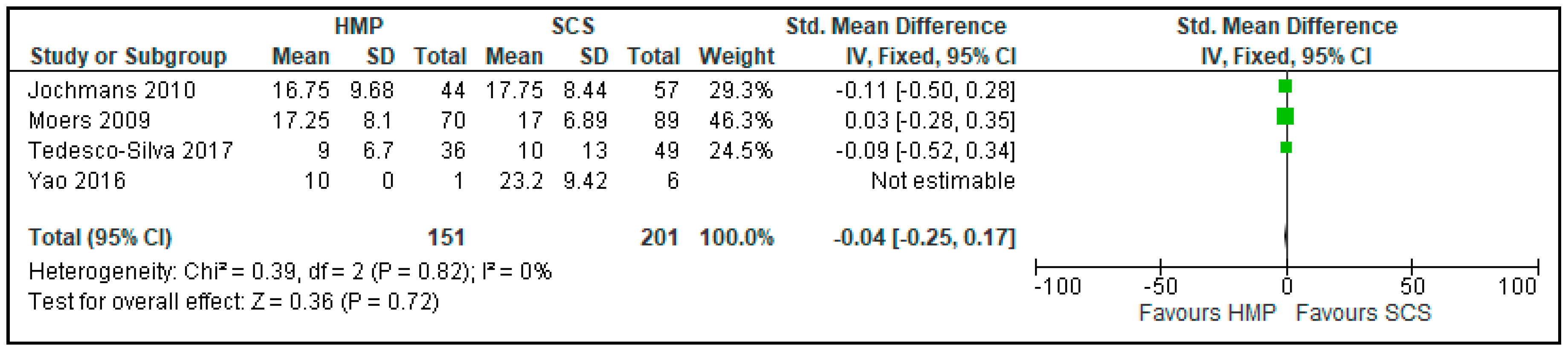
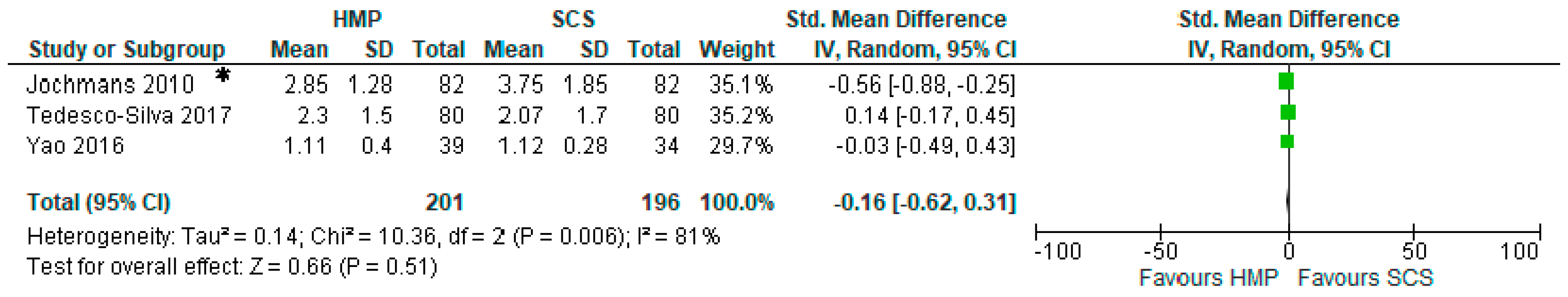
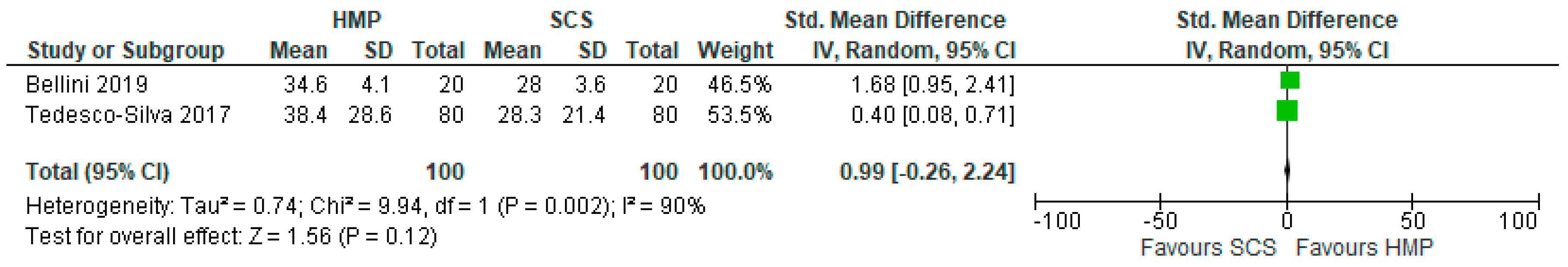
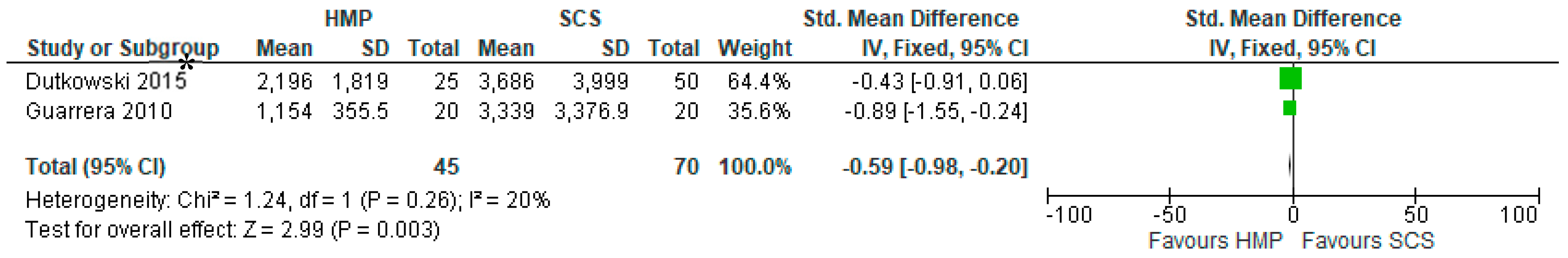
3.7. Comparison of Serum Creatinine One Month after Kidney Transplantation
3.8. One-Year Graft Survival
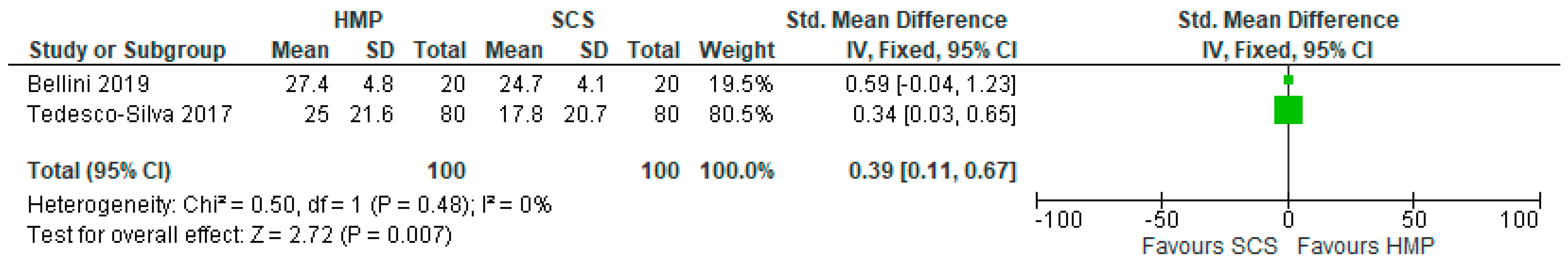
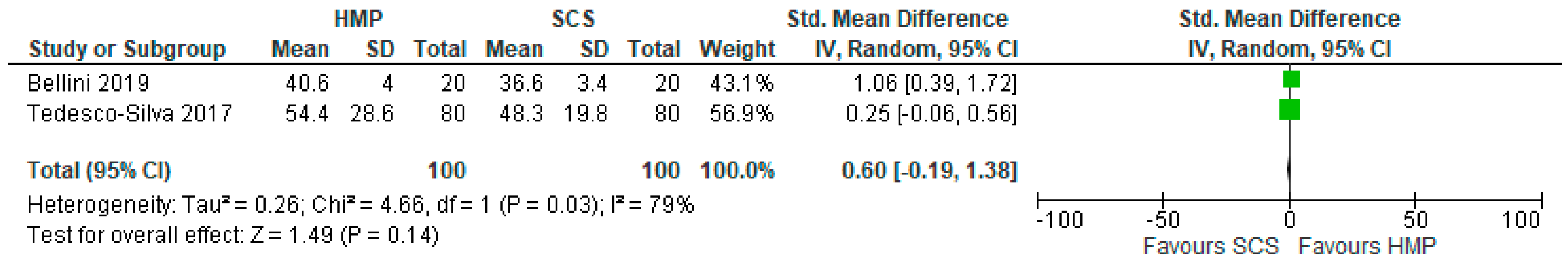
3.9. Post-Transplant Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate in HMP and SCS Kidneys
3.10. Liver Transplant Outcomes
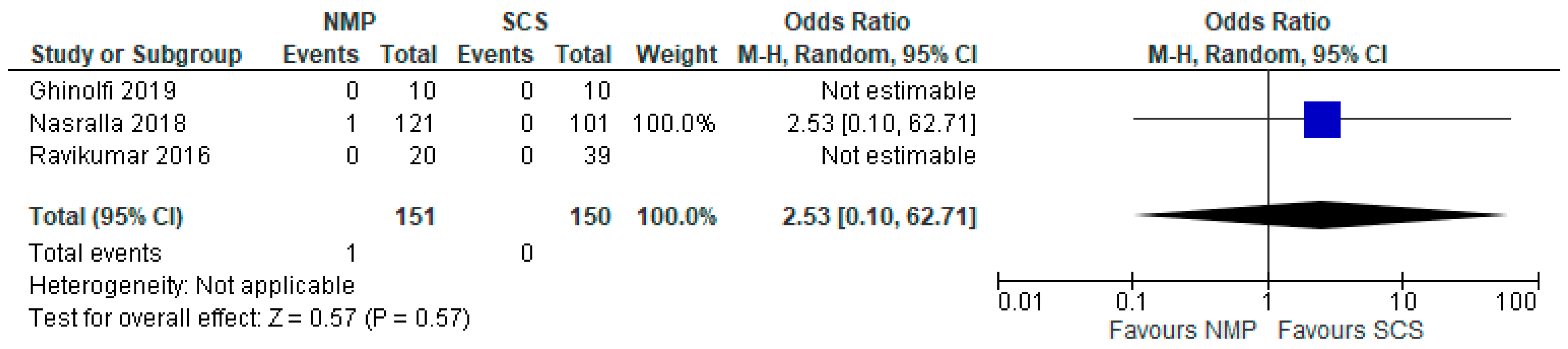
3.11. Primary Non Function
3.12. Early Allograft Dysfunction
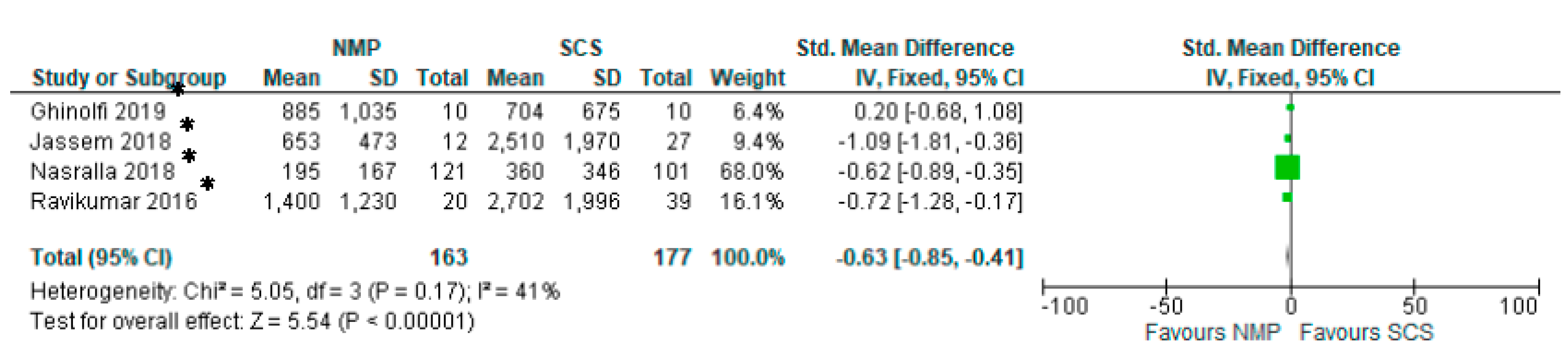
3.13. Serum AST
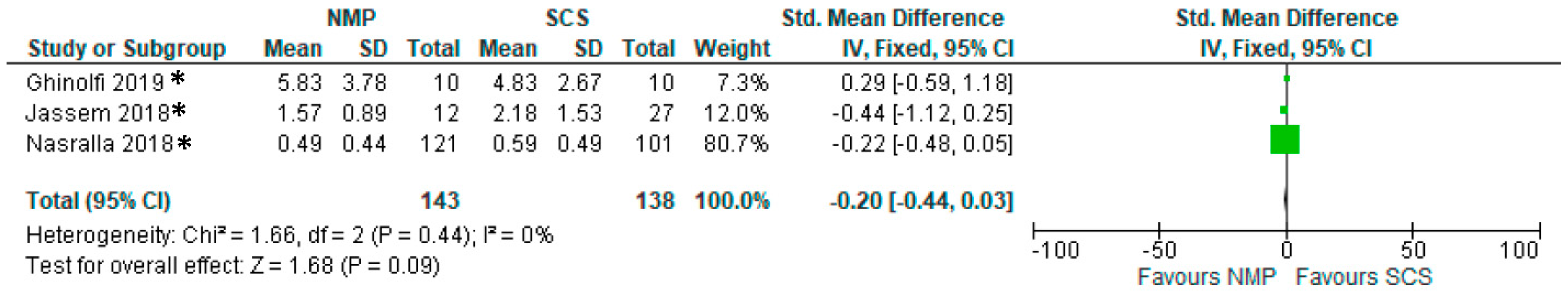
3.14. Serum Bilirubin
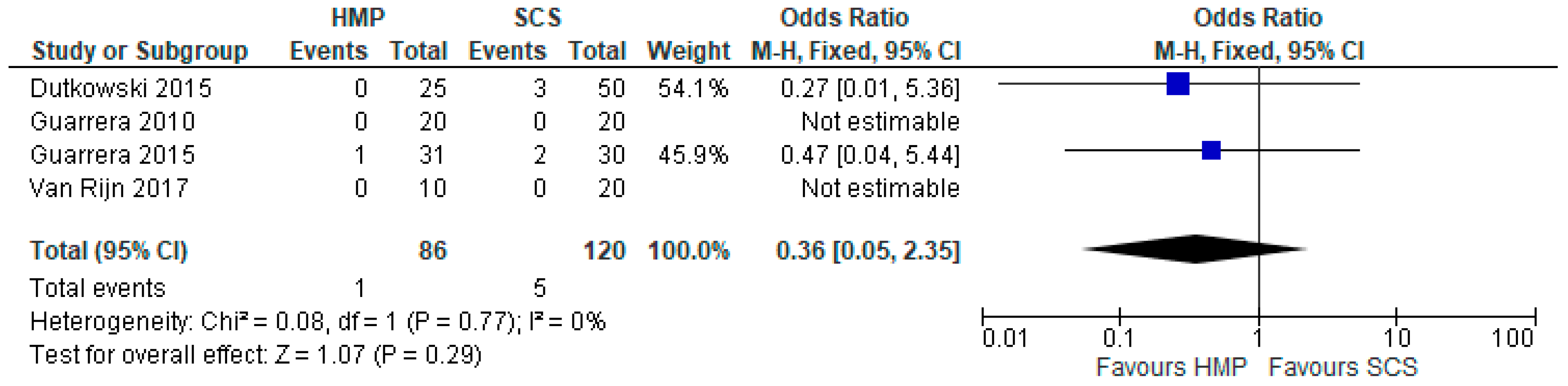
3.15. Biliary Strictures
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AST | Aspartate transaminase |
| DGF | Delayed Graft Function |
| DBD | Donor after Brain Death |
| DCD | Donor after Cardiac Death |
| EAD | Early Allograft Dysfunction |
| eGFR | estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate |
| ECD | Expanded Criteria Donor |
| HMP | Hypothermic Machine Perfusion |
| HTK | Histidine-Tryptophan-Ketoglutarate |
| KPS-1 | Kidney Perfusion Solution 1 |
| MP | Machine Perfusion |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| PNF | Primary Non-Function |
| RCT | Randomized Controlled Trial |
| SCS | Static Cold Storage |
| SMD | Standardised Mean Difference |
| SPS-1 | Static Preservation Solution 1 |
References
- Dube, G.K.; Brennan, C.; Husain, S.A.; Crew, R.J.; Chiles, M.C.; Cohen, D.J.; Mohan, S. Outcomes of kidney transplant from deceased donors with acute kidney injury and prolonged cold ischemia time a retrospective cohort study. Transpl. Int. 2019, 32, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellini, M.I.; D’Andrea, V. Organ preservation: Which temperature for which organ? J. Int. Med Res. 2019, 47, 2323–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olthoff, K.M.; Kulik, L.; Samstein, B.; Kaminski, M.; Abecassis, M.; Emond, J.; Shaked, A.; Christie, J.D. Validation of a current definition of early allograft dysfunction in liver transplant recipients and analysis of risk factors. Liver Transpl. 2010, 16, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokodai, K.; Amada, N.; Kikuchi, H.; Haga, I.; Takayama, T.; Nakamura, A. Body fat percentage as a marker of new-onset diabetes mellitus after kidney transplantation. Transpl. Proc. 2013, 45, 1544–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Wang, W.Q.; Liu, J.M.; Tong, T.J. Estimating the Sample Mean and Standard Deviation from the Sample Size, Median, Range And/or Interquartile Range. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaduzzi, A.; Catena, F.; Montori, G.; Ravaioli, M.; Pinna, A. Hypothermic Machine Perfusion (HMP) versus Static Cold Storage (CS) in Kidney Allograft Preservation. Prospective Case-Control Trial: RO-077. Transpl. Int. 2011, 24, 151. [Google Scholar]
- Bellini, M.I.; Charalampidis, S.; Herbert, P.E.; Bonatsos, V.; Crane, J.; Muthusamy, A.; Dor, F.G.M.F.; Papalois, V. Cold Pulsatile Machine Perfusion versus Static Cold Storage in Kidney Transplantation: A Single Centre Experience. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 7435248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dion, M.S.; McGregor, T.B.; McAlister, V.C.; Luke, P.P.; Sener, A. Hypothermic machine perfusion improves Doppler ultrasonography resistive indices and long-term allograft function after renal transplantation: A single-centre analysis. BJU Int. 2015, 116, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forde, J.C.; Shields, W.P.; Zimmermann, J.A.; Smyth, G.P.; Eng, M.; Power, R.E.; Mohan, P.; Hickey, D.P.; Little, D.M. Single Centre Experience of Hypothermic Continuous Machine Perfusion of Kidneys from Extended Criteria Deceased Heart-Beating Donors: 1826. Transplant. J. 2012, 94, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forde, J.C.; Shields, W.P.; Azhar, M.; Daly, P.J.; Zimmermann, J.A.; Smyth, G.P.; Eng, M.P.; Power, R.E.; Mohan, P.; Hickey, D.P.; et al. Single centre experience of hypothermic machine perfusion of kidneys from extended criteria deceased heart-beating donors: A comparative study. Ir. J. Med Sci. 2016, 185, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallinat, A.; Amrillaeva, V.; Hoyer, D.; Kocabayoglu, P.; Treckmann, J.; Van Meel, M.; Samuel, U.; Minor, T.; Paul, A. End-Ischemic Hypothermic In-House Machine Perfusion improves 1-year graft survival in ECD Kidneys: O258. Transpl. Int. 2015, 28, 95. [Google Scholar]
- Gallinat, A.; Moers, C.; Treckmann, J.; Smits, J.M.; Leuvenink, H.G.; Lefering, R.; Van Heurn, E.; Kirste, G.R.; Squifflet, J.P.; Rahmel, A.; et al. Machine perfusion versus cold storage for the preservation of kidneys from donors >/= 65 years allocated in the Eurotransplant Senior Programme. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 4458–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallinat, A.; Amrillaeva, V.; Hoyer, D.P.; Kocabayoglu, P.; Benko, T.; Treckman, J.W.; Van Meel, M.; Samuel, U.; Minor, T.; Paul, A. Reconditioning by end-ischemic hypothermic in-house machine perfusion: A promising strategy to improve outcome in expanded criteria donors kidney transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2017, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guy, A.; McGrogan, D.; Inston, N.; Ready, A. Hypothermic machine perfusion permits extended cold ischemia times with improved early graft function. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2015, 13, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jochmans, I.; Moers, C.; Smits, J.M.; Leuvenink, H.G.; Treckmann, J.; Paul, A.; Rahmel, A.; Squifflet, J.P.; Van Heurn, E.; Monbaliu, D.; et al. Machine perfusion versus cold storage for the preservation of kidneys donated after cardiac death: A multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Ann. Surg. 2010, 252, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kox, J.; Moers, C.; Monbaliu, D.; Strelniece, A.; Treckmann, J.; Jochmans, I.; Leuvenink, H.; Van Heurn, E.; Pirenne, J.; Paul, A.; et al. The benefits of hypothermic machine preservation and short cold ischemia times in deceased donor kidneys. Transplantation 2018, 102, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.T.; Huang, E.; Bunnapradist, S. Machine Perfusion Versus Cold Storage in Deceased Donor Kidney Transplantation, an Analysis of the OPTN/UNOS Database: Abstract# 633 Poster Board #-Session: P32-I. Am. J. Transplant. 2011, 11, 220. [Google Scholar]
- Merion, R.M.; Oh, H.K.; Port, F.K.; Toledo-Pereyra, L.H.; Turcotte, J.G. A prospective controlled trial of cold-storage versus machine-perfusion preservation in cadaveric renal transplantation. Transplantation 1990, 50, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moers, C.; Smits, J.M.; Maathuis, M.H.; Treckmann, J.; van Gelder, F.; Napieralski, B.P.; van kasterop-kutz, M.; van der heide, J.J.; Squifflet, J.P.; van heurn, E.; et al. Machine perfusion or cold storage in deceased-donor kidney transplantation. New Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafellos, P.; Hadjianastassiou, V.; Roy, D.; Muktadir, A.; Contractor, H.; Vaidya, A.; Friend, P.J. The influence of pulsatile preservation in kidney transplantation from non-heart-beating donors. Transplant. Proc. 2007, 39, 1323–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Moers, C.; Smits, J.; Maathuis, H.; Van Der Heide, J.H.; Van Heurn, E.; Squifflet, J.P.; Pirenne, J.; Ploeg, R.; Treckmann, J. Machine Perfusion versus Cold Storage in Transplantation of Kidneys from older Deceased Donors: Results of a Prospective Randomized Multicentral Trial: 236. Transplantation 2008, 86 (Suppl. 2S), 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plata-Munoz, J.; Muthusamy, A.; Elker, D.; Brockmann, J.; Sinha, S.; Vaidya, A.; Friend, P.; Fuggle, S. Beneficial Effect of Preservation by Machine Perfusion on Postoperative Outocme of Kidneys from Controlled Donors after Cardiac Death: 2325. Transpl. J. 2010, 90, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedigh, A.; Tufveson, G.; Backman, L.; Biglarnia, A.R.; Lorant, T. Initial experience with hypothermic machine perfusion of kidneys from deceased donors in the Uppsala region in Sweden. Transpl. Proc. 2013, 45, 1168–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedesco-Silva, H.; Mello Offerni, J.C.; Ayres Carneiro, V.; Ivani de Paula, M.; Neto, E.D.; Brambate Carvalhinho Lemos, F.; Requiao Moura, L.R.; Pacheco, E.; de Morais Cunha, M.F.; Francisco da Silva, E.; et al. Randomized Trial of Machine Perfusion Versus Cold Storage in Recipients of Deceased Donor Kidney Transplants With High Incidence of Delayed Graft Function. Transpl. Direct 2017, 3, e155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Xie, D.; Hu, X.; Yin, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X. Effect of Hypothermic Machine Perfusion on the Preservation of Kidneys Donated After Cardiac Death: A Single-Center, Randomized, Controlled Trial. Artif. Organs 2017, 41, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, W.; Chen, M.; Zhang, K.; Fu, Y. Hypothermic Machine Perfusion in DCD Kidney Transplantation: A Single Center Experience. Urol. Int. 2016, 96, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zhou, J.; Chen, C.; Han, M.; Wang, X.; He, X. The Application of Machine Perfusion Preservation of Kidneys in Cardiac Death Donor Kidney Transplantation: Abstract# 1464. Transplant 2014, 98, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Dutkowski, P.; Polak, W.G.; Muiesan, P.; Schlegel, A.; Verhoeven, C.J.; Scalera, I.; De Oliveirra, M.L.; Kron, P.; Clavien, P.A. First Comparison of Hypothermic Oxygenated PErfusion Versus Static Cold Storage of Human Donation After Cardiac Death Liver Transplants: An International-matched Case Analysis. Ann. Surg. 2015, 262, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarrera, J.V.; Henry, S.D.; Samstein, B.; Odeh-Ramadan, R.; Kinkhabwala, M.; Goldstein, M.J.; Ratner, L.E.; Renz, J.F.; Lee, H.T.; Brown, R.S.; et al. Hypothermic machine preservation in human liver transplantation: The first clinical series. Am. J. Transpl. 2010, 10, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarrera, J.V.; Henry, S.D.; Samstein, B.; Reznik, E.; Musat, C.; Lukose, T.I.; Ratner, L.E.; Brown, R.S., Jr.; Kato, T.; Emond, J.C. Hypothermic machine preservation facilitates successful transplantation of "orphan" extended criteria donor livers. Am. J. Transpl. 2015, 15, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rijn, R.; Karimian, N.; Matton, A.P.M.; Burlage, L.C.; Westerkamp, A.C.; van den Berg, A.P.; de Kleine, R.H.J.; de Bore, M.T.; Lisman, T.; Porte, R.J. Dual hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion in liver transplants donated after circulatory death. Br. J. Surg. 2017, 104, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nasralla, D.; Coussios, C.C.; Mergental, H.; Akhtar, M.Z.; Butler, A.J.; Ceresa, C.D.L.; Chiocchaia, V.; Dutton, S.J.; Garcia-Valdecasas, J.C.; Heaton, N.; et al. A randomized trial of normothermic preservation in liver transplantation. Nature 2018, 557, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravikumar, R.; Jassem, W.; Mergental, H.; Heaton, N.; Mirza, D.; Perera, M.T.; Quaglia, A.; Holroyd, D.; Vogel, T.; Coussios, C.C.; et al. Liver Transplantation After Ex Vivo Normothermic Machine Preservation: A Phase 1 (First-in-Man) Clinical Trial. Am. J. Transpl. 2016, 16, 1779–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jassem, W.; Xystrakis, E.; Ghnewa, Y.G.; Yuksel, M.; Pop, O.; Martinez-Llordella, M.; Jabri, Y.; Huang, X.; Lozano, J.J.; Quaglia, A.; et al. Normothermic Machine Perfusion (NMP) Inhibits Proinflammatory Responses in the Liver and Promotes Regeneration. Hepatology 2018, 70, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghinolfi, D.; Rreka, E.; De Tata, V.; Franzini, M.; Pezzati, D.; Fierabracci, V.; Masini, M.; Cacciatoinsilla, A.; Bindi, M.L.; Marselli, L.; et al. Pilot, Open, Randomized, Prospective Trial for Normothermic Machine Perfusion Evaluation in Liver Transplantation From Older Donors. Liver Transpl. 2019, 25, 436–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Step | Input |
|---|---|
| 1 | Machine perfusion and (Hypothermic or Normothermic) |
| 2 | (Organ* or kidney or liver) and (Preserv*) |
| 3 | 1 and 2 |
| 4 | Temperature and cell metabolism |
| 5 | 3 or 4 |
| 6 | Transplant* |
| 7 | exp Transplantation/ |
| 8 | 6 or 7 |
| 9 | Renal* or kidney or liver or hepat* |
| 10 | (university of wisconsin or UW or HTK or histidine* or collins or hyperosmolar citrate or HOC or celsior or IGL-1 or institut-George* or custodial or belzer or MPS or KPS or marshall* or hypertonic citrate or soltran or ross) |
| 11 | 8 and 9 and 10 |
| 12 | 5 or 11 |
| Study | Study Type | Machine | Cold Storage Preservation Solution | Donor Type | HMP Grafts (N) | Cold Storage Grafts (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amaduzzi 2011(abstract) [6] | RCT | ? | ? | DCD | 48 | 59 |
| Bellini 2019 [7] | Retrospective | RM3® Waters Medical System | ? | DBD, DCD | 33 | 33 |
| Dion 2015 [8] | Retrospective | LifePort Kidney transporter® | ? | DBD, DCD, ECD | 15 | 15 |
| Forde 2012 (abstract) [9] | Retrospective | LifePort Kidney transporter® | UW | DBD, ECD | 88 | 88 |
| Forde 2016 [10] | Retrospective | LifePort Kidney transporter® | UW | ECD | 93 | 93 |
| Gallinat 2012 [12] | RCT | LifePort Kidney transporter® | HTK or UW | DBD and DCD | 85 | 85 |
| Gallinat 2015 (abstract) [11] | RCT | ? | ? | ECD | 50 | 44 |
| Gallinat 2017 [13] | Prospective | LifePort Kidney transporter® | HTK or UW | DBD | 43 | 43 |
| Guy 2015 [14] | Prospective | LifePort Kidney transporter® | ? | DCD, ECD | 74 | 101 |
| Jochmans 2010 [15] | RCT | LifePort Kidney transporter® | HTK or UW | DBD and DCD | 82 | 82 |
| Kox 2018 [16] | RCT | LifePort Kidney transporter® | HTK or CS-UW | DBD, DCD, ECD | 376 | 376 |
| Kuo 2011 (abstract) [17] | Retrospective | ? | ? | DCD, DBD | 2155 | 2155 |
| Merion 1990 [18] | RCT | MOX-100 | Euro-Collins | DBD | 51 | 51 |
| Moers 2009 [19] | RCT | LifePort Kidney transporter® | HTK or UW or Euro-Collins | DBD and DCD | 336 | 336 |
| Moustafellos 2007 [20] | Prospective | LifePort Kidney transporter® | UW | DCD | 18 | 18 |
| Paul 2008 (abstract) [21] | RCT | ? | ? | ECD | 118 | 118 |
| Plata-Munoz 2010 (abstract) [22] | Retrospective | ? | ? | DCD | 83 | 34 |
| Sedigh 2013 [23] | Retrospective | LifePort Kidney transporter® | HTK, UW, Euro-Collins, Custodiol-N | ECD | 52 | 87 |
| Tedesco-Silva 2017 [24] | RCT | LifePort Kidney transporter® | SPS-1, Celsior preservation solution | DBD | 80 | 80 |
| Wang 2017 [25] | RCT | LifePort Kidney transporter® | ? | DCD | 24 | 24 |
| Yao 2016 [26] | Prospective | LifePort Kidney transporter® | UW | DCD | 39 | 34 |
| Yuan 2014 (abstract) [27] | Prospective | LifePort Kidney transporter® | ? | DCD | 32 | 32 |
| Study | Study Type | Machine | Cold Storage Preservation Solution | Donor Type | HMP Grafts (N) | Cold Storage Grafts (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dutkowski 2015 [28] | Observational | ECOPS device (Organ Assist)® | University Wisconsin | DCD, DBD | 25 | 50 |
| Guarrera 2010 [29] | Observational | Modified Medtronic PBS® | University Wisconsin | DCD, ECD | 20 | 20 |
| Guarrera 2015 [30] | Observational | Modified Medtronic PBS® | University Wisconsin | ECD | 31 | 30 |
| Van Rijn 2017 [31] | Observational | Liver Assist (Organ Assist) ® | According to local guidelines | DCD, DBD | 10 | 20 |
| Study | Study Type | Machine | Cold Storage Preservation Solution | Donor Type | NMP Grafts (N) | Cold Storage Grafts (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ghinolfi 2019 [35] | RCT | Liver Assist (Organ Assist)® | Celsior solution | DBD | 10 | 10 |
| Jassem 2018 [34] | Observational | OrganOx metra® | University Wisconsin | DBD | 12 | 27 |
| Nasralla 2018 [32] | RCT | OrganOx metra® | According to local guidelines | DBD, DCD | 121 | 101 |
| Ravikumar 2016 [33] | Observational | OrganOx metra® | University Wisconsin | DBD, DCD | 20 | 39 |
| Study | Randomisation | Randomisation Description | Inappropriate Randomisation | Double Blind | Double Blinding Description | Inappropriate Double Blinding | Description of Losses | Total Jadad Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gallinat 2017 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Forde 2016 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Dion 2015 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Guy 2015 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Gallinat 2012 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Jochmans 2010 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Merion 1990 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Moers 2009 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Moustafellos 2007 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Sedigh 2013 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Tedesco-Silva 2017 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Bellini 2019 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Wang 2017 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Yao 2016 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Kox 2018 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Gallinat 2015 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Forde 2012 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Amaduzzi 2011 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Kuo 2011 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Paul 2008 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 |
| Plata-Munoz 2010 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Yuan 2014 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Study | Randomisation | Randomisation Described | Inappropriate Randomisation | Double Blind | Double Blinding Description | Inappropriate Double Blinding | Description of Losses | Total Jadad Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dutkowski 2015 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Guarrera 2010 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Van Rijn 2017 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Guarrera 2015 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Study | Randomisation | Randomisation Described | Inappropriate Randomisation | Double Blind | Double Blinding Description | Inappropriate Double Blinding | Description of Losses | Total Jadad Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasralla 2018 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 5 |
| Ravikumar 2016 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Jassem 2018 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Ghinolfi 2019 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bellini, M.I.; Nozdrin, M.; Yiu, J.; Papalois, V. Machine Perfusion for Abdominal Organ Preservation: A Systematic Review of Kidney and Liver Human Grafts. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081221
Bellini MI, Nozdrin M, Yiu J, Papalois V. Machine Perfusion for Abdominal Organ Preservation: A Systematic Review of Kidney and Liver Human Grafts. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(8):1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081221
Chicago/Turabian StyleBellini, Maria Irene, Mikhail Nozdrin, Janice Yiu, and Vassilios Papalois. 2019. "Machine Perfusion for Abdominal Organ Preservation: A Systematic Review of Kidney and Liver Human Grafts" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 8: 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081221
APA StyleBellini, M. I., Nozdrin, M., Yiu, J., & Papalois, V. (2019). Machine Perfusion for Abdominal Organ Preservation: A Systematic Review of Kidney and Liver Human Grafts. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(8), 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081221







