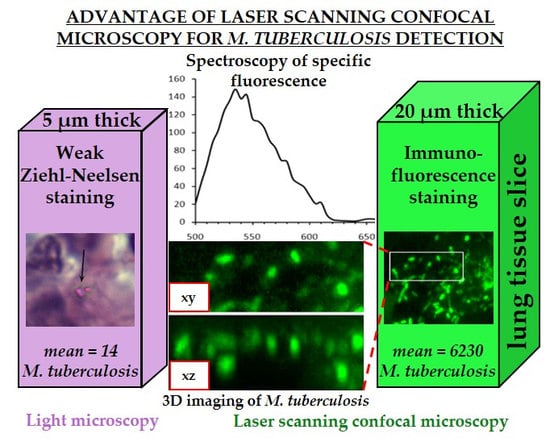
Application of Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy for the Visualization of M. tuberculosis in Lung Tissue Samples with Weak Ziehl–Neelsen Staining
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparations
2.2. Antibody Production
2.3. Antigen Retrieval
2.4. Immunostaining
2.5. Controls
2.6. Ziehl–Neelsen Staining
2.7. Microscopy and Image Processing
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
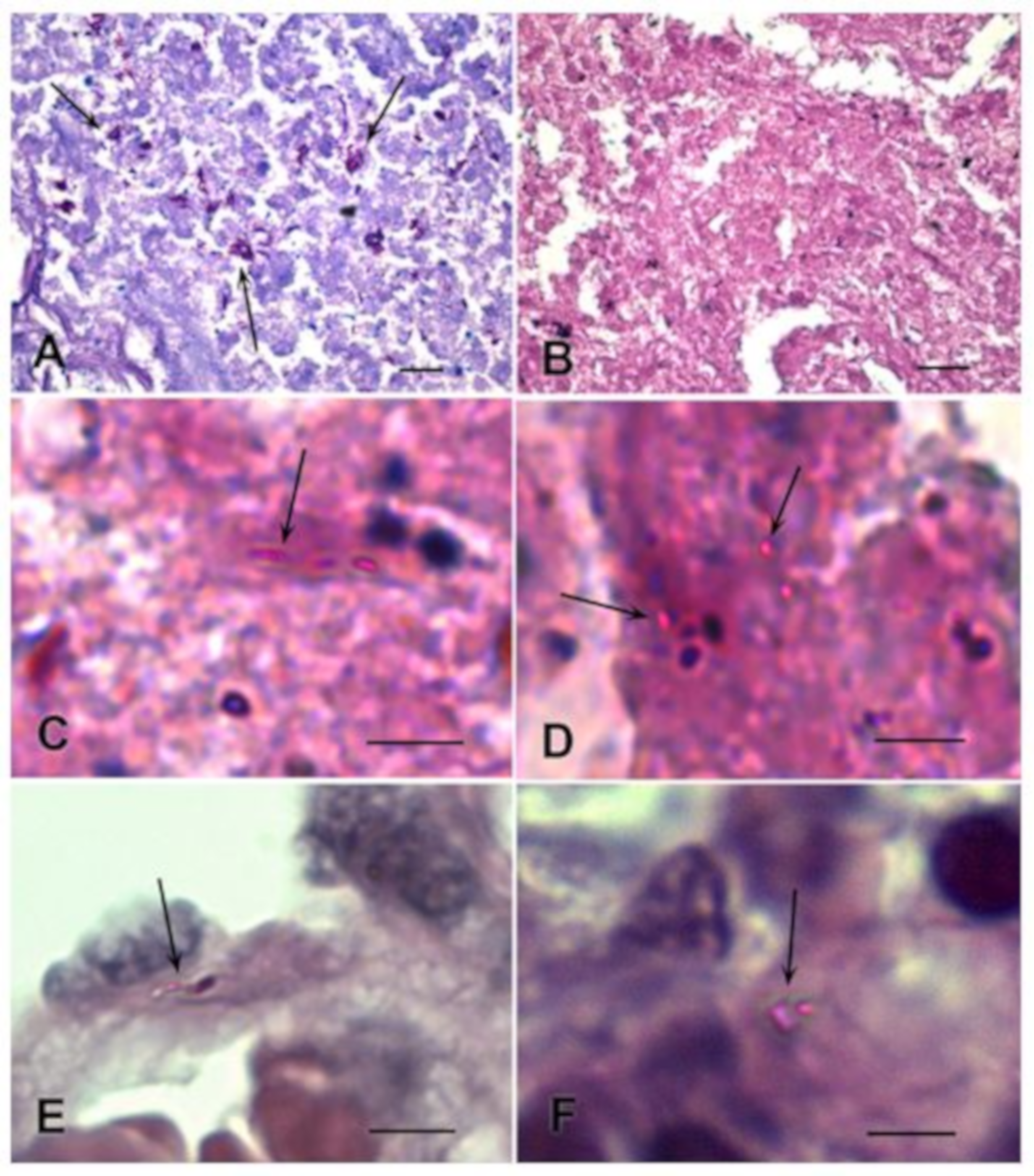
3.1. Detection of M. tuberculosis in Histological Sections Using Ziehl–Neelsen Staining
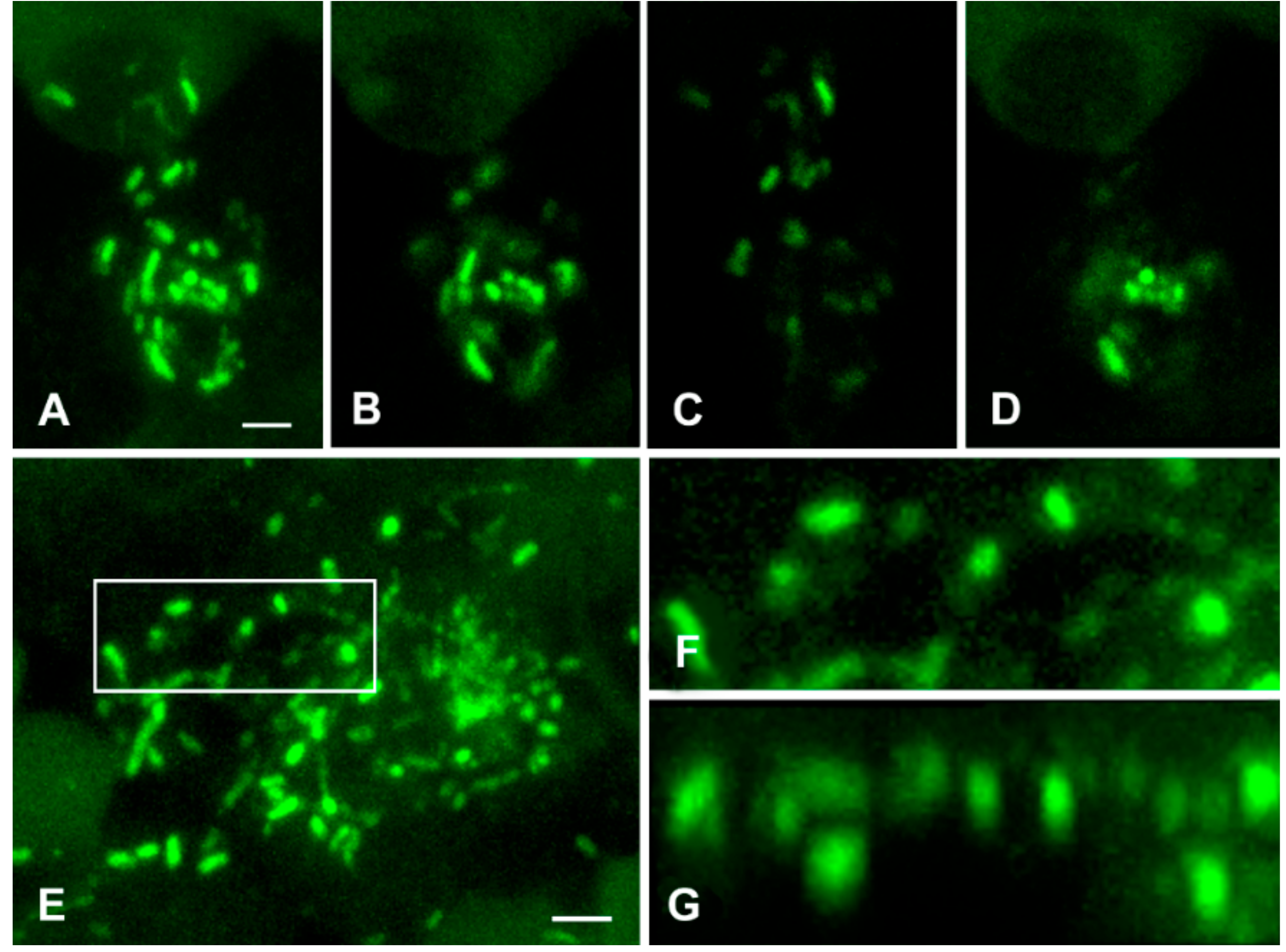
3.2. Detection of M. tuberculosis Using Immunofluorescence Labelling and LSCM
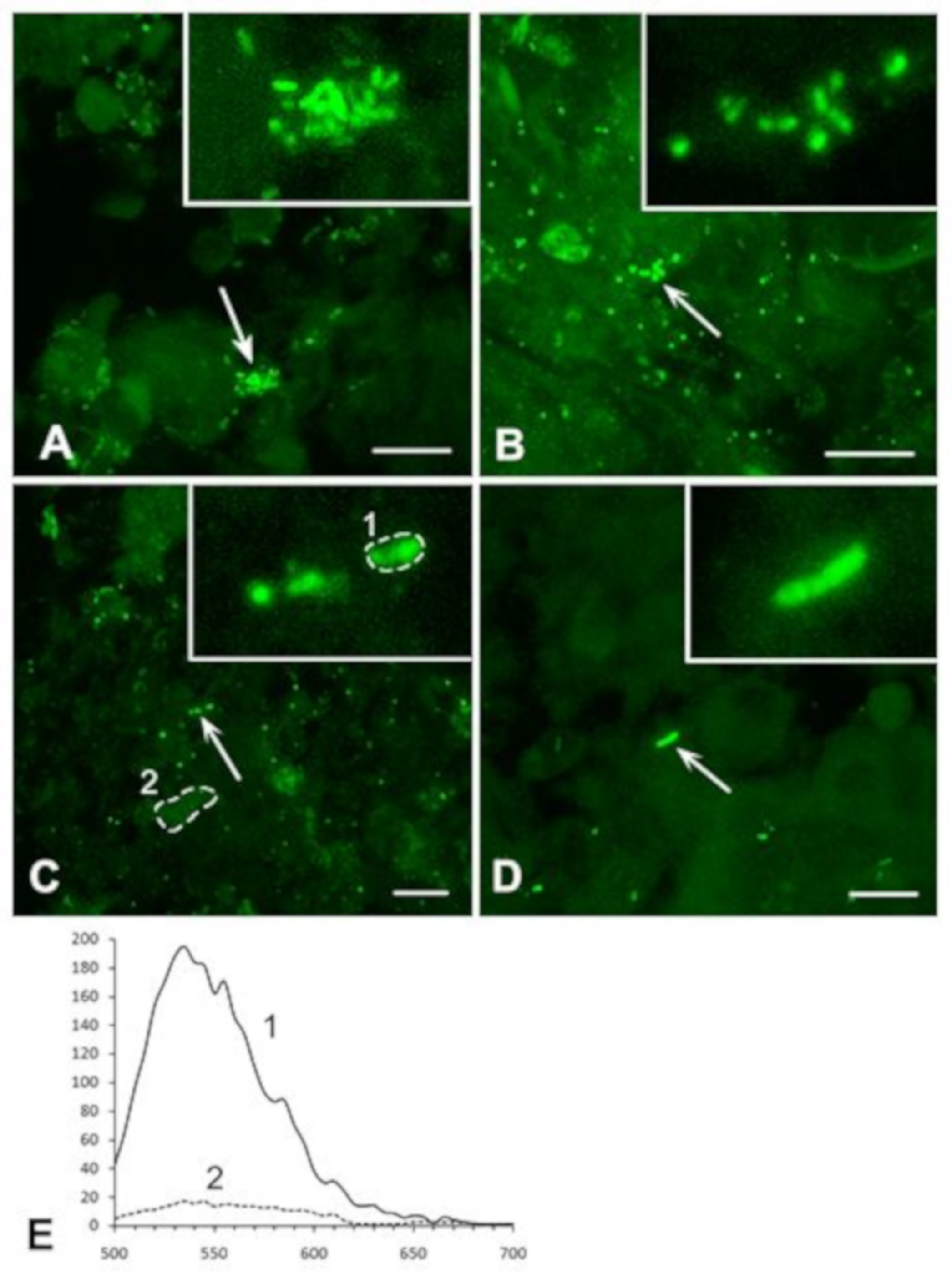
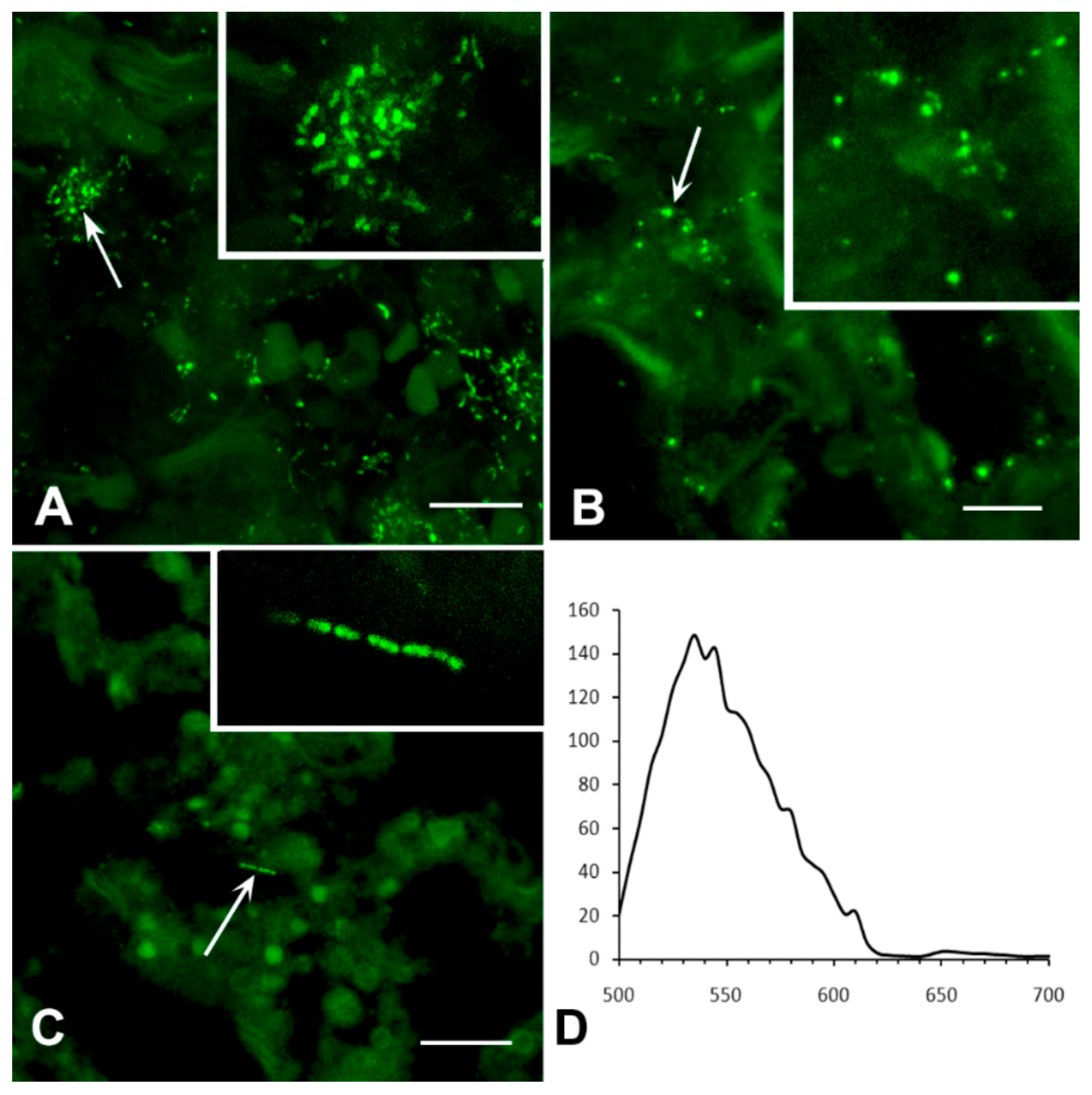
3.2.1. Analysis of M. tuberculosis in the Caseous Necrosis Region
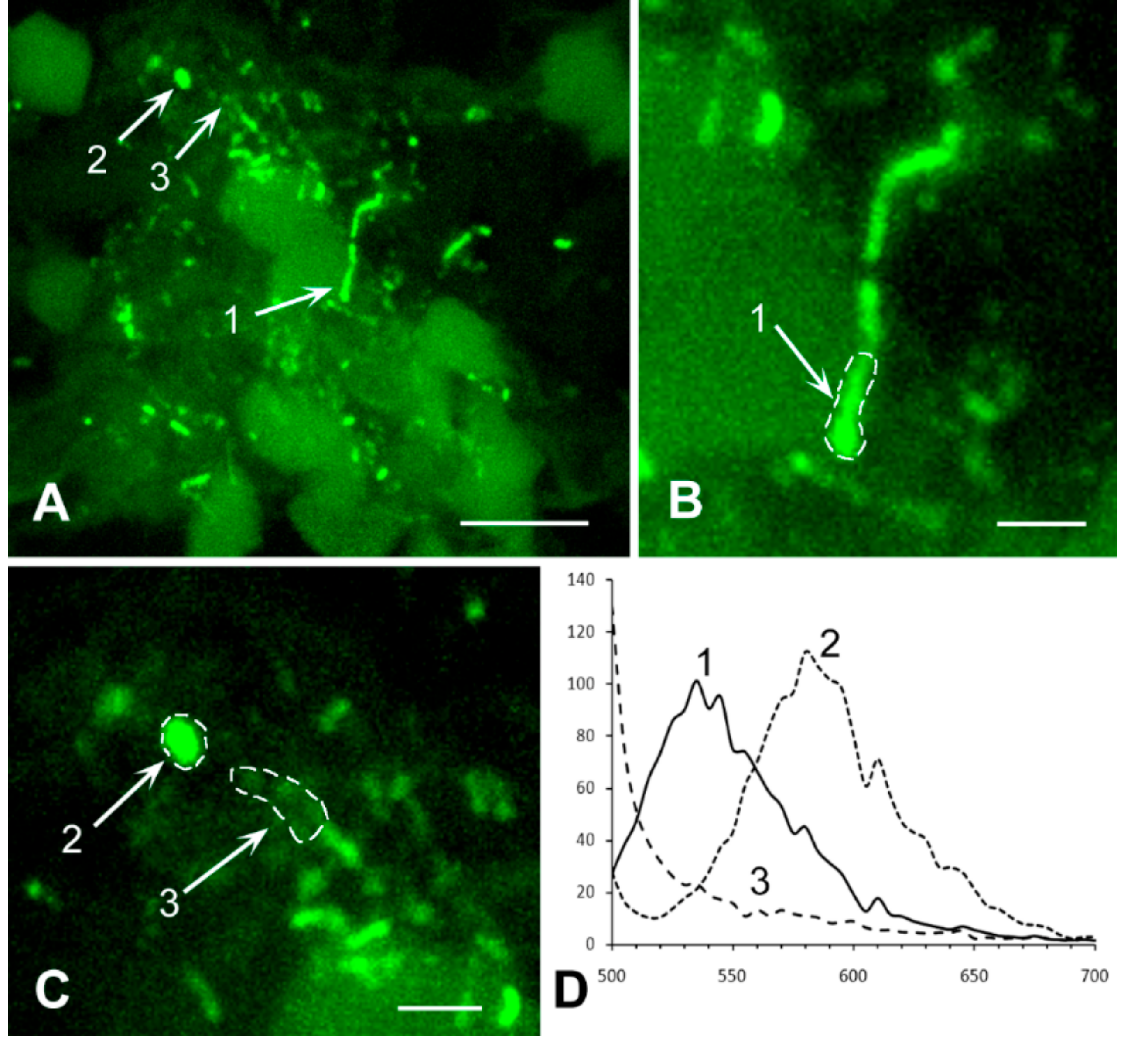
3.2.2. Analysis of M. tuberculosis in the Perifocal Region
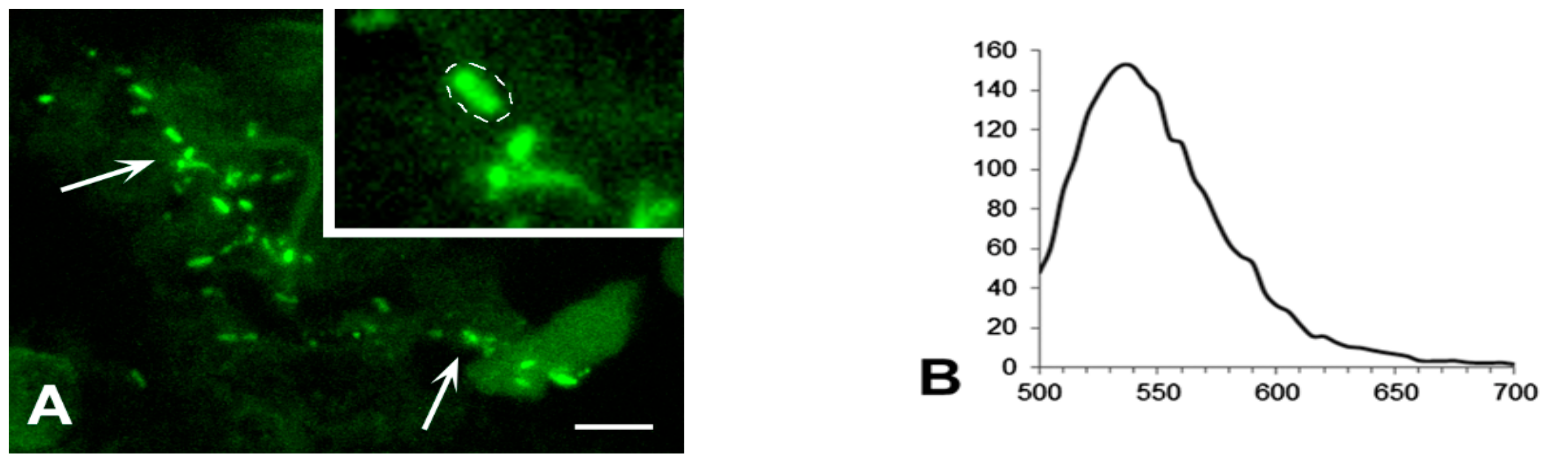
3.3. Exclusion of Non-Specific Fluorescence from the Analysis
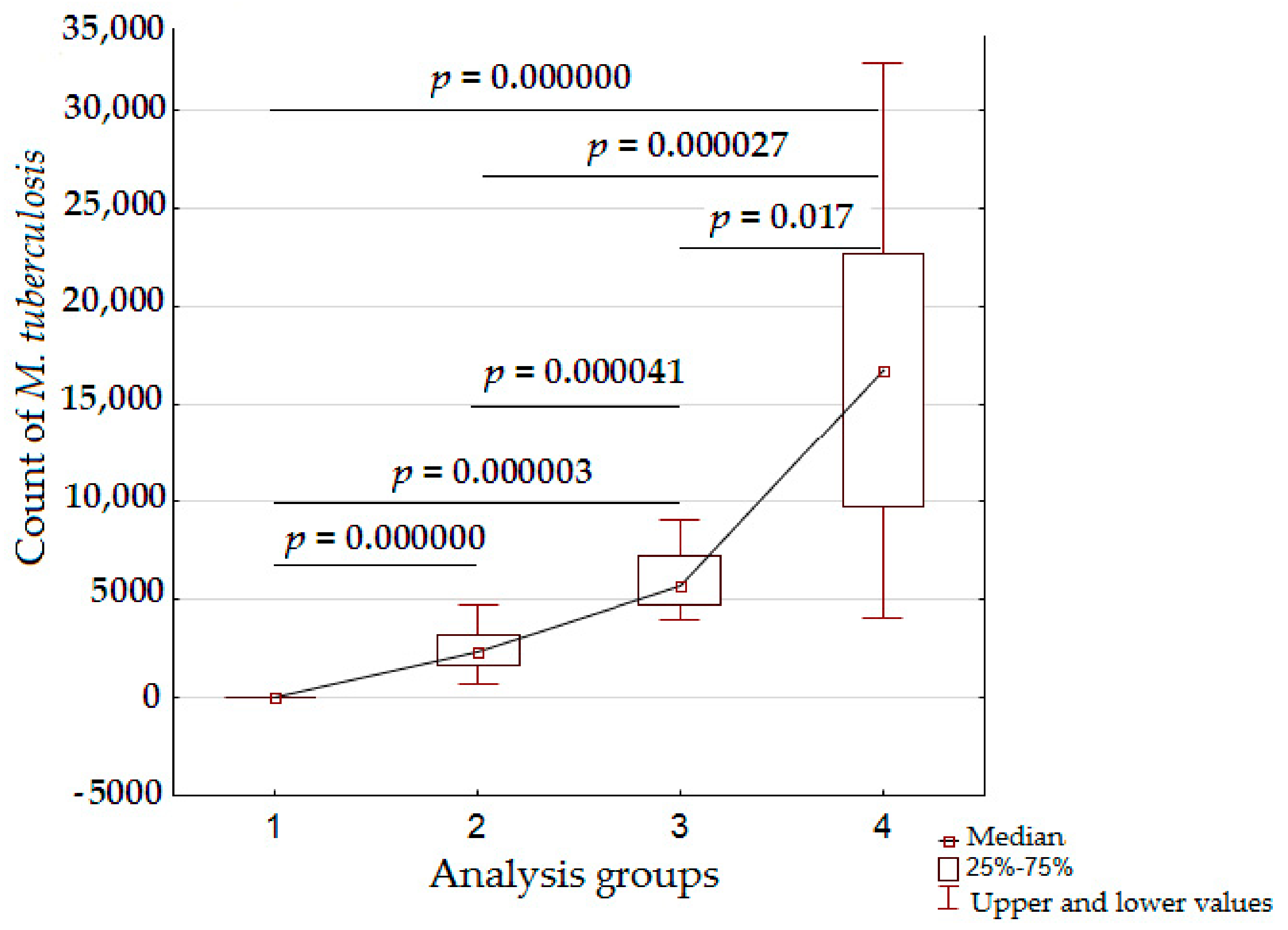
3.4. Analysis of Bacterial Density
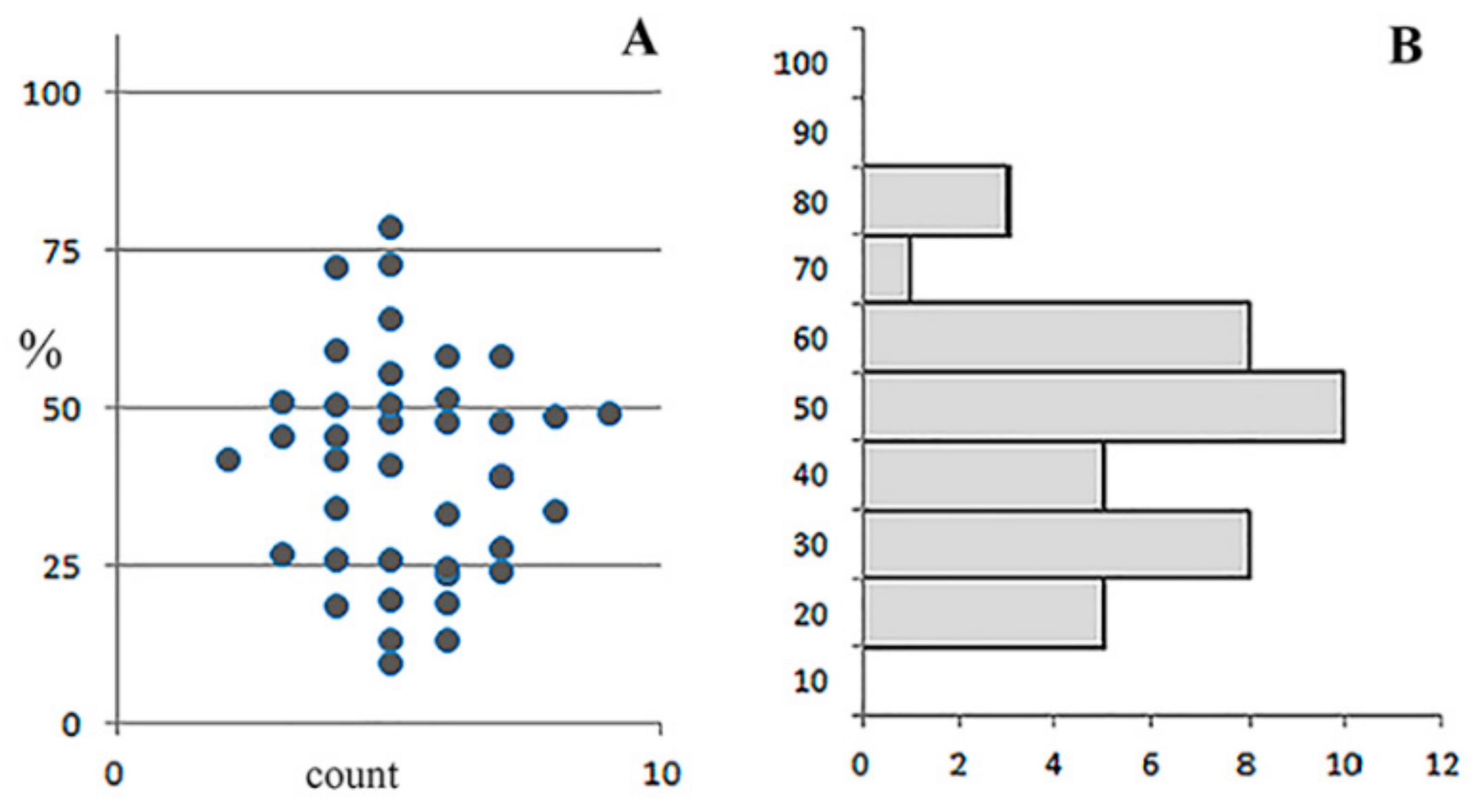
3.5. Detailed Analysis of Bacterial Density, Colony Forms, and Individual Bacterial Morphology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2018; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; p. 243. ISBN 978-92-4-156564-6. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, D.; Agarwal, R.; Aggarwal, A.N.; Jindal, S.K. Sarcoidosis and tuberculosis: The same disease with different manifestations or similar manifestations of different disorders. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2012, 18, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvorakovskaya, M.M.; Maiskaya, M.Y.; Nasyrov, P.A.; Baranova, O.P.; Ariel, B.M. The morphological examination in the differential diagnosis of tuberculosis and sarcoidosis. Arkh. Patol. 2014, 76, 27–31. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Mortaz, E.; Adcock, I.M.; Barnes, P.J. Sarcoidosis: Role of Non-Tuberculosis Mycobacteria and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Int. J. Mycobacteriol. 2014, 3, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivihya-Ndugga, L.E.; van Cleeff, M.R.; Githui, W.A.; Nganga, L.W.; Kibuga, D.K.; Odhiambo, J.A.; Klatser, P.R. A comprehensive comparison of Ziehl-Neelsen and fluorescence microscopy for the diagnosis of tuberculosis in a resource-poor urban setting. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2003, 7, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Steingart, K.R.; Ng, V.; Henry, M.; Hopewell, P.C.; Ramsay, A.; Cunningham, J.; Urbanczik, R.; Perkins, M.D.; Aziz, M.A.; Pai, M. Sputum processing methods to improve the sensitivity of smear microscopy for tuberculosis: A systematic review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinserling, V.A.; Agapov, M.M.; Orlov, A.N. The informative value of various methods for identifying acid-fast bacilli in relation to the degree of tuberculosis process activity. Arkh. Patol. 2017, 95, 40–45. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, M.D.; Kritski, A.L. Diagnostic testing in the control of tuberculosis [Perspective]. Bull. World Health Organ. 2002, 80, 512. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Liu, Z.; Xiu, B.; Yang, X.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, X.; Duan, C.; Que, H.; Zhang, H.; Feng, X. A multiple-antigen detection assay for tuberculosis diagnosis based on broadly reactive polyclonal antibodies. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2017, 20, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohd Azmi, U.Z.; Yusof, N.A.; Kusnin, N.; Abdullah, J.; Suraiya, S.; Ong, P.S.; Raston, N.H.A.; Rahman, S.F.A.; Fathil, M.F.M. Sandwich electrochemical immunosensor for early detection of tuberculosis based on graphene/polyaniline-modified screen-printed gold electrode. Sensors 2018, 18, 3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, R.L.; Taylor, M.G. The specific differentiation of schistosome eggs by the Ziehl-Neelsen technique. Trans. R Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1972, 66, 18–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, S.A.; Pohlenz, J.F. Staining of cryptosporidia by a modified Ziehl-Neelsen technique. Acta. Vet. Scand. 1981, 22, 594–596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marks, J. Notes on the Ziehl-Neelsen staining of sputum. Tubercle 1974, 55, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, P.; Ulrichs, T.; Bandermann, S.; Pradl, L.; Jörg, S.; Krenn, V.; Morawietz, L.; Kaufmann, S.H.; Aichele, P. Cell-wall alterations as an attribute of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in latent infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 188, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, M.M.; Budhwar, P.; Jain, A. Immunocytochemistry versus nucleic acid amplification in fine needle aspirates and tissues of extrapulmonary tuberculosis. J. Cytol. 2012, 29, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, M.M.; Budhwar, P. Immunohistochemical localization of mycobacterium tuberculosis complex antigen with antibody to 38 kDa antigen versus Ziehl Neelsen staining in tissue granulomas of extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Indian J. Tuberc. 2007, 54, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iida, T.; Uchida, K.; Lokman, N.; Furukawa, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Kumasaka, T.; Takemura, T.; Kawachi, H.; Akashi, T.; Eishi, Y. Calcified Granulomatous Lung Lesions Contain Abundant Mycobacterium tuberculosis Components. J. Mycobac. Dis. 2014, 4, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markova, N.; Slavchev, G.; Michailova, L. Unique biological properties of Mycobacterium tuberculosis L-form variants: Impact for survival under stress. Int. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavchev, G.; Michailova, L.; Markova, N. L-form transformation phenomenon in Mycobacterium tuberculosis associated with drug tolerance to ethambutol. Int. J. Mycobacteriol. 2016, 5, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulrichs, T.; Lefmann, M.; Reich, M.; Morawietz, L.; Roth, A.; Brinkmann, V.; Kosmiadi, G.A.; Seiler, P.; Aichele, P.; Hahn, H.; et al. Modified immunohistological staining allows detection of Ziehl-Neelsen-negative Mycobacterium tuberculosis organisms and their precise localization in human tissue. J. Pathol. 2005, 205, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihama, Y.; Hokama, A.; Hibiya, K.; Kishimoto, K.; Nakamoto, M.; Hirata, T.; Kinjo, N.; Cash, H.L.; Higa, F.; Tateyama, M.; et al. Diagnosis of intestinal tuberculosis using a monoclonal antibody to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 6974–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, M.R.; Sviland, L.; Wiker, H.; Mustafa, T. Rapid and Specific Diagnosis of Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis by Immunostaining of Tissues and Aspirates with Anti-MPT64. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2017, 25, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, N.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H. Double staining of bacilli and antigen Ag85B improves the accuracy of the pathological diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 69, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, S.; Shamaei, M.; Pourabdollah, M.; Sadr, M.; Karbasi, M.; Kiani, A.; Bahadori, M. Histopathological findings in immunohistological staining of the granulomatous tissue reaction associated with tuberculosis. Tuberc. Res. Treat. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, M.R.; Mustafa, T.; Wiker, H.G.; Mørkve, O.; Sviland, L. Immunohistochemical diagnosis of abdominal and lymph node tuberculosis by detecting Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex specific antigen MPT64. Diagn. Pathol. 2007, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, M.R.; Mustafa, T.; Wiker, H.G.; Sviland, L. Rapid diagnosis of tuberculosis in aspirate, effusions, and cerebrospinal fluid by immunocytochemical detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex specific antigen MPT64. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2012, 40, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erokhina, M.V.; Nezlin, L.P.; Avdienko, V.G.; Voronezhska, E.E.; Lepekha, L.N. Immunohistochemical Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Tissues of Consumptives Using Laser Scanning Microscopy. Biol. Bull. 2016, 43, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patino, S.; Alamo, L.; Cimino, M.; Casart, Y.; Bartoli, F.; García, M.J.; Salazar, L. Autofluorescence of mycobacteria as a tool for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 3296–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, C.; Lee, C.M.; Dubey, V.S.; Daniel, J.; Abomoelak, B.; Sirakova, T.D.; Pawar, S.; Rogers, L.; Kolattukudy, P.E. A novel in vitro multiple-stress dormancy model for Mycobacterium tuberculosis generates a lipid-loaded, drug-tolerant, dormant pathogen. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodbane, R.; Raoult, D.; Drancourt, M. Dramatic reduction of culture time of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, T.; Mogga, S.J.; Mfinanga, S.G.; Mørkve, O.; Sviland, L. Immunohistochemical analysis of cytokines and apoptosis in tuberculous lymphadenitis. Immunology 2006, 117, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadele, A.; Beyene, D.; Hussein, J.; Gemechu, T.; Birhanu, A.; Mustafa, T.; Tsegaye, A.; Aseffa, A.; Sviland, L. Immunocytochemical detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex specific antigen, MPT64, improves diagnosis of tuberculous lymphadenitis and tuberculous pleuritis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velayati, A.A.; Farnia, P.; Masjedi, M.R.; Zhavnerko, G.K.; Ghanavi, J.; Poleschuyk, N.N. Morphological modification by Tubercle bacilli: No time for denial. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2012, 6, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, L.L.; Steingart, K.R.; Dendukuri, N.; Schiller, I.; Minion, J.; Pai, M.; Ramsay, A.; Henry, M.; Laal, S. Systematic review and meta-analysis of antigen detection tests for the diagnosis of tuberculosis. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 1616–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellani, C.; Fedrigo, M.; Frigo, A.C.; Barbera, M.D.; Thiene, G.; Valente, M.; Adami, F.; Angelini, A. Application of confocal laser scanning microscopy for the diagnosis of amyloidosis. Virchows Arch. 2017, 470, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Erokhina, M.V.; Lepekha, L.N.; Voronezhskaya, E.E.; Nezlin, L.P.; Avdienko, V.G.; Ergeshov, A.E. Application of Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy for the Visualization of M. tuberculosis in Lung Tissue Samples with Weak Ziehl–Neelsen Staining. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081185
Erokhina MV, Lepekha LN, Voronezhskaya EE, Nezlin LP, Avdienko VG, Ergeshov AE. Application of Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy for the Visualization of M. tuberculosis in Lung Tissue Samples with Weak Ziehl–Neelsen Staining. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(8):1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081185
Chicago/Turabian StyleErokhina, Maria V., Larisa N. Lepekha, Elena E. Voronezhskaya, Leonid P. Nezlin, Vadim G. Avdienko, and Atadzhan E. Ergeshov. 2019. "Application of Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy for the Visualization of M. tuberculosis in Lung Tissue Samples with Weak Ziehl–Neelsen Staining" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 8: 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081185
APA StyleErokhina, M. V., Lepekha, L. N., Voronezhskaya, E. E., Nezlin, L. P., Avdienko, V. G., & Ergeshov, A. E. (2019). Application of Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy for the Visualization of M. tuberculosis in Lung Tissue Samples with Weak Ziehl–Neelsen Staining. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(8), 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081185