Hydrogen Sulfide as a Toxic Product in the Small–Large Intestine Axis and its Role in IBD Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Bacterial Culture and Cultivation
2.2. Bacterial Biomass Determination
2.3. Sulfate Determination
2.4. Hydrogen Sulfide Determination
2.5. Lactate and Acetate Determination
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gibson, G.R.; Cummings, J.H.; Macfarlane, G.T. Growth and activities of sulphate-reducing bacteria in gut contents of health subjects and patients with ulcerative colitis. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1991, 86, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Macfarlane, S.; Macfarlane, G.T. Metabolic interactions involving sulphate-reducing and methanogenic bacteria in the human large intestine. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1993, 12, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.H.; Macfarlane, G.T.; Macfarlane, S. Intestinal Bacteria and Ulcerative Colitis. Curr. Issues Intest. Microbiol. 2003, 4, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barton, L.L.; Hamilton, W.A. Sulphate-Reducing Bacteria Environmental and Engineered Systems; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Loubinoux, J.; Bronowicji, J.P.; Pereira, I.A. Sulphate-reducing bacteria in human feces and their association with inflammatory diseases. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2002, 40, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kováč, J.; Vítězová, M.; Kushkevych, I. Metabolic activity of sulfate-reducing bacteria from rodents with colitis. Open Med. 2018, 13, 344–349. [Google Scholar]
- Kushkevych, I.; Vítězová, M.; Fedrová, P.; Vochyanová, Z.; Paráková, L.; Hošek, J. Kinetic properties of growth of intestinal sulphate-reducing bacteria isolated from healthy mice and mice with ulcerative colitis. Acta Vet. Brno 2017, 86, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushkevych, I.; Fafula, R.; Parak, T.; Bartoš, M. Activity of Na+/K+-activated Mg2+-dependent ATP hydrolase in the cell-free extracts of the sulfate-reducing bacteria Desulfovibrio piger Vib-7 and Desulfomicrobium sp. Rod-9. Acta Vet. Brno 2015, 84, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushkevych, I.V. Activity and kinetic properties of phosphotransacetylase from intestinal sulfate-reducing bacteria. Acta Biochem. Pol. 2015, 62, 1037–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushkevych, I.V. Kinetic Properties of Pyruvate Ferredoxin Oxidoreductase of Intestinal Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria Desulfovibrio piger Vib-7 and Desulfomicrobium sp. Rod-9. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2015, 64, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Loubinoux, J.; Mory, F.; Pereira, I.A.; Le Faou, A.E. Bacteremia caused by a strain of Desulfovibrio related to the provisionally named Desulfovibrio fairfieldensis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 931–934. [Google Scholar]
- Pitcher, M.C.; Cummings, J.H. Hydrogen sulphide: A bacterial toxin in ulcerative colitis? Gut 1996, 39, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florin, T.H.; Neale, G.; Goretski, S. Sulfate in food and beverages. J. Food Compos. Anal. 1993, 6, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushkevych, I.; Dordević, D.; Vítězová, M.; Kollár, P. Cross-correlation analysis of the Desulfovibrio growth parameters of intestinal species isolated from people with colitis. Biologia 2018, 73, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushkevych, I.; Dordević, D.; Vítězová, M. Analysis of pH dose-dependent growth of sulfate-reducing bacteria. Open Med. 2019, 14, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushkevych, I.; Dordević, D.; Kollar, P. Analysis of physiological parameters of Desulfovibrio strains from individuals with colitis. Open Life Sci. 2018, 13, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushkevych, I.; Vítězová, M.; Kos, J.; Kollár, P.; Jampilek, J. Effect of selected 8-hydroxyquinoline-2-carboxanilides on viability and sulfate metabolism of Desulfovibrio piger. J. Appl. Biomed. 2018, 16, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushkevych, I.; Dordević, D.; Vítězová, M. Toxicity of hydrogen sulfide toward sulfate-reducing bacteria Desulfovibrio piger Vib-7. Arch. Microbiol. 2019, 201, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushkevych, I.; Kollar, P.; Suchy, P.; Parak, T.; Pauk, K.; Imramovsky, A. Activity of selected salicylamides against intestinal sulfate-reducing bacteria. Neuroendocrinol. Lett. 2015, 36, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kushkevych, I.; Kollar, P.; Ferreira, A.L.; Palma, D.; Duarte, A.; Lopes, M.M.; Bartos, M.; Pauk, K.; Imramovsky, A.; Jampilek, J. Antimicrobial effect of salicylamide derivatives against intestinal sulfate-reducing bacteria. J. Appl. Biomed. 2016, 14, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushkevych, I.; Kos, J.; Kollar, P.; Kralova, K.; Jampilek, J. Activity of ring-substituted 8-hydroxyquinoline- 2-carboxanilides against intestinal sulfate-reducing bacteria Desulfovibrio piger. Med. Chem. Res. 2018, 27, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loubinoux, J.; Valente, F.M.A.; Pereira, I.A.C. Reclassification of the only species of the genus Desulfomonas, Desulfomonas pigra, as Desulfovibrio piger comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 1305–1308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Postgate, J.R. The Sulfate Reducing Bacteria; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Rowan, F.E.; Docherty, N.G.; Coffey, J.C.; O’Connell, P.R. Sulphate-reducing bacteria and hydrogen sulphide in the aetiology of ulcerative colitis. Br. J. Surg. 2009, 96, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushkevych, I.; Vítězová, M.; Vítěz, T.; Bartoš, M. Production of biogas: Relationship between methanogenic and sulfate-reducing microorganisms. Open Life Sci. 2017, 12, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushkevych, I.; Vítězová, M.; Vítěz, T.; Kovac, J.; Kaucká, P.; Jesionek, W.; Bartoš, M.; Barton, L. A new combination of substrates: Biogas production and diversity of the methanogenic microorganisms. Open Life Sci. 2018, 13, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushkevych, I.; Kováč, J.; Vítězová, M.; Vítěz, T.; Bartoš, M. The diversity of sulfate-reducing bacteria in the seven bioreactors. Arch. Microbiol. 2018, 200, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Černý, M.; Vítězová, M.; Vítěz, T.; Bartoš, M.; Kushkevych, I. Variation in the Distribution of Hydrogen Producers from the Clostridiales Order in Biogas Reactors Depending on Different Input Substrates. Energies 2018, 11, 3270. [Google Scholar]
- Kováč, J.; Kushkevych, I. New modification of cultivation medium for isolation and growth of intestinal sulfate-reducing bacteria. In Proceedings of the International PhD Students Conference MendelNet, Brno, Czechia, 6–7 November 2019; pp. 702–707. [Google Scholar]
- Kolmert, A.; Wikstrom, P.; Hallberg, K.B. A fast and simple turbidimetric method for the determination of sulfate in sulfate-reducing bacterial cultures. J. Microbiol. Methods 2000, 41, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cline, J.D. Spectrophotometric determination of hydrogen sulfide in natural water. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1969, 14, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.S.; Pluth, M.D. Chemiluminescent detection of enzymatically produced hydrogen sulfide: Substrate hydrogen bonding influences selectivity for H2S over biological thiols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16697–16704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, N.T.J. Statistical Methods in Biology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Attene-Ramos, M.S.; Wagner, E.D.; Plewa, M.J.; Gaskins, H.R. Evidence that hydrogen sulfide is a genotoxic agent. Mol. Cancer Res. 2006, 4, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, R.O.; Bus, J.S.; Popp, J.A.; Boreiko, C.J.; Andjelkovich, D.A.; Leber, P. A critical review of the literature on hydrogen sulfide toxicity. CRC Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1984, 13, 25–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blachier, F.; Davila, A.M.; Mimoun, S. Luminal sulfide and large intestine mucosa: Friend or foe? Amino Acids 2010, 39, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieshaber, M.K.; Völkel, S. Animal adaptations for tolerance and exploitation of poisonous sulfide. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1998, 60, 33–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
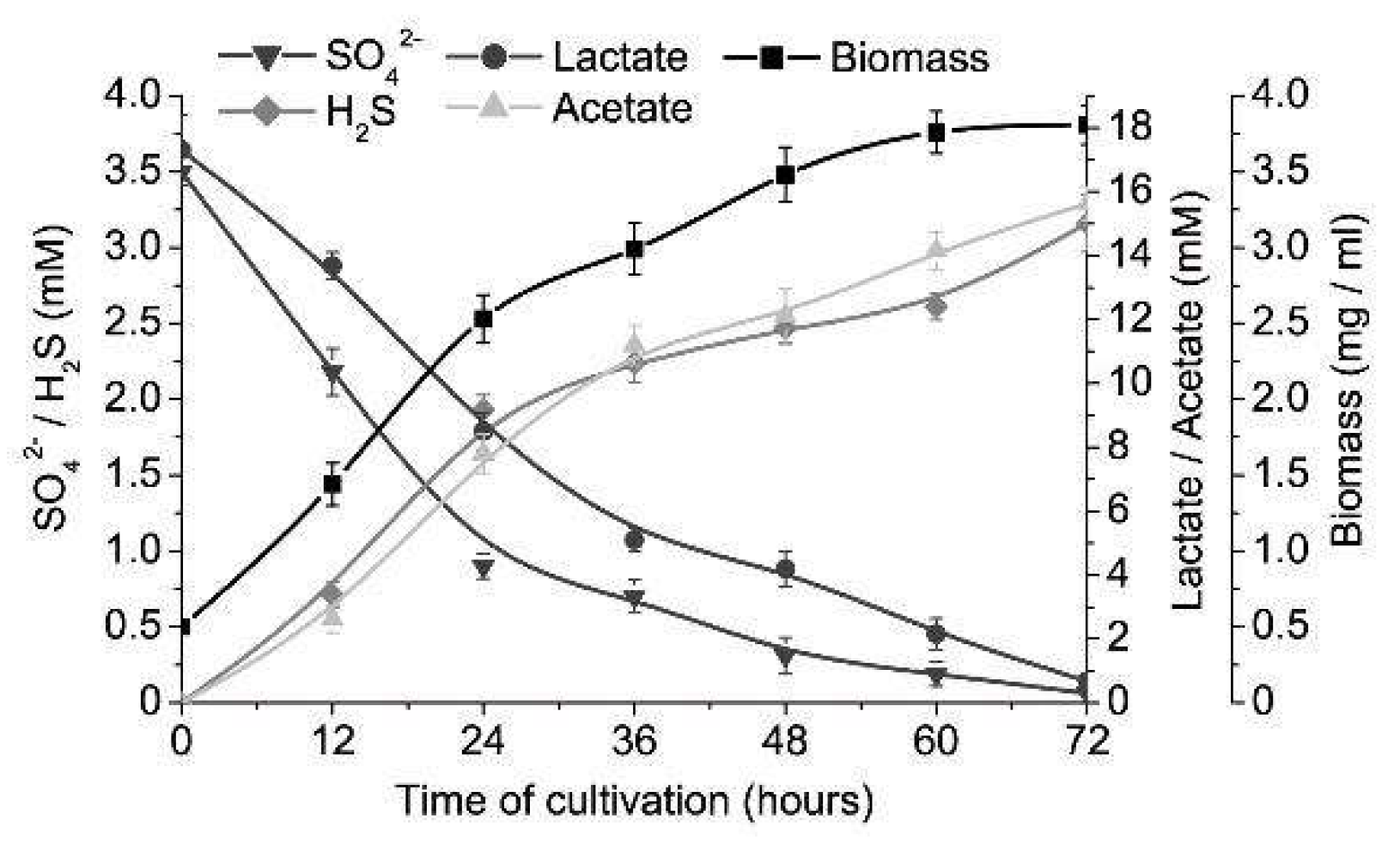
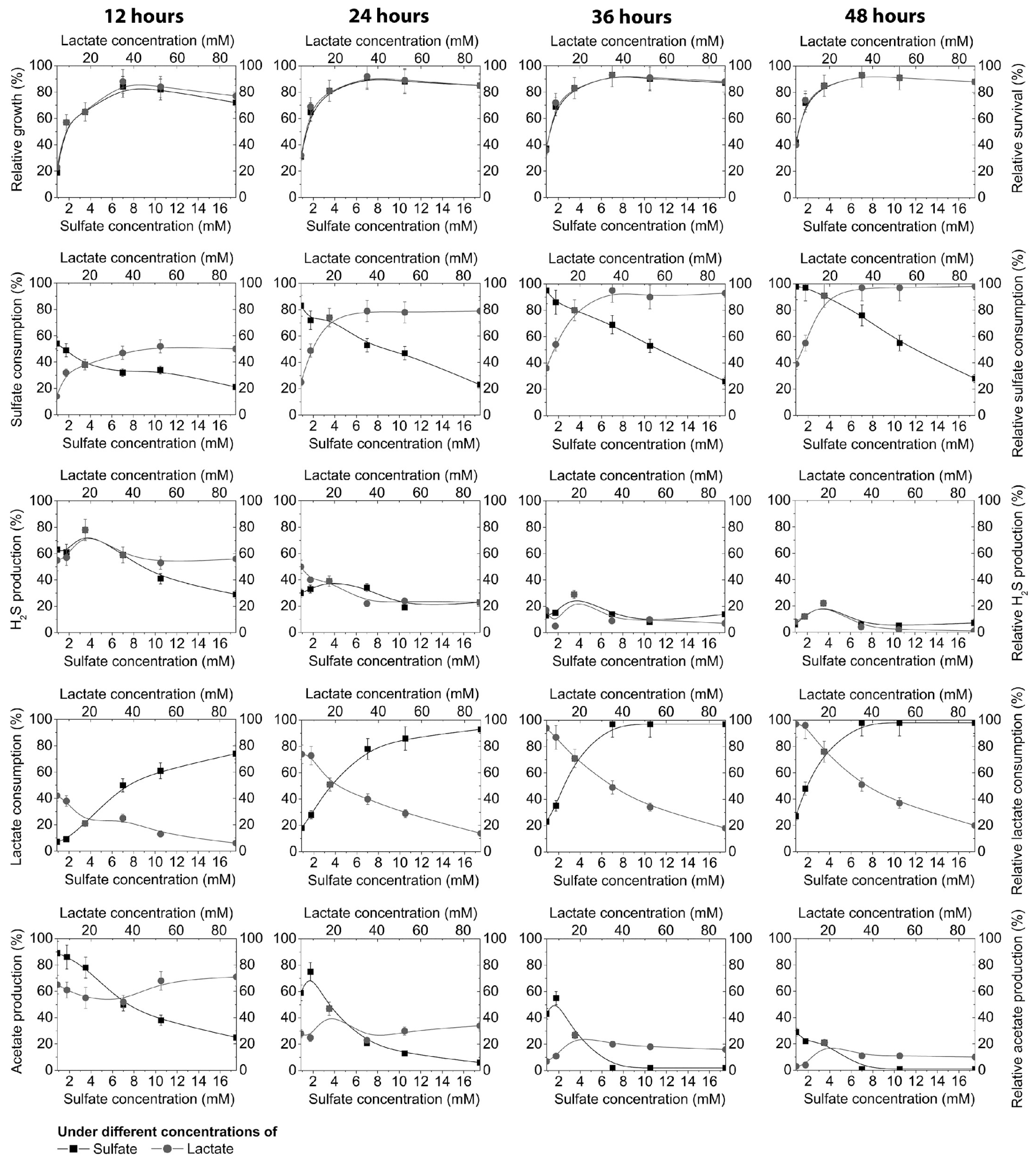

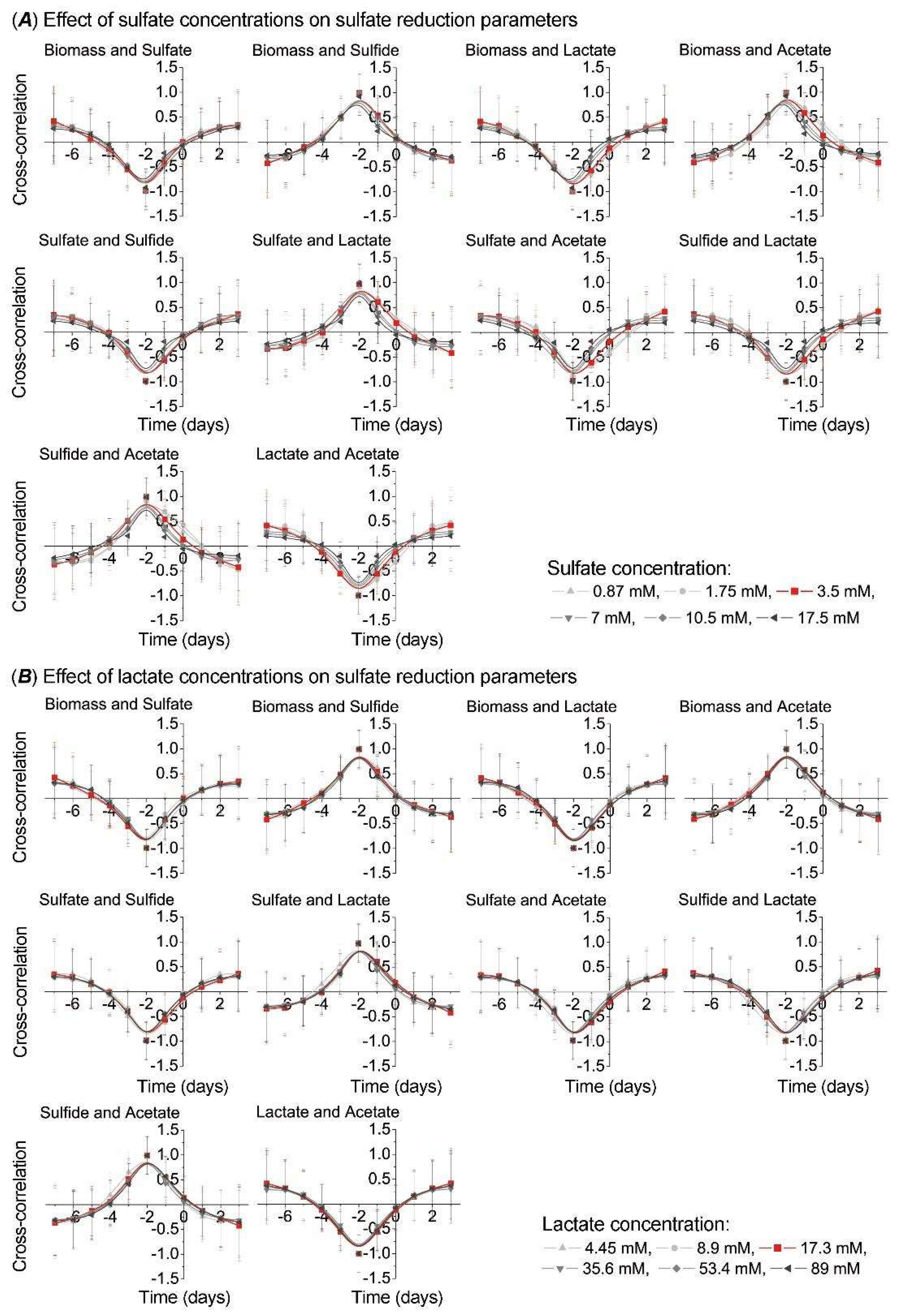
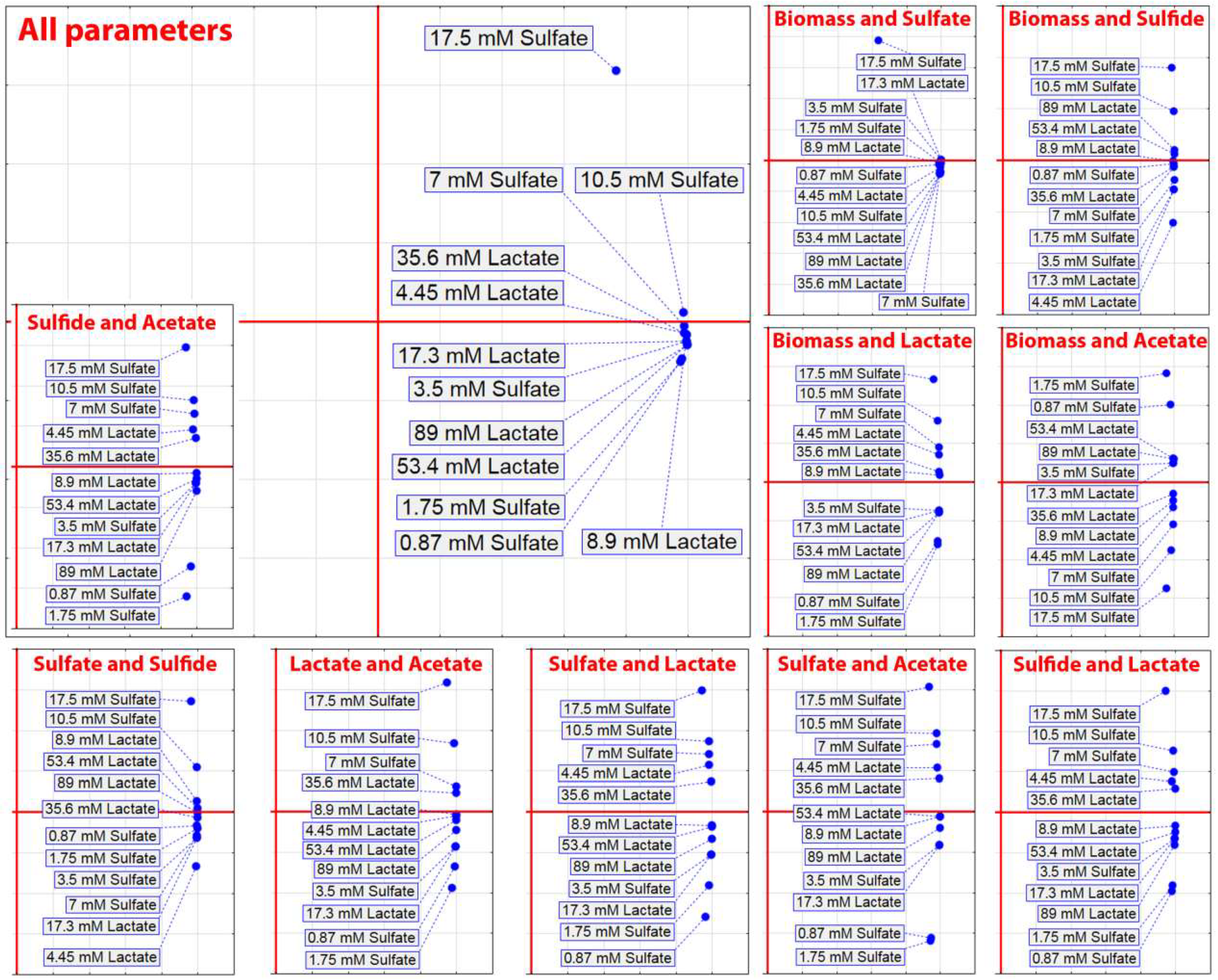
| Electron Acceptor (Sulfate) | Electron Donor (Lactate) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfate (mM) | Lag-Phase (h) | Generation Time Td (h) | µmax (h−1) | Lactate (mM) | Lag-Phase (h) | Generation Time Td (h) | µmax (h−1) |
| 0.87 | 38.2 ± 3.5 | 16.5 ± 1.5 | 0.009 ± 0.0001 | 4.45 | 36.6 ± 3.7 | 14.5 ± 1.35 | 0.009 ± 0.008 |
| 1.75 | 5.9 ± 0.46 | 4.3 ± 0.44 | 0.02 ± 0.001 | 8.9 | 7.1 ± 0.66 | 3.6 ± 0.33 | 0.03 ± 0.001 |
| 3.5 | 6.4 ± 0.62 | 1.8 ± 0.15 | 0.05 ± 0.004 | 17.3 | 6.4 ± 0.60 | 1.8 ± 0.12 | 0.05 ± 0.004 |
| 7.0 | 7.4 ± 0.73 | 1.1 ± 0.10 | 0.08 ± 0.007 | 35.6 | 4.9 ± 0.43 | 1.1 ± 0.10 | 0.08 ± 0.007 |
| 10.5 | 3.3 ± 0.31 | 1.3 ± 0.12 | 0.06 ± 0.005 | 53.4 | 3.1 ± 0.29 | 1.3 ± 0.11 | 0.07 ± 0.005 |
| 17.5 | 5.5 ± 0.59 | 1.6 ± 0.14 | 0.05 ± 0.005 | 89.0 | 5.4 ± 0.51 | 1.5 ± 0.13 | 0.06 ± 0.004 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kushkevych, I.; Dordević, D.; Kollar, P.; Vítězová, M.; Drago, L. Hydrogen Sulfide as a Toxic Product in the Small–Large Intestine Axis and its Role in IBD Development. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8071054
Kushkevych I, Dordević D, Kollar P, Vítězová M, Drago L. Hydrogen Sulfide as a Toxic Product in the Small–Large Intestine Axis and its Role in IBD Development. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(7):1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8071054
Chicago/Turabian StyleKushkevych, Ivan, Dani Dordević, Peter Kollar, Monika Vítězová, and Lorenzo Drago. 2019. "Hydrogen Sulfide as a Toxic Product in the Small–Large Intestine Axis and its Role in IBD Development" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 7: 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8071054
APA StyleKushkevych, I., Dordević, D., Kollar, P., Vítězová, M., & Drago, L. (2019). Hydrogen Sulfide as a Toxic Product in the Small–Large Intestine Axis and its Role in IBD Development. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(7), 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8071054








