Cranio-Facial Characteristics in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Measurements
3. Statistical Methods
4. Results
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodier, P.M.; Bryson, S.E.; Welch, J.P. Minor Malformations and Physical Measurements in Autism: Data from Nova Scotia. Teratology 1997, 55, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldrop, M.F.; Pederson, F.A.; Bell, R.Q. Minor Physical Anomalies and Behavior in Preschool Children. Child Dev. 1968, 39, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgen, H.M.; Hop, J.W.; Hox, J.J.; Beemer, F.A.; Van Engeland, H. Minor Physical Anomalies in Autism: A Meta-Analysis. Mol. Psychiatry 2010, 15, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tripi, G.; Roux, S.; Canziani, T.; Bonnet Brilhault, F.; Barthélémy, C.; Canziani, F. Minor Physical Anomalies in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Early Hum. Dev. 2008, 84, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.; McAlonan, G.M.; Fung, Y.Y.; Fung, G.; Yu, K.K.; Tai, K.S.; Sham, P.C.; Chua, S.E. MRI Study of Minor Physical Anomaly in Childhood Autism Implicates Aberrant Neurodevelopment in Infancy. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aldridge, K.; George, I.D.; Cole, K.K.; Austin, J.R.; Takahashi, T.N.; Duan, Y.; Miles, J.H. Facial Phenotypes in Subgroups of Prepubertal Boys with Autism Spectrum Disorders are Correlated with Clinical Phenotypes. Mol. Autism 2011, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obafemi-Ajayi, T.; Miles, J.H.; Takahashi, T.N.; Qi, W.; Aldridge, K.; Zhang, M.; Xin, S.Q.; He, Y.; Duan, Y. Facial Structure Analysis Separates Autism Spectrum Disorders into Meaningful Clinical Subgroups. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2015, 45, 1302–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutrus, M.; Maybery, M.T.; Alvares, G.A.; Tan, D.W.; Varcin, K.J. Whitehouse AJO Investigating Facial Phenotype in Autism Spectrum Conditions: The Importance of a Hypothesis Driven Approach. Autism Res. 2017, 10, 1910–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feingold, M.; Bossert, W.H. Normal Values for Selected Physical Parameters: An Aid to Syndrome Delineation. Birth Defects Orig. Artic. Ser. 1974, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Farkas, L.G.; Munro, I.R.; Kolar, J.C. Anthropometric Facial Proportions in Medicine; Charles Thomas Publisher Ltd.: Springfield, IL, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Lord, C.; Rutter, M.; Le Couteur, A. Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised: A Revised Version of a Diagnostic Interview for Caregivers of Individuals with Possible Pervasive Developmental Disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 1994, 24, 659–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schopler, E.; Reichler, R.J.; Renner, B.R. The Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS); Western Psychological Services: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler, D. Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children, 3rd ed.; The Psychological Corporation: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, G.H.; Froster, U.G.; Allanson, J.E. Handbook of Normal Physical Measurements; Oxford Medical Publications; Oxford University Press: Evans Road Cary, NC, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Militerni, R.; Bravaccio, C.; Falco, C.; Fico, C. Palermo MT Repetitive Behaviors in Autistic Disorder. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2002, 11, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlonan, G.M.; Li, Q.; Cheung, C. The Timing and Specificity of Prenatal Immune Risk Factors for Autism Modeled in the Mouse and Relevance to Schizophrenia. Neurosignals 2010, 18, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, J.H.; Hillman, R.E. Value of a Clinical Morphology Examination in Autism. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2000, 91, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.L.; Songster, G.S.; Parvin, C.A. Cephalic Index: A Gestational Age-Dependant Biometric Parameter. Obstet. Gynecol. 1989, 74, 600–603. [Google Scholar]
- Rajlakshmi, C.H.; Shyamo, S.M.; Bidhumukhi, T.H.; Chandramani, S.L. Cephalic Index of Foetuses of Manipuri Population—A Baseline Study. J. Anat. Soc. India 2001, 50, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnet-Brilhault, F.; Rajerison, T.A.; Paillet, C.; Guimard-Brunault, M.; Saby, A.; Ponson, L.; Tripi, G.; Malvy, J.; Roux, S. Autism is a Prenatal Disorder: Evidence from Late Gestation Brain Overgrowth. Autism Res. 2018, 11, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacco, R.; Gabriele, S.; Persico, A.M. Head Circumference and Brain Size in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 234, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miles, J.H. Autism Subgroups from a Medical Genetics Perspective. In Autism Spectrum Disorders; Amaral, D.G., Dawson, G., Geschwind, D.H., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA; pp. 705–721.
- Walker, H.A. Incidence Ofminor Physical Anomaly in Autism. J. Autism Child. Schizophr. 1977, 7, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozgen, H.; Hellemann, G.S.; Stellato, R.K.; Lahuis, B.; Van Daalen, E.; Staal, W.G.; Rozendal, M.; Hennekam, R.C.; Beemer, F.A.; van Engeland, H. Morphological Features in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Matched Case–Control Study. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2011, 41, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosconi, M.W.; Cody-Hazlett, H.; Poe, M.D.; Gerig, G.; Gimpel-Smith, R.; Piven, J. Longitudinal Study of Amygdala Volume and Joint Attention in 2- to 4-Year-Old Children with Autism. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, C.M.; Barnes, C.C.; Lord, C.; Courchesne, E. Amygdala Enlargement in Toddlers with Autism Related to Severity of Social and Communication Impairments. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odriozola, P.; Dajani, D.R.; Burrows, C.A.; Gabard-Durnam, L.J.; Goodman, E.; Baez, A.C.; Tottenham, N.; Uddin, L.Q.; Gee, D.G. Atypical Frontoamygdala Functional Connectivity in Youth with Autism. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2018, 7, 100603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardan, A.Y.; Keshavan, M.S.; Sreedhar, S.; Vemulapalli, M.; Minshew, N.J. An MRI Study of Minor Physical Anomalies in Autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2006, 36, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Angkustsiri, K.; Krakowiak, P.; Moghaddam, B.; Wardinsky, T.; Gardner, J.; Kalamkarian, N.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Hansen, R.L. Minor Physical Anomalies in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Autism 2011, 15, 746–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engels, H.; Brockschmidt, A.; Hoischen, A.; Landwehr, C.; Bosse, K.; Walldorf, C.; Toedt, G.; Radlwimmer, B.; Propping, P.; Lichter, P.; et al. DNA Microarray Analysis Identifies Candidate Regions and Genes in Unexplained Mental Retardation. Neurology 2007, 68, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
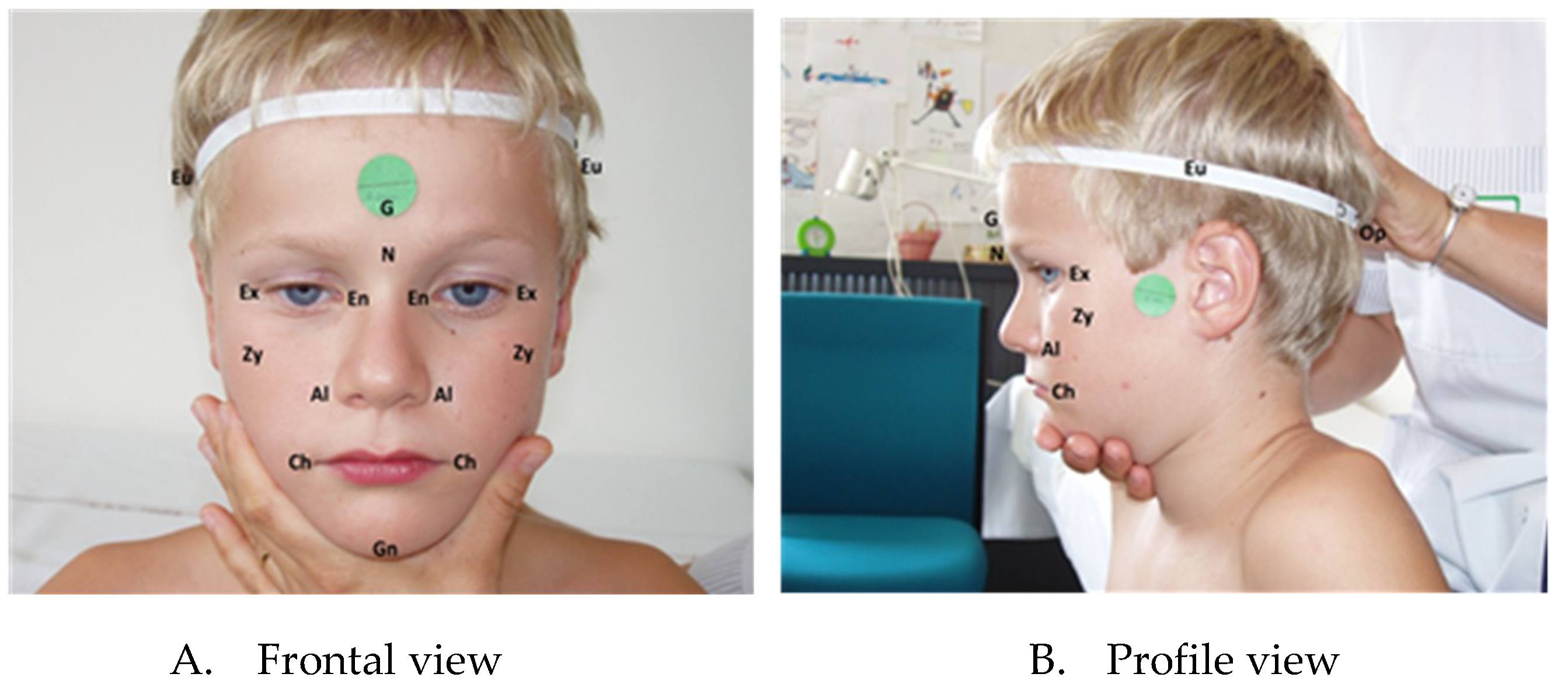
| Linear Measurements & Landmarks | Index Subnormal | Index Supernormal |
|---|---|---|
| Cephalic Index = eu-eu × 100/g-op | head narrow for its length | head wide for its length |
| Facial Index = n-ng × 100/zy-zy | face short for its width | face long for its width |
| Interchantal Index = en-en × 100/ex-ex | orbital hypotelorism | orbital hypertelorism |
| Nasal Index = al-al × 100/n-sn | nose narrow for its height | nose wide for its height |
| Facial-Mouth Width Index = ch-ch × 100/zy-zy | mouth narrow for face width | mouth wide for face width |
| Demographic and Clinical Variables | Anthropometric Variables | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | z-score | Counts within Normal Range (%) | ||
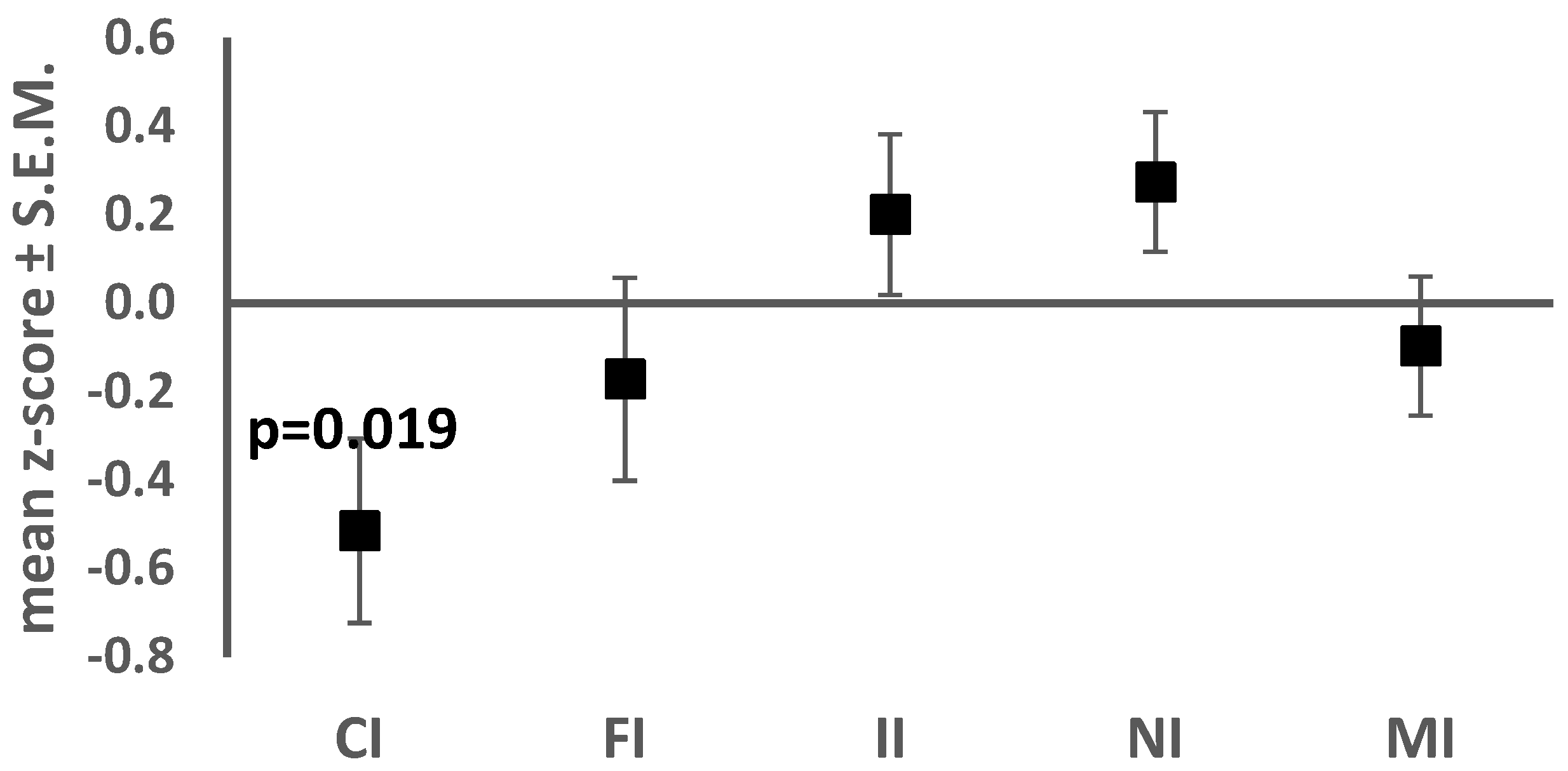
| Age in months | 91.5 ± 26.7 | Cephalic Index | 74.2 ± 5.1 | −0.51 ± 1.20 | 25 (75.8) |
| CARS | 30.4 ± 5.3 | Facial Index | 83.9 ± 6.6 | −0.17 ± 1.32 | 23 (69.7) |
| Global IQ | 59.9 ± 24.2 | Interchantal index | 38.7 ± 2.2 | 0.20 ± 1.04 | 30 (90.9) |
| Verbal IQ | 50 ± 24.4 | Nasal Index | 72.5 ± 5.9 | 0.27 ± 0.91 | 30 (90.9) |
| Non-verbal IQ | 70 ± 26.8 | Mouth-face Index | 36.7 ± 2.1 | −0.09 ± 0.90 | 31 (93.9) |
| Age | CARS | Global IQ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p Value | r | p Value | R | p Value | |
| Cephalic Index z-score | 0.330 | 0.061 | 0.316 | 0.073 | −0.232 | 0.195 |
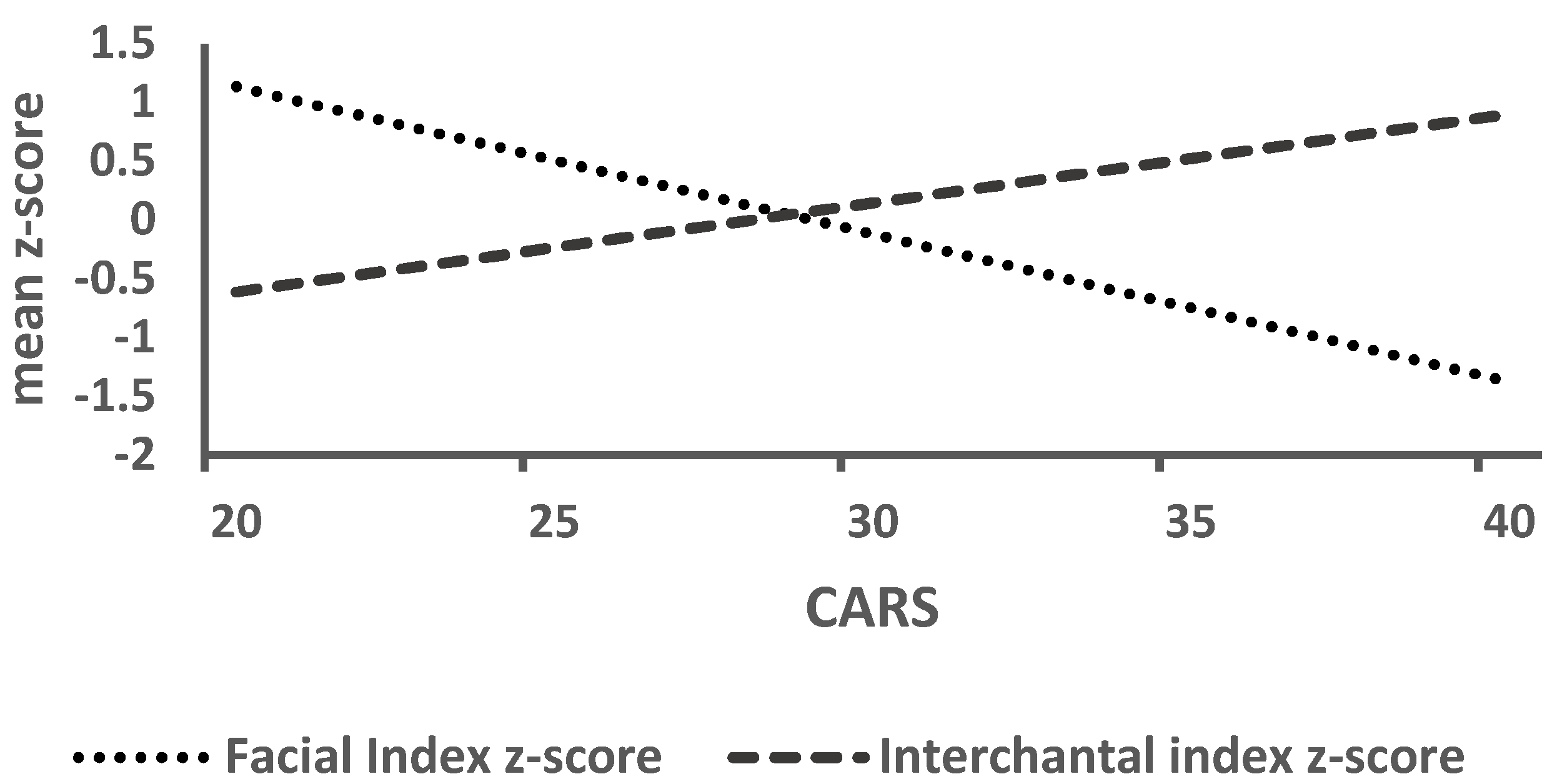
| Facial Index z-score | −0.062 | 0.731 | −0.506 | 0.003 | 0.349 | 0.047 |
| Interchantal Index z-score | 0.143 | 0.427 | 0.385 | 0.028 | −0.122 | 0.499 |
| Nasal Index z-score | −0.045 | 0.806 | −0.275 | 0.122 | 0.138 | 0.445 |
| Mouth-face Index z-score | 0.001 | 0.997 | −0.029 | 0.872 | 0.075 | 0.680 |
| Variable | Coef (SE) | t Value | p Value | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Facial Index z-score | CARS Global IQ | −0.125 (0.054) 0.000 (0.012) | −2.33 0.03 | 0.027 0.977 | (−0.234, −0.015) (−0.024, 0.024) |
| Interchantal Index z-score | CARS Global IQ | 0.111 (0.044) 0.011 (0.010) | 2.51 1.17 | 0.018 0.250 | (0.021, 0.566) (−0.008, 0.031) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tripi, G.; Roux, S.; Matranga, D.; Maniscalco, L.; Glorioso, P.; Bonnet-Brilhault, F.; Roccella, M. Cranio-Facial Characteristics in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD). J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8050641
Tripi G, Roux S, Matranga D, Maniscalco L, Glorioso P, Bonnet-Brilhault F, Roccella M. Cranio-Facial Characteristics in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD). Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(5):641. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8050641
Chicago/Turabian StyleTripi, Gabriele, Sylvie Roux, Domenica Matranga, Laura Maniscalco, Pasqualino Glorioso, Frédérique Bonnet-Brilhault, and Michele Roccella. 2019. "Cranio-Facial Characteristics in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD)" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 5: 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8050641
APA StyleTripi, G., Roux, S., Matranga, D., Maniscalco, L., Glorioso, P., Bonnet-Brilhault, F., & Roccella, M. (2019). Cranio-Facial Characteristics in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD). Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(5), 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8050641







