Complex Microbiome in Brain Abscess Revealed by Whole-Genome Culture-Independent and Culture-Based Sequencing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
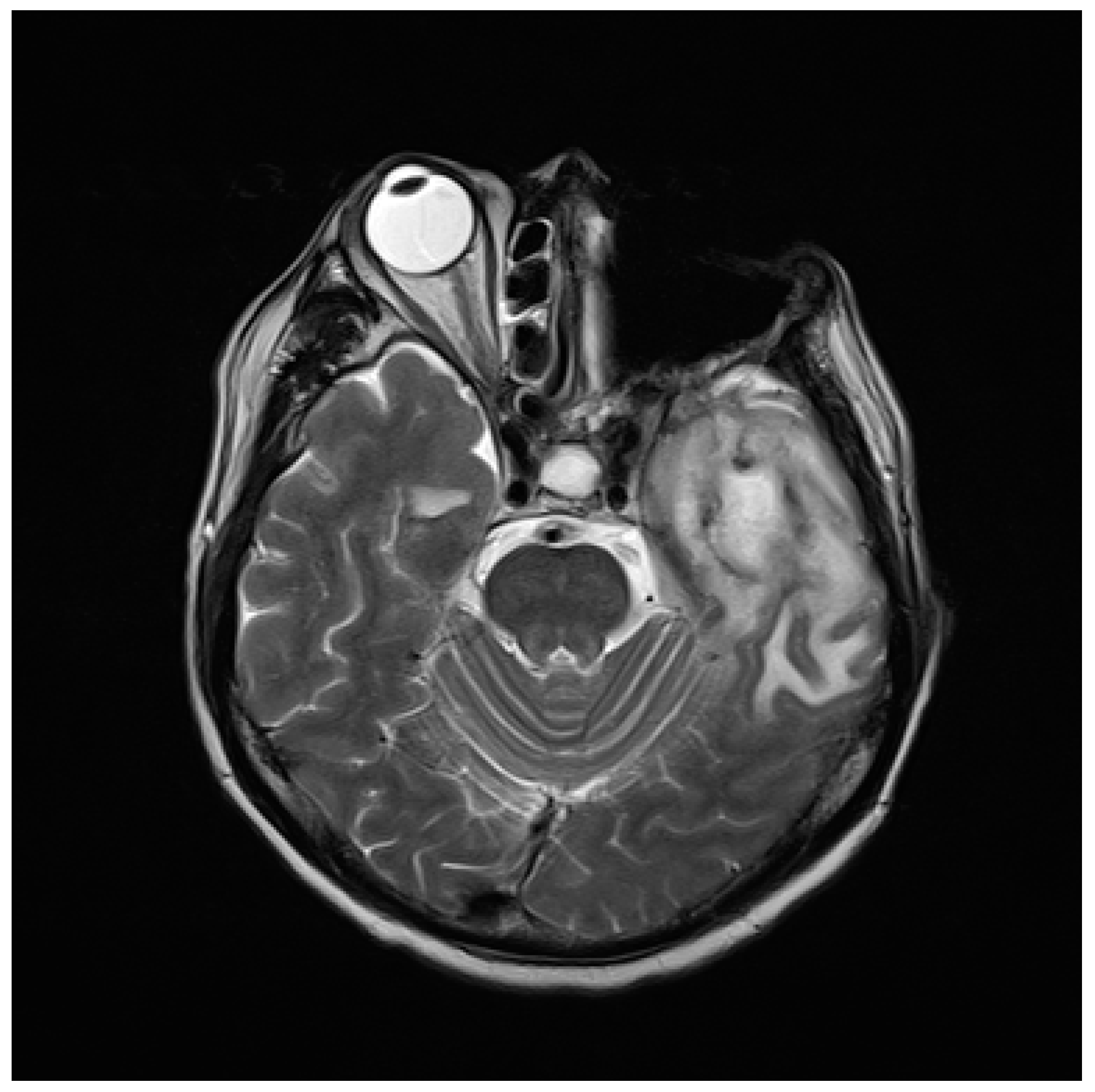
2.1. The Case
2.2. Conventional Bacterial Strain Identification and Susceptibility Test
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. Illumina Library Preparation and Sequencing of Isolates from Brain Abscess
2.5. Nanopore Library Preparation and Sequencing of Isolates from Brain Abscess
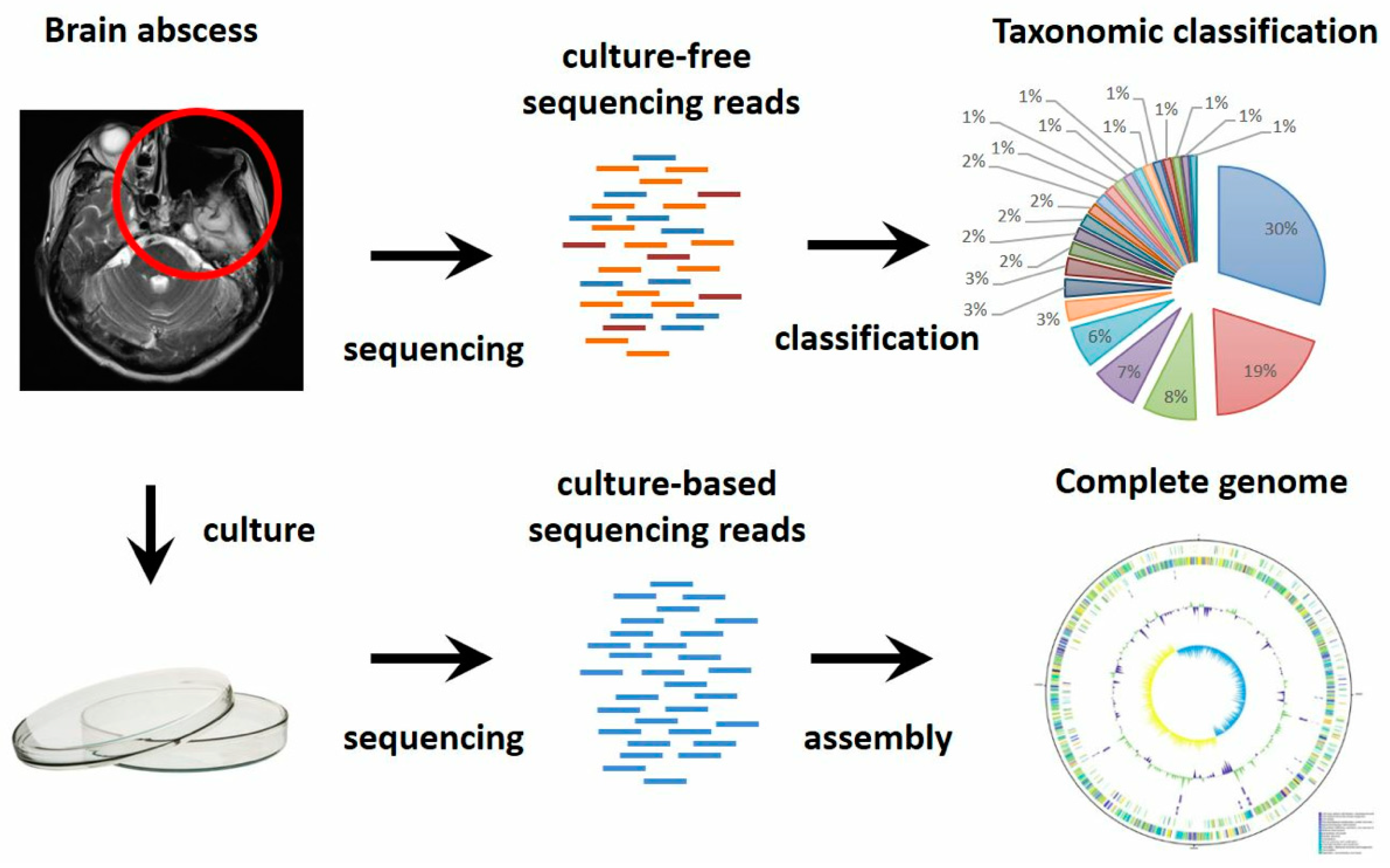
2.6. Metagenomic Sequencing
2.7. Genome Assembly and Gene Annotation
2.8. Taxonomic Classification
2.9. Identification of Antimicrobial-Resistant Genes and Virulence Factors
3. Results
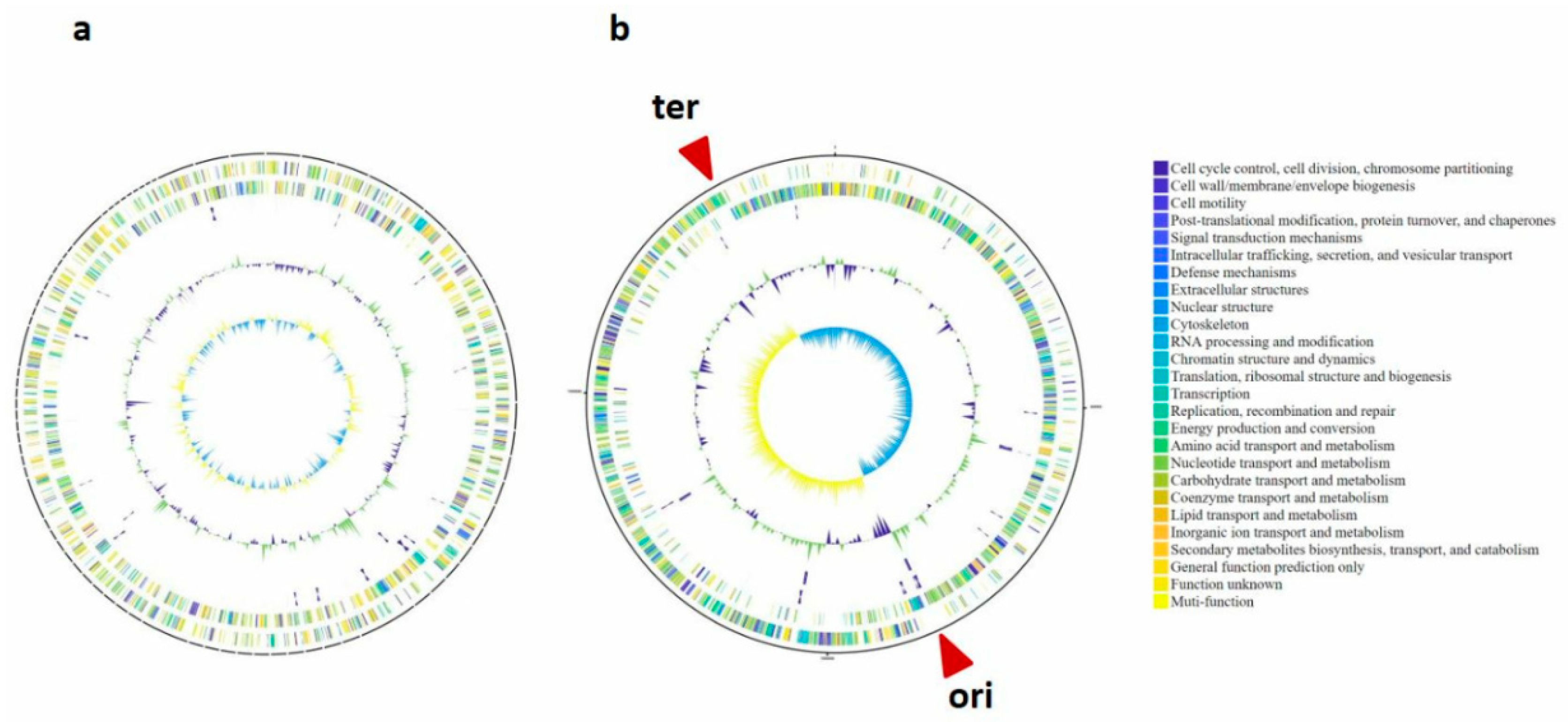
3.1. Novel Bacterial Genome Revealed by Culture-Based Sequencing
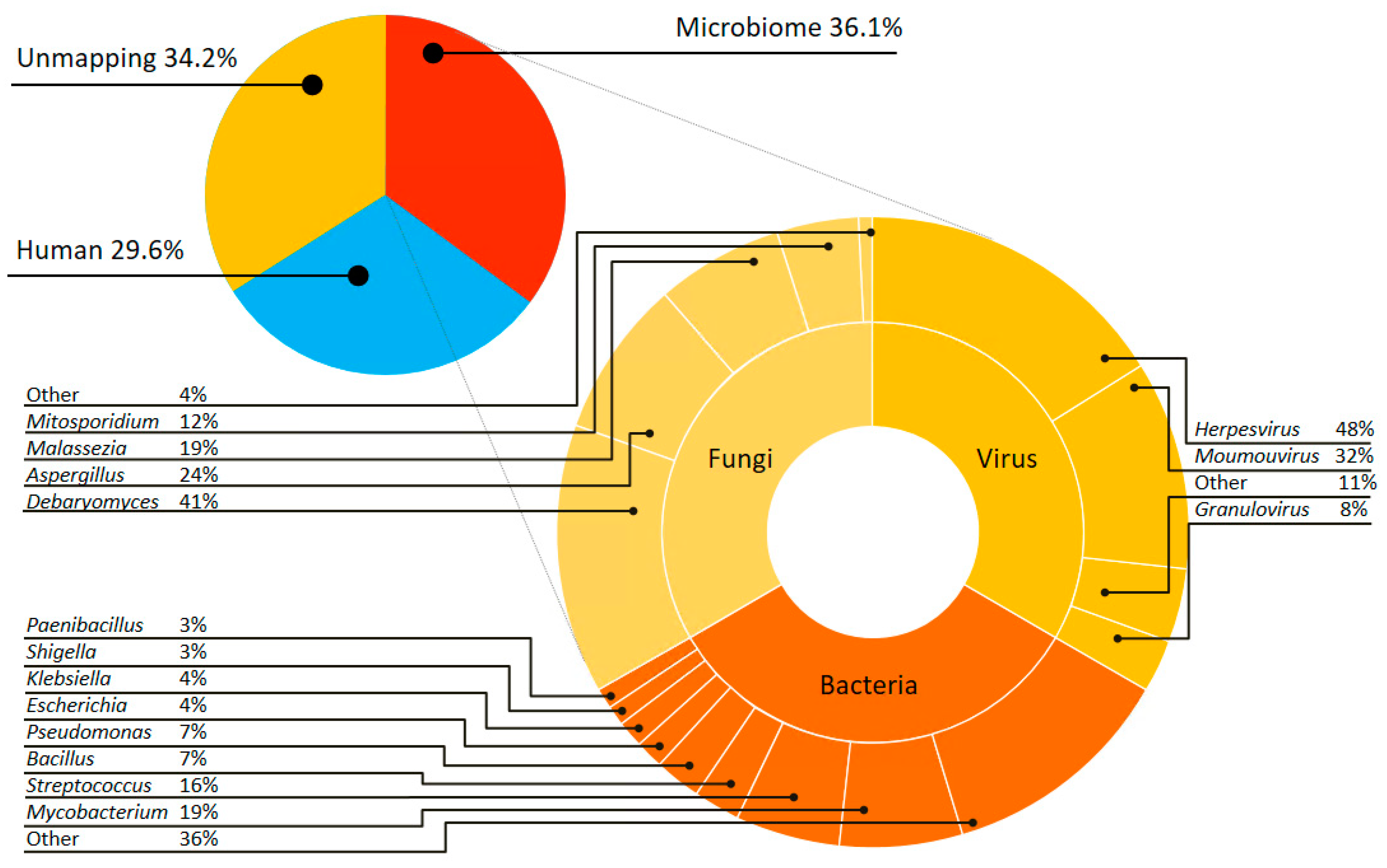
3.2. Complex Communities of Bacteria, Fungi and Virus Revealed by Culture-Independent Metagenomic Sequencing
3.3. Antibiotic Resistance Genes Revealed by Culture-Based and Culture-Independent Metagenomic Sequencing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brouwer, M.C.; Tunkel, A.R.; McKhann, G.M., 2nd; van de Beek, D. Brain abscess. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Louvois, J.; Gortavai, P.; Hurley, R. Bacteriology of abscesses of the central nervous system: A multicentre prospective study. Br. Med. J. 1977, 2, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, K.N.; Mishra, A.M.; Gupta, D.; Husain, N.; Husain, M.; Gupta, R.K. Analysis of microbial etiology and mortality in patients with brain abscess. J. Infect. 2006, 53, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, J.H.; Tseng, M.Y. Brain abscess in 142 patients: Factors influencing outcome and mortality. Surg. Neurol. 2006, 65, 557–562, discussion 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, M.; Humphreys, H.; Smyth, E.; Phillips, J.; Cunney, R.; McNamara, E.; O’Brien, D.; McArdle, O. A twelve-year review of central nervous system bacterial abscesses; presentation and aetiology. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2003, 9, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Masalma, M.; Lonjon, M.; Richet, H.; Dufour, H.; Roche, P.H.; Drancourt, M.; Raoult, D.; Fournier, P.E. Metagenomic analysis of brain abscesses identifies specific bacterial associations. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.C.; Teng, L.J.; Hsueh, P.R. Direct detection of bacterial pathogens in brain abscesses by polymerase chain reaction amplification and sequencing of partial 16s ribosomal deoxyribonucleic acid fragments. Neurosurgery 2004, 55, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Masalma, M.; Armougom, F.; Scheld, W.M.; Dufour, H.; Roche, P.H.; Drancourt, M.; Raoult, D. The expansion of the microbiological spectrum of brain abscesses with use of multiple 16s ribosomal DNA sequencing. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.K.; Dufour, H.; Roche, P.H.; Lonjon, M.; Raoult, D.; Fournier, P.E. Molecular revolution in the diagnosis of microbial brain abscesses. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 2083–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Huang, Y.T.; Wong, C.H.; Chao, W.C.; Wu, Z.Y.; Wei, C.L.; Liu, P.Y. Culture-independent analysis of liver abscess using nanopore sequencing. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.Y.; Feng, W.Y.; Guo, X.; Liu, B.; Liu, G.; Dong, J. The advantages of next-generation sequencing technology in the detection of different sources of abscess. J. Infect. 2019, 78, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Hu, H.; Kang, Y.; Chen, W.; Fang, W.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, A.; Zhou, S.; Cheng, C.; et al. Identification of pathogens in culture-negative infective endocarditis cases by metagenomic analysis. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2018, 17, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koren, S.; Walenz, B.P.; Berlin, K.; Miller, J.R.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Canu: Scalable and accurate long-read assembly via adaptive k-mer weighting and repeat separation. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. Spades: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaser, R.; Sovic, I.; Nagarajan, N.; Sikic, M. Fast and accurate de novo genome assembly from long uncorrected reads. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loman, N.J.; Quick, J.; Simpson, J.T. A complete bacterial genome assembled de novo using only nanopore sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 733–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, M.; Silva, N.D.; Otto, T.D.; Parkhill, J.; Keane, J.A.; Harris, S.R. Circlator: Automated circularization of genome assemblies using long sequencing reads. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, B.; Raphenya, A.R.; Alcock, B.; Waglechner, N.; Guo, P.; Tsang, K.K.; Lago, B.A.; Dave, B.M.; Pereira, S.; Sharma, A.N.; et al. Card 2017: Expansion and model-centric curation of the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D566–D573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zheng, D.; Jin, Q.; Chen, L.; Yang, J. Vfdb 2019: A comparative pathogenomic platform with an interactive web interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D687–D692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.L.; Guo, L.Y.; Wu, H.L.; Feng, W.Y.; Chen, T.M.; Liu, G. Evaluation of next-generation sequencing for the pathogenic diagnosis of children brain abscesses. J. Infect. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, M.C.; Coutinho, J.M.; van de Beek, D. Clinical characteristics and outcome of brain abscess: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology 2014, 82, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.; Clifford, D.B. Bacterial brain abscess. Neurohospitalist 2014, 4, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, R.; Pisa, D.; Marina, A.I.; Morato, E.; Rabano, A.; Rodal, I.; Carrasco, L. Evidence for fungal infection in cerebrospinal fluid and brain tissue from patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 11, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashbee, H.R. Update on the genus malassezia. Med. Mycol 2007, 45, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskar, N.; Mohammad, K.; Kaur, V. Aspergillus brain abscess. J. Ark. Med. Soc. 2013, 110, 41–42. [Google Scholar]
- Tyler, K.L. Acute viral encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakawa, K.; Tomita, M. Measures of compositional strand bias related to replication machinery and its applications. Curr. Genom. 2012, 13, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.L.; Xia, Z.K.; Zhang, F.Z.; Ye, Y.N.; Guo, F.B. Multiple factors drive replicating strand composition bias in bacterial genomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 23111–23126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherrard, L.J.; Schaible, B.; Graham, K.A.; McGrath, S.J.; McIlreavey, L.; Hatch, J.; Wolfgang, M.C.; Muhlebach, M.S.; Gilpin, D.F.; Schneiders, T.; et al. Mechanisms of reduced susceptibility and genotypic prediction of antibiotic resistance in prevotella isolated from cystic fibrosis (cf) and non-cf patients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 2690–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofmark, S.; Jernberg, C.; Jansson, J.K.; Edlund, C. Clindamycin-induced enrichment and long-term persistence of resistant bacteroides spp. And resistance genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 58, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greninger, A.L.; Naccache, S.N.; Federman, S.; Yu, G.; Mbala, P.; Bres, V.; Stryke, D.; Bouquet, J.; Somasekar, S.; Linnen, J.M.; et al. Rapid metagenomic identification of viral pathogens in clinical samples by real-time nanopore sequencing analysis. Genome Med. 2015, 7, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batovska, J.; Lynch, S.E.; Rodoni, B.C.; Sawbridge, T.I.; Cogan, N.O. Metagenomic arbovirus detection using MinION nanopore sequencing. J. Virol. Methods 2017, 249, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.E.; Sogin, M.L.; Baross, J.A. Evolutionary Strategies of Viruses, Bacteria and Archaea in Hydrothermal Vent Ecosystems Revealed through Metagenomics. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.H.; Rinke, C.; Chuvochina, M.; Chaumeil, P.A.; Woodcroft, B.J.; Evans, P.N.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. Recovery of nearly 8,000 metagenome-assembled genomes substantially expands the tree of life. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 1533–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salter, S.J.; Cox, M.J.; Turek, E.M.; Calus, S.T.; Cookson, W.O.; Moffatt, M.F.; Turner, P.; Parkhill, J.; Loman, N.J.; Walker, A.W. Reagent and laboratory contamination can critically impact sequence-based microbiome analyses. BMC Biol. 2014, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhofer, R.; Minich, J.J.; Marotz, C.; Cooper, A.; Knight, R.; Weyrich, L.S. Contamination in low microbial biomass microbiome studies: Issues and recommendations. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greninger, A.L.; Messacar, K.; Dunnebacke, T.; Naccache, S.N.; Federman, S.; Bouquet, J.; Mirsky, D.; Nomura, Y.; Yagi, S.; Glaser, C.; et al. Clinical metagenomic identification of balamuthia mandrillaris encephalitis and assembly of the draft genome: The continuing case for reference genome sequencing. Genome Med. 2015, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species | Genome Size (bp) | GC Content (%) | Genes (Pseudo Genes) | CDSs | tRNAs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prevotella sp. TCVGH | 3,061,518 | 42.6 | 2569(110) | 2409 | 43 |
| Streptococcus constellatus TCV107 | 1,954,689 | 38.11 | 2008(125) | 1809 | 59 |
| Gene | Coverage (%) | Identity (%) | Detected in Isolated Genome | Detected in Metagenomics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ErmF | 100 | 99.38 | y | |
| tetQ | 99.34 | 97.91 | y | y |
| CfxA3 | 100 | 100 | y | |
| CfxA2 | 100 | 99.9 | y |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, J.-H.; Wu, Z.-Y.; Gong, L.; Wong, C.-H.; Chao, W.-C.; Yen, C.-M.; Wang, C.-P.; Wei, C.-L.; Huang, Y.-T.; Liu, P.-Y. Complex Microbiome in Brain Abscess Revealed by Whole-Genome Culture-Independent and Culture-Based Sequencing. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8030351
Lin J-H, Wu Z-Y, Gong L, Wong C-H, Chao W-C, Yen C-M, Wang C-P, Wei C-L, Huang Y-T, Liu P-Y. Complex Microbiome in Brain Abscess Revealed by Whole-Genome Culture-Independent and Culture-Based Sequencing. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(3):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8030351
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Jyun-Hong, Zong-Yen Wu, Liang Gong, Chee-Hong Wong, Wen-Cheng Chao, Chun-Ming Yen, Ching-Ping Wang, Chia-Lin Wei, Yao-Ting Huang, and Po-Yu Liu. 2019. "Complex Microbiome in Brain Abscess Revealed by Whole-Genome Culture-Independent and Culture-Based Sequencing" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 3: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8030351
APA StyleLin, J.-H., Wu, Z.-Y., Gong, L., Wong, C.-H., Chao, W.-C., Yen, C.-M., Wang, C.-P., Wei, C.-L., Huang, Y.-T., & Liu, P.-Y. (2019). Complex Microbiome in Brain Abscess Revealed by Whole-Genome Culture-Independent and Culture-Based Sequencing. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(3), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8030351





