White Matter Changes in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease and Associated Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
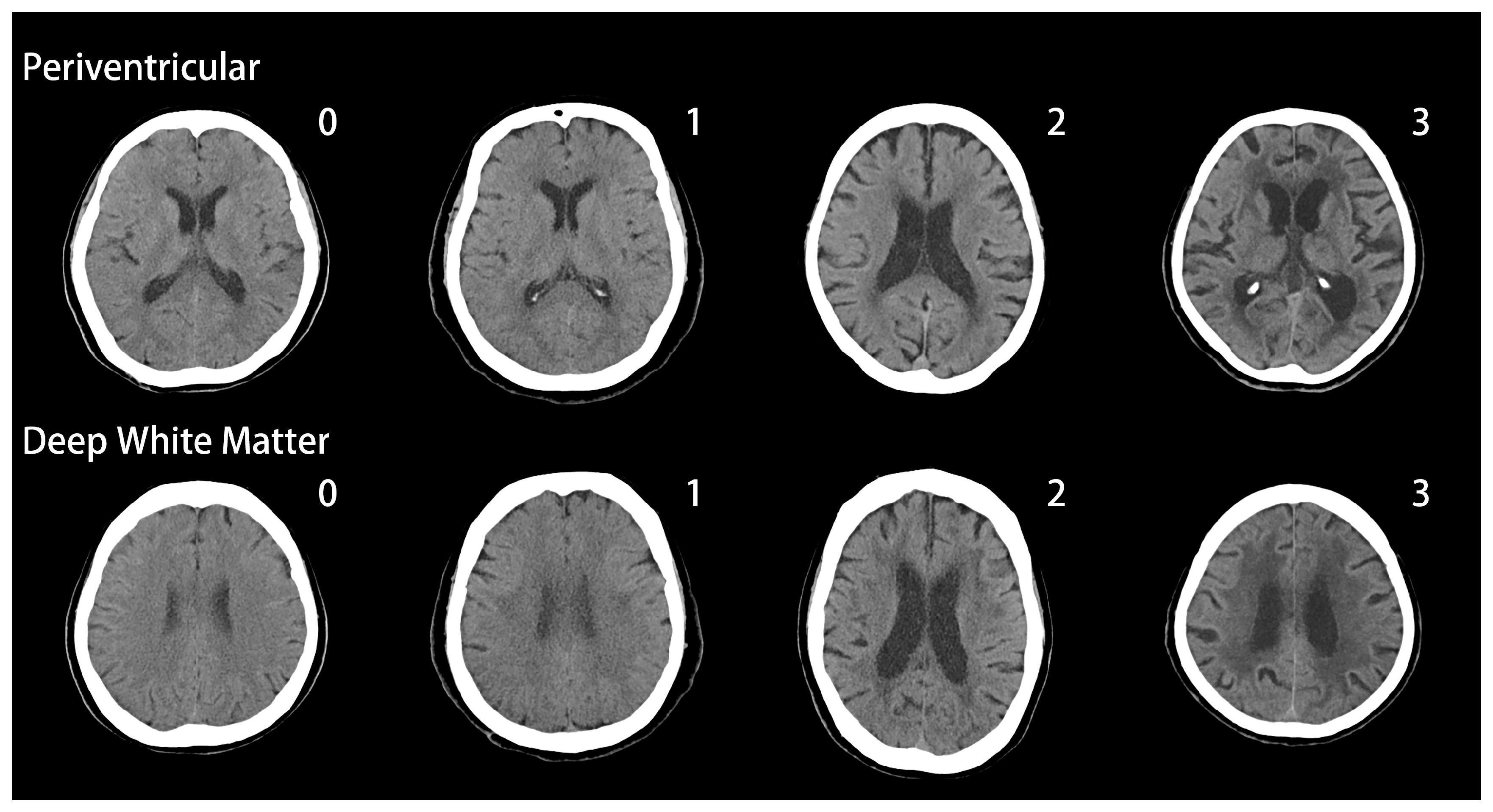
2.2. Evaluation of White Matter Changes
2.3. Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor | ACEI |
| Alzheimer’s disease | AD |
| Age related WMC | ARWMC |
| Clinical dementia rating | CDR |
| Computerized Topography | CT |
| Diabetes mellitus | DM |
| Deep WMCs | DWMCs |
| Hypertension | HTN |
| Mini Mental State Examination | MMSE |
| Magnetic resonance imaging | MRI |
| Neuropsychiatric Inventory | NPI |
| Parieto-occipital ARWMCs | P-O ARWMCs |
| Periventricular WMCs | PVWMCs |
| White matter changes | WMCs |
References
- De Leeuw, F.E.; Barkhof, F.; Scheltens, P. White matter lesions and hippocampal atrophy in alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 2004, 62, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brun, A.; Englund, E. A white matter disorder in dementia of the alzheimer type: A pathoanatomical study. Ann. Neurol. 1986, 19, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaria, R.N. Advances in molecular genetics and pathology of cerebrovascular disorders. Trends Neurosci. 2001, 24, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzali, M.; Falini, A.; Franceschi, M.; Cercignani, M.; Zuffi, M.; Scotti, G.; Comi, G.; Filippi, M. White matter damage in alzheimer’s disease assessed in vivo using diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2002, 72, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’brien, J.T.; Ames, D.; Schwietzer, I. White matter changes in depression and alzheimer’s disease: A review of magnetic resonance imaging studies. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 1996, 11, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazekas, F.; Chawluk, J.B.; Alavi, A.; Hurtig, H.I.; Zimmerman, R.A. Mr signal abnormalities at 1.5 t in alzheimer’s dementia and normal aging. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1987, 8, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.D.; Snowdon, D.A.; Wang, H.; Markesbery, W.R. White matter volumes and periventricular white matter hyperintensities in aging and dementia. Neurology 2000, 54, 838–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisler, K.; Nelson, A.R.; Montagne, A.; Zlokovic, B.V. Cerebral blood flow regulation and neurovascular dysfunction in alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fuh, J.; Mok, V.C. Vascular contribution to cognition in stroke and alzheimer’s disease. Brain Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlokovic, B.V. Neurovascular pathways to neurodegeneration in alzheimer’s disease and other disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-H.; Roe, C.M.; Morris, J.C. Relationship between late-life hypertension, blood pressure, and alzheimer’s disease. Am. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Other Demen. 2011, 26, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, J.C. The clinical dementia rating (CDR): Current version and scoring rules. Neurology 1993, 43, 2412–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, J.C.; Storandt, M.; Miller, J.P.; McKeel, D.W.; Price, J.L.; Rubin, E.H.; Berg, L. Mild cognitive impairment represents early-stage alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol. 2001, 58, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, P.; Wilson, R.; Aggarwal, N.; Tang, Y.; Bennett, D. Mild cognitive impairment risk of alzheimer disease and rate of cognitive decline. Neurology 2006, 67, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahlund, L.; Barkhof, F.; Fazekas, F.; Bronge, L.; Augustin, M.; Sjögren, M.; Wallin, A.; Ader, H.; Leys, D.; Pantoni, L. A new rating scale for age-related white matter changes applicable to mri and ct. Stroke 2001, 32, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahlund, L.-O.; Westman, E.; van Westen, D.; Wallin, A.; Shams, S.; Cavallin, L.; Larsson, E.-M. Imaging biomarkers of dementia: Recommended visual rating scales with teaching cases. Insights Imaging 2017, 8, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, P.S.; Chen, C.H.; Wu, M.N.; Lin, Y.H.; Lai, C.L.; Lin, R.T.; Yang, Y.H. Determinants of cerebral white matter changes in patients with stroke. Intern. Med. J. 2015, 45, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gootjes, L.; Teipel, S.; Zebuhr, Y.; Schwarz, R.; Leinsinger, G.; Scheltens, P.; Möller, H.-J.; Hampel, H. Regional distribution of white matter hyperintensities in vascular dementia, alzheimer’s disease and healthy aging. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2004, 18, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, C.M.; Smith, E.E.; Csapo, I.; Gurol, M.E.; Brylka, D.A.; Killiany, R.J.; Blacker, D.; Albert, M.S.; Guttmann, C.R.; Greenberg, S.M. Spatial distribution of white-matter hyperintensities in alzheimer disease, cerebral amyloid angiopathy, and healthy aging. Stroke 2008, 39, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, A.; Ishii, N.; Nishihara, Y.; Horie, A. Medullary arteries in aging and dementia. Stroke 1991, 22, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartzokis, G.; Cummings, J.L.; Sultzer, D.; Henderson, V.W.; Nuechterlein, K.H.; Mintz, J. White matter structural integrity in healthy aging adults and patients with alzheimer disease: A magnetic resonance imaging study. Arch. Neurol. 2003, 60, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheltens, P.; Barkhof, F.; Valk, J.; Algra, P.; Van Der Hoop, R.G.; Nauta, J.; Wolters, E. White matter lesions on magnetic resonance imaging in clinically diagnosed alzheimer’s disease. Brain 1992, 115, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, M.; Pichet Binette, A.; Brunecker, P.; Köbe, T.; Witte, A.V.; Flöel, A. Divergent regional patterns of cerebral hypoperfusion and gray matter atrophy in mild cognitive impairment patients. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2017, 37, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bracco, L.; Piccini, C.; Moretti, M.; Mascalchi, M.; Sforza, A.; Nacmias, B.; Cellini, E.; Bagnoli, S.; Sorbi, S. Alzheimer’s disease: Role of size and location of white matter changes in determining cognitive deficits. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2004, 20, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, W.R.; Thore, C.R. Review: Cerebral microvascular pathology in ageing and neurodegeneration. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2011, 37, 56–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Reuck, J. The human periventricular arterial blood supply and the anatomy of cerebral infarctions. Eur. Neurol. 1971, 5, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-F.; Wang, H.; Chu, Y.; Huang, Y.-C.; Su, M.-Y. Regional quantification of white matter hyperintensity in normal aging, mild cognitive impairment, and alzheimer’s disease. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2006, 22, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’sullivan, M.; Lythgoe, D.; Pereira, A.; Summers, P.; Jarosz, J.; Williams, S.; Markus, H. Patterns of cerebral blood flow reduction in patients with ischemic leukoaraiosis. Neurology 2002, 59, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snowdon, D.A.; Greiner, L.H.; Mortimer, J.A.; Riley, K.P.; Greiner, P.A.; Markesbery, W.R. Brain infarction and the clinical expression of alzheimer disease: The nun study. JAMA 1997, 277, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, F.A.; Muraskin, J.; Tosto, G.; Narkhede, A.; Wasserman, B.T.; Griffith, E.Y.; Guzman, V.A.; Meier, I.B.; Zimmerman, M.E.; Brickman, A.M. White matter hyperintensities and cerebral amyloidosis: Necessary and sufficient for clinical expression of alzheimer disease? JAMA Neurol. 2013, 70, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Heijer, T.; Launer, L.; Prins, N.; Van Dijk, E.; Vermeer, S.; Hofman, A.; Koudstaal, P.; Breteler, M. Association between blood pressure, white matter lesions, and atrophy of the medial temporal lobe. Neurology 2005, 64, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Leeuw, F.; de Groot, J.C.; Achten, E.; Oudkerk, M.; Ramos, L.; Heijboer, R.; Hofman, A.; Jolles, J.; Van Gijn, J.; Breteler, M. Prevalence of cerebral white matter lesions in elderly people: A population based magnetic resonance imaging study. The rotterdam scan study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2001, 70, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gridley, K.E.; Green, P.S.; Simpkins, J.W. A novel, synergistic interaction between 17 β-estradiol and glutathione in the protection of neurons against β-amyloid 25–35-induced toxicity in vitro. Mol. Pharmacol. 1998, 54, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantoni, L.; Garcia, J.H. Pathogenesis of leukoaraiosis a review. Stroke 1997, 28, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Immink, R.V.; van den Born, B.-J.H.; van Montfrans, G.A.; Koopmans, R.P.; Karemaker, J.M.; van Lieshout, J.J. Impaired cerebral autoregulation in patients with malignant hypertension. Circulation 2004, 110, 2241–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raz, N.; Yang, Y.Q.; Rodrigue, K.M.; Kennedy, K.M.; Lindenberger, U.; Ghisletta, P. White matter deterioration in 15 months: Latent growth curve models in healthy adults. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 429.e1-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, R. Cardiovascular factors in alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1998, 65, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, K.; Vaartjes, I.; Peters, S.A.; Koek, H.L. The influence of vascular risk factors on cognitive decline in patients with alzheimer’s disease. Maturitas 2014, 79, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| N = 501 | |
|---|---|
| Age, year, mean (± SD) | 77.9 (± 7.7) |
| Gender, female, n (%) | 347 (69.3) |
| Hypertension, yes, n (%) | 249 (49.7) |
| Diabetes mellitus, yes, n (%) | 120 (24.0) |
| Education, year, mean (± SD) | 6.6 (± 5.2) |
| MMSE *, mean (± SD) | 16.0 (± 6.2) |
| CDR ** | |
| CDR 0.5, n (%) | 128 (24.5) |
| CDR 1, n (%) | 283 (56.5) |
| CDR 2, n (%) | 90 (18.0) |
| AD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fazekas Scale | Very Mild Dementia CDR 0.5 | Mild Dementia CDR 1 | Moderate Dementia CDR 2 | |
| Periventricular white matter changes | 0 | 35 (27.3%) | 54 (19.1%) | 14 (15.6%) |
| 1 | 44 (34.4%) | 94 (33.2%) | 18 (20.0%) | |
| 2 | 22 (17.2%) | 69 (24.4%) | 23 (25.6%) | |
| 3 | 27 (21.1%) | 66 (23.3%) | 35 (38.9%) | |
| Deep white matter changes | 0 | 75 (58.6%) | 141 (49.8%) | 41 (45.6%) |
| 1 | 19 (14.8%) | 62 (21.9%) | 15 (16.7%) | |
| 2 | 18 (14.1%) | 24 (8.5%) | 6 (6.7%) | |
| 3 | 16 (12.5%) | 56 (19.8%) | 28 (31.1%) | |
| AD N = 501 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Patients | Very Mild Dementia CDR 0.5 | Mild Dementia CDR 1 | Moderate Dementia CDR 2 | p Value | |
| Fazekas scale (Periventricular) | 1.5 ± 1.1 | 1.3 ± 1.1 | 1.5 ± 1.1 | 1.9 ± 1.1 | 0.001 * |
| Fazekas scale (Deep white matter) | 1.0 ± 1.2 | 0.8 ± 1.1 | 1.0 ± 1.2 | 1.2 ± 1.3 | 0.067 |
| ARWMC, total score | 6.2 ± 5.8 | 5.1 ± 5.7 | 6.1 ± 5.6 | 8.2 ± 5.9 | 0.000 * |
| Frontal, score | 2.6 ± 2.2 | 2.2 ± 2.2 | 2.6 ± 2.1 | 3.5 ± 2.2 | 0.000 * |
| Parieto-occipital, score | 2.5 ± 2.3 | 2.1 ± 2.3 | 2.5 ± 2.2 | 3.3 ± 2.3 | 0.000 * |
| Temporal, score | 0.8 ± 1.9 | 0.7 ± 1.8 | 0.8 ± 1.8 | 1.0 ± 2.1 | 0.515 |
| Basal Ganglia, score | 0.3 ± 0.7 | 0.2 ± 0.5 | 0.3 ± 0.7 | 0.4 ± 0.7 | 0.065 |
| Infratentorial, score | 0.0 ± 0.2 | 0.0 ± 0.1 | 0.0 ± 0.2 | 0.0 ± 0.3 | 0.359 |
| Gender (Female) | CDR | Hypertension | Diabetes Mellitus | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Periventricular Fazekas scale | 0.028 * | 0.012 * | 0.030 * | 0.671 |
| Deep white matter Fazekas scale | 0.071 | 0.070 | 0.552 | 0.361 |
| ARWMC, total score | 0.091 | 0.000 * | 0.083 | 0.234 |
| Frontal, score | 0.014 * | 0.000 * | 0.028 * | 0.727 |
| Parieto-occipital, score | 0.168 | 0.000 * | 0.259 | 0.191 |
| Temporal, score | 0.682 | 0.515 | 0.441 | 0.132 |
| Basal Ganglia, score | 0.494 | 0.065 | 0.103 | 0.685 |
| Infratentorial, score | 0.882 | 0.359 | 0.639 | 0.852 |
| Gender (Female) p Value (95% CI) | Age p Value (95% CI) | CDR p Value (95% CI) | Hypertension p Value (95% CI) | Diabetes Mellitus p Value (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Periventricular Fazekas scale | 0.110 (0.928–2.091) | 0.000 *(1.048–1.106) | 0.068 (0.973–2.140) | 0.730 (0.722–1.591) | 0.583 (0.722–1.785) |
| Deep white matter Fazekas scale | 0.197 (0.860–2.082) | 0.019 *(1.005–1.062) | 0.536 (0.758–1.705) | 0.891 (0.641–1.473) | 0.175 (0.856–2.341) |
| ARWMC, total score | 0.249 (−0.448–1.726) | 0.000 *(0.065–0.199) | 0.007 *(0.387–2.489) | 0.148 (−1.837–0.277) | 0.249 (−0.502–1.931) |
| Frontal, score | 0.056 (−0.010–0.800) | 0.000 *(0.042–0.093) | 0.004 *(0.189–0.972) | 0.167 (−0.671–0.116) | 0.818 (−0.400–0.507) |
| Parieto-occipital, score | 0.355 (−0.226–0.628) | 0.000 *(0.030–0.083) | 0.006 *(0.168–0.994) | 0.406 (−0.591–0.240) | 0.290 (−0.220–0.736) |
| Temporal, score | 0.899 (−0.340–0.387) | 0.732 (−0.026–0.019) | 0.302 (−0.167–0.537) | 0.201 (−0.584–0.123) | 0.084 (−0.048–0.766) |
| Basal Ganglia, score | 0.763 (−0.110–0.151) | 0.004 *(0.004–0.020) | 0.269 (−0.055–0.197) | 0.176 (−0.214–0.039) | 0.586 (−0.105–0.187) |
| Infratentorial, score | 0.966 (−0.039–0.038) | 0.698 (−0.002–0.003) | 0.271 (−0.016–0.058) | 0.630 (−0.047–0.028) | 0.844 (−0.039–0.047) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kao, Y.-H.; Chou, M.-C.; Chen, C.-H.; Yang, Y.-H. White Matter Changes in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease and Associated Factors. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8020167
Kao Y-H, Chou M-C, Chen C-H, Yang Y-H. White Matter Changes in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease and Associated Factors. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(2):167. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8020167
Chicago/Turabian StyleKao, Yi-Hui, Mei-Chuan Chou, Chun-Hung Chen, and Yuan-Han Yang. 2019. "White Matter Changes in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease and Associated Factors" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 2: 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8020167
APA StyleKao, Y.-H., Chou, M.-C., Chen, C.-H., & Yang, Y.-H. (2019). White Matter Changes in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease and Associated Factors. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(2), 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8020167





