Effects of Perioperative Magnesium Sulfate Administration on Postoperative Chronic Knee Pain in Patients Undergoing Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Retrospective Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
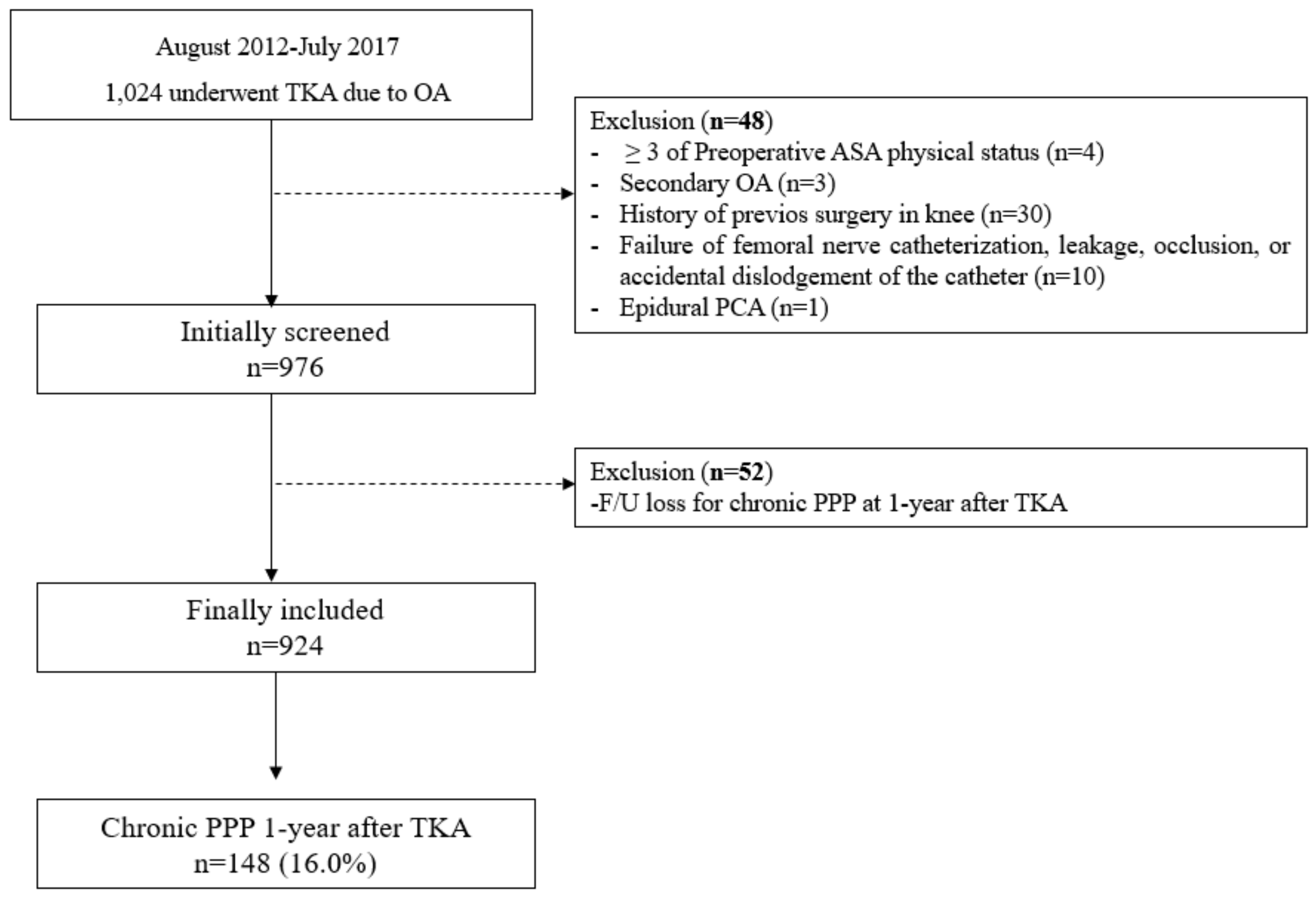
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Perioperative Care for Patients Undergoing TKA
2.4. Surgical Procedures for TKA
2.5. Exposure Variable: Perioperative Magnesium Sulfate Administration
2.6. Primary Endpoint: Presence of Chronic PPP One Year after TKA
2.7. Baseline Characteristics and Confounding Parameters
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Uni- and Multivariable Logistic Regression Analysis
3.2. Sensitivity Analysis after PS Adjustment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maradit Kremers, H.; Larson, D.R.; Crowson, C.S.; Kremers, W.K.; Washington, R.E.; Steiner, C.A.; Jiranek, W.A.; Berry, D.J. Prevalence of total hip and knee replacement in the united states. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2015, 97, 1386–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brander, V.; Stulberg, S.D. Rehabilitation after hip- and knee-joint replacement. An experience- and evidence-based approach to care. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2006, 85, S98–S118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, D.A.; Kluger, M.T.; McNair, P.J.; Lewis, G.N.; Somogyi, A.A.; Borotkanics, R.; Barratt, D.T.; Walker, M. Persistent postoperative pain after total knee arthroplasty: A prospective cohort study of potential risk factors. Br. J. Anaesth. 2018, 121, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, P.; Euasobhon, P. Chronic postsurgical pain: Current evidence for prevention and management. Korean J. Pain 2018, 31, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Ong, K.; Lau, E.; Mowat, F.; Halpern, M. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the united states from 2005 to 2030. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2007, 89, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Health at a Glance 2011; OECD Indicators; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2015; Volume 15, p. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, A.M.; Rome, B.N.; Reichmann, W.M.; Collins, J.E.; Burbine, S.A.; Thornhill, T.S.; Wright, J.; Katz, J.N.; Losina, E. Estimating the burden of total knee replacement in the united states. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2013, 95, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Rubio, L.; Nava, E.; Del Pozo, J.S.G.; Jordan, J. Influence of the perioperative administration of magnesium sulfate on the total dose of anesthetics during general anesthesia. A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Anesth. 2017, 39, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, G.S., Jr.; Castro-Alves, L.J.; Khan, J.H.; McCarthy, R.J. Perioperative systemic magnesium to minimize postoperative pain: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Anesthesiology 2013, 119, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.J.; Kim, E.Y.; Na, H.S.; Kim, T.K.; Kim, M.H.; Do, S.H. Magnesium sulphate attenuates acute postoperative pain and increased pain intensity after surgical injury in staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty: A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Br. J. Anaesth. 2016, 117, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, P.; Neyton, J. Nmda receptor subunits: Function and pharmacology. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2007, 7, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, C.J. Central sensitization: Implications for the diagnosis and treatment of pain. Pain 2011, 152, S2–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolf, C.J.; Thompson, S.W. The induction and maintenance of central sensitization is dependent on n-methyl-d-aspartic acid receptor activation; implications for the treatment of post-injury pain hypersensitivity states. Pain 1991, 44, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richebe, P.; Capdevila, X.; Rivat, C. Persistent postsurgical pain: Pathophysiology and preventative pharmacologic considerations. Anesthesiology 2018, 129, 590–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pockett, S. Spinal cord synaptic plasticity and chronic pain. Anesth. Analg. 1995, 80, 173–179. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, T.K.; Park, J.W.; Shin, H.J.; Na, H.S.; Oh, A.Y.; Hwang, J.W. Perioperative sedative use is not associated with acute kidney injury after total hip or knee arthroplasty. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, T.K.; Chang, C.B.; Shin, H.J.; Han, S.; Do, S.H.; Lee, H.J.; Hwang, J.W. Association between perioperative statin use and postoperative pain after total knee arthroplasty. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2019, 44, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, I.J.; Kang, Y.G.; Chang, C.B.; Do, S.H.; Seong, S.C.; Kim, T.K. Does periarticular injection have additional pain relieving effects during contemporary multimodal pain control protocols for tka? A randomised, controlled study. Knee 2012, 19, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, F.; Eroglu, A. The effect of intravenous magnesium sulfate infusion on sensory spinal block and postoperative pain score in abdominal hysterectomy. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 236024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rosenbaum, P.R.; Rubin, D.B. The central role of the propensity score in observational studies for causal effects. Biometrika 1983, 70, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Pearson-Chauhan, K.M.; McCarthy, R.J.; Buvanendran, A. Predictive factors for developing chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 3372–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehlet, H.; Jensen, T.S.; Woolf, C.J. Persistent postsurgical pain: Risk factors and prevention. Lancet 2006, 367, 1618–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koinig, H.; Wallner, T.; Marhofer, P.; Andel, H.; Horauf, K.; Mayer, N. Magnesium sulfate reduces intra- and postoperative analgesic requirements. Anesth. Analg. 1998, 87, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tuchman, M.; Barrett, J.A.; Donevan, S.; Hedberg, T.G.; Taylor, C.P. Central sensitization and ca(v)alpha(2)delta ligands in chronic pain syndromes: Pathologic processes and pharmacologic effect. J. Pain 2010, 11, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.H.; Nahm, F.S.; Kim, T.K.; Chang, M.J.; Do, S.H. Comparison of postoperative pain in the first and second knee in staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty: Clinical evidence of enhanced pain sensitivity after surgical injury. Pain 2014, 155, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghezel-Ahmadi, V.; Ghezel-Ahmadi, D.; Schirren, J.; Tsapopiorgas, C.; Beck, G.; Bolukbas, S. Perioperative systemic magnesium sulphate to minimize acute and chronic post-thoracotomy pain: A prospective observational study. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.Y.; Na, H.S.; Jeon, Y.T.; Ro, Y.J.; Kim, C.S.; Do, S.H. I.V. Infusion of magnesium sulphate during spinal anaesthesia improves postoperative analgesia. Br. J. Anaesth. 2010, 104, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belluzzi, E.; Stocco, E.; Pozzuoli, A.; Granzotto, M.; Porzionato, A.; Vettor, R.; De Caro, R.; Ruggieri, P.; Ramonda, R.; Rossato, M.; et al. Contribution of infrapatellar fat pad and synovial membrane to knee osteoarthritis pain. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 6390182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Samuel, L.T.; Acuna, A.J.; Faour, M.; Roth, A.; Kamath, A.F.; Mont, M.A. Infrapatellar fat pad resection or preservation during total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review. J. Knee Surg. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankenburg, F.R.; Fitzmaurice, G.M.; Zanarini, M.C. The use of prescription opioid medication by patients with borderline personality disorder and axis ii comparison subjects: A 10-year follow-up study. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2014, 75, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
| Variable | Total 924 Patients (%) | Mean (SD) |
|---|---|---|
| Sex, female | 855 (92.5) | |
| Age, year | 71.7 (6.1) | |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 27.0 (3.4) | |
| Type of surgery | ||
| Unilateral TKA | 467 (50.5) | |
| Staged unilateral TKA | 428 (46.3) | |
| Bilateral TKA | 29 (3.1) | |
| Intraoperative magnesium sulfate infusion | 90 (9.7) | |
| Preoperative ASA physical status | ||
| 1 | 121 (13.1) | |
| 2 | 803 (86.9) | |
| Duration of surgery, min | 99.8 (23.3) | |
| Duration of anesthesia. min | 143.0 (27.5) | |
| Intraoperative sedation | ||
| None | 632 (68.4) | |
| Propofol | 186 (20.1) | |
| Dexmedetomidine | 106 (11.5) | |
| Premedication (n = 320, midazolam, mg) | 2.5 (0.8) |
| Variable | Univariable Model | p-Value | Multivariable Model | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | |||
| Sex, male | 0.77 (0.38, 1.59) | 0.485 | 0.92 (0.44, 1.94) | 0.832 |
| Age, year | 0.99 (0.96, 1.02) | 0.583 | 0.99 (0.96, 1.02) | 0.430 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 1.02 (0.97, 1.08) | 0.383 | 1.00 (0.95, 1.05) | 0.948 |
| Type of surgery | ||||
| Unilateral TKA | 1 | 1 | ||
| Staged unilateral TKA | 2.08 (1.44, 3.01) | <0.001 | 2.06 (1.40, 3.02) | <0.001 |
| Bilateral TKA | 1.63 (0.60, 4.45) | 0.342 | 1.35 (0.26, 6.96) | 0.722 |
| Magnesium group | 0.35 (0.15, 0.81) | 0.015 | 0.38 (0.16, 0.90) | 0.027 |
| Preoperative ASA physical status | ||||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| ≥2 | 1.53 (0.85, 2.75) | 0.155 | 1.43 (0.78, 2.61) | 0.245 |
| Duration of surgery, min | 1.00 (1.00, 1.01) | 0.250 | 1.00 (0.99, 1.01) | 0.726 |
| Duration of anesthesia. min | 1.00 (0.99, 1.01) | 0.449 | ||
| Intraoperative sedation | ||||
| None | 1 | 1 | ||
| Propofol | 1.11 (0.71, 1.71) | 0.653 | 1.06 (0.68, 1.66) | 0.796 |
| Dexmedetomidine | 0.95 (0.53, 1.68) | 0.849 | 1.11 (0.60, 2.03) | 0.746 |
| Premedication (midazolam, mg) | 1.10 (0.88, 1.37) | 0.398 | 1.09 (0.87, 1.36) | 0.466 |
| Variable | CPPP One Year After TKA | Logistic Model | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Event (%) | OR (95% CI) | |||
| Unadjusted | ||||
| Control group | 142/834 (17.0) | 1 | ||
| Magnesium group | 6/90 (6.7) | 0.35 (0.15, 0.81) | 0.015 | |
| After PS adjustment | ||||
| Control group | 37/232 (15.9) | 1 | ||
| Magnesium group | 6/89 (6.7) | 0.38 (0.16, 0.93) | 0.036 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, T.K.; Chung, S.H.; Park, J.; Shin, H.; Chang, C.B.; Kim, T.K.; Do, S.-H. Effects of Perioperative Magnesium Sulfate Administration on Postoperative Chronic Knee Pain in Patients Undergoing Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Retrospective Evaluation. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122231
Oh TK, Chung SH, Park J, Shin H, Chang CB, Kim TK, Do S-H. Effects of Perioperative Magnesium Sulfate Administration on Postoperative Chronic Knee Pain in Patients Undergoing Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Retrospective Evaluation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(12):2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122231
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Tak Kyu, Seung Hyun Chung, Jinwoo Park, Hyunjung Shin, Chong Bum Chang, Tae Kyun Kim, and Sang-Hwan Do. 2019. "Effects of Perioperative Magnesium Sulfate Administration on Postoperative Chronic Knee Pain in Patients Undergoing Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Retrospective Evaluation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 12: 2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122231
APA StyleOh, T. K., Chung, S. H., Park, J., Shin, H., Chang, C. B., Kim, T. K., & Do, S.-H. (2019). Effects of Perioperative Magnesium Sulfate Administration on Postoperative Chronic Knee Pain in Patients Undergoing Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Retrospective Evaluation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(12), 2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122231




