Development of Oxadiazole-Based ODZ10117 as a Small-Molecule Inhibitor of STAT3 for Targeted Cancer Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Structure-Based Computational Database Screening
2.2. Cell-Based High-Throughput Screening
2.3. Reagents
2.4. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
2.5. Protein Extraction and Immunoblot Analysis
2.6. RNA Extraction, cDNA Preparation, and Quantitative Real-time PCR
2.7. Immunoprecipitation
2.8. Immunofluorescence
2.9. Immunohistochemistry
2.10. Cell Viability Assay
2.11. Migration and Invasion Assays
2.12. Flow Cytometry
2.13. Bioluminescence Imaging
2.14. Mouse Xenograft Studies
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Subsection
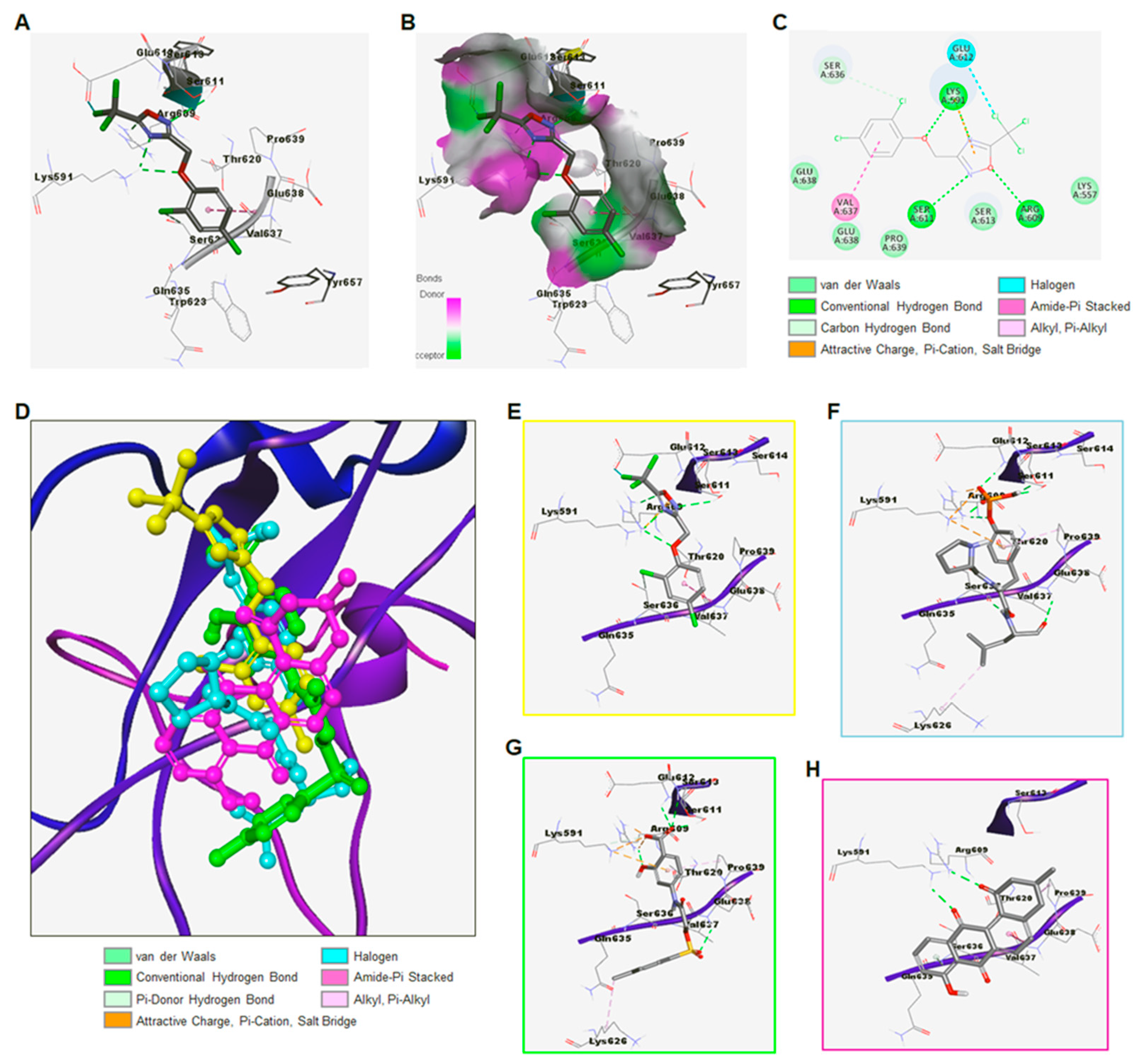
3.1.1. Identification of ODZ17690 as a Hit Compound by Targeting the SH2 Domain of STAT3
3.1.2. Discovery of ODZ10117 as a STAT3 Inhibitor
3.1.3. Synthesis of ODZ10117
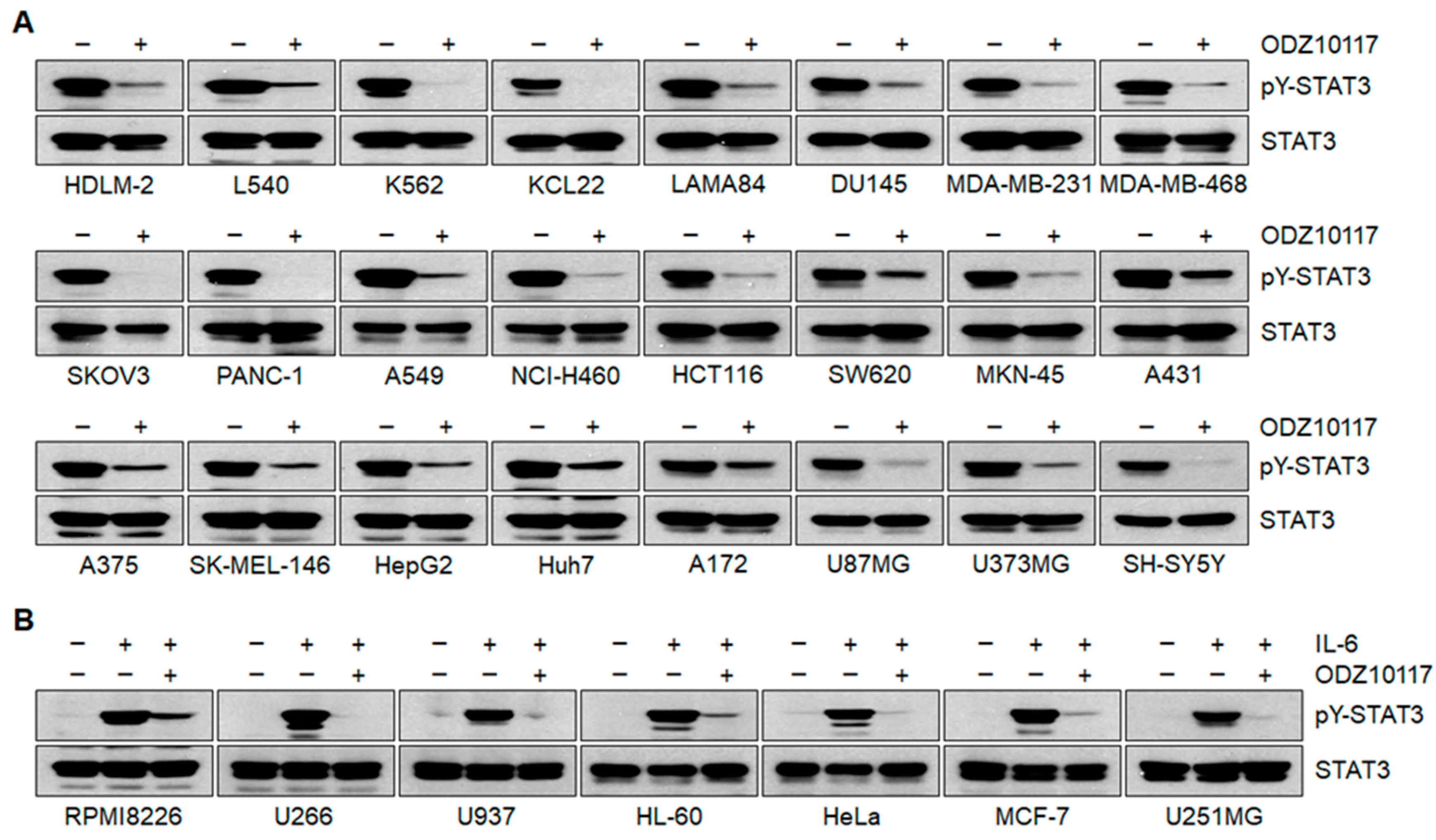
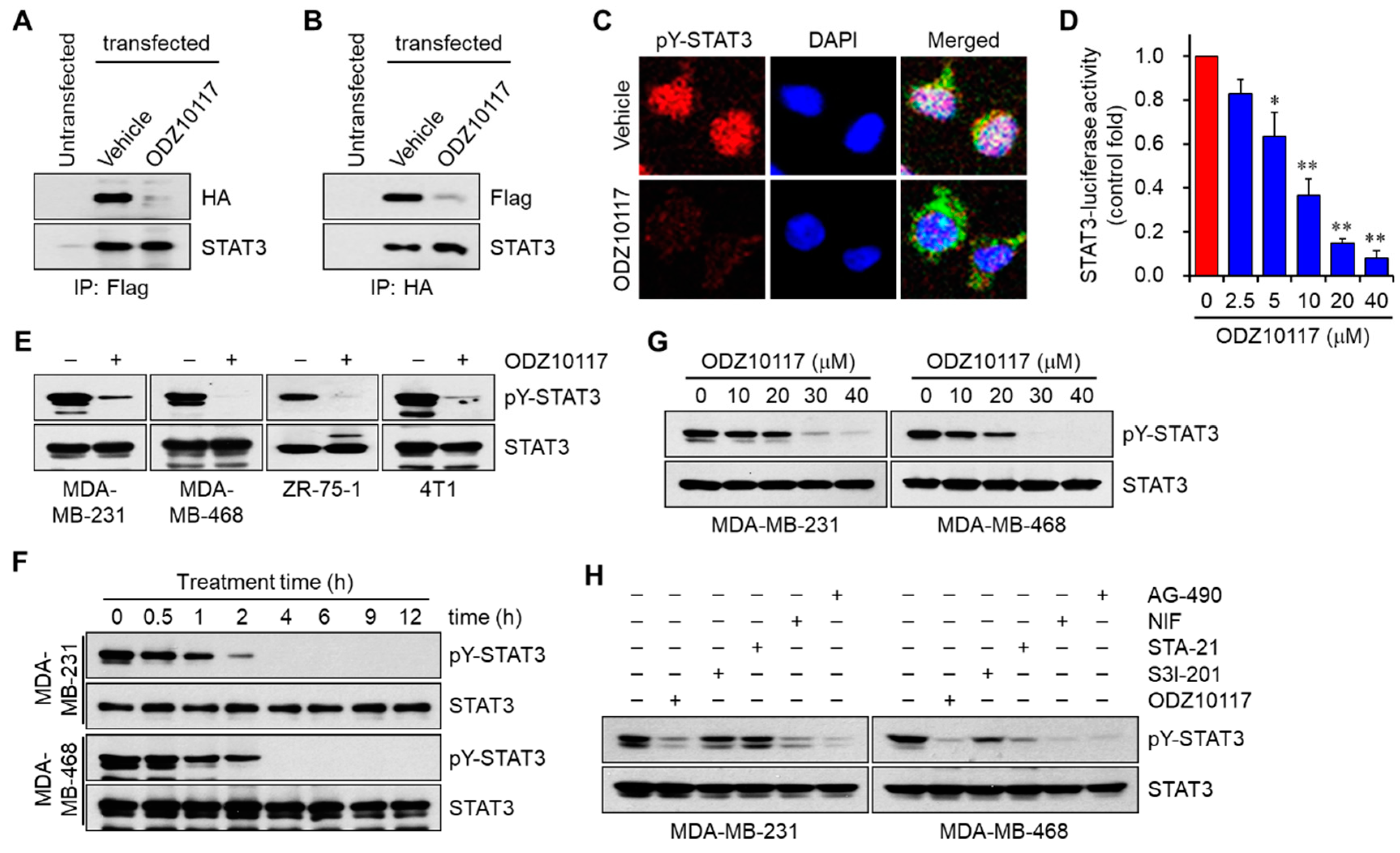
3.1.4. ODZ10117 Inhibits STAT3 Signaling In Vitro
3.1.5. ODZ10117 has a Greater Inhibition on STAT3 Activation than the Known Inhibitors
3.1.6. ODZ10117 Does Not Affect Other STAT Family Proteins and Upstream Regulators of STAT3
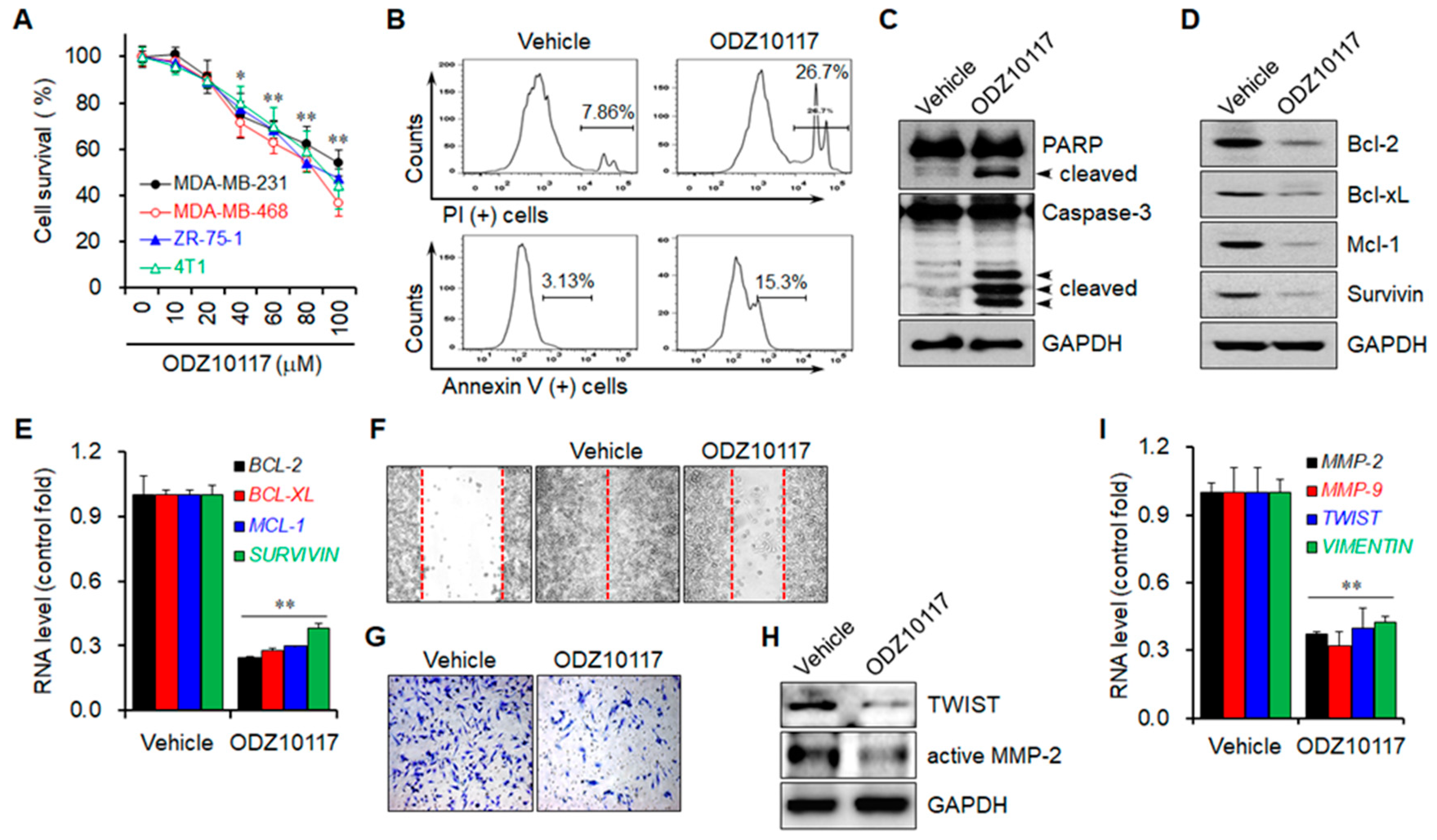
3.1.7. ODZ10117 Decreases Cell Viability by Inducing Apoptosis
3.1.8. ODZ10117 Reduces the Migration and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cells
3.1.9. ODZ10117 Suppresses Tumor Growth in Breast Cancer Xenografts
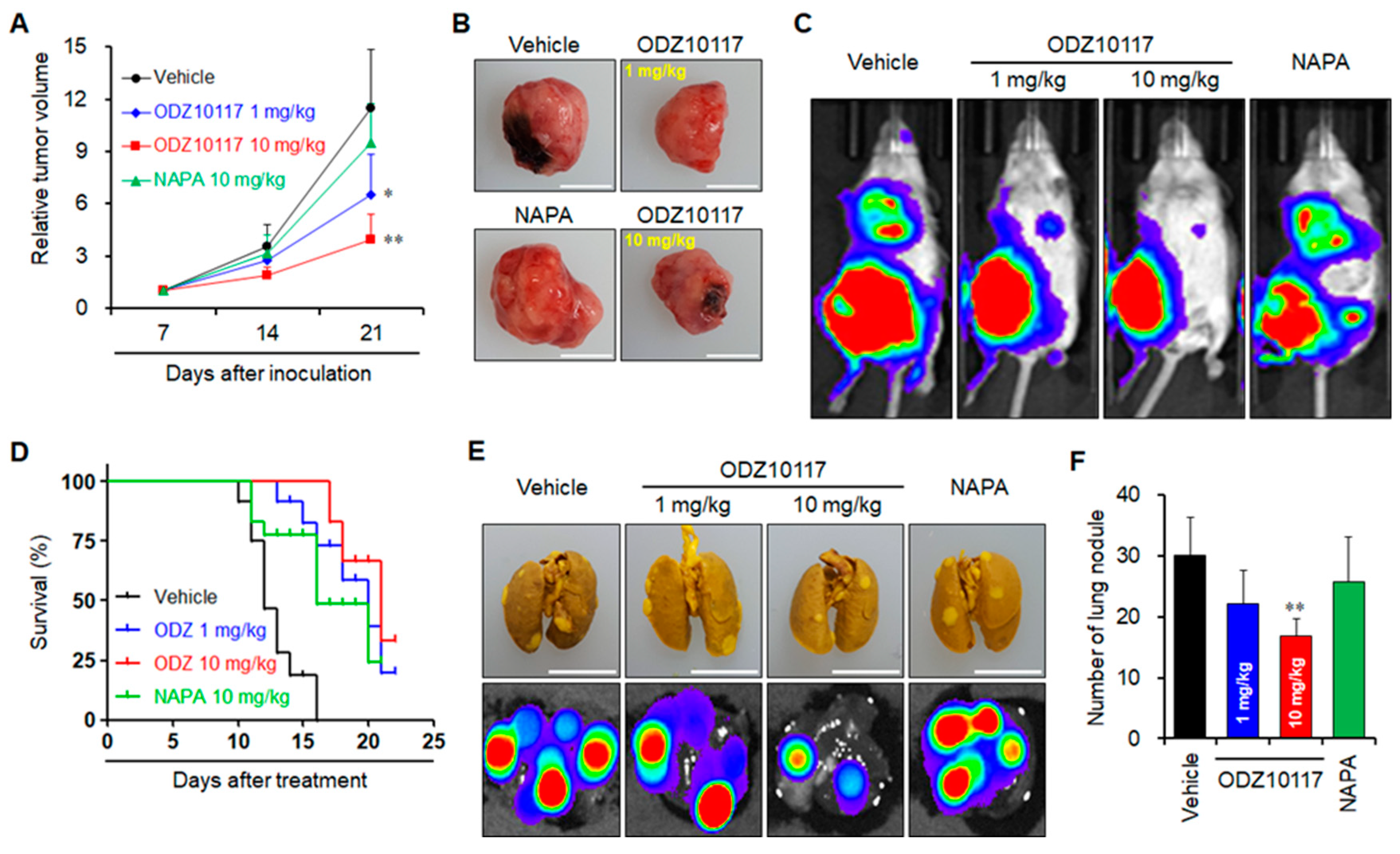
3.1.10. ODZ10117 Suppresses Tumor Growth and Lung Metastasis in Breast Cancer Xenograft
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levy, D.E.; Lee, C.K. What does Stat3 do? J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, C.; Plumlee, C. Interferons pen the JAK-STAT pathway. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2008, 19, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, S.; Nishio, Y.; Inoue, M.; Wang, X.J.; Wei, S.; Matsusaka, T.; Yoshida, K.; Sudo, T.; Naruto, M.; Kishimoto, T. Molecular cloning of APRF, a novel IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 p91-related transcription factor involved in the gp130-mediated signaling pathway. Cell 1994, 77, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Wen, Z.; Darnell, J.E.J. Stat3: a STAT family member activated by tyrosine phosphorylation in response to epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Science 1994, 264, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, J.; Chand, A.; Gough, D.; Ernst, M. Therapeutically exploiting STAT3 activity in cancer—using tissue repair as a road map. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.H.; Yi, E.H.; Ye, S.K. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 as a therapeutic target for cancer and the tumor microenvironment. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2016, 39, 1085–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, J.J.; Holland, S.M.; Staudt, L.M. JAKs and STATs in immunity, immunodeficiency, and cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lee, H.; Herrmann, A.; Buettner, R.; Jove, R. Revisiting STAT3 signalling in cancer: new and unexpected biological functions. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørlie, T.; Perou, C.M.; Tibshirani, R.; Aas, T.; Geisler, S.; Johnsen, H.; Hastie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; van de Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; et al. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10869–10874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiriou, C.; Neo, S.Y.; McShane, L.M.; Korn, E.L.; Long, P.M.; Jazaeri, A.; Martiat, P.; Fox, S.B.; Harris, A.L.; Liu, E.T. Breast cancer classification and prognosis based on gene expression profiles from a population-based study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10393–10398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, G.; Balko, J.M.; Mayer, I.A.; Sanders, M.E.; Gianni, L. Triple-negative breast cancer: challenges and opportunities of a heterogeneous disease. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 13, 674–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Xiang, L.; Li, T.; Bai, Z. Cancer Hallmarks, Biomarkers and Breast Cancer Molecular Subtypes. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 1281–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cejalvo, J.M.; Pascual, T.; Fernández-Martínez, A.; Brasó-Maristany, F.; Gomis, R.R.; Perou, C.M.; Muñoz, M.; Prat, A. Clinical implications of the non-luminal intrinsic subtypes in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 67, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, K.; Resat, H. Constitutive activation of STAT3 in breast cancer cells: A review. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 2570–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirkisoon, S.R.; Carpenter, R.L.; Rimkus, T.; Anderson, A.; Harrison, A.; Lange, A.M.; Jin, G.; Watabe, K.; Lo, H.W. Interaction between STAT3 and GLI1/tGLI1 oncogenic transcription factors promotes the aggressiveness of triple-negative breast cancers and HER2-enriched breast cancer. Oncogene 2018, 37, 2502–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.J.; Yan, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.D. STAT3 as a potential therapeutic target in triple negative breast cancer: a systematic review. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.H.; Yi, E.H.; Li, Y.C.; Park, I.C.; Park, J.Y.; Ye, S.K. Anticancer Activity of Tubulosine through Suppression of Interleukin-6-Induced Janus Kinase 2/Signal Transducer and Activation of Transcription 3 Signaling. J. Breast Cancer 2019, 22, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.; Groner, B.; Müller, C.W. Three-dimensional structure of the Stat3beta homodimer bound to DNA. Nature 1998, 394, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastry, G.M.; Adzhigirey, M.; Day, T.; Annabhimoju, R.; Sherman, W. Protein and ligand preparation: parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2013, 27, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.J.; Foloppe, N. Drug-like bioactive structures and conformational coverage with the LigPrep/ConfGen suite: comparison to programs MOE and catalyst. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 822–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halgren, T.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Friesner, R.A.; Beard, H.S.; Frye, L.L.; Pollard, W.T.; Banks, J.L. Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 2. Enrichment factors in database screening. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiquee, K.; Zhang, S.; Guida, W.C.; Blaskovich, M.A.; Greedy, B.; Lawrence, H.R.; Yip, M.L.; Jove, R.; McLaughlin, M.M.; Lawrence, N.J.; et al. Selective chemical probe inhibitor of Stat3, identified through structure-based virtual screening, induces antitumor activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7391–7396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Wang, R.; Wang, S.; Lin, J. A low-molecular-weight compound discovered through virtual database screening inhibits Stat3 function in breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 4700–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.S.; Kim, H.N.; Shin, K.D.; Yoon, Y.J.; Kim, S.J.; Han, D.C.; Kwon, B.M. Cryptotanshinone inhibits constitutive signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 function through blocking the dimerization in DU145 prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.H.; Yin, C.H.; Guo, Q.; Bach, E.A.; Lee, H.; Sandoval, C.; Jayabose, S.; Ulaczyk-Lesanko, A.; Hall, D.G.; Baeg, G.H. A small-molecule compound identified through a cell-based screening inhibits JAK/STAT pathway signaling in human cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, E.A.; Walker, S.R.; Kepich, A.; Gashin, L.B.; Hideshima, T.; Ikeda, H.; Chauhan, D.; Anderson, K.C.; Frank, D.A. Nifuroxazide inhibits survival of multiple myeloma cells by directly inhibiting STAT3. Blood 2008, 112, 5095–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Rogoff, H.A.; Keates, S.; Gao, Y.; Murikipudi, S.; Mikule, K.; Leggett, D.; Li, W.; Pardee, A.B.; Li, C.J. Suppression of cancer relapse and metastasis by inhibiting cancer stemness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2015, 112, 1839–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renga, J.M.; Wang, P.C. The Salt-Free Synthesis of Aryl Ethers Using Methyl Trichloracetate. Synth. Commun. 1984, 14, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloy, F.; Lenaers, R. The Chemistry of Amidoximes and Related Compounds. Chem. Rev. 1962, 62, 155–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, J.K.; Akabote, V.; Hegde, S.G.; Alagarsamy, P. PTSA-ZnCl2: an efficient catalyst for the synthesis of 1, 2, 4-oxadiazoles from amidoximes and organic nitriles. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 5640–5643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.E.; O’Keefe, R.A.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miklossy, G.; Hilliard, T.S.; Turkson, J. Therapeutic modulators of STAT signalling for human diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.G.; Vignjevic, D.M. Modes of cancer cell invasion and the role of the microenvironment. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 36, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hynes, N.E.; Gullick, W. Therapeutic targeting of signal transduction pathways and proteins in breast cancer. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2006, 11, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azab, S.; Al-Hendy, A. Signal Transduction Pathways in Breast Cancer—Drug Targets and Challenges. In Breast Cancer—Carcinogenesis, Cell Growth and Signalling Pathways; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2015; Volume 6, pp. 109–138. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, E.Z.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Arfuso, F.; Dharmarajan, A.; Wang, C.; Kumar, A.P.; Samy, R.P.; Lim, L.H.; Wang, L.; Goh, B.C.; et al. Targeting transcription factor STAT3 for cancer prevention and therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 162, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, J.; Etemadi, N.; Hollande, F.; Ernst, M.; Buchert, M. The JAK/STAT3 axis: A comprehensive drug target for solid malignancies. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2017, 45, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzner, M.; Ebner, R.; Wolff, H.A.; Ghadimi, B.M.; Wienands, J.; Grade, M. STAT3: A Novel Molecular Mediator of Resistance to Chemoradiotherapy. Cancers (Basel) 2014, 6, 1986–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudino, T.A. Targeted Cancer Therapy: The Next Generation of Cancer Treatment. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2015, 12, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C. Targeted therapy: An elusive cancer target. Nature 2016, 537, S106–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Biehl, A.; Gadina, M.; Hasni, S.; Schwartz, D.M. JAK-STAT Signaling as a Target for Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases: Current and Future Prospects. Drugs 2017, 77, 521–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimri, S.; Sukanya, S.; De, A. Approaching non-canonical STAT3 signaling to redefine cancer therapeutic strategy. Integr. Mol. Med. 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Furtek, S.L.; Backos, D.S.; Matheson, C.J.; Reigan, P. Strategies and Approaches of Targeting STAT3 for Cancer Treatment. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.L.A.; Hirpara, J.L.; Pervaiz, S.; Eu, J.Q.; Sethi, G.; Goh, B.C. Do STAT3 inhibitors have potential in the future for cancer therapy? Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2017, 26, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schust, J.; Sperl, B.; Hollis, A.; Mayer, T.U.; Berg, T. Stattic: A small-molecule inhibitor of STAT3 activation and dimerization. Chem. Biol. 2006, 13, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamaru, A.; Szymanski, S.; Iwado, E.; Aoki, H.; Yokoyama, T.; Fokt, I.; Hess, K.; Conrad, C.; Madden, T.; Sawaya, R.; et al. A novel inhibitor of the STAT3 pathway induces apoptosis in malignant glioma cells both in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 2007, 26, 2435–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, B.-H.; Lee, H.; Song, Y.; Park, J.-S.; Gadhe, C.G.; Choi, J.; Lee, C.-G.; Pae, A.N.; Kim, S.; Ye, S.-K. Development of Oxadiazole-Based ODZ10117 as a Small-Molecule Inhibitor of STAT3 for Targeted Cancer Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8111847
Kim B-H, Lee H, Song Y, Park J-S, Gadhe CG, Choi J, Lee C-G, Pae AN, Kim S, Ye S-K. Development of Oxadiazole-Based ODZ10117 as a Small-Molecule Inhibitor of STAT3 for Targeted Cancer Therapy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(11):1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8111847
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Byung-Hak, Haeri Lee, Yeonghun Song, Joon-Suk Park, Changdev G. Gadhe, Jiwon Choi, Chung-Gi Lee, Ae Nim Pae, Sanghee Kim, and Sang-Kyu Ye. 2019. "Development of Oxadiazole-Based ODZ10117 as a Small-Molecule Inhibitor of STAT3 for Targeted Cancer Therapy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 11: 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8111847
APA StyleKim, B.-H., Lee, H., Song, Y., Park, J.-S., Gadhe, C. G., Choi, J., Lee, C.-G., Pae, A. N., Kim, S., & Ye, S.-K. (2019). Development of Oxadiazole-Based ODZ10117 as a Small-Molecule Inhibitor of STAT3 for Targeted Cancer Therapy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(11), 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8111847





