Evaluation of Outcomes and Quality of Care in Children with Sickle Cell Disease Diagnosed by Newborn Screening: A Real-World Nation-Wide Study in France
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Outcomes
- Vaso-occlusive crisis (including dactylitis) was defined as an acute non-infectious, non-traumatic pain requiring analgesics for more than 12 h and/or hospital admission.
- Acute chest syndrome (ACS) was defined as a new pulmonary infiltrate on chest X-ray, with or without pain, cough, fever (≥38.5 °C), or hypoxemia. Given the overlapping definition of pneumoniae in young children, the latter events were pooled with ACS.
- Acute anemic events were defined by reductions in hemoglobin ≥20% versus steady state.
- Acute splenic sequestration (ASS) was defined as splenic enlargement increased ≥2 cm from baseline associated with acute anemia.
- Stroke was defined as an ischemic or hemorrhagic event lasting >24 h and resulting in focal neurologic deficit.
2.4. Ethics
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
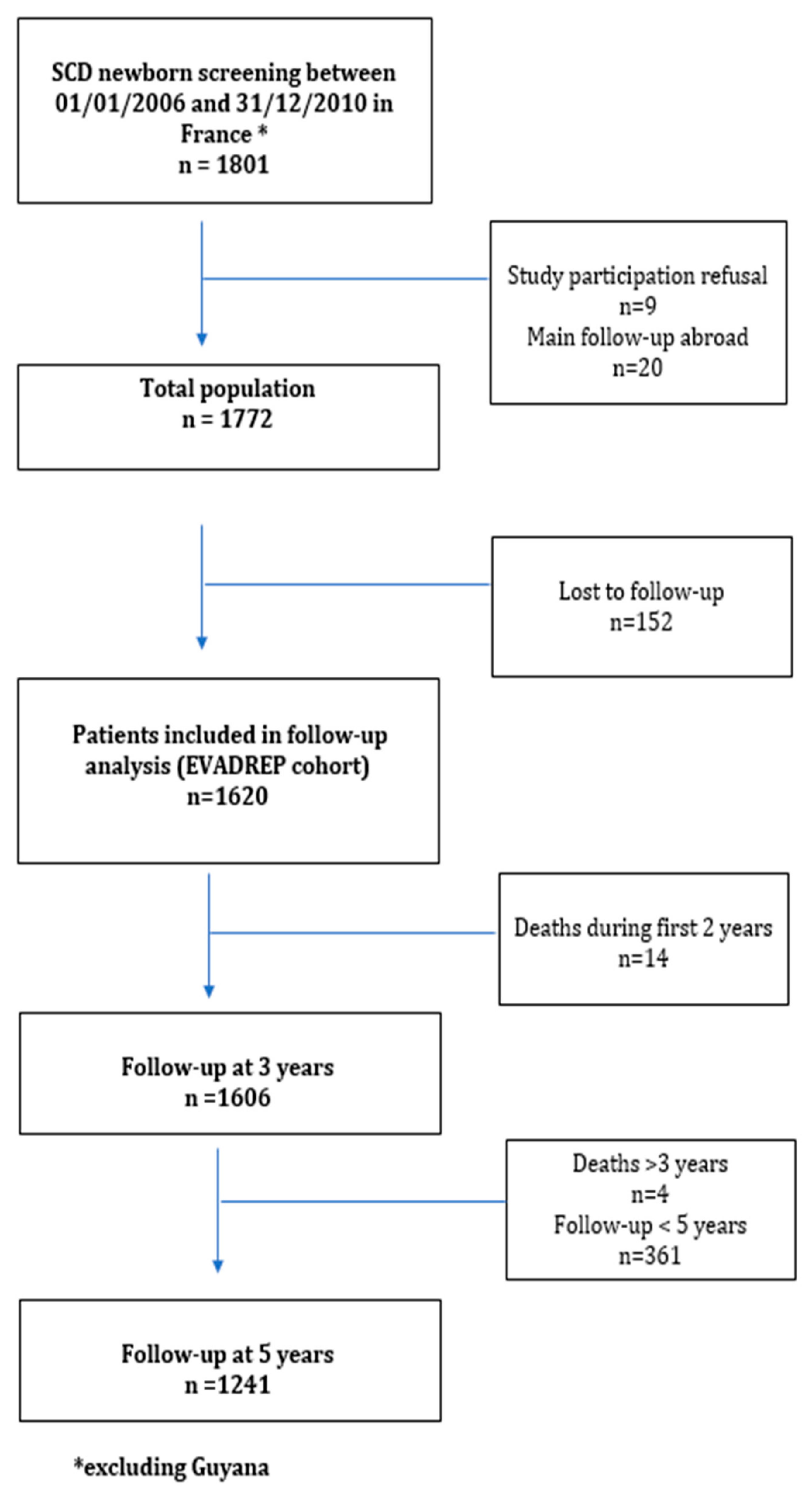
3.1. General Results
3.2. Follow-up Results
3.3. Outcomes
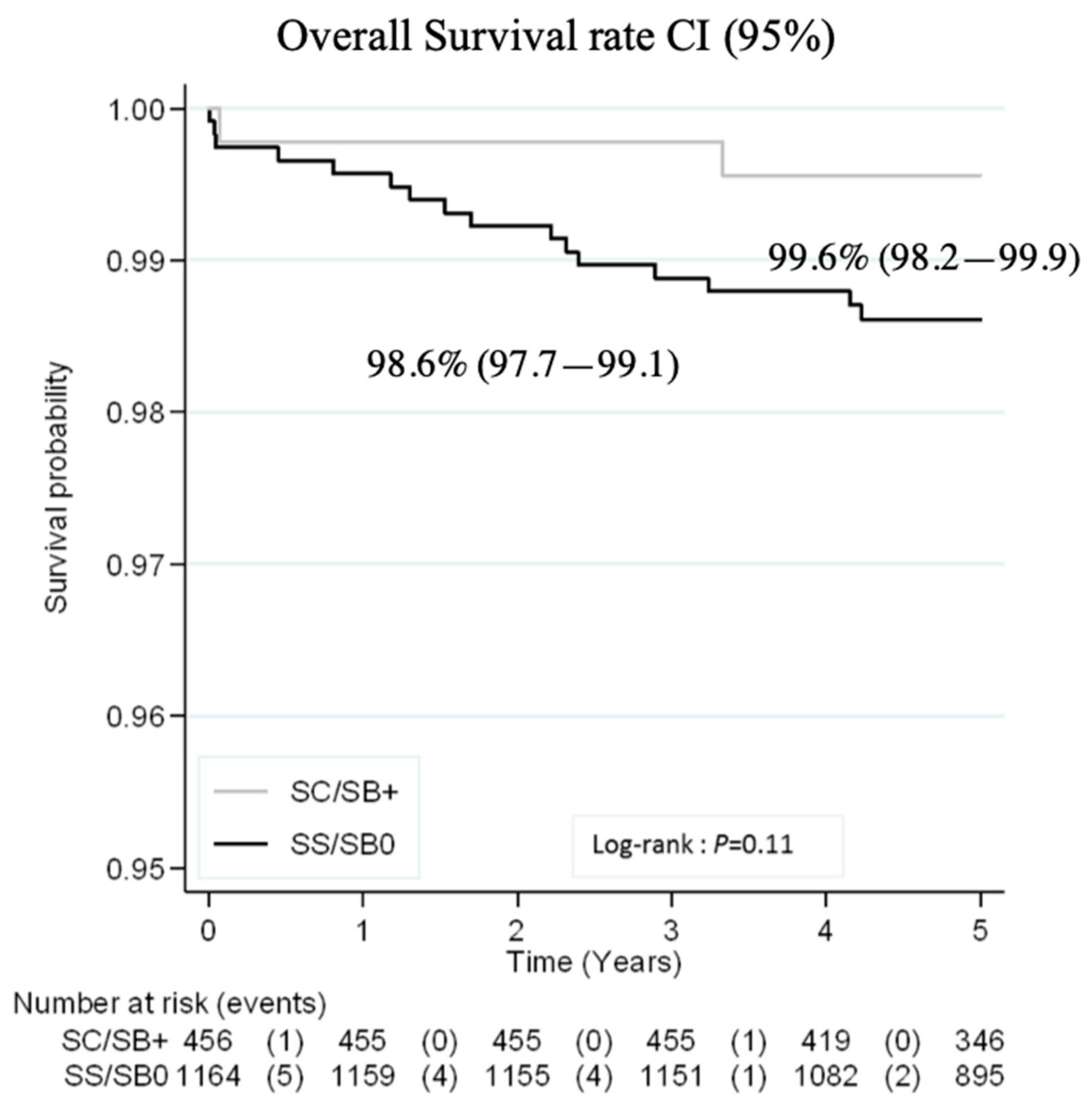
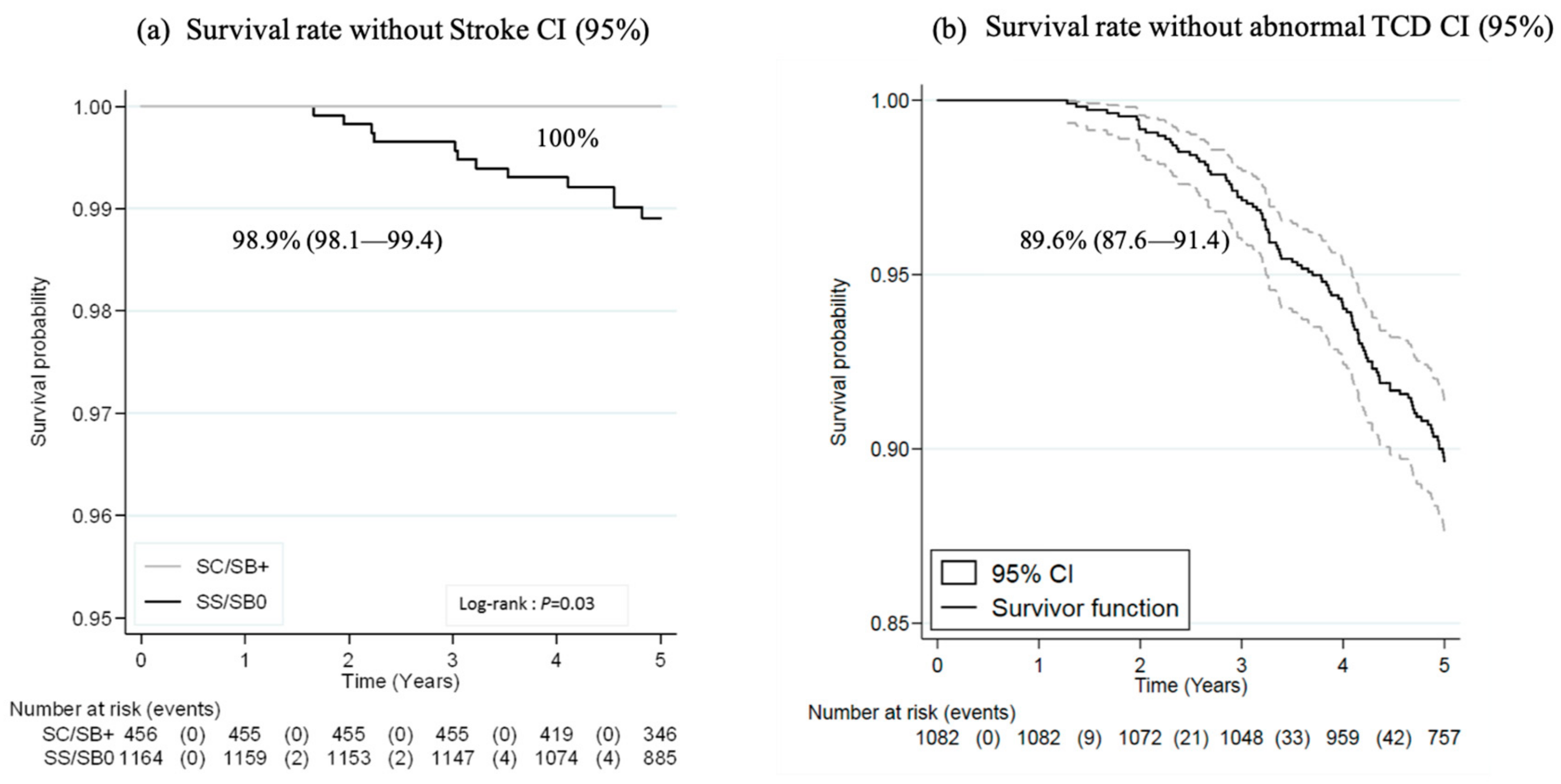
3.3.1. Major Severe Outcomes and Prophylactic Coverage
3.3.2. Other SCD-Related Events:
3.3.3. Disease Modifying Therapy and Other Therapeutic Measures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaston, M.H.; Verter, J.I.; Woods, G.; Pegelow, C.; Presbury, G.; Zarkowsky, H.; Iyer, R.; Lobel, J.S.; Gill, F.M.; Ritchey, K.; et al. Prophylaxis with Oral Penicillin in Children with Sickle Cell Anemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 314, 1593–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamkiewicz, T.V.; Silk, B.J.; Howgate, J.; Baughman, W.; Strayhorn, G.; Sullivan, K.; Farley, M.M. Effectiveness of the 7-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine in Children with Sickle Cell Disease in the First Decade of Life. Pediatric 2008, 121, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarville, M.B.; Goodin, G.S.; Fortner, G.; Li, C.S.; Smeltzer, M.P.; Adams, R.; Wang, W. Evaluation of a comprehensive transcranial doppler screening program for children with sickle cell anemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2008, 50, 818–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernaudin, F.; Verlhac, S.; Arnaud, C.; Kamdem, A.; Chevret, S.; Hau, I.; Coïc, L.; Leveillé, E.; Lemarchand, E.; Lesprit, E.; et al. Impact of early transcranial Doppler screening and intensive therapy on cerebral vasculopathy outcome in a newborn sickle cell anemia cohort. Blood 2011, 117, 1130–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telfer, P.; Coen, P.; Chakravorty, S.; Wilkey, O.; Evans, J.; Newell, H.; Smalling, B.; Amos, R.; Stephens, A.; Rogers, D.; et al. Clinical outcomes in children with sickle cell disease living in England: A neonatal cohort in East London. Haematologica 2007, 92, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, C.T.; Rogers, Z.R.; McCavit, T.L.; Buchanan, G.R. Improved survival of children and adolescents with sickle cell disease. Blood 2010, 115, 3447–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couque, N.; Girard, D.; Ducrocq, R.; Boizeau, P.; Haouari, Z.; Missud, F.; Holvoet, L.; Ithier, G.; Belloy, M.; Odièvre, M.-H.; et al. Improvement of medical care in a cohort of newborns with sickle-cell disease in North Paris: Impact of national guidelines. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 173, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streetly, A.; Sisodia, R.; Dick, M.; Latinovic, R.; Hounsell, K.; Dormandy, E. Evaluation of newborn sickle cell screening programme in England: 2010–2016. Arch. Dis. Child. 2018, 103, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dépistage Néonatal de la Drépanocytose en France, Rapport D’orientation; Haute Autorité de Santé: Saint-Denis, France, 2013.
- Adams, R.; McKie, V.; Nichols, F.; Carl, E.; Zhang, D.-L.; McKie, K.; Figueroa, R.; Litaker, M.; Thompson, W.; Hess, D. The Use of Transcranial Ultrasonography to Predict Stroke in Sickle Cell Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 326, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ALD n° 10—Syndromes Drépanocytaires Majeurs de L’enfant et de L’adolescent. Haute Autorité de Santé. Available online: https://www.has-sante.fr/jcms/c_938890/fr/ald-n-10-syndromes-drepanocytaires-majeurs-de-l-enfant-et-de-l-adolescent (accessed on 18 September 2019).
- La Mortalité Infantile est Stable Depuis dix ans Après des Décennies de Baisse—Insee Focus–117. Available online: https://www.insee.fr/fr/statistiques/3560308 (accessed on 24 July 2019).
- Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Caggana, M.; Kennedy, J.; Zimmerman, R.; Oyeku, S.O.; Werner, E.M.; Grant, A.M.; Green, N.S.; Grosse, S.D. Mortality of New York children with sickle cell disease identified through newborn screening. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamideh, D.; Alvarez, O. Sickle cell disease related mortality in the United States (1999–2009). Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 1482–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, A.B.; Link-Gelles, R.; Azonobi, I.; Hooper, W.C.; Beall, B.W.; Jorgensen, J.H.; Juni, B.; Moore, M. Invasive Pneumococcal Disease among Children with and without Sickle Cell Disease in the United States, 1998–2009. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2013, 32, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oligbu, G.; Collins, S.; Sheppard, C.; Fry, N.; Dick, M.; Streetly, A.; Ladhani, S. Risk of Invasive Pneumococcal Disease in Children with Sickle Cell Disease in England: A National Observational Cohort Study, 2010–2015. Arch. Dis. Child. 2018, 103, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oligbu, G.; Fallaha, M.; Pay, L.; Ladhani, S. Risk of invasive pneumococcal disease in children with sickle cell disease in the era of conjugate vaccines: A systematic review of the literature. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 185, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, S.L.; Jary, H.K.; Gondhi, J.P.; Kleyn, M.; Wagner, A.L.; Dombkowski, K.J. Pneumococcal vaccination coverage among children with sickle cell anemia, sickle cell trait, and normal hemoglobin. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65, e27282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, S.L.; Madden, B.; Freed, G.L.; Dombkowski, K.J. Transcranial Doppler Screening Among Children and Adolescents with Sickle Cell Anemia. JAMA Pediatr. 2016, 170, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong-Wells, J.; Grimes, B.; Sidney, S.; Kronish, D.; Shiboski, S.C.; Adams, R.J.; Fullerton, H.J. Utilization of TCD screening for primary stroke prevention in children with sickle cell disease. Neurology 2009, 72, 1316–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.C.; Ware, R.E.; Miller, S.T.; Iyer, R.V.; Casella, J.F.; Minniti, C.P.; Rana, S.; Thornburg, C.D.; Rogers, Z.R.; Kalpatthi, R.V.; et al. Hydroxycarbamide in very young children with sickle-cell anaemia: A multicentre, randomised, controlled trial (BABY HUG). Lancet 2011, 377, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yawn, B.P.; Buchanan, G.R.; Afenyi-Annan, A.N.; Ballas, S.K.; Hassell, K.L.; James, A.H.; Jordan, L.; Lanzkron, S.M.; Lottenberg, R.; Savage, W.J.; et al. Management of sickle cell disease: Summary of the 2014 evidence-based report by expert panel members. JAMA 2014, 312, 1033–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, R.E.; Davis, B.R.; Schultz, W.H.; Brown, R.C.; Aygun, B.; Sarnaik, S.; Odame, I.; Fuh, B.; George, A.; Owen, W.; et al. Hydroxycarbamide versus chronic transfusion for maintenance of transcranial doppler flow velocities in children with sickle cell anaemia-TCD With Transfusions Changing to Hydroxyurea (TWiTCH): A multicentre, open-label, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernaudin, F.; Dalle, J.H.; Bories, D.; De Latour, R.P.; Robin, M.; Bertrand, Y.; Pondarre, C.; Vannier, J.P.; Neven, B.; Kuentz, M.; et al. Long-term event-free survival, chimerism and fertility outcomes in 234 patients with sickle-cell anemia younger than 30 years after myeloablative conditioning and matched-sibling transplantation in France. Haematologica 2019, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluckman, E.; Cappelli, B.; Bernaudin, F.; Labopin, M.; Volt, F.; Carreras, J.; Simões, B.P.; Ferster, A.; Dupont, S.; De La Fuente, J.; et al. Sickle cell disease: An international survey of results of HLA-identical sibling hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2017, 129, 1548–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacein-Bey-Abina, S.; Magrin, E.; Caccavelli, L.; Bourget, P.; Bartolucci, P.; Weber, L.; Beuzard, Y.; De Montalembert, M.; Blanche, S.; Leboulch, P.; et al. Gene Therapy in a Patient with Sickle Cell Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 848–855. [Google Scholar]

| Total | Paris Area | Province | French West Antilles | Mayotte-Réunion | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | 1620 (100) | 967 (59.6) | 443 (27.3) | 152 (9.4) | 58 (4.4) |
| SS/SB°/SDPunjab | 1164 (71.8) | 703 (72.7) | 336 (75.8) | 74 (48.7) | 51 (87.9) |
| SC/SB+/Other * | 456 (28.2) | 264 (27.3) | 107 (24.2) | 78 (51.3) | 7 (12.1) |
| Sex ratio (M/F) | 824 (50.9) | - | - | - | - |
| Size of Center † | Total | <10 | (10–20) | (20–50) | (50–100) | ≥100 | p Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nb. of centers | 69 | 24 | 18 | 17 | 8 | 2 | - |
| Nb. of patients | 1620 | 125 | 258 | 452 | 516 | 269 | - |
| Nb of patients with continued follow-up, n (%) | 1540 (95.1) | 116 (92.8) | 247 (95.7) | 421 (93.2) | 490 (94.9) | 266 (98.9) | 0.009 |
| No TCD screening N, (%) ** | 81 (7.0) | 15 (16.0) | 18 (9.4) | 25 (7.1) | 18 (5.6) | 5 (2.4) | <0.001 |
| Complete pneumococcal coverage # N, (%) | 768 (47.4) | 31 (24.8) | 89 (34.5) | 206 (45.6) | 230 (44.6) | 212 (78.8) | <0.001 |
| Probability of HU treatment ** n, % | 145 13.7% (11.7–15.9) | 14 16.5% (10.1–26.4) | 28 16.5% (11.7–23.1) | 27 8.4% (5.8–12) | 35 12.1% (8.8–16.4) | 41 21.2% (16–27.7) | <0.001 |
| Probability of TF program ** n, % | 204 18.4% (7.2–20.8) | 10 11.2% (6.2–19.8) | 27 15.0% (10.5–21.2) | 39 11.6% (8.6–15.6) | 56 18.2% (14.3–23) | 72 36.3% (30–43.5) | <0.001 |
| Probability of abnormal TCD ** n, % | 105 10.4% (8.6–12.4) | 8 10.5% (5.4–20.0) | 19 11.5% (7.5– 17.4) | 21 6.8% (4.5-10.3) | 19 7.0% (4.5–10.8) | 38 20.0% (15–26.5) | <0.001 |
| Causes of death (n = 18) |
|---|
| Unrelated causes: n = 6 |
| Pulmonary dysplasia |
| Spinal muscular atrophy |
| Neonatal herpes |
| Premature birth |
| Mitochondriopathy |
| Neonatal Streptococcus B meningitis |
| SCD-related infectious causes: n = 7 |
| Pneumococcal septicemia (n = 3) |
| Pneumococcal meningitis |
| Undocumented sepsis (n = 3) |
| Miscellaneous SCD-related causes: n = 5 |
| Dehydration |
| Acute pancreatitis |
| Acute cardiorespiratory failure |
| Acute splenic sequestration n = 2 |
| All | SS/SB° | SC/SB+ | P Value † | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First transfusion by 3 years by 5 years | 32.8% (30.6–35.2) 50.1% (47.6–52.6) | 43.8% (41.0–46.2) 65.2% (62.3–68.0) | 4.8% (3.2–7.3) 1.8% (9.1–15.2) | <0.001 |
| Splenectomy by 3 years by 5 years | 1.9% (1.4–2.7) 5.1% (4.1–6.3) | 2.7% (1.9–3.8) 7.0% (5.6–8.7) | 0 0.3% (0.04–1.9) | <0.001 |
| Cholecystectomy by 3 years by 5 years | 0.1% (0.03–0.5) 2.7% (2.0–3.7) | 0.2% (0.04–0.7) 3.7% (2.7–5.1) | 0 0 | <0.001 |
| Chronic Transfusion program * by 3 years by 5 years | 7.0% (5.9–8.4) 13.2% (11.6–15.0) | 9.7% (8.1–11.6) 18.4% (16.2–20.8) | 0.2% (0.03–1.6) 0.2% (0.03–1.6) | <0.001 |
| Hydroxyurea by 3 years by 5 years | 1.4% (0.9–2.1) 9.8% (8.4–11.5) | 1.9% (1.3–2.9) 13.7% (11.7–15.9) | 0 0 | <0.001 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brousse, V.; Arnaud, C.; Lesprit, E.; Quinet, B.; Odièvre, M.-H.; Etienne-Julan, M.; Guillaumat, C.; Elana, G.; Belloy, M.; Garnier, N.; et al. Evaluation of Outcomes and Quality of Care in Children with Sickle Cell Disease Diagnosed by Newborn Screening: A Real-World Nation-Wide Study in France. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101594
Brousse V, Arnaud C, Lesprit E, Quinet B, Odièvre M-H, Etienne-Julan M, Guillaumat C, Elana G, Belloy M, Garnier N, et al. Evaluation of Outcomes and Quality of Care in Children with Sickle Cell Disease Diagnosed by Newborn Screening: A Real-World Nation-Wide Study in France. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(10):1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101594
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrousse, Valentine, Cécile Arnaud, Emmanuelle Lesprit, Béatrice Quinet, Marie-Hélène Odièvre, Maryse Etienne-Julan, Cécile Guillaumat, Gisèle Elana, Marie Belloy, Nathalie Garnier, and et al. 2019. "Evaluation of Outcomes and Quality of Care in Children with Sickle Cell Disease Diagnosed by Newborn Screening: A Real-World Nation-Wide Study in France" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 10: 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101594
APA StyleBrousse, V., Arnaud, C., Lesprit, E., Quinet, B., Odièvre, M.-H., Etienne-Julan, M., Guillaumat, C., Elana, G., Belloy, M., Garnier, N., Chamouine, A., Dumesnil, C., De Montalembert, M., Pondarre, C., Bernaudin, F., Couque, N., Boutin, E., Bardakjian, J., Djennaoui, F., ... Thuret, I. (2019). Evaluation of Outcomes and Quality of Care in Children with Sickle Cell Disease Diagnosed by Newborn Screening: A Real-World Nation-Wide Study in France. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(10), 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101594





