Atrial Fibrillation Ablation with Multipolar Phased-Radiofrequency Catheter: The Learning Curve Effect for Procedural Parameters, but not for the Long-Term Outcome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Periprocedural Management
2.3. Ablation Procedure
2.4. Follow-Up
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Procedural Parameters and Acute Effects of Pulmonary Vein Isolation
3.2. Relapse in the Blanking Period
3.3. Long-Term Follow-up
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirchhof, P.; Benussi, S.; Kotecha, D.; Ahlsson, A.; Atar, D.; Casadei, B.; Castella, M.; Diener, H.C.; Heidbuchel, H.; Hendriks, J.; et al. ESC Scientific Document Group. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2893–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calkins, H.; Hindricks, G.; Cappato, R.; Kim, Y.H.; Saad, E.B.; Aguinaga, L.; Akar, J.G.; Badhwar, V.; Brugada, J.; Camm, J.; et al. 2017 HRS/EHRA/ ECAS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 2017, 14, e275–e444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaji, T.; Shizuta, S.; Morimoto, T.; Aizawa, T.; Yamagami, S.; Yoshizawa, T.; Ota, C.; Onishi, N.; Sasaki, Y.; Yahata, M.; et al. Very long-term clinical outcomes after radiofrequency catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: A large single-center experience. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 249, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Jiang, C.Y.; Betts, T.R.; Chen, J.; Deisenhofer, I.; Mantovan, R.; Macle, L.; Morillo, C.A.; Haverkamp, W.; Weerasooriya, R.; et al. STAR AF II Investigators. Approaches to catheter ablation for persistent atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1812–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Belle, Y.; Janse, P.; Rivero-Ayerza, M.J.; Thornton, A.S.; Jessurun, E.R.; Theuns, D.; Jordaens, L. Pulmonary vein isolation using an occluding cryoballoon for circumferential ablation: Feasibility, complications, and short-term outcome. Eur. Heart J. 2007, 28, 2231–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boersma, L.V.; Wijffels, M.C.; Oral, H.; Wever, E.F.; Morady, F. Pulmonary vein isolation by duty-cycled bipolar and unipolar radiofrequency energy with a multielectrode ablation catheter. Heart Rhythm 2008, 5, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharf, C.; Boersma, L.; Davies, W.; Kanagaratnam, P.; Peters, N.S.; Paul, V.; Rowland, E.; Grace, A.; Fynn, S.; Dang, L.; et al. Ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation using multielectrode catheters and duty-cycled radiofrequency energy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 1450–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duytschaever, M.; Anne, W.; Papiashvili, G.; Vandekerckhove, Y.; Tavernier, R. Mapping and isolation of the pulmonary veins using the PVAC catheter. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2010, 33, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal, P.; Aarntzen, A.E.; Smit, J.J.; Adiyaman, A.; Misier, A.R.; Delnoy, P.P.; Elvan, A. Conventional radiofrequency catheter ablation compared to multi-electrode ablation for atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 76, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCready, J.; Chow, A.W.; Lowe, M.D.; Segal, O.R.; Ahsan, S.; de Bono, J.; Dhaliwal, M.; Mfuko, C.; Ng, A.; Rowland, E.R.; et al. Safety and efficacy of multipolar pulmonary vein ablation catheter vs. irrigated radiofrequency ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: A randomized multicenter trial. Europace 2014, 16, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuck, K.H.; Brugada, J.; Fürnkranz, A.; Metzner, A.; Ouyang, F.; Chun, K.R.; Elvan, A.; Arentz, T.; Bestehorn, K.; Pocock, S.J.; et al. Fire and ice investigators. Cryoballoon or radiofrequency ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2235–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.F.; Gao, X.F.; Duan, X.; Chen, B.; Liu, X.H.; Xu, Y.Z. Comparison of catheter ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation between cryoballoon and radiofrequency: A meta-analysis. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2017, 48, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velagić, V.; de Asmundis, C.; Mugnai, G.; Hünük, B.; Hacioğlu, E.; Ströker, E.; Moran, D.; Ruggiero, D.; Poelaert, J.; Verborgh, C.; et al. Learning curve using the second-generation cryoballoon ablation. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2017, 18, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martirosyan, M.; Kiss, A.; Nagy-Baló, E.; Sándorfi, G.; Tint, D.; Édes, I. Learning curve in circular multipolar phased radiofrequency ablation of atrial fibrillation. Cardiol. J. 2015, 22, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wojcik, M.; Berkowitsch, A.; Greis, H.; Zaltsberg, S.; Hamm, C.W.; Pitschner, H.F.; Kuniss, M.; Neumann, T. Learning Curve in Cryoballoon Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. J. 2014, 78, 1612–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Biase, L.; Burkhardt, J.D.; Mohanty, J.; Sanchez, J.D.; Horton, R.; Gallinghouse, G.J.; Lakkireddy, D.; Verma, A.; Khaykin, Y.; Hongo, R.; et al. Periprocedural stroke and management of major bleeding complications in patients undergoing catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: The impact of periprocedural therapeutic international normalized ratio. Circulation 2010, 121, 2550–2556. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Glowniak, A.; Tarkowski, A.; Janczarek, M.; Wysokinski, A. Silent cerebral infarcts following pulmonary vein isolation with different techniques—Incidence and risk factors. Arch. Med. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Debruyne, P.; Nardi, S.; Deneke, T.; De Greef, Y.; Spitzer, S.; Balzer, J.O.; Boersma, L. ERACE Investigators. Evaluation and reduction of asymptomatic cerebral embolism in ablation of atrial fibrillation.; but high prevalence of chronic silent infarction: Results of the ERACE trial. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2013, 6, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Greef, Y.; Dekker, L.; Boersma, L.; Murray, S.; Wieczorek, M.; Spitzer, S.G.; Davidson, N.; Furniss, S.; Hocini, M.; Geller, J.C.; et al. PRECISION GOLD investigators. Low rate of asymptomatic cerebral embolism and improved procedural efficiency with the novel pulmonary vein ablation catheter GOLD: Results of the PRECISION GOLD trial. Europace 2016, 18, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, M.; Lukat, M.; Hoeltgen, R.; Condie, C.; Hilje, T.; Missler, U.; Hirsch, J.; Scharf, C. Investigation into causes of abnormal cerebral MRI findings following PVAC duty-cycled.; phased RF ablation of atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2013, 24, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozluk, E.; Piatkowska, A.; Rodkiewicz, D.; Peller, M.; Kochanowski, J.; Opolski, G. Direct results of a prospective randomized study comparing ablation with the nMARQ catheter and the PVAC catheter used with and without a 3D system (MAPER 3D Study). Arch. Med. Sci. 2017, 15, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boersma, L.V.A.; Kozluk, E.; Maglia, G.; De Sousa, J.; Grebe, O.; Eckhardt, L.; Park, H.; Rovaris, G.; Arribas, F.; Arenal, A.; et al. Procedural outcomes of pulmonary vein isolation with the PVAC Gold ablation catheter: Results from the prospective multicenter gold AF registry. Europace 2018, 20 (Suppl. 1), i123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieragnoli, P.; Paoletti Perini, A.; Ricciardi, G.; Checchi, L.; Giomi, A.; Muraca, I.; Mannucci, L.; Padeletti, L. Recurrences in the blanking period and 12-month success rate by continuous cardiac monitoring after cryoablation of paroxysmal and non-paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2017, 28, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, S.; Khairy, P.; Andrade, J.G.; Hoffmann, B.A.; Levesque, S.; Verma, A.; Weerasooriya, R.; Novak, P.; Arentz, T.; Deisenhofer, I.; et al. ADVICE Trial Investigators. Redefining the Blanking Period After Catheter Ablation for Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation: Insights from the ADVICE (Adenosine Following Pulmonary Vein Isolation to Target Dormant Conduction Elimination) Trial. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2016, 9, e003909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allam, L.E.; Moteleb, A.M.A.E.; Ghanem, M.T. Predictors of Short and Long Term Recurrences of Paroxysmal AF after Radiofrequency Ablation. Is Blanking Period Really Benign? J. Atr. Fibrillation 2018, 11, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glowniak, A.; Tarkowski, A.; Fic, P.; Wojewoda, K.; Wojcik, J.; Wysokinski, A. Second-generation cryoballoon ablation for recurrent atrial fibrillation after an index procedure with radiofrequency versus cryo: Different pulmonary vein reconnection patterns but similar long-term outcome—Results of a multicenter analysis. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2019, 30, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spragg, D.D.; Dalal, D.; Cheema, A.; Scherr, D.; Chilukuri, K.; Cheng, A.; Henrikson, C.A.; Marine, J.E.; Berger, R.D.; Dong, J.; et al. Complications of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: Incidence and predictors. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2008, 19, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sairaku, A.; Nakano, Y.; Oda, N.; Makita, Y.; Kajihara, K.; Tokuyama, T.; Kihara, Y. Learning curve for ablation of atrial fibrillation in medium-volume centers. J. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics | Tierce 1 (n = 42) | Tierce 2 (n = 42) | Tierce 3 (n = 42) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| age in years, mean ± SD | 57.4 ± 9.1 | 57.6 ± 8.1 | 61.7 ± 8.4 | 0.034 |
| male gender, n (%) | 32 (32.7) | 32 (32.7) | 34 (34.7) | 0.83 |
| BMI in kg/m2, mean ± SD | 27.7 ± 3.1 | 27.8 ± 2.7 | 26.7 ± 2.7 | 0.21 |
| congestive heart failure, n (%) | 2 (4.8) | 3 (7.1) | 0 (0) | 0.23 |
| hypertension, n (%) | 31 (73.8) | 25 (59.5) | 31 (73.8) | 0.26 |
| diabetes, n (%) | 6 (14.3) | 8 (19.1) | 7 (16.7) | 0.84 |
| previous stroke, n (%) | 0 (0) | 1 (2.4) | 0 (0) | 0.36 |
| vascular disease, n (%) | 5 (11.9) | 7 (16.7) | 9 (21.4) | 0.50 |
| CHA2DS2-VASc score, mean ± SD | 1.5 ± 1.1/1 (0–5) | 1.5 ± 1.3/1.5 (0–5) | 1.7 ± 1.0/1.5 (0–4) | 0.69 |
| LA diameter in mm, mean ± SD | 43.0 ± 2.7 | 43.0 ± 3.6 | 42.7 ± 3.0 | 0.85 |
| LVEF (%), mean ± SD | 60.2±5.2 | 59.4±6.1 | 60.0±5.1 | 0.75 |
| atypical PV anatomy, n (%) | 7 (16.7) | 18 (42.9) | 16 (38.1) | 0.024 |
| paroxysmal AF, n (%) | 40 (95.2) | 39 (92.9) | 39 (92.9) | 0.88 |
| time from diagnosis, median (range) | 41 (12–132) | 32.5 (12–144) | 30 (12–144) | 0.32 |
| Characteristics | Tierce 1 (n = 42) | Tierce 2 (n = 42) | Tierce 3 (n = 42) | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
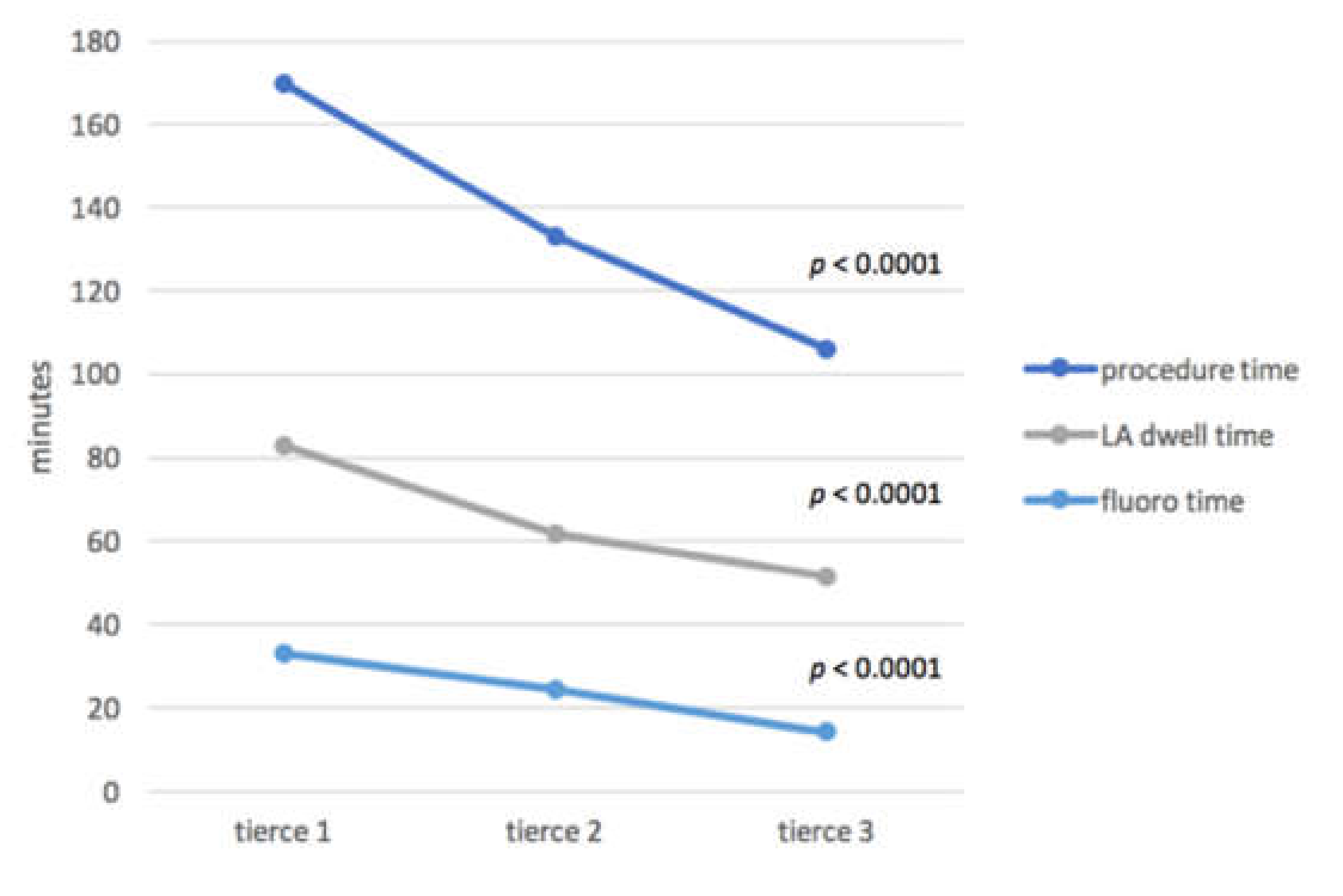
| procedure time, mean ± SD | 169.8 ± 27.5 | 132.9 ± 20.3 | 105.8 ± 19.7 | <0.0001 |
| LA dwell time, mean ± SD | 83.0 ± 18.6 | 61.9 ± 5.5 | 51.4 ± 7.5 | <0.0001 |
| fluoroscopy time, mean ± SD | 32.9±7.7 | 24.3±5.9 | 14.1±4.9 | <0.0001 |
| No of RF applications, median (range) | 24 (24–30) | 24 (20–28) | 23 (20–26) | 0.0024 |
| complications, n (%) | 3 (7.1) | 3 (7.1) | 3 (7.1) | 0.32 |
| acute effect (no of veins isolated), (%) | 169/173 (97.7) | 172/174 (98.9) | 175/179 (97.8) | 0.67 |
| relapse in the blanking period, n (%) | 24/42 (57.1) | 19/42 (45.2) | 23/42 (54.8) | 0.51 |
| arrhythmia free after 12 months, n (%) | 24 (57.1) | 26 (61.9) | 26 (61.9) | 0.88 |
| Parameter | Univariate | Multivariate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p Value | HR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| age | 1.04 (0.99–1.08) | 0.13 | ||
| sex | 0.89 (0.40–2.01) | 0.82 | ||
| AF type | 2.09 (0.71–6.17) | 0.18 | ||
| EHRA | 1.51 (0.84–2.74) | 0.17 | ||
| procedure time | 0.99 (0.98–1.01) | 0.48 | ||
| LA dwell time | 1.01 (0.98–1.04) | 0.42 | ||
| CHA2DS2-VASc | 0.88 (0.59–1.32) | 0.53 | ||
| body mass index | 1.00 (0.90–1.11) | 0.99 | ||
| LA diameter | 1.15 (1.02–1.30) | 0.027 | 1.14 (1.03–1.26) | 0.012 |
| LV ejection fraction | 0.98 (0.92–1.04) | 0.58 | ||
| atypical PV anatomy | 0.70 (0.34–1.44) | 0.33 | ||
| time from AF diagnosis | 1.01 (1.00–1.02) | 0.0044 | 1.01 (1.00–1.02) | 0.003 |
| relapse in blanking period | 7.34 (3.19–16.89) | <0.0001 | 6.67 (3.02–14.74) | <0.0001 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Glowniak, A.; Tarkowski, A.; Wojewoda, K.; Wysokinska, K.; Kozak, M.; Wacinski, P.; Wysokinski, A. Atrial Fibrillation Ablation with Multipolar Phased-Radiofrequency Catheter: The Learning Curve Effect for Procedural Parameters, but not for the Long-Term Outcome. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101589
Glowniak A, Tarkowski A, Wojewoda K, Wysokinska K, Kozak M, Wacinski P, Wysokinski A. Atrial Fibrillation Ablation with Multipolar Phased-Radiofrequency Catheter: The Learning Curve Effect for Procedural Parameters, but not for the Long-Term Outcome. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(10):1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101589
Chicago/Turabian StyleGlowniak, Andrzej, Adam Tarkowski, Katarzyna Wojewoda, Katarzyna Wysokinska, Mariusz Kozak, Piotr Wacinski, and Andrzej Wysokinski. 2019. "Atrial Fibrillation Ablation with Multipolar Phased-Radiofrequency Catheter: The Learning Curve Effect for Procedural Parameters, but not for the Long-Term Outcome" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 10: 1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101589
APA StyleGlowniak, A., Tarkowski, A., Wojewoda, K., Wysokinska, K., Kozak, M., Wacinski, P., & Wysokinski, A. (2019). Atrial Fibrillation Ablation with Multipolar Phased-Radiofrequency Catheter: The Learning Curve Effect for Procedural Parameters, but not for the Long-Term Outcome. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(10), 1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101589






