Advancements in Nucleic Acid Based Therapeutics against Respiratory Viral Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Nucleic Acid-Based Therapeutics
2.1. RNA Therapeutics against Respiratory Viruses
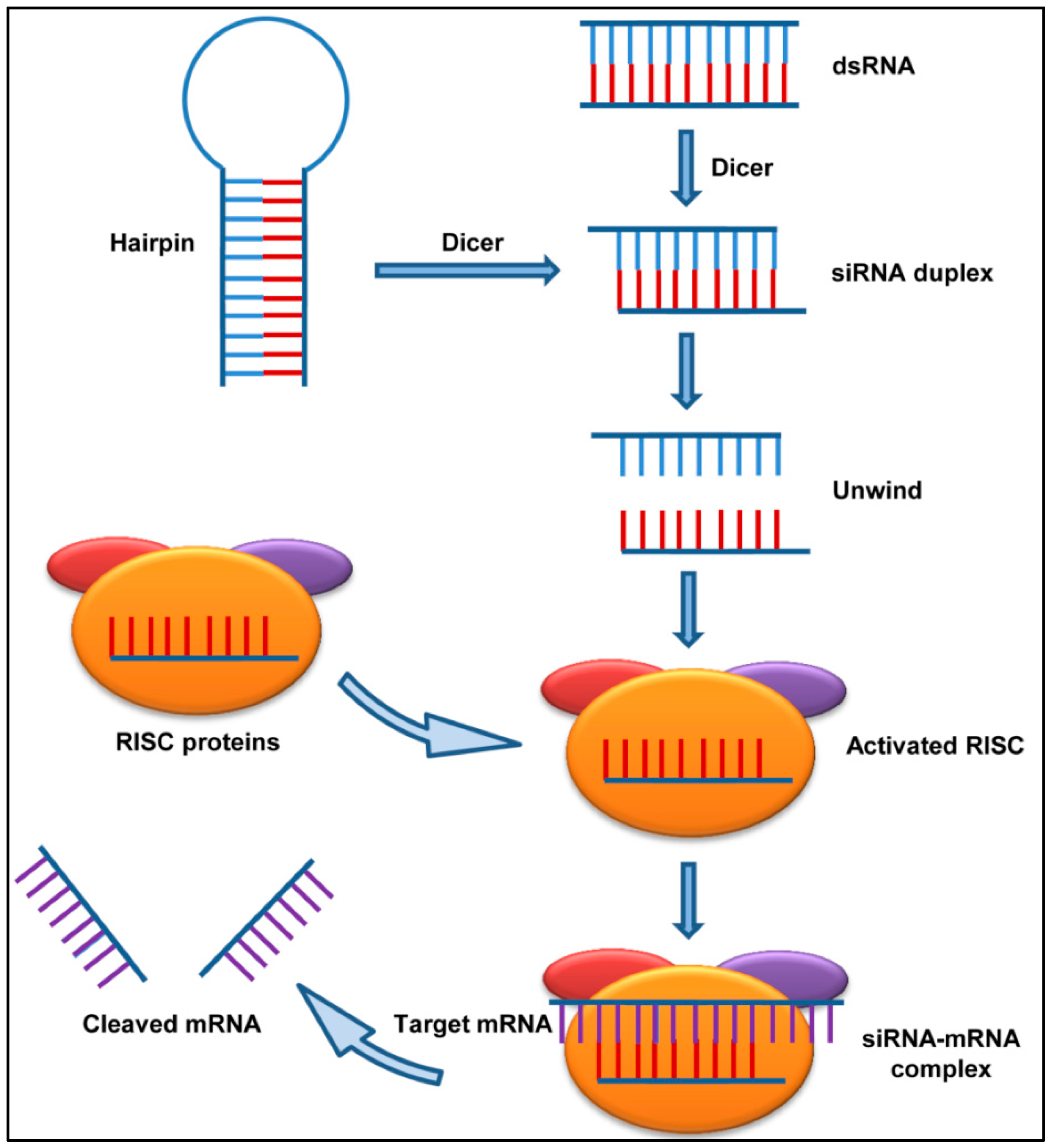
2.1.1. Short Interfering RNAs (siRNAs)
2.1.2. siRNAs against Respiratory Viruses
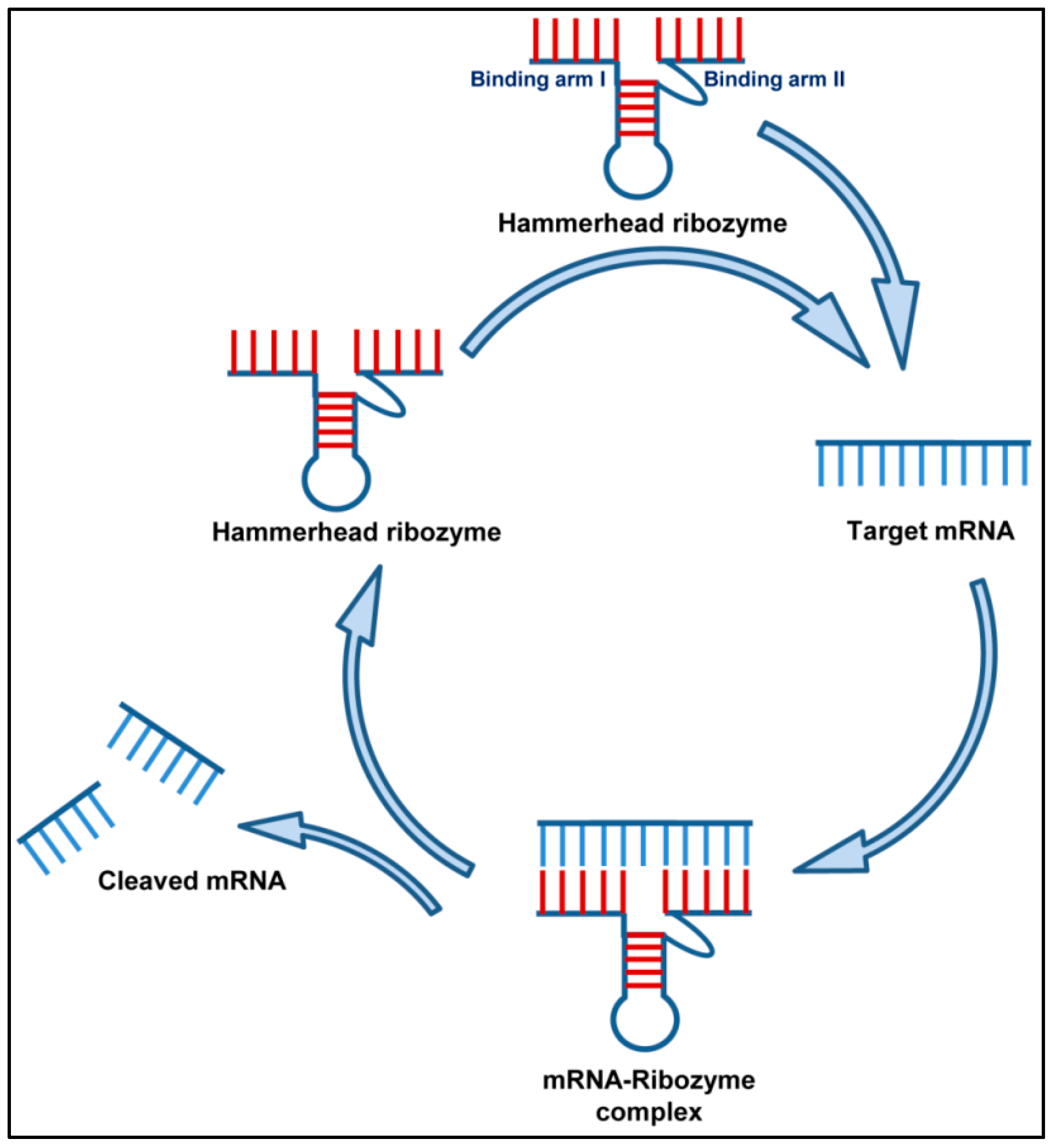
2.1.3. Ribozymes (Rz)
2.1.4. Ribozymes against Respiratory Viruses
2.2. DNA Therapeutics against Respiratory Viruses
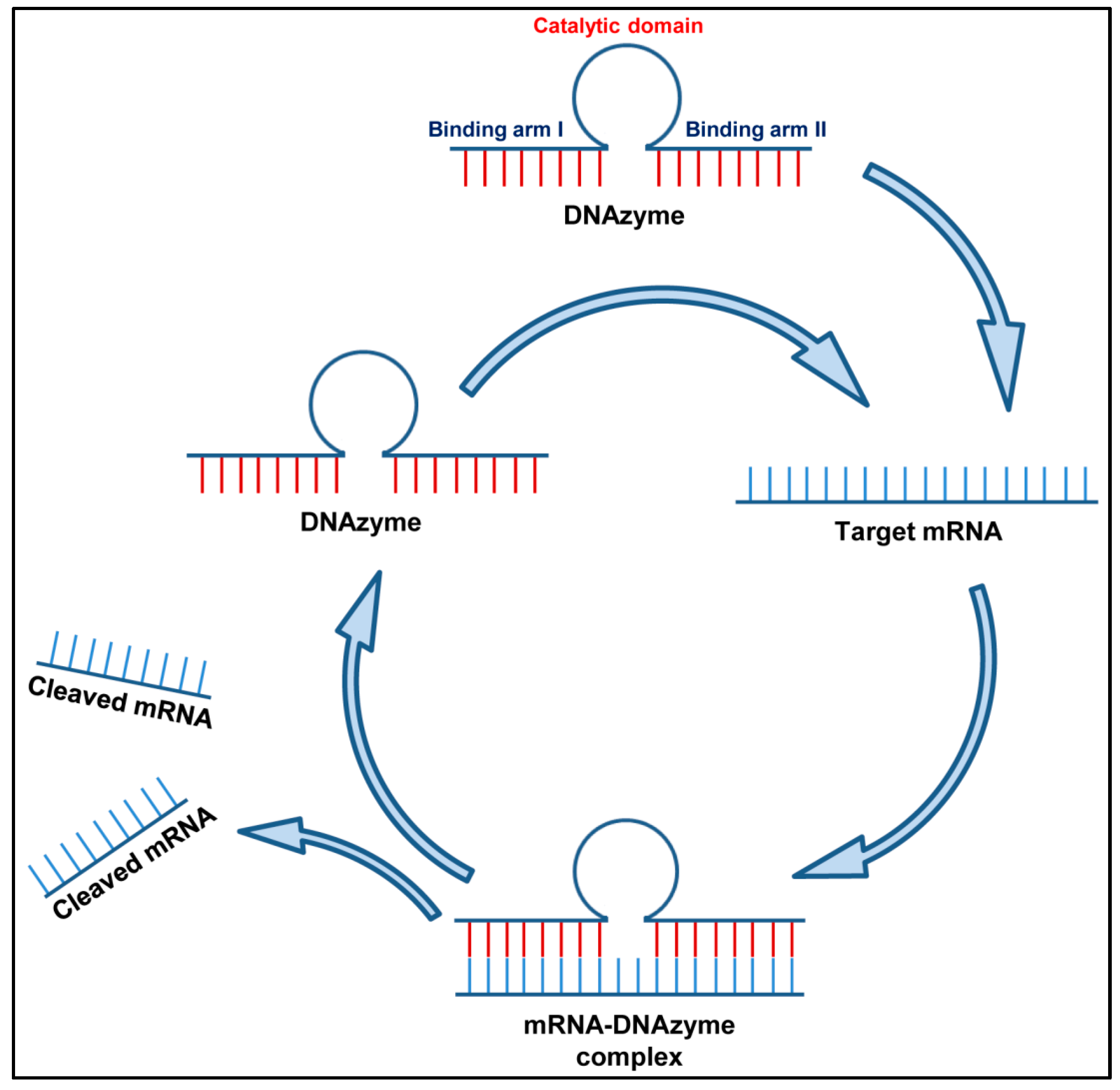
2.2.1. Deoxyribozymes (Dz)
2.2.2. DNAzymes against Respiratory Viruses
2.2.3. Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs)
2.2.4. Antisense Oligonucleotides against Respiratory Viruses
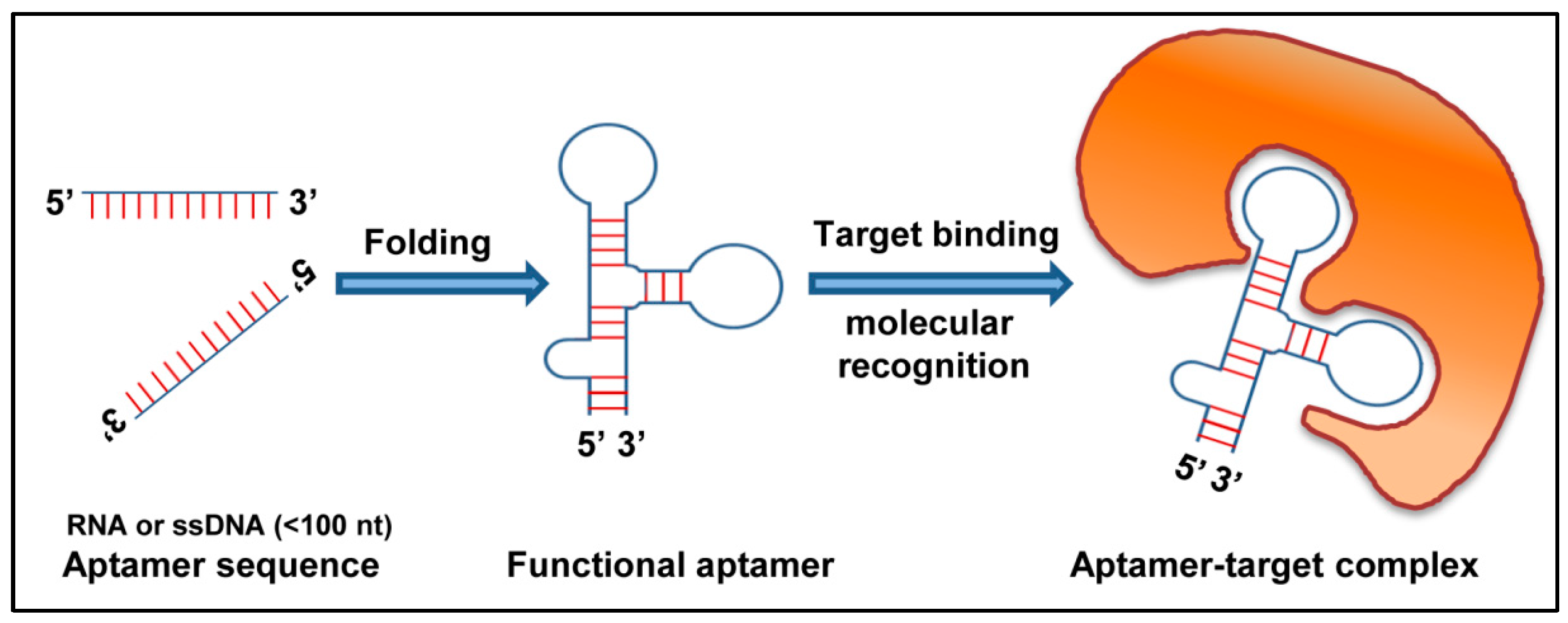
2.3. Aptamers
Aptamers against Respiratory Viruses
3. Methods of Delivery and Challenges
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khanna, M.; Kumar, P.; Choudhary, K.; Kumar, B.; Vijayan, V.K. Emerging influenza virus: A global threat. J. Biosci. 2008, 33, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, M.; Kumar, B.; Gupta, A.; Kumar, P. Pandemic Influenza a H1N1 (2009) Virus: Lessons from the Past and Implications for the Future. Indian J. Virol. 2012, 23, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, M.; Kumar, B.; Gupta, N.; Kumar, P.; Gupta, A.; Vijayan, V.K.; Kaur, H. Pandemic swine influenza virus (H1N1): A threatening evolution. Indian J. Microbiol. 2009, 49, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.; Asha, K.; Khanna, M.; Ronsard, L.; Meseko, C.A.; Sanicas, M. The emerging influenza virus threat: Status and new prospects for its therapy and control. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, S.; Fraser, C.; Donnelly, C.A.; Ghani, A.C.; Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Hedley, A.J.; Leung, G.M.; Ho, L.M.; Lam, T.H.; Thach, T.Q.; et al. Transmission dynamics of the etiological agent of SARS in Hong Kong: Impact of public health interventions. Science 2003, 300, 1961–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perlman, S.; Netland, J. Coronaviruses post-SARS: Update on replication and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monne, I.; Meseko, C.; Joannis, T.; Shittu, I.; Ahmed, M.; Tassoni, L.; Fusaro, A.; Cattoli, G. Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Virus in Poultry, Nigeria, 2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1275–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meseko, C.; Globig, A.; Ijomanta, J.; Joannis, T.; Nwosuh, C.; Shamaki, D.; Harder, T.; Hoffman, D.; Pohlmann, A.; Beer, M.; et al. Evidence of exposure of domestic pigs to Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza H5N1 in Nigeria. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasina, F.O.; Bisschop, S.P.; Ibironke, A.A.; Meseko, C.A. Avian influenza risk perception among poultry workers, Nigeria. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 616–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, M.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, B.; Rajput, R. Protective immunity based on the conserved hemagglutinin stalk domain and its prospects for universal influenza vaccine development. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 546274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudas, R.A.; Karron, R.A. Respiratory syncytial virus vaccines. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gewirtz, A.M.; Sokol, D.L.; Ratajczak, M.Z. Nucleic acid therapeutics: State of the art and future prospects. Blood 1998, 92, 712–736. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Merdan, T.; Kopecek, J.; Kissel, T. Prospects for cationic polymers in gene and oligonucleotide therapy against cancer. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 715–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Boado, R.J.; Pardridge, W.M. Brain-specific expression of an exogenous gene after I.V. administration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12754–12759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehsan, A.; Mann, M.J.; Dell’Acqua, G.; Dzau, V.J. Long-term stabilization of vein graft wall architecture and prolonged resistance to experimental atherosclerosis after E2F decoy oligonucleotide gene therapy. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2001, 121, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, N.M.; McKay, R.; Condon, T.P.; Bennett, C.F. Inhibition of protein kinase C-alpha expression in human A549 cells by antisense oligonucleotides inhibits induction of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) mRNA by phorbol esters. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 16416–16424. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Compagno, D.; Lampe, J.N.; Bourget, C.; Kutyavin, I.V.; Yurchenko, L.; Lukhtanov, E.A.; Gorn, V.V.; Gamper, H.B., Jr.; Toulme, J.J. Antisense oligonucleotides containing modified bases inhibit in vitro translation of Leishmania amazonensis mRNAs by invading the mini-exon hairpin. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 8191–8198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, J.L.; Ely, J.A.; Sun, L.Q.; Symonds, G.P. Ribozymes in gene therapy of HIV-1. Front. Biosci. 1999, 4, D497–D505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Gupta, N.; Subramanian, N.; Mondal, T.; Banerjea, A.C.; Das, S. Sequence-specific cleavage of hepatitis C virus RNA by DNAzymes: Inhibition of viral RNA translation and replication. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, M.; Saxena, L.; Rajput, R.; Kumar, B.; Prasad, R. Gene silencing: A therapeutic approach to combat influenza virus infections. Future Microbiol. 2015, 10, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbashir, S.M.; Harborth, J.; Lendeckel, W.; Yalcin, A.; Weber, K.; Tuschl, T. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature 2001, 411, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, N.; Dasaradhi, P.V.; Mohmmed, A.; Malhotra, P.; Bhatnagar, R.K.; Mukherjee, S.K. RNA interference: Biology, mechanism, and applications. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2003, 67, 657–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, A.J.; Baulcombe, D.C. A species of small antisense RNA in posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science 1999, 286, 950–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fire, A.; Xu, S.; Montgomery, M.K.; Kostas, S.A.; Driver, S.E.; Mello, C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998, 391, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koli, U.; Krishnan, R.A.; Pofali, P.; Jain, R.; Dandekar, P. SiRNA-based therapies for pulmonary diseases. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 1953–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Fraga, M.; Wright, N.; Jimenez, A. RNA interference-based therapeutics: New strategies to fight infectious disease. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 2008, 8, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitko, V.; Barik, S. Phenotypic silencing of cytoplasmic genes using sequence-specific double-stranded short interfering RNA and its application in the reverse genetics of wild type negative-strand RNA viruses. BMC Microbiol. 2001, 1, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Kwok, P.C.; Chow, M.Y.; Tang, P.; Mason, A.J.; Chan, H.K.; Lam, J.K. Formulation of pH responsive peptides as inhalable dry powders for pulmonary delivery of nucleic acids. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 86, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.; Lu, J.J.; Ge, Q.; Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Klibanov, A.M. Full deacylation of polyethylenimine dramatically boosts its gene delivery efficiency and specificity to mouse lung. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5679–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Eisen, H.N.; Chen, J. Use of siRNAs to prevent and treat influenza virus infection. Virus Res. 2004, 102, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoppani, E.; Bassi, I.; Dotti, S.; Lizier, M.; Ferrari, M.; Lucchini, F. Expression of a single siRNA against a conserved region of NP gene strongly inhibits in vitro replication of different Influenza A virus strains of avian and swine origin. Antivir. Res. 2015, 120, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.J.; Tang, Q.; Cheng, D.; Qin, C.; Xie, F.Y.; Wei, Q.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, B.J.; Woodle, M.C.; et al. Using siRNA in prophylactic and therapeutic regimens against SARS coronavirus in Rhesus macaque. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbaniak, K.; Kowalczyk, A.; Markowska-Daniel, I. Influenza A viruses of avian origin circulating in pigs and other mammals. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2014, 61, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pati, D.R.; Khanna, M.; Kumar, B.; Kumar, P.; Rajput, R.; Saxena, L.; Sharvani; Gaur, S.N. Clinical presentation of patients with seasonal influenza and pandemic influenza A (H1N1-2009) requiring hospitalisation. Indian J. Chest Dis. Allied Sci. 2013, 55, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.; Khanna, M.; Kumar, P.; Gupta, A.; Daga, M.; Chawla-Sarkar, M.; Chadha, M.; Mishra, A.; Kaur, H. Quantification of viral load in clinical specimens collected from different body sites of patients infected with influenza viruses. Int. J. Med. Med. Sci. 2011, 3, 144–148. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Kumar, B.; Gupta, A.; Sharma, B.; Vijayan, V.K.; Khare, S.; Singh, V.; Daga, M.K.; Chadha, M.S.; Mishra, A.C.; et al. Diagnosis of Novel Pandemic Influenza Virus 2009 H1N1 in Hospitalized Patients. Indian J. Virol. 2010, 21, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, C.M.; Blanton, L.; Dhara, R.; Brammer, L.; Finelli, L. 2009 Pandemic influenza A (H1N1) deaths among children—United States, 2009–2010. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52 (Suppl. 1), S69–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawood, F.S.; Iuliano, A.D.; Reed, C.; Meltzer, M.I.; Shay, D.K.; Cheng, P.Y.; Bandaranayake, D.; Breiman, R.F.; Brooks, W.A.; Buchy, P.; et al. Estimated global mortality associated with the first 12 months of 2009 pandemic influenza A H1N1 virus circulation: A modelling study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, M.; Saxena, L.; Gupta, A.; Kumar, B.; Rajput, R. Influenza pandemics of 1918 and 2009: A comparative account. Future Virol. 2013, 8, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glezen, W.P. Emerging infections: Pandemic influenza. Epidemiol. Rev. 1996, 18, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meseko, C.; Kumar, B.; Sanicas, M. Preventing zoonotic influenza. In Influenza Therapeutics and Challenges; Saxena, S.K., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscona, A. Neuraminidase inhibitors for influenza. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurt, A.C.; Ho, H.T.; Barr, I. Resistance to anti-influenza drugs: Adamantanes and neuraminidase inhibitors. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2006, 4, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKimm-Breschkin, J.L. Influenza neuraminidase inhibitors: Antiviral action and mechanisms of resistance. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2013, 7 (Suppl. 1), 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, A.C.; Chotpitayasunondh, T.; Cox, N.J.; Daniels, R.; Fry, A.M.; Gubareva, L.V.; Hayden, F.G.; Hui, D.S.; Hungnes, O.; Lackenby, A.; et al. Antiviral resistance during the 2009 influenza A H1N1 pandemic: Public health, laboratory, and clinical perspectives. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.X.; Li, H.; Lu, R.; Li, F.; Dus, M.; Atkinson, P.; Brydon, E.W.; Johnson, K.L.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; Ball, L.A.; et al. Interferon antagonist proteins of influenza and vaccinia viruses are suppressors of RNA silencing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElHefnawi, M.; Alaidi, O.; Mohamed, N.; Kamar, M.; El-Azab, I.; Zada, S.; Siam, R. Identification of novel conserved functional motifs across most Influenza A viral strains. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Q.; McManus, M.T.; Nguyen, T.; Shen, C.H.; Sharp, P.A.; Eisen, H.N.; Chen, J. RNA interference of influenza virus production by directly targeting mRNA for degradation and indirectly inhibiting all viral RNA transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2718–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Q.; Filip, L.; Bai, A.; Nguyen, T.; Eisen, H.N.; Chen, J. Inhibition of influenza virus production in virus-infected mice by RNA interference. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8676–8681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tompkins, S.M.; Lo, C.Y.; Tumpey, T.M.; Epstein, S.L. Protection against lethal influenza virus challenge by RNA interference in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8682–8686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, R.; Khanna, M.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, B.; Sharma, S.; Gupta, N.; Saxena, L. Small interfering RNA targeting the nonstructural gene 1 transcript inhibits influenza A virus replication in experimental mice. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2012, 22, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Sood, V.; Vyas, R.; Gupta, N.; Banerjea, A.C.; Khanna, M. Potent inhibition of influenza virus replication with novel siRNA-chimeric-ribozyme constructs. Antivir. Res. 2010, 87, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Jin, M.; Yu, Z.; Xu, X.; Peng, Y.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Cao, S.; Chen, H. Effective small interfering RNAs targeting matrix and nucleocapsid protein gene inhibit influenza A virus replication in cells and mice. Antivir. Res. 2007, 76, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornung, V.; Guenthner-Biller, M.; Bourquin, C.; Ablasser, A.; Schlee, M.; Uematsu, S.; Noronha, A.; Manoharan, M.; Akira, S.; de Fougerolles, A.; et al. Sequence-specific potent induction of IFN-alpha by short interfering RNA in plasmacytoid dendritic cells through TLR7. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judge, A.D.; Sood, V.; Shaw, J.R.; Fang, D.; McClintock, K.; MacLachlan, I. Sequence-dependent stimulation of the mammalian innate immune response by synthetic siRNA. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, T.; Engelhardt, O.G.; Thomas, B.; Akoulitchev, A.V.; Brownlee, G.G.; Fodor, E. Role of ran binding protein 5 in nuclear import and assembly of the influenza virus RNA polymerase complex. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 11911–11919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchers, A.T.; Chang, C.; Gershwin, M.E.; Gershwin, L.J. Respiratory syncytial virus—A comprehensive review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 45, 331–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralston, S.L.; Lieberthal, A.S.; Meissner, H.C.; Alverson, B.K.; Baley, J.E.; Gadomski, A.M.; Johnson, D.W.; Light, M.J.; Maraqa, N.F.; Mendonca, E.A.; et al. Clinical practice guideline: The diagnosis, management, and prevention of bronchiolitis. Pediatrics 2014, 134, e1474–e1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falsey, A.R.; Walsh, E.E. Respiratory syncytial virus infection in adults. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falsey, A.R. Respiratory syncytial virus infection in elderly and high-risk adults. Exp. Lung Res. 2005, 31 (Suppl. 1), 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, L.J.; Dormitzer, P.R.; Nokes, D.J.; Rappuoli, R.; Roca, A.; Graham, B.S. Strategic priorities for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine development. Vaccine 2013, 31 (Suppl. 2), B209–B215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVincenzo, J.; Cehelsky, J.E.; Alvarez, R.; Elbashir, S.; Harborth, J.; Toudjarska, I.; Nechev, L.; Murugaiah, V.; Van Vliet, A.; Vaishnaw, A.K.; et al. Evaluation of the safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of ALN-RSV01, a novel RNAi antiviral therapeutic directed against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Antivir. Res. 2008, 77, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitko, V.; Musiyenko, A.; Shulyayeva, O.; Barik, S. Inhibition of respiratory viruses by nasally administered siRNA. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVincenzo, J.; Lambkin-Williams, R.; Wilkinson, T.; Cehelsky, J.; Nochur, S.; Walsh, E.; Meyers, R.; Gollob, J.; Vaishnaw, A. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of an RNAi-based therapy directed against respiratory syncytial virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8800–8805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, J.; Zamora, M.R.; Hodges, T.; Musk, A.W.; Sommerwerk, U.; Dilling, D.; Arcasoy, S.; DeVincenzo, J.; Karsten, V.; Shah, S.; et al. ALN-RSV01 for prevention of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after respiratory syncytial virus infection in lung transplant recipients. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2016, 35, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musiyenko, A.; Bitko, V.; Barik, S. RNAi-dependent and -independent antiviral phenotypes of chromosomally integrated shRNA clones: Role of VASP in respiratory syncytial virus growth. J. Mol. Med. (Berl.) 2007, 85, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harpen, M.; Barik, T.; Musiyenko, A.; Barik, S. Mutational analysis reveals a noncontractile but interactive role of actin and profilin in viral RNA-dependent RNA synthesis. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10869–10876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitko, V.; Oldenburg, A.; Garmon, N.E.; Barik, S. Profilin is required for viral morphogenesis, syncytium formation, and cell-specific stress fiber induction by respiratory syncytial virus. BMC Microbiol. 2003, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, E.; Mahoney, N.M.; Almo, S.C.; Barik, S. Profilin is required for optimal actin-dependent transcription of respiratory syncytial virus genome RNA. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ren, L.; Zhao, X.; Hung, T.; Meng, A.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.G. Inhibition of severe acute respiratory syndrome virus replication by small interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 7523–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.J.; Huang, H.W.; Liu, C.Y.; Hong, C.F.; Chan, Y.L. Inhibition of SARS-CoV replication by siRNA. Antivir. Res. 2005, 65, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Fu, L.; Yu, C.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Ning, H.; Zhang, S.; Chen, W.; et al. Silencing SARS-CoV Spike protein expression in cultured cells by RNA interference. FEBS Lett. 2004, 560, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Li, B.; Woodle, M.; Lu, P.Y. Application of siRNA against SARS in the rhesus macaque model. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 442, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyrc, K.; Bosch, B.J.; Berkhout, B.; Jebbink, M.F.; Dijkman, R.; Rottier, P.; van der Hoek, L. Inhibition of human coronavirus NL63 infection at early stages of the replication cycle. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 2000–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckstein, A.; Grossl, T.; Geisler, A.; Wang, X.; Pinkert, S.; Pozzuto, T.; Schwer, C.; Kurreck, J.; Weger, S.; Vetter, R.; et al. Inhibition of adenovirus infections by siRNA-mediated silencing of early and late adenoviral gene functions. Antivir. Res. 2010, 88, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puerta-Fernandez, E.; Romero-Lopez, C.; Barroso-delJesus, A.; Berzal-Herranz, A. Ribozymes: Recent advances in the development of RNA tools. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 27, 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Khanna, M.; Kumar, P.; Sood, V.; Vyas, R.; Banerjea, A.C. Nucleic acid-mediated cleavage of M1 gene of influenza A virus is significantly augmented by antisense molecules targeted to hybridize close to the cleavage site. Mol. Biotechnol. 2012, 51, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.B.; Hobom, G.; Luo, D. Ribozyme mediated destruction of influenza A virus in vitro and in vivo. J. Med. Virol. 1994, 42, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motard, J.; Rouxel, R.; Paun, A.; von Messling, V.; Bisaillon, M.; Perreault, J.P. A novel ribozyme-based prophylaxis inhibits influenza A virus replication and protects from severe disease. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plehn-Dujowich, D.; Altman, S. Effective inhibition of influenza virus production in cultured cells by external guide sequences and ribonuclease P. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7327–7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarev, V.N.; Shmarov, M.M.; Zakhartchouk, A.N.; Yurov, G.K.; Misurina, O.U.; Akopian, T.A.; Grinenko, N.F.; Grodnitskaya, N.G.; Kaverin, N.V.; Naroditsky, B.S. Inhibition of influenza A virus reproduction by a ribozyme targeted against PB1 mRNA. Antivir. Res. 1999, 42, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, E.; Devenish, L.; Engelhardt, O.G.; Palese, P.; Brownlee, G.G.; Garcia-Sastre, A. Rescue of influenza A virus from recombinant DNA. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 9679–9682. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, A.; Fukuda, N.; Lai, Y.; Ueno, T.; Moriyama, M.; Taguchi, F.; Iguchi, A.; Shimizu, K.; Kuroda, K. Development of a chimeric DNA-RNA hammerhead ribozyme targeting SARS virus. Intervirology 2009, 52, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, H.; Ohkawa, J.; Tanishige, N.; Yoshinari, K.; Murata, T.; Yokoyama, K.K.; Taira, K. Selection of the best target site for ribozyme-mediated cleavage within a fusion gene for adenovirus E1A-associated 300 kDa protein (p300) and luciferase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996, 24, 3010–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeman, N.C. DNA in a material world. Nature 2003, 421, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, S.; Hughes, M.D.; Khan, A.; Bibby, M.; Hussain, M.; Nawaz, Q.; Double, J.; Sayyed, P. The delivery of antisense therapeutics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2000, 44, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, S.K. Deoxyribozymes: Selection design and serendipity in the development of DNA catalysts. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, M.; Silverman, S.K. DNA and RNA can be equally efficient catalysts for carbon-carbon bond formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 2936–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.; Asha, K.; Chauhan, S. DNAzyme mediated post-transcriptional gene silencing: A novel therapeutic approach. WebmedCent. Mol. Biol. 2013, 4, WMC004415. [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda, T.; Imamura, Y.; Takaku, H.; Kashiwagi, T.; Hara, K.; Iwahashi, J.; Ohtsu, Y.; Tsumura, N.; Kato, H.; Hamada, N. Inhibition of influenza virus replication in cultured cells by RNA-cleaving DNA enzyme. FEBS Lett. 2000, 481, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Hamazaki, H.; Habu, Y.; Hayashi, M.; Abe, T.; Miyano-Kurosaki, N.; Takaku, H. A new modified DNA enzyme that targets influenza virus A mRNA inhibits viral infection in cultured cells. FEBS Lett. 2004, 560, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Kumar, P.; Rajput, R.; Saxena, L.; Daga, M.K.; Khanna, M. Sequence-specific cleavage of BM2 gene transcript of influenza B virus by 10-23 catalytic motif containing DNA enzymes significantly inhibits viral RNA translation and replication. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2013, 23, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.; Rajput, R.; Pati, D.R.; Khanna, M. Potent Intracellular Knock-Down of Influenza A Virus M2 Gene Transcript by DNAzymes Considerably Reduces Viral Replication in Host Cells. Mol. Biotechnol. 2015, 57, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.Y.; Zhao, X.D.; Jiang, L.P.; Liu, H.L.; Wang, L.J.; Fang, P.; Shen, K.L.; Xie, Z.D.; Wu, Y.P.; Yang, X.Q. Inhibition of respiratory syncytial virus in cultured cells by nucleocapsid gene targeted deoxyribozyme (DNAzyme). Antivir. Res. 2006, 71, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, X.Q.; Xie, Y.Y.; Zhao, X.D.; Jiang, L.P.; Wang, L.J.; Cui, Y.X. Inhibition of respiratory syncytial virus of subgroups A and B using deoxyribozyme DZ1133 in mice. Virus Res. 2007, 130, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Xu, J.; Liu, J.; Yan, X.; Zhu, X.; Xiao, G.; Sun, L.; Tien, P. An efficient RNA-cleaving DNA enzyme can specifically target the 5′-untranslated region of severe acute respiratory syndrome associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV). J. Gene Med. 2007, 9, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, C.F.; Swayze, E.E. RNA targeting therapeutics: Molecular mechanisms of antisense oligonucleotides as a therapeutic platform. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 50, 259–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamecnik, P.C.; Stephenson, M.L. Inhibition of Rous sarcoma virus replication and cell transformation by a specific oligodeoxynucleotide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1978, 75, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, M.L.; Zamecnik, P.C. Inhibition of Rous sarcoma viral RNA translation by a specific oligodeoxyribonucleotide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1978, 75, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, D.K. Recent patents on nucleic acid-based antiviral therapeutics. Recent Pat. Antiinfect. Drug Discov. 2010, 5, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabanov, A.V.; Vinogradov, S.V.; Ovcharenko, A.V.; Krivonos, A.V.; Melik-Nubarov, N.S.; Kiselev, V.I.; Severin, E.S. A new class of antivirals: Antisense oligonucleotides combined with a hydrophobic substituent effectively inhibit influenza virus reproduction and synthesis of virus-specific proteins in MDCK cells. FEBS Lett. 1990, 259, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Jin, Y.; Dale, R.; Sun, L.Q.; Wang, M. Inhibition of highly pathogenic avian H5N1 influenza virus replication by RNA oligonucleotides targeting NS1 gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 365, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, G.; Nordmann, A.; Stein, D.A.; Iversen, P.L.; Klenk, H.D. Morpholino oligomers targeting the PB1 and NP genes enhance the survival of mice infected with highly pathogenic influenza A H7N7 virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, M.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, R.X.; Yang, J.; Xia, X.Z.; Wang, S.Q. In vitro and in vivo protection against the highly pathogenic H5N1 influenza virus by an antisense phosphorothioate oligonucleotide. Antivir. Ther. 2008, 13, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lupfer, C.; Stein, D.A.; Mourich, D.V.; Tepper, S.E.; Iversen, P.L.; Pastey, M. Inhibition of influenza A H3N8 virus infections in mice by morpholino oligomers. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Kumar, B.; Rajput, R.; Saxena, L.; Banerjea, A.C.; Khanna, M. Cross-protective effect of antisense oligonucleotide developed against the common 3′ NCR of influenza A virus genome. Mol. Biotechnol. 2013, 55, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannecchini, S.; Clausi, V.; Nosi, D.; Azzi, A. Oligonucleotides derived from the packaging signal at the 5′ end of the viral PB2 segment specifically inhibit influenza virus in vitro. Arch. Virol. 2009, 154, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannecchini, S.; Wise, H.M.; Digard, P.; Clausi, V.; Del Poggetto, E.; Vesco, L.; Puzelli, S.; Donatelli, I.; Azzi, A. Packaging signals in the 5′-ends of influenza virus PA, PB1, and PB2 genes as potential targets to develop nucleic-acid based antiviral molecules. Antivir. Res. 2011, 92, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenartowicz, E.; Nogales, A.; Kierzek, E.; Kierzek, R.; Martinez-Sobrido, L.; Turner, D.H. Antisense Oligonucleotides Targeting Influenza A Segment 8 Genomic RNA Inhibit Viral Replication. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2016, 26, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jairath, S.; Vargas, P.B.; Hamlin, H.A.; Field, A.K.; Kilkuskie, R.E. Inhibition of respiratory syncytial virus replication by antisense oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Antivir. Res. 1997, 33, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.H.; Stein, D.A.; Guerrero-Plata, A.; Liao, S.L.; Ivanciuc, T.; Hong, C.; Iversen, P.L.; Casola, A.; Garofalo, R.P. Inhibition of respiratory syncytial virus infections with morpholino oligomers in cell cultures and in mice. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, B.W.; Stein, D.A.; Kroeker, A.D.; Moulton, H.M.; Bestwick, R.K.; Iversen, P.L.; Buchmeier, M.J. Inhibition and escape of SARS-CoV treated with antisense morpholino oligomers. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2006, 581, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuman, B.W.; Stein, D.A.; Kroeker, A.D.; Churchill, M.J.; Kim, A.M.; Kuhn, P.; Dawson, P.; Moulton, H.M.; Bestwick, R.K.; Iversen, P.L.; et al. Inhibition, escape, and attenuated growth of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus treated with antisense morpholino oligomers. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 9665–9676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, D.G.; Lee, W.; Choi, J.K.; Kim, S.J.; Plant, E.P.; Almazan, F.; Taylor, D.R.; Enjuanes, L.; Oh, J.W. Interference of ribosomal frameshifting by antisense peptide nucleic acids suppresses SARS coronavirus replication. Antivir. Res. 2011, 91, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavyalova, E.; Kopylov, A. Aptamers to Hemagglutinin: A Novel Tool for Influenza Virus Recognition and Neutralization. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 4835–4853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misono, T.S.; Kumar, P.K. Selection of RNA aptamers against human influenza virus hemagglutinin using surface plasmon resonance. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 342, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopinath, S.C.; Kawasaki, K.; Kumar, P.K. Selection of RNA-aptamer against human influenza B virus. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. (Oxf.) 2005, 49, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopinath, S.C.; Misono, T.S.; Kawasaki, K.; Mizuno, T.; Imai, M.; Odagiri, T.; Kumar, P.K. An RNA aptamer that distinguishes between closely related human influenza viruses and inhibits haemagglutinin-mediated membrane fusion. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Li, Y. Hydrogel based QCM aptasensor for detection of avian influenza virus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiratori, I.; Akitomi, J.; Boltz, D.A.; Horii, K.; Furuichi, M.; Waga, I. Selection of DNA aptamers that bind to influenza A viruses with high affinity and broad subtype specificity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 443, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.; Wang, R.; Hargis, B.; Lu, H.; Li, Y. A SPR aptasensor for detection of avian influenza virus H5N1. Sensors (Basel) 2012, 12, 12506–12518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lum, J.; Wang, R.; Hargis, B.; Tung, S.; Bottje, W.; Lu, H.; Li, Y. An Impedance Aptasensor with Microfluidic Chips for Specific Detection of H5N1 Avian Influenza Virus. Sensors (Basel) 2015, 15, 18565–18578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Seo, H.B.; Kim, B.C.; Kim, S.K.; Song, C.S.; Gu, M.B. Highly sensitive sandwich-type SPR based detection of whole H5Nx viruses using a pair of aptamers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.H.; Kayhan, B.; Ben-Yedidia, T.; Arnon, R. A DNA aptamer prevents influenza infection by blocking the receptor binding region of the viral hemagglutinin. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 48410–48419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musafia, B.; Oren-Banaroya, R.; Noiman, S. Designing anti-influenza aptamers: Novel quantitative structure activity relationship approach gives insights into aptamer-virus interaction. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.M.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, J.M.; Shim, H.S.; Cho, S.J.; Lee, W.K.; Ko, H.W.; Keum, Y.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Pathinayake, P.; et al. Single-stranded DNA aptamer that specifically binds to the influenza virus NS1 protein suppresses interferon antagonism. Antivir. Res. 2013, 100, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Zhang, N.; Singh, K.; Shuai, H.; Chu, H.; Zhou, J.; Chow, B.K.; Zheng, B.J. Cross-protection of influenza A virus infection by a DNA aptamer targeting the PA endonuclease domain. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 4082–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, P.; Perez-Morgado, M.I.; Gonzalez, V.M.; Martin, M.E.; Nieto, A. Inhibition of Influenza Virus Replication by DNA Aptamers Targeting a Cellular Component of Translation Initiation. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, F. The catcher in the RIG-I. Cytokine 2015, 76, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.Y.; Sun, H.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Oh, B.H.; Cha, Y.J.; Kim, B.H.; Yoo, J.Y. 5′-Triphosphate-RNA-independent activation of RIG-I via RNA aptamer with enhanced antiviral activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 2724–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, D.G.; Jeon, I.J.; Kim, J.D.; Song, M.S.; Han, S.R.; Lee, S.W.; Jung, H.; Oh, J.W. RNA aptamer-based sensitive detection of SARS coronavirus nucleocapsid protein. Analyst 2009, 134, 1896–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.J.; Woo, H.M.; Kim, K.S.; Oh, J.W.; Jeong, Y.J. Novel system for detecting SARS coronavirus nucleocapsid protein using an ssDNA aptamer. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011, 112, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.J.; Lee, N.R.; Yeo, W.S.; Jeong, Y.J.; Kim, D.E. Isolation of inhibitory RNA aptamers against severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus NTPase/Helicase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 366, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shum, K.T.; Tanner, J.A. Differential inhibitory activities and stabilisation of DNA aptamers against the SARS coronavirus helicase. ChemBioChem 2008, 9, 3037–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percze, K.; Szakacs, Z.; Scholz, E.; Andras, J.; Szeitner, Z.; Kieboom, C.H.; Ferwerda, G.; Jonge, M.I.; Gyurcsanyi, R.E.; Meszaros, T. Aptamers for respiratory syncytial virus detection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.T.; Lu, C.Y.; Shao, P.L.; Chang, L.Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Chang, Y.H.; Lai, M.J.; Chi, Y.H.; Huang, L.M. In vivo inhibition of influenza A virus replication by RNA interference targeting the PB2 subunit via intratracheal delivery. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barik, S. siRNA for Influenza Therapy. Viruses 2010, 2, 1448–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, B.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Li, M. Inhibition of influenza A virus replication by RNA interference targeted against the PB1 subunit of the RNA polymerase gene. Arch. Virol. 2011, 156, 1979–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, C.Y.; Yang, S.T.; Qin, C.; Hu, J.L.; Xia, X.Z. Inhibition of highly pathogenic avian influenza virus H5N1 replication by the small interfering RNA targeting polymerase A gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 390, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Zhang, W.; Lockey, R.F.; Auais, A.; Piedimonte, G.; Mohapatra, S.S. Respiratory syncytial virus infection in Fischer 344 rats is attenuated by short interfering RNA against the RSV-NS1 gene. Genet. Vaccines Ther. 2007, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Meyer, M. Ribozymes as Antivirals for Respiratory Syncytial Virus. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, H.; Saitoh, H.; Suzuki, T.; Takaku, H. Inhibition of influenza virus by baculovirus-mediated shRNA. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. (Oxf.) 2009, 53, 287–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, J.T.; Williams, B.R.G. Activation of the mammalian immune system by siRNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sioud, M. RNA interference and innate immunity. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morral, N.; Witting, S.R. shRNA-Induced Interferon-Stimulated Gene Analysis. In Cytokine Protocols; De Ley, M., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Lu, M. RNA Interference-Induced Innate Immunity, Off-Target Effect, or Immune Adjuvant? Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opalinska, J.B.; Gewirtz, A.M. Nucleic-acid therapeutics: Basic principles and recent applications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Castanares, M.; Mukherjee, A.; Lupold, S.E. Nucleic Acid Aptamers: Clinical Applications and Promising New Horizons. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 4206–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Pati, D.; Khanna, M.; Kumar, P.; Daga, M.; Singh, V.; Khare, S.; Gaur, S. Age-Sex Distribution and Seasonality Pattern among Influenza Virus Infected Patients in Delhi, 2009–2010. Indian J. Community Med. 2012, 37, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Sharma, B.; Khanna, M.; Singh, V.; Daga, M.; Vijayan, V.; Mishra, A.; Chadha, M.; Sarkar, M.; Kaur, H. Comparison of various immunoassay kits for rapid screening of pandemic influenza H1N1-2009 viruses. J. Public Health Epidemiol. 2010, 2, 175–179. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, B.; Kumar, P.; Rajput, R.; Daga, M.; Singh, V.; Khanna, M. Comparative reproducibility of SYBR Green I and TaqMan real-time PCR chemistries for the analysis of matrix and hemagglutinin genes of Influenza A viruses. Int. J. Collab. Res. Intern. Med. Public Health 2012, 4, 1346–1352. [Google Scholar]
- Kawai, Y.; Kimura, Y.; Lezhava, A.; Kanamori, H.; Usui, K.; Hanami, T.; Soma, T.; Morlighem, J.E.; Saga, S.; Ishizu, Y.; et al. One-step detection of the 2009 pandemic influenza A(H1N1) virus by the RT-SmartAmp assay and its clinical validation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Khanna, M.; Kumar, B.; Rajput, R.; Banerjea, A.C. A conserved matrix epitope based DNA vaccine protects mice against influenza A virus challenge. Antivir. Res. 2012, 93, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinicaltrials.gov. A Safety and Immunogenicity Study of Intranasal Sendai Virus Vectored Respiratory Syncytial Virus (SeVRSV) Vaccine in Healthy Adults. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT03473002 (accessed on 8 October 2018).
| Nucleic Acid Therapies | Disease | Company |
|---|---|---|
| Antisense | ||
| Vitravene | Retinitis | CIBAVision, ISIS Pharmaceuticals |
| Kynamro | Hypercholesterolemia | Genzyme |
| Anti-c-MYC | Cardiovascular restenosis | Phase II AVI Biopharma |
| EPI 2010 (AS against adenosine A1 receptor) | Asthma | Phase II EpiGenesis Pharmaceuticals |
| Genasense (AS against BCL2) | Hematological malignancies Solid tumors, Phase III | Genta |
| GTI 2040 (AS against ribonucleotide reductase) | Solid tumors, Phase I and II | Lorus Therapeutics |
| HGTV (AS against HIV) | HIV, Phase II | Enzo Biochem |
| CpG molecules | Solid tumors Infectious diseases, Phase I/II | Coley Pharmaceutical Group |
| Aptamer | ||
| Macugen™ (pegaptanib sodium), an anti-VEGF RNA aptamer | Diabetic Macular Edema (DME), Phase III | Eyetech Pharma |
| ARC1905 (Anti-C5 Aptamer), Zimura® | Dry ARMD, Phase II | Ophthotech Corp |
| E10030 (Anti-PDGF Pegylated Aptamer, Fovista®) | ARMD, Phase III | Ophthotech Corporation |
| ISIS 3521 (PKC-α) (AS) ISIS 5132 (c-RAF) ISIS 2503 (h-RAS) G 3139 (BCL2) GEM 231 (PKA) | NSCLC, NHL, Phase III Solid tumors, Phase II NSCLC, Phase II NHL, Phase II/III PKA, Phase II | ISIS Pharmaceuticals |
| Ribozyme | ||
| Angiozyme (Ribozyme against VEGFR1) | Breast and colon cancer, Phase II | Ribozyme Pharmaceuticals |
| Heptazyme (Ribozyme against HCV) Herzyme (Ribozyme against HER2) | HCV, Phase II Breast and ovarian cancer, Phase I | Ribozyme Pharmaceuticals |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asha, K.; Kumar, P.; Sanicas, M.; Meseko, C.A.; Khanna, M.; Kumar, B. Advancements in Nucleic Acid Based Therapeutics against Respiratory Viral Infections. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8010006
Asha K, Kumar P, Sanicas M, Meseko CA, Khanna M, Kumar B. Advancements in Nucleic Acid Based Therapeutics against Respiratory Viral Infections. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsha, Kumari, Prashant Kumar, Melvin Sanicas, Clement A. Meseko, Madhu Khanna, and Binod Kumar. 2019. "Advancements in Nucleic Acid Based Therapeutics against Respiratory Viral Infections" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8010006
APA StyleAsha, K., Kumar, P., Sanicas, M., Meseko, C. A., Khanna, M., & Kumar, B. (2019). Advancements in Nucleic Acid Based Therapeutics against Respiratory Viral Infections. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8010006





