Septic Pulmonary Emboli or Pulmonary Metastasis in a Patient with Diabetes Mellitus?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
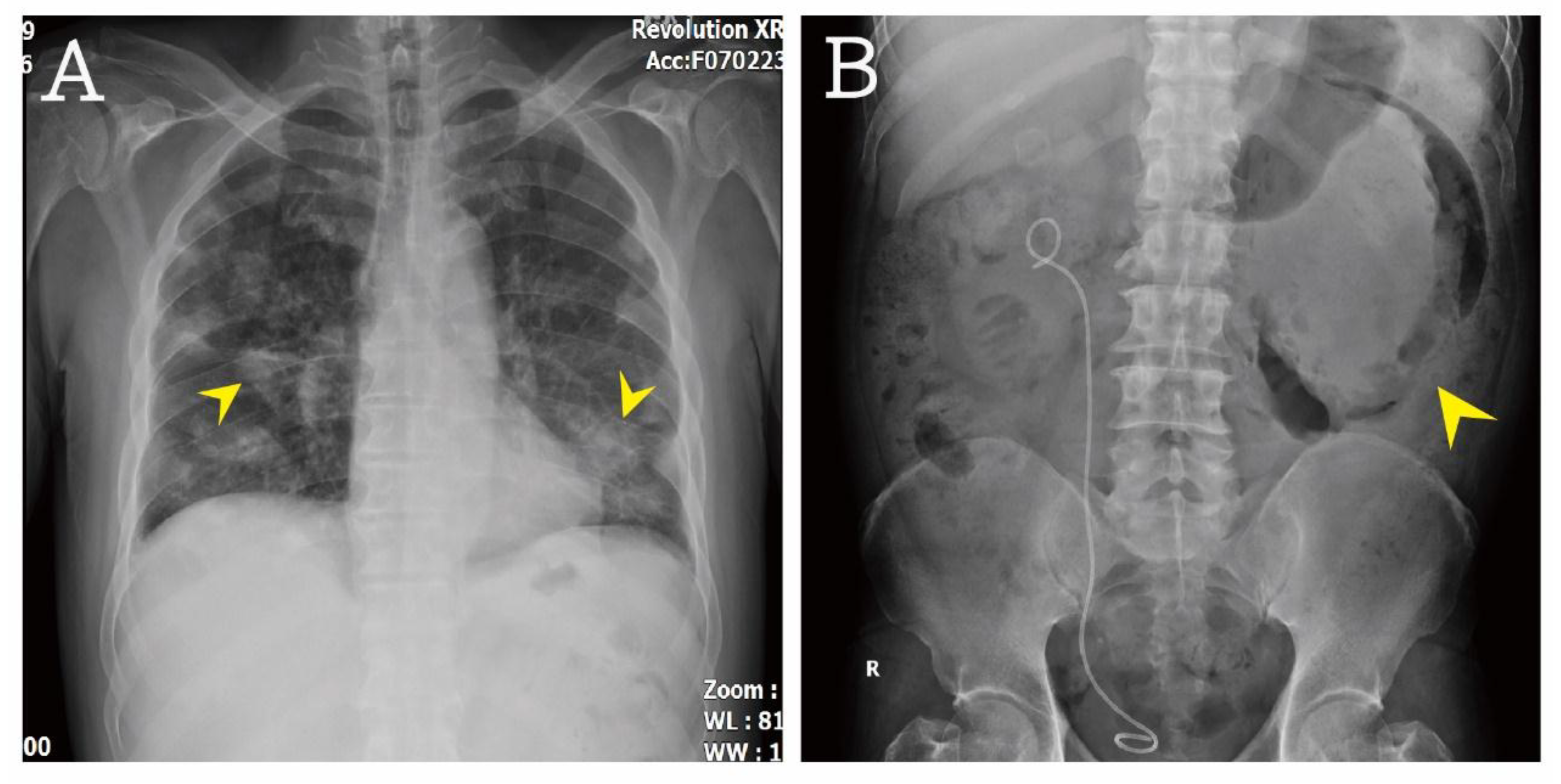
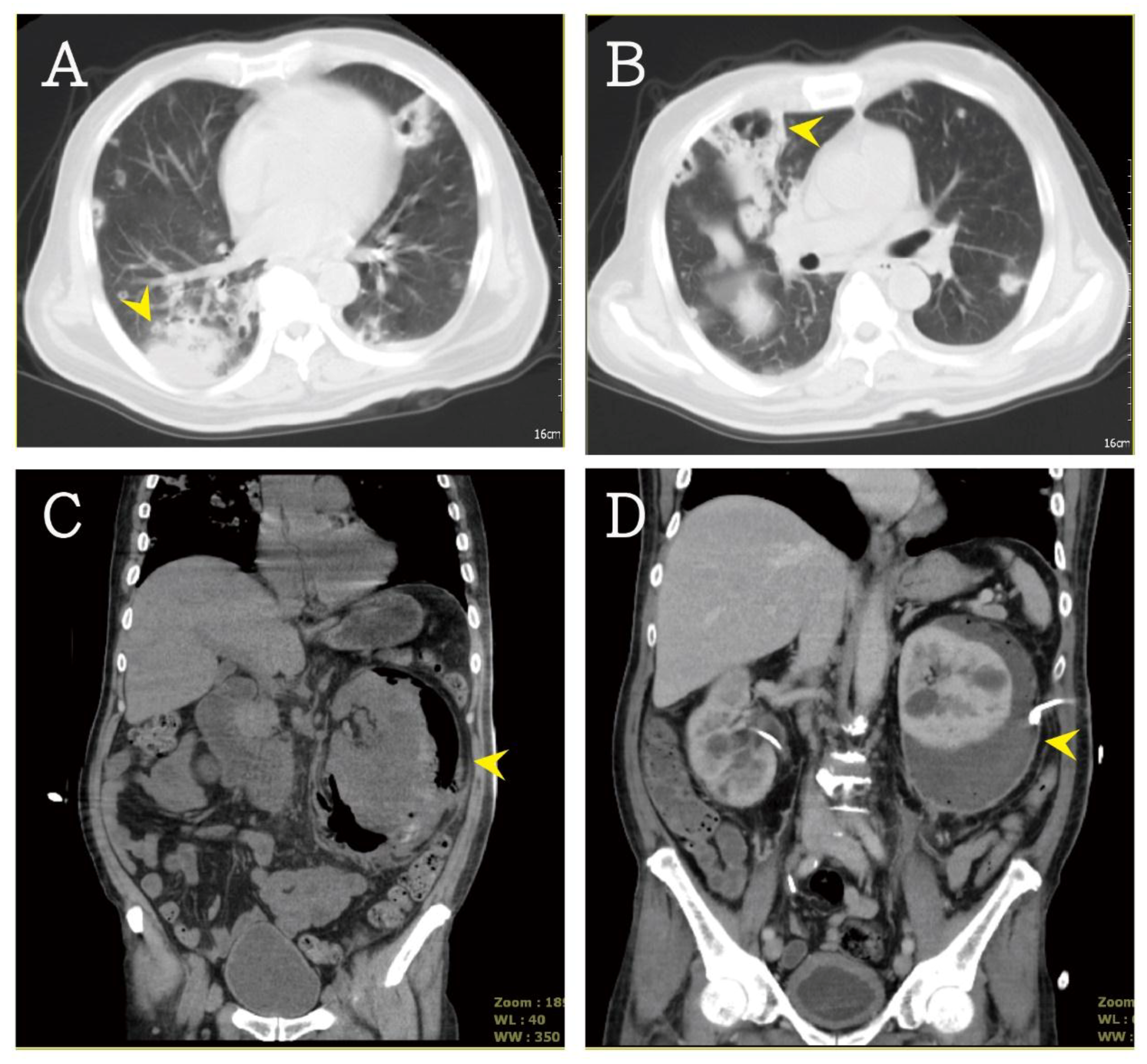
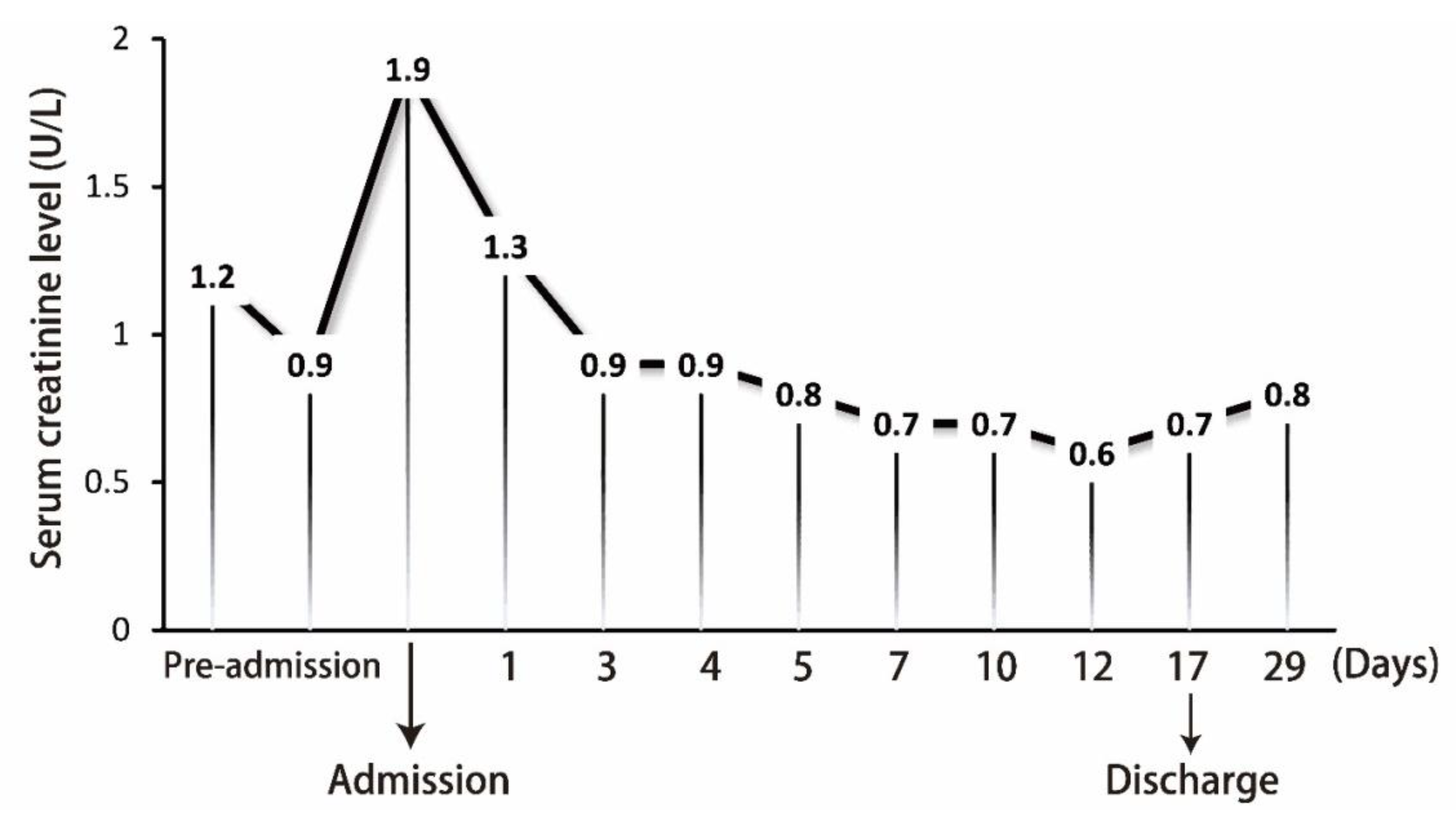
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grayson, D.E.; Abbott, R.M.; Levy, A.D.; Sherman, P.M. Emphysematous infections of the abdomen and pelvis: A pictorial review. Radiographics 2002, 22, 543–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontin, A.R.; Barnes, R.D. Current management of emphysematous pyelonephritis. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2009, 6, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsu, J.H.-L.; Chan, C.-K.; Chu, R.W.-H.; Law, I.-C.; Kong, C.-K.; Liu, P.-L.; Cheung, F.-K.; Yiua, M.-K. Emphysematous pyelonephritis: An 8-year retrospective review across four acute hospitals. Asian J. Surg. 2013, 36, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, M.; Bhatia, A.; Bhalla, A.; Khandelwal, N. Emphysematous pyelonephritis with air in the renal vein and septic emboli in the lungs: A rare presentation. Saudi. J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2014, 25, 1086–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elvas, A.R.; Pereira, B.J.; Carrega, F.; Vicente, L. Fulminant Emphysematous Pyelonephritis Secondary to Urothelial Neoplasia with Reno-Colic Fistula. Acta. Med. Port. 2018, 31, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, R.C.; Amendola, M.A.; Artze, M.E.; Casillas, J.; Jafri, S.Z.; Dickson, P.R.; Morillo, G. Genitourinary tract gas: Imaging evaluation. Radiographics 1996, 16, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.L.; Lee, T.Y.; Bullard, M.J.; Tsai, C.C. Acute gas-producing bacterial renal infection: Correlation between imaging findings and clinical outcome. Radiology 1996, 198, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubee, S.S.; McGlynn, L.; Fordham, M. Emphysematous pyelonephritis. BJU Int. 2011, 107, 1474–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Tseng, C. Emphysematous pyelonephritis: Clinicoradiological classification, management, prognosis, and pathogenesis. Arch. Intern. Med. 2000, 160, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.C.; Chiang, B.J.; Pong, Y.H.; Chen, C.H.; Pu, Y.S.; Hsueh, P.R.; Huang, C.Y. Emphysematous pyelonephritis: Clinical characteristics and prognostic factors. Int. J. Urol. 2014, 21, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.-C.; Hong, J.-H.; Chiang, B.-J.; Pong, Y.-H.; Hsueh, P.-R.; Huang, C.-Y.; Pu, Y.-S. Recommended Initial Antimicrobial Therapy for Emphysematous Pyelonephritis: 51 Cases and 14-Year-Experience of a Tertiary Referral Center. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016, 95, e3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Patient Data | Normal Range | Variables | Patient Data | Normal Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White cell count | 40,250/µL | 3500–11,000/µL | Ketone body | 4.5 mmole/L | <0.6 mmole/L |
| Band-form neutrophils | 2.0% | 0–3% | Serum osmolarity | 336 mOsm/Kg | 280–295 mOsm/Kg |
| Segment-form neutrophils | 86.0% | 45–70% | Venous blood gas | ||
| Lymphocytes | 5.0% | 25–40% | pH value | 7.390 | 7.31–7.41 |
| Eosinophils | 0.0% | 1–3% | pCO2 | 29.2 mmHg | 41–51 mmHg |
| Monocytes | 6.0% | 2–8% | pO2 | 44.5 mmHg | 80–100 mmHg |
| Hemoglobin | 6.7 g/dL | 12–16 g/dL | HCO3 | 17.3 mmole/L | 22–26 mmole/L |
| Platelet counts | 645,000/μL | 150,000–400,000/ μL | ABE | –6.3 mmole/L | –3.3–2.3 mmole/L |
| Blood urine nitrogen (BUN) | 51 mg/dL | 7–18 mg/dL | BEecf | –7.6 mmole/L | – |
| Creatinine | 1.9 mg/dL | 0.55–1.02 mg/dL | O2 saturation | 78.9% | – |
| Sodium | 124 mmole/L | 136–145 mmole/L | Urinalysis | ||
| Potassium | 5.5 mmole/L | 3.5–5.1 mmole/L | Red cell count | 10–19/HPF | 0–2/HPF |
| Glucose | 790 mg/dL | 70–100 mg/dL | White cell count | 10–19/HPF | 0–5/HPF |
| Alanine aminotransferase | 19 U/L | 14–59 U/L | Glucose | 4+ | −/+ |
| Lipase | 768 IU/L | 73–393 IU/L | Ketone body | 1+ | –/+ |
| Total bilirubin | 1.00 mg/dL | 0.0–1.0 mg/dL | Bacteria | 1+/HPF | 0/HPF |
| Troponin I | <0.01 μg/L | <0.01 μg/L | Yeast | 3+/HPF | 0/HPF |
| CRP | 30.03 mg/dL | <0.33 mg/dL |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, M.-Y.; Lee, L.-C.; Chen, Y.-L.; Yeh, Y.-H.; Li, C.-J.; Yiang, G.-T. Septic Pulmonary Emboli or Pulmonary Metastasis in a Patient with Diabetes Mellitus? J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7070176
Wu M-Y, Lee L-C, Chen Y-L, Yeh Y-H, Li C-J, Yiang G-T. Septic Pulmonary Emboli or Pulmonary Metastasis in a Patient with Diabetes Mellitus? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2018; 7(7):176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7070176
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Meng-Yu, Ling-Chi Lee, Yu-Long Chen, Yung-Hsiang Yeh, Chia-Jung Li, and Giou-Teng Yiang. 2018. "Septic Pulmonary Emboli or Pulmonary Metastasis in a Patient with Diabetes Mellitus?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 7, no. 7: 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7070176
APA StyleWu, M.-Y., Lee, L.-C., Chen, Y.-L., Yeh, Y.-H., Li, C.-J., & Yiang, G.-T. (2018). Septic Pulmonary Emboli or Pulmonary Metastasis in a Patient with Diabetes Mellitus? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7(7), 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7070176







