Abstract
Islets of Langerhans are islands of endocrine cells scattered throughout the pancreas. A number of new studies have pointed to the potential for conversion of non-β islet cells in to insulin-producing β-cells to replenish β-cell mass as a means to treat diabetes. Understanding normal islet cell mass and function is important to help advance such treatment modalities: what should be the target islet/β-cell mass, does islet architecture matter to energy homeostasis, and what may happen if we lose a particular population of islet cells in favour of β-cells? These are all questions to which we will need answers for islet replacement therapy by transdifferentiation of non-β islet cells to be a reality in humans. We know a fair amount about the biology of β-cells but not quite as much about the other islet cell types. Until recently, we have not had a good grasp of islet mass and distribution in the human pancreas. In this review, we will look at current data on islet cells, focussing more on non-β cells, and on human pancreatic islet mass and distribution.
Keywords:
islets of Langerhans; insulin; glucagon; somatostatin; pancreatic polypeptide; ghrelin; pancreas; diabetes; endocrine 1. Introduction
The islands or (more commonly) islets of Langerhans, first described by their namesake- Paul Langerhans- in 1969, are islands of mixed populations of endocrine cells that are scattered in the parenchyma of the pancreas. Islets of Langerhans have been much studied in the context of diabetes due to the hormones produced and secreted from the cells which form these micro-organs, which are involved in the regulation of glucose homeostasis. The discovery of insulin, and the demonstration that it can lower blood glucose in dogs, by Frederick Banting and Charles Best in 1921, and its subsequent development for clinical use, in collaboration with John Macleod and James Collip, led to the award of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine to Banting and Macleod in 1923. Since then, the biology of the insulin producing β-cells in the islet came under much scrutiny as the loss of β-cell function, hence the loss of insulin, was associated with diabetes. Initially, much more associated with type 1 diabetes, which is characterised by the loss of β-cell mass due to autoimmune attack of this cell type, loss of functional β-cell mass is now also associated with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
There are multiple developmental cues for islet formation ranging from external cues such as nutritional status (i.e., the maternal nutritional state) to signals from the developing foetus e.g., from the central nervous system [1]. Replenishment of β-cell mass following the loss of significant β-cell mass (circa 90%) in mice has been shown to lead to activation of β-cell duplication [2,3]. Recuperation of β-cell mass following >90% loss of β-cell mass was shown to be via transdifferentiation of other islet cells, e.g., α-cells [4] and δ-cells [5], into β-cells. Data from the literature indicate that whilst loss of pancreatic β-cell mass may lead to disease, there is little or no effect on physiology from near complete loss of α-cell mass, responsible for secretion of glucagon (the counter hormone to insulin) in rodents [6]. With the advent of the possibility to switch islet cell identity as a means to alter islet cell mass as treatment for diabetes [4,5,7,8], it is perhaps timely to review current information on islet cell mass and the function of the different islet cell types.
2. Islet Distribution in the Pancreas: Structure, Size, Location
The total number of islets in a human pancreas has been estimated to be between 3.2 and 14.8 million, with a total islet volume of 0.5 to 2.0 cm3 [9,10,11,12,13,14]. The cellular composition and architecture of pancreatic islets differ between and within species [15,16]. The inter-species differences have previously been shown to correlate with functional differences [17]. Human islets consist of circa 30% glucagon-producing α-cells, circa 60% insulin producing β-cells, with the remainder circa 10% made up of δ-cells (somatostatin-producing), γ- or PP cells (pancreatic polypeptide-producing), and ε-cells (ghrelin-producing) [9,17,18,19,20], with these endocrine cells randomly distributed throughout the islet [15,16,17]. Rodent islets are widely used in biomedical research, and have a different architecture with a core of β-cells surrounded by the other endocrine cell types [16,21,22,23].
Recently, Ionescu–Tirgoviste and colleagues [9] performed a careful evaluation of islet characteristics from a healthy human pancreas by analysing pancreatic sections to produce a three-dimensional islet distribution map. The study revealed that the human pancreas contains on average 3.2 million islets, with a mean islet diameter of 108.92 μm (±6.27 μm), and a mean islet volume of 0.00069 μL (±0.00011 μL) [9]. The majority of islets (~66%) have a surface area of between 1000 and 10,000 μm2. Approximately 24% and 9% of islets had a surface area of more than 100,000 μm2 and less than 1000 μm2, respectively. The islets appear to have a threshold surface area of about 100,000 μm2, where “islets” that have apparently larger surface area than the threshold were made up of clusters of islets [9]. The smaller islets tended to cluster around blood vessels [9]. When islet surface area and distribution were averaged over pancreas section area, Ionescu-Tirgoviste and colleagues concluded that there was a uniform scattering of islets in the body of the pancreas, with the islets adopting an overall spherical structure [9]. This is in contrast to previous reports indicating an uneven distribution of islets in human [24] and rodent pancreas [21,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32], although the differences may be due to differences in the methodologies used for estimating β-cell mass.
Islet mass and distribution in the pancreas may be an important consideration in light of the known metabolic consequences of pancreatectomy, where patients suffer a sudden loss of islet cell mass from surgical resection of the pancreas. Patients that have undergone a 50% (partial) pancreatectomy have reduced insulin secretion (circa 50%) but the region of pancreas that is removed was reported to have different metabolic impact [33]. Thus, removal of the pancreatic tail led to post-operative elevated fasting glucose and post-challenge glycaemia, whilst removal of the pancreatic head caused an improvement in oral glucose tolerance [33]. Earlier studies involving the loss of the pancreatic tail in human subjects also reported lowered insulin secretion and glucose tolerance in patients one year after partial pancreatectomy [34]. Intriguingly, the data from the pancreatectomy studies, together with Ionescu-Tirgoviste and colleagues’ report [9] that there was a uniform scattering of islets in the body of the pancreas, may imply that there are functional differences between the islets in the head and the tail of the pancreas. Thus, it would appear, not all islets are the same and there may be differences in the islet population in the head vs the tail of the pancreas. Such considerations are important beyond academic curiosity. The head and the tail of the pancreas have different developmental origins: the head of the pancreas is formed from the dorsal and ventral pancreatic bud, and the body and tail of the pancreas are formed from the ventral pancreatic bud [35]. Studies in rodents have previously shown that islets originating from the dorsal pancreatic bud had greater capacity to secrete and synthesise insulin than islets of ventral bud origins [26,27,28,29], perhaps hinting at potential programming differences during development in islets (reviewed extensively in [36]) in relation to their function and adaptive responses in adult life. This in turn may have an impact on the therapeutic strategies that may be pliable to increase functional β-cell mass in vivo (see Section 4 below) [26,27,28,29,33,35,36,37,38].
3. α-Cell
It would be fair to say that a lot less is known about the glucagon producing α-cell than the insulin producing β-cell. Glucagon is the counter hormone to insulin, and is typical of the fasted state. The concerted regulation of glucagon and insulin secretion is a major mechanism for the regulation of blood glucose. The major function of the counter-regulatory response is the prevention of hypoglycaemia, a response that is impaired in diabetes [37,38]. The importance of glucagon to the pathophysiology of T2D was first highlighted by Unger and colleagues in the bihormonal hypothesis which states that both hypoinsulinaemia and hyperglucagonaemia contributes to hyperglycaemia in T2D [39,40]. Thus, in T2D, α-cells display elevated glucagon secretion, enhanced glucagon secretion in response to amino acids, and ineffective suppression of glucagon secretion by high plasma glucose [41]. The importance of the regulation of α-cell function in the pathophysiology of T2D is currently the subject of intense research [42,43,44].
Glucagon secretion is regulated by both α-cell intrinsic and paracrine mechanisms. For example, it has been proposed that hyperglucagonaemia in T2D may be a result of the loss of intrinsic regulatory mechanism by glucose and amino acids, and extrinsic regulation by insulin and zinc, in the α-cells [41,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53]. However, the loss of sensitivity to nutrients, insulin and zinc as mechanisms for hyperglucagonaemia have all been disputed [54,55,56,57,58]. The gut hormones—Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 (GLP-1) and Gastric Inhibitory Polypeptide (GIP)—have been proposed to be important in the regulation of glucagon secretion [59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66]. Additionally, there is evidence to suggest that GLP-1 can be produced in human islets, possibly in α-cells [67]. Somatostatin, secreted by pancreatic δ-cells, suppresses glucagon secretion [68,69,70]; it has been proposed that the inhibitory effect of GLP-1 on glucagon secretion [71] is effected indirectly via the stimulation of somatostatin secretion by GLP-1 [72].
The islets of Langerhans are innervated and subject to the regulation by the sympathetic and parasympathetic system such that glucagon secretion is stimulated in hypoglycaemia [73,74,75,76]. One characteristic of T2D is the progressive loss of the stimulation of glucagon and counter-regulatory hormones in patients treated with insulin [77,78]. Moreover, it has been reported that sympathetic innervation during pancreatic development is required for establishment of islet architecture and function [1], with the localisation of non-β cells a primary determinant of islet architecture [16,22,75,79]. Thus, the loss of non-β cell e.g. for the transdifferentiation into β-cells, may lead to the loss overall islet architecture, with implications on islet function.
In summary, the current evidence indicates that the intrinsic, nervous and paracrine regulation of glucagon secretion are not mutually exclusive, and likely act in concert [43,80].
Recently, Collombat and colleagues have demonstrated the potential to transdifferentiate endogenous α-cells in to β-like cells to replenish β-cell function through the administration of gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) [7,8]. Furthermore, the authors showed that there was a continuous replenishment of glucagon-positive cells indicating that GABA treatment, not only induces transdifferentiation of α-cells in to β-like cells, but also maintains an α-cell pool [8]. This is important as it suggests that this treatment may be able to maintain the overall proportion of islet cell types (see Figure 1), although it is currently clear whether this will have effects on islet architecture and function in the long term. Nevertheless, this is a particularly intriguing finding as, whilst it has previously been demonstrated that near complete ablation of α-cells in rodents had little physiological effect [6], partial pancreatectomy in humans have been shown to lead to enhanced responsiveness to glucagon [81], and to secretion of glucagon from extra-pancreatic sites [82,83], both of which leads to altered glucose handling. Thus, although it is useful to be able to make β-like cells from α-cells, maintaining an α-cell population may also be important for the maintenance of glucose homeostasis in humans.
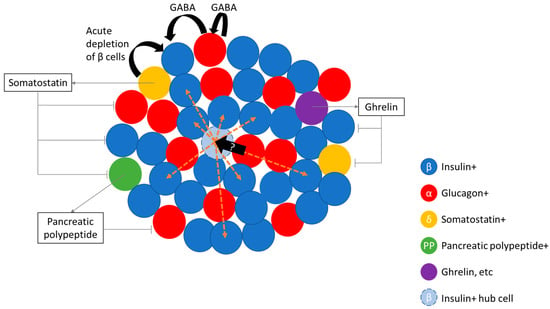
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram showing the interdependency of islet cells. Evidence in the literature points to the possibility of the transdifferentiation (solid black arrows) of α-cells (red circle) via stimulation by gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA), and δ-cells (yellow circle) into insulin-containing β (like)-cells (blue circle). It is currently unclear whether the replenishment of β-cells from the transdifferentiation of α-cells is able to replace hub β-cells (light blue circle) which influence (yellow arrows) the function of other β-cells. Somatostatin, released from δ-cells, can inhibit the release of glucagon, insulin, and pancreatic polypeptide from α-, β-, and PP cells (green circle), respectively. Pancreatic polypeptide, released from PP cells, can inhibit the release of glucagon. Ghrelin, released from ghrelin-positive islet cells (purple circle), can inhibit insulin and somatostatin secretion.
In any cell (re)programming protocol, it is important to have a grasp of the identities/characteristics of the starting cell and the destination cell. The current state of the art is likely to act as a further catalyst for studies in to the α-cell as a result. For example, recent studies focussed on identifying β-cells based on expression profiles of protein-encoding genes and non-coding RNAs, are now also paralleled in α-cells [84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105].
4. β-Cell
The β-cell is the most studied of the islet cell types and has been written about copiously [106,107,108,109,110,111], so it would be superfluous to elaborate too much here. There are important differences between mouse and human β-cells which need to be considered in the design of therapeutic interventions for increasing functional β-cell mass [106].
What is a β-cell? Simplistically, it is a cell that makes insulin that is able to secrete insulin in response to a glucose challenge. Insulin is packaged into secretory granules at concentrations of circa 100 mM [112,113] as a complex with zinc, and released in response to high glucose (and other nutrient) concentrations [113] and stimulation by neurotransmitters that are released in response to food [114]. Insulin secretion is also enhanced by the presence of incretin hormones [114]. Somatostatin, which is secreted by neighbouring δ-cells, inhibit insulin secretion [115], as do epinephrine [116,117], galanin [118], ghrelin [119], leptin [120] and zinc ions [121]. Glucose metabolism in the β-cell differs from other cell types in that the presence of low affinity, high transport capacity glucose transporter(s) (GLUT1 and 2 in humans, Glut2 in mice) [122,123,124,125], and the low affinity hexokinase-glucokinase (GCK) [126,127] results in β-cell glucose metabolism being controlled by substrate availability. Glycolysis and mitchondrial oxidation are closely coupled, due to the lack of expression of “disallowed genes” such as lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and the monocarboxylate transporter (MCT1)[128]. This coupling is disrupted in islets of Langerhans from type 2 diabetic donors [127,129,130], with concomitant expression of disallowed genes such as LDH and MCT1 (reviewed in [109]). Unsurprisingly there is currently much attention on the identity of the islet cell types, with the focus predominantly on the β-cell, especially in the context of coding and non-coding RNA (as mentioned in the Section 3), which may be involved in the regulation of the expression these disallowed or β-cell specific genes.
ATP production leads to closure of the ATP sensitive K+ channel (KATP) channel on the cell surface; the subsequent membrane depolarization leads to opening of voltage-gated L-type calcium channels, influx of calcium and the release of insulin (detailed mechanisms reviewed in [106]).
Interestingly, studies looking at β-cell regeneration in humans following partial pancreatectomy demonstrated an increase in β-cell function [131] but not β-cell mass [132]. Additionally, the same cohort of patients that had previously exhibited post-operative elevated fasting glucose and post-challenge glycaemia [33], showed amelioration of both parameters circa 3 years after pancreatectomy due to increased β-cell function [131]. Taken together with data from Ionescu-Tirgoviste and colleagues [9], which demonstrate that islet distribution is even throughout the human pancreas, the ability to increase function may not be dependent on the location of the β-cell in the pancreas. This compensatory increase in β-cell function is also seen in hyper-functional islets from obese individuals [113,133,134,135,136,137,138] which exhibit a two- to three-fold increase in insulin secretory capcity vs. lean individuals [139,140]. The obesity model also offers a contrary view to human β-cell mass plasticity vs pancreatectomy model: there is convincing data from various sources indicating that β-cell regeneration may occur in pancreases from obese subjects [135,140,141,142,143,144,145,146]. Add to this the potential to transdifferentiate α-cells to β-cells [8], and the potential of transplantation of human pluripotent stem cell-derived β-like cells [147], the future seems bright for restoring β-cell mass. However, one recent development may throw a spanner in the works. There is significant heterogeneity in β-cells within an islet which suggests that the structure of the islet—the connections between cells and the spatial arrangement of islet cells—may be important for the regulation of islet function [110,148,149]. Specialised insulin-positive islet hub cells—which are able to impact on the function of other cells in the islet—may be characteristically different to other insulin-positive cells in the same islet, begging the question as to how this difference was effected [110,148,149]. Did these cells arise from a special subset of progenitor cells, or were they the product of a subset of developmental cues that may have resulted from their position in the overall islet structure/pancreas? If that is the case then simply being able to (randomly) make more β-cells may not be enough to reinstate normal glucose homeostasis. For example, a question may be whether it is possible to replace hub β-cells through the transdifferentiation of α-cells (see Figure 1). It is worth mentioning that diabetes is increasingly acknowledged as a bihormonal disease and thus the study of at least both α- and β-cells are merited. It is possible that our view of the disease will expand as we find out more about the other islet cell types, e.g., the δ-cell (see below).
5. δ-Cell
Somatostatin secreting cells, or δ-cells, are present in the pancreatic islets, the hypothalamus, the central nervous system, peripheral neurons and the gastrointestinal tract [68,79,150,151,152]. δ-cells make up about 10% of the islet cell population. Somatostatin is a negative regulator of insulin, glucagon and pancreatic polypeptide secretion under conditions of nutrient stimulus [116,153,154,155,156], and in a Ca2+ dependent manner [156,157,158,159,160,161] (see Figure 1). δ-cells are electrically excitable, like α- and β-cells (reviewed in [111]). Ghrelin [162] and urocrotin [163] act on δ-cells leading to somatostatin release.Somatostatin is synthesised as a precursor molecule that is processed enzymatically by protein convertase, with the 14 amino acid peptide fragment, somatostatin (SST)-14, as the major peptide released by δ-cells [164,165]. SST-14 binds to the somatostatin receptor (of which there are five subtypes [166], which are G-protein coupled receptors, and lead to the inhibition of adenylyl cyclase [167] or activation of inwardly rectifying K+ channels [168].
δ-cells have been reported to transdifferentiate into β-cells in acute depletion of β-cell mass [5]. The transcription factor Pax4 is involved in the development of both β- and δ-cells during pancreatic specification [169]. Recently it was shown that mis-expression Pax4 in α-cells leads to conversion to β-like cells with no evidence for δ-cell like conversion [7]. It has been shown that the δ-cell fate is maintained by the Hhex gene [170]; loss of Hhex led to disrupted paracrine regulation of insulin secretion, which may potentially contribute to T2D [170,171]. Similarly, as δ-cells also regulate α-cells, loss of δ-cell mass due to transdifferentiation in to β-cells may lead to dysregulated glucagon secretion. In short, the current evidence does not support trasndifferentiation of δ-cells to β-cells as a viable means to replenish β-cell mass.
6. PP Cell
Pancreatic polypeptide containing cells, also called PP cells or F-cells [172,173,174,175,176], make up 1–2% of the islet cell population [177,178,179]. PP cells are more concentrated in the head of the pancreas [180,181], where the cells are found to occupy the outer mantle of rodent islets or lining the capillaries in human islets [79]. Post-prandial pancreatic polypetide release is regulated by vagal and enteric nervous input [182,183,184,185], and is responsive to arginine but not glucose sitmulation [186]. Pancreatic polypeptide has been shown to be an inhibitor of glucagon release at low glucose [187] (see Figure 1). The major function of PP appears to be that of a satiety hormone (reviewed in [188]).
7. Ghrelin-Positive and Other Islet Cell Types
A further three types of islet cells have been described in the literature. These cells contain ghrelin [189,190], serotonin (enterochromaffin cells) [191,192], gastrin (G-cells) [174,193], and small granules of unknown content (P/D1- cells) [174,191,194,195,196,197].
Of these the ghrelin positive cells have recently attracted the most interest. Ghrelin-positive cells are mainly found in the gut [195,198,199,200,201]. Ghrelin-positive cells are also found in the islet, accounting for circa 10% and 1% of islet cell content in foetal and adult islets, respectively [119,189,190,195]. It has been suggested that ghrelin positive cells in the islets are in fact the P/D1 cells, which were described as containing an unknown hormone, as the two cell types share a lot of ultrastructural and distribution similarities [119]. The developmental programme for ghrelin positive cells appear to be different between human, mouse and rat (reviewed in [119]), and thus data on developmental pathways for ghrelin cells elucidated in mice (e.g., [202]) may not apply to humans.
Ghrelin is increased in fasting [203,204,205]; plasma ghrelin content has a reciprocal relationship with plasma insulin content [206,207], and has been shown to be an inhibitor of insulin secretion in human and rodents [208,209,210,211,212,213]. Ghrelin may also be a regulator of glucagon, PP and somatostatin release [210,214,215].
8. Conclusions
The cells in the islets have distinct regulatory function and operate within a complex regulatory network invoking paracrine and neuronal control of energy homeostasis. There are differences in islet architecture and distribution between human and experimental models, which may have an impact on islet function and energy homeostasis. Recent reports have indicated islet cells are plastic and that it may be possible to convert non-β islet cells into β-cells to replenish β-cell mass and function [4,5,7,8]. This knowledge may be important for the development of treatment strategies for diabetes, but will require careful evaluation of the impact of the loss of a particular non-β islet endocrine cell type on energy homeostasis.
Acknowledgments
Gabriela da Silva Xavier thanks Diabetes UK, the MRC, and the European Foundation for the Study of Diabetes for funding in support of her research activities.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Borden, P.; Houtz, J.; Leach, S.D.; Kuruvilla, R. Sympathetic innervation during development is necessary for pancreatic islet architecture and functional maturation. Cell Rep. 2013, 4, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dor, Y.; Brown, J.; Martinez, O.I.; Melton, D.A. Adult pancreatic beta-cells are formed by self-duplication rather than stem-cell differentiation. Nature 2004, 429, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano, D.A.; Rulifson, I.C.; Heiser, P.W.; Swigart, L.B.; Pelengaris, S.; German, M.; Evan, G.I.; Bluestone, J.A.; Hebrok, M. Regulated beta-cell regeneration in the adult mouse pancreas. Diabetes 2008, 57, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorel, F.; Nepote, V.; Avril, I.; Kohno, K.; Desgraz, R.; Chera, S.; Herrera, P.L. Conversion of adult pancreatic alpha-cells to beta-cells after extreme beta-cell loss. Nature 2010, 464, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chera, S.; Baronnier, D.; Ghila, L.; Cigliola, V.; Jensen, J.N.; Gu, G.; Furuyama, K.; Thorel, F.; Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F.; et al. Diabetes recovery by age-dependent conversion of pancreatic delta-cells into insulin producers. Nature 2014, 514, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorel, F.; Damond, N.; Chera, S.; Wiederkehr, A.; Thorens, B.; Meda, P.; Wollheim, C.B.; Herrera, P.L. Normal glucagon signaling and beta-cell function after near-total alpha-cell ablation in adult mice. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2872–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napolitano, T.; Avolio, F.; Courtney, M.; Vieira, A.; Druelle, N.; Ben-Othman, N.; Hadzic, B.; Navarro, S.; Collombat, P. Pax4 acts as a key player in pancreas development and plasticity. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 44, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Othman, N.; Vieira, A.; Courtney, M.; Record, F.; Gjernes, E.; Avolio, F.; Hadzic, B.; Druelle, N.; Napolitano, T.; Navarro-Sanz, S.; et al. Long-term gaba administration induces alpha cell-mediated beta-like cell neogenesis. Cell 2017, 168, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionescu-Tirgoviste, C.; Gagniuc, P.A.; Gubceac, E.; Mardare, L.; Popescu, I.; Dima, S.; Militaru, M. A 3D map of the islet routes throughout the healthy human pancreas. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, K.; Iwama, N.; Takahashi, T. Morphometrical analysis on topographical difference in size distribution, number and volume of islets in the human pancreas. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 1978, 124, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellman, B. Actual distribution of the number and volume of the islets of langerhans in different size classes in non-diabetic humans of varying ages. Nature 1959, 184 (Suppl. 19), 1498–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellman, B. The numerical distribution of the islets of langerhans at different ages of the rat. Acta Endocrinol. 1959, 32, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellman, B. The volumetric distribution of the pancreatic islet tissue in young and old rats. Acta Endocrinol. 1959, 31, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellman, B. The frequency distribution of the number and volume of the islets langerhans in man. I. Studies on non-diabetic adults. Acta Soc. Med. Ups. 1959, 64, 432–460. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.; Miller, K.; Jo, J.; Kilimnik, G.; Wojcik, P.; Hara, M. Islet architecture: A comparative study. Islets 2009, 1, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, D.J.; Kim, A.; Miller, K.; Hara, M. Pancreatic islet plasticity: Interspecies comparison of islet architecture and composition. Islets 2010, 2, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera, O.; Berman, D.M.; Kenyon, N.S.; Ricordi, C.; Berggren, P.O.; Caicedo, A. The unique cytoarchitecture of human pancreatic islets has implications for islet cell function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2334–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brissova, M.; Fowler, M.J.; Nicholson, W.E.; Chu, A.; Hirshberg, B.; Harlan, D.M.; Powers, A.C. Assessment of human pancreatic islet architecture and composition by laser scanning confocal microscopy. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2005, 53, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orci, L.; Baetens, D.; Ravazzola, M.; Stefan, Y.; Malaisse-Lagae, F. Pancreatic polypeptide and glucagon: Non-random distribution in pancreatic islets. Life Sci. 1976, 19, 1811–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichii, H.; Inverardi, L.; Pileggi, A.; Molano, R.D.; Cabrera, O.; Caicedo, A.; Messinger, S.; Kuroda, Y.; Berggren, P.O.; Ricordi, C. A novel method for the assessment of cellular composition and beta-cell viability in human islet preparations. Am. J. Transplant. 2005, 5, 1635–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elayat, A.A.; el-Naggar, M.M.; Tahir, M. An immunocytochemical and morphometric study of the rat pancreatic islets. J. Anat. 1995, 186 Pt 3, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Orci, L.; Unger, R.H. Functional subdivision of islets of langerhans and possible role of d cells. Lancet 1975, 2, 1243–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samols, E.; Bonner-Weir, S.; Weir, G.C. Intra-islet insulin-glucagon-somatostatin relationships. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1986, 15, 33–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Misawa, R.; Zielinski, M.C.; Cowen, P.; Jo, J.; Periwal, V.; Ricordi, C.; Khan, A.; Szust, J.; Shen, J.; et al. Regional differences in islet distribution in the human pancreas--preferential beta-cell loss in the head region in patients with type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baetens, D.; Malaisse-Lagae, F.; Perrelet, A.; Orci, L. Endocrine pancreas: Three-dimensional reconstruction shows two types of islets of langerhans. Science 1979, 206, 1323–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trimble, E.R.; Halban, P.A.; Wollheim, C.B.; Renold, A.E. Functional differences between rat islets of ventral and dorsal pancreatic origin. J. Clin. Investig. 1982, 69, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trimble, E.R.; Renold, A.E. Ventral and dorsal areas of rat pancreas: Islet hormone content and secretion. Am. J. Physiol. 1981, 240, E422–E427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclercq-Meyer, V.; Marchand, J.; Malaisse, W.J. Insulin and glucagon release from the ventral and dorsal parts of the perfused pancreas of the rat. Effects of glucose, arginine, glucagon and carbamylcholine. Horm. Res. 1985, 21, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasaka, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Inoue, Y.; Hirata, Y. Contents and secretion of glucagon and insulin in rat pancreatic islets from the viewpoint of their localization in pancreas. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 1989, 159, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yukawa, M.; Takeuchi, T.; Watanabe, T.; Kitamura, S. Proportions of various endocrine cells in the pancreatic islets of wood mice (Apodemus speciosus). Anat. Histol. Embryol. 1999, 28, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguayo-Mazzucato, C.; Sanchez-Soto, C.; Godinez-Puig, V.; Gutierrez-Ospina, G.; Hiriart, M. Restructuring of pancreatic islets and insulin secretion in a postnatal critical window. PLoS ONE 2006, 1, e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornblad, A.; Cheddad, A.; Ahlgren, U. An improved protocol for optical projection tomography imaging reveals lobular heterogeneities in pancreatic islet and beta-cell mass distribution. Islets 2011, 3, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menge, B.A.; Schrader, H.; Breuer, T.G.; Dabrowski, Y.; Uhl, W.; Schmidt, W.E.; Meier, J.J. Metabolic consequences of a 50% partial pancreatectomy in humans. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, D.M.; Sutherland, D.E.; Najarian, J.S.; Goetz, F.C.; Robertson, R.P. Effects of hemipancreatectomy on insulin secretion and glucose tolerance in healthy humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandol, S.J. The Exocrine Pancreas; Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gittes, G.K. Developmental biology of the pancreas: A comprehensive review. Dev. Biol. 2009, 326, 4–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerich, J.E. Lilly lecture 1988. Glucose counterregulation and its impact on diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 1988, 37, 1608–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerich, J.E.; Campbell, P.J. Overview of counterregulation and its abnormalities in diabetes mellitus and other conditions. Diabetes Metab. Rev. 1988, 4, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, R.H.; Orci, L. The essential role of glucagon in the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1975, 1, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryer, P.E. Minireview: Glucagon in the pathogenesis of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia in diabetes. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunning, B.E.; Gerich, J.E. The role of alpha-cell dysregulation in fasting and postprandial hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes and therapeutic implications. Endocr. Rev. 2007, 28, 253–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, R.H.; Orci, L. Glucagon and the a cell: Physiology and pathophysiology (first two parts). N. Engl. J. Med. 1981, 304, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gromada, J.; Franklin, I.; Wollheim, C.B. Alpha-cells of the endocrine pancreas: 35 years of research but the enigma remains. Endocr. Rev. 2007, 28, 84–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Wang, M.Y.; Du, X.Q.; Charron, M.J.; Unger, R.H. Glucagon receptor knockout prevents insulin-deficient type 1 diabetes in mice. Diabetes 2011, 60, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunning, B.E.; Foley, J.E.; Ahren, B. Alpha cell function in health and disease: Influence of glucagon-like peptide-1. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 1700–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gylfe, E. Glucose control of glucagon secretion-‘there’s a brand-new gimmick every year’. Ups. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 121, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gylfe, E.; Gilon, P. Glucose regulation of glucagon secretion. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 103, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishihara, H.; Maechler, P.; Gjinovci, A.; Herrera, P.L.; Wollheim, C.B. Islet beta-cell secretion determines glucagon release from neighbouring alpha-cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berggren, P.O.; Ostenson, C.G.; Petersson, B.; Hellman, B. Evidence for divergent glucose effects on calcium metabolism in pancreatic beta- and alpha 2-cells. Endocrinology 1979, 105, 1463–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostenson, C.G. Regulation of glucagon release: Effects of insulin on the pancreatic a2-cell of the guinea pig. Diabetologia 1979, 17, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pipeleers, D.G.; Schuit, F.C.; Van Schravendijk, C.F.; Van de Winkel, M. Interplay of nutrients and hormones in the regulation of glucagon release. Endocrinology 1985, 117, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, J.N.; Ramracheya, R.; Zhang, Q.; Johnson, P.R.; Braun, M.; Rorsman, P. Regulation of glucagon secretion by glucose: Paracrine, intrinsic or both? Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13 (Suppl. 1), 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, T.; Harmon, J.S.; Bryan, J.; Robertson, R.P. Zinc, not insulin, regulates the rat alpha-cell response to hypoglycemia in vivo. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knop, F.K.; Vilsboll, T.; Madsbad, S.; Holst, J.J.; Krarup, T. Inappropriate suppression of glucagon during ogtt but not during isoglycaemic i.V. Glucose infusion contributes to the reduced incretin effect in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, J.J. The contribution of incretin hormones to the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 23, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, J.J.; Deacon, C.F.; Schmidt, W.E.; Holst, J.J.; Nauck, M.A. Suppression of glucagon secretion is lower after oral glucose administration than during intravenous glucose administration in human subjects. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolson, T.J.; Bellomo, E.A.; Wijesekara, N.; Loder, M.K.; Baldwin, J.M.; Gyulkhandanyan, A.V.; Koshkin, V.; Tarasov, A.I.; Carzaniga, R.; Kronenberger, K.; et al. Insulin storage and glucose homeostasis in mice null for the granule zinc transporter znt8 and studies of the type 2 diabetes-associated variants. Diabetes 2009, 58, 2070–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravier, M.A.; Rutter, G.A. Glucose or insulin, but not zinc ions, inhibit glucagon secretion from mouse pancreatic alpha-cells. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santeusanio, F.; Faloona, G.R.; Unger, R.H. Suppressive effect of secretin upon pancreatic alpha cell function. J. Clin. Investig. 1972, 51, 1743–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rushakoff, R.J.; Goldfine, I.D.; Carter, J.D.; Liddle, R.A. Physiological concentrations of cholecystokinin stimulate amino acid-induced insulin release in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1987, 65, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Heer, J.; Pedersen, J.; Orskov, C.; Holst, J.J. The alpha cell expresses glucagon-like peptide-2 receptors and glucagon-like peptide-2 stimulates glucagon secretion from the rat pancreas. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 2135–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauck, M.A.; Weber, I.; Bach, I.; Richter, S.; Orskov, C.; Holst, J.J.; Schmiegel, W. Normalization of fasting glycaemia by intravenous GLP-1 ([7-36 amide] or [7-37]) in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabet. Med. 1998, 15, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, C.W.; Carlson, O.D.; Kim, W.; Shin, Y.K.; Charles, C.P.; Kim, H.S.; Melvin, D.L.; Egan, J.M. Exogenous glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide worsens post prandial hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, A.; Vilsboll, T.; Bagger, J.I.; Holst, J.J.; Knop, F.K. The separate and combined impact of the intestinal hormones, GIP, GLP-1, and GLP-2, on glucagon secretion in type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 300, E1038–E1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, A.; Bagger, J.I.; Christensen, M.; Knop, F.K.; Vilsboll, T. Glucagon and type 2 diabetes: The return of the alpha cell. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2014, 14, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marinis, Y.Z.; Salehi, A.; Ward, C.E.; Zhang, Q.; Abdulkader, F.; Bengtsson, M.; Braha, O.; Braun, M.; Ramracheya, R.; Amisten, S.; et al. GLP-1 inhibits and adrenaline stimulates glucagon release by differential modulation of N- and L-type Ca2+ channel-dependent exocytosis. Cell Metab. 2010, 11, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, P.; Lupi, R.; Bugliani, M.; Kirkpatrick, C.L.; Sebastiani, G.; Grieco, F.A.; Del Guerra, S.; D’Aleo, V.; Piro, S.; Marselli, L.; et al. A local glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) system in human pancreatic islets. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 3262–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luft, R.; Efendic, S.; Hokfelt, T. Somatostatin—Both hormone and neurotransmitter? Diabetologia 1978, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaff, L.J.; Taborsky, G.J., Jr. Pancreatic somatostatin is a mediator of glucagon inhibition by hyperglycemia. Diabetes 1987, 36, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starke, A.; Imamura, T.; Unger, R.H. Relationship of glucagon suppression by insulin and somatostatin to the ambient glucose concentration. J. Clin. Investig. 1987, 79, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreymann, B.; Williams, G.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. Glucagon-like peptide-1 7-36: A physiological incretin in man. Lancet 1987, 2, 1300–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Heer, J.; Rasmussen, C.; Coy, D.H.; Holst, J.J. Glucagon-like peptide-1, but not glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide, inhibits glucagon secretion via somatostatin (receptor subtype 2) in the perfused rat pancreas. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 2263–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamy, C.M.; Sanno, H.; Labouebe, G.; Picard, A.; Magnan, C.; Chatton, J.Y.; Thorens, B. Hypoglycemia-activated GLUT2 neurons of the nucleus tractus solitarius stimulate vagal activity and glucagon secretion. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorens, B. Brain glucose sensing and neural regulation of insulin and glucagon secretion. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13 (Suppl. 1), 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorens, B. Neural regulation of pancreatic islet cell mass and function. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16 (Suppl. 1), 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havel, P.J.; Taborsky, G.J., Jr. The contribution of the autonomic nervous system to changes of glucagon and insulin secretion during hypoglycemic stress. Endocr. Rev. 1989, 10, 332–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryer, P.E. Hypoglycemia: Still the limiting factor in the glycemic management of diabetes. Endocr. Pract. 2008, 14, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryer, P.E. Mechanisms of sympathoadrenal failure and hypoglycemia in diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1470–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brereton, M.F.; Vergari, E.; Zhang, Q.; Clark, A. Alpha-, delta- and pp-cells: Are they the architectural cornerstones of islet structure and co-ordination? J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2015, 63, 575–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briant, L.; Salehi, A.; Vergari, E.; Zhang, Q.; Rorsman, P. Glucagon secretion from pancreatic alpha-cells. Ups. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 121, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajorunas, D.R.; Fortner, J.G.; Jaspan, J.; Sherwin, R.S. Total pancreatectomy increases the metabolic response to glucagon in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1986, 63, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasui, K. Effects of total pancreatectomy on the secretion of gut glucagon in humans. Jpn. J. Surg. 1983, 13, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, A.; Bagger, J.I.; Wewer Albrechtsen, N.J.; Christensen, M.; Grondahl, M.; Hartmann, B.; Mathiesen, E.R.; Hansen, C.P.; Storkholm, J.H.; van Hall, G.; et al. Evidence of extrapancreatic glucagon secretion in man. Diabetes 2016, 65, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuit, F.; Van Lommel, L.; Granvik, M.; Goyvaerts, L.; de Faudeur, G.; Schraenen, A.; Lemaire, K. Beta-cell-specific gene repression: A mechanism to protect against inappropriate or maladjusted insulin secretion? Diabetes 2012, 61, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pullen, T.J.; da Silva Xavier, G.; Kelsey, G.; Rutter, G.A. Mir-29a and mir-29b contribute to pancreatic beta-cell-specific silencing of monocarboxylate transporter 1 (MCT1). Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 3182–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pullen, T.J.; Khan, A.M.; Barton, G.; Butcher, S.A.; Sun, G.; Rutter, G.A. Identification of genes selectively disallowed in the pancreatic islet. Islets 2010, 2, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Sanchez, A.; Nguyen-Tu, M.S.; Rutter, G.A. Dicer inactivation identifies pancreatic beta-cell “disallowed” genes targeted by micrornas. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 29, 1067–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dooley, J.; Garcia-Perez, J.E.; Sreenivasan, J.; Schlenner, S.M.; Vangoitsenhoven, R.; Papadopoulou, A.S.; Tian, L.; Schonefeldt, S.; Serneels, L.; Deroose, C.; et al. The microrna-29 family dictates the balance between homeostatic and pathological glucose handling in diabetes and obesity. Diabetes 2016, 65, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagge, A.; Clausen, T.R.; Larsen, S.; Ladefoged, M.; Rosenstierne, M.W.; Larsen, L.; Vang, O.; Nielsen, J.H.; Dalgaard, L.T. Microrna-29a is up-regulated in beta-cells by glucose and decreases glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 426, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalgaard, L.T.; Eliasson, L. An ‘alpha-beta’ of pancreatic islet microribonucleotides. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 88, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliasson, L.; Esguerra, J.L. Role of non-coding rnas in pancreatic beta-cell development and physiology. Acta Physiol. 2014, 211, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esguerra, J.L.; Bolmeson, C.; Cilio, C.M.; Eliasson, L. Differential glucose-regulation of micrornas in pancreatic islets of non-obese type 2 diabetes model goto-kakizaki rat. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esguerra, J.L.; Eliasson, L. Functional implications of long non-coding RNAs in the pancreatic islets of langerhans. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalis, M.; Bolmeson, C.; Esguerra, J.L.; Gupta, S.; Edlund, A.; Tormo-Badia, N.; Speidel, D.; Holmberg, D.; Mayans, S.; Khoo, N.K.; et al. Beta-cell specific deletion of dicer1 leads to defective insulin secretion and diabetes mellitus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poy, M.N.; Eliasson, L.; Krutzfeldt, J.; Kuwajima, S.; Ma, X.; Macdonald, P.E.; Pfeffer, S.; Tuschl, T.; Rajewsky, N.; Rorsman, P.; et al. A pancreatic islet-specific microrna regulates insulin secretion. Nature 2004, 432, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osmai, M.; Osmai, Y.; Bang-Berthelsen, C.H.; Pallesen, E.M.; Vestergaard, A.L.; Novotny, G.W.; Pociot, F.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. Micrornas as regulators of beta-cell function and dysfunction. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2016, 32, 334–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guay, C.; Regazzi, R. Micrornas and the functional beta cell mass: For better or worse. Diabetes Metab. 2015, 41, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kameswaran, V.; Kaestner, K.H. The missing Lnc(RNA) between the pancreatic beta-cell and diabetes. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Bunt, M.; Gaulton, K.J.; Parts, L.; Moran, I.; Johnson, P.R.; Lindgren, C.M.; Ferrer, J.; Gloyn, A.L.; McCarthy, M.I. The mirna profile of human pancreatic islets and beta-cells and relationship to type 2 diabetes pathogenesis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, D.; Misawa, R.; Bravo-Egana, V.; Vargas, N.; Rosero, S.; Piroso, J.; Ichii, H.; Umland, O.; Zhijie, J.; Tsinoremas, N.; et al. Microrna expression in alpha and beta cells of human pancreatic islets. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poy, M.N.; Hausser, J.; Trajkovski, M.; Braun, M.; Collins, S.; Rorsman, P.; Zavolan, M.; Stoffel, M. Mir-375 maintains normal pancreatic alpha- and beta-cell mass. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5813–5818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latreille, M.; Herrmanns, K.; Renwick, N.; Tuschl, T.; Malecki, M.T.; McCarthy, M.I.; Owen, K.R.; Rulicke, T.; Stoffel, M. Mir-375 gene dosage in pancreatic beta-cells: Implications for regulation of beta-cell mass and biomarker development. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 93, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbagallo, D.; Piro, S.; Condorelli, A.G.; Mascali, L.G.; Urbano, F.; Parrinello, N.; Monello, A.; Statello, L.; Ragusa, M.; Rabuazzo, A.M.; et al. miR-296-3p, miR-298-5p and their downstream networks are causally involved in the higher resistance of mammalian pancreatic alpha cells to cytokine-induced apoptosis as compared to beta cells. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, R.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.W.; Xu, C.R.; Gradwohl, G.; Tang, X. Differentially expressed microRNA-483 confers distinct functions in pancreatic beta- and alpha-cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 19955–19966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhawan, S.; Georgia, S.; Tschen, S.I.; Fan, G.; Bhushan, A. Pancreatic beta cell identity is maintained by DNA methylation-mediated repression of arx. Dev. Cell 2011, 20, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rorsman, P.; Ashcroft, F.M. Pancreatic beta-cell electrical activity and insulin secretion: Of mice and men. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 117–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Cohrs, C.M.; Stertmann, J.; Bozsak, R.; Speier, S. Human beta cell mass and function in diabetes: Recent advances in knowledge and technologies to understand disease pathogenesis. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 943–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avrahami, D.; Wang, Y.J.; Klochendler, A.; Dor, Y.; Glaser, B.; Kaestner, K.H. Beta-cells are not uniform after all-novel insights into molecular heterogeneity of insulin-secreting cells. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19 (Suppl. 1), 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutter, G.A.; Pullen, T.J.; Hodson, D.J.; Martinez-Sanchez, A. Pancreatic beta-cell identity, glucose sensing and the control of insulin secretion. Biochem. J. 2015, 466, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutter, G.A.; Hodson, D.J. Minireview: Intraislet regulation of insulin secretion in humans. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 27, 1984–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanno, T.; Gopel, S.O.; Rorsman, P.; Wakui, M. Cellular function in multicellular system for hormone-secretion: Electrophysiological aspect of studies on alpha-, beta- and delta-cells of the pancreatic islet. Neurosci. Res. 2002, 42, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Shen, H.; Atkinson, M.A.; Kennedy, R.T. Detection of exocytosis at individual pancreatic beta cells by amperometry at a chemically modified microelectrode. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 9608–9612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rorsman, P.; Renstrom, E. Insulin granule dynamics in pancreatic beta cells. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 1029–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, N.; Flatt, P.R. Enteroendocrine hormone mimetics for the treatment of obesity and diabetes. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2013, 13, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ensinck, J.W.; Laschansky, E.C.; Vogel, R.E.; Simonowitz, D.A.; Roos, B.A.; Francis, B.H. Circulating prosomatostatin-derived peptides. Differential responses to food ingestion. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 83, 1580–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kailey, B.; van de Bunt, M.; Cheley, S.; Johnson, P.R.; MacDonald, P.E.; Gloyn, A.L.; Rorsman, P.; Braun, M. Sstr2 is the functionally dominant somatostatin receptor in human pancreatic beta- and alpha-cells. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 303, E1107–E1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacey, R.J.; Berrow, N.S.; London, N.J.; Lake, S.P.; James, R.F.; Scarpello, J.H.; Morgan, N.G. Differential effects of beta-adrenergic agonists on insulin secretion from pancreatic islets isolated from rat and man. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 1990, 5, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renstrom, E.; Ding, W.G.; Bokvist, K.; Rorsman, P. Neurotransmitter-induced inhibition of exocytosis in insulin-secreting beta cells by activation of calcineurin. Neuron 1996, 17, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierup, N.; Sundler, F.; Heller, R.S. The islet ghrelin cell. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 52, R35–R49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seufert, J.; Kieffer, T.J.; Leech, C.A.; Holz, G.G.; Moritz, W.; Ricordi, C.; Habener, J.F. Leptin suppression of insulin secretion and gene expression in human pancreatic islets: Implications for the development of adipogenic diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, R.; Soria, B.; Dawson, C.M.; Atwater, I.; Rojas, E. Effects of Zn2+ on glucose-induced electrical activity and insulin release from mouse pancreatic islets. Am. J. Physiol. 1984, 246, C520–C527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorens, B. GLUT2, glucose sensing and glucose homeostasis. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimberg, H.; De Vos, A.; Pipeleers, D.; Thorens, B.; Schuit, F. Differences in glucose transporter gene expression between rat pancreatic alpha- and beta-cells are correlated to differences in glucose transport but not in glucose utilization. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 8971–8975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCulloch, L.J.; van de Bunt, M.; Braun, M.; Frayn, K.N.; Clark, A.; Gloyn, A.L. GLUT2 (SLC2A2) is not the principal glucose transporter in human pancreatic beta cells: Implications for understanding genetic association signals at this locus. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2011, 104, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahren, B. Autonomic regulation of islet hormone secretion—Implications for health and disease. Diabetologia 2000, 43, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonner, C.; Kerr-Conte, J.; Gmyr, V.; Queniat, G.; Moerman, E.; Thevenet, J.; Beaucamps, C.; Delalleau, N.; Popescu, I.; Malaisse, W.J.; et al. Inhibition of the glucose transporter SGLT2 with dapagliflozin in pancreatic alpha cells triggers glucagon secretion. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doliba, N.M.; Qin, W.; Najafi, H.; Liu, C.; Buettger, C.W.; Sotiris, J.; Collins, H.W.; Li, C.; Stanley, C.A.; Wilson, D.F.; et al. Glucokinase activation repairs defective bioenergetics of islets of langerhans isolated from type 2 diabetics. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 302, E87–E102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorrez, L.; Laudadio, I.; Van Deun, K.; Quintens, R.; Hendrickx, N.; Granvik, M.; Lemaire, K.; Schraenen, A.; Van Lommel, L.; Lehnert, S.; et al. Tissue-specific disallowance of housekeeping genes: The other face of cell differentiation. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Guerra, S.; Lupi, R.; Marselli, L.; Masini, M.; Bugliani, M.; Sbrana, S.; Torri, S.; Pollera, M.; Boggi, U.; Mosca, F.; et al. Functional and molecular defects of pancreatic islets in human type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2005, 54, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anello, M.; Lupi, R.; Spampinato, D.; Piro, S.; Masini, M.; Boggi, U.; Del Prato, S.; Rabuazzo, A.M.; Purrello, F.; Marchetti, P. Functional and morphological alterations of mitochondria in pancreatic beta cells from type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menge, B.A.; Breuer, T.G.; Ritter, P.R.; Uhl, W.; Schmidt, W.E.; Meier, J.J. Long-term recovery of beta-cell function after partial pancreatectomy in humans. Metabolism 2012, 61, 620–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menge, B.A.; Tannapfel, A.; Belyaev, O.; Drescher, R.; Muller, C.; Uhl, W.; Schmidt, W.E.; Meier, J.J. Partial pancreatectomy in adult humans does not provoke beta-cell regeneration. Diabetes 2008, 57, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrannini, E.; Natali, A.; Bell, P.; Cavallo-Perin, P.; Lalic, N.; Mingrone, G. Insulin resistance and hypersecretion in obesity. European group for the study of insulin resistance (EGIR). J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seltzer, H.S.; Allen, E.W.; Herron, A.L., Jr.; Brennan, M.T. Insulin secretion in response to glycemic stimulus: Relation of delayed initial release to carbohydrate intolerance in mild diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Investig. 1967, 46, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillioja, S.; Mott, D.M.; Spraul, M.; Ferraro, R.; Foley, J.E.; Ravussin, E.; Knowler, W.C.; Bennett, P.H.; Bogardus, C. Insulin resistance and insulin secretory dysfunction as precursors of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Prospective studies of pima indians. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 1988–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camastra, S.; Manco, M.; Mari, A.; Baldi, S.; Gastaldelli, A.; Greco, A.V.; Mingrone, G.; Ferrannini, E. Beta-cell function in morbidly obese subjects during free living: Long-term effects of weight loss. Diabetes 2005, 54, 2382–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polonsky, K.S.; Given, B.D.; Van Cauter, E. Twenty-four-hour profiles and pulsatile patterns of insulin secretion in normal and obese subjects. J. Clin. Investig. 1988, 81, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perley, M.; Kipnis, D.M. Plasma insulin responses to glucose and tolbutamide of normal weight and obese diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes 1966, 15, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezghenna, K.; Pomies, P.; Chalancon, A.; Castex, F.; Leroy, J.; Niclauss, N.; Nadal, B.; Cambier, L.; Cazevieille, C.; Petit, P.; et al. Increased neuronal nitric oxide synthase dimerisation is involved in rat and human pancreatic beta cell hyperactivity in obesity. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 2856–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandhorst, H.; Brandhorst, D.; Hering, B.J.; Federlin, K.; Bretzel, R.G. Body mass index of pancreatic donors: A decisive factor for human islet isolation. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 1995, 103 (Suppl. 2), 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, K.H.; Ko, S.H.; Cho, J.H.; Lee, J.M.; Ahn, Y.B.; Song, K.H.; Yoo, S.J.; Kang, M.I.; Cha, B.Y.; Lee, K.W.; et al. Selective beta-cell loss and alpha-cell expansion in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in korea. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 2300–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, S.C.; Austin, E.; Assouline-Thomas, B.; Kapeluto, J.; Blaichman, J.; Moosavi, M.; Petropavlovskaia, M.; Rosenberg, L. β-cell mass dynamics and islet cell plasticity in human type 2 diabetes. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 1462–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, I.; Sawada, T.; Nakano, M.; Sakai, T.; Liu, B.; Ansite, J.D.; Zhang, H.J.; Kandaswamy, R.; Sutherland, D.E.; Hering, B.J. Improvement in islet yield from obese donors for human islet transplants. Transplantation 2004, 78, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saisho, Y.; Butler, A.E.; Manesso, E.; Elashoff, D.; Rizza, R.A.; Butler, P.C. Beta-cell mass and turnover in humans: Effects of obesity and aging. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezza, T.; Muscogiuri, G.; Sorice, G.P.; Clemente, G.; Hu, J.; Pontecorvi, A.; Holst, J.J.; Giaccari, A.; Kulkarni, R.N. Insulin resistance alters islet morphology in nondiabetic humans. Diabetes 2014, 63, 994–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneda, S.; Uno, S.; Iwahashi, H.; Fujita, Y.; Yoshikawa, A.; Kozawa, J.; Okita, K.; Takiuchi, D.; Eguchi, H.; Nagano, H.; et al. Predominance of beta-cell neogenesis rather than replication in humans with an impaired glucose tolerance and newly diagnosed diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 2053–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagliuca, F.W.; Millman, J.R.; Gurtler, M.; Segel, M.; Van Dervort, A.; Ryu, J.H.; Peterson, Q.P.; Greiner, D.; Melton, D.A. Generation of functional human pancreatic beta cells in vitro. Cell 2014, 159, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avrahami, D.; Klochendler, A.; Dor, Y.; Glaser, B. Beta cell heterogeneity: An evolving concept. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, N.R.; Mitchell, R.K.; Haythorne, E.; Pessoa, M.P.; Semplici, F.; Ferrer, J.; Piemonti, L.; Marchetti, P.; Bugliani, M.; Bosco, D.; et al. Beta cell hubs dictate pancreatic islet responses to glucose. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arimura, A.; Sato, H.; Dupont, A.; Nishi, N.; Schally, A.V. Somatostatin: Abundance of immunoreactive hormone in rat stomach and pancreas. Science 1975, 189, 1007–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hokfelt, T.; Efendic, S.; Hellerstrom, C.; Johansson, O.; Luft, R.; Arimura, A. Cellular localization of somatostatin in endocrine-like cells and neurons of the rat with special references to the a1-cells of the pancreatic islets and to the hypothalamus. Acta Endocrinol. Suppl. 1975, 200, 5–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokfelt, T.; Johansson, O.; Efendic, S.; Luft, R.; Arimura, A. Are there somatostatin-containing nerves in the rat gut? Immunohistochemical evidence for a new type of peripheral nerves. Experientia 1975, 31, 852–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauge-Evans, A.C.; King, A.J.; Carmignac, D.; Richardson, C.C.; Robinson, I.C.; Low, M.J.; Christie, M.R.; Persaud, S.J.; Jones, P.M. Somatostatin secreted by islet delta-cells fulfills multiple roles as a paracrine regulator of islet function. Diabetes 2009, 58, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gromada, J.; Hoy, M.; Buschard, K.; Salehi, A.; Rorsman, P. Somatostatin inhibits exocytosis in rat pancreatic alpha-cells by G(i2)-dependent activation of calcineurin and depriming of secretory granules. J. Physiol. 2001, 535, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gromada, J.; Hoy, M.; Olsen, H.L.; Gotfredsen, C.F.; Buschard, K.; Rorsman, P.; Bokvist, K. Gi2 proteins couple somatostatin receptors to low-conductance K+ channels in rat pancreatic alpha-cells. Pflüg. Arch. 2001, 442, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Bengtsson, M.; Partridge, C.; Salehi, A.; Braun, M.; Cox, R.; Eliasson, L.; Johnson, P.R.; Renstrom, E.; Schneider, T.; et al. R-type Ca2+-channel-evoked cicr regulates glucose-induced somatostatin secretion. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berts, A.; Ball, A.; Dryselius, G.; Gylfe, E.; Hellman, B. Glucose stimulation of somatostatin-producing islet cells involves oscillatory Ca2+ signaling. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Braun, M.; Ramracheya, R.; Amisten, S.; Bengtsson, M.; Moritoh, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Johnson, P.R.; Rorsman, P. Somatostatin release, electrical activity, membrane currents and exocytosis in human pancreatic delta cells. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 1566–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grill, V.; Efendic, S. Stimulation by calcium and barium of somatostatin release. Evidence for lower sensitivity of D-vis-a-vis B- and A-cells. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1984, 122, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grill, V.; Efendic, S. Abnormal d cell secretion in alloxan-diabetes: Influence by drug and aberrant metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. 1984, 246, E483–E492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grill, V.; Gutniak, M.; Roovete, A.; Efendic, S. A stimulating effect of glucose on somatostatin release is impaired in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1984, 59, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adriaenssens, A.E.; Svendsen, B.; Lam, B.Y.; Yeo, G.S.; Holst, J.J.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M. Transcriptomic profiling of pancreatic alpha, beta and delta cell populations identifies delta cells as a principal target for ghrelin in mouse islets. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 2156–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Meulen, T.; Donaldson, C.J.; Caceres, E.; Hunter, A.E.; Cowing-Zitron, C.; Pound, L.D.; Adams, M.W.; Zembrzycki, A.; Grove, K.L.; Huising, M.O. Urocortin3 mediates somatostatin-dependent negative feedback control of insulin secretion. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcinkiewicz, M.; Ramla, D.; Seidah, N.G.; Chretien, M. Developmental expression of the prohormone convertases PC1 and PC2 in mouse pancreatic islets. Endocrinology 1994, 135, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, B.H.; Baskin, D.G.; Saunders, D.R.; Ensinck, J.W. Distribution of somatostatin-14 and somatostatin-28 gastrointestinal-pancreatic cells of rats and humans. Gastroenterology 1990, 99, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, U.; Sasi, R.; Suresh, S.; Patel, A.; Thangaraju, M.; Metrakos, P.; Patel, S.C.; Patel, Y.C. Subtype-selective expression of the five somatostatin receptors (HSSTR1-5) in human pancreatic islet cells: A quantitative double-label immunohistochemical analysis. Diabetes 1999, 48, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, Y.C.; Srikant, C.B. Somatostatin receptors. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 8, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreienkamp, H.J.; Honck, H.H.; Richter, D. Coupling of rat somatostatin receptor subtypes to a g-protein gated inwardly rectifying potassium channel (GIRK1). FEBS Lett. 1997, 419, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collombat, P.; Hecksher-Sorensen, J.; Serup, P.; Mansouri, A. Specifying pancreatic endocrine cell fates. Mech. Dev. 2006, 123, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; McKenna, L.B.; Bogue, C.W.; Kaestner, K.H. The diabetes gene hhex maintains delta-cell differentiation and islet function. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guardado Mendoza, R.; Perego, C.; Finzi, G.; La Rosa, S.; Capella, C.; Jimenez-Ceja, L.M.; Velloso, L.A.; Saad, M.J.; Sessa, F.; Bertuzzi, F.; et al. Delta cell death in the islet of langerhans and the progression from normal glucose tolerance to type 2 diabetes in non-human primates (baboon, papio hamadryas). Diabetologia 2015, 58, 1814–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, L.I.; Sundler, F.; Hakanson, R.; Pollock, H.G.; Kimmel, J.R. Localization of app, a postulated new hormone, to a pancreatic endocrine cell type. Histochemistry 1974, 42, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, L.I.; Sundler, F.; Hakanson, R. Immunohistochemical localization of human pancreatic polypeptide (HPP) to a population of islet cells. Cell Tissue Res. 1975, 156, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, L.I.; Sundler, F.; Hakanson, R. Pancreatic polypeptide—A postulated new hormone: Identification of its cellular storage site by light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Diabetologia 1976, 12, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekblad, E.; Sundler, F. Distribution of pancreatic polypeptide and peptide YY. Peptides 2002, 23, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solcia, E.; Fiocca, R.; Capella, C.; Usellini, L.; Sessa, F.; Rindi, G.; Schwartz, T.W.; Yanaihara, N. Glucagon- and PP-related peptides of intestinal L cells and pancreatic/gastric A or Pp cells. Possible interrelationships of peptides and cells during evolution, fetal development and tumor growth. Peptides 1985, 6 (Suppl. 3), 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.; Wells, C.A.; Buley, I.D.; Cruickshank, J.K.; Vanhegan, R.I.; Matthews, D.R.; Cooper, G.J.; Holman, R.R.; Turner, R.C. Islet amyloid, increased a-cells, reduced b-cells and exocrine fibrosis: Quantitative changes in the pancreas in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. 1988, 9, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stefan, Y.; Orci, L.; Malaisse-Lagae, F.; Perrelet, A.; Patel, Y.; Unger, R.H. Quantitation of endocrine cell content in the pancreas of nondiabetic and diabetic humans. Diabetes 1982, 31, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundler, F.; Hakanson, R.; Larsson, L.I. Ontogeny of rat pancreatic polypeptide (PP) cells. Cell Tissue Res. 1977, 178, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahier, J.; Wallon, J.; Loozen, S.; Lefevre, A.; Gepts, W.; Haot, J. The pancreatic polypeptide cells in the human pancreas: The effects of age and diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1983, 56, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, Y.; Grasso, S.; Perrelet, A.; Orci, L. The pancreatic polypeptide-rich lobe of the human pancreas: Definitive identification of its derivation from the ventral pancreatic primordium. Diabetologia 1982, 23, 141–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, P.; Reichmann, F.; Farzi, A. Neuropeptide Y, peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide in the gut-brain axis. Neuropeptides 2012, 46, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, B.C.; Chaudhri, O.B.; Bloom, S.R. Bowels control brain: Gut hormones and obesity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2010, 6, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, T.W. Pancreatic polypeptide: A hormone under vagal control. Gastroenterology 1983, 85, 1411–1425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, T.W. Pancreatic polypeptide: A unique model for vagal control of endocrine systems. J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 1983, 9, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, G.C.; Samols, E.; Loo, S.; Patel, Y.C.; Gabbay, K.H. Somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide secretion: Effects of glucagon, insulin, and arginine. Diabetes 1979, 28, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragon, F.; Karaca, M.; Novials, A.; Maldonado, R.; Maechler, P.; Rubi, B. Pancreatic polypeptide regulates glucagon release through PPYR1 receptors expressed in mouse and human alpha-cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.M.; Bloom, S.R. Pancreatic Polypeptide, 2 ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wierup, N.; Svensson, H.; Mulder, H.; Sundler, F. The ghrelin cell: A novel developmentally regulated islet cell in the human pancreas. Regul. Pept. 2002, 107, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierup, N.; Bjorkqvist, M.; Westrom, B.; Pierzynowski, S.; Sundler, F.; Sjolund, K. Ghrelin and motilin are cosecreted from a prominent endocrine cell population in the small intestine. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 3573–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capella, C.; Hage, E.; Solcia, E.; Usellini, L. Ultrastructural similarity of endocrine-like cells of the human lung and some related cells of the gut. Cell Tissue Res. 1978, 186, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alumets, J.; Hakanson, R.; Sundler, F. Distribution, ontogeny and ultrastructure of pancreatic polypeptide (PP) cells in the pancreas and gut of the chicken. Cell Tissue Res. 1978, 194, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suissa, Y.; Magenheim, J.; Stolovich-Rain, M.; Hija, A.; Collombat, P.; Mansouri, A.; Sussel, L.; Sosa-Pineda, B.; McCracken, K.; Wells, J.M.; et al. Gastrin: A distinct fate of neurogenin3 positive progenitor cells in the embryonic pancreas. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rindi, G.; Necchi, V.; Savio, A.; Torsello, A.; Zoli, M.; Locatelli, V.; Raimondo, F.; Cocchi, D.; Solcia, E. Characterisation of gastric ghrelin cells in man and other mammals: Studies in adult and fetal tissues. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2002, 117, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rindi, G.; Savio, A.; Torsello, A.; Zoli, M.; Locatelli, V.; Cocchi, D.; Paolotti, D.; Solcia, E. Ghrelin expression in gut endocrine growths. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2002, 117, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordi, C.; Ferrari, C.; D’Adda, T.; Pilato, F.; Carfagna, G.; Bertele, A.; Missale, G. Ultrastructural characterization of fundic endocrine cell hyperplasia associated with atrophic gastritis and hypergastrinaemia. Virchows Arch. A Pathol. Anat. Histopathol. 1986, 409, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solcia, E.; Usellini, L.; Buffa, R.; Rindi, G.; Villani, L.; Zampatti, C.; Silini, E. Endocrine cells producing regulatory peptides. Experientia 1987, 43, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, M.; Hosoda, H.; Date, Y.; Nakazato, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 1999, 402, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasetto, C.; Karam, S.M.; Ribieras, S.; Masson, R.; Lefebvre, O.; Staub, A.; Alexander, G.; Chenard, M.P.; Rio, M.C. Identification and characterization of a novel gastric peptide hormone: The motilin-related peptide. Gastroenterology 2000, 119, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Date, Y.; Kojima, M.; Hosoda, H.; Sawaguchi, A.; Mondal, M.S.; Suganuma, T.; Matsukura, S.; Kangawa, K.; Nakazato, M. Ghrelin, a novel growth hormone-releasing acylated peptide, is synthesized in a distinct endocrine cell type in the gastrointestinal tracts of rats and humans. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 4255–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovic, V.; Miljic, D.; Pekic, S.; Pesko, P.; Djurovic, M.; Doknic, M.; Damjanovic, S.; Micic, D.; Cvijovic, G.; Glodic, J.; et al. Low plasma ghrelin level in gastrectomized patients is accompanied by enhanced sensitivity to the ghrelin-induced growth hormone release. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 2187–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ahmad, Z.; Rafeeq, M.; Collombat, P.; Mansouri, A. Pax6 inactivation in the adult pancreas reveals ghrelin as endocrine cell maturation marker. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschop, M.; Smiley, D.L.; Heiman, M.L. Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature 2000, 407, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dornonville de la Cour, C.; Bjorkqvist, M.; Sandvik, A.K.; Bakke, I.; Zhao, C.M.; Chen, D.; Hakanson, R. A-like cells in the rat stomach contain ghrelin and do not operate under gastrin control. Regul. Pept. 2001, 99, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshinai, K.; Mondal, M.S.; Nakazato, M.; Date, Y.; Murakami, N.; Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K.; Matsukura, S. Upregulation of ghrelin expression in the stomach upon fasting, insulin-induced hypoglycemia, and leptin administration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 281, 1220–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korbonits, M.; Goldstone, A.P.; Gueorguiev, M.; Grossman, A.B. Ghrelin—A hormone with multiple functions. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2004, 25, 27–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dezaki, K.; Sone, H.; Yada, T. Ghrelin is a physiological regulator of insulin release in pancreatic islets and glucose homeostasis. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 118, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broglio, F.; Arvat, E.; Benso, A.; Gottero, C.; Muccioli, G.; Papotti, M.; van der Lely, A.J.; Deghenghi, R.; Ghigo, E. Ghrelin, a natural GH secretagogue produced by the stomach, induces hyperglycemia and reduces insulin secretion in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 5083–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broglio, F.; Gottero, C.; Benso, A.; Prodam, F.; Destefanis, S.; Gauna, C.; Maccario, M.; Deghenghi, R.; van der Lely, A.J.; Ghigo, E. Effects of ghrelin on the insulin and glycemic responses to glucose, arginine, or free fatty acids load in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 4268–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egido, E.M.; Rodriguez-Gallardo, J.; Silvestre, R.A.; Marco, J. Inhibitory effect of ghrelin on insulin and pancreatic somatostatin secretion. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2002, 146, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, M.; Gregersen, S.; Xiao, J.; Hermansen, K. Effects of ghrelin and other neuropeptides (CART, MCH, orexin A and B, and GLP-1) on the release of insulin from isolated rat islets. Pancreas 2003, 27, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimer, M.K.; Pacini, G.; Ahren, B. Dose-dependent inhibition by ghrelin of insulin secretion in the mouse. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 916–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wierup, N.; Sundler, F. Circulating levels of ghrelin in human fetuses. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2004, 150, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Salehi, A.; Dornonville de la Cour, C.; Hakanson, R.; Lundquist, I. Effects of ghrelin on insulin and glucagon secretion: A study of isolated pancreatic islets and intact mice. Regul. Pept. 2004, 118, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arosio, M.; Ronchi, C.L.; Gebbia, C.; Cappiello, V.; Beck-Peccoz, P.; Peracchi, M. Stimulatory effects of ghrelin on circulating somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide levels. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).