Evaluation of Two-Diabetes Related microRNAs Suitability as Earlier Blood Biomarkers for Detecting Prediabetes and type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Subjects
2.2. Blood Collection
2.3. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription
2.4. Reverse Transcription Quantitative Real-Time PCR
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Basic Characteristics of the Study Subjects
4.2. Relative Expression of miR-375 and miR-9 in the Subject Groups
4.3. Multivariate Regression Analysis
4.4. Correlation between miR-375 and miR-9 with Glycemic Status and Other Clinical Variables
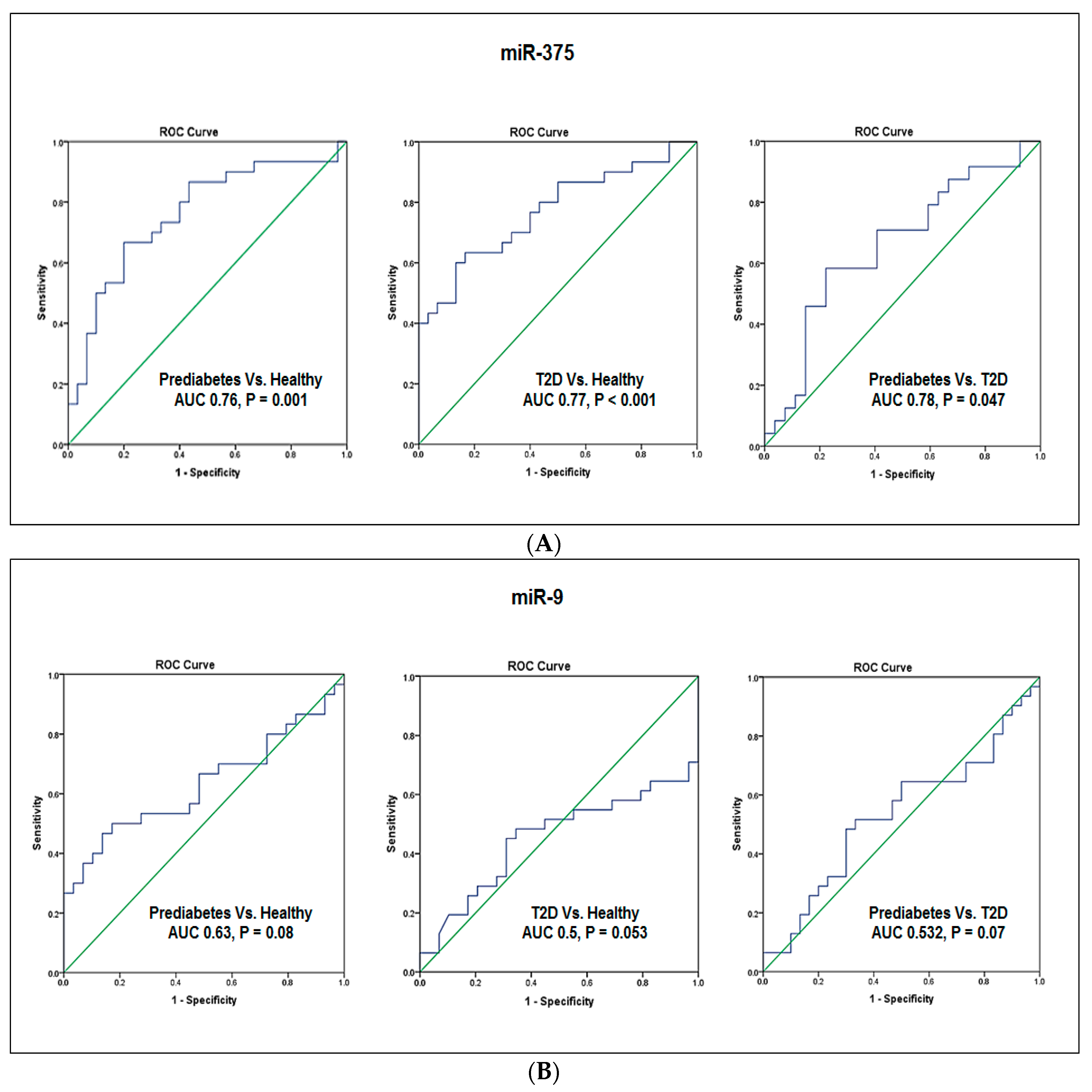
4.5. Evaluation of the Diagnostic Values of Blood miR-375 and miR-9
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Diabetes Federation. International Diabetes Federation IDF Diabetes Atlas, 7th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2015; Available online: http://www.diabetesatlas.org/across-the-globe.html (accessed on 25 January 2018).
- Centers for Disease Control. National Diabetes Statistics Report: Estimates of Diabetes and Its Burden in the United States; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2014. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pdfs/data/statistics/national-diabetes-statistics-report.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2018).
- Stumvoll, M.; Goldstein, B.J.; van Haeften, T.W. Type 2 diabetes: Principles of pathogenesis and therapy. Lancet 2005, 365, 1333–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muoio, D.M.; Newgard, C.B. Mechanisms of disease: Molecular and metabolic mechanisms of insulin resistance and beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, C.; Groop, L. Epigenetics: A molecular link between environmental factors and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2009, 58, 2718–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanefeld, M.; Koehler, C.; Fuecker, K.; Henkel, E.; Schaper, F.; Temelkova-Kurktschiev, T. Insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity pattern is different in isolated impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glucose: The risk factor in Impaired Glucose Tolerance for Atherosclerosis and Diabetes study. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rask-Madsen, C.; King, G.L. Vascular complications of diabetes: Mechanisms of injury and protective factors. Cell Metab. 2013, 8, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Ghani, M.A.; Tripathy, D.; DeFronzo, R.A. Contributions of beta-cell dysfunction and insulin resistance to the pathogenesis of impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glucose. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, D.M.; Davidson, M.B.; Deftonzo, R.A.; Heine, R.J.; Henry, R.R.; Pratley, R.; Zinman, B. Impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance: Implications for care. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabak, A.G.; Herder, C.; Rathmann, W.; Brunner, E.J.; Kivimaki, M. Prediabetes: A high-risk state for developing diabetes. Lancet 2012, 16, 2279–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cai, X.; Mai, W.; Meijun, L.; Yunzhao, H. Association between prediabetes and risk of cardiovascular disease and all cause mortality: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2016, 355, i5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. Screening for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 1998, 21, S20–S22. [Google Scholar]
- Genuth, S.; Alberti, K.G.; Bennett, P.; Buse, J.; Defronzo, R.; Kahan, R.; Kitzmiller, J.; Knowler, W.C.; Lebovitz, H.; Lernmark, A.; et al. Follow-up report on the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2003, 6, 3160–3167. [Google Scholar]
- Beard, E.; Clark, M.; Hurel, S.; Cooke, D. Do people with diabetes understand their clinical marker of long-term glycemic control (HbA1c levels) and does this predict diabetes self-care behaviours and HbA1c? Patient Educ. Couns. 2010, 80, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuso, P. Prediabetes and Lifestyle Modification: Time to prevent a preventable disease. Perm. J. 2014, 18, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuomilehto, J.; Schwarz, P.E.H. Preventing diabetes: Early versus late preventive interventions. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, S115–S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, R.S.; Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Filipowicz, W. Repression of protein synthesis by miRNAs: How many mechanisms? Trends Cell Biol. 2007, 17, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloosterman, W.P.; Plaster, R.H. The diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease. Dev. Cell 2006, 11, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, C.; Doss, C.G.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Agoramoorthy, G. Influence of miRNA in insulin signaling pathway and insulin resistance: Micro-molecules with a major role in type-2 diabetes. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2014, 5, 697–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joglekar, M.V.; Joglekar, V.M.; Hardikar, A.A. Expression of islet-specific microRNAs during human pancreatic development. Gene Expr. Patterns 2009, 9, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poy, M.N.; Eliasson, L.; Krutzfeldt, J.; Kuwajima, S.; Ma, X.; Macdonald, P.E.; Pfeffer, S.; Tuschl, T.; Rajewsky, N.; Rorsman, P.; et al. A pancreatic islet-specific microRNA regulates insulin secretion. Nature 2004, 432, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaisance, V.; Abderrahmani, A.; Perret- Menoud, V.; Jacquemin, P.; Lemaigre, F.; Regazzi, R. MicroRNA-9 controls the expression of Granuphilin/Slp4 and the secretory response of insulin-producing cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 28, 26932–26942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; O’Briant, K.C.; Allen, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, P.; Wischhusen, J.; Happold, C.; Chandran, P.A.; Hofer, S.; Eisele, G.; Weller, M.; Keller, A. A specific miRNA signature in the peripheral blood of glioblastoma patients. J. Neurochem. 2011, 118, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kafaji, G.; Al-Mahroos, G.; Al-Muhtaresh, H.A.; Sabry, M.A.; Abdul Razzak, R.; Salem, A.H. Circulating endothelium-enriched microRNA-126 as a potential biomarker for coronary artery disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Biomarkers 2017, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, A.; Leidinger, P.; Bauer, A.; Elsharawy, A.; Haas, J.; Backes, C.; Wendschlag, A.; Giese, N.; Tjaden, C.; Ott, K.; et al. Toward the blood-borne miRNome of human diseases. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 841–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kafaji, G.; Al-Mahroos, G.; Alsayed, N.A.; Hasan, Z.A.; Nawaz, S.; Bakhiet, M. Peripheral blood microRNA-15a as a potential biomarker for type 2 diabetes mellitus and pre-diabetes. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 7485–7490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Leun, S.W. Identification of microRNA biomarkers in type 2 diabetes: A met-analysis of controlled profiling studies. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 900–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, K.G.; Zimmet, P.Z. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet. Med. 1998, 15, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kafaji, G.; Al Naieb, Z.T.; Bakhiet, M. Increased oncogenic microRNA-18a expression in peripheral blood of patients with prostate cancer: A potential role as new noninvasive biomarker. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Zhu, J.; Han, W.; Jiang, X.; Xu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, Q.; Pang, Z.; Gao, L.; Zhao, L. Significance of serum microRNAs in pre-diabetes and newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: A clinical study. Acta Diabetolol. 2011, 48, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poy, M.N.; Hausserb, J.; Trajkovskia, M.; Braunc, M.; Collinsc, S.; Rorsmanc, P.; Zavolanb, M.; Stoffela, M. miR-375 maintains normal pancreatic alpha- and beta-cell mass. PNAS 2009, 106, 5813–5818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouaamari, A.E.; Baroukh, N.; Martens, G.A.; Lebrun, P.; Pipeleers, D.; Obberghen, E. miR-375 targets 3′-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 and regulates glucose- induced biological responses in pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2708–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, T.; Frantz, C.; Perret-Menoud, V.; Gattesco, S.; Hirling, H.; Regazzi, R. Pancreatic beta-cell protein granuphilin binds Rab3 and Munc-18 and controls exocytosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, B.; Gulanick, M.; Lamendola, C. Risk factors for type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Caediovasc. Nurs. 2002, 16, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portero McLellan, K.C.; Wyne, K.; Villagomez, E.T.; Hsueh, W.A. Therapeutic interventions to reduce the risk of progression from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2014, 20, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erener, S.; Mojibian, M.; Fox, J.K.; Denroche, H.C.; Kieffer, T.J. Circulating miR-375 as a biomarker of β-cell death and diabetes in mice. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latreille, M.; Herrmanns, K.; Renwick, N.; Tuschl, T.; Malecki, M.T.; McCarthy, M.I.; Owen, K.R.; Rülicke, T.; Stoffel, M. miR-375 gene dosage in pancreatic β-cells: Implications for regulation of β-cell mass and biomarker development. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 93, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, C.; Nakatsuka, A.; Eguchi, J.; Teshigawara, S.; Kanzaki, M.; Katayama, A.; Yamaguchi, S.; Takahashi, N.; Murakami, K.; Ogawa, D.; et al. Identification of circulating miR-101, miR-375 and miR-802 as biomarkers for type 2 diabetes. Metabolism 2015, 64, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Forward Primer 5′-3′ | Reverse Primer 5′-3′ | |
|---|---|---|
| miR-375 | GAGCATTTTGTTCGTTCGGC | AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGG |
| miR-9 | GCCCGCTCTTTGGTTATCTAG | CCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT |
| RNU6B | GCTTCGGCAGCACATATACTAAAAT | CGCTTCACGAATTTGCGTGTCAT |
| Characteristics | Prediabetes | T2D | Controls |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of subjects | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Age (years) | 50 ± 5.8 ## | 60 ± 12 ** | 56 ± 5.1 |
| Sex (M/F) | (19/11) | (12/18) | (14/16) |
| FG (mmol/L) | 6.4 ± 5.8 **## | 8.6 ± 13.6 ** | 4.3 ± 0.6 |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.7 ± 0.5 **## | 8.68 ± 2.6 ** | 5.03 ± 0.7 |
| 2 h OGTT (mmol/L) | 8.71 ± 0.69 **## | 13.72 ± 2.03 ** | 6.00 ± 0.75 |
| Diabetes duration (years) | - | 15 ± 4.4 | - |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 25.0 ± 4.7 | 25.7 ± 5.2 | 24.2 ± 4.6 |
| Mean blood pressure (mmHg) | 89 ± 5.4 | 87.5 ± 5.3 | 86.9 ± 4.0 |
| Triglyceride (mmol/L) | 1.53 ± 0.56 | 1.54 ± 0.5 | 1.60 ± 0.6 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 4.1 ± 1.3 | 4.54 ± 1.1 | 4.27 ± 0.6 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 2.08 ± 0.9 | 2.36 ± 1.1 * | 2.14 ± 0.8 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1.32 ± 0.4 | 1.28 ± 0.2 | 1.34 ± 0.3 |
| Prediabetes | T2D | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (A) | ||||||
| miR-375 | ||||||
| Models | OR | 95% CI | p value | OR | 95% CI | p value |
| Model 1 | 1.12 | 1.022–1.168 | 0.009 | 1.123 | 1.049–1.201 | 0.001 |
| Model 2 | 1.11 | 1.023–1.174 | 0.009 | 1.134 | 1.056–1.219 | 0.001 |
| Model 3 | 1.12 | 1.012–1.26 | 0.023 | 1.125 | 1.045–1.212 | 0.022 |
| Model 4 | 1.13 | 1.012–1.168 | 0.022 | 1.126 | 1.045–1.214 | 0.002 |
| miR-9 | ||||||
| Model 1 | 1.11 | 1.005–1.147 | 0.035 | 1.080 | 1.011–1.153 | 0.022 |
| Model 2 | 1.12 | 1.010–1.157 | 0.024 | 1.082 | 1.012–1.157 | 0.021 |
| Model 3 | 1.1 | 1.002–1.150 | 0.044 | 1.078 | 1.007–1.154 | 0.032 |
| Model 4 | 1.1 | 1.006–1.161 | 0.035 | 1.081 | 1.007–1.159 | 0.031 |
| (B) | ||||||
| miR-375 | ||||||
| Models | - | OR | 95% CI | p value | ||
| Model 1 | - | 1.12 | 0.999–1.157 | 0.05 | ||
| Model 2 | - | 1.141 | 1.001–1.528 | 0.001 | ||
| Model 3 | - | 1.143 | 1.001–1.483 | 0.044 | ||
| Model 4 | - | 1.151 | 1.006–1.197 | 0.025 | ||
| miR-9 | ||||||
| Model 1 | - | 1.006 | 0.982–1.030 | 0.64 | ||
| Model 2 | - | 1.001 | 0.976–1.026 | 0.954 | ||
| Model 3 | - | 1.003 | 0.975–1.030 | 0.85 | ||
| Model 4 | - | 0.972 | 0.916–1.031 | 0.33 | ||
| Variables | miR-375 | miR-9 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prediabetes | T2D | Prediabetes | T2D | |||||
| (A) | r | p value | r | p value | r | p value | r | p value |
| FG | 0.30 | 0.006 | 0.20 | 0.020 | 0.20 | 0.002 | 0.30 | 0.020 |
| HbA1c | 0.30 | 0.009 | 0.10 | 0.024 | 0.13 | 0.002 | 0.41 | 0.04 |
| OGGT | 0.35 | 0.002 | 0.40 | 0.041 | 0.44 | <0.001 | 0.42 | 0.07 |
| (B) | r | p value | r | p value | r | p value | r | p value |
| Age | −0.12 | 0.001 | 0.02 | 0.001 | 0.02 | 0.001 | 0.05 | 0.001 |
| Sex | -0.12 | 0.535 | −0.20 | 0.369 | 0.21 | 0.269 | 0.30 | 0.143 |
| Diabetes duration | - | - | 0.13 | 0.507 | - | - | −0.13 | 0.483 |
| BMI | −0.01 | 0.001 | 0.35 | 0.001 | 0.40 | 0.001 | 0.1 | 0.034 |
| Mean blood pressure | 0.28 | 0.001 | 0.11 | 0.001 | 0.11 | 0.001 | 0.12 | 0.001 |
| Triglyceride | −0.30 | 0.001 | −0.20 | 0.006 | −0.20 | 0.006 | −0.11 | 0.010 |
| Total cholesterol | 0.02 | 0.001 | 0.41 | 0.047 | 0.41 | 0.047 | 0.01 | 0.043 |
| LDL | −0.26 | 0.001 | −0.33 | 0.015 | −0.33 | 0.015 | −0.10 | 0.014 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Muhtaresh, H.A.; Al-Kafaji, G. Evaluation of Two-Diabetes Related microRNAs Suitability as Earlier Blood Biomarkers for Detecting Prediabetes and type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7020012
Al-Muhtaresh HA, Al-Kafaji G. Evaluation of Two-Diabetes Related microRNAs Suitability as Earlier Blood Biomarkers for Detecting Prediabetes and type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2018; 7(2):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7020012
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Muhtaresh, Haifa Abdullah, and Ghada Al-Kafaji. 2018. "Evaluation of Two-Diabetes Related microRNAs Suitability as Earlier Blood Biomarkers for Detecting Prediabetes and type 2 Diabetes Mellitus" Journal of Clinical Medicine 7, no. 2: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7020012
APA StyleAl-Muhtaresh, H. A., & Al-Kafaji, G. (2018). Evaluation of Two-Diabetes Related microRNAs Suitability as Earlier Blood Biomarkers for Detecting Prediabetes and type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7(2), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7020012




