Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Impact of Thrombolytic Therapy in Liver Transplantation Following Donation after Circulatory Death
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
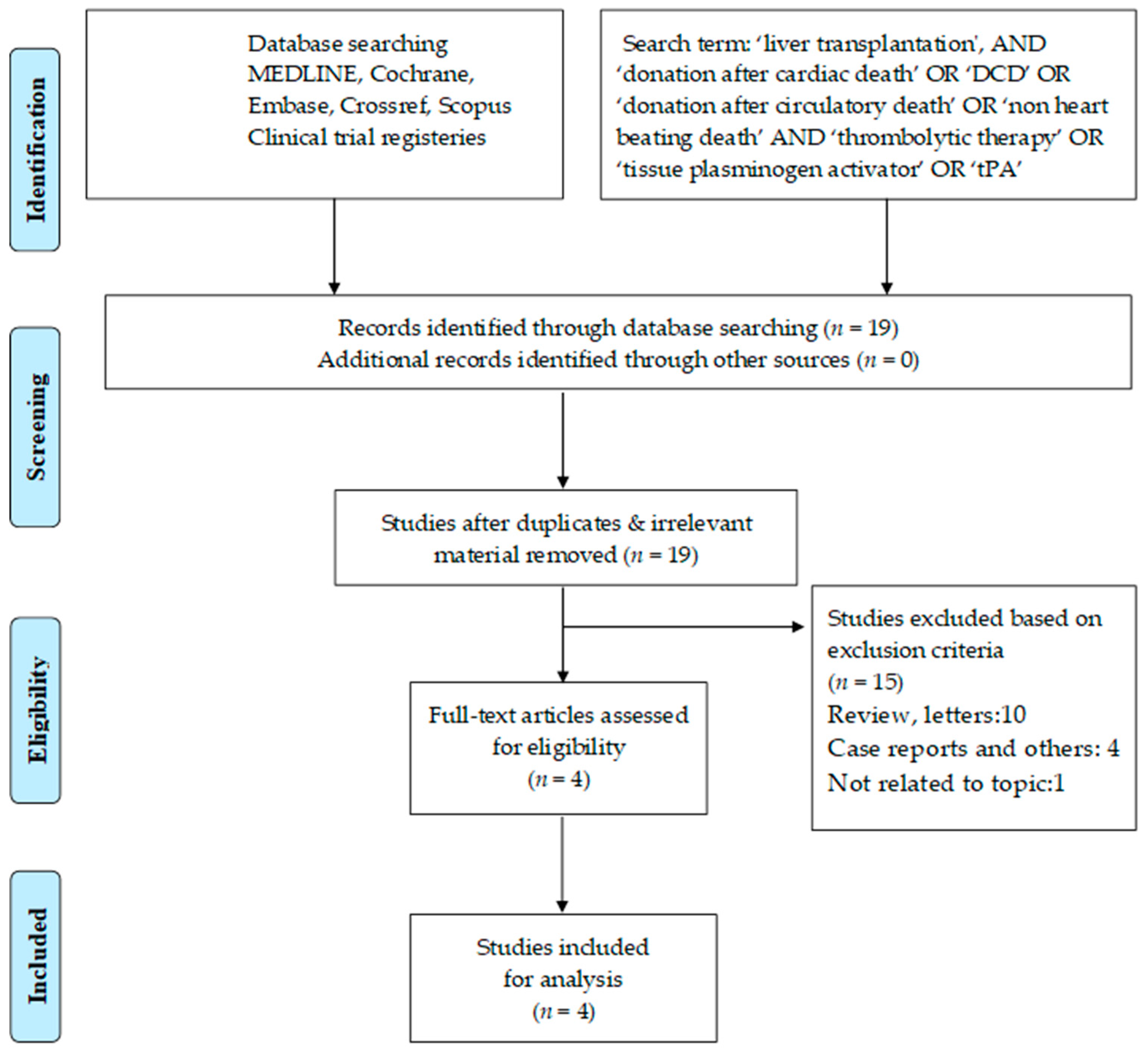
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Statistical Analysis
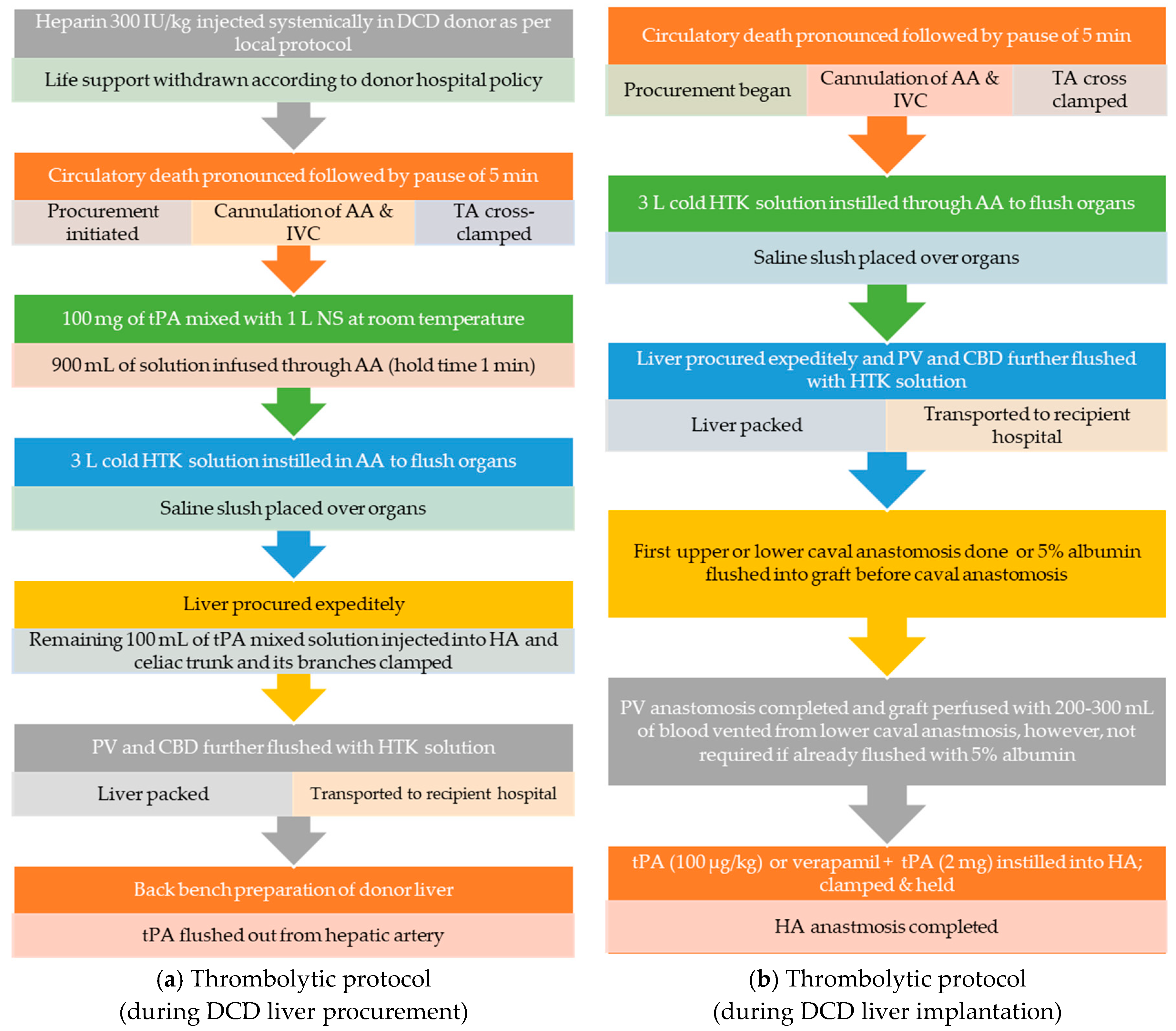
2.5. Protocols for the Use of Thrombolytic (tPA) in DCD Liver Transplant
2.5.1. Thrombolytic (tPA) Protocol during DCD Liver Procurement
2.5.2. Details of Thrombolytic (tPA) Protocol during DCD Liver Implantation
3. Results
3.1. Search Results
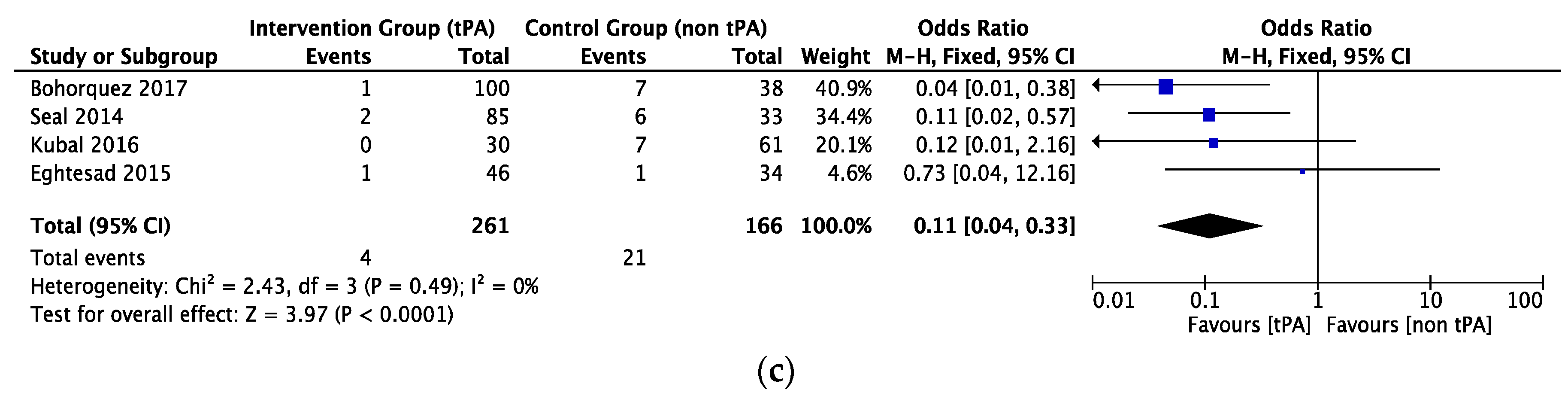
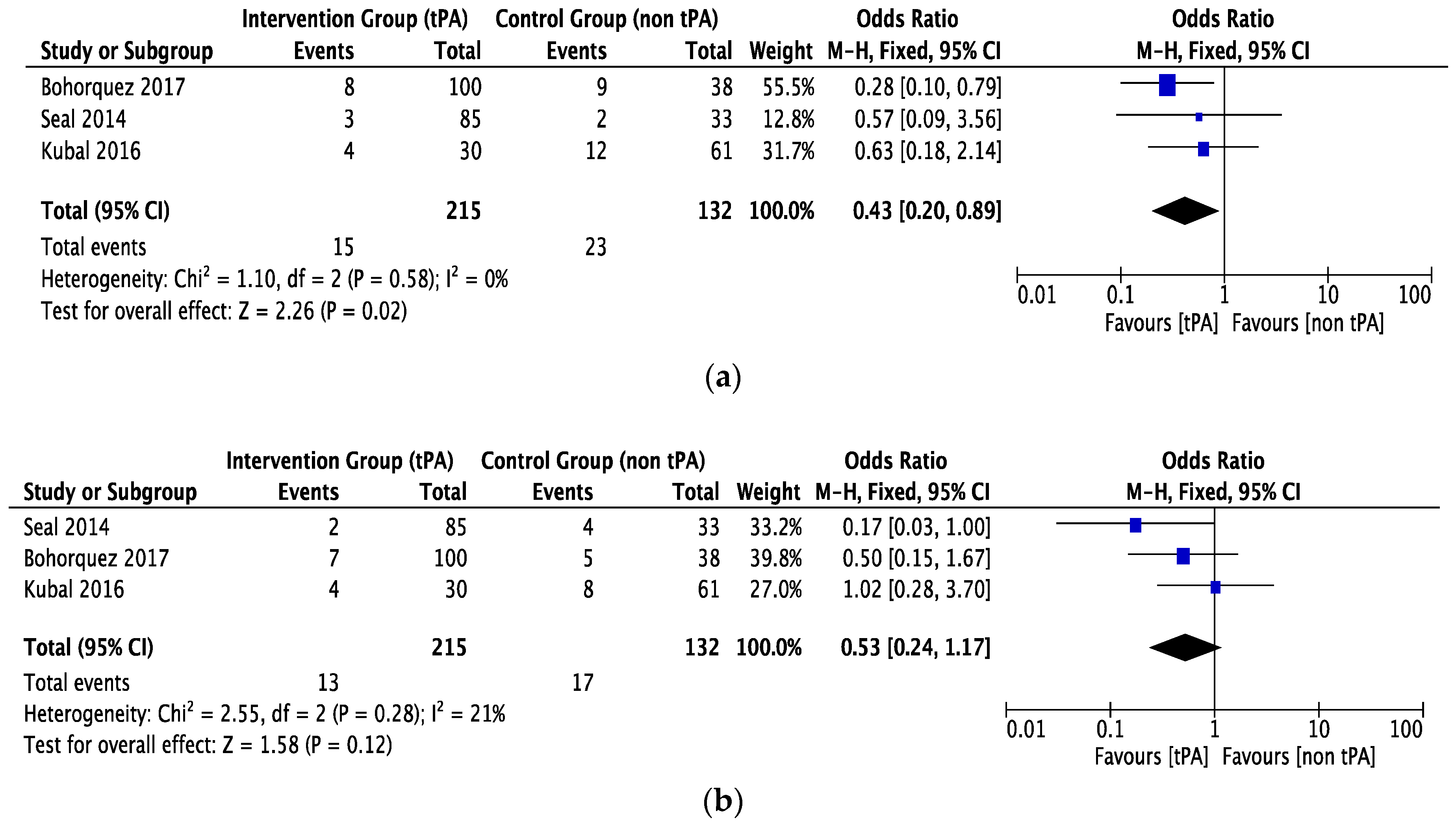
3.2. Biliary Complications.
3.3. Other Complications
3.4. Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviations | Full Name |
| CIT | Cold Ischemia Time |
| DBD | Donation after Brain Death |
| DCD | Donation after Circulatory Death |
| ECD | Extended Criteria Donor |
| EGD | Early graft dysfunction |
| HA | Hepatic Artery |
| HAT | Hepatic Artery Thrombosis |
| IC | Ischemic Cholangiopathy |
| I/R | Ischemia-reperfusion |
| PNF | Primary Non-Function |
| PV | Portal Vein |
| MELD | Model for End-Stage Disease |
| PBG | Peribiliary gland |
| PVP | Peribiliary Vascular Plexus |
| PRS | Post reperfusion syndrome |
| RCT | Randomized Control Trial |
| SCS | Static Cold Storage |
| tPA | Tissue Plasminogen Activator |
| WIT | Warm Ischemia Time |
References
- Marot, A.; Dubois, M.; Trépo, E.; Moreno, C.; Deltenre, P. Liver transplantation for alcoholic hepatitis: A systematic review with meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OPTN. Available online: https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/data/view-data-reports/national-data/ (accessed on 8 November 2018).
- Halpern, S.D.; Barnes, B.; Hasz, R.D.; Abt, P.L. Estimated supply of organ donors after circulatory determination of death: A population-based Cohort study. JAMA 2010, 304, 2592–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K.; Miller, C. The use of marginal grafts in liver transplantation. J. Hepatobiliary. Pancreat. Surg. 2008, 15, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodside, K.J. Donation after cardiac death and liver transplantation. J. Surg. Res. 2013, 184, 800–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jay, C.L.; Skaro, A.I.; Ladner, D.P.; Wang, E.; Lyuksemburg, V.; Chang, Y.; Xu, H.; Talakokkla, S.; Parikh, N.; Holl, J.L.; et al. Comparative effectiveness of donation after cardiac death versus donation after brain death liver transplantation: Recognizing who can benefit. Liver Transplant. 2012, 18, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abt, P.; Crawford, M.; Desai, N.; Markmann, J.; Olthoff, K.; Shaked, A. Liver transplantation from controlled non-heartbeating donors: An increased incidence of biliary complications. Transplantation 2003, 75, 1659–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maheshwari, A.; Maley, W.; Li, Z.; Thuluvath, P.J. Biliary complications and outcomes of liver transplantation from donors after cardiac death. Liver Transplant. 2007, 13, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, D.P.; Fernandez, L.A.; Leverson, G.; Anderson, M.; Mezrich, J.; Sollinger, H.W.; D’Alessandro, A. Biliary complications after liver transplantation from donation after cardiac death donors: An analysis of risk factors and long-term outcomes from a single center. Ann. Surg. 2011, 253, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, E.Y.; Olson, L.C.; Kisthard, J.A.; Perkins, J.D.; Bakthavatsalam, R.; Halldorson, J.B.; Reyes, J.D.; Larson, A.M.; Levy, A.E. Ischemic cholangiopathy following liver transplantation from donation after cardiac death donors. Liver Transplant. 2008, 14, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaro, A.I.; Jay, C.L.; Baker, T.B.; Wang, E.; Pasricha, S.; Lyuksemburg, V.; Martin, J.A.; Feinglass, J.M.; Preczewski, L.B.; Abecassis, M.M. The impact of ischemic cholangiopathy in liver transplantation using donors after cardiac death: The untold story. Surgery 2009, 146, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vellar, I.D. The blood supply of the biliary ductal system and its relevance to vasculobiliary injuries following cholecystectomy. Aust. N. Z. J. Surg. 1999, 69, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adkins, R.B.; Chapman, W.C.; Reddy, V.S. Embryology, anatomy, and surgical applications of the extrahepatic biliary system. Surg. Clin. North Am. 2000, 80, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
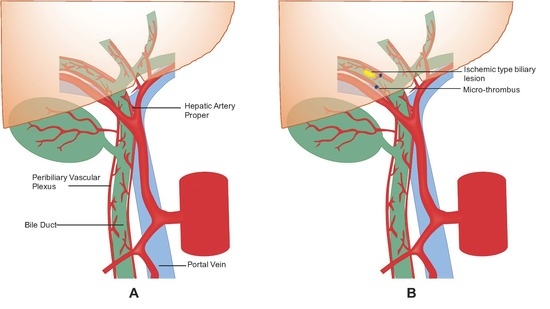
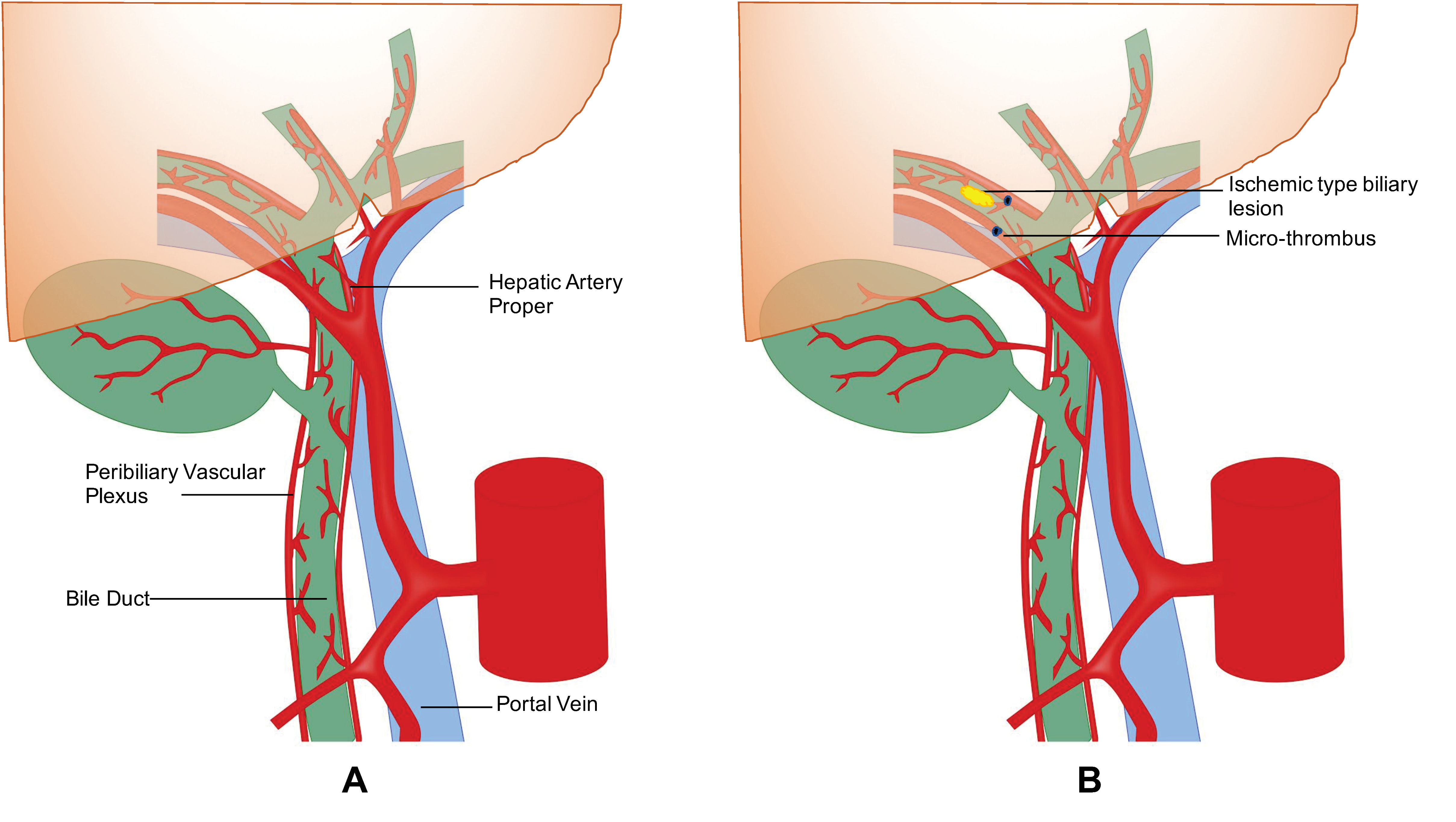
- Op Den Dries, S.; Sutton, M.E.; Lisman, T.; Porte, R.J. Protection of bile ducts in liver transplantation: Looking beyond ischemia. Transplantation 2011, 92, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Op Den Dries, S.; Westerkamp, A.C.; Karimian, N.; Gouw, A.S.; Bruinsma, B.G.; Markmann, J.F.; Lisman, T.; Yeh, H.; Uygun, K.; Martins, P.N.; et al. Injury to peribiliary glands and vascular plexus before liver transplantation predicts formation of non-anastomotic biliary strictures. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtani, O.; Kikuta, A.; Ohtsuka, A.; Taguchi, T.; Murakami, T. Microvasculature as studied by the microvascular corrosion casting/scanning electron microscope method. I. Endocrine and digestive system. Arch. Histol. Jpn. 1983, 46, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, K.; Sherman, I.; Phillips, M.J.; Fisher, M.M. Three-dimensional observations of the hepatic arterial terminations in rat, hamster and human liver by scanning electron microscopy of microvascular casts. Hepatology 1985, 5, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K.; Eghtesad, B.; Gunasekaran, G.; Fujiki, M.; Uso, T.D.; Quintini, C.; Aucejo, F.N.; Kelly, D.M.; Winans, C.G.; Vogt, D.P.; et al. Use of tissue plasminogen activator in liver transplantation from donation after cardiac death donors. Am. J. Transplant. 2010, 10, 2665–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, J.I.; Richter, S.; Vollmar, B.; Menger, M.D.; Minor, T. Warm preflush with streptokinase improves microvascular procurement and tissue integrity in liver graft retrieval from non-heart-beating donors. Transplantation 2000, 69, 1780–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minor, T.; Hachenberg, A.; Tolba, R.; Pauleit, D.; Akbar, S. Fibrinolytic preflush upon liver retrieval from non-heart beating donors to enhance postpreservation viability and energetic recovery upon reperfusion. Transplantation 2001, 71, 1792–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubal, C.; Mangus, R.; Fridell, J.; Saxena, R.; Rush, N.; Wingler, M.; Ekser, B.; Tector, J. Optimization of perioperative conditions to prevent ischemic cholangiopathy in donation after circulatory death donor liver transplantation. Transplantation 2016, 100, 1699–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meunier, J.M.; Chang, W.T.; Bluett, B.; Wenker, E.; Lindsell, C.J.; Shaw, G.J. Temperature Affects Thrombolytic Efficacy Using rt-PA and Eptifibatide, an In Vitro Study. Ther. Hypothermia. Temp. Manag. 2012, 2, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seal, J.B.; Bohorquez, H.; Reichman, T.; Kressel, A.; Ghanekar, A.; Cohen, A.; McGilvray, I.D.; Cattral, M.S.; Bruce, D.; Greig, P.; et al. Thrombolytic protocol minimizes ischemic-type biliary complications in liver transplantation from donation after circulatory death donors. Liver Transplant. 2015, 21, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohorquez, H.; Seal, J.B.; Cohen, A.J.; Kressel, A.; Bugeaud, E.; Bruce, D.S.; Carmody, I.C.; Reichman, T.W.; Battula, N.; Alsaggaf, M.; et al. Safety and outcomes in 100 consecutive donation after circulatory death liver transplants using a protocol that includes thrombolytic therapy. Am. J. Transplant. 2017, 17, 2155–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietersen, L.C.; den Dulk, A.C.; Braat, A.E.; Putter, H.; Korkmaz, K.S.; Baranski, A.G.; Schaapherder, A.F.; Dubbeld, J.; van Hoek, B.; Ringers, J. Flushing the liver with urokinase before transplantation does not prevent nonanastomotic biliary strictures. Liver Transplant. 2016, 22, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yenari, M.A.; Palmer, J.T.; Bracci, P.M.; Steinberg, G.K. Thrombolysis with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) is temperature dependent. Thromb. Res. 1995, 77, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroup, D.F.; Berlin, J.A.; Morton, S.C.; Olkin, I.; Williamson, G.D.R.D. MOOSE Guidelines for Meta-Analyses and Systematic Reviews of Observational Studies. JAMA 2000, 283, 2008–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Available online: https://training.cochrane.org/handbook (accessed on 8 November 2018).
- Hozo, S.P.; Djulbegovic, B.; Hozo, I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2005, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chootrakool, H.; Shi, J.Q.; Yue, R. Meta-analysis and sensitivity analysis for multi-arm trials with selection bias. Stat. Med. 2011, 30, 1183–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavridis, D.; Welton, N.J.; Sutton, A.; Salanti, G. A selection model for accounting for publication bias in a full network meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2014, 33, 5399–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeks, J.J.; Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G. Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses. Cochrane Handb. Syst. Rev. Interv. Cochrane B Ser. 2008, 243–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghtesad, B.; Hashimoto, K.; Watson, M.; Nazzal, M.; Quintini, C.; Kelly, D.; Diago, T.; Kawamura, N.; El-Gazzaz, G.; Fujiki, M.; et al. Use of tissue plasminogen activator (TPA) in liver transplantation from donation after cardiac death (DCD) donors: A controlled randomized trial. Am. J. Transplant. 2015, 15, 275. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, A. Pharmacokinetics of the recombinant thrombolytic agents: What is the clinical significance of their different pharmacokinetic parameters? BioDrugs 1999, 11, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, V.G.; George, S.J. Carbon monoxide releasing molecule-2 attenuates the anticoagulant and amplifies the hypofibrinolytic effects of hypothermia in human plasma in vitro. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2011, 22, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Pals, J.; Götberg, M.I.; Götberg, M.; Hultén, L.M.; Magnusson, M.; Jern, S.; Erlinge, D. Hypothermia in cardiogenic shock reduces systemic t-PA release. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2011, 32, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffey, J.C.; Wanis, K.N.; Monbaliu, D.; Gilbo, N.; Selzner, M.; Vachharajani, N.; Levstik, M.A.; Marquez, M.; Doyle, M.B.M.; Pirenne, J.; et al. The influence of functional warm ischemia time on DCD liver transplant recipients’ outcomes. Clin. Transplant. 2017, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blok, J.J.; Detry, O.; Putter, H.; Rogiers, X.; Porte, R.J.; van Hoek, B.; Pirenne, J.; Metselaar, H.J.; Lerut, J.P.; Ysebaert, D.K.; et al. Longterm results of liver transplantation from donation after circulatory death. Liver Transplant. 2016, 22, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merion, R.M.; Pelletier, S.J.; Goodrich, N.; Englesbe, M.J.; Delmonico, F.L. Donation after cardiac death as a strategy to increase deceased donor liver availability. Ann. Surg. 2006, 244, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jay, C.L.; Lyuksemburg, V.; Ladner, D.P.; Wang, E.; Caicedo, J.C.; Holl, J.L.; Abecassis, M.M.; Skaro, A.I. Ischemic cholangiopathy after controlled donation after cardiac death liver transplantation: A meta-analysis. Ann. Surg. 2011, 253, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.X.; Na, N.; Li, J.J.; Fan, L.; Weng, R.H.; Jiang, N. Outcomes of controlled donation after cardiac death compared with donation after brain death in liver transplantation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transplant. Proc. 2018, 50, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariciotti, L.; Rocha, C.; Perera, M.T.P.; Gunson, B.K.; Bramhall, S.R.; Isaac, J.; Buckels, J.A.; Mayer, A.D.; Muiesan, P.; Mirza, D.F. Is it time to extend liver acceptance criteria for controlled donors after cardiac death? Transplantation 2011, 92, 1140–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renz, J.F. Is DCD for liver transplantation DNR? Am. J. Transplant. 2008, 8, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElroy, L.M.; Daud, A.; Davis, A.E.; Lapin, B.; Baker, T.; Abecassis, M.M.; Levitsky, J.; Holl, J.L.; Ladner, D.P. A meta-analysis of complications following deceased donor liver transplant. Am. J. Surg. 2014, 208, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monbaliu, D.; Pirenne, J.; Talbot, D. Liver transplantation using donation after cardiac death donors. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selck, F.W.; Grossman, E.B.; Ratner, L.E.; Renz, J.F. Utilization, outcomes, and retransplantation of liver allografts from donation after cardiac death: Implications for further expansion of the deceased-donor pool. Ann. Surg. 2008, 248, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alessandro, A.M.; Fernandez, L.A.; Chin, L.T.; Fernandez, L.A.; Foley, D.P.; Becker, Y.T.; Odorico, J.S.; Knechtle, S.J.; Kalayoglu, M.; Sollinger, H.W.; et al. Donation after cardiac death: The university of wisconsin experience. Ann. Transplant. 2004, 9, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blackstock, M.J.; Ray, D.C. Organ donation after circulatory death: An update. Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 2014, 21, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanatta, J.M.; Dean, A.G.; Hathaway, D.K.; Nair, A.; Modanlou, K.A.; Campos, L.; Nezakatgoo, N.; Satapathy, S.K.; Eason, J.D. Liver transplant using donors after cardiac death: A single-center approach providing outcomes comparable to donation after brain death. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2013, 11, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, K.J.; Scalera, I.; Muiesan, P. Donation After Cardiac Death in Liver Transplantation. Regen. Med. Appl. Organ Transplant. 2014, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Shahrestani, S.; Chew, H.C.; Crawford, M.; Macdonald, P.S.; Laurence, J.; Hawthorne, W.J.; Dhital, K.; Pleass, H. Donation after circulatory death for liver transplantation: A meta-analysis on the location of life support withdrawal affecting outcomes. Transplantation 2016, 100, 1513–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detry, O.; Deroover, A.; Meurisse, N.; Hans, M.F.; Delwaide, J.; Lauwick, S.; Kaba, A.; Joris, J.; Meurisse, M.; Honoré, P. Donor age as a risk factor in donation after circulatory death liver transplantation in a controlled withdrawal protocol programme. Br. J. Surg. 2014, 101, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalea, J.R.; Redfield, R.R.; Foley, D.P. Liver transplant outcomes using ideal donation after circulatory death livers are superior to using older donation after brain death donor livers. Liver Transplant. 2016, 22, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burlage, L.C.; Karangwa, S.A.; Lisman, T.; Martins, P.N.; Porte, R.J. Thrombolytic protocol minimizes ischemic-type biliary complications in liver transplantation from donation after circulatory death donors. Liver Transplant. 2015, 21, 1231–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.M.; Bhutiani, N.; Wei, D.; Goldstein, L.; Jones, C.M.; Cannon, R.M. A literature-based cost analysis of tissue plasminogen activator for prevention of biliary stricture in donation after circulatory death liver transplantation. Am. J. Surg. 2018, 216, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Study design | Retrospective, prospective, randomized, or non-randomized |
| Study group | DCD Liver transplant |
| Study size | Any |
| Length of follow-up | Any |
| Source | Peer-reviewed journals, posters |
| Language | Any |
| Outcome measure | ITBLs, biliary complications, HAT, re-transplantation, blood transfusion, and graft and patient survival |
| Study | Sample Size (tPA vs. Non-tPA) | Donor Age (Years) (tPA vs. Non-tPA) | MELD Score (tPA vs. Non-tPA) | WIT Functional (Min) (tPA vs. Non-tPA) | CIT (Min) (tPA vs. Non-tPA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seal (2014) [23] | 85 vs. 33 | 36.3 ± 14.8 vs. 38.0 ± 14.9 (P = 0.99) | 20.1 ± 8.2 vs. 16.5 ± 10.8 (P = 0.38) | 21.1 ± 8.3 vs. 23.5 ± 7.6 (P = 0.16) | 306.0 ± 72.0 vs. 258.0 ± 60.0 (P = 0.004) |
| Eghtesad (Randomized) (2015) [33] | 11 vs. 12 | 61.8 ± 5.9 vs. 56.0 ± 11.0 (P = 0.13) | 22.0 ± 5.0 vs. 23.0 ± 5.0 (P = 0.63) | 21.0 ± 7.0 vs. 23.0 ± 4.0 (P = 0.40) | 389.0 ± 36.0 vs. 373.0 ± 76.0 (P = 0.53) |
| Eghtesad (Non-randomized) (2015) [33] | 35 vs. 22 | 56.0 ± 9.0 vs. 56.0 ± 11.0 (P = 0.99) | 22.0 ± 7.0 vs. 23.0 ± 6.0 (P = 0.58) | 25.0 ± 7.0 vs. 24.0 ± 7.0 (P = 0.63) | 387.0 ± 68.0 vs. 389.0 ± 107.0 (P = 0.93) |
| Kubal (2016) [21] | 30 vs. 61 | 31.5 ± 13.3 vs. 36.2 ± 14.7 (P = 0.14) | 23.2 ± 8.9 vs. 16.0 ± 5.8 (P < 0.001) | 19.0 ± 5.2 vs. 26.2 ± 7.2 (P = 0.01) | 288.0 ± 41.5 vs. 429.0 ± 138.5 (P < 0.001) |
| Bohorquez (2017) [24] | 100 vs. 38 | 37.8 ± 14.6 vs. 37.6 ± 14.6 (P = 0.95) | 20.7 ± 5.4 vs. 20.8 ± 5.7 (P = 0.92) | 20.4 ± 7.5 vs. 18.7 ± 10.6 (P = 0.3) | 304.0 ± 92.2 vs. 240.6 ± 45.7 (P < 0.001) |
| Study | ITBLs (tPA vs. Non tPA) | Total Biliary Complications (tPA vs. Non-tPA) | Bile Leak (tPA vs. Non-tPA) | Anastomotic Strictures (tPA vs. Non-tPA) | HAT (tPA vs. Non-tPA) | Blood Transfusion (pRBC) (tPA vs. Non-tPA) | Graft Survival (1-Year) (tPA vs. Non-tPA) | Patient Survival (1-Year) (tPA vs. Non-tPA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seal (2014) [23] | 2/85 (2.35%) vs. 7/33 (21.21%) (P = 0.002) | 14/85 (16.47%) vs. 11/33 (33.33%) (P = 0.02) | NA | NA | NA | 3.2 ± 3.4 vs. 3.1 ± 2.3 (P = 0.74) | 82/85 (96.47%) vs. 23/33 (69.69%) (P < 0.001) | 83/85 (97.64%) vs. 29/33 (87.87%) (P = 0.08) |
| Eghtesad (Randomized + non-randomized) (2015) [33] | 1/34 (2.94%) vs. 1/46 (2.17%) (P = 0.83) | NA | NA | NA | 1/34 (2.94%) vs. 3/46 (6.52%) (P = 0.40) | NA | NA | NA |
| Kubal (2016) [21] | 0/30 (0%) vs. 11/61 (18.03%) (P = 0.01) | 8/30 (26.66%) vs. 43/61 (70.50%) (P < 0.001) | 1/30 (3.33%) vs. 4/61 (6.51%) (P = 0.85) | 7/30 (23.33%) vs. 28/61 (45.90%) (P = 0.06) | 0/30 (0%) vs. 2/61 (3.27%) (P = 0.80) | 4.2 ± 3.2 vs. 7.2 ± 6.0 (P = 0.01) | 26/30 (86.67%) vs. 49/61 (80.32%) (P = 0.14) | 26/30 (86.67%) vs. 53/61 (86.88%) (P = 0.90) |
| Bohorquez (2017) [24] | 3/100 (3.0%) vs. 2/38 (5.26%) (P = 0.63) | 25/100 (25.0%) vs. 9/38 (23.68%) (P = 0.87) | 5/100 (5.0%) vs. 2/38 (5.26%) (P = 0.89) | 19/100 (19.0%) vs. 5/38 (13.15%) (P = 0.42) | 3/100 (3.0%) vs. 3/38 (7.89%) (P = 0.20) | 3.4 ± 4.4 vs. 4.5 ± 3.8 (P = 0.16) | 92/100 (92.0%) 29/38 (76.31%) (P = 0.02) | 93/100 (93.0%) vs. 33/38 (86.84%) (P = 0.41) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jayant, K.; Reccia, I.; Virdis, F.; Shapiro, A.M.J. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Impact of Thrombolytic Therapy in Liver Transplantation Following Donation after Circulatory Death. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7110425
Jayant K, Reccia I, Virdis F, Shapiro AMJ. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Impact of Thrombolytic Therapy in Liver Transplantation Following Donation after Circulatory Death. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2018; 7(11):425. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7110425
Chicago/Turabian StyleJayant, Kumar, Isabella Reccia, Francesco Virdis, and A. M. James Shapiro. 2018. "Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Impact of Thrombolytic Therapy in Liver Transplantation Following Donation after Circulatory Death" Journal of Clinical Medicine 7, no. 11: 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7110425
APA StyleJayant, K., Reccia, I., Virdis, F., & Shapiro, A. M. J. (2018). Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Impact of Thrombolytic Therapy in Liver Transplantation Following Donation after Circulatory Death. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7(11), 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7110425