Fibrotic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Key Issues in Diagnosis and Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Diagnosis of Fibrotic HP
2.1. Exposures
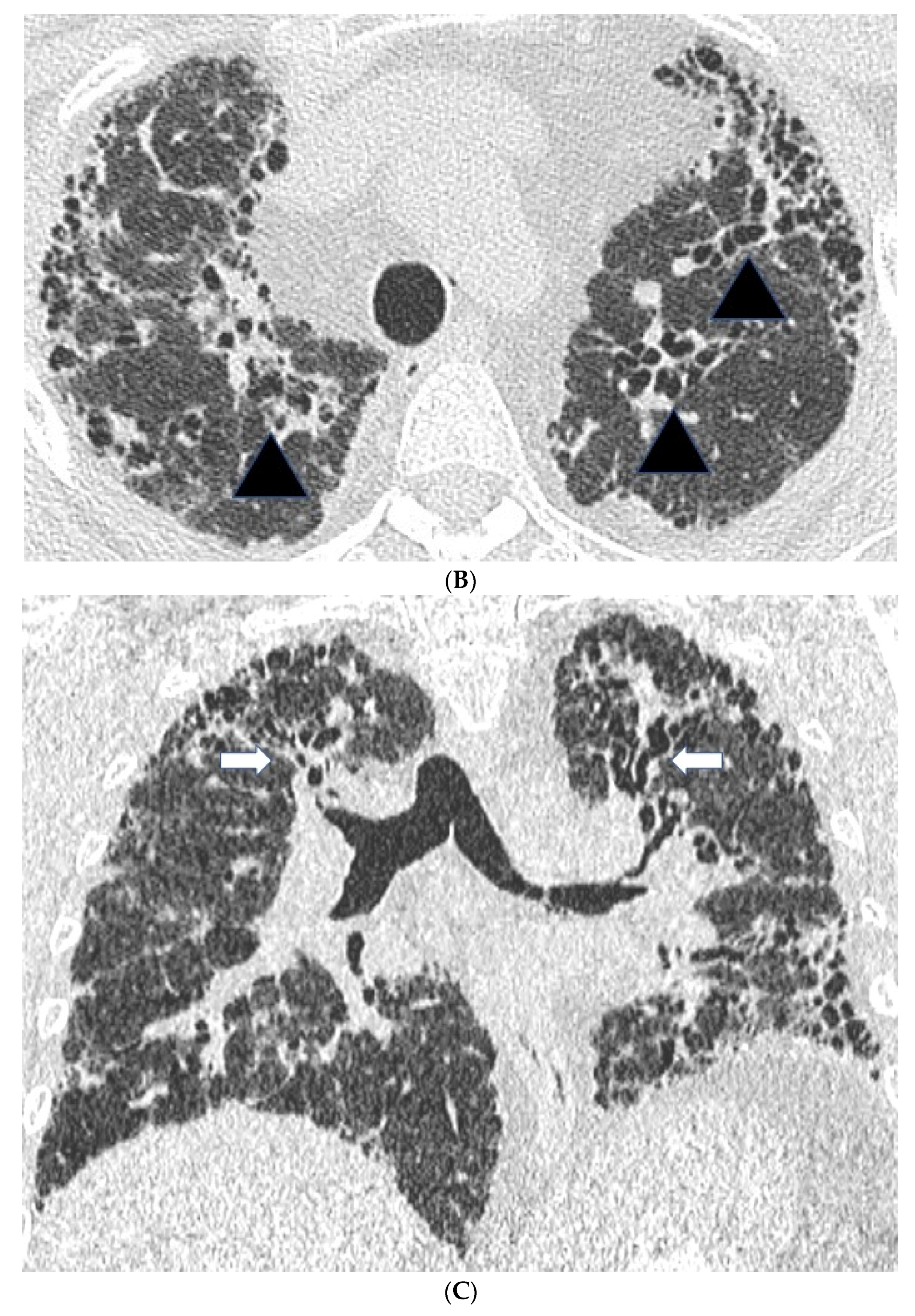
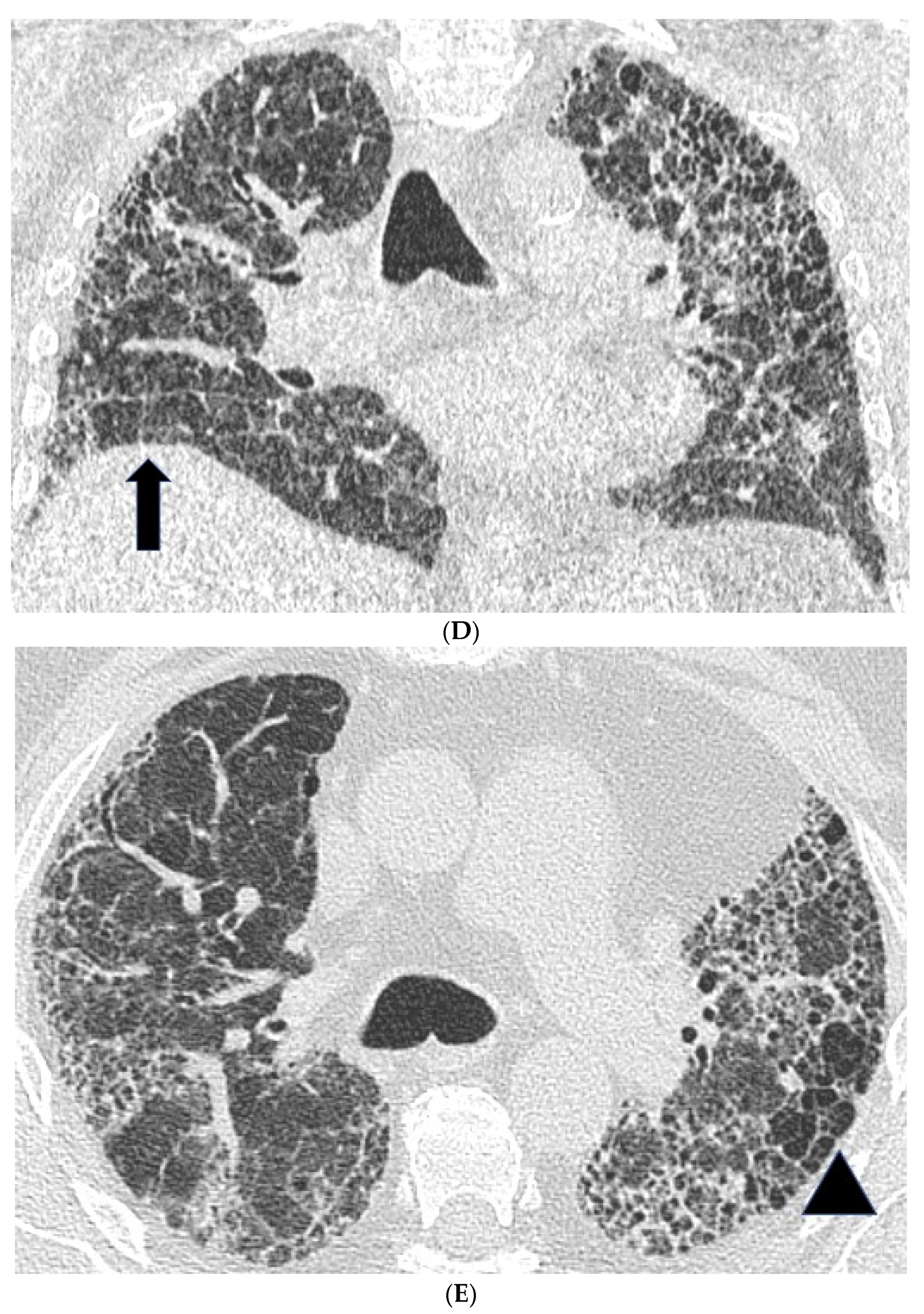
2.2. High Resolution CT Findings
2.3. Serum Antibodies against Suspected Antigens
2.4. Bronchoalveolar Lavage (BAL)
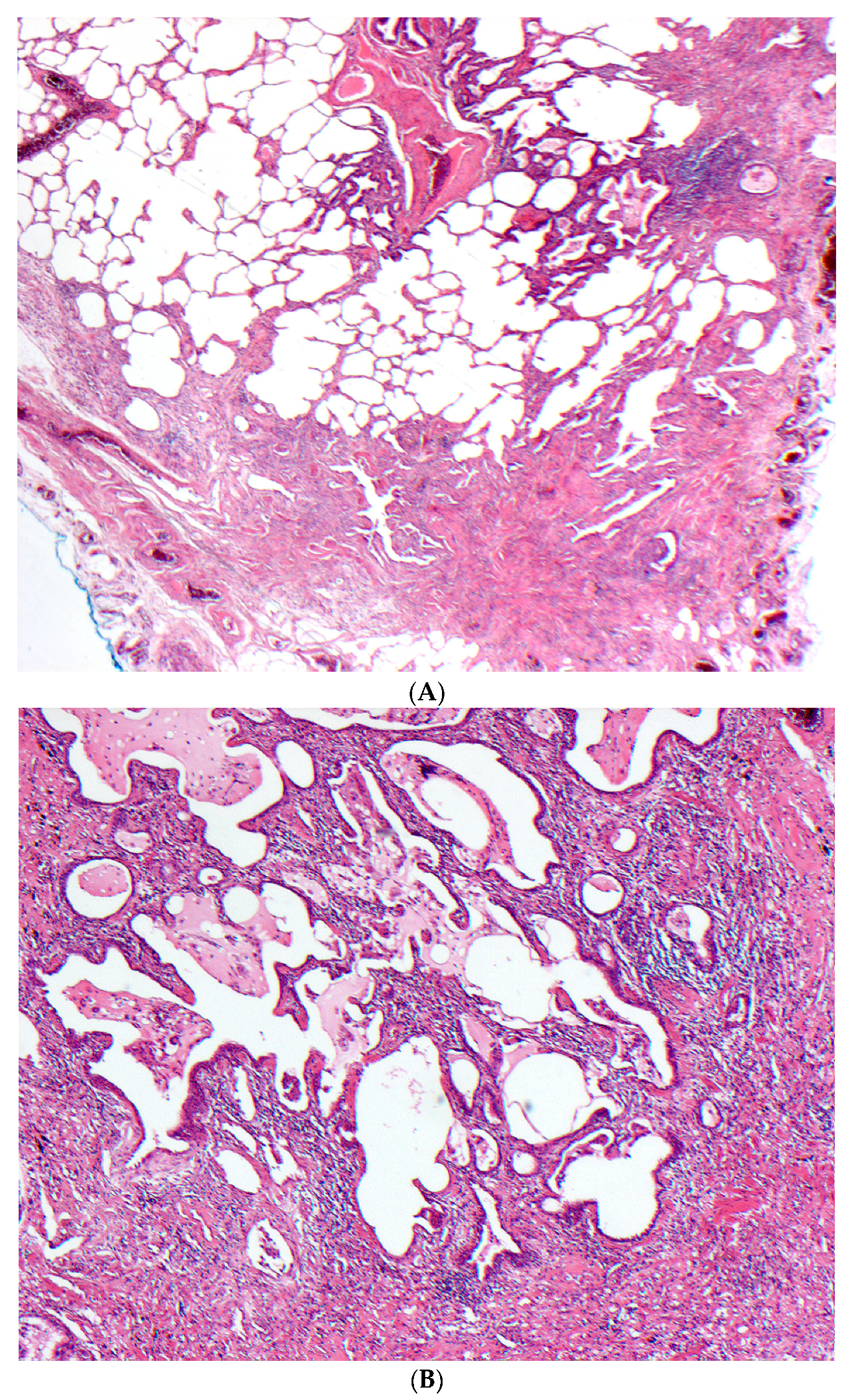
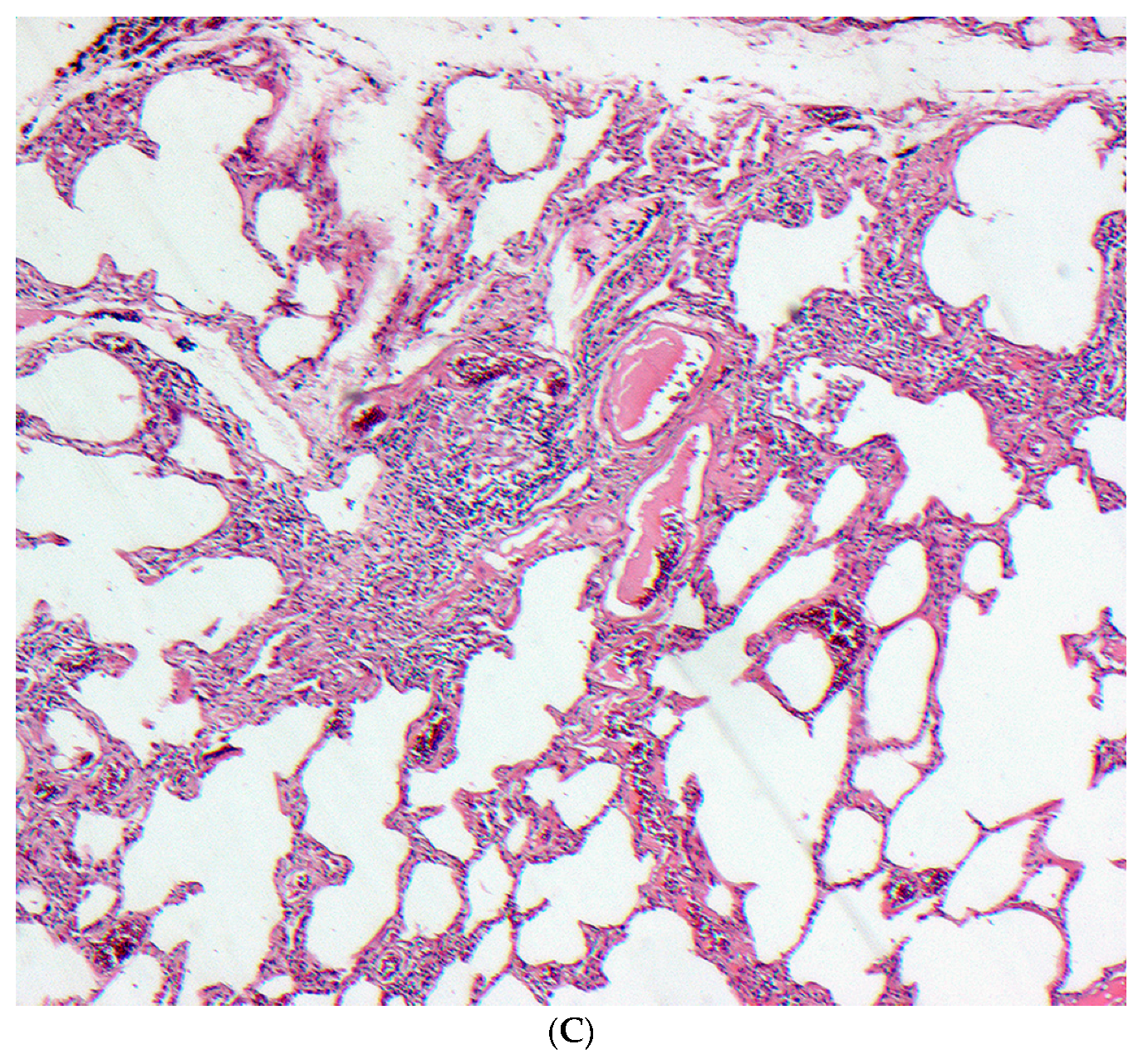
2.5. Histopathology
2.5.1. Distinguishing Fibrotic HP Associated with a UIP/Fibrotic NSIP Pattern from UIP/IPF
2.5.2. Cryobiopsy
3. Management of Fibrotic HP
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lacasse, Y.; Selman, M. Clinical diagnosis of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 168, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, M.; Israel-Assayag, E. Pathogenesis of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 4, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willems, S.; Verleden, S.E. Multiplex protein profiling of bronchoalveolar lavage in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Ann. Thorac. Med. 2013, 8, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sennekamp, J.; Muller-Wening, D. Guidelines for diagnosing extrinsic allergic alveolitis (hypersensitivity pneumonitis) (German Extrinsic Allergic Alveolitis Study Group). Pneumologie 2007, 61, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaxiola, M.; Buendia-Roldan, I. Morphologic diversity of chronic pigeon breeder’s disease: Clinical features and survival. Respir. Med. 2011, 105, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, H.; Schubel, K. Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia: Survival is influenced by the underlying cause. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Rochwerg, B. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline: Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An Update of the 2011 Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, e3–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, S.L.; Wells, A.U. Multicentre evaluation of multidisciplinary team meeting agreement on diagnosis in diffuse parenchymal lung disease: A case-cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Anstrom, K.J. Prednisone, azathioprine, and N-acetylcysteine for pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1968–1977. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hisauchi-Kojima, K.; Sumi, Y. Purification of the antigenic components of pigeon dropping extract, the responsible agent for cellular immunity in pigeon breeder’s disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 103, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, M.J.; Benavent, M.I. Detection of specific antibodies to pigeon serum and bloom antigens by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay in pigeon breeder’s disease. Occup. Environ. Med. 2000, 57, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grammer, L.C.; Roberts, M. Clinical and serologic follow-up of four children and five adults with bird-fancier’s lung. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1990, 85, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltoun, C.A.; Harris, K.E. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis resulting from community exposure to Canada goose droppings: When an external environmental antigen becomes an indoor environmental antigen. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2000, 84, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inase, N.; Ohtani, Y. A clinical study of hypersensitivity pneumonitis presumably caused by feather duvets. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006, 96, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez Perez, E.R.; Swigris, J.J. Identifying an inciting antigen is associated with improved survival in patients with chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest 2013, 144, 1644–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanak, V.; Golbin, J.M. Causes and presenting features in 85 consecutive patients with hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2007, 82, 812–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K.; Suga, M. Occupational hypersensitivity pneumonitis in Japan: Data on a nationwide epidemiological study. Occup. Environ. Med. 1995, 52, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roussel, S.; Reboux, G. Microbiological evolution of hay and relapse in patients with farmer’s lung. Occup. Environ. Med. 2004, 61, e3. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vincken, W.; Roels, P. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis due to Aspergillus fumigatus in compost. Thorax 1984, 39, 74–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleyn, J.G.; Johnson, W.M. Microbial aerosols and actinomycetes in etiological considerations of mushroom workers’ lungs. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1981, 41, 1454–1460. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Glazer, C.S.; Martyny, J.W. Nontuberculous mycobacteria in aerosol droplets and bulk water samples from therapy pools and hot tubs. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2007, 4, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, C.M.; Burton, C.M. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis in workers exposed to metalworking fluids. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2014, 57, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullinan, P.; D’Souza, E. Lesson of the month: Extrinsic allergic (bronchiolo)alveolitis and metal working fluids. Thorax 2014, 69, 1059–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diego, C.; Cullinan, P. Extrinsic Allergic Alveolitis. In Interstitial Lung Disease; Du Bois, R.M., Richeldi, L., Eds.; European Respiratory Society: London, UK, 2009; Volume 46, pp. 112–125. [Google Scholar]
- Fenclova, Z.; Pelclova, D. Occupational hypersensitivity pneumonitis reported to the Czech National Registry of Occupational Diseases in the period 1992–2005. Ind. Health 2009, 47, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansell, D.M.; Wells, A.U. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: Correlation of individual CT patterns with functional abnormalities. Radiology 1996, 199, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, S.L.; Sverzellati, N. Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis: High resolution computed tomography patterns and pulmonary function indices as prognostic determinants. Eur. Radiol. 2012, 22, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, C.I.; Churg, A. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: Spectrum of high-resolution CT and pathologic findings. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 188, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franquet, T.; Hansell, D.M. Lung cysts in subacute hypersensitivity pneumonitis. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2003, 27, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, C.I.; Muller, N.L. Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis: Differentiation from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and nonspecific interstitial pneumonia by using thin-section CT. Radiology 2008, 246, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanak, V.; Golbin, J.M. High-resolution CT findings of parenchymal fibrosis correlate with prognosis in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest 2008, 134, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, J.; Bartholmai, B.J. Automated computer-based CT stratification as a predictor of outcome in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Eur. Radiol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husman, K.; Vohlonen, I. Precipitins against microbes in mouldy hay in the sera of farmers with farmer’s lung or chronic bronchitis and of healthy farmers. Eur. J. Respir. Dis. Suppl. 1987, 152, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diment, J.A.; Pepys, J. Avian erythrocyte agglutination tests with the sera of bird fanciers. J. Clin. Pathol. 1977, 30, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Venegas, A.; Sansores, R.H. Utility of a provocation test for diagnosis of chronic pigeon Breeder’s disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 158, 862–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtani, Y.; Kojima, K. Inhalation provocation tests in chronic bird fancier’s lung. Chest 2000, 118, 1382–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morell, F.; Roger, A. Bird fancier’s lung: A series of 86 patients. Medicine 2008, 87, 110–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, X.; Sanchez-Ortiz, M. Diagnostic yield of specific inhalation challenge in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 1658–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtani, Y.; Saiki, S. Chronic bird fancier’s lung: Histopathological and clinical correlation. An application of the 2002 ATS/ERS consensus classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Thorax 2005, 60, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrera, L.; Mendoza, F. Functional diversity of T-cell subpopulations in subacute and chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 177, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caillaud, D.M.; Vergnon, J.M. Bronchoalveolar lavage in hypersensitivity pneumonitis: A series of 139 patients. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 2012, 11, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selman, M.; Pardo, A. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: Insights in diagnosis and pathobiology. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Thoracic Society; European Respiratory Society. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, June 2001 and by the ERS Executive Committee, June 2001. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 277–304. [Google Scholar]
- Ohshimo, S.; Bonella, F. Significance of bronchoalveolar lavage for the diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 179, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welker, L.; Jorres, R.A. Predictive value of BAL cell differentials in the diagnosis of interstitial lung diseases. Eur. Respir. J. 2004, 24, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morell, F.; Villar, A. Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis in patients diagnosed with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A prospective case-cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2013, 1, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios, R.J. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: Histopathology. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2008, 132, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reyes, C.N.; Wenzel, F.J. The pulmonary pathology of farmer’s lung disease. Chest 1982, 81, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Padilla, R.; Gaxiola, M. Bronchiolitis in chronic pigeon breeder’s disease. Morphologic evidence of a spectrum of small airway lesions in hypersensitivity pneumonitis induced by avian antigens. Chest 1996, 110, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Myers, J.L. Hypersensitivity pneumonia: The role of lung biopsy in diagnosis and management. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25 (Suppl. S1), S58–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reghellin, D.; Poletti, V. Cathepsin-K is a sensitive immunohistochemical marker for detection of micro-granulomas in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2010, 27, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Katzenstein, A.L.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Diagnosis of usual interstitial pneumonia and distinction from other fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Hum. Pathol. 2008, 39, 1275–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churg, A.; Muller, N.L. Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2006, 30, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vourlekis, J.S.; Schwarz, M.I. Nonspecific interstitial pneumonitis as the sole histologic expression of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am. J. Med. 2002, 112, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Jones, K.D. Pathological Findings and Prognosis in a Large Prospective Cohort of Chronic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis. Chest 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, S.L.; Wells, A.U. Relationship between fibroblastic foci profusion and high resolution CT morphology in fibrotic lung disease. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churg, A.; Sin, D.D. Pathologic patterns and survival in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2009, 33, 1765–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiba, S.; Tsuchiya, K. Chronic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis with a Usual Interstitial Pneumonia-Like Pattern: Correlation between Histopathologic and Clinical Findings. Chest 2016, 149, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravaglia, C.; Bonifazi, M. Safety and Diagnostic Yield of Transbronchial Lung Cryobiopsy in Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Diseases: A Comparative Study versus Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Lung Biopsy and a Systematic Review of the Literature. Respiration 2016, 91, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iftikhar, I.H.; Alqhothani, L. Transbronchial Lung Cryobiopsy and Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Lung Biopsy in the Diagnosis of Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Disease: A meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morisset, J.; Johannson, K.A. Use of Mycophenolate Mofetil or Azathioprine for the Management of Chronic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis. Chest 2017, 151, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lota, H.K.; Keir, G.J. Novel use of rituximab in hypersensitivity pneumonitis refractory to conventional treatment. Thorax 2013, 68, 780–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keir, G.J.; Maher, T.M. Rituximab in severe, treatment-refractory interstitial lung disease. Respirology 2014, 19, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuyts, W.A.; Antoniou, K.M. Combination therapy: The future of management for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinicaltrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02496182?term=NCT02496182&rank=1 (accessed on 2 May 2017).
- Clinicaltrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02999178?term=NCT02999178&rank=1 (accessed on 2 May 2017).


| Features | Fibrotic HP | IPF |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||
| Sex | No difference | More frequent in men |
| Smoking | Protective | Risk factor |
| Age | No predilection | More frequent > 55 years |
| Clinical symptoms/history | ||
| Clubbing | Often | Often |
| Squeaks | Typical | Absent |
| Bibasal crackles | Frequent | Frequent |
| Systemic disease features (fever, joint pains, fatigue) | Often | Absent |
| Exposure to antigens | Frequent | Rare |
| Positive precipitins | Frequent | Rare |
| Imaging (CT) | ||
| Distribution | Upper lobe predominance | Peripheral, predominantly basal |
| Mosaic attenuation | Frequent | Absent/Limited |
| Nodules | Frequent | Absent |
| Interlobular septal thickening | Often | Absent/Limited |
| Honeycombing | Often | Frequent (typical for UIP pattern) |
| Bronchocentricity | Frequent | Absent |
| Discrete cysts | Often | Absent |
| Consolidation | Rare | Absent |
| Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) | Lymphocytosis > 25–30% | Lymphocytosis < 20% |
| Histological | ||
| Fibroblast foci | Often | Frequent |
| Granulomas/giant cells/Schaumann bodies | Frequent | Rare |
| Organizing pneumonia | Rare | Rare |
| Honeycombing | Often | Frequent |
| Paraseptal subpleural distribution | Often | Frequent |
| Bronchocentricity | Frequent | Absent |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kouranos, V.; Jacob, J.; Nicholson, A.; Renzoni, E. Fibrotic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Key Issues in Diagnosis and Management. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm6060062
Kouranos V, Jacob J, Nicholson A, Renzoni E. Fibrotic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Key Issues in Diagnosis and Management. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2017; 6(6):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm6060062
Chicago/Turabian StyleKouranos, Vasileios, Joseph Jacob, Andrew Nicholson, and Elizabetta Renzoni. 2017. "Fibrotic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Key Issues in Diagnosis and Management" Journal of Clinical Medicine 6, no. 6: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm6060062
APA StyleKouranos, V., Jacob, J., Nicholson, A., & Renzoni, E. (2017). Fibrotic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Key Issues in Diagnosis and Management. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 6(6), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm6060062






