Impact of Contralateral Implant Placement in Unilateral Implant-Based Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction: A Single Center Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
- There was an absolute indication to placement of a contralateral implant when no other symmetrization procedure was planned (mastopexy or breast reduction) irrespective of the size of the breast.
- Patients who undergo contralateral mastopexy alone benefit from the association of a contralateral implant and thus this results in an absolute indication as well. The option of placing a contralateral implant was discussed with the patient and evaluated case by case.
- In patients who need a breast reduction, the indication for implant placement can be considered relative and should be evaluated case by case.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burget, G.C.; Menick, F.J. The Subunit Principle in Nasal Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1985, 76, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalex-Ulloa, M.; Castillo, A.; Stevens, E.; Fuertes, G.A.; Leonelli, F.; Ubaldo, F. Preliminary study of the total restoration of the facial skin. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1954, 13, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahabedian, M.Y. Managing the opposite breast: Contralateral symmetry procedures. Cancer J. 2008, 14, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, S.S.; Baldwin, B. A comparison of outcomes using three different methods of breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1992, 90, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusic, A.L.; Klassen, A.F.; Scott, A.M.B.; Klok, J.A.B.; Cordeiro, P.G.; Cano, S.J. Development of a new patient-reported outcome measure for breast surgery: The BREAST-Q. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 124, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosa, K.B.; Qi, J.; Kim, H.M.; Hamill, J.B.; Wilkins, E.G.; Pusic, A.L. Long-term Patient-Reported Outcomes in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction. JAMA Surg. 2018, 153, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razdan, S.N.; Panchal, H.; Albornoz, C.R.; Pusic, A.L.; McCarthy, C.C.; Cordeiro, P.G.; Disa, J.J.; Mehrara, B.J.; Matros, E. Impact of Contralateral Symmetry Procedures on Long-Term Patient-Reported Outcomes following Unilateral Prosthetic Breast Reconstruction. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2019, 35, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, R.B.; Packowski, K.; Horick, N.; Rosado, N.B.; Chinta, S.B.; Koh, D.J.; Sobti, N.; Specht, M.C.; Liao, E.C. The Timing of Acute and Late Complications Following Mastectomy and Implant-based Reconstruction. Ann. Surg. 2023, 278, e203–e208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Solbas, S.; Lorenzo-Liñán, M.Á.; Castro-Luna, G. Long-Term Quality of Life (BREAST-Q) in Patients with Mastectomy and Breast Reconstruction. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsunder, M.G.; Polanco, T.O.; McCarthy, C.M.M.; Allen, R.J.J.; Matros, E.M.; Coriddi, M.; Mehrara, B.J.; Pusic, A.M.; Nelson, J.A.M. Understanding Preoperative Breast Satisfaction among Patients Undergoing Mastectomy and Immediate Reconstruction: BREAST-Q Insights. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2021, 148, 891e–902e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oemrawsingh, A.; Clarijs, M.E.; Pusic, A.L.; Lingsma, H.F.; Verhoef, C.; Hazelzet, J.A.; Koppert, L.B. BREAST-Q Breast-Conserving Therapy Module: Normative Data from a Dutch Sample of 9059 Women. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2022, 150, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.H.; Chiang, I.H.; Wang, C.H.; Chiao, H.Y.; Chou, C.Y.; Tzeng, Y.S.; Chen, T.M.; Chen, S.G. Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction Combined With Contralateral Breast Augmentation for Taiwanese Women with Small Breasts. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2017, 78, S102–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, M.S.; Priano, V.; Franchelli, S.; Puggioni, V.; Merlo, D.F.; Mannucci, M.; Santi, P.L. Factors affecting symmetrization of the contralateral breast: A 7-year unilateral postmastectomy breast reconstruction experience. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2011, 35, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Meir, E.D.; Lin, S.J.; Momoh, A.O.; Tobias, A.M.; Colakoglu, S.; Yueh, J.H.; Slavin, S.A.; Lee, B.T. The lateral chest wall: A separate aesthetic unit in breast surgery. Plast. Reconstr. Surg 2011, 128, 626e–634e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mundy, L.R.; Homa, K.; Klassen, A.F.D.; Pusic, A.L.; Kerrigan, C.L.M. Breast Cancer and Reconstruction: Normative Data for Interpreting the BREAST-Q. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 139, 1046e–1055e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devulapalli, C.; Bello, R.J.; Moin, E.; Alsobrooks, J.B.; Fallas, P.B.; Ohkuma, R.; Manahan, M.A.; Sacks, J.M.M.; Cooney, C.M.; Rosson, G.D. The Effect of Radiation on Quality of Life throughout the Breast Reconstruction Process: A Prospective, Longitudinal Pilot Study of 200 Patients with Long-Term Follow-Up. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 141, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.Y.; Hong, S.E.; Hong, M.K.; Woo, K.-J. The influence of contralateral breast augmentation on the development of complications in direct-to-implant breast reconstruction. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2020, 73, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, M.; Cogliandro, A.; Signoretti, M.; Persichetti, P. Analysis of Symmetry Stability Following Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction and Contralateral Management in 582 Patients with Long-Term Outcomes. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2018, 42, 936–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losken, A.; Carlson, G.W.; Bostwick, J.; Jones, G.E.; Schoemann, M. Trends in Unilateral Breast Reconstruction and Management of the Contralateral Breast: The Emory Experience. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2002, 110, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champaneria, M.C.; Wong, W.W.; Hill, M.E.; Gupta, S.C. The evolution of breast reconstruction: A historical perspective. World J. Surg. 2012, 36, 730–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli Coppola, M.; Schaffer, C.; Jaber, G.J.; Sapino, G.; di Summa, P.G. Maximizing Aesthetic Outcomes in Delayed Breast Reconstruction: The Be.A.U.T-I.F.U.L. DIEP® Step-by-Step Inset Technique. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2025, 49, 1959–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
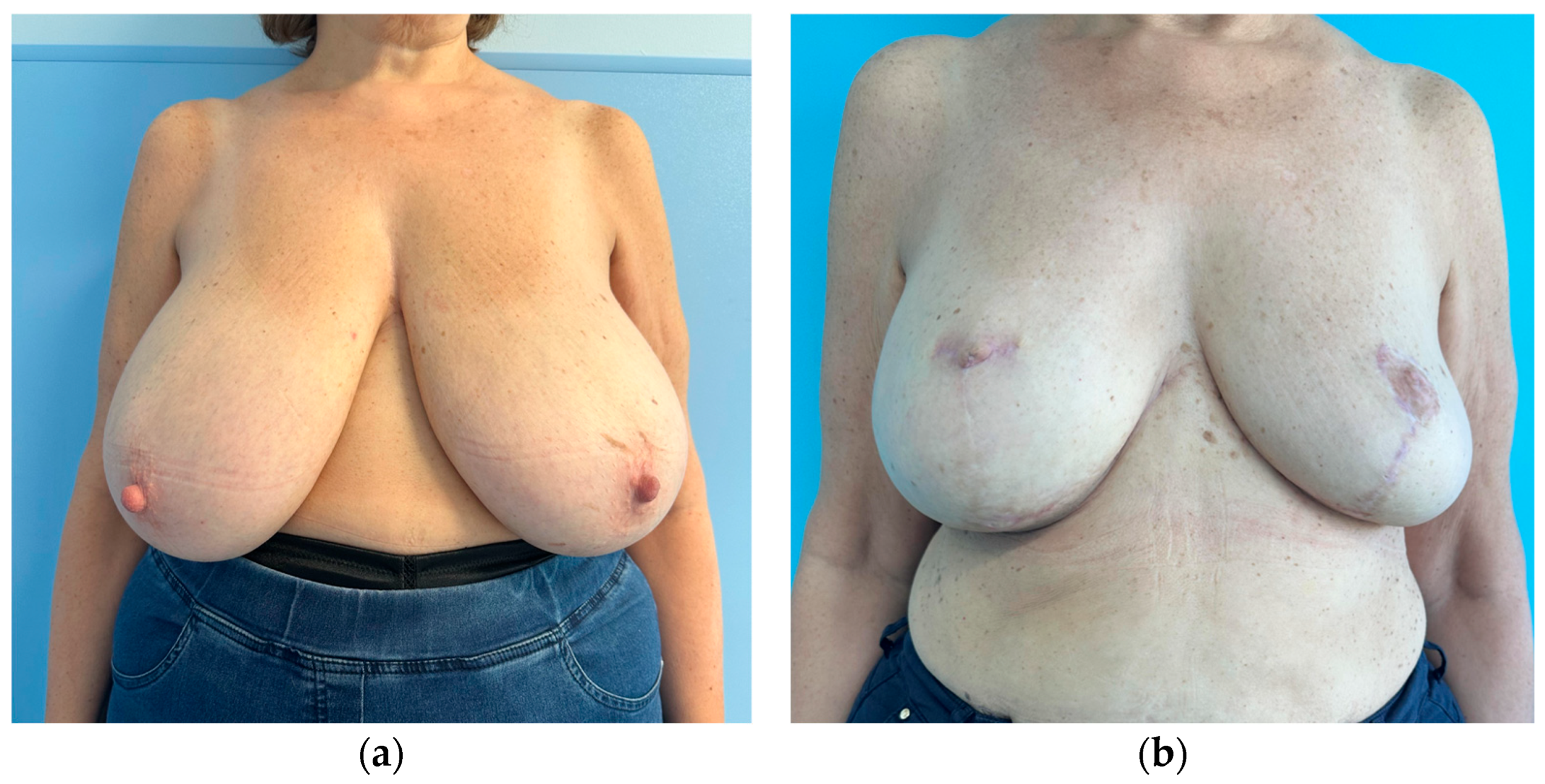
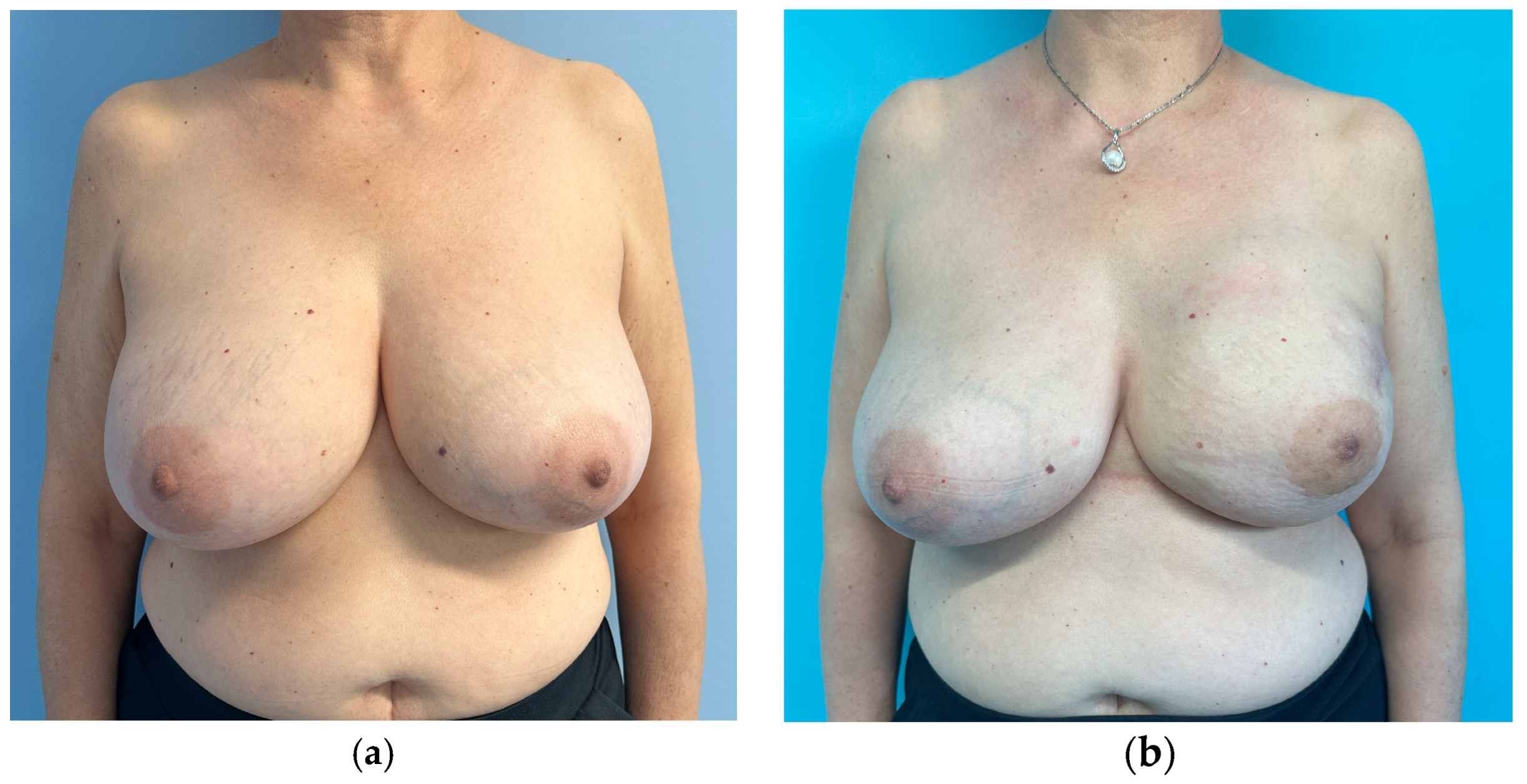
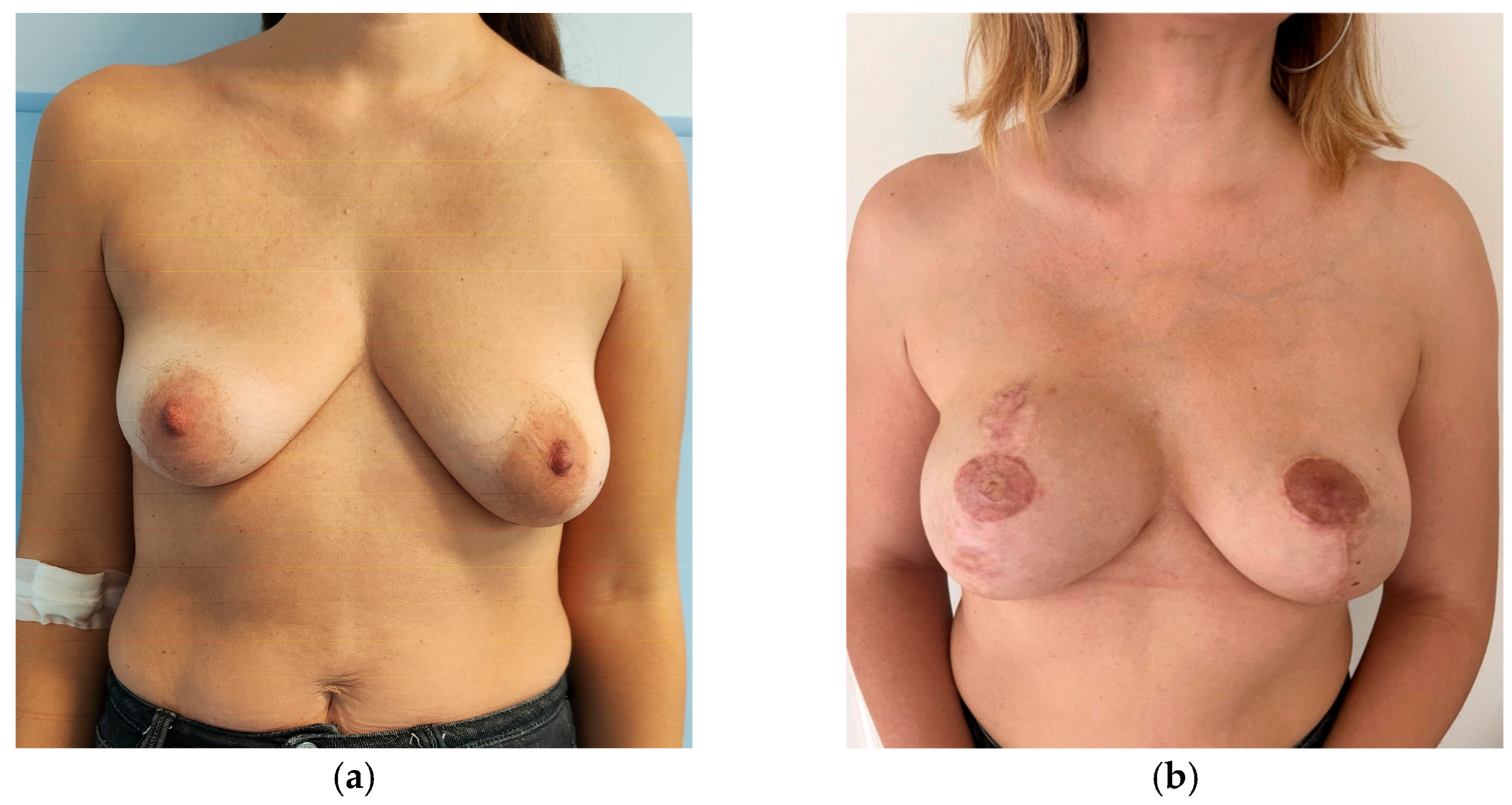
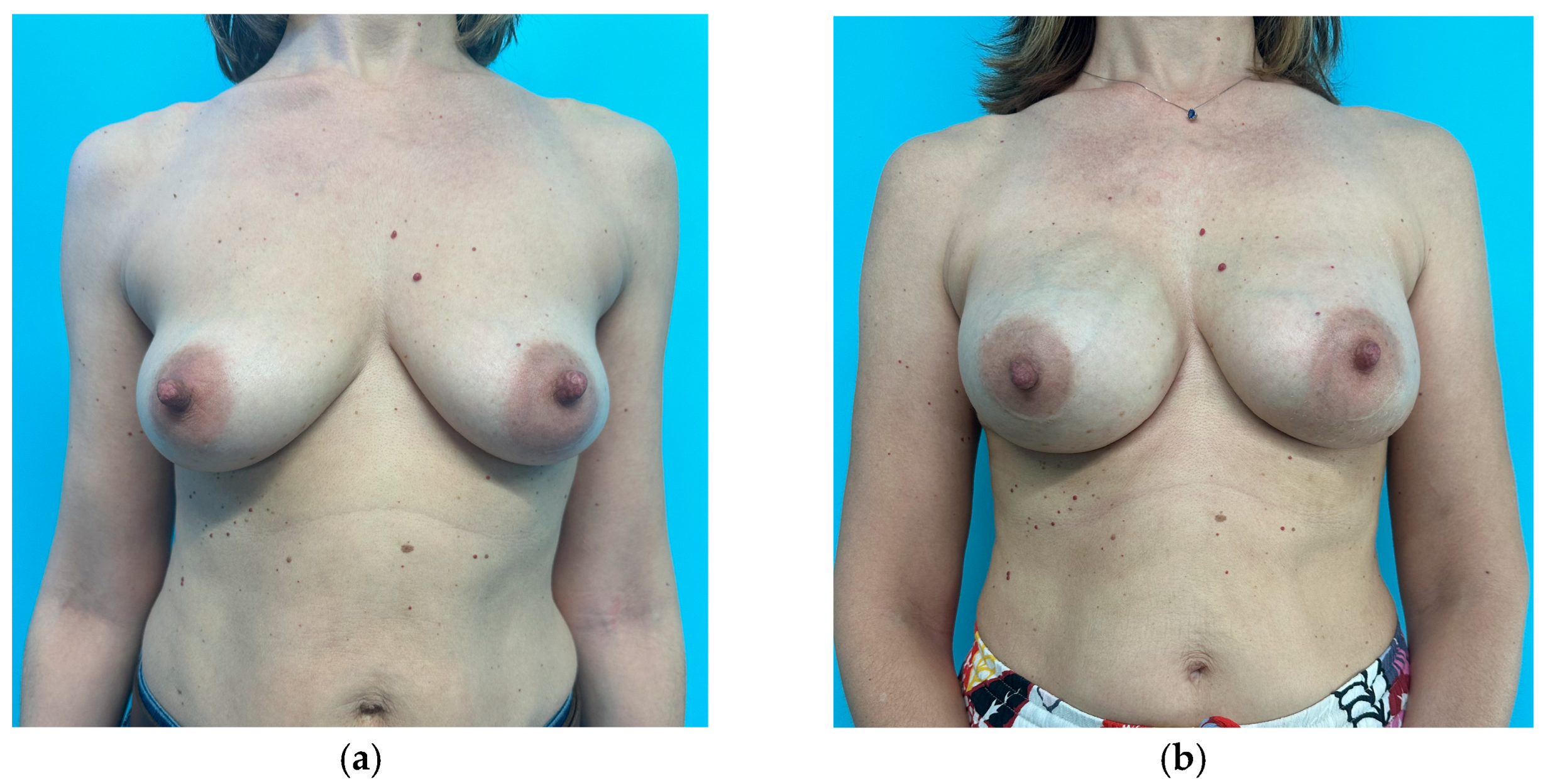
| Subgroup | Unilateral Breast Implant (Mean ± SD) | Bilateral Breast Implant (Mean ± SD) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient no. | 31 | 21 | |
| Age, years | 53.18 ± 9.21 | 50.65 ± 7.52 | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 25.87 ± 5.15 | 24.52 ± 7.31 | |
| Diabetes | |||
| Yes | 6 | 3 | |
| No | 25 | 18 | |
| Smoke | |||
| Yes | 11 | 9 | |
| No | 20 | 12 | |
| Hypertension | |||
| Yes | 6 | 5 | |
| No | 25 | 16 | |
| Mastectomy type | |||
| NSM | 13 | 10 | |
| SSM | 9 | 7 | |
| SRM | 9 | 4 | |
| Mastectomy weight, g | 357.58 ± 118.01 | 347.38 ± 95.48 | |
| Neoadjuvant chemotherapy | |||
| Yes | 5 | 6 | |
| No | 26 | 15 | |
| Previous radiation therapy | |||
| Yes | 0 | 1 | |
| No | 31 | 20 | |
| Adjuvant chemotherapy | |||
| Yes | 15 | 11 | |
| No | 16 | 10 | |
| Adjuvant radiation therapy | |||
| Yes | 8 | 8 | |
| No | 23 | 13 | |
| Implant size (reconstructed breast), cc | 391.22 ± 126.02 | 385.23 ± 91.69 | |
| Contralateral implant size, cc | / | 225.23 ± 70.66 |
| Subgroup | N (%) | Unilateral Breast Implant | Bilateral Breast Implant | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | |||
| Patient no. | 52 (100.00%) | 31 (100.00%) | 21 (100.00%) | |
| Complications no. | 20 (38.46%) | 12 (38.71%) | 8 (38.10%) | |
| Hematoma/Hemorragia | ||||
| Yes | 1 (1.92%) | 0 (0.00%) | 1 (4.76%) | |
| No | 50 (96.15%) | 31 (100.00%) | 20 (95.24%) | |
| Skin flap necrosis | ||||
| Yes—minor | 6 (11.54%) | 5 (16.13%) | 1 (4.76%) | |
| Yes—major | 3 (5.77%) | 2 (6.45%) | 1 (4.76%) | |
| No | 43 (82.69%) | 24 (77.42%) | 19 (90.48%) | |
| Seroma | ||||
| Yes | 1 (1.92%) | 1 (3.23%) | 0 (0.00%) | |
| No | 50 (96.15%) | 30 (96.77%) | 21 (100.00%) | |
| Infection | ||||
| Yes | 6 (11.54%) | 2 (6.45%) | 4 (19.05%) | |
| No | 46 (88.46%) | 29 (93.55%) | 17 (80.95%) | |
| Implant malposition | ||||
| Yes | 1 (1.92%) | 0 (0.00%) | 1 (4.76%) | |
| No | 51 (98.08%) | 31 (100.00%) | 20 (95.24%) | |
| Capsular contracture | ||||
| Yes | 1 (1.92%) | 0 (0.00%) | 1 (4.76%) | |
| No | 51 (98.08%) | 31 (100.00%) | 20 (95.24%) | |
| Implant rupture | ||||
| Yes | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | |
| No | 51 (100.00%) | 31 (100.00%) | 21 (100.00%) | |
| Reconstruction failure | ||||
| Yes | 2 (3.85%) | 1 (3.23%) | 1 (4.76%) | |
| No | 50 (96.15%) | 30 (96.77%) | 20 (95.24%) |
| Unilateral Breast Implant | Bilateral Breast Implant | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (±SD) | Mean (±SD) | ||
| Symmetry | 2.297 (±0.853) | 1.825 (±0.444) | 0.037 |
| Shape | 2.375 (±0.886) | 1.85 (±0.572) | 0.022 |
| Ptosis | 2.187 (±0.903) | 1.675 (±0.403) | 0.017 |
| Overall evaluation | 2.312 (±0.850) | 1.9 (±0.672) | 0.069 |
| BREAST-Questionnaire Reconstruction Module Version 2.0 | Unilateral Breast Implant | Bilateral Breast Implant | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (±SD) | Mean (±SD) | ||
| Satisfaction with Breasts (Postoperative) | 60.218 (16.653) | 65.315 (13.275) | 0.247 |
| Psyschosocial Well-Being (Preoperative) | 37.947 (6.628) | 38.093 (6.683) | 0.938 |
| Psychosocial Well-Being (Postoperative) | 65.052 (16.899) | 65.612 (14.634) | 0.902 |
| Sexual Well-Being (Preoperative) | 30.210 (17.415) | 31 (17.121) | 0.872 |
| Sexual Well-Being (Postoperative) | 74.052 (25.968) | 75.225 (25.468) | 0.873 |
| Variable | β (Coefficient) | Robust SE | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 114.16 | 22.93 | 69.22–159.11 | <0.001 |
| Contralateral Breast Implant (yes) | (+3.24) | 5.05 | (−6.65)–(+13.14) | 0.520 |
| Age (years) | (−0.21) | 0.33 | (−0.87)–(+0.44) | 0.522 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | (−1.53) | 0.58 | (−2.66)–(−0.40) | 0.0078 |
| Radiation (yes) | (−19.77) | 7.83 | (−35.11)–(−4.43) | 0.0115 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
D’Arpa, S.; D’Amico, G.A.; Jaber, G.J.; Colonna, M.R.; David, M. Impact of Contralateral Implant Placement in Unilateral Implant-Based Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction: A Single Center Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2026, 15, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm15010375
D’Arpa S, D’Amico GA, Jaber GJ, Colonna MR, David M. Impact of Contralateral Implant Placement in Unilateral Implant-Based Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction: A Single Center Retrospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2026; 15(1):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm15010375
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Arpa, Salvatore, Giuseppe Antonio D’Amico, Giulio Jad Jaber, Michele Rosario Colonna, and Massimo David. 2026. "Impact of Contralateral Implant Placement in Unilateral Implant-Based Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction: A Single Center Retrospective Cohort Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 15, no. 1: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm15010375
APA StyleD’Arpa, S., D’Amico, G. A., Jaber, G. J., Colonna, M. R., & David, M. (2026). Impact of Contralateral Implant Placement in Unilateral Implant-Based Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction: A Single Center Retrospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 15(1), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm15010375







