Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy in Sepsis Survivors with Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction: An Observational Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Subjects and Clinical Data Collection
2.2. Ethical Approval
2.3. Clinical Data Collection
2.4. Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE)
2.5. Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy (GDMT)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics of Sepsis Survivors
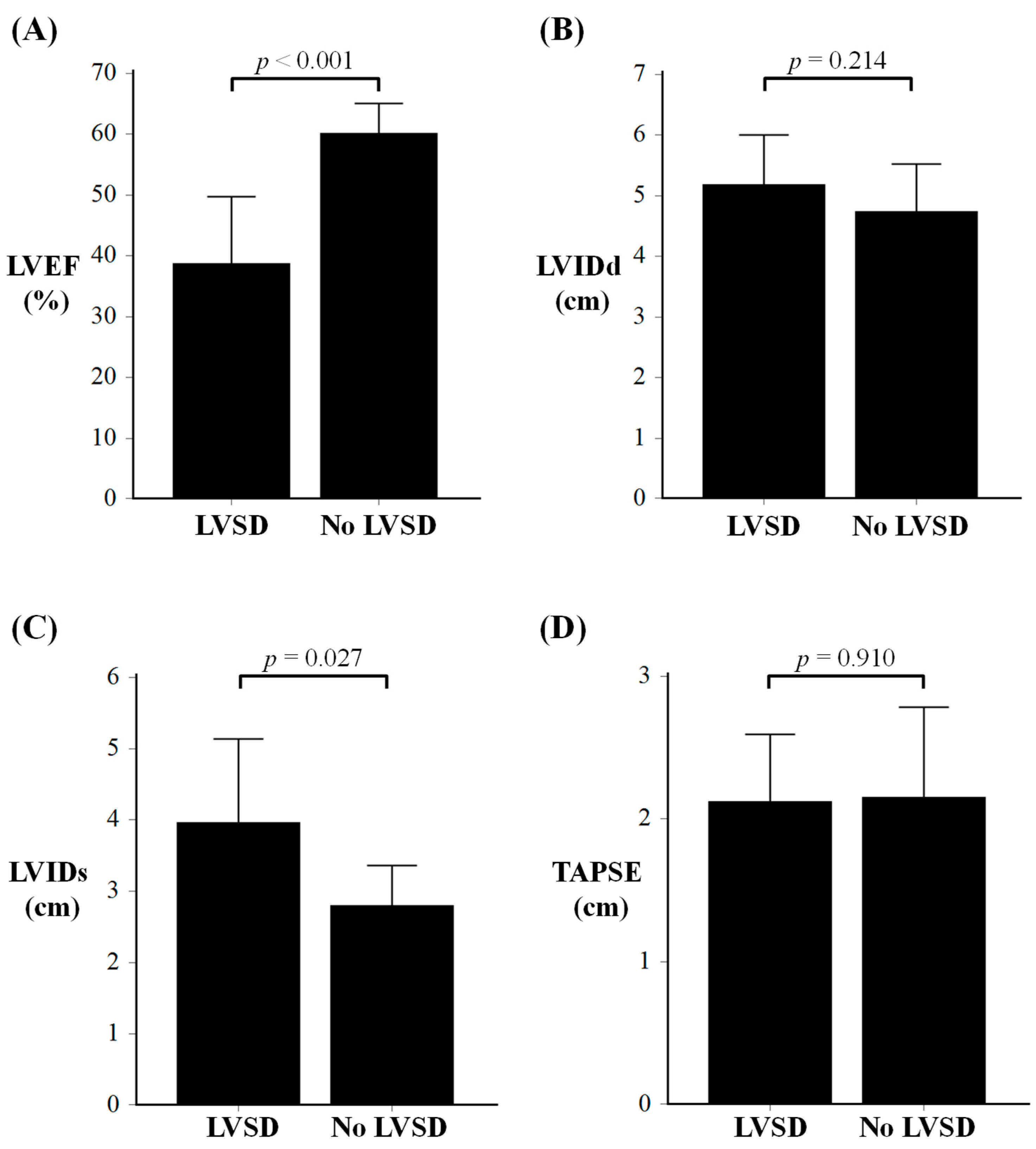
3.2. TTE and Medical Therapy in Sepsis Survivors
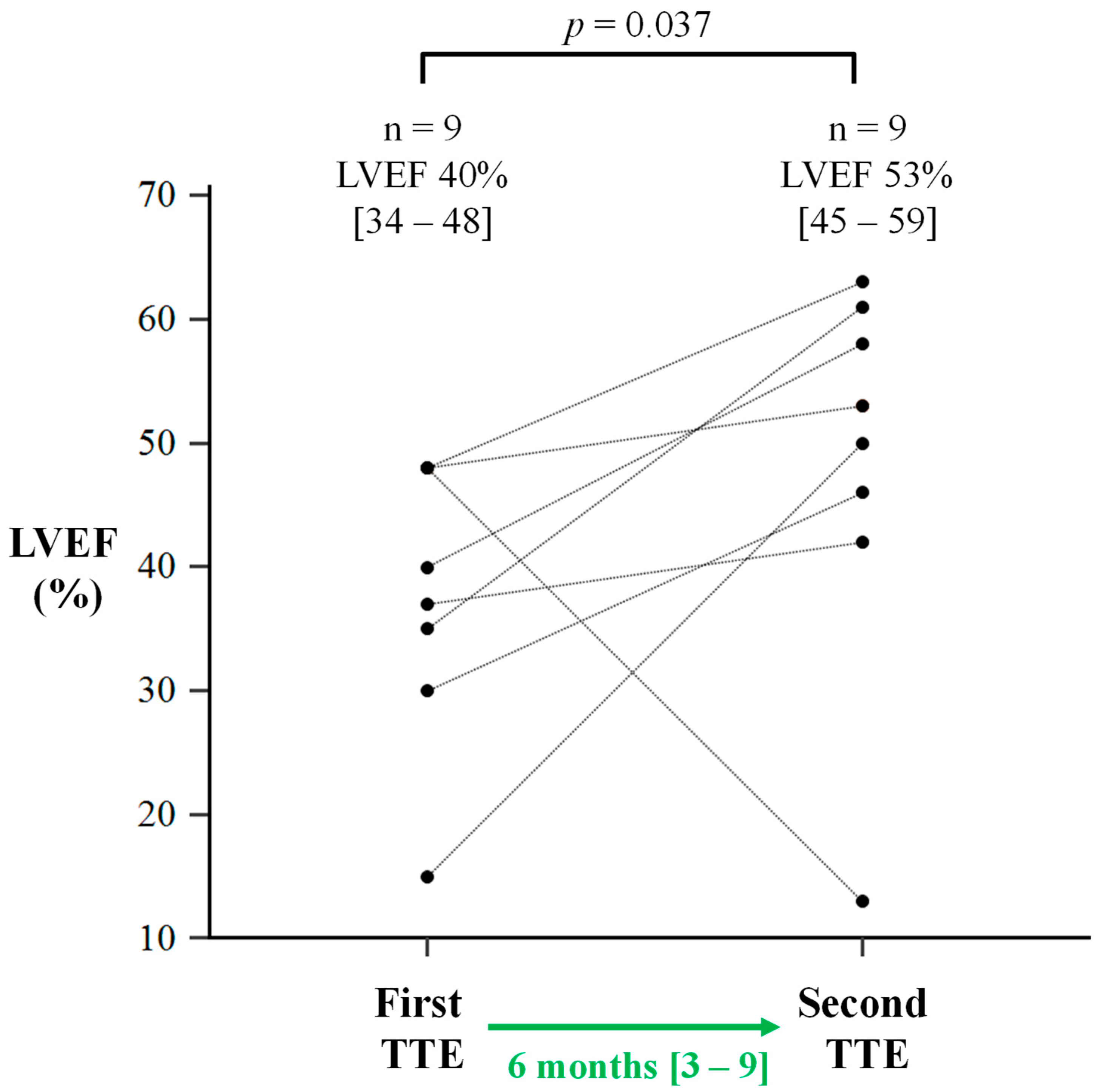
3.3. Changes in LVEF in Sepsis Survivors with LV Systolic Dysfunction
4. Discussion
4.1. Post-Sepsis LV Dysfunction
4.2. Role of GDMT in Post-Sepsis LV Dysfunction
4.3. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rudd, K.E.; Johnson, S.C.; Agesa, K.M.; Shackelford, K.A.; Tsoi, D.; Kievlan, D.R.; Colombara, D.V.; Ikuta, K.S.; Kissoon, N.; Finfer, S.; et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, M.M.; Shelhamer, J.H.; Bacharach, S.L.; Green, M.V.; Natanson, C.; Frederick, T.M.; Damske, B.A.; Parrillo, J.E. Profound but reversible myocardial depression in patients with septic shock. Ann. Intern. Med. 1984, 100, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, M.M.; Suffredini, A.F.; Natanson, C.; Ognibene, F.P.; Shelhamer, J.H.; Parrillo, J.E. Responses of left ventricular function in survivors and nonsurvivors of septic shock. J. Crit. Care 1989, 4, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Heureux, M.; Sternberg, M.; Brath, L.; Turlington, J.; Kashiouris, M.G. Sepsis-Induced Cardiomyopathy: A Comprehensive Review. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2020, 22, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravikumar, N.; Sayed, M.A.; Poonsuph, C.J.; Sehgal, R.; Shirke, M.M.; Harky, A. Septic Cardiomyopathy: From Basics to Management Choices. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2021, 46, 100767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malomo, S.; Oswald, T.; Stephenson, E.; Yip, A.; Alway, T.; Hadjivassilev, S.; Coombs, S.; Ellery, S.; Lee, J.; James, R.; et al. Characterisation of Post-Sepsis Cardiomyopathy Using Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraiwa, H.; Kasugai, D.; Okumura, T.; Murohara, T. Clinical implications of septic cardiomyopathy: A narrative review. Medicine 2024, 103, e37940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jentzer, J.C.; Lawler, P.R.; Van Houten, H.K.; Yao, X.; Kashani, K.B.; Dunlay, S.M. Cardiovascular Events Among Survivors of Sepsis Hospitalization: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e027813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosyakovsky, L.B.; Angriman, F.; Katz, E.; Adhikari, N.K.; Godoy, L.C.; Marshall, J.C.; Ferreyro, B.L.; Lee, D.S.; Rosenson, R.S.; Sattar, N.; et al. Association between sepsis survivorship and long-term cardiovascular outcomes in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, S.; Kennedy, J.N.; Jentzer, J.C.; Senussi, M.H.; Seymour, C.W. Cardiac Function Before Sepsis and Clinical Outcomes. JAMA 2024, 331, 1496–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: Developed by the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) With the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muehlberg, F.; Blaszczyk, E.; Will, K.; Wilczek, S.; Brederlau, J.; Schulz-Menger, J. Characterization of critically ill patients with septic shock and sepsis-associated cardiomyopathy using cardiovascular MRI. ESC Heart Fail. 2022, 9, 2147–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, Y.; Crouser, E.D.; Raman, S.V. Nonischemic myocardial changes detected by cardiac magnetic resonance in critical care patients with sepsis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 1037–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittinger, C.A.; Dünser, M.W.; Torgersen, C.; Luckner, G.; Lorenz, I.; Schmid, S.; Joannidis, M.; Moser, P.; Hasibeder, W.R.; Halabi, M.; et al. Histologic pathologies of the myocardium in septic shock: A prospective observational study. Shock 2013, 39, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, D.; Ishisaka, Y.; Maeda, T.; Prasitlumkum, N.; Nishida, K.; Dugar, S.; Sato, R. Prevalence and Prognosis of Sepsis-Induced Cardiomyopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Intensive Care Med. 2023, 38, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakynthinos, G.E.; Giamouzis, G.; Xanthopoulos, A.; Oikonomou, E.; Kalogeras, K.; Karavidas, N.; Dimeas, I.E.; Gialamas, I.; Gounaridi, M.I.; Siasos, G.; et al. Septic Cardiomyopathy: Difficult Definition, Challenging Diagnosis, Unclear Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnabelsi, T.S.; Gupta, V.A.; Su, L.C.; Thompson, K.L.; Leung, S.W.; Sorrell, V.L. Usefulness of Findings by Multimodality Imaging to Stratify Risk of Major Adverse Cardiac Events After Sepsis at 1 and 12 months. Am. J. Cardiol. 2020, 125, 1732–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, M.; Mehta, A.; Machanahalli Balakrishna, A.; Kalyan Sundaram, A.; Kanwar, A.; Singh, M.; Vallabhajosyula, S. Right Ventricular Dysfunction in Sepsis: An Updated Narrative Review. Shock 2023, 59, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavalle, C.; Mariani, M.V.; Severino, P.; Palombi, M.; Trivigno, S.; D’Amato, A.; Silvetti, G.; Pierucci, N.; Di Lullo, L.; Chimenti, C.; et al. Efficacy of Modern Therapies for Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction in Specific Population Subgroups: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Cardiorenal Med. 2024, 14, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sepsis Survivors (n = 25) | |
|---|---|
| Age, years | 56 ± 11 |
| Male | 13 (52) |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 28 ± 5 |
| Sepsis cause | |
| Pneumonia | 9 (36) |
| Unknown origin | 3 (12) |
| Endocarditis | 5 (20) |
| Abscess/soft tissue | 5 (20) |
| Gastrointestinal | 2 (8) |
| Urinary tract infection | 1 (4) |
| Sepsis care setting | |
| ICU | 11 (44) |
| HDU/CCU | 4 (16) |
| Ward-based care | 10 (40) |
| Sepsis support requirements | |
| Intubation | 5 (20) |
| Vasopressor | 5 (20) |
| Inotrope | 4 (13) |
| Sepsis peak serum biomarkers | |
| Peak CRP, mg/L | 247 [70–317] |
| Peak WCC, ×109/L | 15.4 [10.6–22.8] |
| Peak Hs-cTnT, ng/L | 108 [16–1176] |
| Post-sepsis cardiac symptoms | |
| Chest pain | 9 (36) |
| Dyspnoea | 9 (36) |
| Palpitations | 4 (16) |
| Co-morbidities | |
| Atrial fibrillation | 10 (40) |
| Smoking (ex-smoker or current) | 9 (36) |
| Hypercholesterolaemia | 7 (28) |
| Hypertension | 6 (24) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 5 (20) |
| COPD/asthma | 4 (16) |
| Ischaemic heart disease | 3 (12) |
| Previous stroke | 3 (12) |
| CKD | 1 (4) |
| LVSD (n = 11) | No LVSD (n = 14) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 57 ± 11 | 55 ± 12 | 0.696 |
| Echocardiography data | |||
| LVEF, % | 39 ± 11 | 60 ± 5 | <0.001 |
| LVIDd, cm | 5.2 ± 0.8 | 4.7 ± 0.8 | 0.214 |
| LVIDs, cm | 4.0 ± 1.2 | 2.8 ± 0.6 | 0.027 |
| Septal wall, cm | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 0.571 |
| Posterior wall, cm | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 0.858 |
| TAPSE, cm | 2.1 ± 0.5 | 2.2 ± 0.6 | 0.910 |
| LA volume, cm2 | 58 ± 29 | 71 ± 42 | 0.472 |
| Medications | |||
| ACE-I/ARB/ARNI | 10 (91) | 5 (36) | 0.012 |
| Beta-blocker | 9 (82) | 6 (43) | 0.099 |
| MRA | 8 (73) | 0 (0) | <0.001 |
| SGLT-2 inhibitor | 6 (55) | 1 (7) | 0.021 |
| Loop diuretics | 5 (45) | 1 (7) | 0.056 |
| Anti-platelet drugs | 5 (45) | 5 (36) | 0.697 |
| Statin | 4 (36) | 6 (43) | 1.000 |
| Anticoagulation | 4 (36) | 4 (29) | 0.695 |
| NT-proBNP | 914 [464–4540] | - | - |
| Initial TTE (n = 9) | Repeat TTE (n = 9) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TTE data | |||
| LVEF, % | 40 [34–48] | 53 [45–59] | 0.037 |
| LVIDd, cm | 5.3 ± 0.8 | 5.0 ± 0.7 | 0.254 |
| LVIDs, cm | 4.1 ± 1.2 | 3.7 ± 0.8 | 0.361 |
| Septal wall, cm | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 0.798 |
| Posterior wall, cm | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 0.007 |
| TAPSE, cm | 2.1 ± 0.5 | 2.1 ± 0.5 | 0.902 |
| TTE interval, months | 6 [3–9] | ||
| LVEF change | |||
| Improvement (>5%) | 8 (89) | ||
| LVEF increase, % | 16 ± 11 | ||
| Deterioration (>5%) | 1 (11) | ||
| GDMT | |||
| ACE-I/ARB/ARNI | 8 (89) | ||
| Beta-blocker | 7 (78) | ||
| MRA | 7 (78) | ||
| SGLT2-inhibitor | 4 (44) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oswald, T.; Malomo, S.; Alway, T.; Hadjivassilev, S.; Coombs, S.; Ellery, S.; Lee, J.; Phillips, C.; Philips, B.; James, R.; et al. Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy in Sepsis Survivors with Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction: An Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3253. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093253
Oswald T, Malomo S, Alway T, Hadjivassilev S, Coombs S, Ellery S, Lee J, Phillips C, Philips B, James R, et al. Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy in Sepsis Survivors with Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction: An Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(9):3253. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093253
Chicago/Turabian StyleOswald, Thomas, Samuel Malomo, Thomas Alway, Stanislav Hadjivassilev, Steven Coombs, Susan Ellery, Joon Lee, Claire Phillips, Barbara Philips, Rachael James, and et al. 2025. "Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy in Sepsis Survivors with Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction: An Observational Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 9: 3253. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093253
APA StyleOswald, T., Malomo, S., Alway, T., Hadjivassilev, S., Coombs, S., Ellery, S., Lee, J., Phillips, C., Philips, B., James, R., Hildick-Smith, D., Parish, V., & Liu, A. (2025). Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy in Sepsis Survivors with Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction: An Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 3253. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093253







