Repurposing Atorvastatin, HMGCO-A Reductase Inhibitor, in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis: A Randomized Controlled Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Inclusion Criteria
2.2. Exclusion Criteria
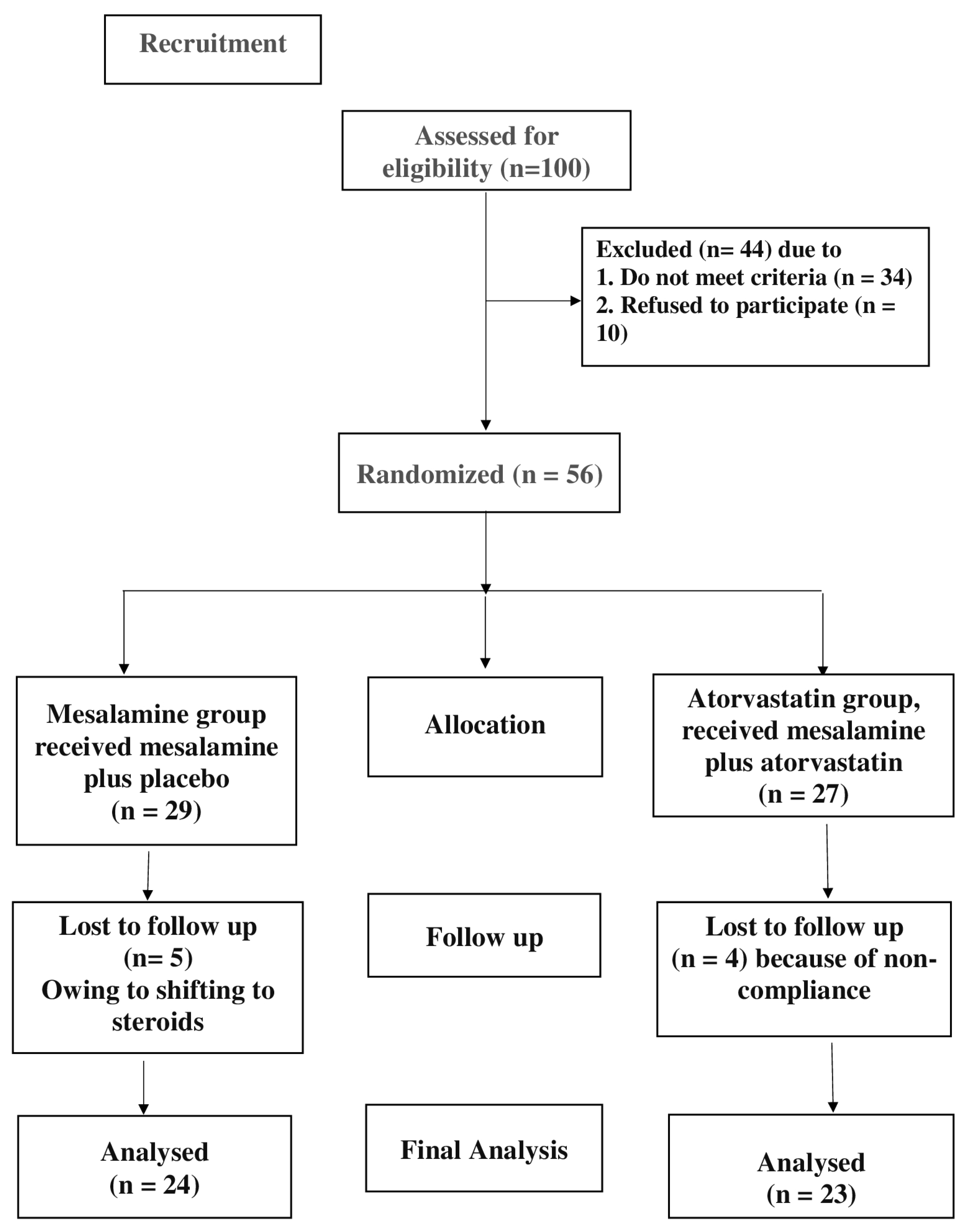
2.3. Study Design
2.4. Sample Size Calculations
2.5. Study Protocol
2.6. Follow-Up
2.7. Evaluation of Colitis
- Bowel movements: Indicates diarrhea frequency, serving as a measure of disease severity.
- Blood in stool: A key marker of mucosal inflammation and ulceration.
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR): Reflects systemic inflammation levels.
- Hemoglobin: Assesses the impact of chronic inflammation and potential blood loss.
- Serum albumin: Evaluates nutritional status and disease severity.
- Constant factor (200): Applied for standardizing the scale.
2.8. Therapeutic Assessments
2.9. Sample Collection
2.10. Biochemical Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Effect of Study Drugs on Disease Activity Index
3.3. Effect of Studied Drugs on Biological Markers
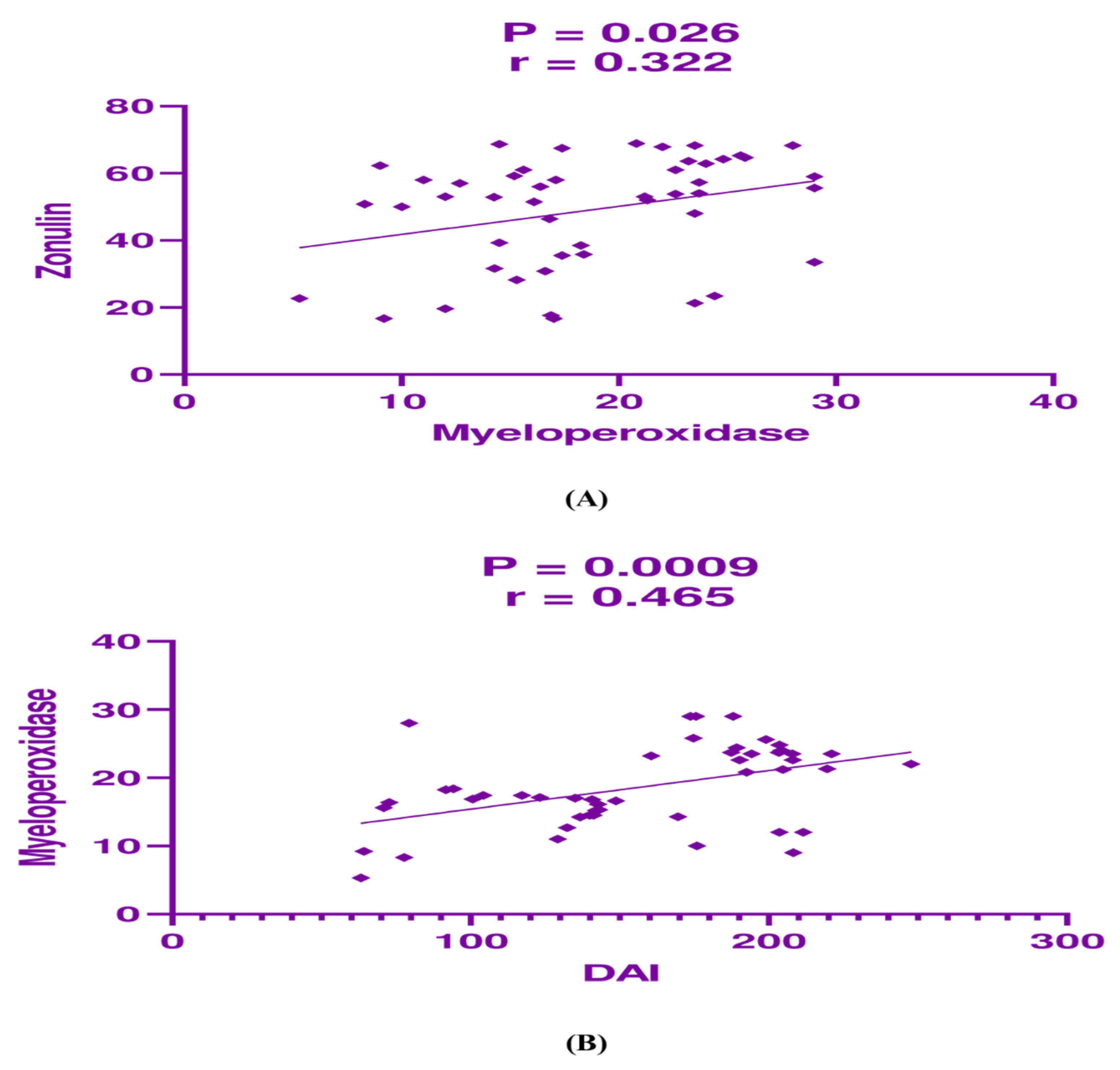
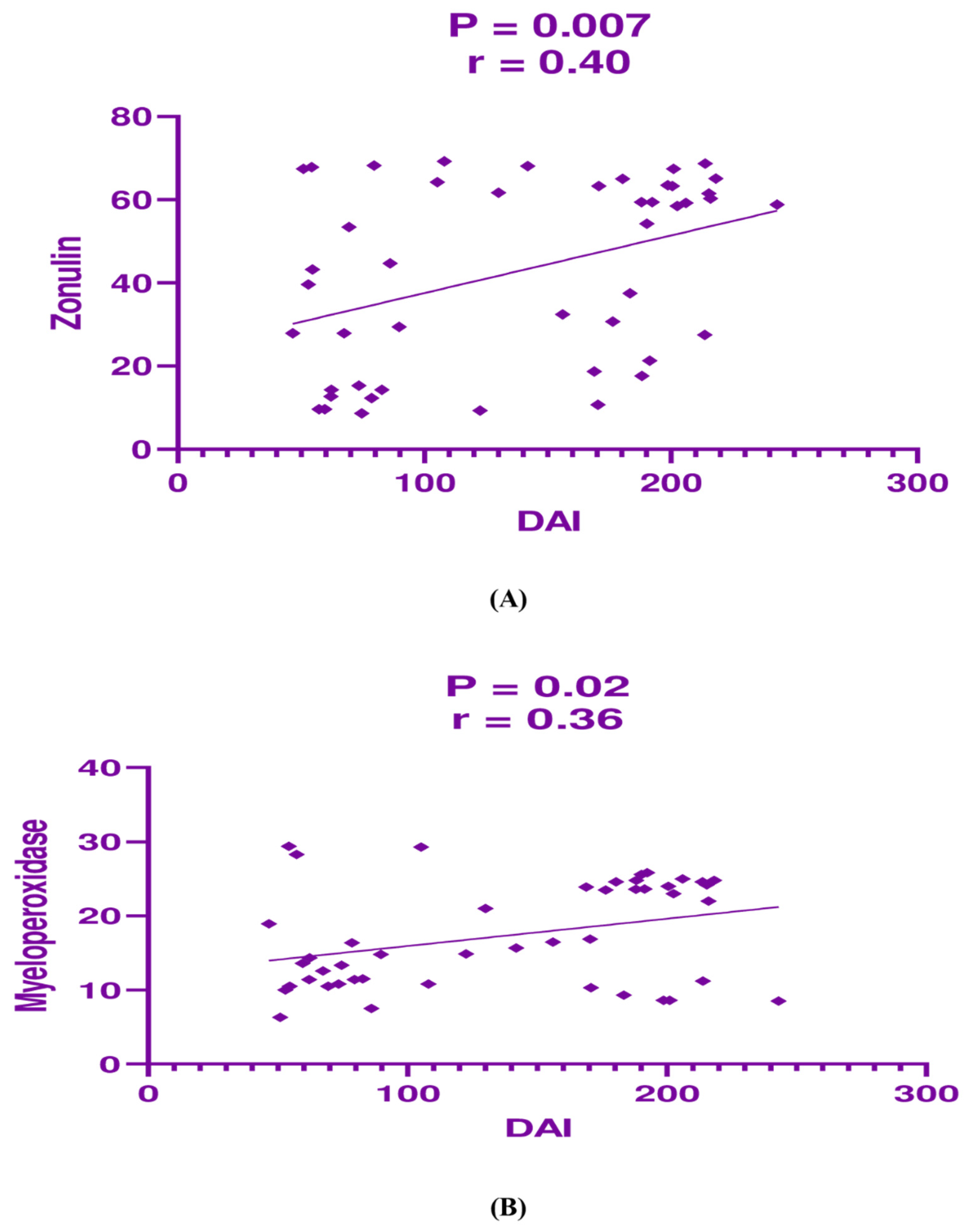
3.4. Correlation Analysis Between the Studied Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swaminathan, A.; Borichevsky, G.; Frampton, C.; Day, A.; Hampton, M.; Kettle, A.; Gearry, R. Comparison of fecal calprotectin and myeloperoxidase in predicting outcomes in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2025, 31, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madill-Thomsen, K.S.; Venner, J.M.; Parsons, D.E.; Famulski, K.S.; Thiesen, A.L.; Hoque, S.; Kroeker, K.I.; Wong, K.; Peerani, F.; Dieleman, L.A. Relating the molecular phenotype of ulcerative colitis to the clinical course. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombel, J.-F.; Shin, A.; Gibson, P.R. AGA clinical practice update on functional gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: Expert review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 380–390.e381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.-C.; Stappenbeck, T.S. Genetics and pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2016, 11, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliu, A.; Bosch, D.H.; Keszthelyi, D.; Rezazadeh Ardabili, A.; Colombel, J.F.; Sawyer, R.; Törnblom, H.; Hart, A.; Jonkers, D.M.; Pierik, M.J. A practical approach to persistent gastrointestinal symptoms in inflammatory bowel disease in remission. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 59, 1470–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jiang, F.; Xu, N.; Dong, G.; Jiang, J.; Wang, M.; Li, C.; Li, R. Anthocyanin Extracted from Purple Sweet Potato Alleviates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice by Suppressing Pyroptosis and Altering Intestinal Flora Structure. J. Med. Food 2024, 27, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, M.; Allin, K.H.; Mehandru, S.; Faith, J.; Jess, T.; Colombel, J.-F. The appendix and ulcerative colitis—An unsolved connection. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurath, M.F. Strategies for targeting cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 24, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahub, S.; Kumar, R.M.; Lin, K.-C.; Banga, I.; Choi, N.K.; Garcia, N.M.; Muthukumar, S.; Rubin, D.T.; Prasad, S. Continuous monitoring of CRP, IL-6, and calprotectin in inflammatory bowel disease using a perspiration-based wearable device. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2025, 31, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhang, H.; Xie, S.; Wu, K. Recent advances in epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: Insights from the past two years. Chin. Med. J. 2025, 10, 1097. [Google Scholar]
- Temido, M.J.; Honap, S.; Jairath, V.; Vermeire, S.; Danese, S.; Portela, F.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Overcoming the challenges of overtreating and undertreating inflammatory bowel disease. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 10, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirten, R.P.; Lin, K.-C.; Whang, J.; Shahub, S.; Churcher, N.K.; Helmus, D.; Muthukumar, S.; Sands, B.; Prasad, S. Longitudinal monitoring of IL-6 and CRP in inflammatory bowel disease using IBD-AWARE. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2024, 16, 100435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrami, S.; Babaei, N.; Esmaeili Gouvarchin Ghaleh, H.; Mohajeri Borazjani, J.; Farzanehpour, M. Investigating the effects of combined treatment of mesalazine with Lactobacillus casei in the experimental model of ulcerative colitis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2024, 11, 1456053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Górecka, A.; Jura-Półtorak, A.; Koźma, E.M.; Szeremeta, A.; Olczyk, K.; Komosińska-Vassev, K. Biochemical modulators of tight junctions (TJs): Occludin, claudin-2 and zonulin as biomarkers of intestinal barrier leakage in the diagnosis and assessment of inflammatory bowel disease progression. Molecules 2024, 29, 4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymanska, E.; Wierzbicka, A.; Dadalski, M.; Kierkus, J. Fecal Zonulin as a noninvasive biomarker of intestinal permeability in pediatric patients with inflammatory bowel diseases—Correlation with disease activity and fecal calprotectin. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegh, C.; De Roos, N.; Hovenier, R.; Meijerink, J.; Besseling-Van Der Vaart, I.; Van Hemert, S.; Witteman, B. Intestinal permeability measured by urinary sucrose excretion correlates with serum zonulin and faecal calprotectin concentrations in UC patients in remission. J. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 2019, 2472754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Scott, M.K.; Steinberg, E.; Kalesinskas, L.; Habtezion, A.; Shah, N.H.; Khatri, P. Computational drug repositioning of atorvastatin for ulcerative colitis. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2021, 28, 2325–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-C.; Lei, S.-Y.; Zhang, D.-H.; He, Q.-Y.; Sun, Y.-Y.; Zhu, H.-J.; Qu, Y.; Zhou, S.-Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, C. The pleiotropic effects of statins: A comprehensive exploration of neurovascular unit modulation and blood–brain barrier protection. Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M.; Bharwani, S.; Jordan, P.; Joh, T.; Manas, K.; Warren, A.; Harada, H.; Carter, P.; Elrod, J.W.; Wolcott, M. The 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitor pravastatin reduces disease activity and inflammation in dextran-sulfate induced colitis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 305, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.K.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, E.-K.; Park, D.K.; Kwon, K.A.; Chung, J.-W.; Kim, K.O.; Kim, Y.J. Anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects of rosuvastatin by regulation of oxidative stress in a dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis model. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktunc, E.; Kayhan, B.; Arasli, M.; Gun, B.D.; Barut, F. The effect of atorvastatin and its role on systemic cytokine network in treatment of acute experimental colitis. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2011, 33, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.J.; Kim, T.W.; Seo, J.N.; Oh, K.I.; Choi, E.Y.; Shin, H.S.; Park, Y.E. Effect of Atorvastatin, a HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitor, in Experimental Colitis in Mice. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2004, 38, 401–407. [Google Scholar]
- Rashidian, A.; Muhammadnejad, A.; Dehpour, A.-R.; Mehr, S.E.; Akhavan, M.M.; Shirkoohi, R.; Chamanara, M.; Mousavi, S.-E.; Rezayat, S.-M. Atorvastatin attenuates TNBS-induced rat colitis: The involvement of the TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway. Inflammopharmacology 2016, 24, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, A.; Yang, Q.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Shi, M.; Xiao, Q.; Cao, Y.; He, Y.; Zhou, J. Atorvastatin promotes the expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and attenuates murine colitis. Immunology 2016, 149, 432–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, N.; Jung, H.C.; Song, I.S. Simvastatin inhibits NF-κB signaling in intestinal epithelial cells and ameliorates acute murine colitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2007, 7, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Mahdy, N.A.; El-Sayad, M.E.S.; El-Kadem, A.H.; Abu-Risha, S.E.S. Targeting IL-10, ZO-1 gene expression and IL-6/STAT-3 trans-signaling by a combination of atorvastatin and mesalazine to enhance anti-inflammatory effects and attenuates progression of oxazolone-induced colitis. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 35, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahaa, M.M.; Hegazy, S.K.; Maher, M.M.; Bahgat, M.M.; El-Haggar, S.M. Pentoxifylline in patients with ulcerative colitis treated with mesalamine by modulation of IL-6/STAT3, ZO-1, and S1P pathways: A randomized controlled double-blinded study. Inflammopharmacology 2024, 32, 3247–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Haggar, S.M.; Hegazy, S.K.; Maher, M.M.; Bahgat, M.M.; Bahaa, M.M. Repurposing metformin as adjuvant therapy in patients with ulcerative colitis treated with mesalamine: A randomized controlled double-blinded study. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 138, 112541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binsaleh, A.Y.; El-Haggar, S.M.; Hegazy, S.K.; Maher, M.M.; Bahgat, M.M.; Elmasry, T.A.; Alrubia, S.; Alsegiani, A.S.; Eldesoqui, M.; Bahaa, M.M. The adjunctive role of metformin in patients with mild to moderate ulcerative colitis: A randomized controlled study. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1507009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarfaj, S.J.; El-Haggar, S.M.; Hegazy, S.K.; Maher, M.M.; Bahgat, M.M.; Elmasry, T.A.; Alrubia, S.; Alsegiani, A.S.; Bahaa, M.M. Effect of a high dose atorvastatin as adjuvant therapy to mesalamine in attenuating inflammation and symptoms in patients with ulcerative colitis: A randomized controlled pilot study. Front. Med. 2025, 11, 1490178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, J.; Lewis, M. The size of a pilot study for a clinical trial should be calculated in relation to considerations of precision and efficiency. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2012, 65, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehgal, P.; Colombel, J.F.; Aboubakr, A.; Narula, N. Systematic review: Safety of mesalazine in ulcerative colitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 1597–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, A.J.; Duncan, T.G.; Goodman, A.M.; Mills, D.J.; Rohlf, J.L. Efficacy of metformin in type II diabetes: Results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-response trial. Am. J. Med. 1997, 103, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.; Okada, M.; Yao, T.; Ueki, M.; Arima, S.; Okumura, M. An index of disease activity in patients with ulcerative colitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. (Springer Nat.) 1992, 87, 971. [Google Scholar]
- Rivière, P.; Suen, C.L.W.; Chaparro, M.; De Cruz, P.; Spinelli, A.; Laharie, D. Acute severe ulcerative colitis management: Unanswered questions and latest insights. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gou, Y.; Cai, S.; Chen, Y.; Hou, X.; Zhang, J.; Bi, C.; Gu, P.; Yang, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, W. Atorvastatin improved ulcerative colitis in association with gut microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolism. Life Sci. 2024, 351, 122790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarada, T.N.; Rokne, J.G.; Alhajj, R. A review of computational drug repositioning: Strategies, approaches, opportunities, challenges, and directions. J. Cheminform. 2020, 12, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpakom, S.; Iorio, F.; Eyers, P.A.; Escott, K.J.; Hopper, S.; Wells, A.; Doig, A.; Guilliams, T.; Latimer, J.; McNamee, C. Drug repurposing: Progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldossary, K.M.; Ali, L.S.; Abdallah, M.S.; Bahaa, M.M.; Elmasry, T.A.; Elberri, E.I.; Kotkata, F.A.; El Sabaa, R.M.; Elmorsi, Y.M.; Kamel, M.M. Effect of a high dose atorvastatin as added-on therapy on symptoms and serum AMPK/NLRP3 inflammasome and IL-6/STAT3 axes in patients with major depressive disorder: Randomized controlled clinical study. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1381523. [Google Scholar]
- Alarfaj, S.J.; Bahaa, M.M.; Elmasry, T.A.; Elberri, E.I.; El-Khateeb, E.; Hamouda, A.O.; Salahuddin, M.M.; Kamal, M.; Gadallah, A.-N.A.-A.; Eltantawy, N. Fenofibrate as an Adjunct Therapy for Ulcerative Colitis: Targeting Inflammation via SIRT1, NLRP3, and AMPK Pathways: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2024, 18, 5239–5253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarfaj, S.; Bahaa, M.; Yassin, H.; El-Khateeb, E.; Kotkata, F.; El-Gammal, M.; Elberri, A.; Habba, E.; El-Deen, E.Z.; Khrieba, M. A randomized placebo-controlled, double-blind study to investigate the effect of a high oral loading dose of cholecalciferol in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients, new insights on serum STAT-3 and hepassocin. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 7607–7619. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El-Haggar, S.M.; Hegazy, S.K.; Abd-Elsalam, S.M.; Bahaa, M.M. Pentoxifylline, a nonselective phosphodiesterase inhibitor, in adjunctive therapy in patients with irritable bowel syndrome treated with mebeverine. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 145, 112399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Haggar, S.M.; Hegazy, S.K.; Abd-Elsalam, S.M.; Bahaa, M.M. Open-label pilot study of ethosuximide as adjunctive therapy for relieving abdominal pain related to irritable bowel syndrome. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2022, 47, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawky, D.; Salamah, A.; Abd-Elsalam, S.; Habba, E.; Elnaggar, M.; Elsawy, A.; Baiomy, N.; Bahaa, M.; Gamal, R. Nitazoxanide-based therapeutic regimen as a novel treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection in children and adolescents: A randomized trial. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 3132–3137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vital, K.D.; Cardoso, B.G.; Lima, I.P.; Campos, A.B.; Teixeira, B.F.; Pires, L.O.; Dias, B.C.; de Alcantara Candido, P.; Cardoso, V.N.; Fernandes, S.O.A. Therapeutic effects and the impact of statins in the prevention of ulcerative colitis in preclinical models: A systematic review. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 37, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagarajan, N.; Nam, J.; Al Noah, Z.; Murthy, S. Disease modifying effect of statins in dextran sulfate sodium model of mouse colitis. Inflamm. Res. 2008, 57, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamija, P.; Hota, D.; Kochhar, R.; Sachdev, A.; Chakrabarti, A. Randomized clinical trial: Atorvastatin versus placebo in patients with acute exacerbation of mild to moderate ulcerative colitis. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 33, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, S.; Emami, H.; Vucic, E.; Singh, P.; Vijayakumar, J.; Fifer, K.M.; Alon, A.; Shankar, S.S.; Farkouh, M.; Rudd, J.H. High-dose atorvastatin reduces periodontal inflammation: A novel pleiotropic effect of statins. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 2382–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.; Devaraj, S.; Jialal, I.; Siegel, D. Comparison effect of atorvastatin (10 versus 80 mg) on biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in subjects with metabolic syndrome. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 102, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grip, O.; Janciauskiene, S.; Bredberg, A. Use of atorvastatin as an anti-inflammatory treatment in Crohn’s disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 155, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekinejad, H.; Shafie-Irannejad, V.; Hobbenaghi, R.; Tabatabaie, S.H.; Moshtaghion, S.-M. Comparative protective effect of hawthorn berry hydroalcoholic extract, atorvastatin, and mesalamine on experimentally induced colitis in rats. J. Med. Food 2013, 16, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crockett, S.D.; Hansen, R.A.; Stürmer, T.; Schectman, R.; Darter, J.; Sandler, R.S.; Kappelman, M.D. Statins are associated with reduced use of steroids in inflammatory bowel disease: A retrospective cohort study. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2012, 18, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, M.; Bharwani, S.; Jordan, P.; Elrod, J.; Grisham, M.; Jackson, T.; Lefer, D.; Alexander, J.S. Increased disease activity in eNOS-deficient mice in experimental colitis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 35, 1679–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, R.A.; Balaraman, R.; Sailor, G.U.; Sen, D.B. Protective effect of simvastatin and rosuvastatin on trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis in rats. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2015, 47, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klebanoff, S.J. Myeloperoxidase: Friend and foe. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2005, 77, 598–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoodi, I.; Kochhar, R.; Dutta, U.; Vaishnavi, C.; Prasad, K.; Vaiphei, K.; Hussain, S.; Singh, K. Evaluation of fecal myeloperoxidase as a biomarker of disease activity and severity in ulcerative colitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 1336–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansberry, D.R.; Shah, K.; Agarwal, P.; Agarwal, N. Fecal myeloperoxidase as a biomarker for inflammatory bowel disease. Cureus 2017, 9, e1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, T.C.; Peterson, M.R.; Raoul, J.M. The effect of pentoxifylline and its metabolite-1 on inflammation and fibrosis in the TNBS model of colitis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 662, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepgül, G.; Tanrıkulu, S.; Ünalp, H.R.; Akguner, T.; Erbil, Y.; Olgaç, V.; Ademoğlu, E. Preventive effect of pentoxifylline on acute radiation damage via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory pathways. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekinejad, M.; Verki, M.M.; Khoramjouy, M.; Alenabi, A.; Hallaj-Salahipour, M.; Malekinejad, H. Cardioprotective effects of atorvastatin are mediated through PPARγ in paraquat-exposed rats. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2019, 74, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh-Tabrizi, N.; Malekinejad, H.; Varasteh, S.; Cheraghi, H. Atorvastatin protected from paraquat-induced cytotoxicity in alveolar macrophages via down-regulation of TLR-4. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 49, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Caviglia, G.P.; Dughera, F.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Rosso, C.; Abate, M.L.; Pellicano, R.; Bresso, F.; Smedile, A.; Saracco, G.M.; Astegiano, M. Serum zonulin in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A pilot study. Minerva Med. 2019, 110, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Mahdy, N.A.; El-Sayad, M.E.-S.; El-Kadem, A.H.; Abu-Risha, S.E.-S. Metformin alleviates inflammation in oxazolone induced ulcerative colitis in rats: Plausible role of sphingosine kinase 1/sphingosine 1 phosphate signaling pathway. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2021, 43, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A. All disease begins in the (leaky) gut: Role of zonulin-mediated gut permeability in the pathogenesis of some chronic inflammatory diseases. F1000Research 2020, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturgeon, C.; Fasano, A. Zonulin, a regulator of epithelial and endothelial barrier functions, and its involvement in chronic inflammatory diseases. Tissue Barriers 2016, 4, e1251384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, E.L.; Sidaway, J.E.; Cross, M.J. Statin regulated ERK5 stimulates tight junction formation and reduces permeability in human cardiac endothelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 186–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidari, M.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Z.; Ganjehei, L.; Mortazavi, A.; Warier, N.; Vanderslice, P.; Dixon, R.A. Atorvastatin preserves the integrity of endothelial adherens junctions by inhibiting vascular endothelial cadherin tyrosine phosphorylation. Exp. Cell Res. 2012, 318, 1673–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagozian, R.; Burakoff, R. The role of mesalamine in the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2007, 3, 893. [Google Scholar]
- Rousseaux, C.; Lefebvre, B.; Dubuquoy, L.; Lefebvre, P.; Romano, O.; Auwerx, J.; Metzger, D.; Wahli, W.; Desvergne, B.; Naccari, G.C. Intestinal antiinflammatory effect of 5-aminosalicylic acid is dependent on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1205–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, C.G.; Sangfelt, P.; Wagner, M.; Hansson, T.; Lettesjö, H.; Carlson, M. Fecal levels of leukocyte markers reflect disease activity in patients with ulcerative colitis. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2007, 67, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoodi, I.; Kochhar, R.; Dutta, U.; Vaishnavi, C.; Prasad, K.K.; Vaiphei, K.; Kaur, S.; Singh, K. Fecal lactoferrin, myeloperoxidase and serum C-reactive are effective biomarkers in the assessment of disease activity and severity in patients with idiopathic ulcerative colitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 24, 1768–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaminathan, A.; Borichevsky, G.M.; Edwards, T.S.; Hirschfeld, E.; Mules, T.C.; Frampton, C.M.; Day, A.S.; Hampton, M.B.; Kettle, A.J.; Gearry, R.B. Faecal myeloperoxidase as a biomarker of endoscopic activity in inflammatory bowel disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2022, 16, 1862–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Placebo Group (n = 24) | Atorvastatin Group (n = 23) | p Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Character | Before Treatment | After Treatment | p Value | Before Treatment | After Treatment | p Value | After Treatment |
| Bleeding score | 1 (1–1) | 1 (0–1) | 0.003 * | 1 (1–2) | 0 (0–1) | 0.0007 * | 0.03 ** |
| Diarrhoea score | 2 (2–3) | 1 (0–1.75) | 0.001 * | 2 (1–3) | 0 (0–75) | 0.0009 * | 0.04 ** |
| Haemoglobin (mg/mL) | 11.57 ± 0.936 | 13.99 ± 0.891 | 0.004 # | 12.17 ± 1.46 | 15.48 ± 1.28 | 0.0007 # | 0.003 ## |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.040 ± 0.738 | 5.104 ± 0.560 | 0.03 # | 4.227 ± 0.750 | 5.101 ± 0.751 | 0.02 # | 0.986 |
| ESR | 22.38 ± 4.13 | 12.21 ± 2.91 | <0.0001 # | 23.04 ± 3.77 | 9.870 ± 3.09 | <0.0001 # | 0.012 ## |
| DAI | 201.2 (187.6–208) | 127.8 (82.5–141.9) | <0.0001 * | 192.4 (180.4–213.7) | 73.45 (57.2–89.67) | <0.0001 * | 0.001 ** |
| Character | Placebo Group (n = 24) | Atorvastatin Group (n = 23) | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Treatment | After Treatment | p Value | Before Treatment | After Treatment | p Value | After Treatment | |
| Zonulin (ng/mL) | 57.65 (52.25–64.05) | 42.85 (31–57.75) | 0.01 * | 59.40 (37.5–63.5) | 27.9 (12.5–53.4) | 0.0007 * | 0.04 ** |
| Myeloperoxidase (ng/mL) | 23.35 (20.9–24.3) | 16.25 (14.34–17.33) | 0.0002 * | 23.65 (11.2–24.8) | 13.36 (10.8–16.38) | 0.0005 * | 0.03 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AlRasheed, H.A.; El-Haggar, S.M.; Hegazy, S.K.; Maher, M.M.; Bahgat, M.M.; Bahaa, M.M. Repurposing Atorvastatin, HMGCO-A Reductase Inhibitor, in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis: A Randomized Controlled Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3077. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093077
AlRasheed HA, El-Haggar SM, Hegazy SK, Maher MM, Bahgat MM, Bahaa MM. Repurposing Atorvastatin, HMGCO-A Reductase Inhibitor, in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis: A Randomized Controlled Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(9):3077. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093077
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlRasheed, Hayam Ali, Sahar M. El-Haggar, Sahar K. Hegazy, Maha M. Maher, Monir M. Bahgat, and Mostafa M. Bahaa. 2025. "Repurposing Atorvastatin, HMGCO-A Reductase Inhibitor, in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis: A Randomized Controlled Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 9: 3077. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093077
APA StyleAlRasheed, H. A., El-Haggar, S. M., Hegazy, S. K., Maher, M. M., Bahgat, M. M., & Bahaa, M. M. (2025). Repurposing Atorvastatin, HMGCO-A Reductase Inhibitor, in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis: A Randomized Controlled Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 3077. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093077






