Identifying Key Predictors of Sarcopenic Obesity in Italian Severely Obese Older Adults: Deep Learning Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Eligibility Participants
2.2. Dependent Variable
2.3. Independent Variables
- Sociodemographic characteristics included sex (female/male), age (years), level of education (elementary, middle, or high graduation), marital status (single, divorced, married, or widowed), current employment status (yes/no), and retirement status (yes/no).
- Lifestyle characteristics included alcohol consumption (never, monthly or less, 2/4 times a month, and ≥ 4 times a week); smoking (never smoked, Former smoker, and currently smoking); and regular physical activity before hospitalization (yes or no).
- Clinical and anthropometric characteristics included the sum of morbidities (total number of chronic conditions including back pain, arthritis, cancer, diabetes, hypertension, bronchitis or asthma, sleep apnea, cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, brain stroke, osteoporosis, labyrinthitis, and urinary incontinence); reported fall last year (yes/no); height (cm); weight (kg); Body Mass Index (BMI/kg/m2); waist circumference (WC/cm); systolic blood pressure (mmHg); diastolic blood pressure (mmHg); lean mass total DXA (LM/kg); fat mass total DXA (FM%); and appendicular lean mass total DXA (ALM/kg).
- Physical performance tests included the 6-minute walking test (6m-WT): the distance the participant can walk in six minutes, measured in meters; hand grip strength (HGS), measured in the dominant hand by a dynamometer (Lafayette Instrument, Inc., Lafayette, LA, USA); stair climb test [25]: the time taken by the participant to climb a set of stairs, measured in seconds; short physical performance battery (SPPB) [26] components: standing balance (SB), Walk 4 meters–time and speed scores (4m-WT), sit-to-stand five repetitions (5-SST), with a SPPB Total Score; physical performance test (PPT) [27] components: Write A Sentence, Simulated A Feeding, Pick A Book, Put On A Jacket, Pick Up A Coin on The Ground, 360-degree Turn, Walking 15 meters, resulting in a total score for the physical performance test; senior fitness test (SFT) [28] components: 30-second chair stand (30s-SST), 30-second arm curl, 2-minute Step Test, Chair Sit and Reach, Back Scratch, Get Up and Go Test).
2.4. Correlation, Variance Inflation Factor, and Tolerance Analysis
2.5. Data Normalization and Sampling
2.6. Grid Search CV Analysis in Dataset
2.7. Neural Network Model and Cross-Validation Analysis
2.8. Cross-Validation and Model Training in Dataset
2.9. Performance Evaluation of Model Training and Validation in Dataset
3. Results
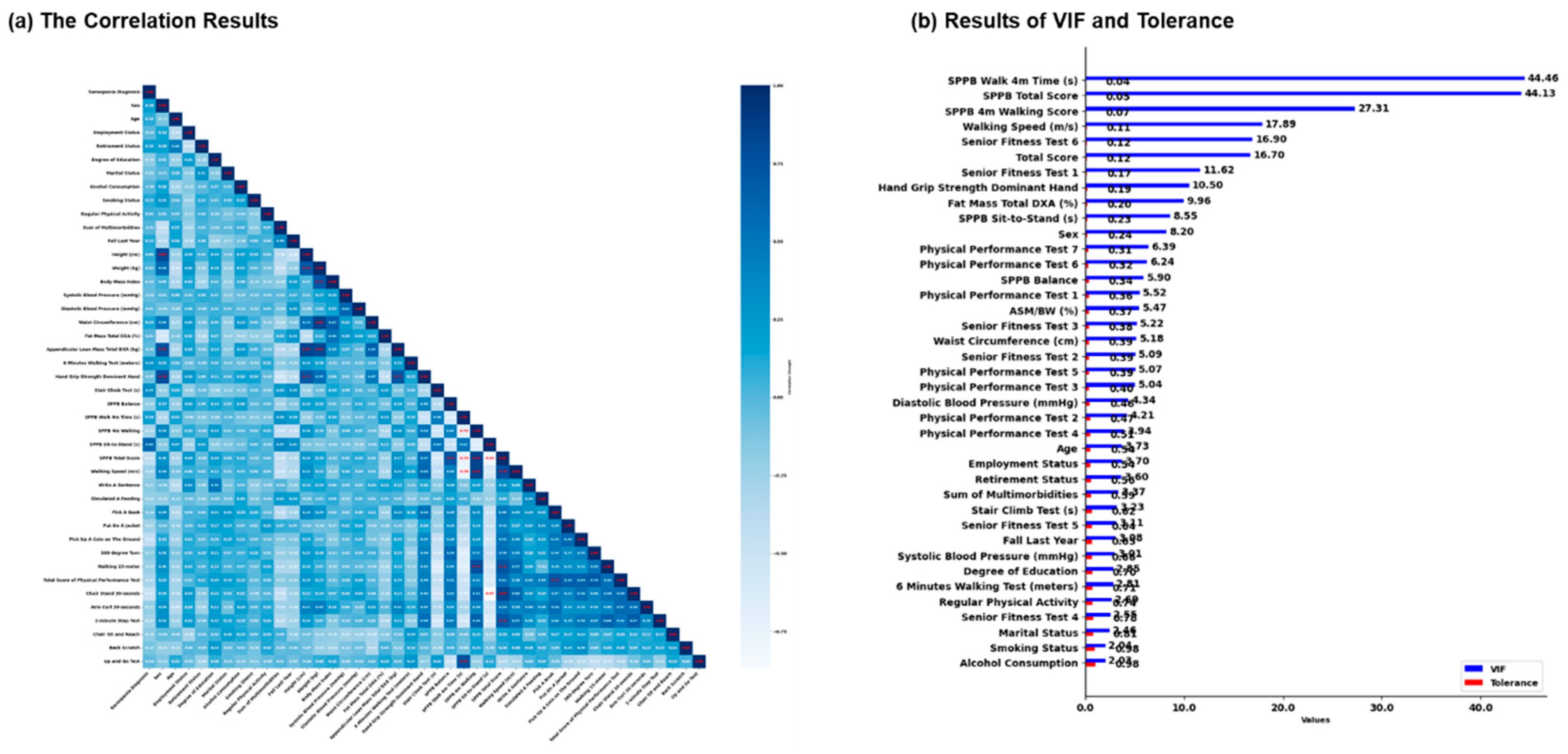
3.1. The Results of Correlation, VIF, and Tolerance in Dataset
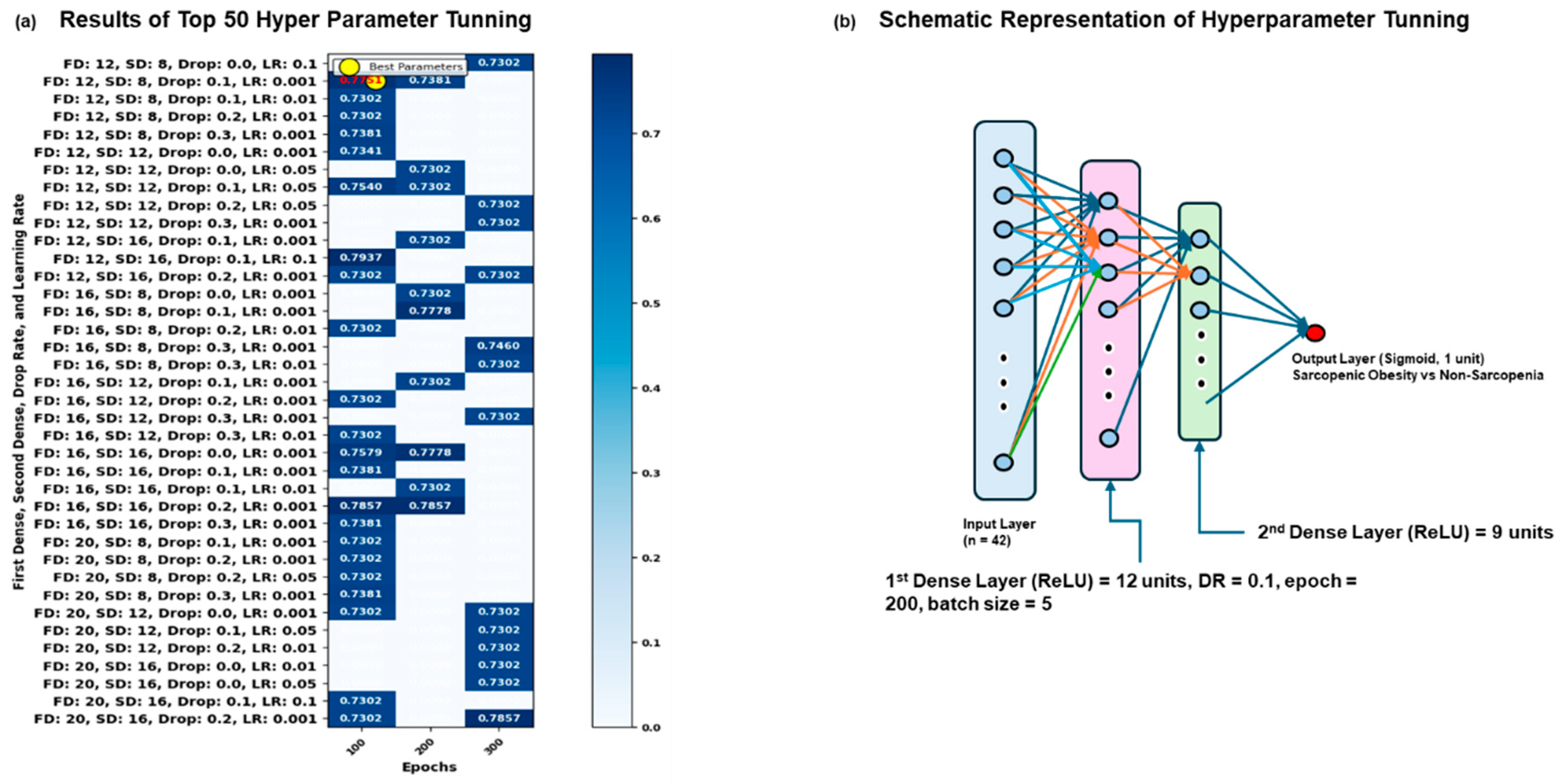
3.2. Results of Grid Search Analysis in Dataset
3.3. Results of Sequential Deep Neural Network Model Results
3.4. Results of Validation and Training Results of Sequential Deep Neural Network Model
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SO | Sarcopenic Obesity |
| IRCCS | Istituto di Ricovero e Cura a Carattere Scientifico |
| ESPEN | European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism |
| EASO | European Association for the Study of Obesity |
| 5-SST | Five-Repetition Sit-To-Stand Test |
| HGS | Handgrip Strength |
| ALM | Appendicular Lean Mass |
| 6m-WT | 6-Minute Walking Test |
| 30s-SST | 30-Second Chair Stand Test |
| WC | Waist Circumference |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| FM | Fat Mass |
| ALM/W | Appendicular Lean Mass Adjusted To Body Weight |
| DXA | Dual X-ray Absorptiometry |
| SPPB | Short Physical Performance Battery |
| VIF | Variance Inflation Factor |
| AUC-ROC | Area Under The ROC Curve |
| AUPRC | Precision-Recall Curve |
| NO | Nitric Oxide |
References
- Dogra, S.; Dunstan, D.W.; Sugiyama, T.; Stathi, A.; Gardiner, P.A.; Owen, N. Active Aging and Public Health: Evidence, Implications, and Opportunities. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2022, 43, 439–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Larsson, S.C. Epidemiology of sarcopenia: Prevalence, risk factors, and consequences. Metabolism 2023, 144, 155533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, E.; Pinel, A.; Guillet, C.; Capel, F.; Pereira, B.; De Antonio, M.; Pouget, M.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Eglseer, D.; Topinkova, E.; et al. Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity and Mortality Among Older People. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e243604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donini, L.M.; Busetto, L.; Bischoff, S.C.; Cederholm, T.; Ballesteros-Pomar, M.D.; Batsis, J.A.; Bauer, J.M.; Boirie, Y.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Dicker, D.; et al. Definition and Diagnostic Criteria for Sarcopenic Obesity: ESPEN and EASO Consensus Statement. Obes. Facts 2022, 15, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Nguyen, T.T.; Zhang, Y.; Ryu, D.; Gariani, K. Sarcopenic obesity: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, cardiovascular disease, mortality, and management. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1185221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Mei, F.; Shang, Y.; Hu, K.; Chen, F.; Zhao, L.; Ma, B. Global prevalence of sarcopenic obesity in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 4633–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielewicz, A.L.; Marra, A.; Tringali, G.; De Micheli, R.; Abbruzzese, L.; Fanari, P.; Codecasa, F.; Lazzer, S.; Mendonça, V.A.; Lacerda, A.C.R.; et al. Analysis of sarcopenic obesity prevalence and diagnostic agreement according to the 2022 ESPEN and EASO Consensus in hospitalized older adults with severe obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1366229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hwang, S.J.; McMahon, G.M.; Curhan, G.C.; McLean, R.R.; Murabito, J.M.; Fox, C.S. Mid-adulthood cardiometabolic risk factor profiles of sarcopenic obesity. Obesity 2016, 24, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batsis, J.A.; Mackenzie, T.A.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Bartels, S.J. Sarcopenia, sarcopenic obesity, and functional impairments in older adults: National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 1999–2004. Nutr. Res. 2015, 35, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, M.; Lee, S.; Makino, K.; Harada, K.; Katayama, O.; Tomida, K.; Yamaguchi, R.; Nishijima, C.; Fujii, K.; Misu, Y.; et al. Sarcopenic Obesity and Risk of Disability in Community-Dwelling Japanese Older Adults: A 5-Year Longitudinal Study. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2023, 24, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkok, S.; Aydin, C.O.; Sacar, D.E.; Catikkas, N.M.; Erdogan, T.; Bozkurt, M.E.; Kilic, C.; Karan, M.A.; Bahat, G. Sarcopenic obesity versus sarcopenia alone with the use of probable sarcopenia definition for sarcopenia: Associations with frailty and physical performance. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 2509–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xie, X.; Dou, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Deng, R.; Cheng, A.S.K. Association of sarcopenic obesity with the risk of all-cause mortality among adults over a broad range of different settings: A updated meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2019, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samper-Ternent, R.; Al Snih, S. Obesity in Older Adults: Epidemiology and Implications for Disability and Disease. Rev. Clin. Gerontol. 2012, 22, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinel, A.; Guillet, C.; Capel, F.; Pouget, M.; De Antonio, M.; Pereira, B.; Topinkova, E.; Eglseer, D.; Barazzoni, R.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; et al. Identification of factors associated with sarcopenic obesity development: Literature review and expert panel voting. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 43, 1414–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.H.; Seo, J.W.; Li, X.; Ahn, S.Y.; Sung, Y.; Kim, D.Y. Neural network model for prediction of possible sarcopenic obesity using Korean national fitness award data (2010–2023). Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedrikovetski, S.; Seow, W.; Kroon, H.M.; Traeger, L.; Moore, J.W.; Sammour, T. Artificial intelligence for body composition and sarcopenia evaluation on computed tomography: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2022, 149, 110218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, M.; Kim, W. Sarcopenia Prediction for Elderly People Using Machine Learning: A Case Study on Physical Activity. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrini Usubini, A.; Bottacchi, M.; Bondesan, A.; Caroli, D.; Castelnuovo, G.; Sartorio, A. A three-week in-hospital multidisciplinary body weight reduction program exerts beneficial effects on physical and mental health and fatiguability of elderly patients with obesity. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 1054941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Physical status: The use and interpretation of anthropometry. World Health Organ. Tech. Rep. Ser. 1995, 854, 1–452. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Faith, M.S.; Kotler, D.; Shih, R.; Heymsfield, S.B. Regional skeletal muscle measurement: Evaluation of new dual-energy X- ray absorptiometry model. J. Appl. Physiol. 1999, 87, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesari, M.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Newman, A.B.; Simonsick, E.M.; Harris, T.B.; Penninx, B.W.; Brach, J.S.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Satterfield, S.; Bauer, D.C.; et al. Added Value of Physical Performance Measures in Predicting Adverse Health-Related Events: Results from the Health, Aging, and Body Composition Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2009, 57, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahat, G.; Kilic, C.; Topcu, Y.; Aydin, K.; Karan, M.A. Fat percentage cutoff values to define obesity and prevalence of sarcopenic obesity in community-dwelling older adults in Turkey. Aging Male 2020, 23, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, M.E.; Crimmins, E.M. The Impact of Insulin Resistance and Inflammation on the Association Between Sarcopenic Obesity and Physical Functioning. Obesity 2012, 20, 2101–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bean, J.F.; Kiely, D.K.; LaRose, S.; Alian, J.; Frontera, W.R. Is Stair Climb Power a Clinically Relevant Measure of Leg Power Impairments in At-Risk Older Adults? Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2007, 88, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guralnik, J.M.; Simonsick, E.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Glynn, R.J.; Berkman, L.F.; Blazer, D.G.; Scherr, P.A.; Wallace, R.B. A short physical performance battery assessing lower extremity function: Association with self-reported disability and prediction of mortality and nursing home admission. J. Gerontol. 1994, 49, M85–M94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuben, D.B.; Siu, A.L. An Objective Measure of Physical Function of Elderly Outpatients: The Physical Performance Test. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1990, 38, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langhammer, B.; Stanghelle, J.K. The Senior Fitness Test. J. Physiother. 2015, 61, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumby, D.K. Work: What is it good for? (Absolutely nothing)—A critical theorist’s perspective. Ind. Organ. Psychol. 2019, 12, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilaru, R.; Amodio, S.; Li, Y.; Wells, C.; Love, S.; Zeng, Y.; Ye, J.; Jelizarow, M.; Balakumar, A.; Fronc, M.; et al. An Overview of Current Statistical Methods for Implementing Quality Tolerance Limits. Ther. Innov. Regul. Sci. 2024, 58, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovetta, A. Raiders of the Lost Correlation: A Guide on Using Pearson and Spearman Coefficients to Detect Hidden Correlations in Medical Sciences. Cureus 2020, 12, e11794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanayak, S.; Singh, T. Cardiovascular Disease Classification Based on Machine Learning Algorithms Using GridSearchCV, Cross Validation and Stacked Ensemble Methods. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 1613, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabiri, B.; Asri BEl Rhanoui, M. Mechanism of Overfitting Avoidance Techniques for Training Deep Neural Networks. International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems. ICEIS Proc. 2022, 1, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Z. Performance Evaluation of Machine Learning Methods for Breast Cancer Prediction. Appl. Comput. Math. 2018, 7, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, A.; Carrasco, A.; Martín, A.; de las Heras, A. The impact of class imbalance in classification performance metrics based on the binary confusion matrix. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 91, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, B.T.; Jaafari, A.; Avand, M.; Al-Ansari, N.; Du, T.D.; Hai Yen, H.P.; Phong, T.V.; Nguyen, D.H.; Le, H.V.; Mafi-Gholami, D.; et al. Performance Evaluation of Machine Learning Methods for Forest Fire Modeling and Prediction. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, R.E.; Mathur, R.; Schmidt, A.F.; Bhaskaran, K.; Fatemifar, G.; Eastwood, S.V.; Finan, C.; Denaxas, S.; Smeeth, L.; Chaturvedi, N. Associations between measures of sarcopenic obesity and risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality: A cohort study and mendelian randomization analysis using the UK biobank. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e011638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Xu, Y. Association of sarcopenic obesity with the risk of all-cause mortality: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2016, 16, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkisas, S.; Lamers, S.; Degerickx, R.; Van Mieghem, E.; Vandewoude, M.; Verhoeven, V.; Cock, A.-M.D. The relation between mortality, intramuscular adipose tissue and sarcopenia in hospitalized geriatric patients. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2018, 9, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.P.; Chong, M.S.; Tay, L.; Yang, Y.X.; Leung, B.P.; Yeo, A.; Yew, S.; Tan, C.H.; Lim, W.S. Inter-muscular adipose tissue is associated with adipose tissue inflammation and poorer functional performance in central adiposity. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2019, 81, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsijani, S.; Santanasto, A.J.; Miljkovic, I.; Boudreau, R.M.; Goodpaster, B.H.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Newman, A.B. The Relationship Between Intermuscular Fat and Physical Performance Is Moderated by Muscle Area in Older Adults. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2021, 76, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliani, H.K.; Shea, N.W.; Gerstner, G.R.; Mota, J.A.; Blackburn, J.T.; Ryan, E.D. The Influence of Age and Obesity-Altered Muscle Tissue Composition on Muscular Dimensional Changes: Impact on Strength and Function. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2020, 75, 2286–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Valencak, T.G.; Shan, T. Fat infiltration in skeletal muscle: Influential triggers and regulatory mechanism. IScience 2024, 27, 109221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.P.; Leung, B.P.; Ding, Y.Y.; Tay, L.; Ismail, N.H.; Yeo, A.; Yew, S.; Chong, M.S. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1: A proinflammatory cytokine elevated in sarcopenic obesity. Clin. Interv. Aging 2015, 10, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.W.; Li, C.I.; Li, T.C.; Liu, C.S.; Lin, C.H.; Lin, W.Y.; Lin, C.C. Association of Sarcopenic Obesity with Higher Serum High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein Levels in Chinese Older Males—A Community-Based Study (Taichung Community Health Study-Elderly, TCHS-E). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, M.; Vasuri, F.; Trisolino, G.; Bellavista, E.; Santoro, A.; Degiovanni, A.; Martucci, E.; D’Errico-Grigioni, A.; Caporossi, D.; Capri, M.; et al. Increased Plin2 Expression in Human Skeletal Muscle Is Associated with Sarcopenia and Muscle Weakness. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Wong, P.Y.; Chung, Y.L.; Chow, S.K.-H.; Cheung, W.H.; Law, S.W.; Chan, J.C.N.; Wong, R.M.Y. Deciphering the “obesity paradox” in the elderly: A systematic review and meta-analysis of sarcopenic obesity. Obes. Rev. 2023, 24, e13534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.I.; Huang, K.C.; Chan, D.C.; Wu, C.H.; Lin, C.C.; Hsiung, C.A.; Hsu, C.C.; Chen, C.Y. The impacts of sarcopenia and obesity on physical performance in the elderly. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 9, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.H.; Won, C.W.; Kim, W. Effect of sarcopenic obesity on deterioration of physical function in the elderly. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2020, 89, 104065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiotto, L.; Muollo, V.; Tatangelo, T.; Schena, F.; Rossi, A.P. Exercise and physical performance in older adults with sarcopenic obesity: A systematic review. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 913953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Gonçalves, L.; Santos Lopes da Silva, L.; Rodrigues Benjamim, C.J.; Tasinafo, M.F.; Bohn, L.; Ferreira Abud, G.; Ortiz, G.U.; de Freitas, E.C. The Effects of Different Exercise Training Types on Body Composition and Physical Performance in Older Adults with Sarcopenic Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2023, 27, 1076–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batsis, J.A.; Villareal, D.T. Sarcopenic obesity in older adults: Aetiology, epidemiology and treatment strategies. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 513–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, C.M.; Batsis, J.A.; Donini, L.M.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Siervo, M. Sarcopenic obesity in older adults: A clinical overview. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2024, 20, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.E.; Rejeski, W.J.; Blair, S.N.; Duncan, P.W.; Judge, J.O.; King, A.C.; Macera, C.A.; Castaneda-Sceppa, C. Physical activity and public health in older adults: Recommendation from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Circulation 2007, 116, 1094–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eglseer, D.; Traxler, M.; Schoufour, J.D.; Weijs, P.J.M.; Voortman, T.; Boirie, Y.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Reiter, L.; Bauer, S. Nutritional and exercise interventions in individuals with sarcopenic obesity around retirement age: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Rev. 2023, 81, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, Y.; Wakabayashi, H.; Yamada, M.; Kim, H.; Harada, A.; Arai, H. Interventions for Treating Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Studies. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, e1–e553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.T.; Chung, Y.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Ho, S.Y.; Wu, H.J. Effects of Different Types of Exercise on Body Composition, Muscle Strength, and IGF-1 in the Elderly with Sarcopenic Obesity. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2017, 65, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Soh, K.G.; Omar Dev, R.D.; Talib, O.; Xiao, W.; Soh, K.L.; Ong, S.L.; Zhao, C.; Galeru, O.; Casaru, C. Aerobic Exercise Combination Intervention to Improve Physical Performance Among the Elderly: A Systematic Review. Front. Physiol. 2022, 12, 798068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cândido, L.M.; Bae, J.-H.; Kim, D.Y.; Bayartai, M.-E.; Abbruzzese, L.; Fanari, P.; De Micheli, R.; Tringali, G.; Danielewicz, A.L.; Sartorio, A. Identifying Key Predictors of Sarcopenic Obesity in Italian Severely Obese Older Adults: Deep Learning Approach. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093069
Cândido LM, Bae J-H, Kim DY, Bayartai M-E, Abbruzzese L, Fanari P, De Micheli R, Tringali G, Danielewicz AL, Sartorio A. Identifying Key Predictors of Sarcopenic Obesity in Italian Severely Obese Older Adults: Deep Learning Approach. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(9):3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093069
Chicago/Turabian StyleCândido, Leticia Martins, Jun-Hyun Bae, Dae Young Kim, Munkh-Erdene Bayartai, Laura Abbruzzese, Paolo Fanari, Roberta De Micheli, Gabriella Tringali, Ana Lúcia Danielewicz, and Alessandro Sartorio. 2025. "Identifying Key Predictors of Sarcopenic Obesity in Italian Severely Obese Older Adults: Deep Learning Approach" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 9: 3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093069
APA StyleCândido, L. M., Bae, J.-H., Kim, D. Y., Bayartai, M.-E., Abbruzzese, L., Fanari, P., De Micheli, R., Tringali, G., Danielewicz, A. L., & Sartorio, A. (2025). Identifying Key Predictors of Sarcopenic Obesity in Italian Severely Obese Older Adults: Deep Learning Approach. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093069








