Laboratory Findings and Clinical Features in IgA Vasculitis: Identifying Predictors of Kidney Involvement and Disease Relapse in Pediatric Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population and Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
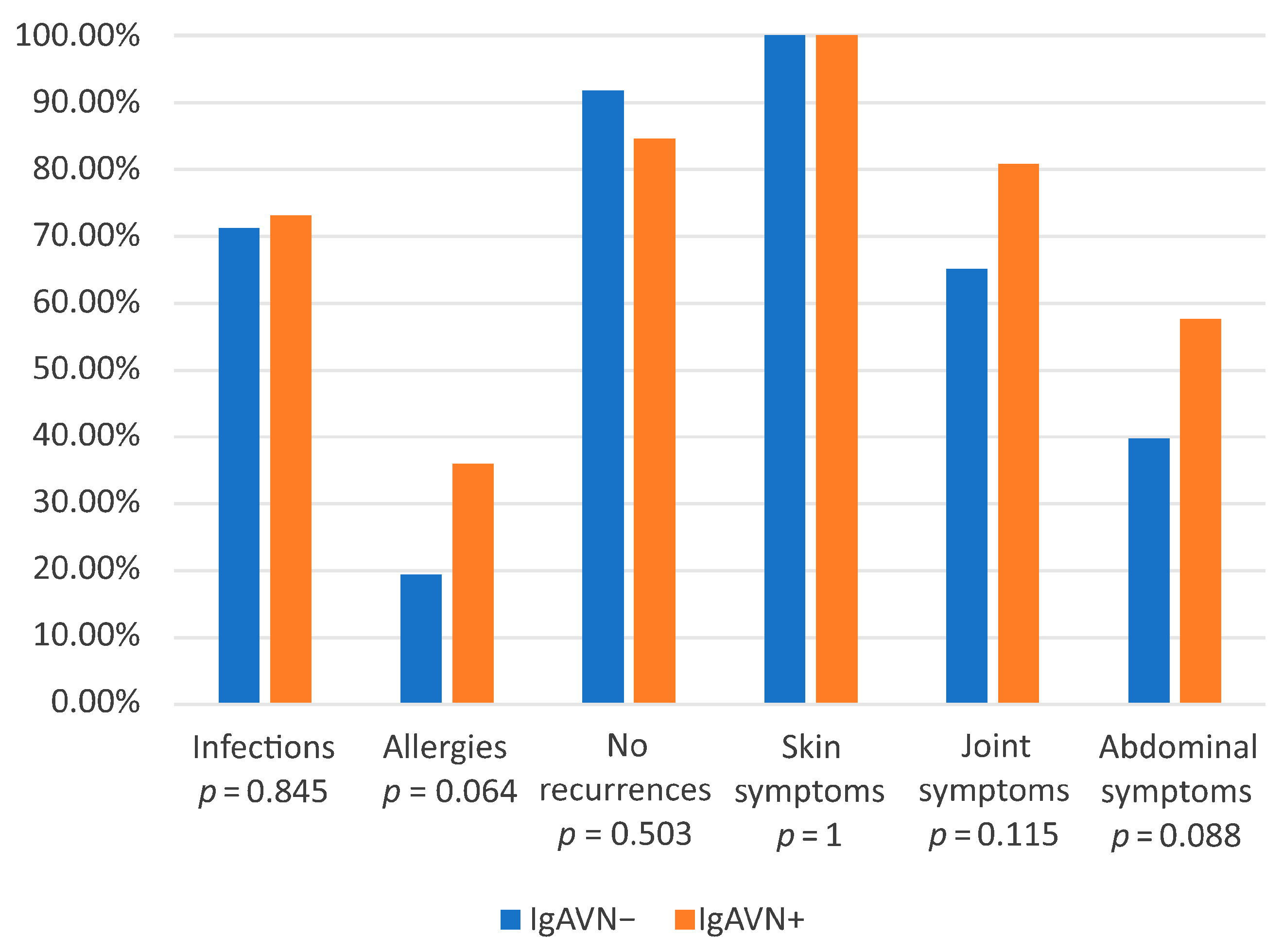
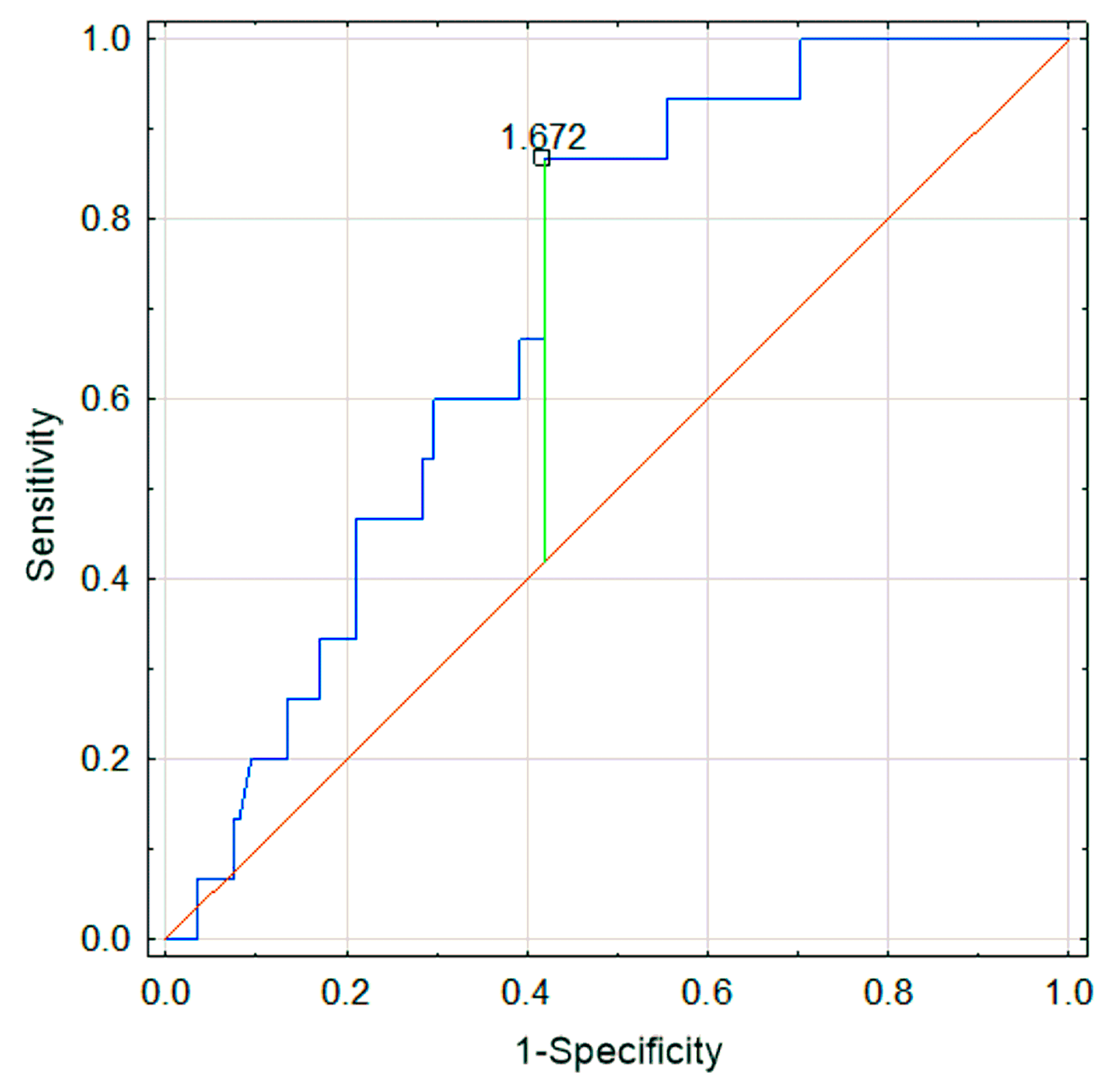
3.2. Comparison of IgAVN− and IgAVN+ Groups
- a.
- First Episode
- b.
- Second Episode
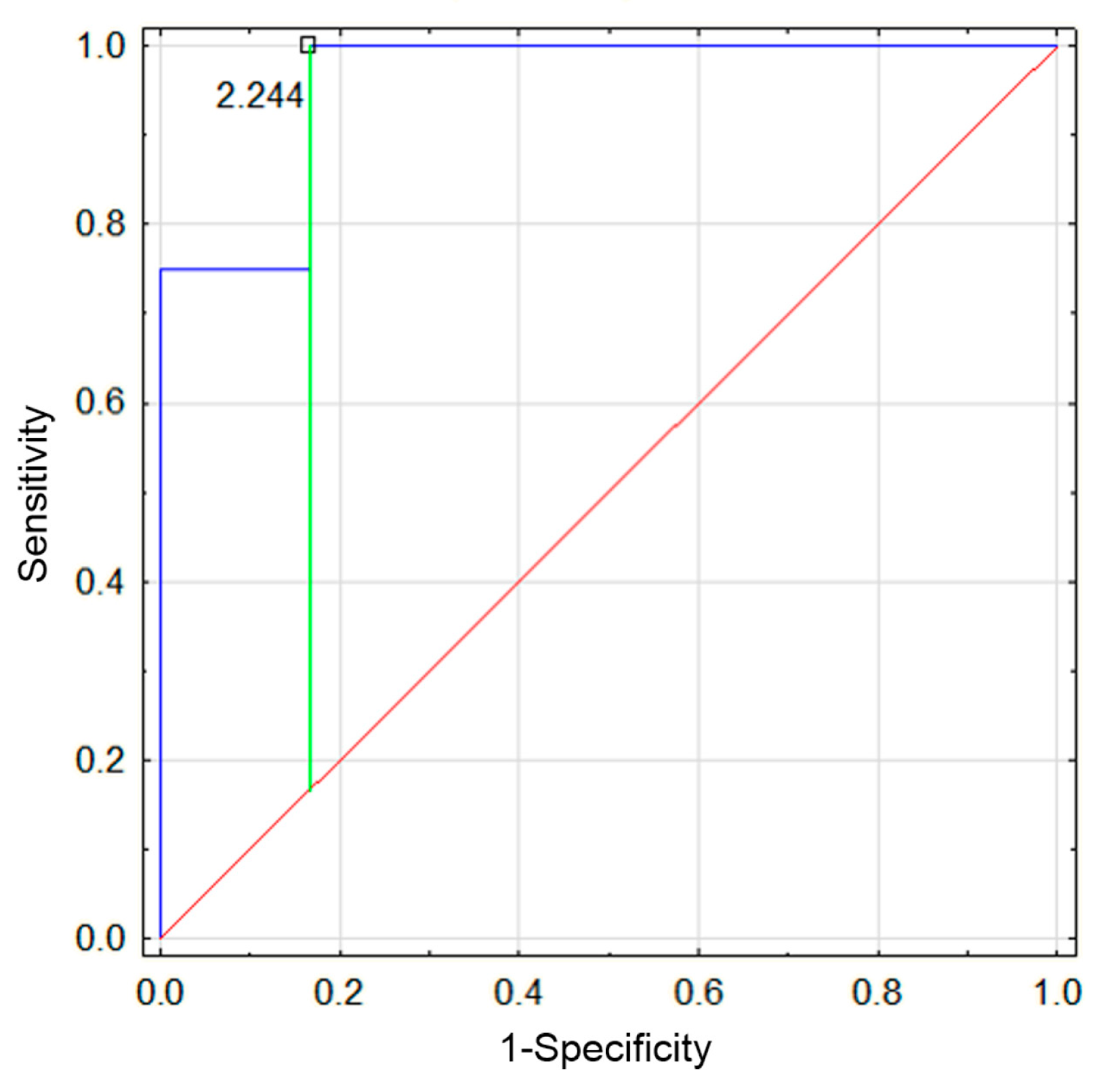
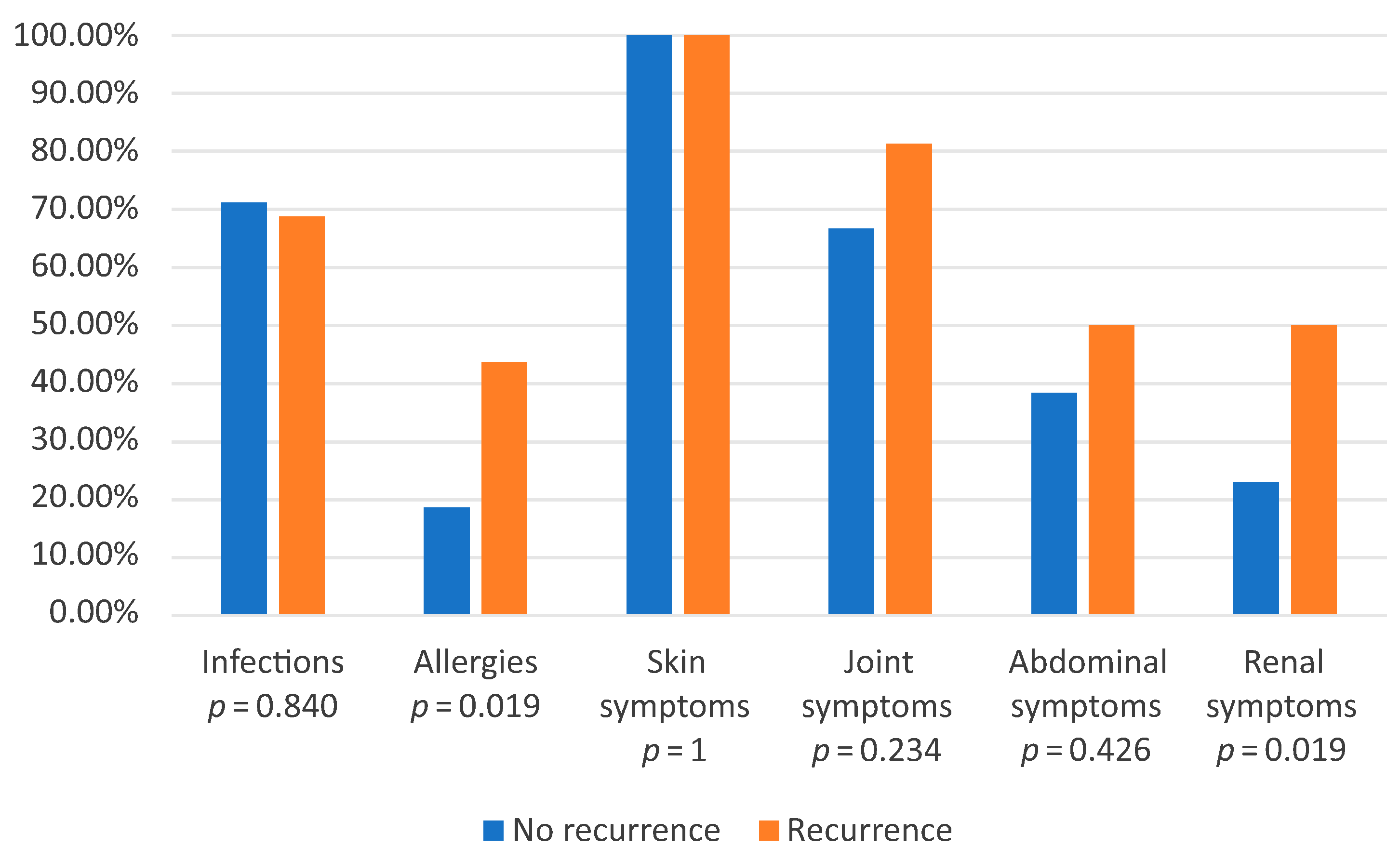
3.3. Comparison of Recurrence Group and Group with One Episode
3.4. Comparison of Results Between the First and Second Episodes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oni, L.; Sampath, S. Childhood IgA Vasculitis (Henoch Schonlein Purpura)-Advances and Knowledge Gaps. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.K.C.; Barankin, B.; Leong, K.F. Henoch-Schonlein Purpura in Children: An Updated Review. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2020, 16, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Huang, X.; Yu, G.; Qiao, J.; Cheng, J.; Wu, J.; Chen, J. Pathogenesis of IgA Vasculitis: An Up-To-Date Review. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 771619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breda, L.; Carbone, I.; Casciato, I.; Gentile, C.; Grasso, E.A.; di Donato, G.; Chiarelli, F.; Verrotti, A. Epidemiological and clinical aspects of immunoglobulin A vasculitis in childhood: A retrospective cohort study. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2021, 47, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lava, S.A.G.; Milani, G.P.; Fossali, E.F.; Simonetti, G.D.; Agostoni, C.; Bianchetti, M.G. Cutaneous Manifestations of Small-Vessel Leukocytoclastic Vasculitides in Childhood. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 53, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelusic, M.; Sestan, M.; Giani, T.; Cimaz, R. New Insights and Challenges Associated with IgA Vasculitis and IgA Vasculitis With Nephritis—Is It Time to Change the Paradigm of the Most Common Systemic Vasculitis in Childhood? Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 853724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Wu, X. IgA vasculitis update: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and biomarkers. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 921864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Lopez-Mejias, R.; Pina, T.; Blanco, R.; Castaneda, S. IgA Vasculitis: Genetics and Clinical and Therapeutic Management. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2018, 20, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marro, J.; Williams, C.; Wadden, L.; Pain, C.; Oni, L. 640 A case series on recurrent and persisting IgA vasculitis in children. Arch. Dis. Child. 2022, 107 (Suppl. S2), A259. [Google Scholar]
- Dyga, K.; Szczepanska, M. IgA vasculitis with nephritis in children. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 29, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saulsbury, F.T. Henoch-Schonlein purpura in children. Report of 100 patients and review of the literature. Medicine 1999, 78, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhimma, R.; Langman, C.B.; Scheinfeld, N.S.; Jones, E.L.; Nandlal, L. IgA Vasculitis (Henoch-Schonlein Purpura) Clinical Presentation. Available online: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/984105-clinical (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Liao, C.H.; Tsai, M.; Yang, Y.H.; Chiang, B.L.; Wang, L.C. Onset age is a risk factor for refractory pediatric IgA vasculitis: A retrospective cohort study. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2020, 18, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Zhu, Q.; Hu, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Jing, X.; Guo, Q. Association of Childhood IgA Vasculitis With Allergic Rhinitis and Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Kidney Int. Rep. 2024, 9, 2759–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sestan, M.; Kifer, N.; Frkovic, M.; Sapina, M.; Srsen, S.; Batnozic Varga, M.; Ovuka, A.; Held, M.; Gudelj Gracanin, A.; Kozmar, A.; et al. Gastrointestinal involvement and its association with the risk for nephritis in IgA vasculitis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2021, 13, 1759720X211024828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizerska-Wasiak, M.; Turczyn, A.; Cichon-Kawa, K.; Maldyk, J.; Miklaszewska, M.; Drozdz, D.; Bienias, B.; Sikora, P.; Drozynska-Duklas, M.; Zurowska, A.; et al. IgA vasculitis nephritis clinical course and kidney biopsy—National study in children. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2021, 19, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felix, A.; Assad, Z.; Bidet, P.; Caseris, M.; Dumaine, C.; Faye, A.; Melki, I.; Kaguelidou, F.; Valtuille, Z.; Ouldali, N.; et al. Common Seasonal Pathogens and Epidemiology of Henoch-Schonlein Purpura Among Children. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e245362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Shan, Y. AB1443 Triggering IgA Vasculitis by food allergen exposure, vitamin D deficiency, and IL-33-activated type 2 immune responses. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82 (Suppl. S1), 1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Lei, L.; Zhang, H.; Ling, C.; Ni, J.; Lv, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, X. Serum levels of galactose-deficient IgA1 in Chinese children with IgA nephropathy, IgA vasculitis with nephritis, and IgA vasculitis. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2021, 25, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillebout, E.; Jamin, A.; Ayari, H.; Housset, P.; Pierre, M.; Sauvaget, V.; Viglietti, D.; Deschenes, G.; Monteiro, R.C.; Berthelot, L.; et al. Biomarkers of IgA vasculitis nephritis in children. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahorec, R. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, past, present and future perspectives. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2021, 122, 474–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosmann, J.; Krusemark, A.; Dittrich, S.; Ammer, T.; Rauh, M.; Woelfle, J.; Metzler, M.; Zierk, J. Age- and sex-specific pediatric reference intervals for neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio, and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2022, 44, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaszczura, M. Ocena Stężenia Wybranych Cytokin (IL-17A, IL-18, IL-23, IP-10, CCL5) Oraz Wskaźników Neutrofile/Limfocyty i Płytki Krwi/Limfocyty u Dzieci w Ostrej Fazie Choroby Schönleina Henocha. Ph.D. Thesis, Medical University of Silesia, Polska Platforma Medyczna, Katowice, Poland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Shi, S.; Liu, L.; Lv, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, H. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as an independent inflammatory indicator for poor renal prognosis in adult IgA vasculitis with nephritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 111, 109178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | All Patients (N = 173) |
|---|---|
| Demographics | |
| Male/female | 1.08:1 |
| Age (years) | 6.55 [1.24–17.65] |
| Clinical features | |
| Skin involvement (n%) | 173 (100%) |
| Abdominal involvement (n%) | 73 (42.20%) |
| Joint involvement (n%) | 118 (68.20%) |
| Renal involvement (n%) | 73 (42.20%) |
| Allergies (n%) | 37 (21.39%) |
| Food (n%) | 20 (11.56%) |
| Respiratory (n%) | 13 (7.51%) |
| Skin (n%) | 8 (4.06%) |
| Presence of infection (n%) | 122 (70.52%) |
| Duration of hospitalization | 7.72 [1–64] |
| Occurrence of relapses | 9.25% |
| Laboratory Values | |
| WBC (103/µL) | 10.57 ± 3.91 |
| LIMF (%) | 34.98 ± 11.42 |
| NEU (%) | 53.41 ± 13.12 |
| HGB (g/dL) | 12.39 ± 1.13 |
| PLT (103/µL) | 372.1 ± 116.3 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 27.42 ± 7.98 |
| Creatine (mg/dL) | 0.40 ± 0.15 |
| IgG (mg/dL) | 1060.5 ± 331.4 |
| IgA (mg/dL) | 194.5 ± 103.1 |
| IgM (mg/dL) | 113.98 ± 56.9 |
| C3 (mg/dL) | 113.62 ± 25.1 |
| C4 (mg/dL) | 24.7 ± 11.8 |
| Episode I | Episode II | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FACTORS | IgAVN− (N = 147) | IgAVN+ (N = 26) | p * | IgAVN− (N = 12) | IgAVN+ (N = 4) | p * |
| Age (years) | 6.24 ± 3.42 | 8.28 ± 4.01 | 0.007 | 7.21 ± 4.19 | 12.32 ± 6.21 | 0.080 |
| Hospitalization Duration (Days) | 5.52 ± 5.4 | 20.04 ± 11.14 | 0.000 | 4 ± 2.3 | 11.5 ± 10.3 | 0.026 |
| Interval Between Hospitalizations (Days) | - | - | - | 122 ± 188 | 103 ± 80 | 0.848 |
| WBC (103/µL) | 10.56 ± 3.90 | 10.66 ± 4.06 | 0.908 | 9.25 ± 1.91 | 10.68 ± 3.93 | 0.334 |
| LIMF (%) | 35.14 ± 11.26 | 34.13 ± 12.48 | 0.686 | 40.78 ± 11.64 | 19.53 ± 8.88 | 0.005 |
| NEU (%) | 53.31 ± 13.00 | 53.96 ± 14.04 | 0.821 | 49.73 ± 12.30 | 69.68 ± 11.51 | 0.013 |
| HGB (g/dL) | 12.41 ± 1.03 | 12.28 ± 1.58 | 0.574 | 12.27 ± 0.86 | 13.53 ± 1.24 | 0.039 |
| PLT (103/µL) | 371.2 ± 119.8 | 377.2 ± 96.1 | 0.814 | 391.9 ± 72.5 | 304.5 ± 122.2 | 0.099 |
| NLR | 1.83 ± 1.12 | 2.05 ± 1.48 | 0.381 | 1.4 ± 0.72 | 5.18 ± 4.89 | 0.015 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 26.45 ± 7.02 | 31.84 ± 10.46 | 0.002 | 24.3 ± 3.09 | 27.25 ± 7.93 | 0.318 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.37 ± 0.12 | 0.5 ± 0.23 | 0.000 | 0.86 ± 1.71 | 0.6 ± 0.22 | 0.767 |
| GFR (ml/min/1.73 m2) | 134.86 ± 33.69 | 119.4 ± 132.22 | 0.052 | 137.48 ± 67.09 | 103.25 ± 18.78 | 0.420 |
| IgG (mg/dL) | 1074.3 ± 329.1 | 1021 ± 341.8 | 0.500 | 1156.8 ± 474.0 | 1550 | 0.460 |
| IgA (mg/dL) | 178.7 ± 94.8 | 252.8 ± 113.1 | 0.001 | 244 ± 93.7 | 342 ± 58 | 0.199 |
| IgM (mg/dL) | 118.7 ± 57.0 | 98.9 ± 55.0 | 0.138 | 162.9 ± 86.1 | 280 | 0.241 |
| C3 (mg/dL) | 113.9 ± 27.1 | 112.8 ± 18.3 | 0.857 | - | - | - |
| C4 (mg/dL) | 25.3 ± 13.1 | 22.9 ± 6.3 | 0.378 | - | - | - |
| FACTOR | Recurrence Group (N = 16) | Non-Recurrence Group (N = 157) | p * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 8.14 ± 5.06 | 6.38 ± 3.37 | 0.061 |
| Interval Between Hospitalizations (Days) | 117.2 ± 164.8 | - | - |
| WBC (103/µL) | 11.88 ± 3.96 | 10.44 ± 3.90 | 0.176 |
| LIMF (%) | 28.12 ± 7.20 | 35.68 ± 11.55 | 0.014 |
| NEU (%) | 60.99 ± 7.77 | 52.64 ± 13.32 | 0.018 |
| HGB (g/dL) | 12.41 ±1.03 | 12.28 ± 1.58 | 0.574 |
| PLT (103/µL) | 369.47 ± 61.18 | 372.36 ± 120.57 | 0.927 |
| NLR | 2.4 ± 0.9 | 1.8 ± 1.2 | 0.078 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 26.63 ± 5.74 | 27.52 ± 8.24 | 0.683 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.39 ± 0.15 | 0.4 ± 0.15 | 0.888 |
| GFR (ml/min/1.73 m2) | 143.20 ± 38.00 | 129.7 ± 33.4 | 0.258 |
| IgG (mg/dL) | 1025.8 ± 394 | 1066.7 ± 321.6 | 0.673 |
| IgA (mg/dL) | 220.5 ± 110.1 | 190.9 ± 102.1 | 0.299 |
| IgM (mg/dL) | 147.3 ± 92.9 | 108.9 ± 48.2 | 0.022 |
| C3 (mg/dL) | 116.2 ± 21.4 | 113.2 ± 25.7 | 0.681 |
| C4 (mg/dL) | 21.5 ± 4.8 | 25.2 ± 12.5 | 0.282 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Podraza, Z.; Poplicha, K.; Ufniarski, T.; Ucieklak, J.; Łysiak, N.; Mizerska-Wasiak, M. Laboratory Findings and Clinical Features in IgA Vasculitis: Identifying Predictors of Kidney Involvement and Disease Relapse in Pediatric Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3055. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093055
Podraza Z, Poplicha K, Ufniarski T, Ucieklak J, Łysiak N, Mizerska-Wasiak M. Laboratory Findings and Clinical Features in IgA Vasculitis: Identifying Predictors of Kidney Involvement and Disease Relapse in Pediatric Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(9):3055. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093055
Chicago/Turabian StylePodraza, Zofia, Karol Poplicha, Tomasz Ufniarski, Jarosław Ucieklak, Natalia Łysiak, and Małgorzata Mizerska-Wasiak. 2025. "Laboratory Findings and Clinical Features in IgA Vasculitis: Identifying Predictors of Kidney Involvement and Disease Relapse in Pediatric Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 9: 3055. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093055
APA StylePodraza, Z., Poplicha, K., Ufniarski, T., Ucieklak, J., Łysiak, N., & Mizerska-Wasiak, M. (2025). Laboratory Findings and Clinical Features in IgA Vasculitis: Identifying Predictors of Kidney Involvement and Disease Relapse in Pediatric Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 3055. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093055






