Trends in Celecoxib Prescribing: A Single Institution 16-Month Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
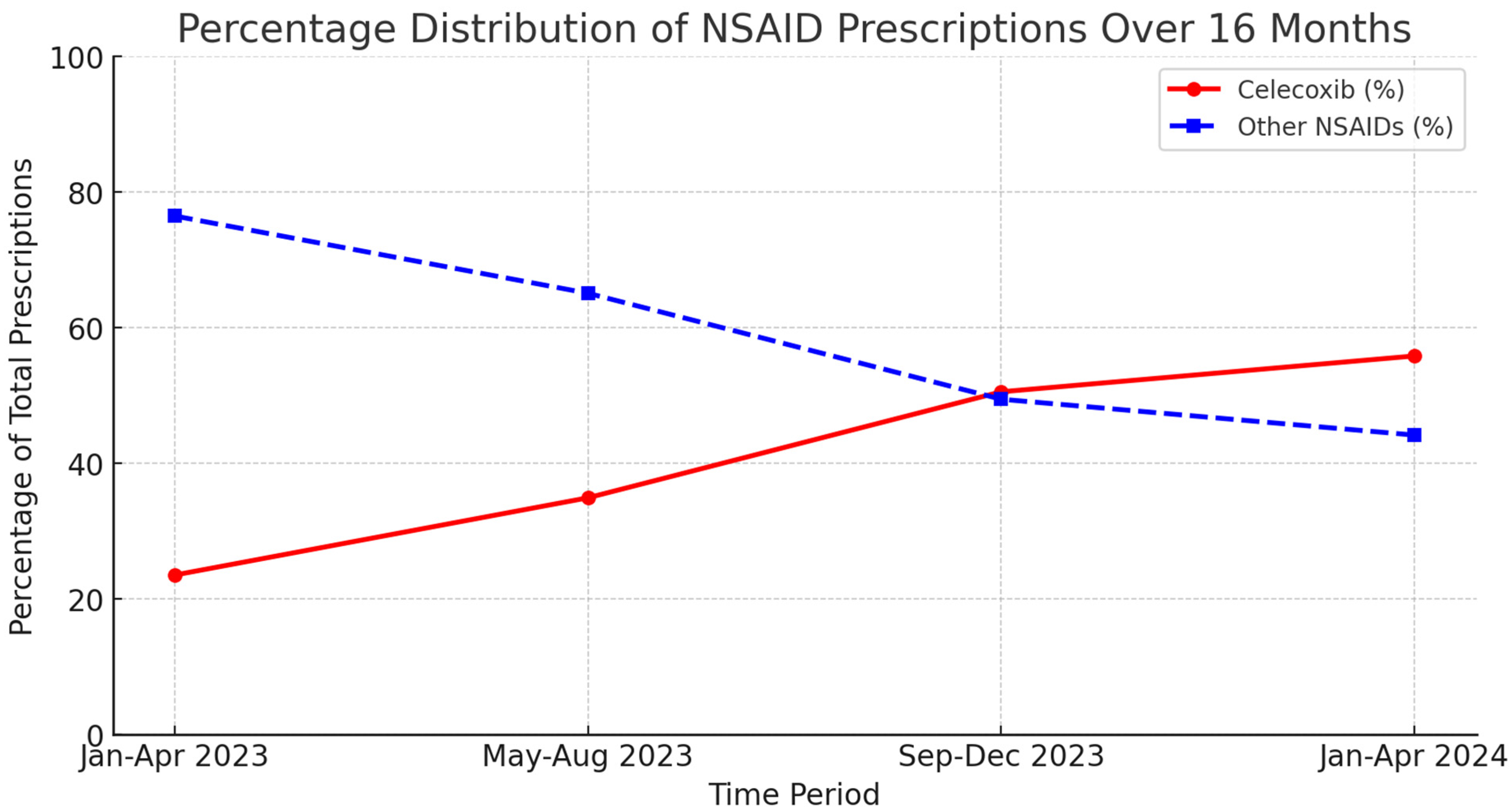
3. Results
4. Discussion
Implications for Clinical Practice
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yong, R.J.; Mullins, P.M.; Bhattacharyya, N. Prevalence of chronic pain among adults in the United States. Pain 2022, 163, E328–E332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treede, R.-D.; Rief, W.; Barke, A.; Aziz, Q.; Bennett, M.I.; Benoliel, R.; Cohen, M.; Evers, S.; Finnerup, N.B.; First, M.B.; et al. Chronic pain as a symptom or a disease: The IASP Classification of Chronic Pain for the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11). Pain 2019, 160, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubhaug, A.; Hansen, J.L.; Hallberg, S.; Gustavsson, A.; Eggen, A.E.; Nielsen, C.S. The costs of chronic pain-Long-term estimates. Eur. J. Pain 2024, 28, 960–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowal, J.; Wilson, K.G.; McWilliams, L.A.; Péloquin, K.; Duong, D. Self-perceived burden in chronic pain: Relevance, prevalence, and predictors. Pain 2012, 153, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.P.; Vase, L.; Hooten, W.M. Chronic pain: An update on burden, best practices, and new advances. Lancet 2021, 397, 2082–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadi, M.A.; McHugh, G.A.; Closs, S.J. Impact of Chronic Pain on Patients’ Quality of Life: A Comparative Mixed-Methods Study. J. Patient Exp. 2019, 6, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcher, M.H.; Von Korff, M.; Bushnell, M.C.; Porter, L. Prevalence and Profile of High-Impact Chronic Pain in the United States. J. Pain 2019, 20, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, P.M.; Yong, R.J.; Bhattacharyya, N. Associations between chronic pain, anxiety, and depression among adults in the United States. Pain Pract. 2023, 23, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaskin, D.J.; Richard, P. The economic costs of pain in the United States. J. Pain 2012, 13, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieleman, J.L.; Cao, J.; Chapin, A.; Chen, C.; Li, Z.; Liu, A.; Horst, C.; Kaldjian, A.; Matyasz, T.; Scott, K.W.; et al. US Health Care Spending by Payer and Health Condition, 1996–2016. JAMA 2020, 323, 863–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wu, W. Multimodal non-invasive non-pharmacological therapies for chronic pain: Mechanisms and progress. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhee, M.E.; Vaegter, H.B.; Graven-Nielsen, T. Alterations in pronociceptive and antinociceptive mechanisms in patients with low back pain: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Pain 2020, 161, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vane, J.R.; Botting, R.M. Mechanism of action of antiinflammatory drugs. Int. J. Tissue React. 1998, 20, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drini, M. Peptic ulcer disease and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Aust. Prescr. 2017, 40, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puljak, L.; Marin, A.; Vrdoljak, D.; Markotic, F.; Utrobicic, A.; Tugwell, P. Celecoxib for osteoarthritis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 5, CD009865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemett, D.; Goa, K.L. Celecoxib: A review of its use in osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and acute pain. Drugs 2000, 59, 957–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedaiwi, M.K.; Sari, I.; Wallis, D.; O’Shea, F.D.; Salonen, D.; Haroon, N.; Omar, A.; Inman, R.D. Clinical Efficacy of Celecoxib Compared to Acetaminophen in Chronic Nonspecific Low Back Pain: Results of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Arthritis Care Res. 2016, 68, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, C.O.; Bird, S.R.; Smugar, S.S.; Xu, X.; Tershakovec, A.M. Responder analysis and correlation of outcome measures: Pooled results from two identical studies comparing etoricoxib, celecoxib, and placebo in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2008, 16, 1289–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rother, M.; Lavins, B.J.; Kneer, W.; Lehnhardt, K.; Seidel, E.J.; Mazgareanu, S. Efficacy and safety of epicutaneous ketoprofen in Transfersome (IDEA-033) versus oral celecoxib and placebo in osteoarthritis of the knee: Multicentre randomised controlled trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, 1178–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, C.O.; Sebba, A.I.; Rubin, B.R.; Ruoff, G.E.; Kremer, J.; Bird, S.; Smugar, S.S.; Fitzgerald, B.J.; O’Brien, K.; Tershakovec, A.M. Efficacy and safety of etoricoxib 30 mg and celecoxib 200 mg in the treatment of osteoarthritis in two identically designed, randomized, placebo-controlled, non-inferiority studies. Rheumatology 2007, 46, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Luo, M.; Liang, H.; Pan, J.; Yang, W.; Zeng, L.; Liang, G.; Hou, S.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J. Meta-analysis Comparing Celecoxib with Diclofenac Sodium in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis. Pain Med. Off. J. Am. Acad. Pain Med. 2020, 22, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foeldvari, I.; Szer, I.S.; Zemel, L.S.; Lovell, D.J.; Giannini, E.H.; Robbins, J.L.; West, C.R.; Steidle, G.; Krishnaswami, S.; Bloom, B.J. A prospective study comparing celecoxib with naproxen in children with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 36, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pain Management Best Practices Inter-Agency Task Force Report: Updates, Gaps, Inconsistencies, and Recommendations. 2019. Available online: https://www.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/pain-mgmt-best-practices-draft-final-report-05062019.pdf (accessed on 24 February 2025).
- Dowell, D.; Ragan, K.R.; Jones, C.M.; Baldwin, G.T.; Chou, R. CDC Clinical Practice Guideline for Prescribing Opioids for Pain—United States, 2022. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2023, 71, 1–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, R.; Smith, D.; Franklin, G.; Gronseth, G.; Pignone, M.; David, W.S.; Armon, C.; Perkins, B.A.; Bril, V.; Rae-Grant, A.; et al. Oral and Topical Treatment of Painful Diabetic Polyneuropathy: Practice Guideline Update Summary: Report of the AAN Guideline Subcommittee. Neurology 2022, 98, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolasinski, S.L.; Neogi, T.; Hochberg, M.C.; Oatis, C.; Guyatt, G.; Block, J.; Callahan, L.; Copenhaver, C.; Dodge, C.; Felson, D.; et al. 2019 American College of Rheumatology/Arthritis Foundation Guideline for the Management of Osteoarthritis of the Hand, Hip, and Knee. Arthritis Care Res. 2020, 72, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anekar, A.A.; Hendrix, J.M.; Cascella, M. WHO Analgesic Ladder. J. R. Coll. Physicians Edinb. 2023, 38, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Fort, J.G.; Goldstein, J.L.; Levy, R.A.; Hanrahan, P.S.; Bello, A.E.; Andrade-Ortega, L.; Wallemark, C.; Agrawal, N.M.; Eisen, G.M.; et al. Celecoxib versus naproxen and diclofenac in osteoarthritis patients: SUCCESS-I study. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, J.B.; Ekman, E.F.; Spalding, W.M.; Bhadra, P.; McCabe, D.; Berger, M.F. The effectiveness of a weak opioid medication versus a cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2) selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug in treating flare-up of chronic low-back pain: Results from two randomized, double-blind, 6-week studies. J. Int. Med. Res. 2009, 37, 1789–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkhuizen, A.; Steinfeld, S.; Robbins, J.; West, C.; Coombs, J.; Zwillich, S. Celecoxib is efficacious and well tolerated in treating signs and symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 33, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, P.L.; Lanas, A.; McKenna, F.; Patrignani, P.; Simon, L.S. Celecoxib: A review of its use for symptomatic relief in the treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Drugs 2011, 71, 2457–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieper, J.; Klopsch, T.; Richter, M.; Kapelle, A.; Rudwaleit, M.; Schwank, S.; Regourd, E.; May, M. Comparison of two different dosages of celecoxib with diclofenac for the treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis: Results of a 12-week randomised, double-blind, controlled study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivitz, A.J.; Espinoza, L.R.; Sherrer, Y.R.; Liu-Dumaw, M.; West, C.R. A Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of Celecoxib 200 mg and Celecoxib 400 mg Once Daily in Treating the Signs and Symptoms of Psoriatic Arthritis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 37, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Thorn, C.F.; Bertagnolli, M.M.; Grosser, T.; Altman, R.B.; Klein, T.E. Celecoxib Pathways: Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics. Pharmacogenetics Genom. 2012, 22, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, N.M.; McLachlan, A.J.; Day, R.O.; Williams, K.M. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of celecoxib. A selective cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitor. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2000, 38, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penning, T.D.; Talley, J.J.; Bertenshaw, S.R.; Carter, J.S.; Collins, P.W.; Docter, S.; Graneto, M.J.; Lee, L.F.; Malecha, J.W.; Miyashiro, J.M.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of the 1,5-diarylpyrazole class of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors: Identification of 4-[5-(4-methylphenyl)-3-trifluoromethyl- 1H-pyrazol- l-yl]benzene sulfonamide (SC-58635, celecoxib). J. Med. Chem. 1997, 40, 1347–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, M.M. Celecoxib, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Clin. Ther. 1999, 21, 1497–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, L.M.; Wu, K.C.; Mahida, Y.R.; Jenkins, D.; Hawkey, C.J. Cyclooxygenase (COX) 1 and 2 in normal, inflamed, and ulcerated human gastric mucosa. Gut 2000, 47, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombardier, C.; Laine, L.; Reicin, A.; Shapiro, D.; Burgos-Vargas, R.; Davis, B.; Day, R.; Ferraz, M.B.; Hawkey, C.J.; Hochberg, M.C.; et al. Comparison of upper gastrointestinal toxicity of rofecoxib and naproxen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. VIGOR Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 1520–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.D.; McMurray, J.J.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Wittes, J.; Fowler, R.; Finn, P.; Anderson, W.F.; Zauber, A.; Hawk, E.; Bertagnolli, M. Cardiovascular risk associated with celecoxib in a clinical trial for colorectal adenoma prevention. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.B.; Faich, G.; Whelton, A.; Maurath, C.; Ridge, N.J.; Verburg, K.M.; Geis, G.; Lefkowith, J.B. Comparison of thromboembolic events in patients treated with celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase-2 specific inhibitor, versus ibuprofen or diclofenac. Am. J. Cardiol. 2002, 89, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, S.E.; Yeomans, N.D.; Solomon, D.H.; Lüscher, T.F.; Libby, P.; Husni, M.E.; Graham, D.Y.; Borer, J.S.; Wisniewski, L.M.; Wolski, K.E.; et al. Cardiovascular Safety of Celecoxib, Naproxen, or Ibuprofen for Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2519–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, B.-R.; Chen, J.-Q.; Zhang, X.-W.; Gao, Q.-Y.; Li, W.-H.; Yan, L.-J.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Wu, C.-J.; Xing, J.-L.; Liu, J.-P. Cardiovascular safety of celecoxib in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0261239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeomans, N.D.; Graham, D.Y.; Husni, M.E.; Solomon, D.H.; Stevens, T.; Vargo, J.; Wang, Q.; Wisniewski, L.M.; Wolski, K.E.; Borer, J.S.; et al. Randomised clinical trial: Gastrointestinal events in arthritis patients treated with celecoxib, ibuprofen or naproxen in the PRECISION trial. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 1453–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeid, S.; Libby, P.; Husni, E.; Wang, Q.; Wisniewski, L.M.; Davey, D.A.; Wolski, K.E.; Xia, F.; Bao, W.; Walker, C.; et al. Cardiorenal risk of celecoxib compared with naproxen or ibuprofen in arthritis patients: Insights from the PRECISION trial. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2022, 8, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, F.E.; Faich, G.; Goldstein, J.L.; Simon, L.S.; Pincus, T.; Whelton, A.; Makuch, R.; Eisen, G.; Agrawal, N.M.; Stenson, W.F.; et al. Gastrointestinal toxicity with celecoxib vs nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: The CLASS study: A randomized controlled trial. Celecoxib Long-term Arthritis Safety Study. JAMA 2000, 284, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, I.A.; Baek, H.-J.; Cho, C.-S.; Lee, Y.-A.; Chung, W.T.; Park, Y.E.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, Y.-B.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.-S.; et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety profiles of a pelubiprofen versus celecoxib in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A 6-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, phase III, non-inferiority clinical trial. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2014, 15, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chan, F.K.L.; Lanas, A.; Scheiman, J.; Berger, M.F.; Nguyen, H.; Goldstein, J.L. Celecoxib versus omeprazole and diclofenac in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis (CONDOR): A randomised trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coxib and traditional NSAID Trialists’ (CNT) Collaboration; Bhala, N.; Emberson, J.; Merhi, A.; Abramson, S.; Arber, N.; Baron, J.A.; Bombardier, C.; Cannon, C.; Farkouh, M.E.; et al. Vascular and upper gastrointestinal effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Meta-analyses of individual participant data from randomised trials. Lancet 2013, 382, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.K.; Mak, R.Y.; Kwok, T.S.; Tsang, J.S.; Leung, M.Y.; Funabashi, M.; Macedo, L.G.; Dennett, L.; Wong, A.Y. Prevalence, Incidence, and Factors Associated With Non-Specific Chronic Low Back Pain in Community-Dwelling Older Adults Aged 60 Years and Older: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Pain 2022, 23, 509–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, Q. Prevalence trend and disparities in rheumatoid arthritis among us adults, 2005–2018. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, J.; Culbreth, G.; Vos, T.; Haile, L.; Rafferty, Q.; Lo, J.; Cruz, J.; Smith, A.; Vollset, S.E.; Hagins, H.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of osteoarthritis, 1990–2020 and projections to 2050: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023, 5, e508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halter, J.B.; Musi, N.; Horne, F.M.; Crandall, J.P.; Goldberg, A.; Harkless, L.; Hazzard, W.R.; Huang, E.S.; Kirkman, M.S.; Plutzky, J.; et al. Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease in Older Adults: Current Status and Future Directions. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, G.T.; De Cosmo, S.; Viazzi, F.; Mirijello, A.; Ceriello, A.; Guida, P.; Giorda, C.; Cucinotta, D.; Pontremoli, R.; Fioretto, P.; et al. Diabetic kidney disease in the elderly: Prevalence and clinical correlates. BMC Geriatr. 2018, 18, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soenen, S.; Rayner, C.K.; Jones, K.L.; Horowitz, M. The Aging Gastrointestinal Tract. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2016, 19, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Quinn, R.R.; Lam, N.N.; Elliott, M.J.; Xu, Y.; James, M.T.; Manns, B.; Ravani, P. Accounting for Age in the Definition of Chronic Kidney Disease. JAMA Intern. Med. 2021, 181, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soejima, K.; Sato, H.; Hisaka, A. Age-Related Change in Hepatic Clearance Inferred from Multiple Population Pharmacokinetic Studies: Comparison with Renal Clearance and Their Associations with Organ Weight and Blood Flow. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2022, 61, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorfinkel, L.R.; Hasin, D.; Saxon, A.J.; Wall, M.; Martins, S.S.; Cerdá, M.; Keyes, K.; Fink, D.S.; Keyhani, S.; Maynard, C.C.; et al. Trends in Prescriptions for Non-opioid Pain Medications Among U.S. Adults With Moderate or Severe Pain, 2014–2018. J. Pain 2022, 23, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlhamer, J.M.; Connor, E.M.; Bose, J.; Lucas, J.W.; Zelaya, C.E. Prescription Opioid Use Among Adults With Chronic Pain: United States, 2019. Natl. Health Stat. Rep. Number 2019, 162, 1–9. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/index.htm (accessed on 24 February 2025).
- Jalodia, R.; Abu, Y.F.; Oppenheimer, M.R.; Herlihy, B.; Meng, J.; Chupikova, I.; Tao, J.; Ghosh, N.; Dutta, R.K.; Kolli, U.; et al. Opioid Use, Gut Dysbiosis, Inflammation, and the Nervous System. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2022, 17, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.D.; Edlund, M.J.; Zhang, L.; Unützer, J.; Wells, K.B. Association Between Mental Health Disorders, Problem Drug Use, and Regular Prescription Opioid Use. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 2087–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.D. Depression Effects on Long-term Prescription Opioid Use, Abuse, and Addiction. Clin. J. Pain 2018, 34, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, R.R.; Wasan, A.D.; Michna, E.; Greenbaum, S.; Ross, E.; Jamison, R.N. Elevated pain sensitivity in chronic pain patients at risk for opioid misuse. J. Pain 2011, 12, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, P.M.; Allen, C.L.; Barnes, K.A.; Peck, M.; Mogk, J.M. Persistent pain, long-term opioids, and restoring trust in the patient-clinician relationship. J. Pain 2025, 27, 104694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lappin, R. CDC Guideline for Prescribing Opioids for Chronic Pain—United States, 2016. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2023, 65, 150–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encinosa, W.; Bernard, D.; Selden, T.M. Opioid and non-opioid analgesic prescribing before and after the CDC’s 2016 opioid guideline. Int. J. Health Econ. Manag. 2022, 22, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varrassi, G.; Yeam, C.T.; Rekatsina, M.; Pergolizzi, J.V.; Zis, P.; Paladini, A. The Expanding Role of the COX Inhibitor/Opioid Receptor Agonist Combination in the Management of Pain. Drugs 2020, 80, 1443–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindu, S.; Mazumder, S.; Bandyopadhyay, U. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and organ damage: A current perspective. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 180, 114147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.; Lemtouni, S.; Weiss, K.; Pergolizzi, J.V. Pain Management in the Elderly: An FDA Safe Use Initiative Expert Panel’s View on Preventable Harm Associated with NSAID Therapy. Curr. Gerontol. Geriatr. Res. 2012, 2012, 196159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doomra, R.; Goyal, A. NSAIDs and self-medication: A serious concern. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2020, 9, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdolrasulnia, M.; Weichold, N.; Shewchuk, R.; Saag, K.; Cobaugh, D.J.; LaCivita, C.; Weissman, N.; Allison, J. Agreement between medical record documentation and patient-reported use of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2006, 63, 744–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, G.N.C.; Leitaõ, A.C.C.; Alencar, R.L.; Xavier, R.M.F.; Daher, E.D.F.; Silva, G.B. Pathophysiological aspects of nephropathy caused by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Braz. J. Nephrol. 2018, 41, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriuttha, P.; Sirichanchuen, B.; Permsuwan, U. Hepatotoxicity of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Int. J. Hepatol. 2018, 2018, 5253623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cerda, I.H.; Jung, H.; Guerrero, M.C.; Diez Tafur, R.; Yong, R.J.; Robinson, C.L.; Hasoon, J.J. Trends in Celecoxib Prescribing: A Single Institution 16-Month Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2823. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082823
Cerda IH, Jung H, Guerrero MC, Diez Tafur R, Yong RJ, Robinson CL, Hasoon JJ. Trends in Celecoxib Prescribing: A Single Institution 16-Month Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(8):2823. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082823
Chicago/Turabian StyleCerda, Ivo H., Helen Jung, Maria C. Guerrero, Rodrigo Diez Tafur, Robert Jason Yong, Christopher L. Robinson, and Jamal J. Hasoon. 2025. "Trends in Celecoxib Prescribing: A Single Institution 16-Month Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 8: 2823. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082823
APA StyleCerda, I. H., Jung, H., Guerrero, M. C., Diez Tafur, R., Yong, R. J., Robinson, C. L., & Hasoon, J. J. (2025). Trends in Celecoxib Prescribing: A Single Institution 16-Month Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(8), 2823. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082823







