Current Role of the Nonsteroid Treatment of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss (ISSNHL): A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
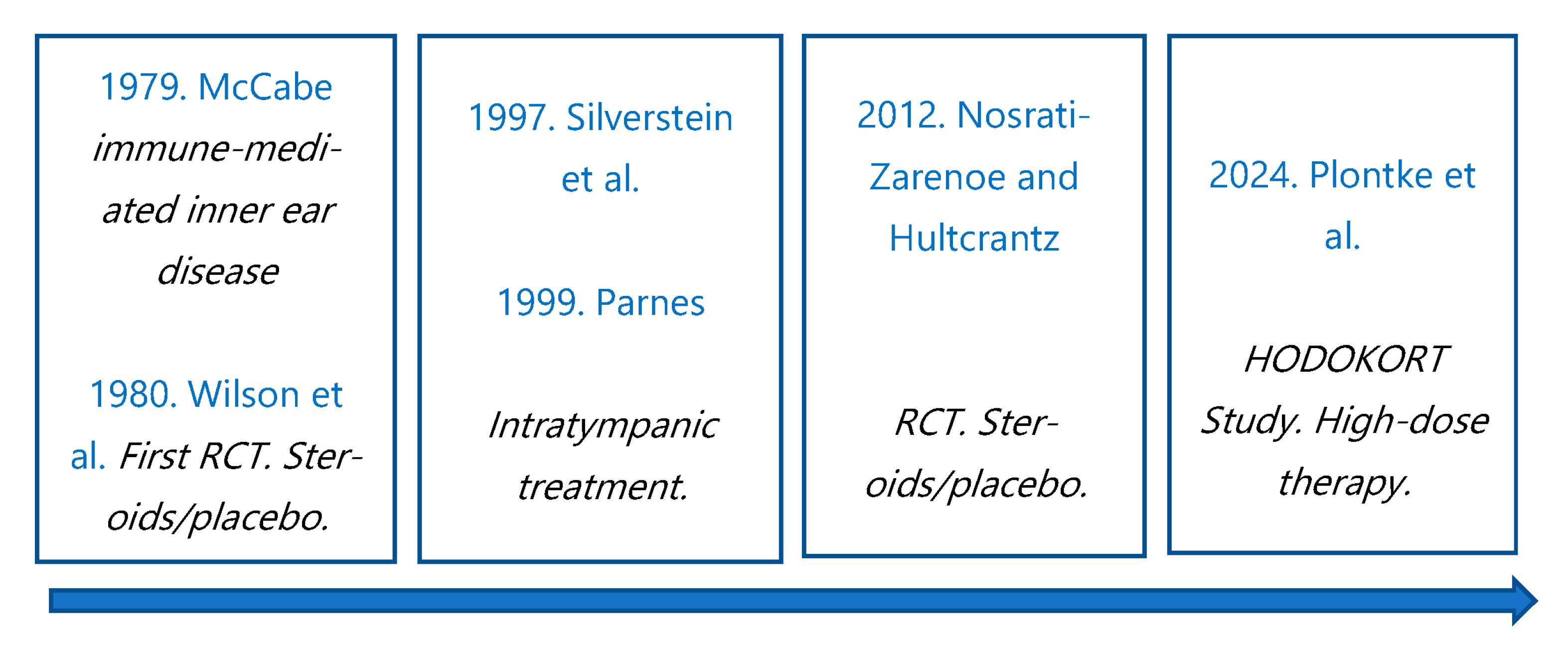
3. Development of Steroid Treatment
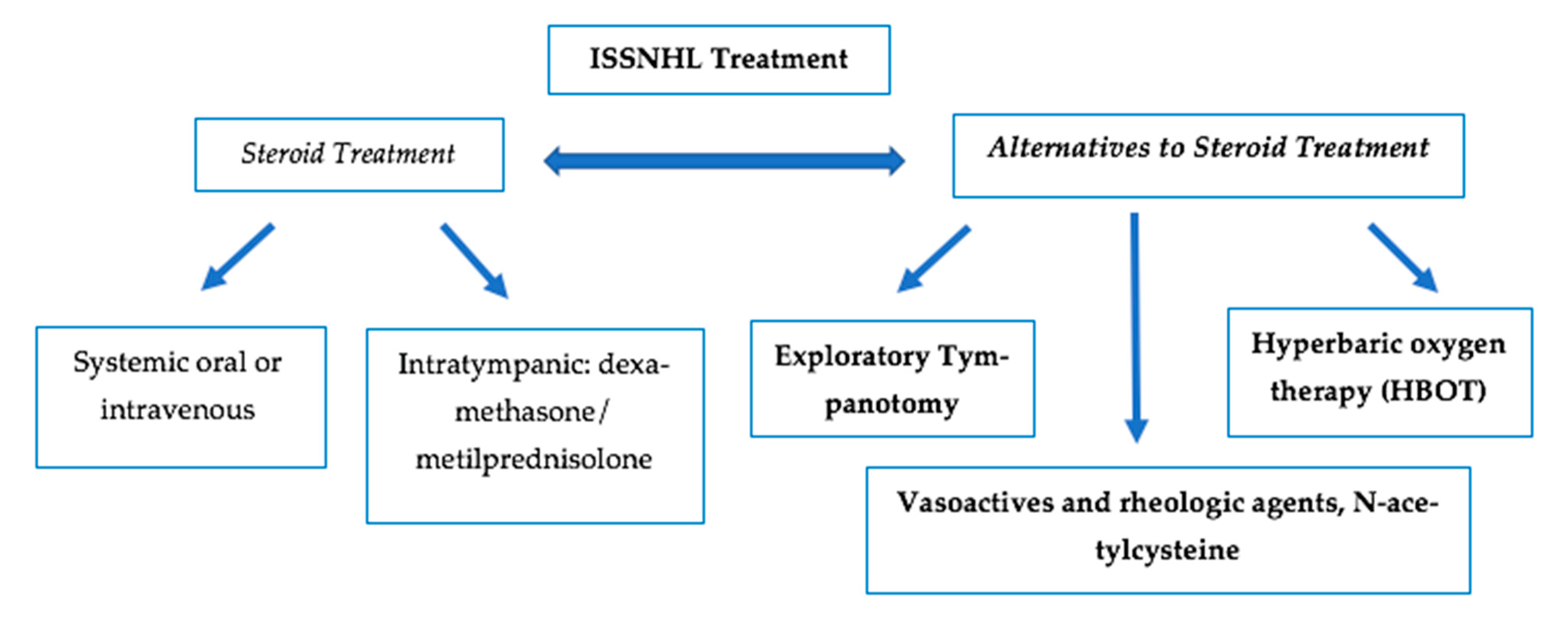
4. Alternatives to Steroids in ISSNHL
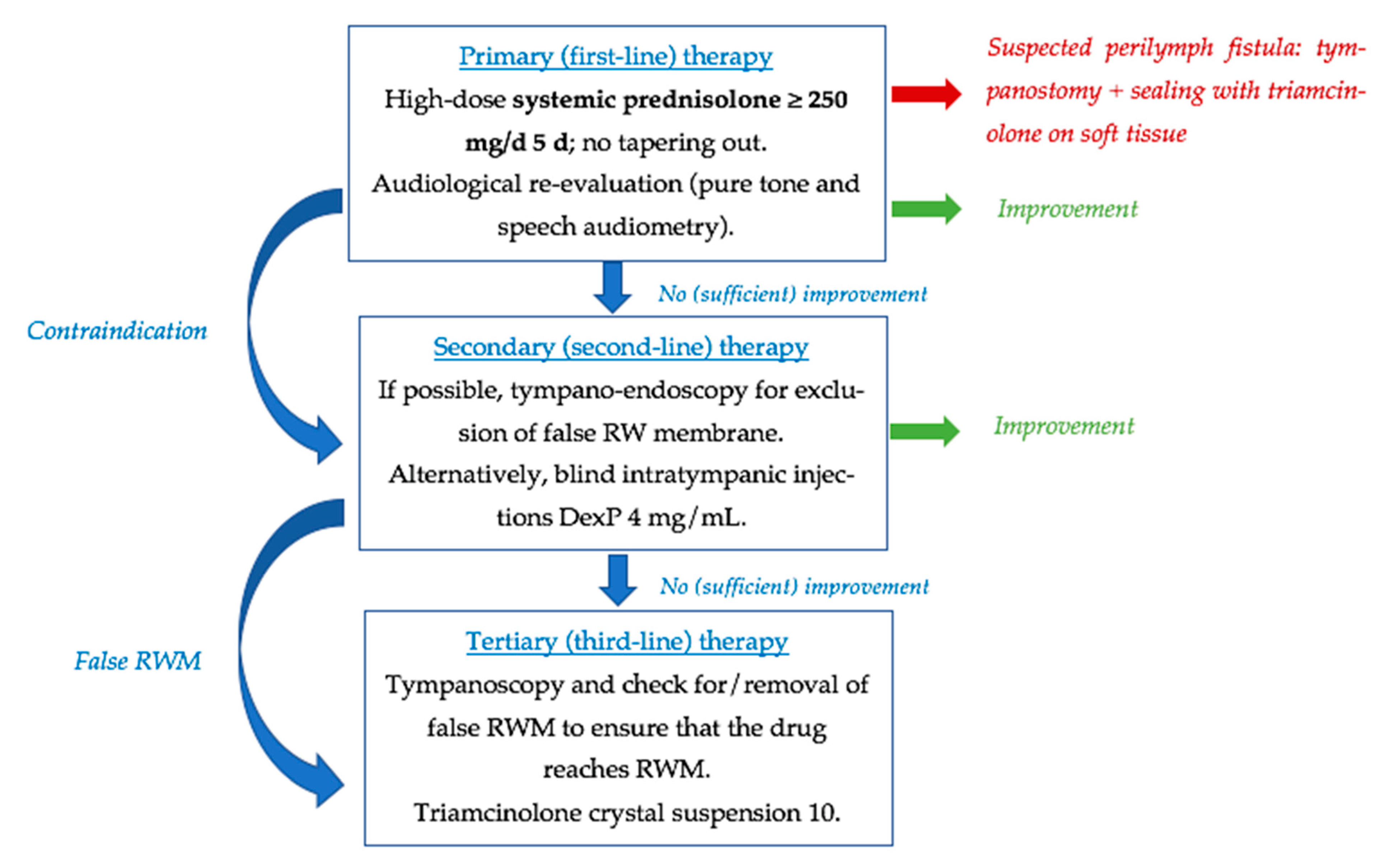
4.1. Exploratory Tympanotomy
4.2. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT)
4.3. Other Therapies: Vasoactives and Rheologic Agents; Antivirals and N-acetylcysteine
4.3.1. Vasoactives and Rheologic Agents
Prostaglandins
Defibrinogenation Therapy
Apheresis Therapy
4.3.2. Antivirals
4.3.3. N-acetylcysteine
| PROSTAGLANDINS | |||
| Study | Main Finding | Type of Study | Level of Evidence |
| Ogawa et al. [69] | Greater hearing gains at 4 or 8 kHz with PT + PGE1 treatment compared with PT alone | RCT | 2 |
| Okada et al. [70] | Better hearing prognosis with PT + PGE1 treatment than with PT alone | Retrospective multicenter database study | 3 |
| Hara et al. [71] | Significant improvement with PT + PGE1 + HBOT compared to PT + PGE1 alone | Retrospective study | 3 |
| DEFIBRINOGENATION THERAPY | |||
| Study | Main Finding | Type of Study | Level of Evidence |
| Kubo et al. [72] | Overall recovery rate significantly higher with DF than PT | RCT | 2 |
| Jiang et al. [73] | No significant difference observed in short-term outcomes with or without batroxobin treatment | Retrospective study | 3 |
| Jiang and Zuo [74] | DF can improve efficacy of combination therapy for hearing loss > 100 dB HL | Retrospective case–control study | 3 |
| Weiss et al. [75] | No difference in hearing results with ancrod treatment vs. placebo | RCT | 2 |
| Wang et al. [80] | Significant improvement with DF + Ginaton + glucocorticoids treatment | Retrospective case–control study | 3 |
| N-ACETYLCYSTEINE | |||
| Study | Main Finding | Type of Study | Level of Evidence |
| Kranzer et al. [81] | Otoprotective effect of NAC in preventing aminoglycoside-induced ototoxicity while tuberculosis treatment | SR/Meta-analysis | 1 |
| Angeli et al. [84] | Significant improvement with oral prednisolone + IT dexamethasone + NAC | Case–control | 2 |
| Chen et al. [85] | Better hearing improvement in patients treated with NAC alone | Case–control | 2 |
| Kouka et al. [89] | Better hearing outcomes with PT + NAC compared to PT alone | Retrospective observational study | 3 |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herrera, M.; García-Berrocal, J.R.; García-Arumi, A.; Lavilla, M.J.; Plaza, G.; Grupo de Trabajo de la Comisión de Audiología de la SEORL. Update on consensus on diagnosis and treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp. 2019, 70, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Tsai-Do, B.S.; Schwartz, S.R.; Bontempo, L.J.; Faucett, E.A.; Finestone, S.A.; Hollingsworth, D.B.; Kelley, D.M.; Kmucha, S.T.; Moonis, G.; et al. Clinical practice guideline: Sudden hearing loss (update). Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 161, S1–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.A.; Chung, J.H. Contemporary Review of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Management and Prognosis. J. Audiol. Otol. 2024, 28, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachler, R.J.; Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Archer, S.M.; Rosenfeld, R.M.; Schwartz, S.R.; Barrs, D.M.; Brown, S.R.; Fife, T.D.; Ford, P.; Ganiats, T.G.; et al. Clinical practice guideline: Sudden hearing loss. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 146, S1–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plontke, S. Diagnosis and therapy of sudden hearing loss. GMS Curr. Top Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 16, Doc05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.R.; Byl, F.M.; Laird, N. The efficacy of steroids in the treatment of idiopathic sudden hearing loss. A double-blind clinical study. Arch. Otolaryngol. Chic. Ill 1960 1980, 106, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, B.F. Autoinmune sensorineural hearing loss. Ann. Otol. Rhino. Laryngol. 1979, 88, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, M.; Younes, E.; Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Ito, J.; Plontke, S.; O’Leary, S.; Sterkers, O. International consensus (ICON) on treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2018, 135, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, M.; Uzsaly, J.; Bodzai, G.; Pap, I.; Lippai, B.; Dergez, T.; Németh, A.; Gerlinger, I.; Szanyi, I.; Bakó, P. Efficacy of high dose systemic versus combined (systemic and intratympanic) corticosteroid therapy in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A prospective randomized trial and risk factor analysis. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2024, 45, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, H.; Choo, D.; Rosenberg, S.I.; Kuhn, J.; Seidman, M.; Stein, I. Intratympanic steroid treatment of inner ear disease and tinnitus (preliminary report). Ear Nose Throat J. 1996, 75, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnes, L.S.; Sun, A.-H.; Freeman, D.J. Corticosteroid pharmacokinetics in the inner ear fluids: An animal study followed by clinical application. Laryngoscope 1999, 109, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosrati-Zarenoe, R.; Hultcrantz, E. Corticosteroid treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: Randomized triple-blind placebo-controlled trial. Otol. Neurotol. 2012, 33, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plontke, S.K.; Girndt, M.; Meisner, C.; Fischer, I.; Böselt, I.; Löhler, J.; Ludwig-Kraus, B.; Richter, M.; Steighardt, J.; Reuter, B.; et al. High-Dose Glucocorticoids for the Treatment of Sudden Hearing Loss. NEJM Evid. 2024, 3, EVIDoa2300172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipo, R.; Attanasio, G.; Russo, F.Y.; Viccaro, M.; Mancini, P.; Covelli, E. Intratympanic steroid therapy in moderate sudden hearing loss: A randomized, triple blind, placebo-controlled trial. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavigne, P.; Lavigne, F.; Saliba, I. Intratympanic corticosteroids injections: A systematic review of literature. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 273, 2271–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Feng, G.; Wang, H.; Feng, Y. Intratympanic Steroid Therapy as a Salvage Treatment for Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss After Failure of Conventional Therapy: A Meta-analysis of Randomized, Controlled Trials. Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S.S. Intratympanic dexamethasone for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: Clinical and laboratory evaluation. Otol. Neurotol. 2001, 22, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoda, R.; Masuyama, K.; Habu, K.; Yumoto, E. Initial steroid hormone dose in the treatment of idiopathic sudden deafness. Am. J. Otol. 2000, 21, 819–825. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.Y.; Halpin, C.; Raush, S.D. Oral steroid treatment of sudden onset sensorineural hearing loss: A ten year retrospective analysis. Otol. Neurotol. 2003, 24, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Mubiru, S.; O´Leary, S. Steroids for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, 7, CD003998. [Google Scholar]
- Conlin, A.E.; Parnes, L.S. Treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: I. A systematic review. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2007, 133, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crane, R.A.; Camilon, M.; Nguyen, S.; Meyer, T.A. Steroids for treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado-Fernández, M.; Kornetsky, S.; Rubio-Rodríguez, L. Ethics of placebo control trials for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 155, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, A.; Lualhati, A.; Lin, H.; Burchette, R.; Cueva, R. A prospective, multi-centered study of the treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss with combination therapy versus high-dose prednisone alone: A 139 patient follow-up. Otol. Neurotol. 2014, 35, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Yin, X.; Du, X.; Sun, C. Combined Intratympanic and Systemic Use of Steroids as a First-Line Treatment for Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized, Controlled Trials. Otol. Neurotol. 2017, 38, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebau, A.; Pogorzelski, O.; Salt, A.N.; Plontke, S.K. Hearing Changes After Intratympanically Applied Steroids for Primary Therapy of Sudden Hearing Loss: A Meta-analysis Using Mathematical Simulations of Drug Delivery Protocols. Otol. Neurotol. 2017, 38, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plontke, S.K.; Meisner, C.; Agrawal, S.; Cayé-Thomasen, P.; Galbraith, K.; Mikulec, A.A.; Parnes, L.; Premakumar, Y.; Reiber, J.; Schilder, A.G.; et al. Intratympanic corticosteroids for sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 7, CD008080. [Google Scholar]
- Andrianakis, A.; Moser, U.; Kiss, P.; Holzmeister, C.; Andrianakis, D.; Tomazic, P.V.; Wolf, A.; Graupp, M. Comparison of two different intratympanic corticosteroid injection protocols as salvage treatments for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 279, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Wakasugi, T.; Kitamura, T.; Koizumi, H.; Do, B.H.; Ohbuchi, T. Comparison of 2 and 4 Intratympanic Steroid Injections in the Treatment of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Ann. Otol. Rhino Laryngol. 2018, 127, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, K.; Shi, Y.; Li, W.; Cheng, Y.; Nurtai, M.; Ma, J.; Yu, R. Intratympanic steroid as salvage therapy for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: An overview of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2025, 282, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrianakis, A.; Moser, U.; Wolf, A.; Kiss, P.; Holzmeister, C.; Tomazic, P.V.; Graupp, M. Intratympanic Triamcinolone Acetonide as a Salvage Treatment for Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Audiol. Neurootol. 2021, 2021, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rommelspacher, H.; Bera, S.; Brommer, B.; Ward, R.; Kwiatkowska, M.; Zygmunt, T.; Theden, F.; Üsekes, B.; Eren, N.; Nieratschker, M.; et al. A single dose of AC102 restores hearing in a guinea pig model of noise-induced hearing loss to almost prenoise levels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroud, M.H.; Calcaterra, T.C. Spontaneus perilymph fistulas. Laryngoscope 1970, 113, 303–306. [Google Scholar]
- Goodhill, V. Labyrinthine membrane rupture in sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Proc. R Soc. Med. 1976, 69, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prenzler, N.K.; Schwab, B.; Kaplan, D.M.; El-Saied, S. The role of explorative tympanotomy in patients with sudden sensorineural hearing loss with and without perilymphatic fistula. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2018, 39, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoch, S.; Vomhof, T.; Teymoortash, A. Critical Evaluation of Round Window Membrane Sealing in the Treatment of Idiopathic Sudden Unilateral Hearing Loss. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 8, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.P.; Drewermann, S.; Voelter, C.; Dazert, S. Prognostic factors regarding the hearing outcome in severe to profound sudden sensorineural hearing loss treated by tympanotomy and sealing of labyrinthine windows after ineffective systemic corticosteroid application. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 275, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann-Harildstad, G.; Stenklev, N.C.; Myrvoll, E.; Jablonski, G.; Klingenberg, O. Beta-trace protein as a diagnostic marker for perilymphatic fluid fistula: A prospective controlled pilot study to test a sample collection technique. Otol. Neurotol. 2011, 32, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.; Mihailovic, D.; Riemann, C.; Kilgué, A.; Pfeiffer, C.J.; Gehl, H.B.; Scholtz, L.U.; Todt, I. MRI-Based Inner Ear Assessment and Cochlin Tomoprotein-Based Evaluation of Perilymphatic Fistula in Patients with Sudden Hearing Loss. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilgue, A.; Kim, R.; Scholtz, L.U.; Riemann, C.; Pfeiffer, C.J.; Schürmann, M.; Todt, I. Window Coverage and Liquid Biopsy in the First-Line Therapy of Severe Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrking, E.; Wisst, F.; Remmert, S.; Sommer, K. Intraoperative assessment of perilymphatic fistulas with intrathecal administration of fluorescein. Laryngoscope 2002, 112, 1614–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, M.; Plaza, G. Aetiology of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Vascular, Viral or due to Perilymphatic Fistula. In Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Nagai, T.; Nagai, M. Labyrinthine window rupture as a cause of acute sensorineural hearing loss. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 269, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Heilen, S.; Lang, C.P.; Warnecke, A.; Lenarz, T.; Durisin, M. Exploratory tympanotomy in sudden sensorineural hearing loss for the identification of a perilympathic fistula-retrospective analysis and review of the literature. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2020, 134, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampfner, D.; Anagiotos, A.; Luers, J.C.; Hüttenbrink, K.B.; Preuss, S.F. Analysis of 101 patients with severe to profound sudden unilateral hearing loss treated with explorative tympanotomy and sealing of the round window membrane. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 271, 2145–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuzuki, N.; Wasano, K. Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A review focused on the contribution of vascular pathologies. Auris Nasus Larynx 2024, 51, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoes, J.; Vlaminck, S.; Seica, R.M.F.; Acke, F.; Miguets, A.C.E. Cardiovascular risk and sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 2023, 133, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, E.S.; Swisher, A.R.; Ansari, G.N.; Rivero, A. Cardiovascular risk factors in patients with sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2023, 168, 907–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oussoren, F.K.; Schermer, T.R.; van Leenwen, R.B.; Bruintjes, T.D. Cardiovascular risk factors, cerebral small vessel disease, and subsequent risk of stroke in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: Systematic review and meta-analyses of the current literature. Audiol. Neurootol. 2024, 29, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Jang, S.I.; Hurh, K.; Park, E.C.; Kim, S.H. Association between Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss and the Risk of Cardio Cerebrovascular Disease. Laryngoscope 2024, 134, 2372–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitoh, R.; Nishio, S.Y.; Sato, H.; Ikezono, T.; Morita, S.; Wada, T.; Usami, S.I. Research Group on Intractable Hearing Disorders and Japan Audiological Society. Clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute sensorineural hearing loss. Auris Nasus Larynx 2024, 51, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Ji, X.; Wu, J. The role of hyperbaric oxygen in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Med. Gas. Res. 2024, 4, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshua, T.G.; Ayub, A.; Wijesinghe, P.; Nunez, D.A. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for patients with sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2022, 148, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayoumy, A.B.; Lammet van der Veen, E.; Alexander de Ru, J. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy vs Medical Therapy for Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 145, 699–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, T.M.; Hwang, D.; Lee, J.S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.M. Addition of hyperbaric oxygen therapy vs medical therapy alone for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 144, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody-Antonio, S.A.; Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Derebey, M.J. Is it time to encourage hyperbaric oxygen therapy in combination with medical treatment for sudden sensorineural hearing loss? JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2022, 148, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alter, I.L.; Hamiter, M.; Lalwani, A.K. Is Hyperbaric Oxygen Effective in the Treatment of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss? Laryngoscope 2024, 134, 504–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, X.; Lei, Q.; Jin, X.; Deng, X.; Xie, H. Efficacy of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in treating sudden sensorineural hearing loss: An umbrella review. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1453055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Lozano, J.; Martínez Pizarro, S. Eficacia de la oxigenoterapia hiperbárica como adyuvante en la pérdida auditiva neurosensorial repentina. Revisión Sistemática. Rev. ORL 2024, 15, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erygit, B.; Ziylan, F.; Yaz, F.; Thomeer, H.G.X.M. The effectivenesss of hyberbaric oxygen in patients with idiopathic sensorineural hearing loss: A systematyc review. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 275, 2893–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Feng, Y.; Xia, L.; Sun, C. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy versus intratympanic steroid for salvage treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Otol. Neurotol. 2021, 42, e980–e986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, B.; Niu, K.; Ku, W.; Xie, W.; Dai, Q.; Hellström, S.; Duan, M. Comparison of the therapeutic results with/without additional hyperbaric oxygen therapy in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A randomized prospective study. Audiol. Neurootol. 2021, 26, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavaliere, M.; De Luca, P.; Scarpa, A.; Strzalkowski, A.M.; Ralli, M.; Calvanese, M.; Savignano, L.; Viola, P.; Cassandro, C.; Chiarella, G.; et al. Combination of hyperbaric oxygen therapy and oral steroids for the treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: Early or late? Medicina 2022, 58, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, T.C.; Chao, W.C.; Yang, C.H.; Tsai, M.S.; Tsai, Y.T.; Lee, Y.C. Intratympanic steroid injection versus hyperbaric oxygen therapy in refractory sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A meta-analysis. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 279, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.H.; Wu, R.W.; Hwang, C.F. Comparison of intratympanic steroid injection, hyperbaric oxygen and combination therapy in refractory sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otol. Neurotol. 2012, 34, 1411–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Qiu, X.; Hu, J.; Ma, Z. Comparison of intratympanic dexamethasone therapy and hyperbaric oxygen therapy for salvage treatment of refractory high-frequency sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2018, 39, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Chang, C.H.; Chang, C.J.; Ko, J.Y.; Wu, S.Y.; Kuo, P.H. Salvage therapy for refractory sudden sensorineural hearing loss (RSSNHL): A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Int. J. Audiol. 2024, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanda, N.; Sawabe, M.; Kabaya, K.; Kawaguchi, M.; Fukushima, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Maseki, S.; Niwa, M.; Mori, H.; Hyodo, Y.; et al. Clinical impact of hyperbaric oxygen therapy combined with steroid treatment for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A case-control study. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2024, 4, e1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, K.; Takei, S.; Inoue, Y.; Kanzaki, J. Effect of prostaglandin E1 on idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A double-blinded clinical study. Otol. Neurotol. 2002, 23, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Hato, N.; Nishio, S.Y.; Kitoh, R.; Ogawa, K.; Kanzaki, S.; Sone, M.; Fukuda, S.; Hara, A.; Ikezono, T.; et al. The effect of initial treatment on hearing prognosis in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A nationwide survey in Japan. Acta. Otolaryngol. 2017, 137, S30–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, S.; Kusunoki, T.; Honma, H.; Kidokoro, Y.; Ikeda, K. Efficacy of the additional effect of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in combination of systemic steroid and prostaglandin E1 for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2020, 41, 102363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, T.; Matsunaga, T.; Asai, H.; Kawamoto, K.; Kusakari, J.; Nomura, Y.; Oda, M.; Yanagita, N.; Niwa, H.; Uemura, T.; et al. Efficacy of defibrinogenation and steroid therapies on sudden deafness. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1988, 114, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Huang, H.; Mei, L.; He, C.; Cai, X.; Jiang, L.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, X. Short-term effects of intravenous batroxobin in treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A propensity score-matched study. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1102297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.Z.; Zuo, W.Q. Batroxobin can improve the efficacy of combination therapy for profound sudden sensorineural hearing loss greater than but not less than 100 dB HL. J. Laryngol. Otol. JLO 2024, 138, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, B.G.; Spiegel, J.L.; Becker, S.; Strieth, S.; Olzowy, B.; Bertlich, M.; Fořt, T.; Lenarz, T.; Ihler, F.; Canis, M. Randomized, placebo-controlled study on efficacy, safety and tolerability of drug-induced defibrinogenation for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: The lessons learned. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2023, 280, 4009–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Q.; Han, B.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Z. Efficacy and fibrinogen correlations of defibrinogen therapy in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, T.; Kaiser, T.; Scholz, M.; Bachmann, A.; Ceglarek, U.; Hesse, G.; Hagemeyer, B.; Stumvoll, M.; Thiery, J.; Dietz, A. Fibrinogen is not a prognostic factor for response to HELP-apheresis in sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSHL). Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 272, 3693–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Herraiz, N.; Saz-Lara, A.; Cavero-Redondo, I.; Lever-Megina, C.G.; Martínez-Cifuentes, Ó.; Otero-Luis, I. Efficacy of Apheresis in the Remission of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Ther. 2025, 47, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, B.E.; Durstenfeld, A.; Roehm, P.C. Viral causes of hearing loss: A review for hearing health professionals. Trends Hear. 2014, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, F. Sordera Brusca Neurosensorial Idiopática. Análisis de Factores de Riesgo Cardiovascular y Genéticos. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Conlin, A.E.; Parnes, L.S. Treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: II. A Meta-analysis. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2007, 133, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Park, S.M.; Han, C.; Lee, J.W.; Kong, T.H.; Seo, Y.J. Does Herpes Virus Reactivation Affect Prognosis in Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss? Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 10, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranzer, K.; Elamin, W.F.; Cox, H.; Seddon, J.A.; Ford, N.; Drobniewski, F. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of N-acetylcysteine in preventing aminoglycoside-induced ototoxicity: Implications for the treatment of multidrug-resistant TB. Thorax 2015, 70, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeli, S.I.; Abi-Hachem, R.N.; Vivero, R.J.; Telischi, F.T.; Machado, J.J. L-N-Acetylcysteine treatment is associated with improved hearing outcome in sudden idiopathic sensorineural hearing loss. Acta. Otolaryngol. 2012, 132, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Young, Y.H. N-acetylcysteine as a single therapy for sudden deafness. Acta. Otolaryngol. 2017, 137, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Chen, S.; Xu, K.; Jin, Y.; Niu, X.; Xie, L.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, X.Z.; Sun, Y. N-Acetylcysteine Combined with Dexamethasone Treatment Improves Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss and Attenuates Hair Cell Death Caused by ROS Stress. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 18, 659486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.L.; Ho, C.Y.; Chin, S.C. Effects of oral N-acetylcysteine combined with oral prednisolone on idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Medicine 2022, 101, e29792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Wang, M.; Niu, X.; Yu, H.; Yue, J.X.; Sun, Y. Effect of N-acetyl-cysteine treatment on sensorineural hearing loss: A meta-analysis. World J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2022, 8, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouka, M.; Bevern, N.; Bitter, J.; Guntinas-Lichius, O. N-Acetylcysteine combined with prednisolone treatment shows better hearing outcome than treatment with prednisolone alone for patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A retrospective observational study. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2024, 281, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES/CONSENSUS STATEMENTS
| SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
|
CLINICAL TRIALS
| META-ANALYSIS
|
| Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Main Finding | Type of Study | Level of Evidence |
| Erygit et al. [60] | Significant improvement with HBOT. | SR/Meta-analysis | 1 |
| Lei et al. [61] | Advantage of both IT steroids + HBOT. Not notable variation in the effect between them when used as rescue treatment. | SR/Meta-analysis | 1 |
| Joshua et al. [53] | Significant improvement with the addition of HBOT (10.3 db). | SR/Meta-analysis | 1 |
| Tong et al. [62] | More significant improvement with HBOT + PT compared with PT alone; substantial improvement in patients with a younger age, rapidly started treatment, and mild–moderate hearing loss. | RCT | 2 |
| Cavaliere et al. [63] | The best results were obtained when monotherapy with HBOT was initiated in the first 7 days, while the HBOT and oral steroid combination showed more substantial benefits later. | RCT | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Izquierdo, C.; Herrera, M.; Avdiyuk, A.; Rodríguez-Ocaña, D.; Plaza, G. Current Role of the Nonsteroid Treatment of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss (ISSNHL): A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2811. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082811
Rodríguez-Izquierdo C, Herrera M, Avdiyuk A, Rodríguez-Ocaña D, Plaza G. Current Role of the Nonsteroid Treatment of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss (ISSNHL): A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(8):2811. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082811
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Izquierdo, Concepción, Mayte Herrera, Anastasiya Avdiyuk, Daniel Rodríguez-Ocaña, and Guillermo Plaza. 2025. "Current Role of the Nonsteroid Treatment of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss (ISSNHL): A Narrative Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 8: 2811. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082811
APA StyleRodríguez-Izquierdo, C., Herrera, M., Avdiyuk, A., Rodríguez-Ocaña, D., & Plaza, G. (2025). Current Role of the Nonsteroid Treatment of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss (ISSNHL): A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(8), 2811. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082811