Point-of-Care Virtual Planning and 3D Printing in Facial Trauma: A 10-Year Experience at a Single Institution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Data Collection
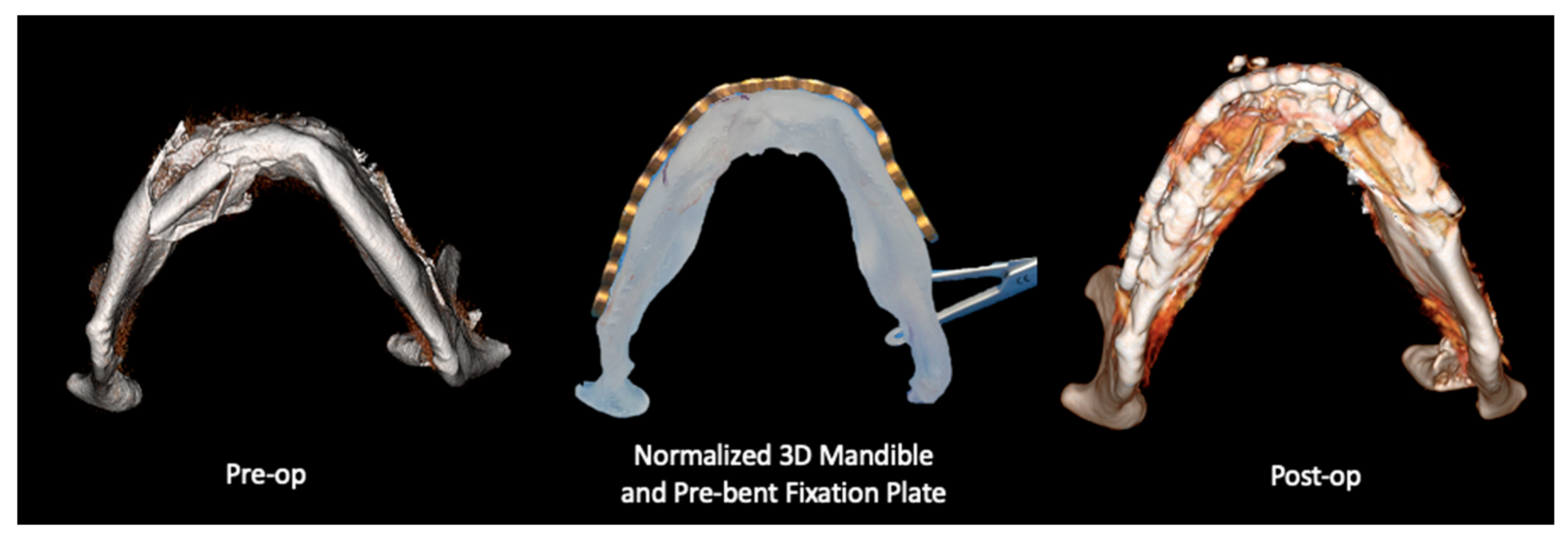
2.2.1. Three-Dimensional (3D) Segmentation Workflow
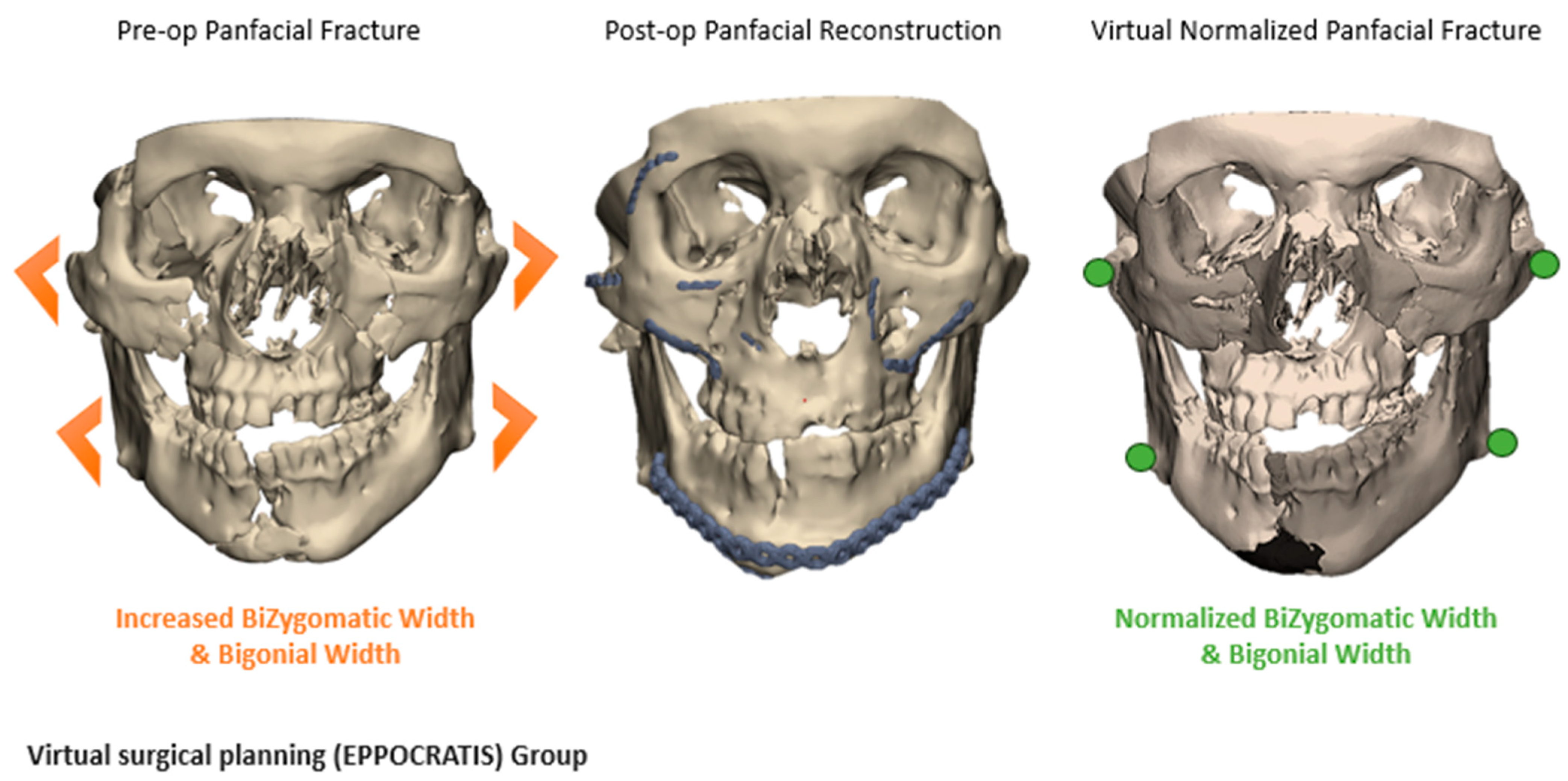
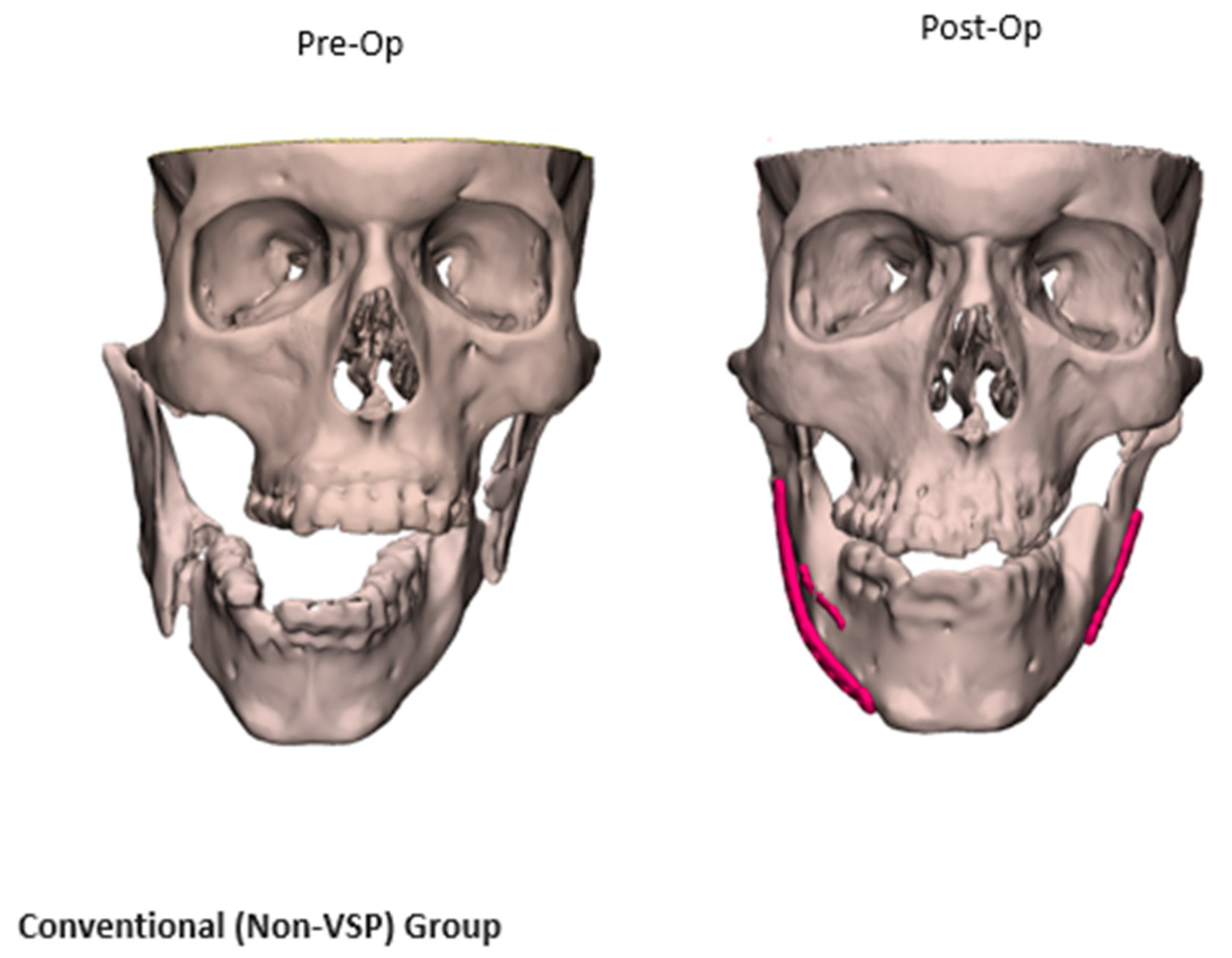
2.2.2. Comparative Analysis of VSP and Non-VSP Groups
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Patients’ Characteristics
3.2. Injury Mechanisms and Fracture Patterns
3.3. VSP vs. Non-VSP Groups’ Characteristics
3.4. VSP vs. Non-VSP Groups’ Characteristics
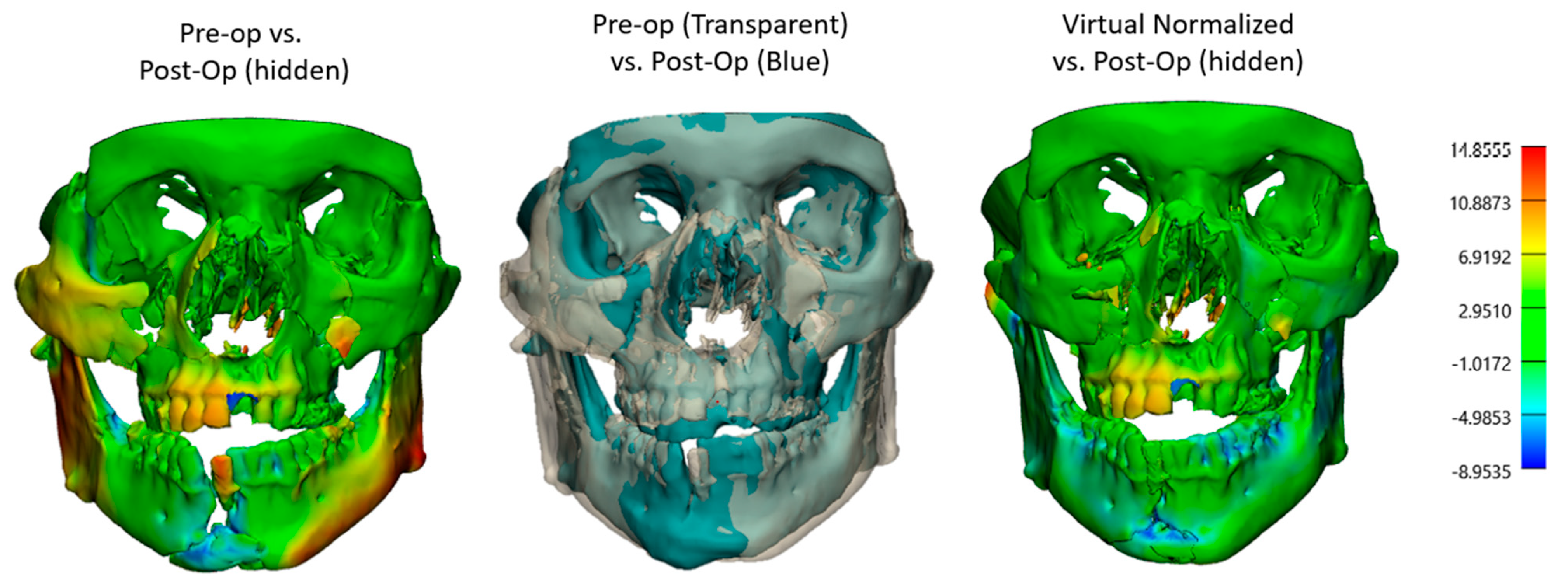
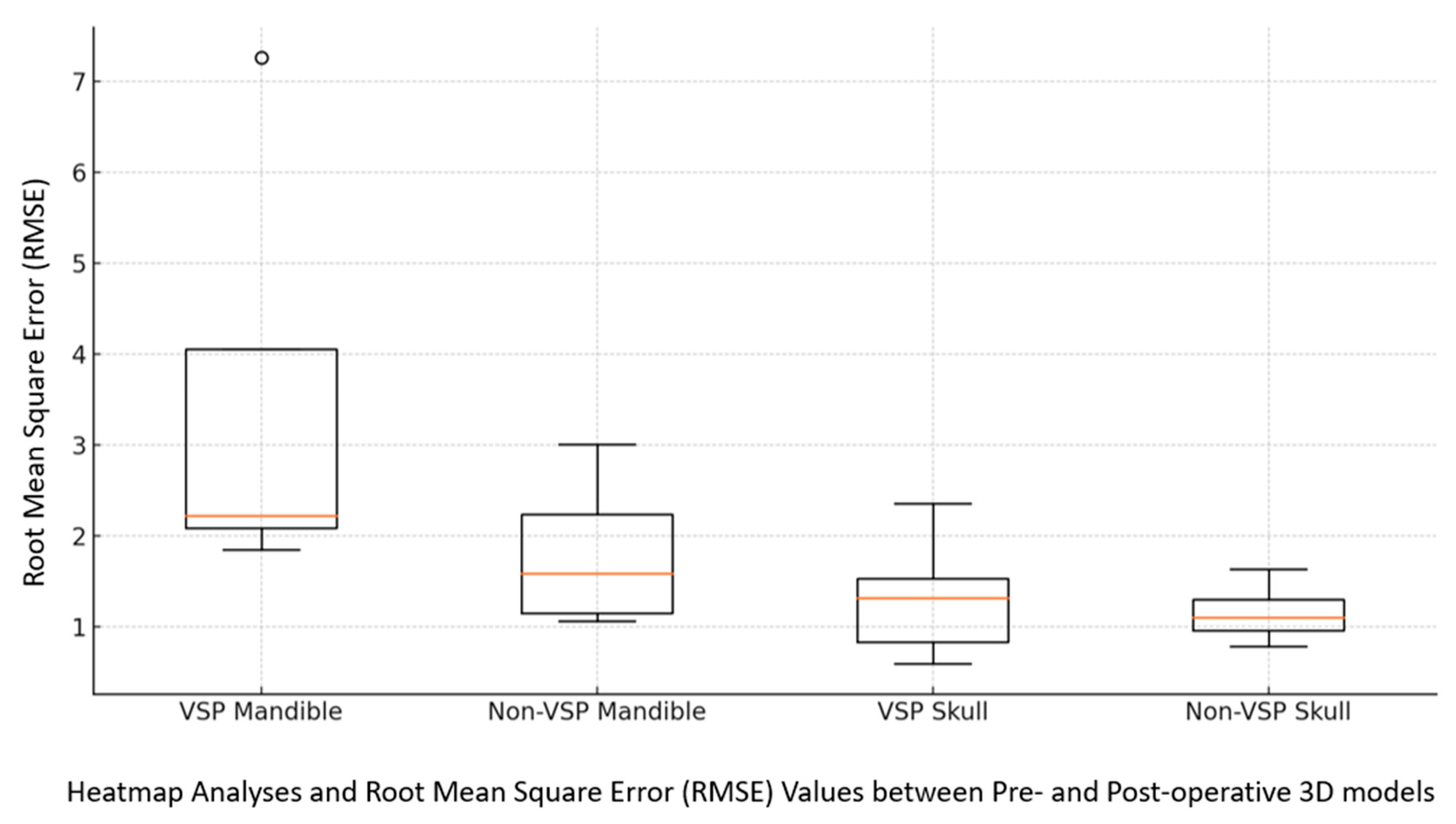
3.5. Fracture Reduction Accuracy
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3D | Three-dimensional |
| VSP | Virtual surgical planning |
| 3DP | Three-dimensional printing |
| RMSE | Root mean square error |
| EPPOCRATIS | Expedited Preoperative Point of Care for Fracture Reduction to Normalized Anatomy and Three-Dimensional Printing to Improve Surgical Outcomes |
References
- Catapano, J.; Fialkov, J.A.; Binhammer, P.A.; McMillan, C.; Antonyshyn, O.M. A New System for Severity Scoring of Facial Fractures: Development and Validation. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2010, 21, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, E.J.; Price, D.L.; Van Abel, K.M.; Janus, J.R.; Moore, E.T.; Martin, E.; Morris, J.M.; Alexander, A.E. Association of Virtual Surgical Planning with External Incisions in Complex Maxillectomy Reconstruction. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2021, 147, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassfeld, S.; Mühling, J. Computer assisted oral and maxillofacial surgery--a review and an assessment of technology. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2001, 30, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanasono, M.M.; Jacob, R.F.; Bidaut, L.; Robb, G.L.; Skoracki, R.J. Midfacial reconstruction using virtual planning, rapid prototype modeling, and stereotactic navigation. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2010, 126, 2002–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, S.; Cevidanes, L.H.; Styner, M.; Kim, H.; Reyes, M.; Proffit, W.; Turvey, T. Comparison of actual surgical outcomes and 3-dimensional surgical simulations. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 68, 2412–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sears, V.A.; Morris, J.M. Establishing a Point-of-Care Virtual Planning and 3D Printing Program. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2022, 36, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranckx, J.J.; Desmet, O.; Bila, M.; Wittesaele, W.; Wilssens, N.; Poorten, V.V. Maxillomandibular Reconstruction Using Insourced Virtual Surgical Planning and Homemade CAD/CAM: A Single-Center Evolution in 75 Patients. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2023, 152, 143e–154e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-H.; Papay, F.A.; Yanof, J.; West, K.; Bassiri Gharb, B.; Rampazzo, A.; Gastman, B.; Schwarz, G.S. Mixed Reality and 3D Printed Models for Planning and Execution of Face Transplantation. Ann. Surg. 2021, 274, e1238–e1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf, B.A.; Morris, J.M.; Kuruoglu, D. EPPOCRATIS: A Point-of-Care Utilization of Virtual Surgical Planning and Three-Dimensional Printing for the Management of Acute Craniomaxillofacial Trauma. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf, B.; Kuruoglu, D.; Cantwell, S.R.; Alexander, A.E.; Dickens, H.J.; Morris, J.M. EPPOCRATIS: Expedited Preoperative Point-of-Care Reduction of Fractures to Normalized Anatomy and Three-Dimensional Printing to Improve Surgical Outcomes. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2022, 149, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, B.J.; Park, E.P.; Christensen, B.J.; Danrad, R. On-Site 3-Dimensional Printing and Preoperative Adaptation Decrease Operative Time for Mandibular Fracture Repair. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 76, 1950.e1–1950.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materialise. Point-of-Care 3D Printing; Materialise Healthcare; Materialise: Leuven, Belgium, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Aissa, J.; Boos, J.; Sawicki, L.M.; Heinzler, N.; Krzymyk, K.; Sedlmair, M.; Kröpil, P.; Antoch, G.; Thomas, C. Iterative metal artefact reduction (MAR) in postsurgical chest CT: Comparison of three iMAR-algorithms. Br. J. Radiol. 2017, 90, 20160778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittner-Frank, M.; Strassl, A.; Unger, E.; Hirtler, L.; Eckhart, B.; Koenigshofer, M.; Stoegner, A.; Nia, A.; Popp, D.; Kainberger, F.; et al. Accuracy Analysis of 3D Bone Fracture Models: Effects of Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging and Image Segmentation. J. Imaging Inform. Med. 2024, 37, 1889–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbate, V.; Committeri, U.; Troise, S.; Bonavolontà, P.; Vaira, L.A.; Gabriele, G.; Biglioli, F.; Tarabbia, F.; Califano, L.; Dell’Aversana Orabona, G. Virtual Surgical Reduction in Atrophic Edentulous Mandible Fractures: A Novel Approach Based on “in House” Digital Work-Flow. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.T.; Lin, H.H.; Liou, E.J.; Lo, L.J. Three-dimensional surgical simulation improves the planning for correction of facial prognathism and asymmetry: A qualitative and quantitative study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.T.; Denadai, R.; Lo, L.-J.; Lin, H.-H. Average 3D Skeletofacial Model as a Template for Maxillomandibular Repositioning During Virtual Orthognathic Surgical Planning. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2024, 153, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seruya, M.; Fisher, M.; Rodriguez, E.D. Computer-Assisted versus Conventional Free Fibula Flap Technique for Craniofacial Reconstruction: An Outcomes Comparison. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 132, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troise, S.; De Fazio, G.R.; Committeri, U.; Spinelli, R.; Nocera, M.; Carraturo, E.; Salzano, G.; Arena, A.; Abbate, V.; Bonavolontà, P.; et al. Mandibular reconstruction after post-traumatic complex fracture: Comparison analysis between traditional and virtually planned surgery. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2025, 126, 102029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Wu, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, C.; Xu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S. Classifying and standardizing panfacial trauma according to anatomic categories and Facial Injury Severity Scale: A 10-year retrospective study. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavattero, E.; Ramieri, G.; Roccia, F.; Gerbino, G. Comparison of the Outcomes of Complex Orbital Fracture Repair with and without a Surgical Navigation System: A Prospective Cohort Study with Historical Controls. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 139, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, L.; Bouchard, S.; Bonapace-Potvin, M.; Bergeron, F. Intraoperative Surgical Navigation Reduces the Surgical Time Required to Treat Acute Major Facial Fractures. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 144, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

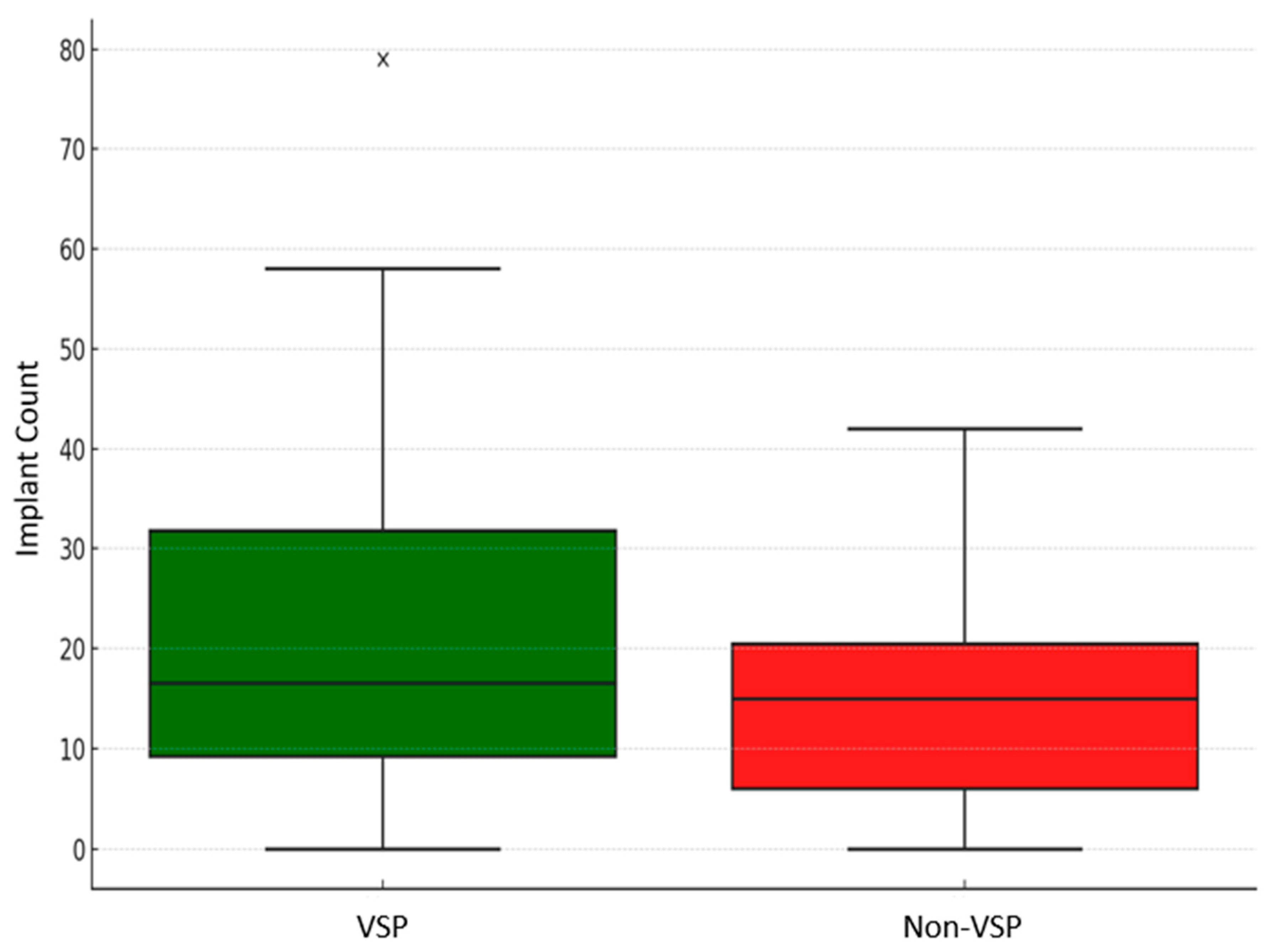



| Demographics and Comorbidities | Overall (n = 44) | VSP Group (n = 23) | Non-VSP Group (n = 21) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Age, mean (SD) in years | 35.6 (17) | 34 (15.7) | 37.4 (18) | 0.43 |
| Gender | Male (cisgender) (%) | 36 (82%) | 20 (87%) | 16 (76.2%) | 0.37 |
| BMI | BMI, mean (SD), kg/m2 | 26.14 (6.5) | 24.5 (6.4) | 27.9 (6) | 0.08 |
| Race and ethnicity | White (non-Hispanic, non-Latino) | 36 (81.2%) | 18 | 18 | 0.14 |
| Black | 2 (4.5%) | _ | 2 | ||
| Hispanic/Latino | 2 (4.5%) | 2 | _ | ||
| Asian | 2 (4.5%) | 2 | _ | ||
| Other | 2 (4.5%) | _ | 1 | ||
| Social Hx ^ | Alcohol use (%) | 14 (31.8%) | 7 (30.4%) | 7 (33.3%) | 0.84 |
| Alcoholic drinks/week (SD) | 6 (3.6) | 4.5 (1.5) | _ | ||
| Smoker (%) | 15 (34%) | 7 (30.4%) | 8 (38.1%) | 0.6 | |
| Smoking index (pack/year) (SD) | 7 | 382.3 (277.1) | 247.5 (123.1) | _ | |
| Drug use | 7 (15.9%) | 3 (13%) | 4 (19%) | 0.6 | |
| Comorbidities | Hypertension | _ | 2 | 1 | 0.6 |
| Diabetes mellitus | _ | 2 | 2 | 0.57 | |
| Others: Hyperlipidemia Coronary artery disease | _ | 4 | 5 |
| Demographics and Comorbidities | Overall (n = 44) | VSP Group (n = 23) | Non-VSP Group (n = 21) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanism of injury (%) | Motor Vehicle Accident (MVA) | 14 (31.8%) | 10 | 4 | 0.09 |
| Assault | 13 (29.5%) | 7 | 6 | 0.9 | |
| Falls | 4 (9.1%) | 3 | 1 | 0.4 | |
| Sports | 6 (13.6%) | 2 | 4 | 0.3 | |
| Animal Attack | 3 (6.8%) | 1 | 2 | 0.51 | |
| Not mentioned | 4 (9.1%) | ||||
| Surgical service | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | 44 (100.0%) | 23 | 21 | _ |
| Oculoplastic Surgery | 10 (22.7%) | 8 | 2 | 0.05 * | |
| Otolaryngology | 7 (15.9%) | 7 | 0 | 0.01 * | |
| Neurosurgery | 6 (13.6%) | 4 | 2 | 0.46 | |
| Orthopedic Surgery | 5 (11.4%) | 4 | 1 | 0.19 | |
| Reconstruction presentation | Primary (1ry) | 40 (91%) | 20 | 20 | _ |
| Secondary (2ry) | 4 (9.9%) | 3 | 1 | _ | |
| Fracture pattern (%) | Naso-orbito-ethmoid (NOE) Complex Fracture | 9 (20.5%) | 6 (26.1%) | 3 (14.3%) | 0.34 |
| Nasal Fracture | 4 (9.1%) | 1 (0.04%) | 3 (14.3%) | 0.26 | |
| Zygomaticomaxillary Complex (ZMC) Fracture | 20 (45.5%) | 10 (43.5%) | 10 (47.6%) | 0.79 | |
| Orbital Fracture | 5 (11.4%) | 4 (17.4%) | 1 (0.05%) | 0.2 | |
| Mandibular Fracture | 20 (45.5%) | 11 (47.8%) | 9 (42.9%) | 0.75 | |
| Panfacial + | 7 (15.9%) | 4 | 3 | 0.6 | |
| Frontal Sinus Involvement ++ | 6 (13.6%) | 4 | 2 | 0.5 | |
| Laterality | Unilateral (Rt/Lt) | 18 (44%) | 8 | 10 | 0.48 |
| Bilateral | 23 (56.1%) | 13 | 10 | ||
| Le Fort type (if mentioned) | Type I | 7 (63.6%) | 3 | 4 | 0.6 |
| Type II | 7 (63.6%) | 4 | 3 | 0.8 | |
| Type III | 4 (36.4%) | 2 | 2 | 0.9 | |
| Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) | 13 to 15: Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (mTBI) | 39 (88.6%) | 19 | 20 | 0.8 |
| 9 to 12: Moderate TBI | 4 (9.1%) | 3 | 1 | 0.2 | |
| 3 to 8: Severe TBI | 1 (2.3%) | 1 | _ | _ | |
| Abbreviated Injury Scale (AIS) grades | Minor | 18 (50.0%) | |||
| Moderate | 10 (27.8%) | ||||
| Severe (Not Life-Threatening) | 8 (22.2%) | ||||
| Severe (Life-Threatening, Survival Probable) | _ | ||||
| Surgery: patient class | Outpatient | 27 (61.4%) | 12 | 15 | 0.3 |
| Inpatient | 17 (38.6%) | 11 | 6 | ||
| ASA status | ASA 1 | 19 (43.2%) | 8 (34.8%) | 11 (52.4%) | 0.17 |
| ASA 2 | 16 (36.4%) | 8 (34.8%) | 8 (38.1%) | ||
| ASA 3 | 7 (15.9%) | 5 (21.7%) | 2 (9.5%) | ||
| ASA 4 | 2 (4.5%) | 2 (8.7%) | _ |
| Median (IQR) | SD | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anesthesia Time (hours): VSP Non-VSP | 5.8 (4.1–8.3) 4.6 (3.7–5.6) | 3.4 2.7 | 0.03 * |
| Procedure Time (hours): VSP Non-VSP | 3.8 (2.5–5.6) 2.7 (2.1–3.6) | 2.8 2.2 | 0.03 * |
| Length of Stay (days): VSP Non-VSP | 1.0 (1.0–3.0) 1.0 (0–1.0) | 6 4.1 | 0.3 |
| Blood Loss (cc): VSP Non-VSP | 50 (20–200) 50 (20–150) | 122.3 78.3 | 0.7 |
| Follow-Up Duration (days): VSP Non-VSP | 65 (34–169) 43 (30–74) | 238 356 | 0.2 |
| Anesthesia Time (minutes)/Implant: VSP Non-VSP | 15.4 (11.3–33.8) 19.3 (15.7–31.4) | 18.1 16.5 | 0.4 |
| Procedure Time (minutes)/Implant: VSP Non-VSP | 10.5 (6.7–22.5) 10.9 (9–17.7) | 11.6 11 | 0.5 |
| Blood Loss (cc)/Implant: VSP Non-VSP | 3.4 (1.7–5.4) 4.1 (2.1–6.4) | 3.9 5.1 | 0.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussein, S.M.; Kuruoglu, D.; Morris, J.M.; Sears, V.A.; Shehab, A.A.; Gibreel, W.; Sharaf, B.A. Point-of-Care Virtual Planning and 3D Printing in Facial Trauma: A 10-Year Experience at a Single Institution. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082788
Hussein SM, Kuruoglu D, Morris JM, Sears VA, Shehab AA, Gibreel W, Sharaf BA. Point-of-Care Virtual Planning and 3D Printing in Facial Trauma: A 10-Year Experience at a Single Institution. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(8):2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082788
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussein, Sara M., Doga Kuruoglu, Jonathan M. Morris, Victoria A. Sears, Abdallah A. Shehab, Waleed Gibreel, and Basel A. Sharaf. 2025. "Point-of-Care Virtual Planning and 3D Printing in Facial Trauma: A 10-Year Experience at a Single Institution" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 8: 2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082788
APA StyleHussein, S. M., Kuruoglu, D., Morris, J. M., Sears, V. A., Shehab, A. A., Gibreel, W., & Sharaf, B. A. (2025). Point-of-Care Virtual Planning and 3D Printing in Facial Trauma: A 10-Year Experience at a Single Institution. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(8), 2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082788






