Migraine and Tension-Type Headache Are Associated with Multiple Sclerosis: A Case–Control Study
Abstract
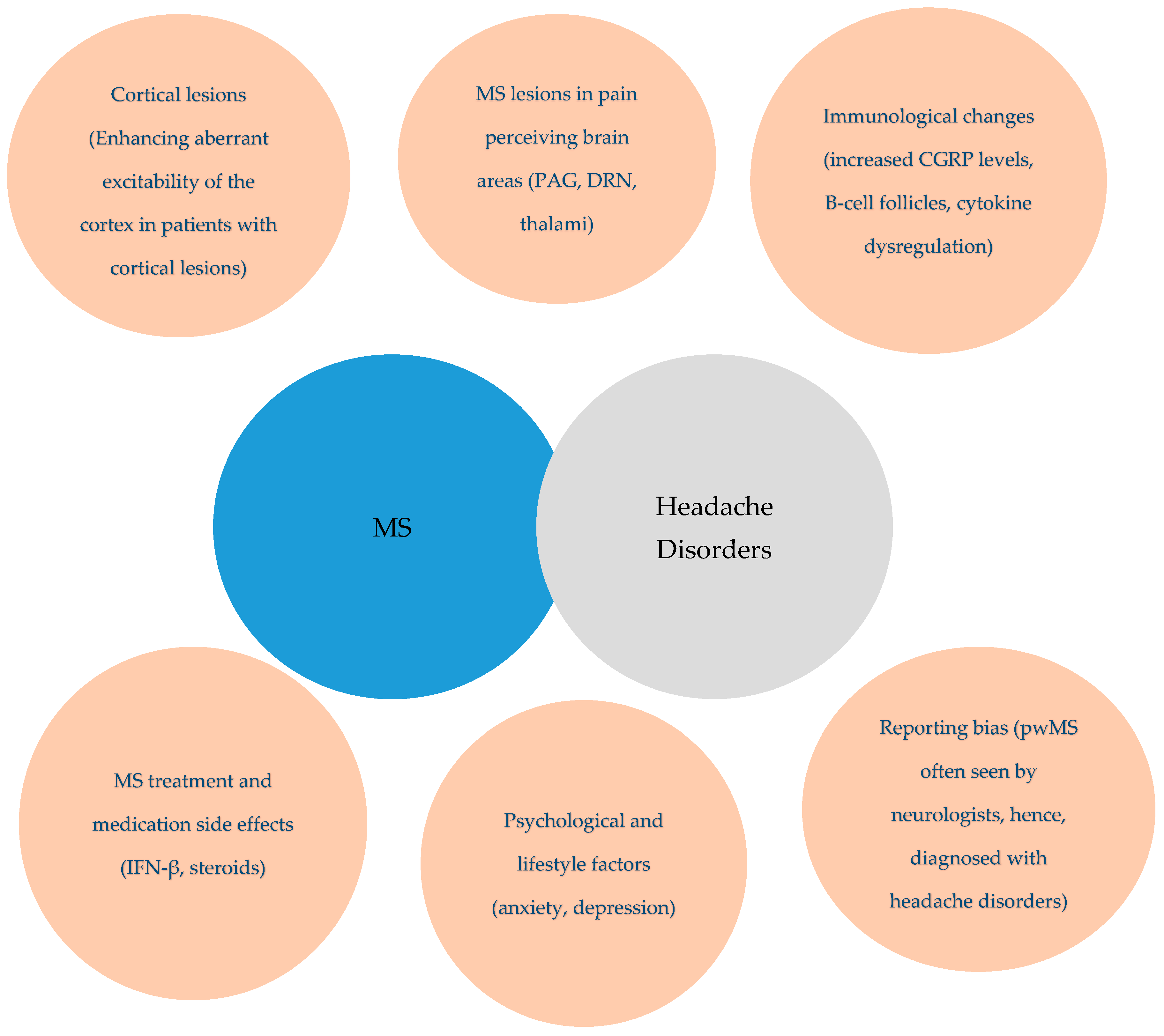
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Study Procedures and Data Collection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethical Considerations
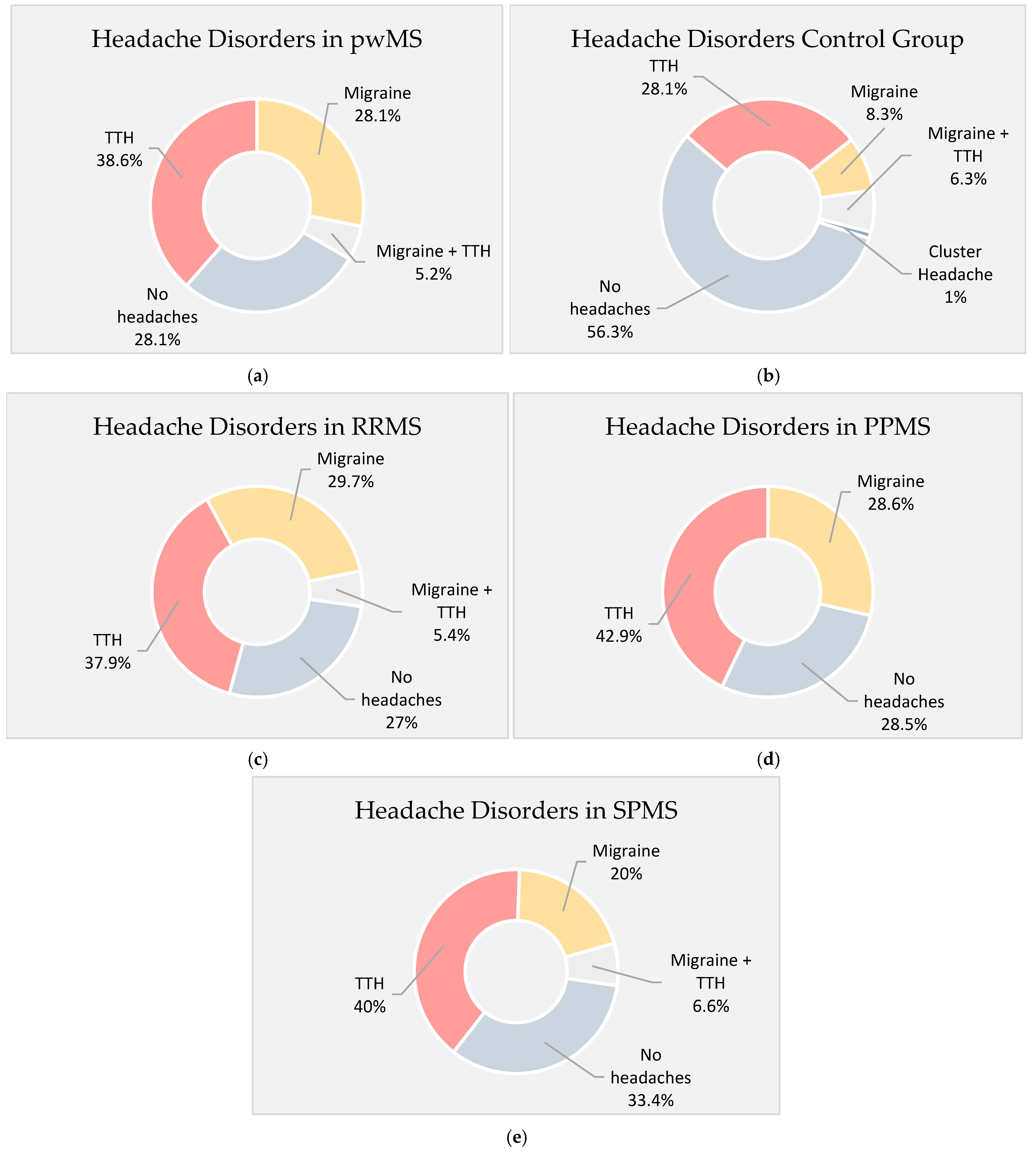
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CGRP | Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal Fluid |
| DRN | Dorsal Raphe Nucleus |
| EDSS | Expanded Disability Status Scale |
| HC | Healthy Controls |
| ICHD-3 | International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd Edition |
| LC | Locus Coeruleus |
| MS | Multiple Sclerosis |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| PAG | Periaqueductal Gray |
| PPMS | Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis |
| pwMS | People with Multiple Sclerosis |
| RRMS | Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SPMS | Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis |
| TTH | Tension-Type Headache |
References
- Stewart, W.F.; Lipton, R.B.; Liberman, J. Variation in migraine prevalence by race. Neurology 1996, 47, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosati, G. The prevalence of multiple sclerosis in the world: An update. Neurol. Sci. 2001, 22, 117–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Mantia, L. Headache and multiple sclerosis: Clinical and therapeutic correlations. Neurol. Sci. 2009, 30 (Suppl. S1), S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gklinos, P.; Mitsikostas, D.D. Migraine in multiple sclerosis patients: Potential links and treatment approach. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2023, 24, 1845–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kister, I.; Munger, K.L.; Herbert, J.; Ascherio, A. Increased risk of multiple sclerosis among women with migraine in the nurses’ health study II. Mult. Scler. J. 2012, 18, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorzon, M.; Zivadinov, R.; Nasuelli, D.; Dolfini, P.; Bosco, A.; Bratina, A.; Tommasi, M.A.; Locatelli, L.; Cazzato, G. Risk factors of multiple sclerosis: A case-control study. Neurol. Sci. 2003, 24, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, S.M.; Espir, M. Migraine and multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1969, 32, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolak, L.A.; Brown, S. Headaches and multiple sclerosis: A clinical study and review of the literature. J. Neurol. 1990, 237, 300–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, D.; La Mantia, L.; Rigamonti, A.; Usai, S.; Mascoli, N.; Milanese, C.; Bussone, G.; Besta, C. Prevalence of primary headaches in people with multiple sclerosis. Cephalalgia 2004, 24, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, H.; Matsushita, T.; Isobe, N.; Ishizu, T.; Ohyagi, Y.; Kira, J. Frequency of chronic headaches in Japanese patients with multiple sclerosis: With special reference to opticospinal and common forms of multiple sclerosis. Headache 2009, 49, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putzki, N.; Pfriem, A.; Limmroth, V.; Yaldizli, O.; Tettenborn, B.; Diener, H.C.; Katsarava, Z. Prevalence of migraine, tension-type headache, and trigeminal neuralgia in multiple sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2009, 16, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kister, I.; Caminero, A.B.; Monteith, T.S.; Soliman, A.; Bacon, T.E.; Bacon, J.H.; Kalina, J.T.; Inglese, M.; Herbert, J.; Lipton, R.B. Migraine is comorbid with multiple sclerosis and associated with a more symptomatic MS course. J. Headache Pain 2010, 11, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsiari, C.G.; Vikelis, M.; Paraskevopoulou, E.S.; Sfikakis, P.P.; Mitsikostas, D.D. Headache in systemic lupus erythematosus vs. multiple sclerosis: A prospective comparative study. Headache 2011, 51, 1398–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorgun, M.H.; Yucesan, C.; Yasemin, G. Headache in multiple sclerosis. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 43, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, G.; Marano, E.; Morra, V.B.; Lanzillo, R.; De Vito, M.; Parente, E.; Orefice, G. Multiple sclerosis and headache co-morbidity: A case-control study. Neurol. Sci. 2007, 28, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villani, V.; Prosperini, L.; Ciuffoli, A.; Pizzolato, R.; Salvetti, M.; Pozzilli, C.; Sette, G. Primary headache and multiple sclerosis: Preliminary results of a prospective study. Neurol. Sci. 2008, 29, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, A.; Patti, F.; Fermo, S.L.; Liberto, A.; Castiglione, A.; Laisa, P.; Garifoli, A.; La Naia, F.; Maimone, D.; Sorbello, V.; et al. Headache and multiple sclerosis: A population-based case-control study in Catania, Sicily. Cephalalgia 2008, 28, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möhrke, J.; Kropp, P.; Zettl, U.K. Headaches in multiple sclerosis patients might imply an inflammatorial process. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisset, X.; Ouchchane, L.; Guy, N.; Bayle, D.J.; Dallel, R.; Clavelou, P. Migraine headaches and pain with neuropathic characteristics: Comorbid conditions in patients with multiple sclerosis. Pain 2013, 154, 2691–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busillo, V.; Pizza, V.; Cassano, D.; Busillo, A.; Somma, M.R.; Capasso, A. Headache and multiple sclerosis. Pharmacologyonline 2014, 1, 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Terlizzi, R.; Merli, E.; Buccellato, E.; Giannini, G.; Favoni, V.; Pierangeli, G.; Salvi, F.; Cortelli, P.; Cevoli, S. P037. Headache in multiple sclerosis: Prevalence and clinical features in a case control-study. J. Headache Pain 2015, 16, A83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustavsen, M.W.; Celius, E.G.; Winsvold, B.S.; Moen, S.M.; Nygaard, G.O.; Berg-Hansen, P. Migraine and frequent tension-type headache are not associated with multiple sclerosis in a Norwegian case-control study. Mult. Scler. J.—Exp. Transl. Clin. 2016, 2, 2055217316682976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.; Wang, S.L.; Ugurlu, C.; Amezcua, L. Headaches in multiple sclerosis: Cross-sectional study of a multiethnic population. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2016, 143, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özer, G.; Ergün, U.; İnan, L.E. Headache in multiple sclerosis from a different perspective. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 9, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt, M.; Kropp, P.; Hoffmann, F.; Zettl, U.K. Headache at the time of first symptom manifestation of multiple sclerosis: A prospective, longitudinal study. Eur. Neurol. 2018, 80, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhardt, M.; Kropp, P.; Hoffmann, F.; Zettl, U.K. Headache in the course of multiple sclerosis: A prospective study. J. Neural Transm. 2019, 126, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckmann, Y.; Türe, S. Headache characteristics in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2019, 27, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gklinos, P.; Mitsikostas, D.D. Headache disorders in multiple sclerosis: Is there an association? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2024, 85, 105536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakpoor, J.; Handel, A.E.; Giovannoni, G.; Dobson, R.; Ramagopalan, S.V. Meta-analysis of the relationship between multiple sclerosis and migraine. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, J.R.; Chang, J.; Dublin, A.B.; Vijayan, N. The association of brainstem lesions with migraine-like headache: An imaging study of multiple sclerosis. Headache 2005, 45, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortorella, P.; Rocca, M.A.; Colombo, B.; Annovazzi, P.; Comi, G.; Filippi, M. Assessment of MRI abnormalities of the brainstem from patients with migraine and multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2006, 244, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biscetti, L.; De Vanna, G.; Cresta, E.; Corbelli, I.; Gaetani, L.; Cupini, L.; Calabresi, P.; Sarchielli, P. Headache and Immunological/Autoimmune Disorders: A Comprehensive Review of Available Epidemiological Evidence with Insights on Potential Underlying Mechanisms. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcziak, L.K.; Russo, A.F. Dural Immune Cells, CGRP, and Migraine. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 874193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jette, N.; Patten, S.; Williams, J.; Becker, W.; Wiebe, S. Comorbidity of Migraine and Psychiatric Disorders—A National Population-Based Study. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2008, 48, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmazny, A.; Hamdy, S.M.; Abdel-Naseer, M.; Shalaby, N.M.; Shehata, H.S.; Kishk, N.A.; Nada, M.A.; Mourad, H.S.; Hegazy, M.I.; Abdelalim, A.; et al. Interferon-Beta-Induced Headache in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis: Frequency and Characterization. J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantia, L.L.; D’Amico, D.; Rigamonti, A.; Mascoli, N.; Bussone, G.; Milanese, C. Interferon Treatment May Trigger Primary Headaches in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Mult. Scler. J. 2006, 12, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2021 Nervous System Disorders Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of disorders affecting the nervous system, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Neurol. 2024, 23, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.J.; Banwell, B.L.; Barkhof, F.; Carroll, W.M.; Coetzee, T.; Comi, G.; Correale, J.; Fazekas, F.; Filippi, M.; Freedman, M.S.; et al. Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions of the McDonald criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 629–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtzke, J.F. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: An expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 1983, 33, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-P.; Kwon, S.-H. Cognitive Effects of Antiepileptic Drugs. J. Clin. Neurol. 2008, 4, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branconnier, R.J.; DeVitt, D.R.; Cole, J.O.; Spera, K.F. Amitriptyline Selectively Disrupts Verbal Recall from Secondary Memory of the Normal Aged. Neurobiol. Aging 1982, 3, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spring, B.; Gelenberg, A.J.; Garvin, R.; Thompson, S. Amitriptyline, Clovoxamine and Cognitive Function: A Placebo-Controlled Comparison in Depressed Outpatients. Psychopharmacology 1992, 108, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, W.B.; Bradley, K.C.; Anjum, M.W.; Gebeline-Myers, C. Duloxetine Prophylaxis for Episodic Migraine in Persons without Depression: A Prospective Study. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2013, 108, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Azorín, D.; Martínez-Badillo, C.; Muñiz, J.C.; Gago-Veiga, A.B.; Sánchez, N.M.; González-Quintanilla, V.; Porta-Etessam, J.; Sierra-Mencía, A.; González-García, N.; González-Osorio, Y.; et al. CandeSpartan Study: Candesartan Spanish Response-Prediction and Tolerability Study in Migraine. Cephalalgia Int. J. Headache 2024, 44, 3331024241248833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Demographical and Clinical Data | ||
|---|---|---|
| MS | Controls | |
| Gender | ||
| Female—n (%) | 69 (71.9) | 66 (68.75%) |
| Male—n (%) | 27 (28.1) | 30 (31.25%) |
| Ethnicity—n (%) | ||
| Caucasian | 96 (100) | 96 (100) |
| Age (years) mean ± SD | 42.15 (12.81) | 37.16 (12.63) |
| Presenting symptom for pwMS—n (%) | ||
| Sensory | 33 (34%) | |
| Optic neuritis | 19 (20%) | |
| Motor | 14 (15%) | |
| Balance | 8 (8%) | |
| Diplopia | 7 (7%) | |
| Polysymptomatic | 12 (13%) | |
| Bladder symptoms | 2 (2%) | |
| Pain | 1 (1%) | |
| Diagnosis Method | ||
| Imaging + LP | 88 (92%) | |
| Imaging only | 8 (8%) | |
| Exclusion of Other Diagnoses | ||
| Imaging + CSF analysis + blood tests (MOG, AQP4) | 62 (65%) | |
| Imaging + CSF analysis | 26 (27%) | |
| Imaging only | 8 (8%) | |
| Mean age at MS diagnosis ± SD | 32.5 (6.3) | |
| Disease duration (years) mean ± SD | 8.57 (8.52) | |
| EDSS mean ± SD | 3.13 (1.88) | |
| Disease subtype | ||
| RRMS—n (%) | 77 (77.1) | |
| PPMS—n (%) | 7 (7.3) | |
| SPMS—n (%) | 15 (15.6) | |
| LP findings | ||
| Oligoclonal bands positive | 78 (81%) | |
| Oligoclonal bands negative | 10 (10%) | |
| Did not undergo LP | 8 (8%) | |
| Imaging Findings | ||
| Mean number of total MS lesions ± SD | 15.8 ± 6.3 | |
| Active lesions ± SD | 0.24 ± 0.67 | |
| Black holes ± SD | 3.26 ± 0.69 | |
| Disease modifying treatments—n (%) | ||
| Ocrelizumab | 41 (43.16) | |
| Dimethyl-Fumarate | 13 (13.68) | |
| Glatiramer Acetate | 10 (10.53) | |
| Natalizumab | 7 (7.37) | |
| None | 7 (7.37) | |
| Fingolimod | 6 (6.32) | |
| Rituximab | 3 (3.16) | |
| Teriflunomide | 3 (3.16) | |
| Interferon beta-1a | 2 (2.11) | |
| Ofatumumab | 1 (1.05) | |
| Mycophenolate Mofetil | 1 (1.05) |
| Headache Characteristics | ||
|---|---|---|
| MS | Controls | |
| Migraine—n (%) | 32 (33.3) | 14 (14.5) |
| Episodic—n (%) | 28 (87.5) | 12 (85.7) |
| Chronic—n (%) | 4 (12.5) | 2 (14.3) |
| Aura—n (%) | 4 (12.5) | 1 (7.1) |
| Photo/phonophobia—n (%) | 21 (77%) | 10 (71.4%) |
| Mean pain intensity (VAS ± SD) | 7.3 ± 1 | 6.4 ± 1.3 |
| Mean episode duration (hours) ± SD) | 17 ± 20 | 17 ± 20 |
| Mean headache days per month ± SD | 5.5 ± 5.4 | 2.6 ± 1.5 |
| TTH—n (%) | 42 (43.7) | 33 (34.6) |
| FTTH—n (%) | 39 (93%) | 30 (90.9) |
| CTTH—n (%) | 3 (7%) | 3 (9.1) |
| Mean pain intensity (VAS)± SD) | 5.7 ± 1.3 | 5.3 ± 1.3 |
| Mean episode duration (hours) ± SD | 5.5 ± 9.3 | 2.2 ± 1.1 |
| Mean headache days per month ± SD | 3.4 ± 4.7 | 2.7 ± 2.7 |
| Unadjusted | Adjusted | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Any headache | 3.29 (1.80 to 5.99) | p = 0.0001 | 4.54 (2.28 to 9.04) | p = 0.17 × 10−5 |
| Migraine | 2.18 (1.05 to 4.49) | p = 0.04 | 2.21 (1.05 to 4.63) | p = 0.04 |
| TTH | 1.82 (1.02 to 3.25) | p = 0.04 | 2.16 (1.16 to 4) | p = 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gklinos, P.; Evangelopoulos, M.-E.; Velonakis, G.; Mitsikostas, D.D. Migraine and Tension-Type Headache Are Associated with Multiple Sclerosis: A Case–Control Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2778. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082778
Gklinos P, Evangelopoulos M-E, Velonakis G, Mitsikostas DD. Migraine and Tension-Type Headache Are Associated with Multiple Sclerosis: A Case–Control Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(8):2778. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082778
Chicago/Turabian StyleGklinos, Panagiotis, Maria-Eleftheria Evangelopoulos, Georgios Velonakis, and Dimos Dimitrios Mitsikostas. 2025. "Migraine and Tension-Type Headache Are Associated with Multiple Sclerosis: A Case–Control Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 8: 2778. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082778
APA StyleGklinos, P., Evangelopoulos, M.-E., Velonakis, G., & Mitsikostas, D. D. (2025). Migraine and Tension-Type Headache Are Associated with Multiple Sclerosis: A Case–Control Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(8), 2778. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082778









