Review of the Literature: Surgery Indications for Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Selection Process
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Data Items
- Title, authors, year of publication, and journal;
- Study design: RCT/nonrandomized, retrospective, or prospective cohort study;
- Country;
- Participants: total number of eyes, age, sex, means of diagnosis, criteria for diagnosis, surgical indications (Fuchs’ dystrophy and bullous keratoplasty), surgical techniques, preoperative visual acuity, CCT preoperative, 1-month postoperative CCT, mean reduction in CCT (%).
3. Physiopathology
3.1. Role of the Corneal Endothelium
3.2. Endothelial Density
3.3. Fuchs’ Dystrophy and Endothelium
3.4. Fuchs’ Dystrophy and Descemet’s Membrane
3.5. Fuchs’ Dystrophy and Genetics
4. Epidemiology
5. Surgical Techniques
5.1. Descemet Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSAEK)
5.2. Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty (DMEK)
5.3. Current Trend for Endothelial Keratoplasty
6. Preoperative Assessment of Fuchs’ Dystrophy Patients
6.1. Symptoms
6.2. Visual Acuity
6.2.1. Preoperative Visual Acuity in Studies Reporting the Results of Keratoplasty in Fuchs’ Dystrophy
6.2.2. Relationship Between Preoperative Visual Acuity and Visual Recovery
6.3. Slit-Lamp Examination
6.4. Optical Coherence Tomography
Ratio Between Central and Peripheral Corneal Thicknesses
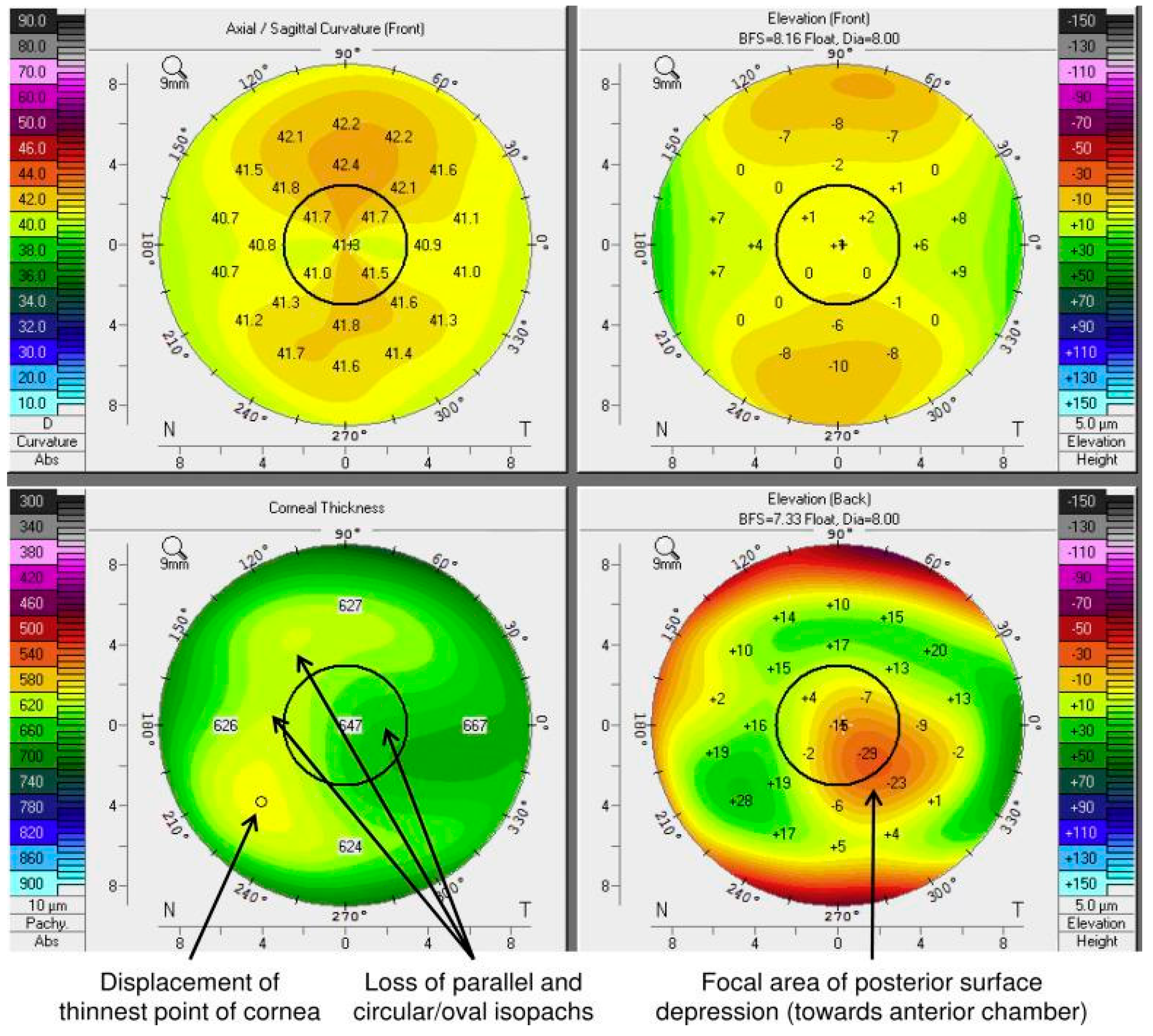
6.5. Elevation Corneal Topography with Scheimpflug Camera
- -
- Loss of parallelism or regularity of isopatches;
- -
- Displacement of the finest point;
- -
- Posterior focal depression.
6.6. Corneal Densitometry
6.7. Specular Microscopy
6.8. In Vivo Confocal Microscopy
6.9. Aberrometry
7. Surgery-Associated Risks in Fuchs’ Dystrophy Patients
7.1. Cataract Surgery
Endothelial Decompensation Following Phacoemulsification/Descemet’s Membrane Detachment
7.2. Keratoplasty
7.2.1. Keratoplasty Complications Limiting Graft Survival
7.2.2. Graft Rejection
7.2.3. Glaucoma
7.2.4. Increased Endothelial Cell Loss Leading to Late Endothelial Failure
7.2.5. IOL Opacification
| Stage | Guttae | Size of Guttae | Endothelium Around the Guttae | Remote Endothelium |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Isolated with well-defined, clear central spot | <1 cell | Normal | Normal |
| 2 | Isolated | 1 cell | Elongated cells forming a rosette with a blurred outline around the guttae | Normal |
| 3 | Beginning of confluence Regular round guttae with a central spot well defined as round or oval Irregular guttae with a central spot with ill-defined limits and of variable intensity | 5 to 10 cells | Rosettes | Normal |
| 4 | Confluent, multilobed images with several clear spots Isolated guttae irregularly distributed | Large areas | Abnormal | Abnormal |
| 5 | Inverted endothelial reflection with clear outlines a lot more brilliant than the normal cellular surface surrounding black zones | Large areas | Not visible | Not visible |
7.2.6. Ocular Surface Disorders
8. Benefits and Risks of the Triple Procedure (Endothelial Keratoplasty Combined with Cataract Surgery)
8.1. Cataract Surgery in Patients with Endothelial Dysfunction
8.1.1. Cataract Surgery Before Endothelial Keratoplasty
8.1.2. Triple Procedure Versus Endothelial Keratoplasty in Phakic Patients
8.1.3. Cataract Surgery After Endothelial Keratoplasty
8.2. Contribution of Imaging Technologies in Combined Surgery Decision
8.2.1. OCT
8.2.2. Corneal Densitometry
8.2.3. In Vivo Confocal Microscopy
8.3. Refraction and Hyperopic Shift
8.4. Cataract Surgery Technique in Fuchs’ Dystrophy
8.4.1. Type of Incision
8.4.2. Type of Cataract Surgery
9. Discussion
- -
- A preoperative visual acuity below 20/40.
- -
- A clinical corneal edema.
- -
- An important visual impact evaluated by V-Fuchs questionnaire;
- -
- A CCT > 625 µm;
- -
- Ratio thickness center–periphery (4 mm with respect to the center) in OCT at 1.03 ± 0.07 (advanced stage) and 0.95 ± 0.07 (moderate stage);
- -
- At least two out of three indicators in OCT analysis with the Scheimpflug’ technique:
- ○
- The loss of parallelism or of the regularity of the isopaches;
- ○
- The displacement of the finest point;
- ○
- Posterior focal depression;
- -
- An increased corneal densitometry, particularly in the anterior layers between 0 and 2 mm of the corneal apex;
- -
- Other criteria (non-determinant):
- -
- Age;
- -
- Gender;
- -
- Genetic background.
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bourne, W.M. Corneal Endothelium—Past, Present, and Future. Eye Contact Lens 2010, 36, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahn, C.F.; Glassman, R.M.; MacCallum, D.K.; Lillie, J.H.; Meyer, R.F.; Robinson, B.J.; Rich, N.M. Postnatal development of corneal endothelium. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1986, 27, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Nucci, P. Normal Endothelial Cell Density Range in Childhood. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1990, 108, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, W.M.; Nelson, L.R.; Hodge, D.O. Central corneal endothelial cell changes over a ten-year period. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1997, 38, 779–782. [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa, K.; Kojima, M.; Sasaki, H.; Shui, Y.-B.; Chew, S.J.; Cheng, H.-M.; Ono, M.; Morikawa, Y.; Sasaki, K. Prevalence of Primary Cornea guttata and Morphology of Corneal Endothelium in Aging Japanese and Singaporean Subjects. ORE 2002, 34, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, R.W.; Matsuda, M.; Schultz, R.O.; Edelhauser, H.F. Changes in the normal corneal endothelial cellular pattern as a function of age. Curr. Eye Res. 1985, 4, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, E. Dystrophia epithelialis corneae. Graefes Arh. Ophthalmol. 1910, 76, 478–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustonen, R.K.; McDonald, M.B.; Srivannaboon, S.; Tan, A.L.; Doubrava, M.W.; Kim, C.K. In vivo confocal microscopy of Fuchs’ endothelial dystrophy. Cornea 1998, 17, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayes, J.; Holmberg, A. The fine structure of the cornea in Fuchs’ endothelial dystrophy. Investig. Ophthalmol. 1964, 3, 47–67. [Google Scholar]
- Geroski, D.H.; Matsuda, M.; Yee, R.W.; Edelhauser, H.F. Pump Function of the Human Corneal Endothelium: Effects of Age and Cornea Guttata. Ophthalmology 1985, 92, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmanson, J.P.G.; Sheldon, T.M.; Goosey, J.D. Fuchs’ endothelial dystrophy: A fresh look at an aging disease. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 1999, 19, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borderie, V.M.; Baudrimont, M.; Vallee, A.; Ereau, T.L.; Gray, F.; Laroche, L. Corneal endothelial cell apoptosis in patients with Fuchs’ dystrophy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 2501–2505. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, D.V.; McGhee, C.N. Contemporary in vivo confocal microscopy of the living human cornea using white light and laser scanning techniques: A major review. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2007, 35, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelliher, C.; Chakravarti, S.; Vij, N.; Mazur, S.; Stahl, P.J.; Engler, C.; Matthaei, M.; Yu, S.M.; Jun, A.S. A cellular model for the investigation of Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Exp. Eye Res. 2011, 93, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, P.; Stark, W.J.; Maumenee, I.H.; Hirst, L.W.; Maumenee, A.E. Hereditary Fuchs’ Dystrophy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1980, 90, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baratz, K.H.; Tosakulwong, N.; Ryu, E.; Brown, W.L.; Branham, K.; Chen, W.; Tran, K.D.; Schmid-Kubista, K.E.; Heckenlively, J.R.; Swaroop, A.; et al. E2-2 Protein and Fuchs’s Corneal Dystrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieben, E.D.; Aleff, R.A.; Tosakulwong, N.; Butz, M.L.; Highsmith, W.E.; Edwards, A.O.; Baratz, K.H. A Common Trinucleotide Repeat Expansion within the Transcription Factor 4 (TCF4, E2-2) Gene Predicts Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottsch, J.D.; Sundin, O.H.; Liu, S.H.; Jun, A.S.; Broman, K.W.; Stark, W.J.; Vito, E.C.L.; Narang, A.K.; Thompson, J.M.; Magovern, M. Inheritance of a Novel COL8A2 Mutation Defines a Distinct Early-Onset Subtype of Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 1934–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoega, G.M.; Arnarsson, A.; Sasaki, H.; Söderberg, P.G.; Jonasson, F. The 7-year cumulative incidence of cornea guttata and morphological changes in the corneal endothelium in the Reykjavik Eye Study. Acta Ophthalmol. 2013, 91, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewenstein, A.; Geyer, O.; Hourvitz, D.; Lazar, M. The association of Fuch’s corneal endothelial dystrophy with angle closure glaucoma. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1991, 75, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitts, J.F.; Jay, J.L. The association of Fuchs’s corneal endothelial dystrophy with axial hypermetropia, shallow anterior chamber, and angle closure glaucoma. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1990, 74, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Miyajima, T.; Melangath, G.; Miyai, T.; Vasanth, S.; Deshpande, N.; Kumar, V.; Tone, S.O.; Gupta, R.; Zhu, S.; et al. Ultraviolet A light induces DNA damage and estrogen-DNA adducts in Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy causing females to be more affected. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, B.O.; Laaser, K.; Cursiefen, C.; Kruse, F.E. A Method to Confirm Correct Orientation of Descemet Membrane During Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 149, 922–925.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaub, F.; Enders, P.; Snijders, K.; Schrittenlocher, S.; Siebelmann, S.; Heindl, L.M.; Bachmann, B.O.; Cursiefen, C. One-year outcome after Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty (DMEK) comparing sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) 20% versus 100% air for anterior chamber tamponade. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 101, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbins, K.R.B.; Price, F.W.; Whitson, W.E. Trends in the Indications for Penetrating Keratoplasty in the Midwestern United States. Cornea 2000, 19, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birbal, R.S.; Baydoun, L.; Ham, L.; Miron, A.; van Dijk, K.; Dapena, I.; Jager, M.J.; Böhringer, S.; Oellerich, S.; Melles, G.R.J. Effect of surgical indication and preoperative lens status on Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty outcomes. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, S0002939419306129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeno, A.; Naor, J.; Lee, H.M.; Hunter, W.S.; Rootman, D.S. Three Decades of Corneal Transplantation: Indications and Patient Characteristics. Cornea 2000, 19, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gain, P.; Jullienne, R.; He, Z.; Aldossary, M.; Acquart, S.; Cognasse, F.; Thuret, G. Global Survey of Corneal Transplantation and Eye Banking. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016, 134, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flockerzi, E.; Maier, P.; Böhringer, D.; Reinshagen, H.; Kruse, F.; Cursiefen, C.; Reinhard, T.; Geerling, G.; Torun, N.; Seitz, B. Trends in Corneal Transplantation from 2001 to 2016 in Germany: A Report of the DOG–Section Cornea and its Keratoplasty Registry. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 188, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, A.; Leung, E.H.; Yoo, S.H. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Descemet’s Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty Versus Descemet’s Stripping Endothelial Keratoplasty in the United States. Ophthalmology 2019, 126, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Meulen, I.J.E.; Patel, S.V.; Lapid-Gortzak, R.; Nieuwendaal, C.P.; McLaren, J.W.; van den Berg, T.J.T.P. Quality of vision in patients with fuchs endothelial dystrophy and after descemet stripping endothelial keratoplasty. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2011, 129, 1537–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wacker, K.; Baratz, K.; Fautsch, M.; Patel, S. Medical and Semi-surgical Treatments for Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Klin. Monatsbl Augenheilkd. 2018, 235, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Oie, Y.; Fujimoto, H.; Soma, T.; Koh, S.; Tsujikawa, M.; Maeda, N.; Nishida, K. Relationship between Corneal Guttae and Quality of Vision in Patients with Mild Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 2103–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker, K.; Baratz, K.H.; Bourne, W.M.; Patel, S.V. Patient-Reported Visual Disability in Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy Measured by the Visual Function and Corneal Health Status Instrument. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 1854–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewing, V.; Fritz, M.; Müller, C.; Böhringer, D.; Reinhard, T.; Patel, S.V.; Wacker, K. The German version of the Visual Function and Corneal Health Status (V-FUCHS): A Fuchs dystrophy-specific visual disability instrument. Ophthalmologe 2020, 117, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.-H.; Ang, M.; Htoon, H.M.; Tan, D. Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty Versus Descemet Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty and Penetrating Keratoplasty. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 207, 288–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, R.E.; Guerra, P.S.; Sousa, D.C.; Gonçalves, A.I.; Quintas, A.M.; Rodrigues, W. DMEK versus DSAEK for Fuchs’ endothelial dystrophy: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 29, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshari, N.A.; Pittard, A.B.; Siddiqui, A.; Klintworth, G.K. Clinical Study of Fuchs Corneal Endothelial Dystrophy Leading to Penetrating Keratoplasty: A 30-Year Experience. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2006, 124, 777–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, F.W.; Price, M.O. Descemet’s stripping with endothelial keratoplasty in 200 eyes: Early challenges and techniques to enhance donor adherence. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2006, 32, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahar, I.; Kaiserman, I.; McAllum, P.; Slomovic, A.; Rootman, D. Comparison of Posterior Lamellar Keratoplasty Techniques to Penetrating Keratoplasty. Ophthalmology 2008, 115, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.O.; Giebel, A.W.; Fairchild, K.M.; Price, F.W. Descemet’s Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty. Ophthalmology 2009, 116, 2361–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terry, M.A.; Shamie, N.; Chen, E.S.; Phillips, P.M.; Shah, A.K.; Hoar, K.L.; Friend, D.J. Endothelial Keratoplasty for Fuchs’ Dystrophy with Cataract. Ophthalmology 2009, 116, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busin, M.; Madi, S.; Santorum, P.; Scorcia, V.; Beltz, J. Ultrathin Descemet’s Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty with the Microkeratome Double-Pass Technique: Two-Year Outcomes. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnereau, C.; Quilendrino, R.; Dapena, I.; Liarakos, V.S.; Alfonso, J.F.; Arnalich-Montiel, F.; Böhnke, M.; Pereira, N.C.; Dirisamer, M.; Parker, J.; et al. Multicenter Study of Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty: First Case Series of 18 Surgeons. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014, 132, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Calvo-de-Mora, M.; Quilendrino, R.; Ham, L.; Liarakos, V.S.; van Dijk, K.; Baydoun, L.; Dapena, I.; Oellerich, S.; Melles, G.R.J. Clinical Outcome of 500 Consecutive Cases Undergoing Descemet’s Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker, K.; Bourne, W.M.; Patel, S.V. Effect of Graft Thickness on Visual Acuity After Descemet Stripping Endothelial Keratoplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 163, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickman, M.M.; Kruit, P.J.; Remeijer, L.; van Rooij, J.; Van der Lelij, A.; Wijdh, R.H.J.; van den Biggelaar, F.J.H.M.; Berendschot, T.T.J.M.; Nuijts, R.M.M.A. A Randomized Multicenter Clinical Trial of Ultrathin Descemet Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSAEK) versus DSAEK. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 2276–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlögl, A.; Tourtas, T.; Kruse, F.E.; Weller, J.M. Long-term Clinical Outcome After Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 169, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockmann, T.; Pilger, D.; Brockmann, C.; Maier, A.-K.B.; Bertelmann, E.; Torun, N. Predictive Factors for Clinical Outcomes after Primary Descemet’s Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty for Fuchs’ Endothelial Dystrophy. Curr. Eye Res. 2019, 44, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourabaly, M.; Chetrit, Y.; Provost, J.; Georgeon, C.; Kallel, S.; Temstet, C.; Bouheraoua, N.; Borderie, V. Influence of graft thickness and regularity on vision recovery after endothelial keratoplasty. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birbal, R.S.; Ni Dhubhghaill, S.; Bourgonje, V.J.A.; Hanko, J.; Ham, L.; Jager, M.J.; Böhringer, S.; Oellerich, S.; Melles, G.R.J. Five-Year Graft Survival and Clinical Outcomes of 500 Consecutive Cases After Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty. Cornea 2020, 39, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunker, S.L.; Dickman, M.M.; Wisse, R.P.L.; Nobacht, S.; Wijdh, R.H.J.; Bartels, M.C.; Tang, M.L.; van den Biggelaar, F.J.H.M.; Kruit, P.J.; Nuijts, R.M.M.A. DMEK versus ultrathin DSAEK: A multicenter randomized controlled clinical trial. Ophthalmology 2020, 127, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrittenlocher, S.; Bachmann, B.; Cursiefen, C. Impact of donor tissue diameter on postoperative central endothelial cell density in Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty. Acta Ophthalmol. 2019, 97, e618–e622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krachmer, J.H.; Purcell, J.J.; Young, C.W.; Bucher, K.D. Corneal endothelial dystrophy. A study of 64 families. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1978, 96, 2036–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repp, D.J.; Hodge, D.O.; Baratz, K.H.; McLaren, J.W.; Patel, S.V. Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eghrari, A.O.; Mumtaz, A.A.; Garrett, B.; Rezaei, M.; Akhavan, M.S.; Riazuddin, S.A.; Gottsch, J.D. Automated Retroillumination Photography Analysis for Objective Assessment of Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy. Cornea 2017, 36, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.L.B.; Li, Y.; Huang, D. Clinical and research applications of anterior segment optical coherence tomography—A review. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2009, 37, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuerten, D.; Plange, N.; Koch, E.C.; Koutsonas, A.; Walter, P.; Fuest, M. Central corneal thickness determination in corneal edema using ultrasound pachymetry, a Scheimpflug camera, and anterior segment OCT. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2015, 253, 1105–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocheux, R.; Pernot, P.; Borderie, V.; Plamann, K.; Irsch, K. Quantitative measures of corneal transparency, derived from objective analysis of depth-resolved corneal images, demonstrated with full-field optical coherence tomographic microscopy. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaub, F.; Enders, P.; Bluhm, C.; Bachmann, B.O.; Cursiefen, C.; Heindl, L.M. Two-Year Course of Corneal Densitometry After Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 175, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.Y.; Wacker, K.; Baratz, K.H.; Patel, S.V. Determining Subclinical Edema in Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy: Revised Classification using Scheimpflug Tomography for Preoperative Assessment. Ophthalmology 2019, 126, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.V.; Hodge, D.O.; Treichel, E.J.; Spiegel, M.R.; Baratz, K.H. Predicting the Prognosis of Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy by Using Scheimpflug Tomography. Ophthalmology 2020, 127, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.V.; Hodge, D.O.; Treichel, E.J.; Spiegel, M.R.; Baratz, K.H. Repeatability of Scheimpflug Tomography for Assessing Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, S000293942030057X. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnawaiseh, M.; Zumhagen, L.; Wirths, G.; Eveslage, M.; Eter, N.; Rosentreter, A. Corneal Densitometry, Central Corneal Thickness, and Corneal Central-to-Peripheral Thickness Ratio in Patients with Fuchs Endothelial Dystrophy. Cornea 2016, 35, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, H.-Y.; Hsiao, C.-H.; Chen, P.Y.-F.; Ma, D.H.-K.; Chang, C.-J.; Tan, H.-Y. Corneal Backscatters as an Objective Index for Assessing Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy: A Pilot Study. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 2017, 8747013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirabayashi, K.E.; Chamberlain, W.; Rose-Nussbaumer, J.; Austin, A.; Stell, L.; Lin, C.C. Corneal Light Scatter After Ultrathin Descemet Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty Versus Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty in Descemet Endothelial Thickness Comparison Trial: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Cornea 2020, 39, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benetz, B.A.; Lass, J.H. Specular Microscopy. Cornea 2018, 37, S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, R.A.; Leibowitz, H.M.; Oak, S.S.; Chang, R.; Berrospi, A.R.; Theodore, J. Endothelial Mosaic in Fuchs’ Dystrophy: A Qualitative Evaluation with the Specular Microscope. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1981, 99, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Mori, Y.; Ogata, M.; Minami, K.; Miyata, K. Central and Peripheral Corneal Endothelial Cell Analysis with Slit-Scanning Wide-Field Contact Specular Microscopy: Agreement with Noncontact Specular Microscopy. Cornea 2019, 38, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, L.; Dapena, I.; Liarakos, V.S.; Baydoun, L.; van Dijk, K.; Ilyas, A.; Oellerich, S.; Melles, G.R.J. Midterm Results of Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty: 4 to 7 Years Clinical Outcome. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 171, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baydoun, L.; Ham, L.; Borderie, V.; Dapena, I.; Hou, J.; Frank, L.E.; Oellerich, S.; Melles, G.R.J. Endothelial Survival After Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty: Effect of Surgical Indication and Graft Adherence Status. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2015, 133, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira-Soto, L.; Efron, N. Morphology of Corneal Nerves Using Confocal Microscopy. Cornea 2001, 20, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, M.; Morishige, N.; Chikama, T.; Nishida, T. Comparison of Confocal Biomicroscopy and Noncontact Specular Microscopy for Evaluation of the Corneal Endothelium. Cornea 2003, 22, 512–515. [Google Scholar]
- Bucher, F.; Adler, W.; Lehmann, H.C.; Hos, D.; Steven, P.; Cursiefen, C.; Heindl, L.M. Corneal nerve alterations in different stages of Fuchs’ endothelial corneal dystrophy: An in vivo confocal microscopy study. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2014, 252, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, Z.A.; Tran, J.A.; Jurkunas, U.V. Peripheral Endothelial Cell Count Is a Predictor of Disease Severity in Advanced Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Cornea 2017, 36, 1166–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker, K.; McLaren, J.W.; Amin, S.R.; Baratz, K.H.; Patel, S.V. Corneal High-Order Aberrations and Backscatter in Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.R.; Baratz, K.H.; McLaren, J.W.; Patel, S.V. Corneal Abnormalities Early in the Course of Fuchs’ Endothelial Dystrophy. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 2325–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, J.W.; Bachman, L.A.; Kane, K.M.; Patel, S.V. Objective Assessment of the Corneal Endothelium in Fuchs’ Endothelial Dystrophy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 1184–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seery, L.S.; McLaren, J.W.; Kittleson, K.M.; Patel, S.V. Retinal Point-Spread Function after Corneal Transplantation for Fuchs’ Dystrophy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claesson, M.; Armitage, W.J.; Stenevi, U. Corneal oedema after cataract surgery: Predisposing factors and corneal graft outcome. Acta Ophthalmol. 2009, 87, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odayappan, A.; Shivananda, N.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Krishnan, T.; Nachiappan, S.; Krishnamurthy, S. A retrospective study on the incidence of post-cataract surgery Descemet’s membrane detachment and outcome of air descemetopexy. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 102, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, S.; Wang, P.; Woreta, F.A.; Aziz, K.; Makary, M.; Ghous, Z.; Srikumaran, D. Postoperative Complications in Medicare Beneficiaries Following Endothelial Keratoplasty Surgery. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 219, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasari, A.; Price, M.O.; Feng, M.T.; Price, F.W. Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty for Failed Penetrating Keratoplasty: Visual Outcomes and Graft Survival. Cornea 2019, 38, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, T.I.; Gauché, L.; Böhringer, D.; Maier, P.; Heinzelmann, S.; Glegola, M.; Kammrath Betancor, P.; Reinhard, T. Ten-year outcomes after DMEK, DSAEK, and PK: Insights on graft survival, endothelial cell density loss, rejection and visual acuity. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunker, S.L.; Veldman, M.H.J.; Winkens, B.; van den Biggelaar, F.J.H.M.; Nuijts, R.M.M.A.; Kruit, P.J.; Dickman, M.M. Real-World Outcomes of DMEK: A Prospective Dutch registry study. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 222, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straiko, M.D.; Bauer, A.J.; Straiko, M.M.W.; Potts, L.B.; Chen, S.-Y.; Tran, K.D.; Terry, M.A. Donor DMEK Tissue Characteristics: Association with Rebubble Rate and 6-Month Endothelial Cell Loss. Cornea 2020, 39, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundlach, E.; Pilger, D.; Dietrich-Ntoukas, T.; Joussen, A.M.; Torun, N.; Maier, A.-K.B. Impact of Re-bubbling after Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty on Long-term Results. Curr. Eye Res. 2021, 46, 784–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber-Hollbach, N.; Baydoun, L.; López, E.F.; Frank, L.E.; Dapena, I.; Liarakos, V.S.; Schaal, S.-C.; Ham, L.; Oellerich, S.; Melles, G.R.J. Clinical Outcome of Rebubbling for Graft Detachment After Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty. Cornea 2017, 36, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, M.; Mehta, J.S.; Lim, F.; Bose, S.; Htoon, H.M.; Tan, D. Endothelial Cell Loss and Graft Survival after Descemet’s Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty and Penetrating Keratoplasty. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 2239–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.O.; Gorovoy, M.; Price, F.W.; Benetz, B.A.; Menegay, H.J.; Lass, J.H. Descemet’s Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.O.; Fairchild, K.M.; Price, D.A.; Price, F.W. Descemet’s stripping endothelial keratoplasty five-year graft survival and endothelial cell loss. Ophthalmology 2011, 118, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borderie, V.M.; Boëlle, P.-Y.; Touzeau, O.; Allouch, C.; Boutboul, S.; Laroche, L. Predicted long-term outcome of corneal transplantation. Ophthalmology 2009, 116, 2354–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graffi, S.; Leon, P.; Nahum, Y.; Gutfreund, S.; Spena, R.; Mattioli, L.; Busin, M. Outcomes of ultrathin Descemet stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty (UT-DSAEK) performed in eyes with failure of primary Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty (DMEK). Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 103, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Schrittenlocher, S.; Siebelmann, S.; Le, V.N.H.; Matthaei, M.; Franklin, J.; Bachmann, B.; Cursiefen, C. Risk factors for endothelial cell loss after Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty (DMEK). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnazaryan, D.; Sese, A.H.; Hollick, E.J. Endothelial cell loss after Descemet’s membrane endothelial keratoplasty for Fuchs endothelial dystrophy: DMEK compared to triple-DMEK. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 218, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.Y.; Ormonde, S.; Brookes, N.H.; Moffatt, S.L.; Sherwin, T.; Pendergrast, D.G.C.; McGhee, C.N.J. The New Zealand National Eye Bank: Survival and Visual Outcome 1 Year After Penetrating Keratoplasty. Cornea 2011, 30, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giers, B.C.; Tandogan, T.; Auffarth, G.U.; Choi, C.Y.; Auerbach, F.N.; Sel, S.; Mayer, C.; Khoramnia, R. Hydrophilic intraocular lens opacification after posterior lamellar keratoplasty—A material analysis with special reference to optical quality assessment. BMC Ophthalmol. 2017, 17, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildirim, T.M.; Łabuz, G.; Hammer, M.; Son, H.-S.; Schickhardt, S.K.; Auffarth, G.U.; Khoramnia, R. A Novel Approach for Assessing Visual Impairment Caused by Intraocular Lens Opacification: High-Resolution Optical Coherence Tomography. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 226, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ademmer, V.; Agha, B.; Shajari, M.; Kohnen, T.; Schmack, I. Impact of DMEK on visual quality in patients with Fuchs’ endothelial dystrophy. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2021, 260, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaniol, K.; Schwinde, J.H.; Hoffmann, M.; Borrelli, M.; Schrader, S.; Geerling, G. The influence of ocular surface parameters on the visual outcome of Descemet-membrane endothelial keratoplasty. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 1202. [Google Scholar]
- Alnawaiseh, M.; Zumhagen, L.; Rosentreter, A.; Eter, N. Changes in Anterior, Posterior, and Total Corneal Astigmatism after Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 2017, 4068963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, T.; Kobayashi, A.; Takahashi, H.; Oyakawa, I.; Kato, N.; Yamaguchi, T. Optical characteristics after Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty: 1-year results. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahar, I.; Kaiserman, I.; Levinger, E.; Sansanayudh, W.; Slomovic, A.R.; Rootman, D.S. Retrospective Contralateral Study Comparing Descemet Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty with Penetrating Keratoplasty. Cornea 2009, 28, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, R.J.; Braga-Mele, R.; Chen, S.H.; Miller, K.M.; Pineda, R.; Tweeten, J.P.; Musch, D.C. Cataract in the Adult Eye Preferred Practice Pattern®. Ophthalmology 2017, 124, P1–P119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Cleynenbreugel, H.; Remeijer, L.; Hillenaar, T. Cataract surgery in patients with Fuchs’ endothelial corneal dystrophy: When to consider a triple procedure. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, A.C.S. Corneal thickness and endothelial density before and after cataract surgery. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2001, 85, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Yoshida, M.; Manabe, S.; Hirata, A. Cataract surgery in eyes with low corneal endothelial cell density. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2011, 37, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhart, Z.N.; Feng, M.T.; Price, F.W.; Price, M.O. One-year outcomes in eyes remaining phakic after Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2014, 40, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.O.; Price, D.A.; Fairchild, K.M.; Price, F.W. Rate and risk factors for cataract formation and extraction after Descemet stripping endothelial keratoplasty. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 94, 1468–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.; Dirisamer, M.; Naveiras, M.; Tse, W.H.W.; van Dijk, K.; Frank, L.E.; Ham, L.; Melles, G.R.J. Outcomes of Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty in phakic eyes. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2012, 38, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, F.U.; Cabrerizo, J.; Quilendrino, R.; Dapena, I.; Ham, L.; Melles, G.R.J. Outcomes of phacoemulsification after Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2013, 39, 836–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, P.; Amiran, M.D.; Lichtinger, A.; Yeung, S.N.; Slomovic, A.R.; Rootman, D.S. Outcomes of Descemet stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty in patients with previous glaucoma drainage device insertion. Cornea 2012, 31, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baydoun, L.; Tong, C.M.; Tse, W.W.; Chi, H.; Parker, J.; Ham, L.; Melles, G.R.J. Endothelial cell density after descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty: 1 to 5-year follow-up. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 154, 762–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitzman, G.D.; Gottsch, J.D.; Stark, W.J. Cataract surgery in patients with Fuchs’ corneal dystrophy: Expanding recommendations for cataract surgery without simultaneous keratoplasty. Ophthalmology 2005, 112, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnalich-Montiel, F.; Mingo-Botín, D.; De Arriba-Palomero, P. Preoperative Risk Assessment for Progression to Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty Following Cataract Surgery in Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 208, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillenaar, T.; Cals, R.H.H.; Eilers, P.H.C.; Wubbels, R.J.; van Cleynenbreugel, H.; Remeijer, L. Normative Database for Corneal Backscatter Analysis by In Vivo Confocal Microscopy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 7274–7281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.X.; Lee, W.B.; Hammersmith, K.M.; Kuo, A.N.; Li, J.Y.; Shen, J.F.; Weikert, M.P.; Shtein, R.M. Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty: Safety and Outcomes. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.B.; Jacobs, D.S.; Musch, D.C.; Kaufman, S.C.; Reinhart, W.J.; Shtein, R.M. Descemet’s Stripping Endothelial Keratoplasty: Safety and Outcomes: A Report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology 2009, 116, 1818–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, B.; Kuo, A.N.; Afshari, N.A.; Carlson, A.N.; Kim, T. Refractive Change After Descemet Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty Surgery and Its Correlation with Graft Thickness and Diameter. Cornea 2009, 28, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.H. One-Year Results and Anterior Segment Optical Coherence Tomography Findings of Descemet Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty Combined with Phacoemulsification. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2008, 126, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, M.; Grewing, V.; Böhringer, D.; Lapp, T.; Maier, P.; Reinhard, T.; Wacker, K. Avoiding Hyperopic Surprises After Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty in Fuchs Dystrophy Eyes by Assessing Corneal Shape. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 197, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnawaiseh, M.; Zumhagen, L.; Rosentreter, A.; Eter, N. Intraocular lens power calculation using standard formulas and ray tracing after DMEK in patients with Fuchs endothelial dystrophy. BMC Ophthalmol. 2017, 17, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrame, G.; Salvetat, M.L.; Driussi, G.; Chizzolini, M. Effect of incision size and site on corneal endothelial changes in cataract surgery. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2002, 28, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesiewska-Junk, H.; Kaluzny, J.; Malukiewicz-Wisniewska, G. Long-Term Evaluation of Endothelial Cell Loss after Phacoemulsification. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 12, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Yan, H.; Zhang, G. Femtosecond laser–assisted cataract surgery in Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. Long-Term Outcomes J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2018, 44, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, W.W.D.; Chai, H.-C.C.; Shen, L.; Manotosh, R.; Anna Tan, W.T. Comparing Outcomes of Phacoemulsification with Femtosecond Laser–Assisted Cataract Surgery in Patients with Fuchs Endothelial Dystrophy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 196, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewe, S.Y.; Abell, R.G.; Vote, B.J. Femtosecond laser-assisted versus phacoemulsification for cataract extraction and intraocular lens implantation: Clinical outcomes review. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2018, 29, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Study | Year | Surgical Indication | Surgical Techniques | Number of Eyes | Preoperative Visual Acuity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuchs’ Dystrophy (%) | Bullous Keratopathy (%) | LogMar | Snellen | Decimal | <20/40 (%) | ||||
| Afshari et al. [38] | 2006 | 100 | 0 | PK | 546 | 0.50 | 20/64 | 0.31 | 16.9 |
| Price et al. [39] | 2006 | 90 | 10 | DSEK | 200 | 0.69 | 20/100 | 0.2 | |
| Bahar et al. [40] | 2008 | 35.4 | 64.6 | PK | 48 | 1.27 ± 7.5 lines | 20/372 | 0.05 | |
| 41.2 | 58.8 | DLEK | 68 | 1.12 ± 7.4 lines | 20/263 | 0.07 | |||
| 50 | 50 | DSEK | 16 | 0.52 ± 1.1 lines | 20/66 | 0.27 | |||
| 62.2 | 37.8 | DSAEK | 45 | 0.9 ± 5 lines | 20/160 | 0.12 | |||
| Price et al. [41] | 2009 | 85 | 15 | DMEK | 60 | 0.39 | 20/50 | 0.4 | |
| Terry et al. [42] | 2009 | 100 | 0 | DSAEK | 203 | 0.49 | 20/62 [20/2000–20/20] | 0.32 | |
| Busin et al. [43] | 2013 | 69.6 | 30.4 | UT-DSAEK | 250 | 0.76 ± 4.9 lines | 20/115 | 0.17 | 6.9 |
| Monnereau et al. [44] | 2014 | 68.2 | 31.8 | DMEK | 275 | 14.5 | |||
| Rodríguez et al. [45] | 2015 | 89.2 | 10.8 | DMEK | 499 | 38 | |||
| Wackrer et al. [46] | 2016 | 100 | 0 | DSEK | 100 | 0.45 ± 1.9 lines | 20/63 | 0.35 | |
| Dickman et al. [47] | 2016 | 100 | 0 | DSAEK | 32 | 0.35 ± 2.2 lines [0.27–0.42] | 20/44 | 0.45 [0.37–0.54] | |
| 100 | 0 | UT-DSAEK | 34 | 0.37 ± 1.8 lines [0.31–0.43] | 20/47 | 0.43 [0.37–0.49] | |||
| Schlögl et al. [48] | 2016 | 91 | 9 | DMEK | 97 | 0.64 ± 4.1 lines | 20/87 | 0.23 | 19% |
| Schaub et al. [24] | 2017 | 100 | 0 | DMEK | 160 | 0.4 ± 1.9 lines | 20/50 | 0.39 | |
| Woo et al. [36] | 2019 | 24.4 | 75.6 | PK | 405 | 1.7 ± 5 lines | 20/1000 | 0.02 | |
| 39 | 61 | DSAEK | 423 | 1.2 ± 6 lines | 20/317 | 0.06 | |||
| 63.6 | 36.4 | DMEK | 121 | 0.9 ± 6 lines | 20/159 | 0.12 | |||
| Brockmann et al. [49] | 2019 | 100 | 0 | DMEK | 108 | 0.57 ± 2.2 lines | 20/74 | 0.27 | |
| Tourabaly et al. [50] | 2019 | 97.3 | 2.7 | DMEK | 38 | 0.48 ± 3.1 lines | 20/60 | 0.33 | |
| 83.3 | 16.7 | Nanothin DSAEK | 18 | 0.85 ± 5.7 lines | 20/141 | 0.14 | |||
| 90.3 | 9.7 | UT-DSAEK | 52 | 0.84 ± 3.8 lines | 20/138 | 0.14 | |||
| 96 | 4 | Fine DSAEK (100–150 µm) | 25 | 0.97 ± 4.3 lines | 20/186 | 0.11 | |||
| 94.1 | 5.9 | DSAEK (>150 µm) | 17 | 0.76 ± 4.4 lines | 20/115 | 0.17 | |||
| Birbal et al. [26] | 2020 | 85.3 | 14.7 | DMEK | 799 | 0.46 ± 3.8 lines | 20/57 | 0.35 | 40.7 |
| Birbal et al. [51] | 2020 | 89.2 | 10.8 | DMEK | 451 | 0.49 ± 3.9 lines | 20/62 | 0.32 | 40.1 |
| Dunker et al. [52] | 2020 | 100 | 0 | UT-DSAEK | 25 | 0.31 ± 1.3 lines [0.26–0.37] | 20/41 | 0.49 | |
| 100 | 0 | DMEK | 29 | 0.37 ± 1.8 lines [0.30–0.44] | 20/47 | 0.43 | |||
| Stage of the Disease | Grade | Criteria (Central guttae/Corneal Paracentral) |
|---|---|---|
| Not affected | 0 | Absence of guttae |
| Intermediary | 1 | 1 to 12 non-merging guttae |
| 2 | More than 12 non-merging guttae | |
| 3 | Confluent guttae over 1 to 2 mm | |
| Severe | 4 | Confluent guttae over 2 to 5 mm |
| 5 | Confluent guttae > 5 mm | |
| 6 | Confluent guttae > 5 mm with epithelial edema/visible stroma |
| Study | Year | Surgical Indications | Surgical Techniques | Number of Eyes | Preoperative CCT (μm) | 1-Month Postoperative CCT (μm) | Mean Reduction in CCT (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuchs’ Dystrophy (%) | Bullous Keratopathy (%) | |||||||
| Afshari et al. JAMA Ophtalmology [38] | 2006 | 100 | 0 | PK | 259 | 681 [539–940] | NC | NC |
| Price et al. Ophtalmology [41] | 2009 | 85 | 15 | DMEK | 60 | 656 [506–1030] | 528 [424–678] | 19.5 |
| Rodríguez-Calvo-de-Mora et al. Ophtalmology [45] | 2015 | 89.2 | 10.8 | DMEK | 499 | 667 ± 92 | 525 ± 46 | 20 ± 11 |
| Wackrer et al. Ophtalmology [46] | 2016 | 100 | 0 | DSEK | 100 | 696 ± 60 | 656 ± 48 | 6 |
| Dickman et al. Ophtalmology [47] | 2016 | 100 | 0 | UT-DSAEK | 34 | 643 ± 62 [621–665] | NC | NC |
| 100 | 0 | DSAEK | 32 | 641 ± 64 [618–664] | NC | NC | ||
| Schölg et al. AJO [48] | 2016 | 91 | 9 | DMEK | 97 | 644 ± 67 | 538 ± 61 | 18 |
| Schaub et al. AJO [60] | 2017 | 10 | 0 | DMEK | 160 | 596 ± 53 [395–808] | 527 ± 56 [430–647] | 12.5 |
| Brockmann et al. Current Eye Research [49] | 2019 | 100 | 0 | DMEK | 108 | 660 ± 84 | 535 ± 82 | 19 |
| Tourabaly et al. British Journal of Ophtalmology [50] | 2019 | 97.3 | 2.7 | DMEK | 38 | 622 ± 58 | 529 ± 48 | 15 |
| 83.3 | 16.7 | Nanofine DSAEK | 18 | 673 ± 62 | 550 ± 50 | 18 | ||
| 90.3 | 9.7 | UT-DSAEK | 52 | 661 ± 77 | 597 ± 51 | 10 | ||
| 96 | 4 | Fine DSAEK (100–150 µm) | 25 | 657 ± 83 | 622 ± 39 | 6 | ||
| 94.1 | 5.9 | DSAEK (>150 µm) | 17 | 715 ± 110 | 681 ± 42 | 5 | ||
| Birbal et al. AJO [26] | 2020 | 85.3 | 14.7 | DMEK | 799 | 687 ± 144 | 522 ± 54 | 22 |
| Birbal et al. Cornea [51] | 2020 | 89.2 | 10.8 | DMEK | 425 | 667 ± 192 | 525 ± 46 | 20 ± 11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tourabaly, M.; Knoeri, J.; Georgeon, C.; Borderie, V. Review of the Literature: Surgery Indications for Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2365. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072365
Tourabaly M, Knoeri J, Georgeon C, Borderie V. Review of the Literature: Surgery Indications for Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(7):2365. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072365
Chicago/Turabian StyleTourabaly, Moïse, Juliette Knoeri, Cristina Georgeon, and Vincent Borderie. 2025. "Review of the Literature: Surgery Indications for Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 7: 2365. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072365
APA StyleTourabaly, M., Knoeri, J., Georgeon, C., & Borderie, V. (2025). Review of the Literature: Surgery Indications for Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(7), 2365. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072365







