Effectiveness of Physiotherapy for Improving Participation, Gross Motor Function, Gait and Balance in Children and Adolescents with Cerebral Palsy: Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
2.3. Sample Size Calculation
2.4. Study Sample
- Exclusion criteria: children and adolescents who have received a botulinum toxin injection in their lower limbs 6 weeks before this study or during the intervention; have undergone surgery on lower limbs in the 6 months prior to their participation in this study or during this study; or who present inability to follow the planned program due to moving to another city or another reason.
2.5. Randomization and Blinding
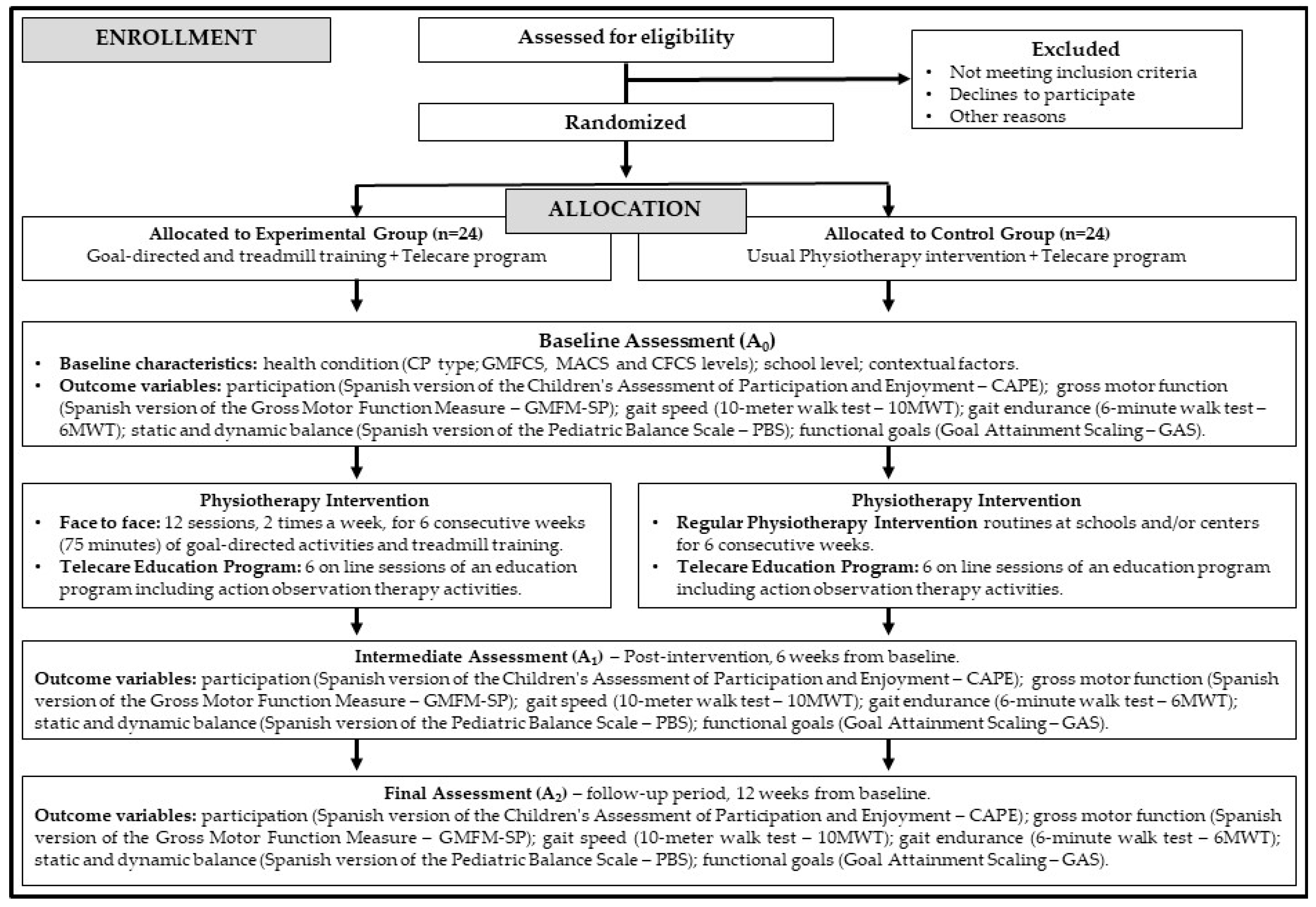
2.6. Study Flow
2.7. Outcome Variables
2.8. Interventions
2.8.1. Experimental Group Intervention
2.8.2. Control Group Intervention
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- te Velde, A.; Morgan, C.; Novak, I.; Tantsis, E.; Badawi, N. Early Diagnosis and Classification of Cerebral Palsy: An Historical Perspective and Barriers to an Early Diagnosis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wimalasundera, N.; Stevenson, V.L. Cerebral palsy. Pract. Neurol. 2016, 16, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadowska, M.; Sarecka-Hujar, B.; Kopyta, I. Cerebral Palsy: Current Opinions on Definition, Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Classification and Treatment Options. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 1505–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, S.; Goldsmith, S.; Webb, A.; Ehlinger, V.; Hollung, S.J.; McConnell, K.; Arnaud, C.; Smithers-Sheedy, H.; Oskoui, M.; Khandaker, G.; et al. Global prevalence of cerebral palsy: A systematic analysis. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2022, 64, 1494–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckung, E.; Hagberg, G. Neuroimpairments, activity limitations, and participation restrictions in children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2002, 44, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries, L.; Fiss, A.; McCoy, S.W.; Bartlett, D.J. Description of Primary and Secondary Impairments in Young Children with Cerebral Palsy. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2016, 28, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiariti, V.; Mahdi, S.; Bölte, S. International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health Core Sets for cerebral palsy, autism spectrum disorder, and attention-deficit–hyperactivity disorder. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2018, 60, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashiguchi, Y.; Ohata, K.; Osako, S.; Kitatani, R.; Aga, Y.; Masaki, M.; Yamada, S. Number of Synergies Is Dependent on Spasticity and Gait Kinetics in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2018, 30, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Nandy, A.; Kesar, T.M. Gait deficits and dynamic stability in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Biomech. 2020, 71, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palisano, R.J.; Chiarello, L.A.; Orlin, M.; Oeffinger, D.; Polansky, M.; Maggs, J.; Bagley, A.; Gorton, G.; The Children’s Activity and Participation Group. Determinants of intensity of participation in leisure and recreational activities by children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2011, 53, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, E.; Regalado, I.C.R.; Galvão, E.R.V.P.; Ferreira, H.N.C.; Badia, M.; Baz, B.O. I Want to Play: Children with Cerebral Palsy Talk About Their Experiences on Barriers and Facilitators to Participation in Leisure Activities. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2020, 32, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, I.; Morgan, C.; Fahey, M.; Finch-Edmondson, M.; Galea, C.; Hines, A.; Langdon, K.; Mc Namara, M.; Paton, M.C.; Popat, H.; et al. State of the Evidence Traffic Lights 2019: Systematic Review of Interventions for Preventing and Treating Children with Cerebral Palsy. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2020, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faccioli, S.; Pagliano, E.; Ferrari, A.; Maghini, C.; Siani, M.F.; Sgherri, G.; Cappetta, G.; Borelli, G.; Farella, G.M.; Foscan, M.; et al. Evidence-based management and motor rehabilitation of cerebral palsy children and adolescents: A systematic review. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1171224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, B.R.; Elliott, E.J.; Coggan, S.; Pinto, R.Z.; Jirikowic, T.; McCoy, S.W.; Latimer, J. Interventions to improve gross motor performance in children with neurodevelopmental disorders: A meta-analysis. BMC Pediatr. 2016, 16, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackman, M.; Sakzewski, L.; Morgan, C.; Boyd, R.N.; Brennan, S.E.; Langdon, K.; Toovey, R.A.M.; Greaves, S.; Thorley, M.; Novak, I. Interventions to improve physical function for children and young people with cerebral palsy: International clinical practice guideline. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2022, 64, 536–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zai, W.; Xu, N.; Wu, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R. Effect of task-oriented training on gross motor function, balance and activities of daily living in children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2022, 101, e31565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toovey, R.; Bernie, C.; Harvey, A.R.; McGinley, J.L.; Spittle, A.J. Task-specific gross motor skills training for ambulant school-aged children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review. BMJ Paediatr. Open. 2017, 1, e000078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yun, C. Effectiveness of treadmill training on gait function in children with cerebral palsy: Meta-analysis. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2020, 16, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birgani, P.M.; Ashtiyani, M.; Rasooli, A.; Shahrokhnia, M.; Shahrokhi, A.; Mirbagheri, M.M. Can an anti-gravity treadmill improve stability of children with cerebral palsy? In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 5465–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfian, M.; Dadashi, F.; Rafieenazari, Z.; Shahroki, A.; Rasteh, M.; Molavi, M.; Mirbagheri, A.; Mirbagheri, M. The Effects of Anti-gravity Treadmill Training on Gait Characteristics in Children with Cerebral Palsy. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 5256–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinaro, A.; Micheletti, S.; Pagani, F.; Garofalo, G.; Galli, J.; Rossi, A.; Fazzi, E.; Buccino, G. Action Observation Treatment in a tele-rehabilitation setting: A pilot study in children with cerebral palsy. Disabil. Rehabil. 2022, 44, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccino, G. Action observation treatment: A novel tool in neurorehabilitation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, D.; Fullen, B.; Rio, E.; Segurado, R.; Stokes, D.; O’Sullivan, C. Effect of Action Observation Therapy in the Rehabilitation of Neurologic and Musculoskeletal Conditions: A Systematic Review. Arch. Rehabil. Res. Clin. Transl. 2021, 3, 100106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almasri, N.A.; An, M.; Palisano, R.J. Parents’ Perception of Receiving Family-Centered Care for Their Children with Physical Disabilities: A Meta-Analysis. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2018, 38, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camden, C.; Silva, M. Pediatric Teleheath: Opportunities Created by the COVID-19 and Suggestions to Sustain Its Use to Support Families of Children with Disabilities. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2021, 41, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aderonmu, J.A. Emerging challenges in meeting physiotherapy needs during COVID-19 through telerehabilitation. Bull. Fac. Phys. Ther. 2020, 25, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamboosi, M.E.; Al-Khathami, S.S.; El-Shamy, S.M. The effectiveness of tele-rehabilitation on improvement of daily living activities in children with cerebral palsy: Narrative review. Bull. Fac. Phys. Ther. 2021, 26, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seron, P.; Oliveros, M.; Gutierrez-Arias, R.; Fuentes-Aspe, R.; Torres-Castro, R.; Merino-Osorio, C.; Nahuelhual, P.; Inostroza, J.; Jalil, Y.; Solano, R.; et al. Effectiveness of Telerehabilitation in Physical Therapy: A Rapid Overview. Phys. Ther. 2021, 101, pzab053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butcher, N.J.; Monsour, A.; Mew, E.J.; Chan, A.-W.; Moher, D.; Mayo-Wilson, E.; Terwee, C.B.; Chee-A-Tow, A.; Baba, A.; Gavin, F.; et al. Guidelines for reporting outcomes in trial protocols: The SPIRIT-outcomes 2022 extension. JAMA 2022, 328, 2345–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, K.F.; Altman, D.G.; Moher, D. CONSORT 2010 Statement: Updated Guidelines for Reporting Parallel Group Randomised Trials. PLoS Med. 2010, 7, e1000251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butcher, N.J.; Monsour, A.; Mew, E.J.; Chan, A.; Moher, D.; Mayo-Wilson, E.; Terwee, C.B.; Chee-A-Tow, A.; Baba, A.; Gavin, F.; et al. Guidelines for Reporting Outcomes in Trial Reports: The CONSORT-Outcomes 2022 Extension. JAMA 2022, 328, 2252–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Rodríguez, N. Ley Orgánica 3/2018, de 5 de diciembre, de Protección de Datos Personales y garantía de los derechos digitales. AIS Ars Iuris Salmanticensis 2019, 7, 254–259. Available online: https://revistas.usal.es/cuatro/index.php/ais/article/view/21320 (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Ryan, J.M.; Cassidy, E.E.; Noorduyn, S.G.; O’Connell, N.E. Exercise interventions for cerebral palsy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 6, CD011660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Tan, Z.; Yun, G.; Cao, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Chen, T. Effectiveness of exercise interventions for children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Rehabil. Med. 2021, 53, jrm00176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino-Andrés, J.; García de Mateos-López, A.; Damiano, D.L.; Sánchez-Sierra, A. Effect of muscle strength training in children and adolescents with spastic cerebral palsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rehabil. 2022, 36, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palisano, R.J.; Rosenbaum, P.; Bartlett, D.; Livingston, M.H. Content validity of the expanded and revised Gross Motor Function Classification System. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2008, 50, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, A.; Krumlinde-Sundholm, L.; Rösblad, B.; Beckung, E.; Arner, M.; Öhrvall, A.; Rosenbaum, P. The Manual Ability Classification System (MACS) for children with cerebral palsy: Scale development and evidence of validity and reliability. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2006, 48, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidecker, M.J.; Paneth, N.; Rosenbaum, P.L.; Kent, R.D.; Lillie, J.; Eulenberg, J.B.; Chester, K., Jr.; Johnson, B.; Michalsen, L.; Evatt, M.; et al. Developing and validating the Communication Function Classification System for individuals with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2011, 53, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, E.; Badia, M.; Orgaz, B.; Verdugo, M.A. Cross-cultural validation of the Children’s Assessment of Participation and Enjoyment (CAPE) in Spain. Child. Care Health Dev. 2014, 40, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferre-Fernández, M.; Murcia-González, M.A.; Ríos-Díaz, J. Translation and cross-cultural adaptation of the Gross Motor Function Measure to the Spanish population of children with cerebral palsy. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 71, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeffinger, D.; Bagley, A.; Rogers, S.; Gorton, G.; Kryscio, R.; Abel, M.; Damiano, D.; Barnes, D.; Tylkowski, C. Outcome tools used for ambulatory children with cerebral palsy: Responsiveness and minimum clinically important differences. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2008, 50, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.; Beath, T.; Bell, J.; Jacobson, G.; Phair, T.; Salbach, N.M.; Wright, F.V. Test–retest reliability of the 10-metre fast walk test and 6-minute walk test in ambulatory school-aged children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2008, 50, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graser, J.V.; Letsch, C.; van Hedel, H.J.A. Reliability of timed walking tests and temporo-spatial gait parameters in youths with neurological gait disorders. BMC Neurol. 2016, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacau, L.d.A.P.; de Santana-Filho, V.J.; Maynard, L.G.; Gomes, N.; Mansueto Fernandes, M.; Carvalho, V.O. Reference Values for the Six-Minute Walk Test in Healthy Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Braz. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2016, 31, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Guisado, C.I.; González López-Arza, M.V.; Montanero Fernández, J. Adaptación transcultural y validación de la versión en español de la Pediatric Balance Scale. Fisioter. Órgano Asoc. Española Fisioter. 2018, 40, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Shen, I.; Chen, C.; Wu, C.; Liu, W.; Chung, C. Validity, responsiveness, minimal detectable change, and minimal clinically important change of Pediatric Balance Scale in children with cerebral palsy. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2013, 34, 916–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, J.M.; Schwab, S.M.; Huijs, L.; Sheehan, A.; Harpster, K. ICF-inspired goal-setting in developmental rehabilitation: An innovative framework for pediatric therapists. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2021, 37, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.; Cross, A.; Rosenbaum, P.; Gorter, J.W. Use of the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health to support goal-setting practices in pediatric rehabilitation: A rapid review of the literature. Disabil. Rehabil. 2021, 43, 884–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, H. The transferability of goal attainment scaling (GAS) for child life specialists working in pediatric rehabilitation: A critical review of the literature. J. Child. Life Psychosoc. Theory Pract. 2020, 1, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Costa, I.; Abuín-Porras, V.; Terán-García, P.; Férez-Sopeña, A.; Calvo-Fuente, V.; Soto-Vidal, C.; Pacheco-da-Costa, S. Effectiveness of a Telecare Physical Therapy Program in Improving Functionality in Children and Adolescents with Cerebral Palsy: A Cases Study. Children 2023, 10, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, L.W.M.E.; Geijen, M.M.E.; Kleijnen, J.; Rameckers, E.A.A.; Schnackers, M.L.A.P.; Smeets, R.J.E.M.; Janssen-Potten, Y.J.M. Feasibility and effectiveness of home-based therapy programmes for children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review. BMJ Open. 2020, 10, e035454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beani, E.; Menici, V.; Sicola, E.; Ferrari, A.; Feys, H.; Klingels, K.; Mailleux, L.; Boyd, R.; Cioni, G.; Sgandurra, G. Effectiveness of the home-based training program Tele-UPCAT (Tele-monitored UPper Limb Children Action Observation Training) in unilateral cerebral palsy: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2023, 59, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
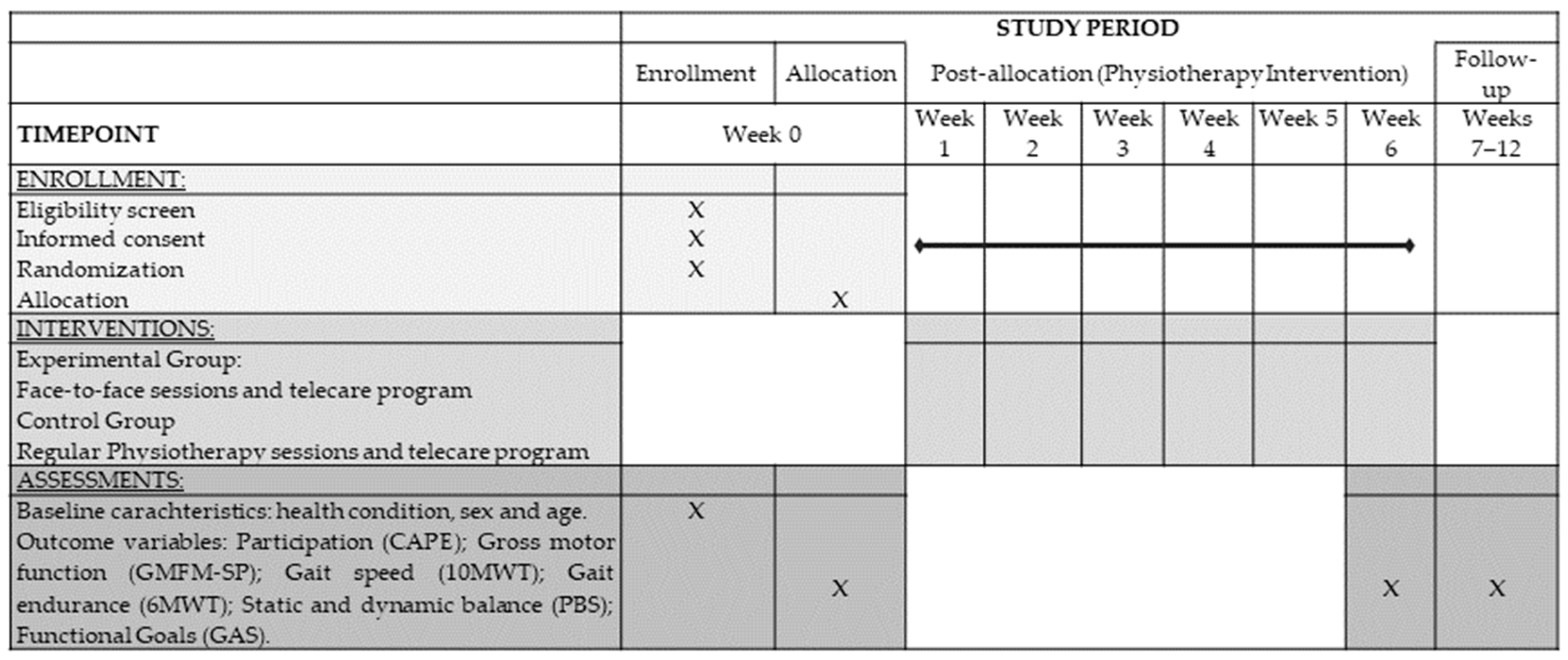

| Baseline Assessment (A0) | Intermediate Assessment (A1) | Follow-Up Assessment (A2) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Descriptive characteristics | x | ||
| Participation | x | x | x |
| Gross Motor Function | x | x | x |
| Gait speed and endurance | x | x | x |
| Static and dynamic balance | x | x | x |
| Functional Goals | x | x | x |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pacheco-da-Costa, S.; Rodríguez-Costa, I.; Abuín-Porras, V.; Asúnsolo-del-Barco, Á.; Calvo-Fuente, V.; Soto-Vidal, C. Effectiveness of Physiotherapy for Improving Participation, Gross Motor Function, Gait and Balance in Children and Adolescents with Cerebral Palsy: Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072214
Pacheco-da-Costa S, Rodríguez-Costa I, Abuín-Porras V, Asúnsolo-del-Barco Á, Calvo-Fuente V, Soto-Vidal C. Effectiveness of Physiotherapy for Improving Participation, Gross Motor Function, Gait and Balance in Children and Adolescents with Cerebral Palsy: Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(7):2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072214
Chicago/Turabian StylePacheco-da-Costa, Soraya, Isabel Rodríguez-Costa, Vanesa Abuín-Porras, Ángel Asúnsolo-del-Barco, Victoria Calvo-Fuente, and Concepción Soto-Vidal. 2025. "Effectiveness of Physiotherapy for Improving Participation, Gross Motor Function, Gait and Balance in Children and Adolescents with Cerebral Palsy: Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 7: 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072214
APA StylePacheco-da-Costa, S., Rodríguez-Costa, I., Abuín-Porras, V., Asúnsolo-del-Barco, Á., Calvo-Fuente, V., & Soto-Vidal, C. (2025). Effectiveness of Physiotherapy for Improving Participation, Gross Motor Function, Gait and Balance in Children and Adolescents with Cerebral Palsy: Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(7), 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072214






