The Impact of Weight Categories on the Association Between Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter and Known Risk Factors: A Nationwide Inpatient Data Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Study Outcome and Statistical Analysis
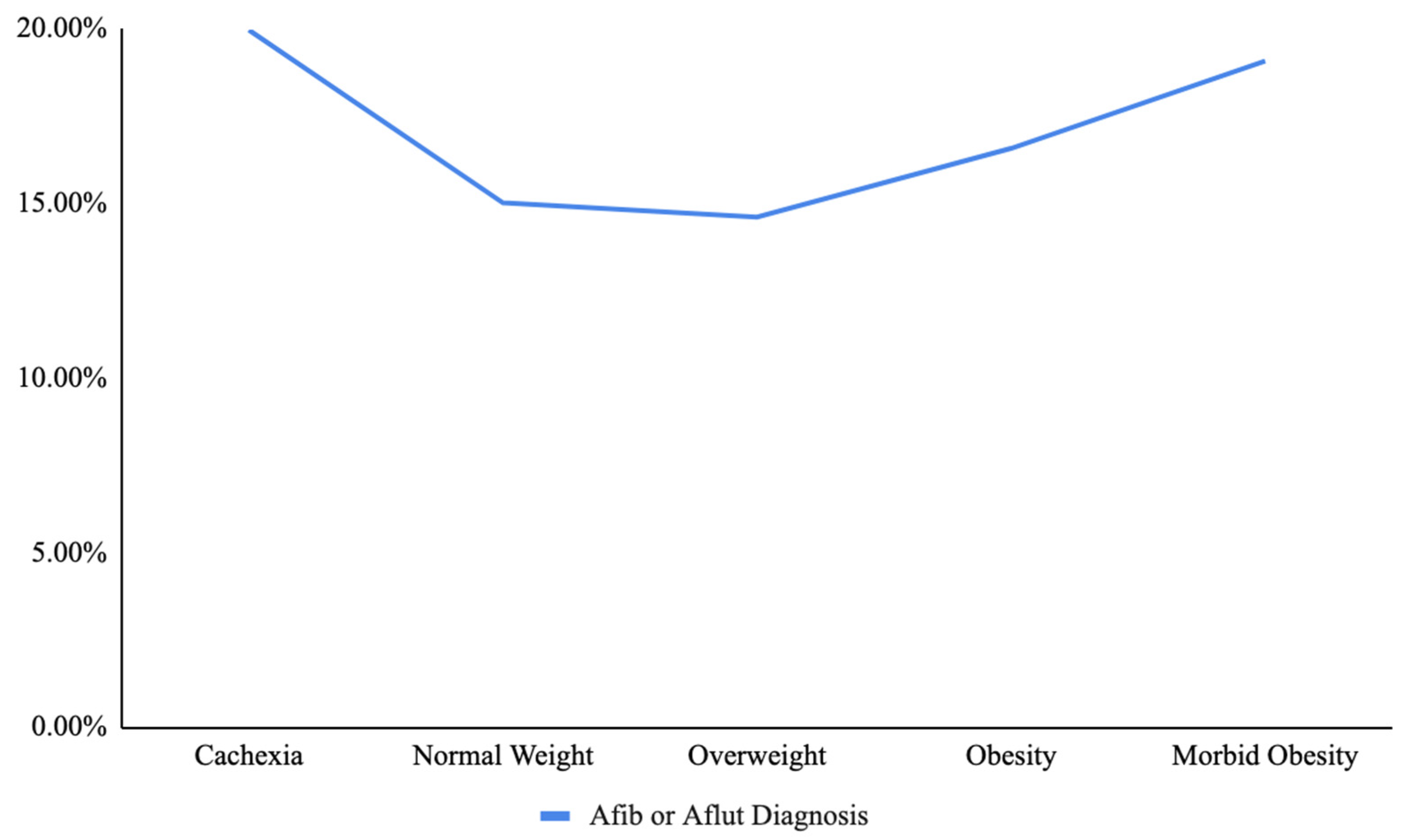
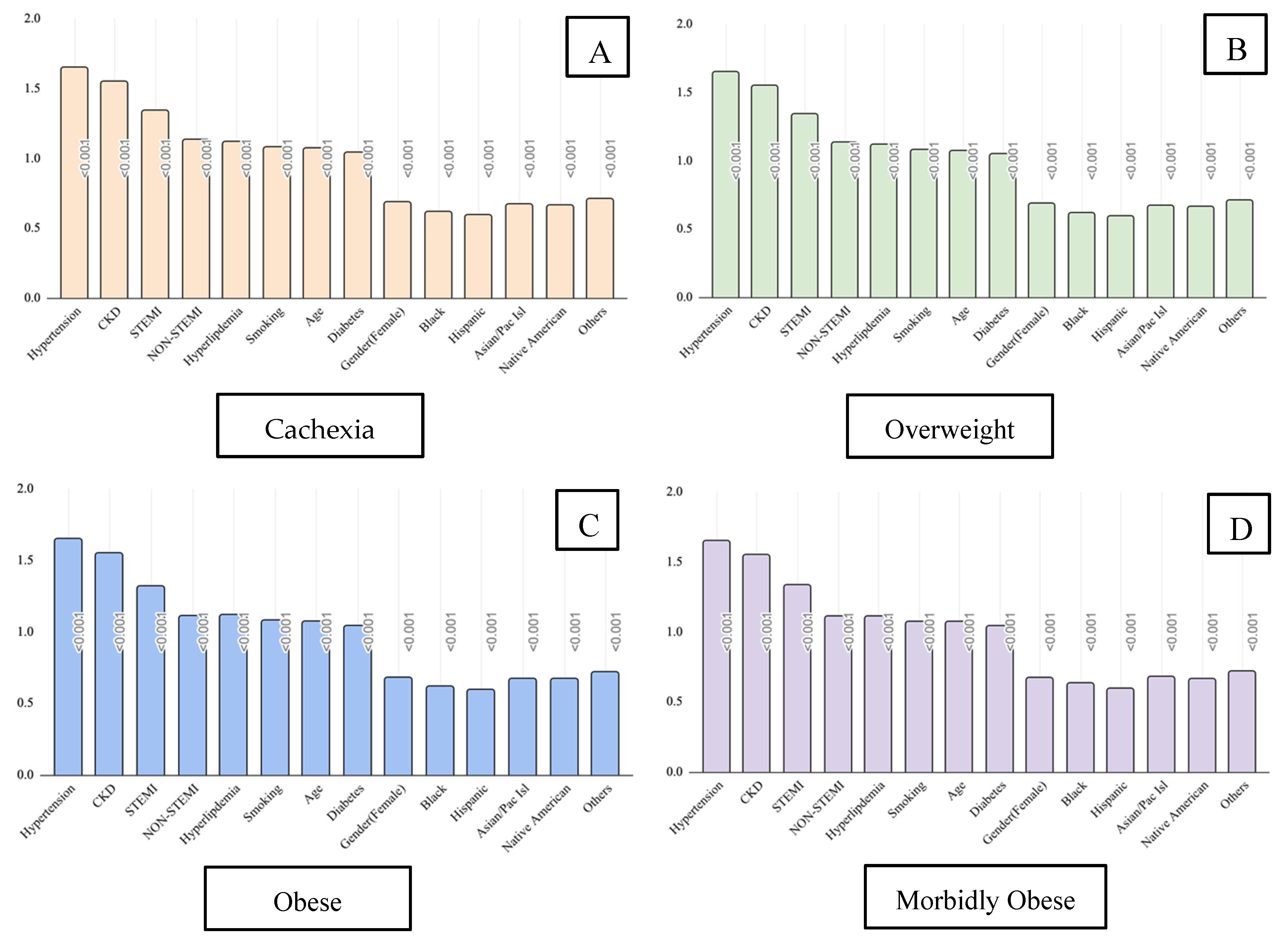
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, X.J.; Wang, B.B.; Hou, F.F.; Jiao, Y.; Li, H.-W.; Lv, S.-P.; Li, F.-H. Global burden of atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter and its attributable risk factors from 1990 to 2019. Europace 2023, 25, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; He, J.; Han, Y.; Han, S.; Li, P.; Liao, H.; Guo, J. Global burden of atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter and its attributable risk factors from 1990 to 2021. Europace 2024, 26, euae195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joglar, J.A.; Chung, M.K.; Armbruster, A.L.; Benjamin, E.J.; Chyou, J.Y.; Cronin, E.M.; Deswal, A.; Eckhardt, L.L.; Goldberger, Z.D.; Gopinathannair, R.; et al. Correction to: 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2024, 149, e167. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, M.K.; Eckhardt, L.L.; Chen, L.Y.; Ahmed, H.M.; Gopinathannair, R.; Joglar, J.A.; Noseworthy, P.A.; Pack, Q.R.; Sanders, P.; Trulock, K.M.; et al. Lifestyle and Risk Factor Modification for Reduction of Atrial Fibrillation: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020, 141, e750–e772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, S.S.; Levy, D.; Vasan, R.S.; Wang, T.J. The Framingham Heart Study and the epidemiology of cardiovascular disease: A historical perspective. Lancet 2014, 383, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Krijthe, B.P.; Aspelund, T.; Stepas, K.A.; Pencina, M.J.; Moser, C.B.; Sinner, M.F.; Sotoodehnia, N.; Fontes, J.D.; Janssens, A.C.J.W.; et al. Simple risk model predicts incidence of atrial fibrillation in a racially and geographically diverse population: The CHARGE-AF consortium. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2013, 2, e000102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariansen, I.; Reims, H.M.; Gjesdal, K.; Olsen, M.H.; Ibsen, H.; Devereux, R.B.; Okin, P.M.; Kjeldsen, S.E.; Dahlöf, B.; Wachtell, K. Impact of alcohol habits and smoking on the risk of new-onset atrial fibrillation in hypertensive patients with ECG left ventricular hypertrophy: The LIFE study. Blood Press. 2012, 21, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, N.; Xie, D.; Tao, K.; Chen, J.; Deo, R.; Horwitz, E.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Kallem, R.K.; Keane, M.G.; Lora, C.M.; et al. Atrial Fibrillation and Risk of ESRD in Adults with CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 11, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagkaris, C.; Zacharopoulou, L. Thyroid Disease (TD), Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) and Valvular Heart Disease (VHD) as modifiable risk factors of Atrial Fibrillation. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 58, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederiksen, T.C.; Dahm, C.C.; Preis, S.R.; Lin, H.; Trinquart, L.; Benjamin, E.J.; Kornej, J. The bidirectional association between atrial fibrillation and myocardial infarction. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2023, 20, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healey, J.S.; Connolly, S.J. Atrial fibrillation: Hypertension as a causative agent, risk factor for complications, and potential therapeutic target. Am. J. Cardiol. 2003, 91, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leopoulou, M.; Theofilis, P.; Kordalis, A.; Papageorgiou, N.; Sagris, M.; Oikonomou, E.; Tousoulis, D. Diabetes mellitus and atrial fibrillation-from pathophysiology to treatment. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 512–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Johnsen, S.P.; Guo, Y.; Lip, G.Y.H. Epidemiology of Atrial Fibrillation: Geographic/Ecological Risk Factors, Age, Sex, Genetics. Card. Electrophysiol. Clin. 2021, 13, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Levy, D.; Vaziri, S.M.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Belanger, A.J.; Wolf, P.A. Independent risk factors for atrial fibrillation in a population-based cohort. The Framingham Heart Study. JAMA 1994, 271, 840–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudis, C.A. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and atrial fibrillation: An unknown relationship. J. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N.R.; Taylor, K.S.; Taylor, C.J.; Aveyard, P. Weight change and the risk of incident atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart 2019, 105, 1799–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.X.; Sullivan, T.; Sun, M.T.; Mahajan, R.; Pathak, R.K.; Middeldorp, M.; Twomey, D.; Ganesan, A.N.; Rangnekar, G.; Roberts-Thomson, K.C.; et al. Obesity and the Risk of Incident, Post-Operative, and Post-Ablation Atrial Fibrillation: A Meta-Analysis of 626,603 Individuals in 51 Studies. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2015, 1, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khera, R.; Krumholz, H.M. With Great Power Comes Great Responsibility: Big Data Research From the National Inpatient Sample. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2017, 10, e003846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedrow, U.B.; Conen, D.; Ridker, P.M.; Cook, N.R.; Koplan, B.A.; Manson, J.E.; Buring, J.E.; Albert, C.M. The long- and short-term impact of elevated body mass index on the risk of new atrial fibrillation the WHS (women’s health study). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 2319–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, D.; Sen, A.; Schlesinger, S.; Norat, T.; Janszky, I.; Romundstad, P.; Tonstad, S.; Riboli, E.; Vatten, L.J. Body mass index, abdominal fatness, fat mass and the risk of atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 32, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.H.; Choi, E.K.; Han, K.D.; Lee, S.-R.; Lim, W.-H.; Cha, M.-J.; Cho, Y.; Oh, I.-Y.; Oh, S. Underweight is a risk factor for atrial fibrillation: A nationwide population-based study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 215, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.C.; Yang, Y.Y.; Chuang, S.L.; Chung, Y.W.; Wang, C.H.; Lin, L.Y. Underweight is a major risk factor for atrial fibrillation in Asian people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Zhi, H.; Yang, S.; Yu, E.Y.; Wang, L. Body Mass Index and the Risk of Atrial Fibrillation: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naser, N.; Dilic, M.; Durak, A.; Kulic, M.; Pepic, E.; Smajic, E.; Kusljugic, Z. The Impact of Risk Factors and Comorbidities on The Incidence of Atrial Fibrillation. Mater. Sociomed. 2017, 29, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamberlain, A.M.; Alonso, A.; Gersh, B.J.; Manemann, S.M.; Killian, J.M.; Weston, S.A.; Byrne, M.; Roger, V.L. Multimorbidity and the risk of hospitalization and death in atrial fibrillation: A population-based study. Am. Heart J. 2017, 185, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavousi, M. Differences in Epidemiology and Risk Factors for Atrial Fibrillation Between Women and Men. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Andrews, M.; DeJean, L.; Debski, N.; Exarchakis, A.; Fleming, J.; Gandhi, R.; Hum, C.; Kalladanthyil, A.; Maddigunta, R.; et al. Risk Factors Associated With Atrial Fibrillation in Elderly Patients. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2023, 15, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Munjal, J.S.; Jhajj, P.; Jhajj, S.; Jain, R. Obesity and Atrial Fibrillation: A Narrative Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e31205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, V.; Lambiase, P. Obesity and Atrial Fibrillation: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology and Novel Therapeutic Opportunities. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. Rev. 2019, 8, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarese, A.; Sardu, C.; Shu, J.; Santulli, G. Why is chronic obstructive pulmonary disease linked to atrial fibrillation? A systematic overview of the underlying mechanisms. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 276, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, E.Z.; Safford, M.M.; Muntner, P.; Khodneva, Y.; Dawood, F.Z.; Zakai, N.A.; Thacker, E.L.; Judd, S.; Howard, V.J.; Howard, G.; et al. Atrial fibrillation and the risk of myocardial infarction. JAMA Intern. Med. 2014, 174, 107–114, Erratum in JAMA Intern. Med. 2014, 174, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shetry, M.; Mahfouz, R.; Frere, A.F.; Abdeldayem, M. The interplay between atrial fibrillation and acute myocardial infarction. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2021, 82, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadde, S.; Kalluru, R.; Cherukuri, S.P.; Chikatimalla, R.; Dasaradhan, T.; Koneti, J. Atrial Fibrillation in Chronic Kidney Disease: An Overview. Cureus 2022, 14, e27753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.Y.; Gupta, D.; Wong, C.F.; Lip, G.Y.H. Pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation and chronic kidney disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 1046–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, Y.L.; Kang, M.; Kang, E.; Ryu, H.; Kim, Y.; Han, S.S.; Ahn, C.; Oh, K. Association of Chronic Kidney Disease With Atrial Fibrillation in the General Adult Population: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e028496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volgman, A.S.; Bairey Merz, C.N.; Benjamin, E.J.; Curtis, A.B.; Fang, M.C.; Lindley, K.J.; Pepine, C.J.; Vaseghi, M.; Waldo, A.L.; Wenger, N.K.; et al. Sex and Race/Ethnicity Differences in Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 2812–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannel, W.B.; Abbott, R.D.; Savage, D.D.; McNamara, P.M. Epidemiologic features of chronic atrial fibrillation: The Framingham study. N. Engl. J. Med. 1982, 306, 1018–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbadebo, T.D.; Okafor, H.; Darbar, D. Differential impact of race and risk factors on incidence of atrial fibrillation. Am. Heart J. 2011, 162, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.G.; Newton-Cheh, C.; Almgren, P.; Melander, O.; Platonov, P.G. Genetic polymorphisms for estimating risk of atrial fibrillation in the general population: A prospective study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2012, 172, 742–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sha, R.; Baines, O.; Hayes, A.; Tompkins, K.; Kalla, M.; Holmes, A.P.; O’Shea, C.; Pavlovic, D. Impact of Obesity on Atrial Fibrillation Pathogenesis and Treatment Options. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2024, 13, e032277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wats, K.; Kiser, A.; Makati, K.; Sood, N.; DeLurgio, D.; Greenberg, Y.; Yang, F. The Convergent Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Procedure: Evolution of a Multidisciplinary Approach to Atrial Fibrillation Management. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. Rev. 2020, 9, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagris, M.; Vardas, E.P.; Theofilis, P.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Oikonomou, E.; Tousoulis, D. Atrial Fibrillation: Pathogenesis, Predisposing Factors, and Genetics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | ICD-10 Code(s) |
|---|---|
| Atrial Fibrillation and Flutter | I48 |
| Cachexia | R64 |
| Overweight | E66.3 |
| Obesity | E66.9, E66.8, E66.0 |
| Morbid Obesity | E66.01, E66.2 |
| Smoking | F17.20, Z72.0, Z87.891 |
| Diabetes | E08–E13 |
| Hypertension | I10, I11.0, I11.9, I120, I129, I13.0, I13.10, I13.11, I13.2, I15.0, I15.1, I15.2, I15.9, I16.0, I16.1, I16.9 |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease | J41.0, J41.1, J41.8, J42., J43.0, J43.1, J43.2, J43.8, J43.9, J44.0, J44.1, J44.9, J47.0, J47.1, J47.9, J684 |
| Chronic Kidney Disease | I13.11, I13.2, N289, Q613, N181, N182, N183, N1830, N1831, N1832, N184, N185, N186, N189, R880, N19 |
| ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction | I21.01, I21.02, I21.09, I21.11, I21.19, I21.21, I21.29, I21.3, I21.9, I21.A1, I21.A9, I22.0, I22.1, I22.5, I22.9 |
| Non-ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction | I21.4, I22.2 |
| Old Myocardial Infarction | I25.2 |
| Variable | Cachexia | Overweight | Obesity | Morbid Obesity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | CI | OR | CI | OR | CI | OR | CI | |
| Smoking | 1.08 | 1.07–1.08 | 1.08 | 1.08–1.09 | 1.08 | 1.07–1.08 | 1.07 | 1.07–1.08 |
| DM | 1.04 | 1.04–1.05 | 1.05 | 1.04–1.05 | 1.04 | 1.04–1.04 | 1.04 | 1.04–1.04 |
| HTN | 1.65 | 1.64–1.66 | 1.65 | 1.64–1.66 | 1.65 | 1.64–1.66 | 1.65 | 1.64–1.66 |
| CKD | 1.55 | 1.54–1.55 | 1.55 | 1.54–1.55 | 1.55 | 1.54–1.55 | 1.55 | 1.54–1.55 |
| HLD | 1.12 | 1.12–1.13 | 1.12 | 1.12–1.12 | 1.12 | 1.11–1.12 | 1.11 | 1.1–1.11 |
| STEMI | 1.34 | 1.33–1.36 | 1.34 | 1.33–1.36 | 1.32 | 1.31–1.34 | 1.33 | 1.32–1.35 |
| Non-STEMI | 1.13 | 1.12–1.14 | 1.13 | 1.12–1.14 | 1.11 | 1.1–1.12 | 1.11 | 1.1–1.12 |
| Age | 1.07 | 1.07–1.07 | 1.07 | 1.07–1.07 | 1.07 | 1.07–1.07 | 1.07 | 1.07–1.07 |
| Gender (Female) | 0.69 | 0.69–0.69 | 0.69 | 0.69–0.69 | 0.68 | 0.68–0.68 | 0.67 | 0.67–0.68 |
| Race (Black) | 0.62 | 0.61–0.62 | 0.62 | 0.61–0.62 | 0.62 | 0.62–0.63 | 0.63 | 0.62–0.63 |
| Race (Hispanic) | 0.59 | 0.58–0.59 | 0.59 | 0.58–0.59 | 0.59 | 0.58–0.59 | 0.59 | 0.58–0.59 |
| Race (Asian/Pacific Islander) | 0.67 | 0.66–0.68 | 0.67 | 0.66–0.68 | 0.67 | 0.66–0.68 | 0.68 | 0.67–0.69 |
| Race (Native American) | 0.66 | 0.64–0.69 | 0.66 | 0.64–0.69 | 0.67 | 0.64–0.69 | 0.66 | 0.64–0.69 |
| Race (Other) | 0.71 | 0.7–0.73 | 0.71 | 0.70–0.73 | 0.72 | 0.7–0.73 | 0.72 | 0.7–0.73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sparling, K.; Hashemzadeh, M.; Movahed, M.R. The Impact of Weight Categories on the Association Between Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter and Known Risk Factors: A Nationwide Inpatient Data Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2187. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072187
Sparling K, Hashemzadeh M, Movahed MR. The Impact of Weight Categories on the Association Between Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter and Known Risk Factors: A Nationwide Inpatient Data Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(7):2187. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072187
Chicago/Turabian StyleSparling, Kennedy, Mehrtash Hashemzadeh, and Mohammad Reza Movahed. 2025. "The Impact of Weight Categories on the Association Between Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter and Known Risk Factors: A Nationwide Inpatient Data Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 7: 2187. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072187
APA StyleSparling, K., Hashemzadeh, M., & Movahed, M. R. (2025). The Impact of Weight Categories on the Association Between Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter and Known Risk Factors: A Nationwide Inpatient Data Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(7), 2187. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072187





