Reduction in Overall Time with Corticotomy Using Piezosurgery in Orthodontics: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Registration
2.2. Reporting Format
2.3. Patient, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome (PICO) Framework
2.4. Eligibility Criteria
2.5. Information Sources and Search Strategy
2.6. Data Extraction
2.7. Quality Assessment
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
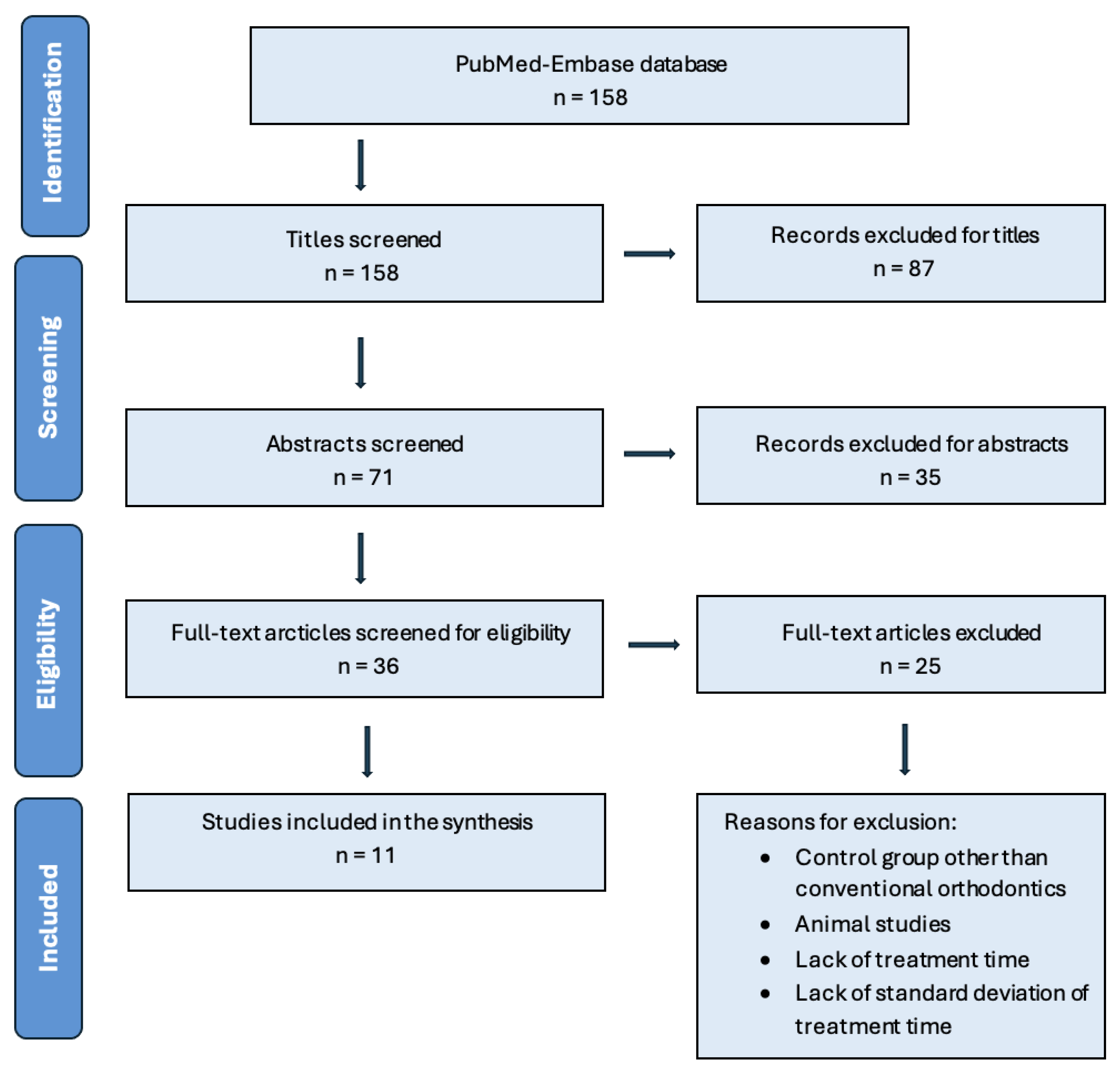
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Characteristics of the Included Trials
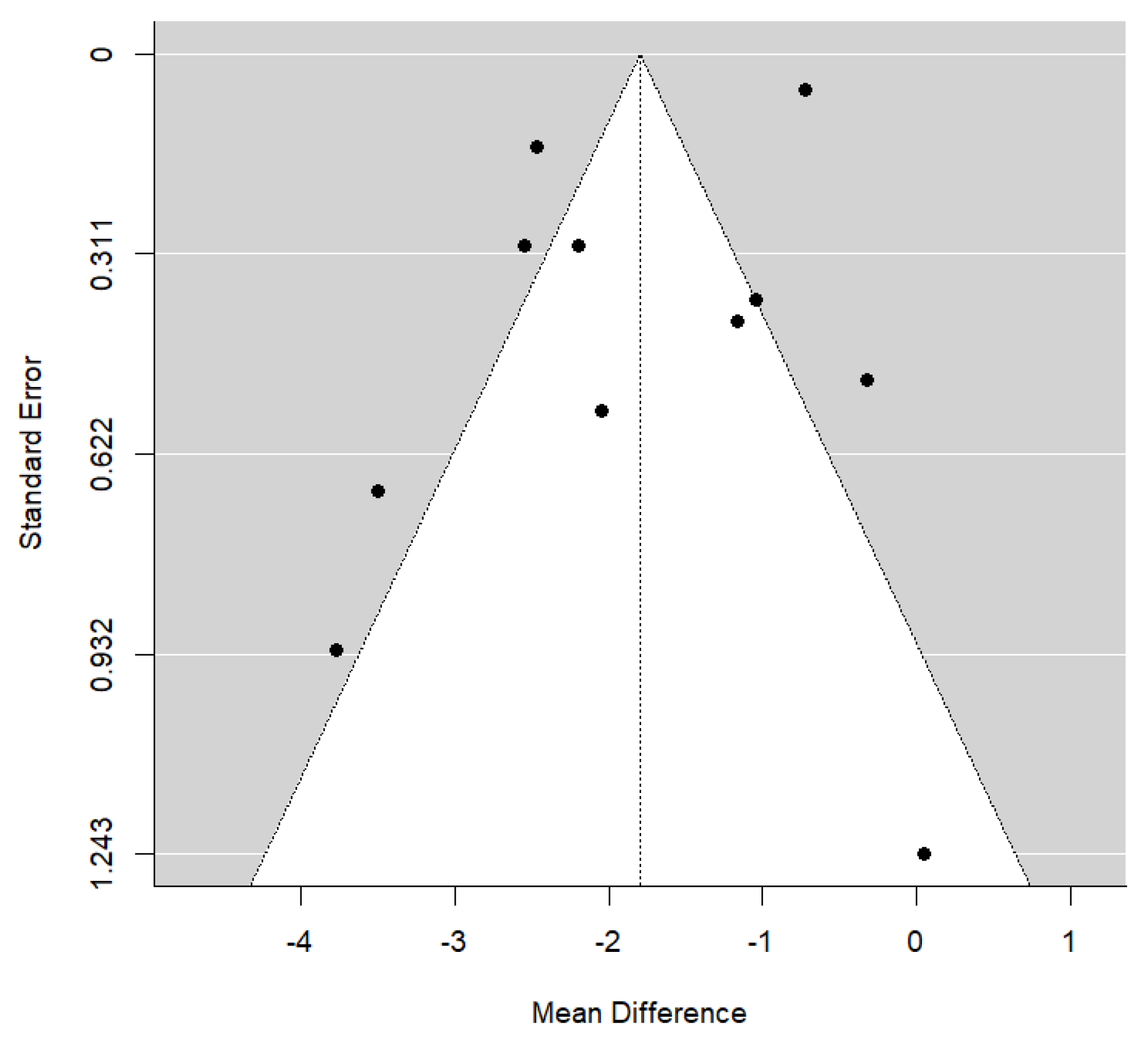
3.3. Synthesis of Results from Meta-Analysis
3.4. Piezocision-Assisted Corticotomy vs. Control
| Study (Year) | Treatment | Extractions | Treatment Test Group | Treatment Control Group | Overall Treatment Time (Piezocision Group) (Months) | Overall Treatment Time (Control Group) (months) | Difference in OTT (Control Group is Reference) (Months) | Statistical Significance | Rate of OTM (Distance/Time) | Authors’ Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sultana S et al. (2022) [4] | Severe anterior maxillary crowding | First maxillary premolars | Piezocision (PD: 3 mm PL: 4–5 mm) | Orthodontics only | 4.04 ± 0.60 | 5.08 ± 0.72 | −1.04 | Significantly shorter (20.4% fewer days) | Significantly faster (1.27 times faster) | Piezocision significantly reduces OTM time at the leveling and alignment stage without any adverse effect. The Piezocision group experienced no or mild pain and were satisfied with the treatment |
| Alfawal AMH et al. (2018) [17] | Canine retraction | First maxillary premolars | Piezocision (PD: 3 mm PL: 10 mm) | Orthodontics only | 3.3 ± 0.75 | 4.49 ± 1.00 | −1.19 | Significantly shorter (25% reduction in treatment time) | Significantly faster (1.5–2 times faster) | Piezocision accelerates OTM. |
| Charavet C et al. (2019) [21] | Mild overcrowding | N/A | Piezocision (PD: 3 mm PL: 5 mm) | Orthodontics only | 9.11 ± 2.63 | 12.88 ± 1.83 | −3.77 | Significantly shorter (36% reduction in treatment time) | Significantly faster (1.6 times faster) | Piezocision accelerates OTM. Scars were observed on 66% of patients. |
| Al Imam G et al. (2019) [13] | Retraction of four upper incisors | First maxillary premolars | Piezocision (PD: 3 mm) | Orthodontics only | 2.02 ± 0.20 | 2.74 ± 0.16 | −0.72 | Significantly shorter (27% reduction in treatment time) | Significantly faster (1.53 times faster) | Piezocision accelerates OTM and decreases treatment time. |
| Gibreal et al. (2023) [22] | Severe anterior maxillary crowding | First maxillary premolars | Piezocision (PD: 3 mm PL: 5–8 mm) | Orthodontics only | 2.12 ± 0.38 | 4.59 ± 0.44 | −2.47 | Significantly shorter (53% reduction in treatment time) | Significantly faster (2.16 times faster) | Piezocision accelerates OTM. |
| Gibreal et al. (2019) [15] | Severe anterior mandibular crowding | First mandibular premolars | Piezocision (PD: 3 mm PL: 5–8 mm) | Orthodontics only | 1.76 ± 0.08 | 4.31 ± 1.26 | −2.55 | Significantly shorter (59% reduction in treatment time) | Significantly faster (2.45 times faster) | Piezocision accelerates OTM in severe crowding cases when accompanied with premolar extractions |
| Aksakalli et al. (2015) [16] | Bilateral upper canine distalization | First maxillary premolars | Piezocision (PD: 3 mm) | Orthodontics only | 3.53 ± 0.81 | 5.58 ± 0.94 | −2.05 | Significantly shorter (36% reduction in treatment time) | Significantly faster (2 times faster) | Piezocision accelerates OTM, decreases OTT, is helpful for posterior anchorage control, and does not negatively affect periodontal health. |
| Tuncer et al. (2017) [14] | En-masse retraction | Class I: All 4 first premolars Class II: First maxillary premolars | Piezocision (PD: 3 mm) | Orthodontics only | 9.31 ± 4.09 | 9.26 ± 2.54 | +0.05 | Insignificantly longer | Insignificant difference | Piezosurgery showed no significant effect in accelerating en-masse retraction, despite potentially altering tissue reactions. |
| Uribe et al. (2017) [18] | Severe anterior mandibular crowding | N/A | Piezocision (PD: 1 mm) | Orthodontics only | 3.35 ± 1.14 | 3.67 ± 1.51 | −0.32 | Insignificantly shorter | Insignificant difference | No treatment time difference between piezocision and conventional orthodontics. |
| Gibreal et al. (2022) [20] | Severe anterior mandibular crowding | First maxillary premolars | Piezocision (PD: 3 mm PL: 5 mm) | Orthodontics only | 2.03 ± 0.41 | 4.23 ± 1.16 | −2.2 | Significantly shorter (48% reduction in treatment time) | Significantly faster (2 times faster) | Minimally invasive 3D-guided Piezocision is effective in accelerating OTM. |
| Ma et al. (2015) [19] | Traction of impacted mandibular third molars | N/A | Piezocision | Orthodontics only | 3.99 ± 2.29 | 7.49 ± 1.30 | −3.5 | Significantly shorter (46% reduction in treatment time) | Significantly faster (1.87 times faster) | Piezocision accelerates the traction of third molars. |
3.5. Location Impact
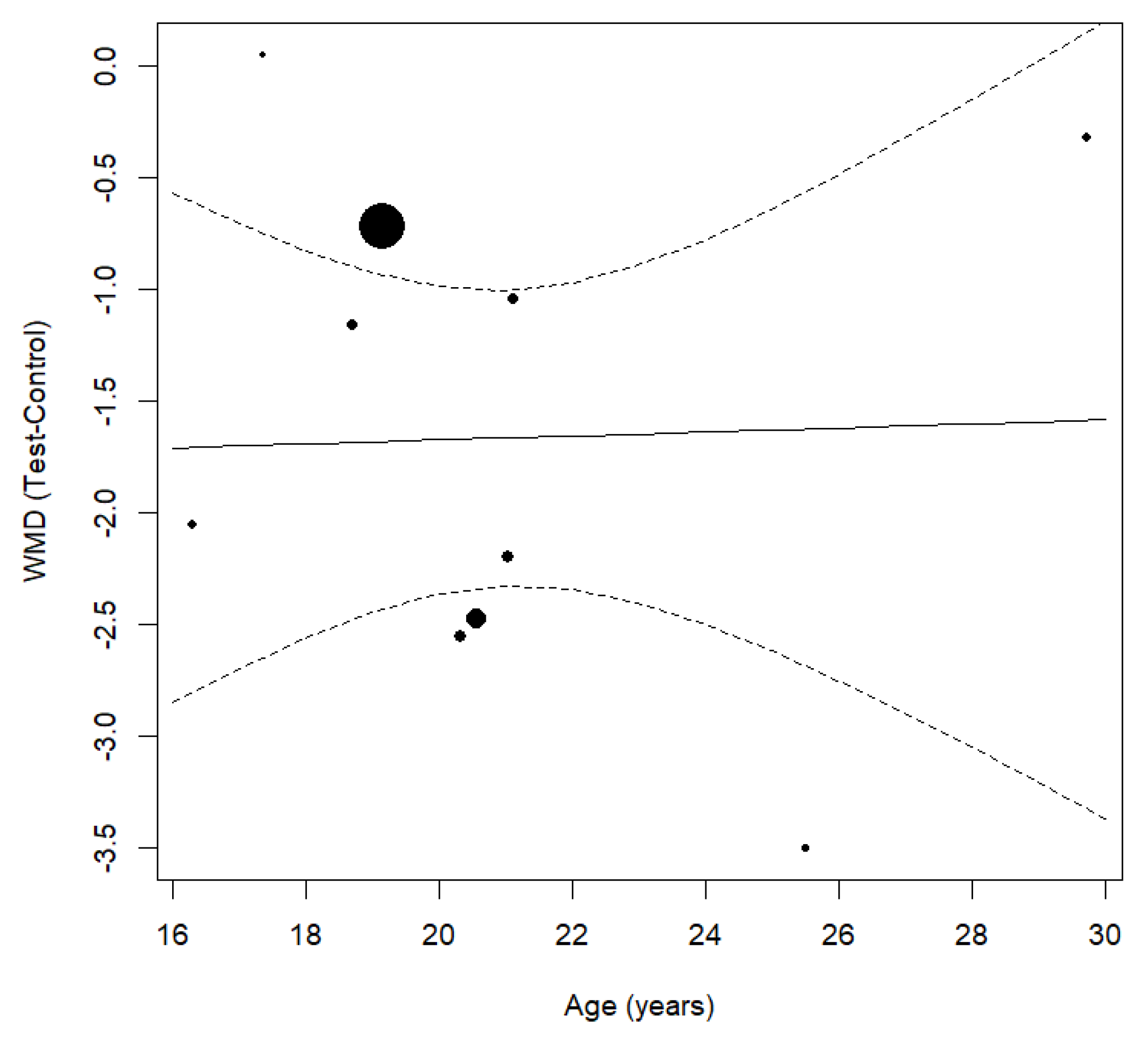
3.6. Age Impact
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OTM | orthodontic tooth movement |
| RAP | regional acceleratory phenomenon |
References
- Keser, E.I.; Dibart, S. Sequential piezocision: A novel approach to accelerated orthodontic treatment. Am. J. Orthod. 2013, 144, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcko, M.T.; Wilcko, W.M.; Bissada, N.F. An Evidence-Based Analysis of Periodontally Accelerated Orthodontic and Osteogenic Techniques: A Synthesis of Scientific Perspectives. Semin. Orthod. 2008, 14, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wu, J.; Jiang, J.; Liang, C.; Wang, N.E.; Jing, W.; Xu, L. Periodontal Effect of Periodontally Accelerated Osteogenic Orthodontics in Skeletal Angle Class III: A Nonrandomized, Controlled Trial. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2020, 40, e169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, S.; Ab Rahman, N.; Zainuddin, S.L.A.; Ahmad, B. Effect of piezocision procedure in levelling and alignment stage of fixed orthodontic treatment: A randomized clinical trial. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibart, S.; Keser, E.; Nelson, D. Piezocision™-assisted orthodontics: Past, present, and future. Semin. Orthod. 2015, 21, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keser, E.; Naini, F.B. Accelerated orthodontic tooth movement: Surgical techniques and the regional acceleratory phenomenon. Maxillofac. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2022, 44, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apalimova, A.; Roselló, À.; Jané-Salas, E.; Arranz-Obispo, C.; Marí-Roig, A.; López-López, J. Corticotomy in orthodontic treatment: Systematic review. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, E.; Fida, M.; Malik, D.S.; Irfan, S.; Gul, M. Comparison between conventional and piezocision-assisted orthodontics in relieving anterior crowding: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Orthod. 2025, 43, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viwattanatipa, N.; Charnchairerk, S. The effectiveness of corticotomy and piezocision on canine retraction: A systematic review. Korean J. Orthod. 2018, 48, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, P.W. Popping the (PICO) question in research and evidence-based practice. Appl. Nurs. Res. 2002, 15, 197–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Juni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savović, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Imam, G.; AAjaj, M.; Hajeer, M.Y.; Al-Mdalal, Y.; Almashaal, E. Evaluation of the effectiveness of piezocision-assisted flapless corticotomy in the retraction of four upper incisors: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Dent. Med. Probl. 2019, 56, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunçer, N.İ.; Arman-Özçırpıcı, A.; Oduncuoğlu, B.F.; Göçmen, J.S.; Kantarcı, A. Efficiency of piezosurgery technique in miniscrew supported en-masse retraction: A single-centre, randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Orthod. 2017, 39, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibreal, O.; Hajeer, M.Y.; Brad, B. Efficacy of piezocision-based flapless corticotomy in the orthodontic correction of severely crowded lower anterior teeth: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Orthod. 2019, 41, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksakalli, S.; Calik, B.; Kara, B.; Ezirganli, S. Accelerated tooth movement with piezocision and its periodontal-transversal effects in patients with Class II malocclusion. Angle Orthod. 2015, 86, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfawal, A.M.H.; Hajeer, M.Y.; Ajaj, M.A.; Hamadah, O.; Brad, B. Evaluation of piezocision and laser-assisted flapless corticotomy in the acceleration of canine retraction: A randomized controlled trial. Head Face Med. 2018, 14, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, F.; Davoody, L.; Mehr, R.; Jayaratne, Y.S.N.; Almas, K.; Sobue, T.; Allareddy, V.; Nanda, R. Efficiency of piezotome-corticision assisted orthodontics in alleviating mandibular anterior crowding—A randomized clinical trial. Eur. J. Orthod. 2017, 39, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Xu, G.; Yang, C.; Xie, Q.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, S. Efficacy of the technique of piezoelectric corticotomy for orthodontic traction of impacted mandibular third molars. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 53, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibreal, O.; Al-Modallal, Y.; Al-Assaf, M. Evaluation of the Efficacy of 3D-guided Piezosurgery in Accelerating Mandibular Orthodontic Teeth Alignment: A Randomized Controlled Trial in Adults. Dentistry 3000 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charavet, C.; Lecloux, G.; Jackers, N.; Albert, A.; Lambert, F. Piezocision-assisted orthodontic treatment using CAD/CAM customized orthodontic appliances: A randomized controlled trial in adults. Eur. J. Orthod. 2019, 41, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibreal, O.; Al-Modallal, Y.; Mahmoud, G.; Gibreal, A. The efficacy and accuracy of 3D-guided orthodontic piezocision: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, H.M. The Regional Acceleratory Phenomenon: A Review. Henry Ford Hosp. Med. J. 1983, 31, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, G.; Campbell, P.M.; Buschang, R.P.; Buschang, P.H.; Rossouw, P.E. Effects of increased surgical trauma on rates of tooth movement and apical root resorption in foxhound dogs. J. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2010, 13, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Keywords |
|---|
| Accelerated orthodontics |
| Corticotomy |
| Orthodontic tooth movement |
| Orthodontic treatment |
| Piezocision |
| Treatment time reduction |
| Search Term | PubMed Search Strategy | Embase Search Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Piezosurgery | (“Piezosurgery”[MeSH] OR piezo*) | ‘piezosurgery’ OR ‘piezo*’ |
| Orthodontics | (“Orthodontics”[MeSH] OR orthodontic) | ‘orthodontics’ OR ‘orthodontic’ |
| Time Factors | (“Time Factors”[MeSH] OR treatment time) | ‘time factors’ OR ‘treatment time’ |
| Combined Strategy | ((“Piezosurgery”[MeSH] OR piezo*) AND (“Orthodontics”[MeSH] OR orthodontic) AND (“Time Factors”[MeSH] OR treatment time)) | (‘piezosurgery’ OR ‘piezo*’) AND (‘orthodontics’ OR ‘orthodontic’) AND (‘time factors’ OR ‘treatment time’) |
| Study (Year) | Study Design | Range, Mean Age | n (Patients) | Follow-Up | Comparison Protocols | Location | Setting |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sultana S et al. (2022) [4] | RCT | 21.07, SD ± 2.69 (18–30) | 13 | Before treatment, 1 and 2 months post-treatment, and at the end of leveling and alignment stage | Piezocision | Maxillary | The Orthodontics Unit of University Sains Malaysia, Malaysia |
| Alfawal AMH et al. (2018) [17] | RCT | 18.70, SD ± 3.6 | 18 | Two-week interval and 1-, 2-, 3-, and 4-month measurements taken | Piezocision | Maxillary | Orthodontic Department of the University of Damascus Dental School, Syria |
| Charavet C et al. (2019) [21] | RCT | 27.90, SD ± 7.6 | 24 | Every 2 weeks, archwires were changed only when full bracket engagement was achieved | Piezocision | Maxillary and mandibular | University Hospital Liege, Belgium |
| Al Imam G et al. (2019) [13] | RCT | 19.15, SD ± 3.40 | 42 | Maxillary alginate impressions taken at the onset and every 3 weeks until week 12. Cephalometry at onset and week 12 | Piezocision | Maxillary | Department of Orthodontics at the University of Damascus Dental School, Syria |
| Gibreal et al. (2023) [22] | RCT | 20.56, SD ± 3.71 | 32 | Wire changes made when necessary, until full alignment was achieved | Piezocision | Maxillary | Department of Orthodontics at the University of Damascus Dental School, Syria |
| Gibreal et al. (2019) [15] | RCT | 20.32, SD ± 1.96 | 36 | Two-week interval. Little’s Irregularity Index (LII) was calculated at monthly intervals | Piezocision | Mandibular | Departments of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Orthodontics at the University of Damascus Dental School, Syria |
| Aksakalli et al. (2015) [16] | RCT | 16.30, SD ± 2.4 | 10 | Two-week interval. Pre- and post-distalization model casts | Piezocision | Maxillary | Department of Orthodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Bezmialem Vakif University, Istanbul, Turkey |
| Tuncer et al. (2017) [14] | RCT | 17.35, SD ± 2.6 | 30 | Rates were measured on days 15, 30, 60, 90, and 120. Dental casts were obtained before and after treatment | Piezocision | Maxillary | Department of Orthodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Baskent University Ankara, Turkey |
| Uribe et al. (2017) [18] | RCT | 29.73, SD ± 11.19 | 29 | Experimental subjects were monitored 1 week post-surgery. All subjects were followed monthly after the first wire placement, with mandibular study casts taken every 4–5 weeks | Piezocision | Mandibular | Division of Orthodontics, Department of Craniofacial Sciences, University of Connecticut School of Dental Medicine, Farmington, USA |
| Gibreal et al. (2022) [20] | RCT | 21.03, SD ± 1.96 | 34 | Two-week interval. Little’s Irregularity Index (LII) was calculated using dental casts before, 1 month, 2 months, and after treatment | Piezocision | Mandibular | Department of Orthodontics at the University of Damascus Dental School, Syria |
| Ma et al. (2015) [19] | RCT | 25.50, SD ± 5.2 | 30 | Forty-eight h post-surgery. Monthly monitoring after the orthodontic appliance was inserted | Piezocision | Mandibular | Department of Oral Surgery, Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital affiliated with Shanghai Jiao Tong University, School of Medicine, Shanghai, China |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ebrahim Zaidan, N.; Hernández-Alfaro, F.; Wang, H.-L.; Gargallo-Albiol, J. Reduction in Overall Time with Corticotomy Using Piezosurgery in Orthodontics: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1947. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061947
Ebrahim Zaidan N, Hernández-Alfaro F, Wang H-L, Gargallo-Albiol J. Reduction in Overall Time with Corticotomy Using Piezosurgery in Orthodontics: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(6):1947. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061947
Chicago/Turabian StyleEbrahim Zaidan, Nur, Federico Hernández-Alfaro, Hom-Lay Wang, and Jordi Gargallo-Albiol. 2025. "Reduction in Overall Time with Corticotomy Using Piezosurgery in Orthodontics: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 6: 1947. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061947
APA StyleEbrahim Zaidan, N., Hernández-Alfaro, F., Wang, H.-L., & Gargallo-Albiol, J. (2025). Reduction in Overall Time with Corticotomy Using Piezosurgery in Orthodontics: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(6), 1947. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061947







