The Expression of F2RL1, P2RX2, P2RX3 and P2RY2 in the Esophagus of Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Their Relationship to Reflux Symptoms—A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Group and Sample Collection
2.2. RNA Isolation
2.3. Real-Time PCR
2.4. Dilated Intracellular Spaces
2.5. Health-Related Quality of Life
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
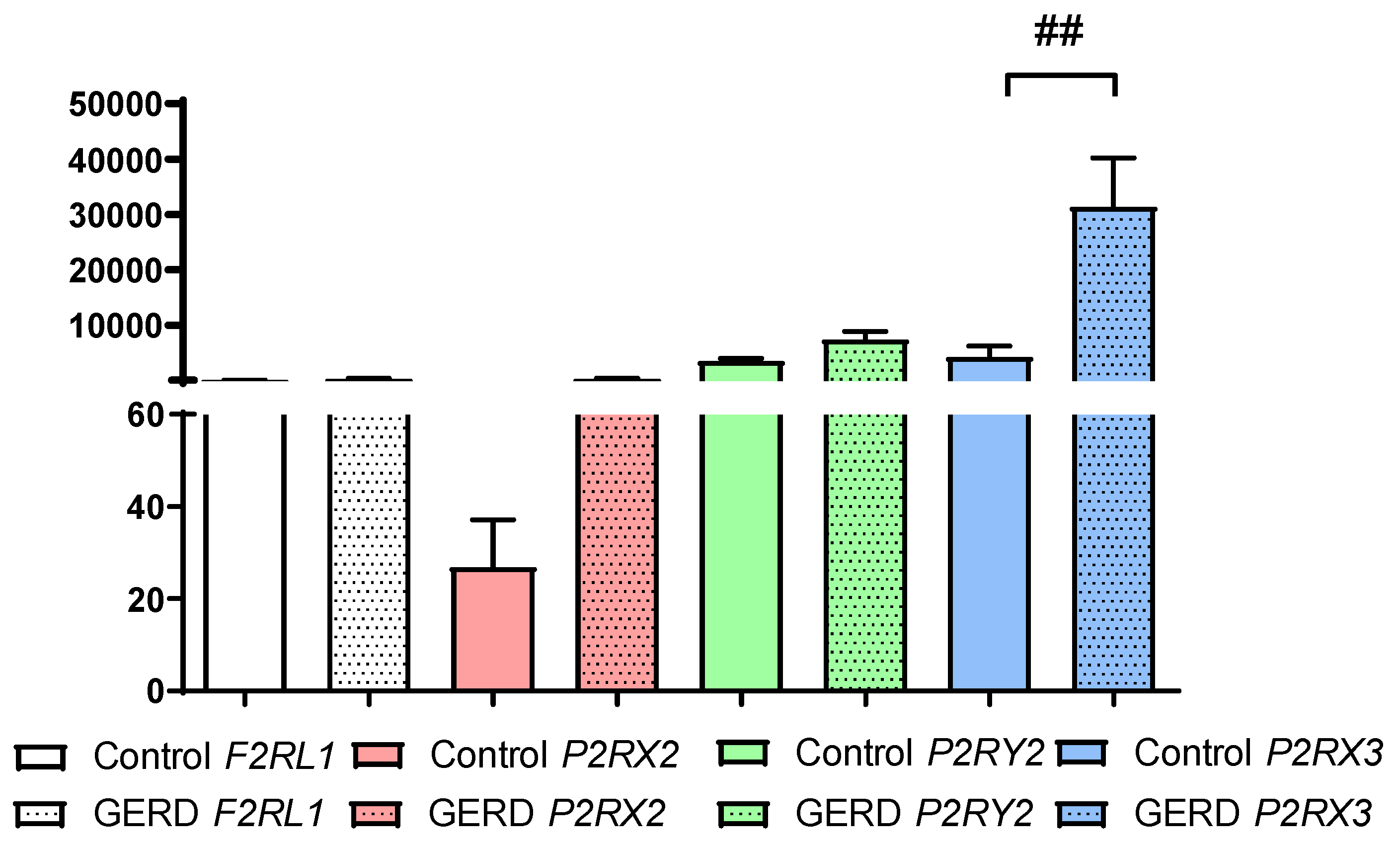
3.1. The Expression of F2RL, P2RX2, P2RX3 and P2RY2 in Patients with GERD
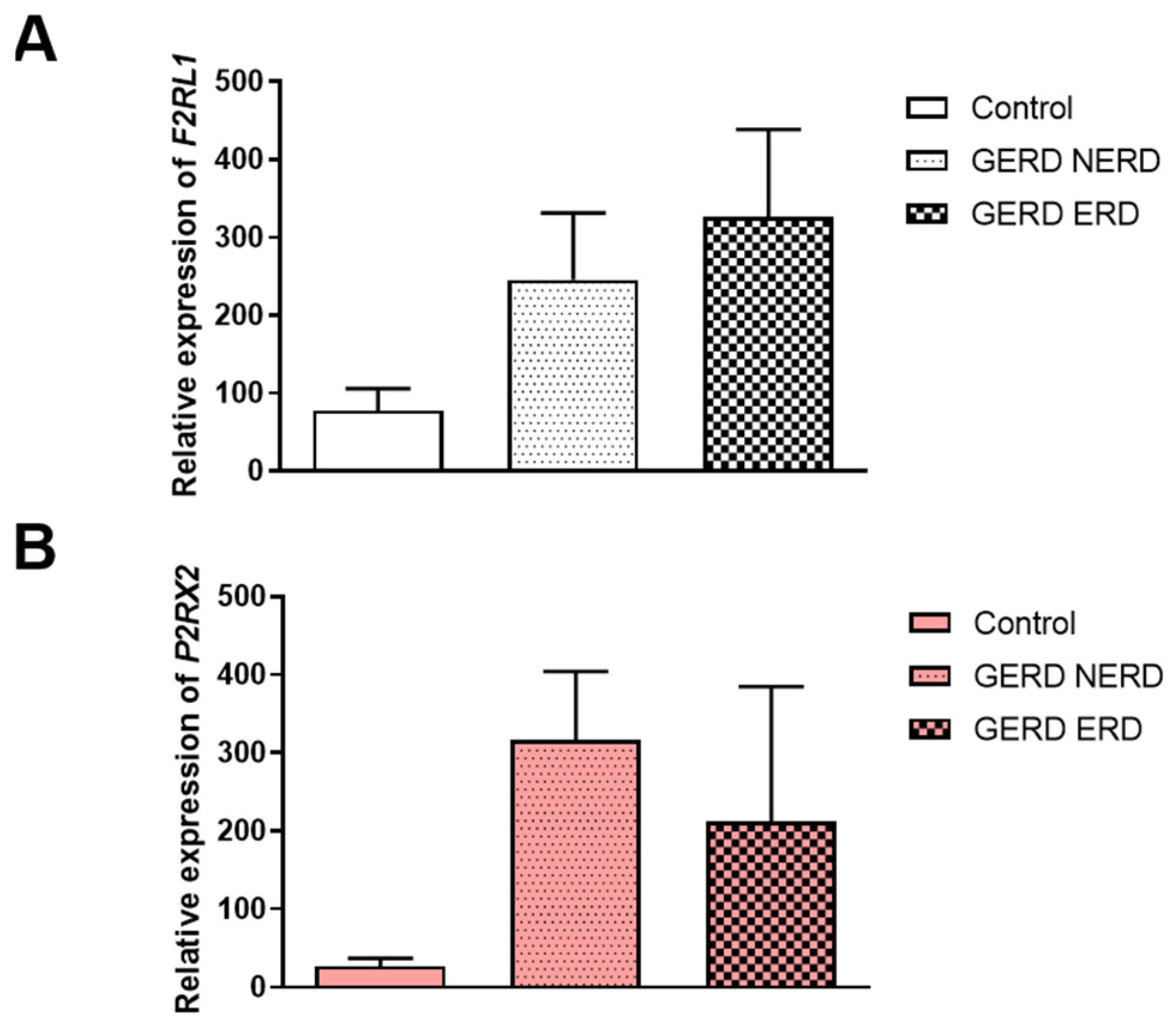
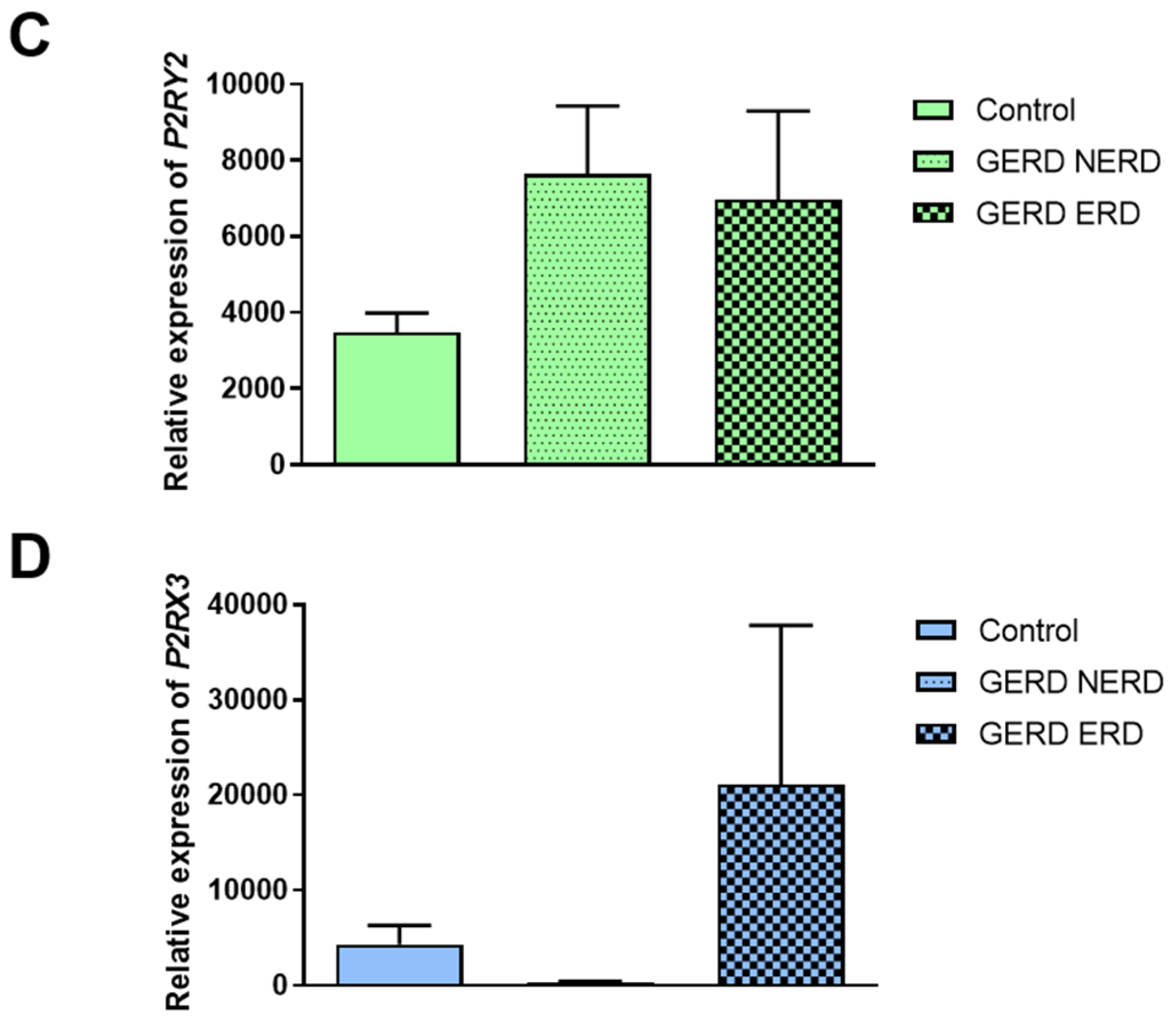
3.2. The Expression of F2RL1, P2RX2, P2RX3 and P2RY2 in NERD or ERD Type of GERD Patients
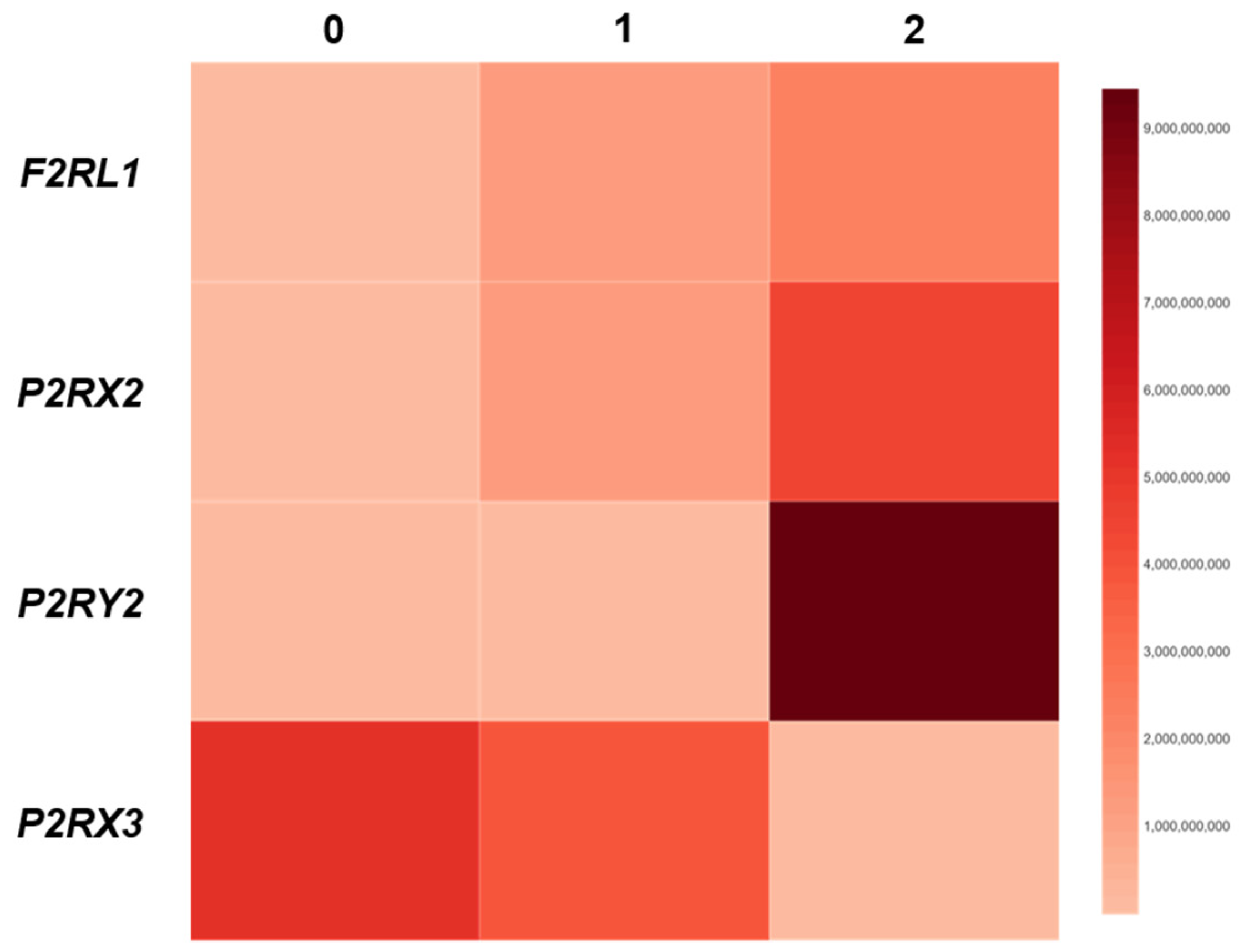
3.3. The Association Between F2RL1, P2RX2, P2RX3 and P2RY2 Expression and DIS Score in Patients with GERD
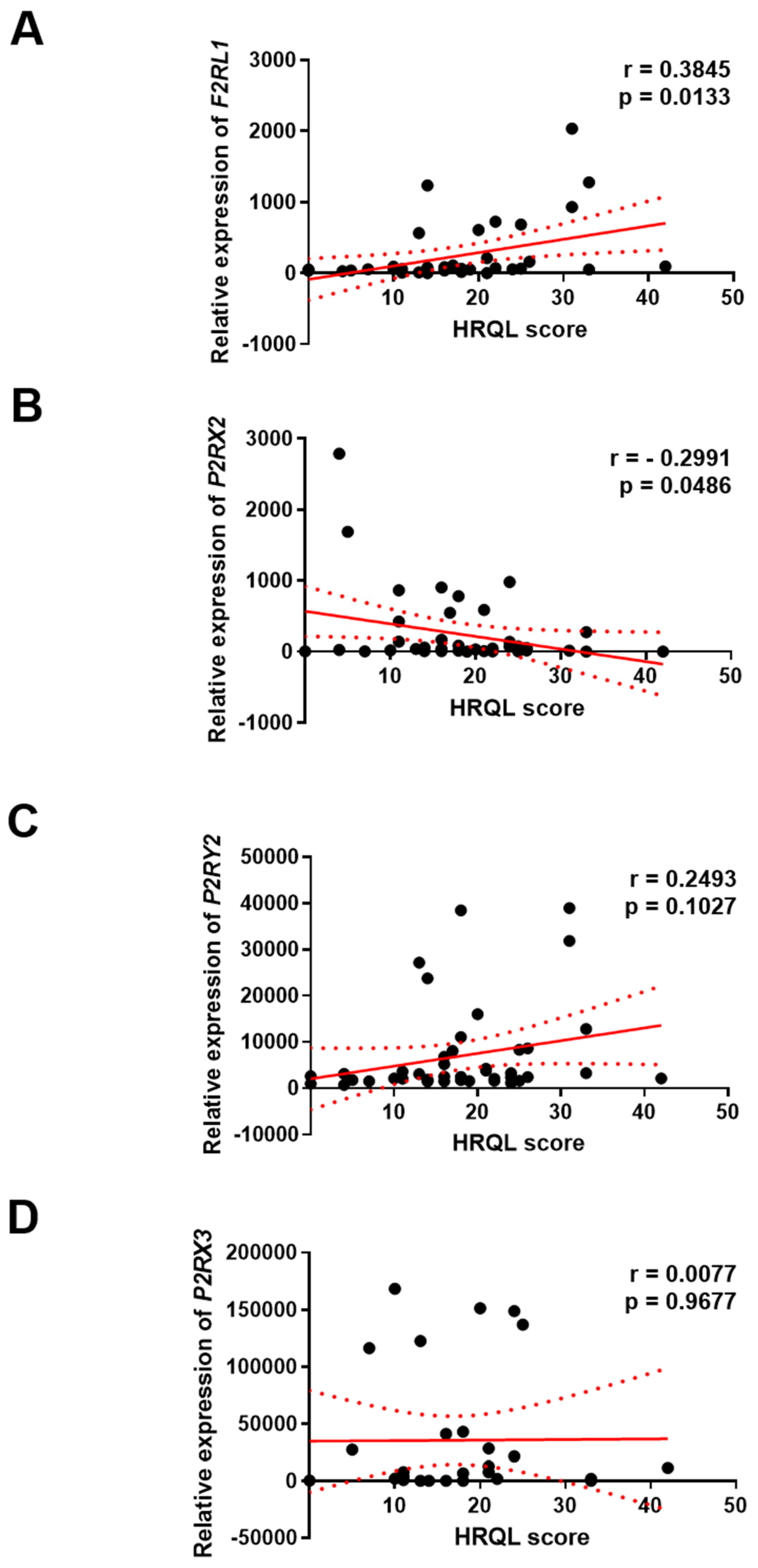
3.4. The Association Between F2RL1, P2RX2, P2RX3 and P2RY2 Expression and HRQL of GERD Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vakil, N.; Van Zanten, S.V.; Kahrilas, P.; Dent, J.; Jones, R.; Bianchi, L.K.; Cesario, K.B. The Montreal Definition and Classification of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Global Evidence-Based Consensus. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 1900–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Serag, H.B.; Sweet, S.; Winchester, C.C.; Dent, J. Update on the Epidemiology of Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease: A Systematic Review. Gut 2014, 63, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustaoglu, A.; Nguyen, A.; Spechler, S.; Sifrim, D.; Souza, R.; Woodland, P. Mucosal Pathogenesis in Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disease. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 32, e14022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundell, L.; Vieth, M.; Gibson, F.; Nagy, P.; Kahrilas, P.J. Systematic Review: The Effects of Long-Term Proton Pump Inhibitor Use on Serum Gastrin Levels and Gastric Histology. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 42, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altomare, A.; Michele Pier Luca Guarino Sara Emerenziani, M.P.; Cicala, M.; Drewes, A.M.; Krarup, A.L.; Brock, C.; Lottrup, C.; Frøkjær, J.B.; Souza, R.F.; Nardone, G.; et al. Gastrointestinal Sensitivity and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1300, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, R.F. Bringing GERD Management up to PAR-2. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 1944–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustaoglu, A.; Woodland, P. Sensory Phenotype of the Oesophageal Mucosa in Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandulski, A.; Wex, T.; Mönkemüller, K.; Kuester, D.; Fry, L.C.; Roessner, A.; Malfertheiner, P. Proteinase-Activated Receptor-2 in the Pathogenesis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 1934–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacenik, D.; Fichna, J.; Małecka-Wojciesko, E.; Mokrowiecka, A. Protease-Activated Receptors—Key Regulators of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Progression. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 7487–7497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergnolle, N. Modulation of Visceral Pain and Inflammation by Protease-Activated Receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 141, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, T.S.; Lu, H.; Sung, J.; Yeom, J.H.; Perrino, B.A.; Koh, S.D. The Functional Role of Protease-Activated Receptors on Contractile Responses by Activation of Ca2+ Sensitization Pathways in Simian Colonic Muscles. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2018, 315, G921–G931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Ninomiya, H.; Ohkura, S.; Ozaki, H.; Nasu, T. Impairment of PAR-2-Mediated Relaxation System in Colonic Smooth Muscle after Intestinal Inflammation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 148, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.C. Protease-Activated Receptor-1 (PAR1) and PAR2 but Not PAR4 Mediate Relaxations in Lower Esophageal Sphincter. Regul. Pept. 2007, 142, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inci, K.; Edebo, A.; Olbe, L.; Casselbrant, A. Expression of Protease-Activated-Receptor 2 (PAR-2) in Human Esophageal Mucosa. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 44, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagorodnyuk, V.P.; Chen, B.N.; Costa, M.; Brookes, S.J.H. Mechanotransduction by Intraganglionic Laminar Endings of Vagal Tension Receptors in the Guinea-Pig Oesophagus. J. Physiol. 2003, 553, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.J.; O’Donnell, T.A.; Blackshaw, L.A. P2X Purinoceptor-Induced Sensitization of Ferret Vagal Mechanoreceptors in Oesophageal Inflammation. J. Physiol. 2000, 523 Pt 2, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, C.; Fabbri, A.; Bortolotti, M.; Cenacchi, G.; Areni, A.; Scialpi, C.; Miglioli, M.; Di Febo, G. Dilated Intercellular Spaces as a Marker of Oesophageal Damage: Comparative Results in Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease with or without Bile Reflux. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 18, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelman, H.D.; Streutker, C.; Vieth, M.; Neumann, H.; Neurath, M.F.; Upton, M.P.; Sagaert, X.; Wang, H.H.; El-Zimaity, H.; Abraham, S.C.; et al. The Esophageal Mucosa and Submucosa: Immunohistology in GERD and Barrett’s Esophagus. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1300, 144–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, W.J.; Orlando, R.C. The Pathogenesis of Heartburn in Nonerosive Reflux Disease: A Unifying Hypothesis. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velanovich, V. The Development of the GERD-HRQL Symptom Severity Instrument. Dis. Esophagus 2007, 20, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Kim, N.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, J.S.; Jung, H.C. Increased TRPV1 and PAR2 MRNA Expression Levels Are Associated Only with the Esophageal Reflux Symptoms, but Not with the Extraesophageal Reflux Symptoms. Medicine 2016, 95, e4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, N.; Kuroda, M.; Suzuki, T.; Kamada, K.; Uchiyama, K.; Handa, O.; Takagi, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kuramoto, H. Role of Nociceptors/Neuropeptides in the Pathogenesis of Visceral Hypersensitivity of Nonerosive Reflux Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 2237–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Rehim, D.M.; Fath El-Bab, H.K.; Kamal, E.M. Expression of Proteinase-Activated Receptor-2 in the Esophageal Mucosa of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Patients: A Histomorphologic and Immunohistochemical Study. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2015, 23, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulamu, W.; Yisireyili, M.; Aili, A.; Takeshita, K.; Alimujiang, A.; Aipire, A.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Aizezi, M.; Li, Z.; et al. Chronic Stress Augments Esophageal Inflammation, and Alters the Expression of Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 and Protease-activated Receptor 2 in a Murine Model. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 5386–5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altomare, A.; Guarino, M.P.L.; Cocca, S.; Emerenziani, S.; Cicala, M. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Update on Inflammation and Symptom Perception. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 6523–6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelsett, L.; Malfertheiner, P.; Wex, T.; Kandulski, A. Mucosal Two-Step Pathogenesis in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Repeated Weakly Acidic Stimulation and Activation of Protease-Activated Receptor-2 on Mucosal Interleukin-8 Secretion. Digestion 2018, 98, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, J.; Oshima, T.; Chen, X.; Fukui, H.; Watari, J.; Miwa, H. Trypsin Impaired Epithelial Barrier Function and Induced IL-8 Secretion through Basolateral PAR-2: A Lesson from a Stratified Squamous Epithelial Model. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 303, G1105–G1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Woodland, P.; Sifrim, D. Esophageal Mucosal Integrity in Nonerosive Reflux Disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 48, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farré, R.; Fornari, F.; Blondeau, K.; Vieth, M.; De Vos, R.; Bisschops, R.; Mertens, V.; Pauwels, A.; Tack, J.; Sifrim, D. Acid and weakly acidic solutions impair mucosal integrity of distal exposed and proximal non-exposed human oesophagus. Gut 2010, 59, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caviglia, R.; Ribolsi, M.; Maggiano, N.; Gabbrielli, A.M.; Emerenziani, S.; Guarino, M.P.L.; Carotti, S.; Habib, F.R.; Rabitti, C.; Cicala, M. Dilated intercellular spaces of esophageal epithelium in nonerosive reflux disease patients with physiological esophageal acid exposure. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieh, K.R.; Yi, C.H.; Liu, T.T.; Tseng, H.L.; Ho, H.C.; Hsieh, H.T.; Chen, C.L. Evidence for Neurotrophic Factors Associating with TRPV1 Gene Expression in the Inflamed Human Esophagus. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, 971–e252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaya, F.; Shimosato, G.; Nagano, M.; Ueda, M.; Hashimoto, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Tanaka, M. NGF and GDNF Differentially Regulate TRPV1 Expression That Contributes to Development of Inflammatory Thermal Hyperalgesia. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 20, 2303–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecea, B.; Gallego, D.; Farré, R.; Opazo, A.; Aulí, M.; Jiménez, M.; Clavé, P. Regional functional specialization and inhibitory nitrergic and non-nitrergic coneurotransmission in the human esophagus. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 300, G782–G794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mokrowiecka, A.; Bartoszek, A.; Fabisiak, A.; Wróbel, A.; Fichna, J.; Wierzchniewska-Ławska, A.; Jacenik, D.; Małecka-Wojciesko, E. The Expression of F2RL1, P2RX2, P2RX3 and P2RY2 in the Esophagus of Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Their Relationship to Reflux Symptoms—A Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061884
Mokrowiecka A, Bartoszek A, Fabisiak A, Wróbel A, Fichna J, Wierzchniewska-Ławska A, Jacenik D, Małecka-Wojciesko E. The Expression of F2RL1, P2RX2, P2RX3 and P2RY2 in the Esophagus of Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Their Relationship to Reflux Symptoms—A Pilot Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(6):1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061884
Chicago/Turabian StyleMokrowiecka, Anna, Adrian Bartoszek, Adam Fabisiak, Agata Wróbel, Jakub Fichna, Agnieszka Wierzchniewska-Ławska, Damian Jacenik, and Ewa Małecka-Wojciesko. 2025. "The Expression of F2RL1, P2RX2, P2RX3 and P2RY2 in the Esophagus of Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Their Relationship to Reflux Symptoms—A Pilot Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 6: 1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061884
APA StyleMokrowiecka, A., Bartoszek, A., Fabisiak, A., Wróbel, A., Fichna, J., Wierzchniewska-Ławska, A., Jacenik, D., & Małecka-Wojciesko, E. (2025). The Expression of F2RL1, P2RX2, P2RX3 and P2RY2 in the Esophagus of Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Their Relationship to Reflux Symptoms—A Pilot Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(6), 1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061884








