Comparison Between Intravitreal Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Monotherapy and Vitrectomy in Age-Related Macular Degeneration with Large Submacular Hemorrhages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
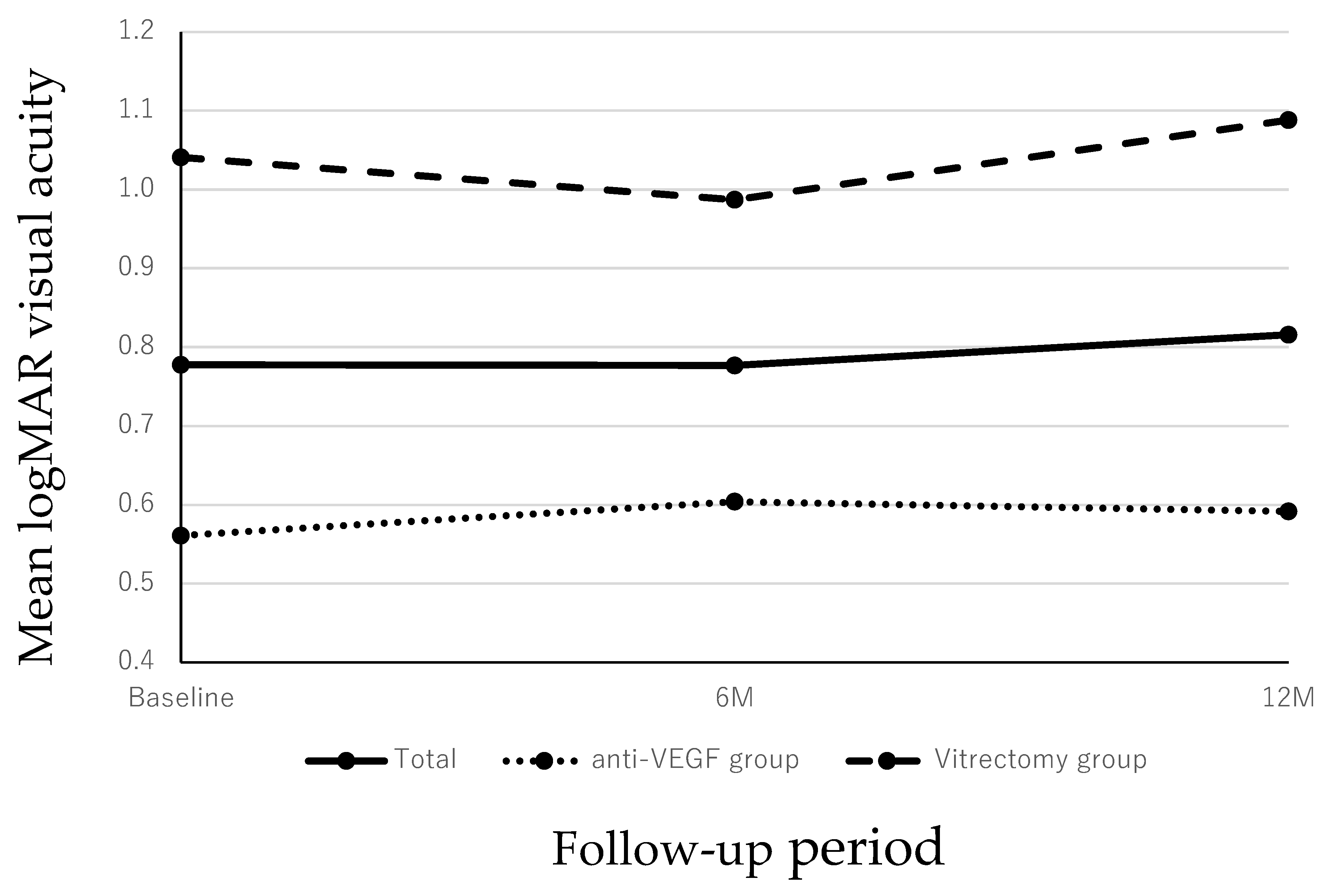
3.1. Changes in the BCVAs
3.2. Factors Affecting the BCVA at 12 Months and the BCVA Improvement
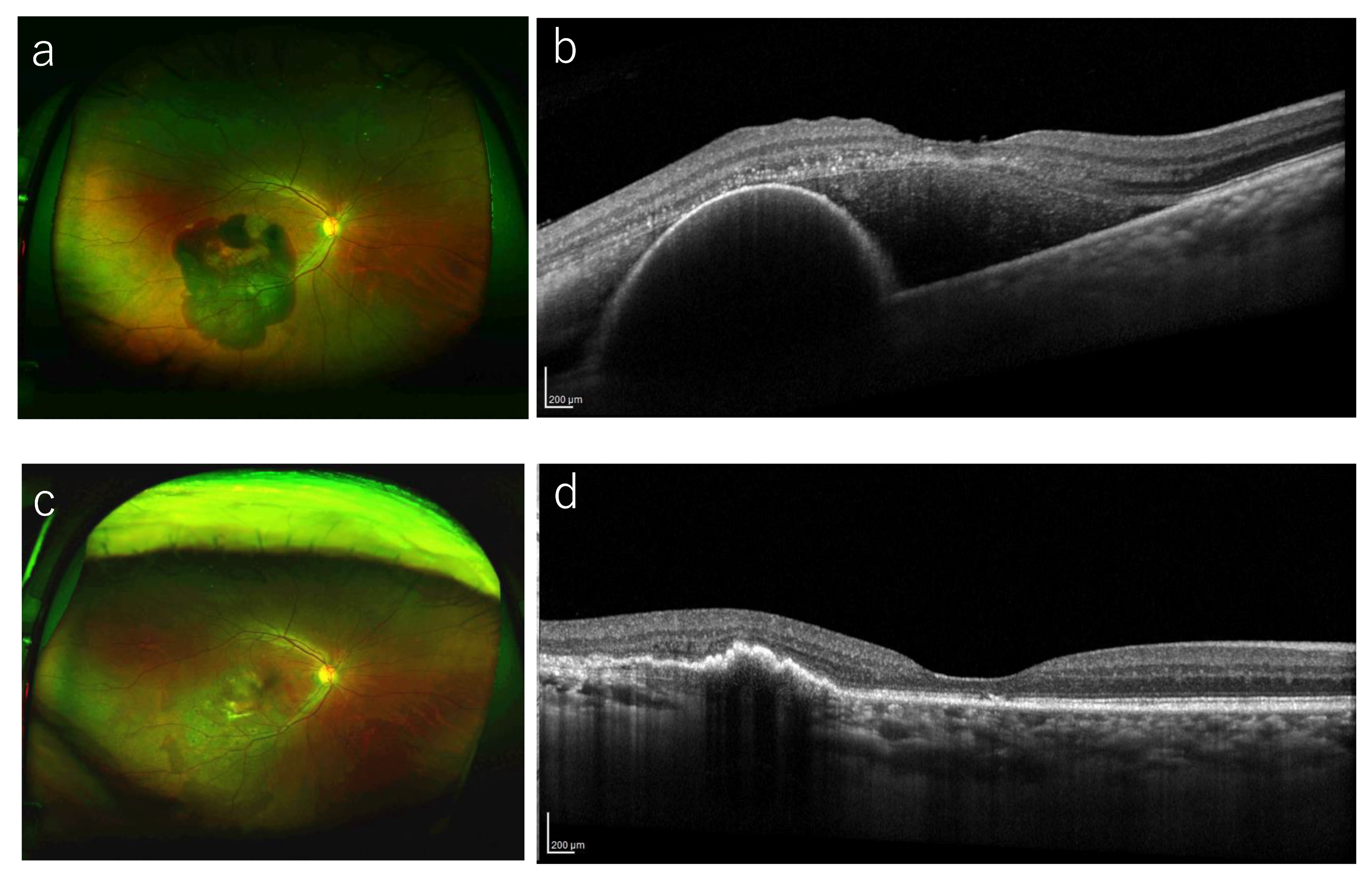
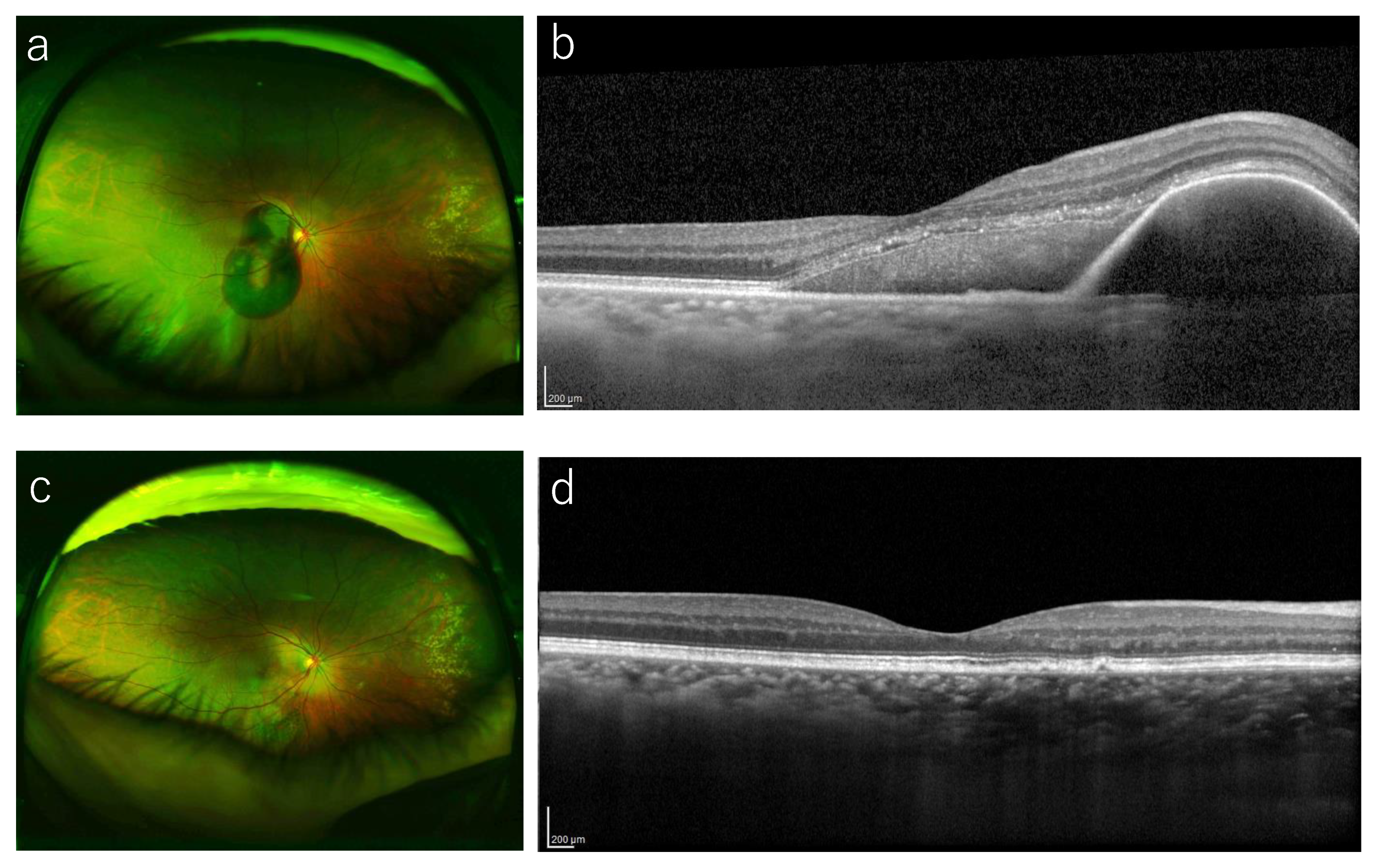
3.3. Complications During the Follow-Up Period
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| nAMD | neovascular age-related macular degeneration |
| SMH | submacular hemorrhage |
| PD | pneumatic displacement |
| tPA | tissue plasminogen activator |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| VH | vitreous hemorrhage |
| VA | visual acuity |
| SD-OCT | spectral-domain optical coherence tomography |
| DA | disc area |
| RRD | rhegmatogenous retinal detachment |
| IVA | intravitreal injections of aflibercept |
| IVBr | intravitreal injections of brolucizumab |
| BCVA | best-corrected visual acuity |
| IOL | intraocular lens |
| CFT | central foveal thickness |
| PED | pigment epithelial detachment |
| logMAR | logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution |
References
- Congdon, N.; O’Colmain, B.; Klaver, C.C.; Klein, R.; Munoz, B.; Friedman, D.S.; Kempen, J.; Taylor, H.R.; Mitchell, P.; Eye Diseases Prevalence Research, G. Causes and prevalence of visual impairment among adults in the United States. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2004, 122, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, R.R.; Jonas, J.B.; Flaxman, S.R.; Keeffe, J.; Leasher, J.; Naidoo, K.; Parodi, M.B.; Pesudovs, K.; Price, H.; White, R.A.; et al. Prevalence and causes of vision loss in high-income countries and in Eastern and Central Europe: 1990–2010. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 98, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glatt, H.; Machemer, R. Experimental subretinal hemorrhage in rabbits. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1982, 94, 762–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avery, R.L.; Fekrat, S.; Hawkins, B.S.; Bressler, N.M. Natural history of subfoveal subretinal hemorrhage in age-related macular degeneration. Retina 1996, 16, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, A.S.; Johnson, M.W.; Schneiderman, T.E.; Regillo, C.D.; Tornambe, P.E.; Poliner, L.S.; Blodi, B.A.; Elner, S.G. Management of submacular hemorrhage with intravitreous tissue plasminogen activator injection and pneumatic displacement. Ophthalmology 1999, 106, 1900–1906, discussion 1906–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadonosono, K.; Arakawa, A.; Yamane, S.; Inoue, M.; Yamakawa, T.; Uchio, E.; Yanagi, Y. Displacement of submacular hemorrhages in age-related macular degeneration with subretinal tissue plasminogen activator and air. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyman, G.A.; Nelson, N.C., Jr.; Alturki, W.; Blinder, K.J.; Paris, C.L.; Desai, U.R.; Harper, C.A., 3rd. Tissue plasminogen activating factor assisted removal of subretinal hemorrhage. Ophthalmic Surg. 1991, 22, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shienbaum, G.; Garcia Filho, C.A.; Flynn, H.W., Jr.; Nunes, R.P.; Smiddy, W.E.; Rosenfeld, P.J. Management of submacular hemorrhage secondary to neovascular age-related macular degeneration with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor monotherapy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 155, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama-Inoue, M.; Kitajima, Y.; Yanagi, Y.; Inoue, T.; Kadonosono, K. Intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor monotherapy in age-related macular degeneration with submacular hemorrhage. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, A.; Mehra, D.; Ghalibafan, S.; Patel, S.; Buali, F.; Panneerselvam, S.; Perez, N.; Hoyek, S.; Flynn, H.W., Jr.; Patel, N.; et al. Efficacy and safety of anti-vegf injections and surgery for age-related macular degeneration-related submacular hemorrhage: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmol. Retina 2024, 9, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mun, Y.; Park, K.H.; Park, S.J.; Cho, H.J.; Kim, C.G.; Kim, J.W.; Park, D.G.; Sagong, M.; Kim, J.H.; Woo, S.J. Comparison of treatment methods for submacular hemorrhage in neovascular age-related macular degeneration: Conservative versus active surgical strategy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, S.S.; Cheong, K.X.; Chan, H.H.; Choo, J.Q.H.; Tsai, A.S.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Yeo, I.Y.S.; Cheung, C.M.G.; Teo, K.Y.C. Pneumatic displacement of submacular haemorrhage secondary to neovascular age-related macular degeneration and polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Eye 2024, 38, 3374–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzelay, A.; Daniels, A.; Cohen, G.Y.; Barak, A.; Schwartz, S.; Katz, G. Pneumatic displacement with intravitreal tPA injection versus vitrectomy with sub retinal tPA injection in small and medium sub macular hemorrhages- a multicenter comparative study. BMC Ophthalmol. 2024, 24, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrielle, P.H.; Delyfer, M.N.; Glacet-Bernard, A.; Conart, J.B.; Uzzan, J.; Kodjikian, L.; Arndt, C.; Tadayoni, R.; Soudry-Faure, A.; Creuzot Garcher, C.P. Surgery, tissue plasminogen activator, antiangiogenic agents, and age-related macular degeneration study: A randomized controlled trial for submacular hemorrhage secondary to age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology 2023, 130, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Cho, H.J.; Yoo, S.G.; Kim, J.H.; Han, J.I.; Lee, T.G.; Kim, J.W. Intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor monotherapy for large submacular hemorrhage secondary to neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Eye 2015, 29, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamei, M.; Tano, Y. Tissue plasminogen activator-assisted vitrectomy: Surgical drainage of submacular hemorrhage. Dev. Ophthalmol. 2009, 44, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Chang, Y.S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, C.G.; Yoo, S.J.; Cho, H.J. Intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor for submacular hemorrhage from choroidal neovascularization. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total (n = 31) | Anti-VEGF Group (n = 17) | Vitrectomy Group(n = 14) | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 31 | 17 | 14 | |
| Sex (Male/Female) | 24/7 | 15/2 | 9/5 | 0.198 |
| Age, mean ± SD, year (range) | 73.4 ± 9.3(range, 48 to 95) | 71.1 ± 8.6 (range, 48 to 83) | 76.3 ± 9.7 (range, 56 to 95) | 0.121 |
| Lens status, phakia/IOL | 22/9 | 15/2 | 7/7 | 0.004 |
| Anticoagulant medication (+/−) | 24/7 | 14/3 | 10/4 | 0.671 |
| Type of AMD (PCV/Type 1 MNV) | 21/10 | 10/7 | 11/3 | 0.280 |
| Duration of symptoms (days) | 13.7 ± 9.3 (range, 1 to 40) | 16.5 ± 10.6 (range, 4 to 40) | 10.3 ± 6.2 (range, 1 to 23) | 0.062 |
| Mean size of submacular hemorrhage (DAs) | 5.2 ± 1.9 (range, 3.0 to 10.7) | 4.7 ± 1.3 (range, 3.0 to 6.9) | 5.7 ± 2.4 (range, 3.3 to 10.7) | 0.150 |
| Mean baseline logMAR BCVA | 0.78 ± 0.48 | 0.56 ± 0.27 | 1.04 ± 0.55 | 0.004 |
| Mean central foveal thickness (µm) | 853 ± 341 | 713 ± 251 | 1024 ± 365 | 0.009 |
| Mean thickness of SMH at the fovea(µm) | 522 ± 351 | 396 ± 195 | 675 ± 438 | 0.025 |
| Mean thickness of hemorrhagic PED at the fovea (µm) | 191 ± 321 | 159 ± 238 | 230 ± 407 | 0.549 |
| Dependent Variables | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Postoperative BCVA * | Improvement of the visual acuity ** | ||||||
| Independent variables | Partial Regression Coefficient | Standard Error | p value | Partial Regression Coefficient | Standard Error | p value | |
| Lens status | 0.361 | 0.155 | 0.028 | 0.389 | 0.149 | 0.015 | |
| Use of anticoagulants | ― | ― | ― | −0.335 | 0.172 | 0.063 | |
| Disc areas | ― | ― | ― | −0.054 | 0.040 | 0.191 | |
| Central foveal thickness | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.008 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.002 | |
| Baseline visual acuity | 0.436 | 0.177 | 0.021 | -0.605 | 0.187 | 0.003 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miyazato, M.; Maruyama-Inoue, M.; Tanaka, S.; Inoue, T.; Yanagi, Y.; Kadonosono, K. Comparison Between Intravitreal Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Monotherapy and Vitrectomy in Age-Related Macular Degeneration with Large Submacular Hemorrhages. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051477
Miyazato M, Maruyama-Inoue M, Tanaka S, Inoue T, Yanagi Y, Kadonosono K. Comparison Between Intravitreal Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Monotherapy and Vitrectomy in Age-Related Macular Degeneration with Large Submacular Hemorrhages. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(5):1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051477
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiyazato, Misa, Maiko Maruyama-Inoue, Shin Tanaka, Tatsuya Inoue, Yasuo Yanagi, and Kazuaki Kadonosono. 2025. "Comparison Between Intravitreal Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Monotherapy and Vitrectomy in Age-Related Macular Degeneration with Large Submacular Hemorrhages" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 5: 1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051477
APA StyleMiyazato, M., Maruyama-Inoue, M., Tanaka, S., Inoue, T., Yanagi, Y., & Kadonosono, K. (2025). Comparison Between Intravitreal Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Monotherapy and Vitrectomy in Age-Related Macular Degeneration with Large Submacular Hemorrhages. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(5), 1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051477






