Challenges in Saving Trauma Patients in Seoul Based on the 2016–2020 Community-Based Severe Trauma Survey
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
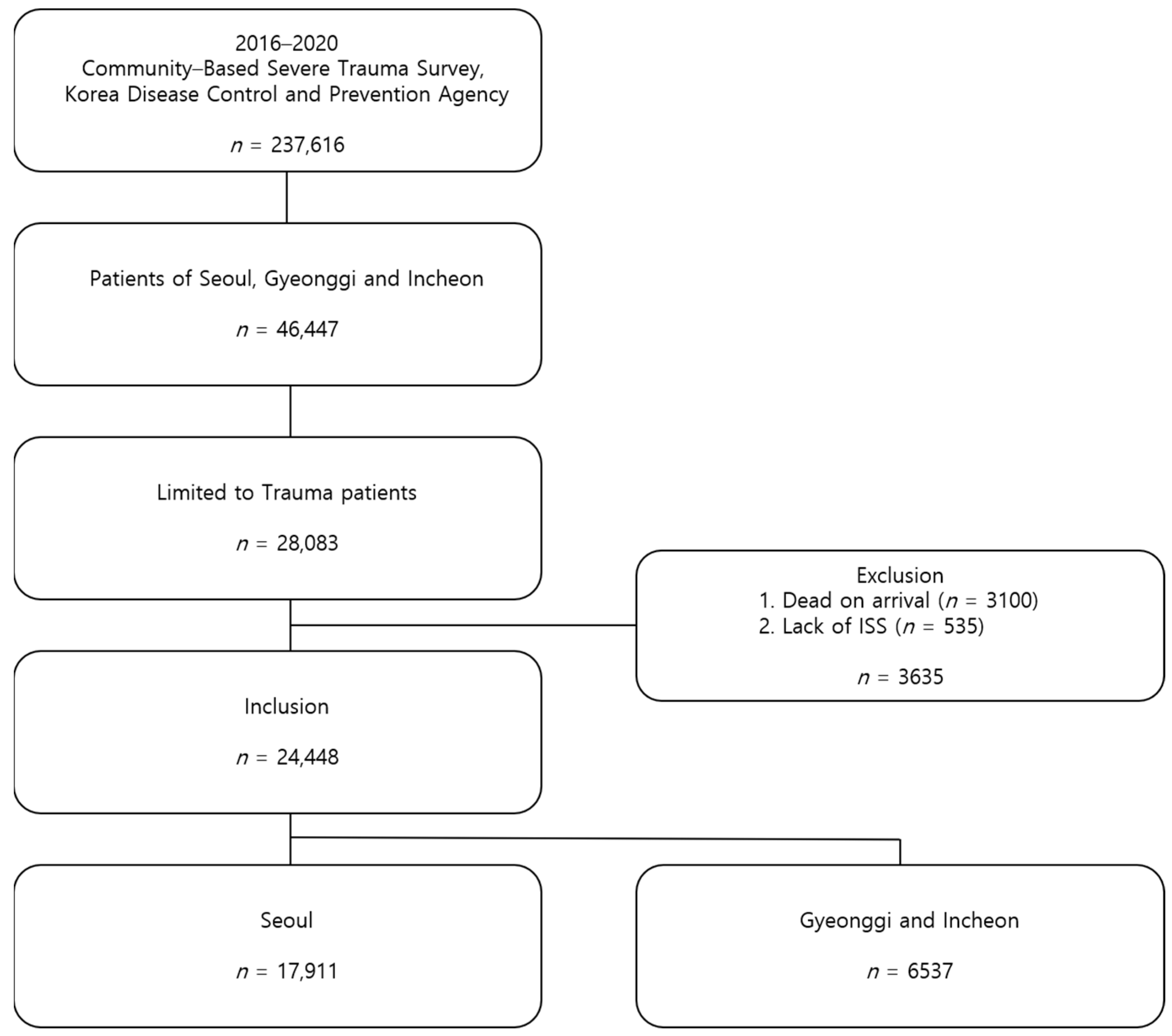
2.1. Study Design and Data Collection
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Study Settings
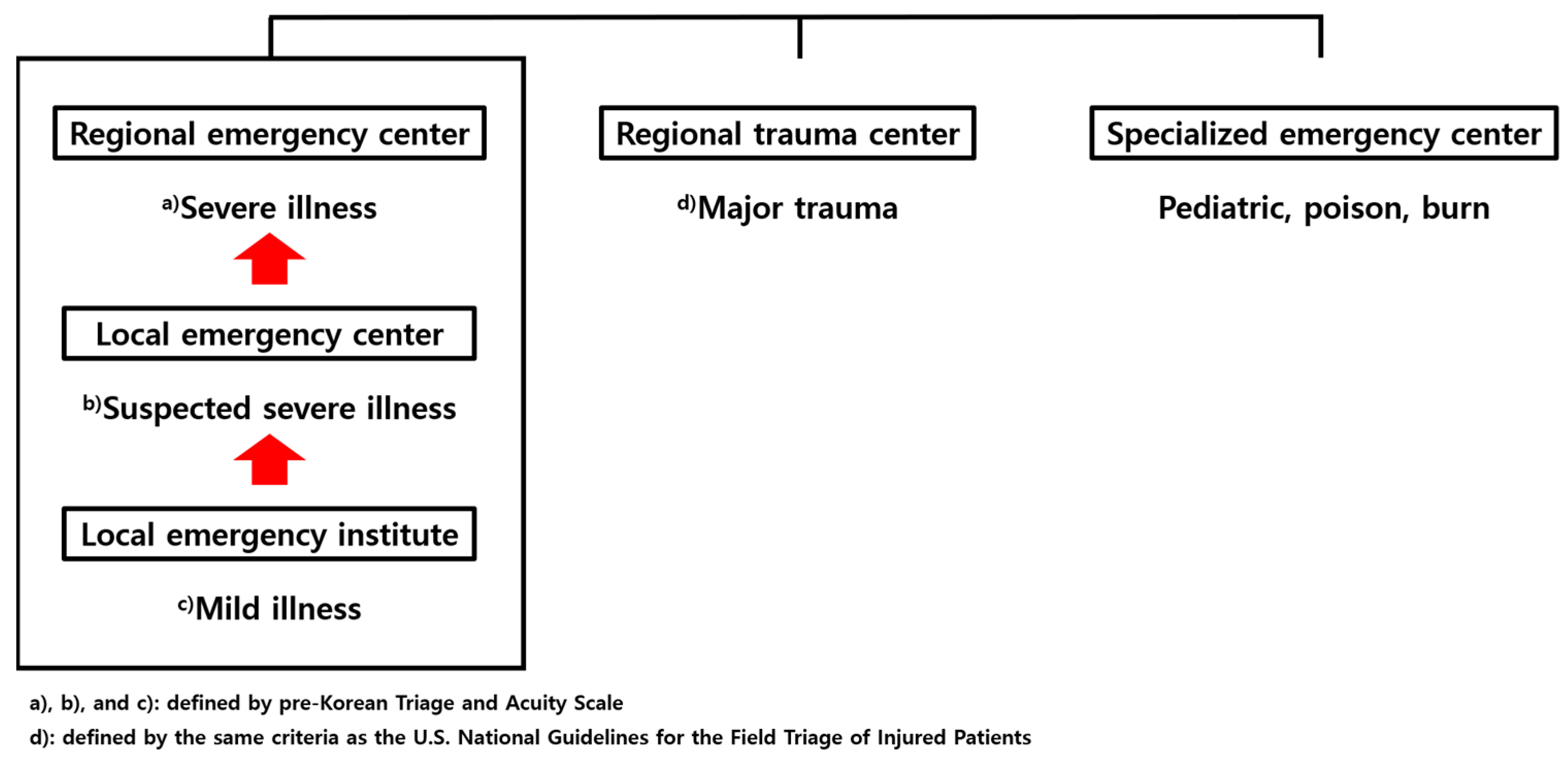
Emergency Medical Facility Type in the Republic of Korea
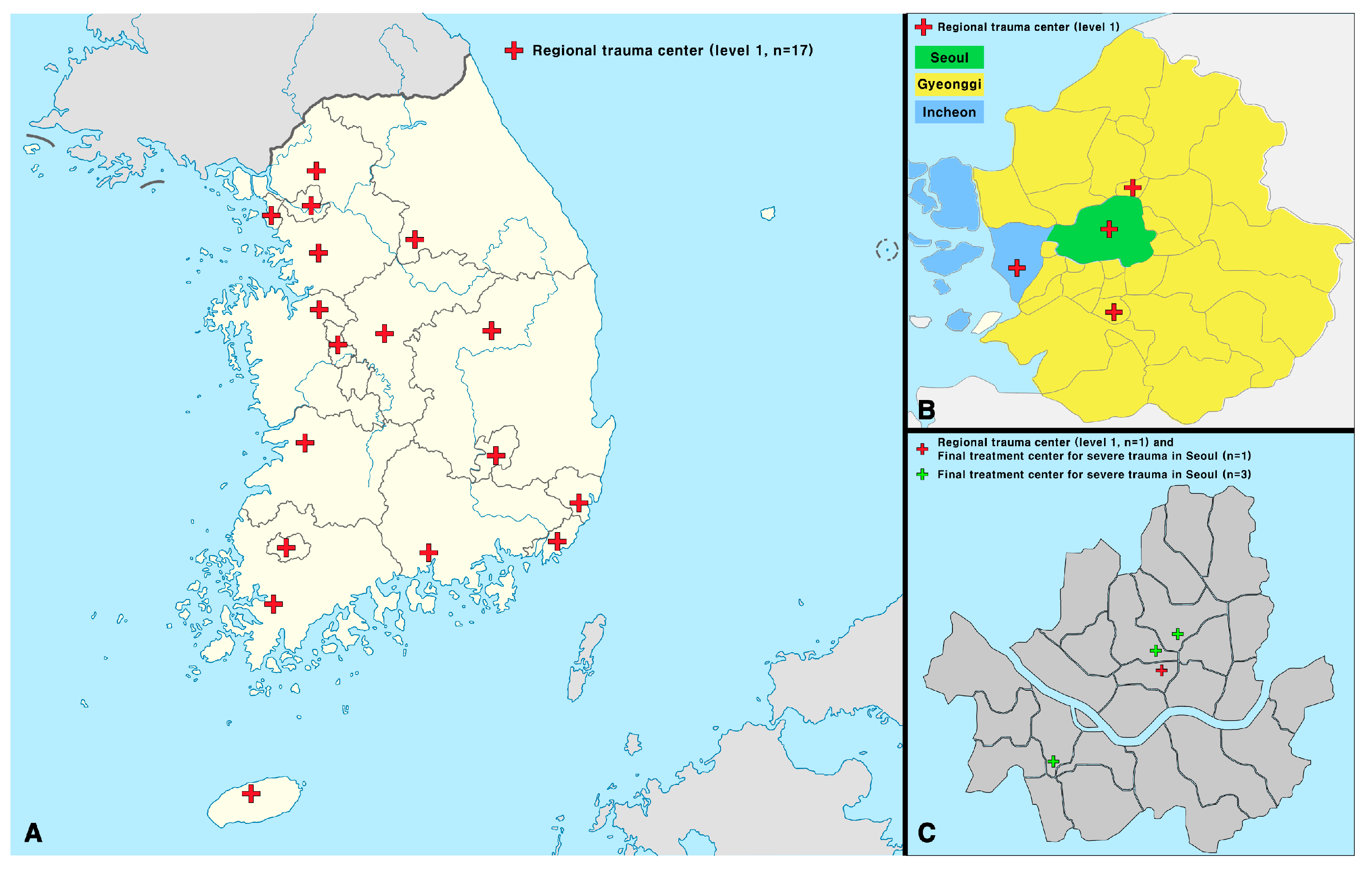
2.4. Trauma Center Status in Seoul
2.5. The Insurance System in the Republic of Korea
2.6. Trauma Severity Definition
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Reporting Guidelines
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- National Emergency Medical Center. Status of Regional Trauma Center Selection and Designation in Korea. Available online: https://www.e-gen.or.kr/nemc/business_others.do?contentsno=85 (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Mock, C. WHO releases Guidelines for trauma quality improvement programmes. Inj. Prev. 2009, 15, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, I.H.; Yun, J.H.; Lee, S.K. Preventable Trauma Death Rate in South Korea. Korean J. Neurotrauma 2023, 19, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Kim, I.; Park, S.K.; Cho, H.; Park, C.Y.; Yun, J.H.; Kim, O.H.; Park, J.O.; Lee, K.J.; Hong, K.J.; et al. Preventable trauma death rate after establishing a national trauma system in Korea. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2019, 34, e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiara, O.; Cimbanassi, S.; Pitidis, A.; Vesconi, S. Preventable trauma deaths: From panel review to population based-studies. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2006, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Spinella, P.C. Zero preventable deaths after traumatic injury: An achievable goal. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017, 82 (6S Suppl. 1), S2–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.; Lee, M.; Kim, Y.; Moon, J.; Huh, Y.; Song, S.; Kim, S.; Ko, J.I.; Jung, K. Trauma system establishment and outcome improvement: A retrospective national cohort study in South Korea. Int. J. Surg. 2023, 109, 2293–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Health and Welfare. Research on Preventable Trauma Death Assessment; Government Publication No. 11-1352000-002750-11; National Archives of Korea: Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- American College of Surgeons. Committee on Trauma; Resources for Optimal Care of the Injured Patient 2022. p. 7. Available online: https://www.facs.org/quality-programs/trauma/quality/verification-review-and-consultation-program/standards/2022-resources-repository/access/ (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Yu, B.; Lee, G.; Lee, M.A.; Choi, K.; Hyun, S.; Jeon, Y.; Yoon, Y.-C.; Lee, J. Trauma Volume and Performance of a Regional Trauma Center in Korea: Initial 5-Year Analysis. J. Trauma Inj. 2020, 33, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health and Welfare. Korea’s Pre-Hospital Emergency Patient Severity Classification Guidelines, Notice of Enactment. 2024. Available online: https://www.mohw.go.kr/board.es?mid=a10409020000&bid=0026&act=view&list_no=1483273 (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- National Fire Agency. 119 Rescue Field First Aid Standard Practice Guidelines. 2019. Available online: https://www.nfa.go.kr/nfa/publicrelations/legalinformation/archives/?boardId=bbs_0000000000000018&mode=view&cntId=26&category=&pageIdx= (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Han, K.S.; Kim, W.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Jeong, J.; Kang, H.; Lee, C.; Lee, S.W. Research for improvement of the national evaluation program for emergency medical center in Korea. J. Korean Med. Assoc. 2020, 63, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, J.; Seo, E.W.; Jung, K.; Kwon, J. Understanding Regional Trauma Centers and managing a trauma care system in South Korea: A systematic review. Ann. Surg. Treat. Res. 2023, 104, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoul Metropolitan Government. Citizens’ Health Bureau; Public Health Planning Designation of Final Treatment Centers for Severe Trauma. Available online: https://opengov.seoul.go.kr/press/22543746 (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Ministry of Health and Welfare. KTDB Annual Report 11; Publication Number NMC-2023-0081-10; Ministry of Health and Welfare: Sejong-Si, Republic of Korea, 2023; Volume 3–4, Available online: https://www.e-gen.or.kr/nemc/statistics_annual_report.do?brdclscd=04 (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Lee, Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, G. Ethical consideration of national health insurance reform for universal health coverage in the Republic of Korea. Asian Bioeth. Rev. 2019, 11, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shon, C.; Kim, J.; You, M. Effects of a Medical Aid program on medical utilization patterns for low-income patients with affective disorder in Seoul. Medicine 2022, 101, e29255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Rhie, J.; Yoon, J.D.; Kim, J.; Won, J. Current situation and issue of Industrial Accident Compensation insurance. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2012, 27, S47–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, M.; Segui-Gomez, M.; Lescohier, I.; Di Scala, C.; McDonald-Smith, G. An overview of the injury severity score and the new injury severity score. Inj. Prev. 2001, 7, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, C.S.; Gabbe, B.J.; Cameron, P.A. Defining major trauma using the 2008 Abbreviated Injury Scale. Injury 2016, 47, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pape, H.C.; Lefering, R.; Butcher, N.; Peitzman, A.; Leenen, L.; Marzi, I.; Lichte, P.; Josten, C.; Bouillon, B.; Schmucker, U.; et al. The definition of polytrauma revisited: An international consensus process and proposal of the new ‘Berlin definition’. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2014, 77, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, C. Major trauma and the injury severity score—Where should we set the bar? Annu. Proc. Assoc. Adv. Automot. Med. 2007, 51, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- New York State Department of Health. New York State Trauma Centers, New York City Region. Available online: https://www.health.ny.gov/professionals/ems/state_trauma/ (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- American College of Surgeons. Trauma Center Lists, Columbus. Available online: https://www.facs.org/hospital-and-facilities/?searchTerm=&institution=VerifiedTraumaCenter&address=columbus&sort=a-z&page=1 (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare. Guidelines for Evaluation of Regional Trauma Centers in Classified; Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare: Sejong-Si, Republic of Korea, 2024; pp. 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, D.E.; Vincent, L.E.; Fox, E.E.; O’Keeffe, T.; Inaba, K.; Bulger, E.; Holcomb, J.B.; Cotton, B.A. Every minute counts: Time to delivery of initial massive transfusion cooler and its impact on mortality. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017, 83, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoori, I.S.; Aslam, F.; Ashraf, G.; Akram, H. Understanding chronic disease risk factors and multimorbidity. Int. J. Community Med. Public Health 2020, 7, 1990–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Police Science Institute. Comprehensive Analysis of ‘Safety Speed Limit 5030’. Publication Number 11-1332522-000003-10. Available online: https://psi.police.ac.kr/police/board/view.do?bbsId=BBSMSTR_000000000152&pageIndex=1&nttId=158769&menuNo=115002000000 (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Bae, W. A Community-based Study of Severe Trauma, Death, and Disability, from 2015 to 2020. Public Health Wkly. Rep. 2023, 16, 837–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| ISS < 9 | ISS 9–15 | ISS > 15 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seoul | Gyeonggi-Incheon | p-Value | Seoul | Gyeonggi-Incheon | p-Value | Seoul | Gyeonggi-Incheon | p-Value | |
| Numbers | 11,296 | 3761 | 3617 | 1447 | 2998 | 1329 | |||
| Sex | 0.042 | 0.003 | 0.172 | ||||||
| Male | 7437 (65.8) | 2545 (67.7) | 2560 (70.8) | 1084 (74.9) | 2218 (74.0) | 1010 (76.0) | |||
| Female | 3859 (34.2) | 1216 (32.3) | 1057 (29.2) | 363 (25.1) | 780 (26.0) | 319 (24.0) | |||
| Age (mean) | 44.0 ± 23.6 | 40.7 ± 23.1 | <0.001 | 53.8 ± 20.9 | 50.7 ± 19.8 | <0.001 | 53.1 ± 19.6 | 51.4 ± 18.6 | 0.006 |
| INSURANCE | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| NHI | 7602 (67.3) | 2438 (64.8) | 2196 (60.7) | 721 (49.8) | 1592 (53.1) | 573 (43.1) | |||
| MVI | 2451 (21.7) | 846 (22.5) | 1014 (28.0) | 494 (34.1) | 1002 (33.4) | 514 (38.7) | |||
| WCI | 43 (0.4) | 84 (2.2) | 68 (1.9) | 100 (6.9) | 94 (3.1) | 129 (9.7) | |||
| MAP type 1 | 596 (5.3) | 171 (4.5) | 167 (4.6) | 41 (2.8) | 114 (3.8) | 36 (2.7) | |||
| MAP type 2 | 152 (1.3) | 50 (1.3) | 41 (1.1) | 17 (1.2) | 36 (1.2) | 5 (0.4) | |||
| NHI loss (a) | 300 (2.7) | 163 (4.3) | 85 (2.4) | 71 (4.9) | 103 (3.4) | 68 (5.1) | |||
| Others (b) | 152 (1.3) | 9 (0.2) | 46 (1.3) | 3 (0.2) | 57 (1.9) | 4 (0.3) | |||
| ISS (median) (c) | 1 [1, 4] | 2 [1, 4] | <0.001 | 10 [9, 12] | 10 [9, 13] | <0.001 | 22 [17, 26] | 22 [17, 27] | 0.287 |
| HOSPITAL LEVEL | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Regional trauma centers | 26 (0.2) | 1404 (37.3) | 23 (0.6) | 732 (50.6) | 56 (1.9) | 856 (64.4) | |||
| Regional emergency centers | 2769 (24.5) | 460 (12.2) | 988 (27.3) | 159 (11.0) | 902 (30.1) | 155 (11.7) | |||
| Local emergency centers/institutes | 8501 (75.3) | 1897 (50.4) | 2606 (72.0) | 556 (38.4) | 2040 (68.0) | 318 (23.9) | |||
| MECHANISM OF INJURY | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Motor vehicle collisions | 3478 (30.8) | 1125 (29.9) | 1571 (43.4) | 666 (46.0) | 1478 (49.3) | 736 (55.4) | |||
| Falls and slippages | 5914 (52.4) | 1788 (47.5) | 1818 (50.3) | 631 (43.6) | 1403 (46.8) | 503 (37.8) | |||
| Blunt injury | 1113 (9.9) | 465 (12.4) | 112 (3.1) | 69 (4.8) | 64 (2.1) | 52 (3.9) | |||
| Penetrative injury | 700 (6.2) | 297 (7.9) | 103 (2.8) | 54 (3.7) | 49 (1.6) | 13 (1.0) | |||
| Machine | 91 (0.8) | 86 (2.3) | 13 (0.4) | 27 (1.9) | 4 (0.1) | 25 (1.9) | |||
| Death (after ER visit) | 51 (0.5) | 11 (0.3) | 0.241 | 229 (6.3) | 101 (7.0) | 0.434 | 722 (24.1) | 319 (24.0) | 0.986 |
| ISS < 9 | ISS 9–15 | ISS > 15 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seoul | Gyeonggi-Incheon | p-Value | Seoul | Gyeonggi-Incheon | p-Value | Seoul | Gyeonggi-Incheon | p-Value | |
| Numbers | 11,296 | 3761 | 3617 | 1447 | 2998 | 1329 | |||
| Time from 119 call time to ER visit (min) | 23 [18, 29] | 24 [18, 32] | <0.001 | 23 [18, 30] | 25 [18, 34] | <0.001 | 22 [17, 28] | 25 [18, 35] | <0.001 |
| Number of surgeries performed | 773 (6.8) | 459 (12.2) | <0.001 | 1276 (35.3) | 654 (45.2) | <0.001 | 1533 (51.1) | 883 (66.4) | <0.001 |
| Time from the ER visit to surgery (min) | 1522 [482, 5712] | 1107 [327, 5055.5] | 0.001 | 1733.5 [454, 6362.8] | 1368 [252.8, 6935.2] | 0.002 | 646 [220, 7325] | 584 [155.5, 6286.5] | <0.001 |
| Number of angio-embolizations performed | 19 (0.2) | 5 (0.1) | 0.815 | 54 (1.5) | 29 (2.0) | 0.241 | 190 (6.3) | 112 (8.4) | 0.015 |
| Time from the ER visit to angio-embolization (hr) | 12.7 [2.9, 131.9] | 2.7 [2.3, 7.3] | 0.189 | 4.4 [3.1, 7.0] | 3.5 [2.9, 5.2] | 0.252 | 4.4 [3.2, 6.6] | 2.8 [1.9, 5.7] | 0.001 |
| Number of transfusions performed | 228 (2.0) | 96 (2.6) | 0.059 | 539 (14.9) | 228 (15.8) | 0.47 | 1251 (41.7) | 503 (37.8) | 0.018 |
| Time from the ER visit to the first transfusion (min) | 113 [60, 259] | 90.5 [38.5, 194] | 0.02 | 172 [82, 339.8] | 86 [37.2, 206.2] | <0.001 | 130 [67, 238] | 81 [27, 165] | <0.001 |
| GOS initial | 0.296 | 0.332 | 0.156 | ||||||
| Severe disability | 27 (0.2) | 4 (0.1) | 18 (0.5) | 3 (0.2) | 11 (0.4) | 1 (0.1) | |||
| Moderate disability | 141 (1.2) | 46 (1.2) | 85 (2.4) | 32 (2.2) | 29 (1.0) | 17 (1.3) | |||
| No disability | 11,128 (98.5) | 3711 (98.7) | 3514 (97.2) | 1412 (97.6) | 2958 (98.7) | 1311 (98.6) | |||
| Seoul (n = 17,911) | ISS < 9 | ISS 9–15 | ISS > 15 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariable | Multivariable | Univariable | Multivariable | Univariable | Multivariable | |||||||
| Crude OR (95%CI) | Crude p-Value | Adjusted OR (95%CI) | Adjusted p-Value | Crude OR (95%CI) | Crude p-Value | Adjusted OR (95%CI) | Adjusted p-Value | Crude OR (95%CI) | Crude p-Value | Adjusted OR (95%CI) | Adjusted p-Value | |
| Sex (reference = Female) | 1.14 (0.65,2.02) | 0.641 | 0.85 (0.63,1.15) | 0.299 | 1.11 (0.92,1.34) | 0.278 | ||||||
| Age | 1.08 (1.06,1.1) | <0.001 | 1.08 (1.05,1.1) | <0.001 | 1.03 (1.02,1.04) | <0.001 | 1.04 (1.03,1.04) | <0.001 | 1.02 (1.02,1.03) | <0.001 | 1.03 (1.02,1.03) | <0.001 |
| Insurance (reference = NHI) | ||||||||||||
| MVI | 1.55 (0.83,2.89) | 0.164 | 0.93 (0.68,1.27) | 0.652 | 1.16 (0.96,1.39) | 0.119 | ||||||
| WCI | 0 (0,∞) | 0.996 | 0.45 (0.11,1.85) | 0.267 | 0.27 (0.12,0.59) | 0.001 | 0.26 (0.12,0.59) | 0.001 | ||||
| MAP type 1 | 2.57 (1.06,6.19) | 0.036 | 1.19 (0.47,3) | 0.714 | 0.74 (0.36,1.55) | 0.429 | 0.81(0.5,1.3) | 0.38 | ||||
| MAP type 2 | 0 (0,∞) | 0.992 | 0.37 (0.05,2.71) | 0.328 | 0.81 (0.35,1.87) | 0.629 | ||||||
| NHI loss (a) | 0 (0,∞) | 0.988 | 2.67 (1.44,4.94) | 0.002 | 2.89 (1.49,5.59) | 0.002 | 2.32 (1.54,3.5) | <0.001 | 2.52 (1.63,3.9) | <0.001 | ||
| Others (b) | 0 (0,∞) | 0.992 | 2.22 (0.93,5.33) | 0.074 | 2.45 (1.43,4.2) | 0.001 | 2.43 (1.37,4.32) | 0.003 | ||||
| ISS | 1.09 (0.95,1.26) | 0.212 | 0.96 (0.89,1.03) | 0.275 | 1.07 (1.06,1.08) | <0.001 | 1.08 (1.07,1.09) | <0.001 | ||||
| Hospital level (reference = regional trauma centers) | ||||||||||||
| Regional emergency centers | 0.15 (0.02,1.14) | 0.066 | 0.26 (0.02,2.76) | 0.263 | 432,305.86 (0,9.03) | 0.966 | 403,412.26 (0,∞) | 0.977 | 1.82 (0.85,3.91) | 0.124 | 2.39 (1.03,5.58) | 0.043 |
| Local emergency centers/institutes | 0.1 (0.01,0.76) | 0.026 | 0.15 (0.01,1.58) | 0.114 | 376,635.35 (0,7.87) | 0.966 | 305,502.31 (0,∞) | 0.977 | 1.97 (0.93,4.19) | 0.079 | 2.4 (1.04,5.53) | 0.041 |
| Mechanism (reference = Motor vehicle collisions) | ||||||||||||
| Falls and slippages | 0.93 (0.52,1.65) | 0.8 | 1.19 (0.9,1.57) | 0.215 | 1.1 (0.93,1.3) | 0.273 | ||||||
| Blunt injury | 0.16 (0.02,1.22) | 0.078 | 0.73 (0.29,1.84) | 0.511 | 0.53 (0.26,1.09) | 0.085 | ||||||
| Penetrative injury | 0.26 (0.03,1.95) | 0.19 | 0.31 (0.08,1.28) | 0.106 | 1.06 (0.55,2.05) | 0.869 | ||||||
| Machine | 0 (0,∞) | 0.984 | 0 (0,∞) | 0.975 | 0 (0,3.14) | 0.963 | ||||||
| Time from 119 call time to ER visit | 1 (0.98,1.01) | 0.788 | 0.97 (0.95,0.98) | <0.001 | 0.96 (0.95,0.98) | <0.001 | 1 (1,1) | 0.592 | ||||
| Number of surgeries performed | 0.85 (0.26,2.74) | 0.786 | 0.68 (0.5,0.92) | 0.011 | 0.73 (0.54,1) | 0.05 | 0.62 (0.53,0.74) | <0.001 | 0.62 (0.52,0.75) | <0.001 | ||
| Number of angio-embolizations performed | 12.47 (1.63,95.25) | 0.015 | 14.07 (1.33,148.85) | 0.028 | 3.93 (2,7.72) | <0.001 | 5.07 (2.41,10.67) | <0.001 | 1.5 (1.09,2.06) | 0.013 | 1.2 (0.84,1.71) | 0.312 |
| Gyeonggi-Incheon (n = 6537) | ISS < 9 | ISS 9 –15 | ISS > 15 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariable | Multivariable | Univariable | Multivariable | Univariable | Multivariable | |||||||
| Crude OR (95%CI) | Crude p-Value | Adjusted OR (95%CI) | Adjusted p-Value | Crude OR (95%CI) | Crude p-Value | Adjusted OR (95%CI) | Adjusted p-Value | Crude OR (95%CI) | Crude p-Value | Adjusted OR (95%CI) | Adjusted p-Value | |
| Sex (reference = Female) | 1.75 (0.53,5.74) | 0.358 | 1.35 (0.87,2.1) | 0.179 | 1.4 (1.05,1.86) | 0.021 | 1.27 (0.93,1.73) | 0.126 | ||||
| Age | 1.03 (1,1.06) | 0.044 | 1.02 (0.99,1.05) | 0.275 | 1.03 (1.02,1.05) | <0.001 | 1.04 (1.02,1.05) | <0.001 | 1.03 (1.02,1.03) | <0.001 | 1.02 (1.02,1.03) | <0.001 |
| Insurance (reference = NHI) | ||||||||||||
| MVI | 0 (0,∞) | 0.992 | 1.14 (0.74,1.77) | 0.552 | 0.76 (0.57,1.01) | 0.055 | ||||||
| WCI | 0 (0,∞) | 0.997 | 0.57 (0.2,1.62) | 0.292 | 0.71 (0.45,1.14) | 0.155 | ||||||
| MAP type 1 | 1.59 (0.2,12.6) | 0.662 | 0 (0,∞) | 0.981 | 1.08 (0.51,2.3) | 0.832 | ||||||
| MAP type 2 | 0 (0,∞) | 0.998 | 0.86 (0.11,6.6) | 0.882 | 0.7 (0.08,6.36) | 0.755 | ||||||
| NHI loss (a) | 1.67 (0.21,13.23) | 0.629 | 1.99 (0.93,4.24) | 0.075 | 1.35 (0.79,2.32) | 0.279 | ||||||
| Others (b) | 0 (0,∞) | 0.999 | 0 (0,∞) | 0.995 | 0.94 (0.1,9.11) | 0.957 | ||||||
| ISS | 1.32 (1.03,1.7) | 0.03 | 1.53 (1.15,2.03) | 0.004 | 0.87 (0.77,0.98) | 0.021 | 0.86 (0.75,0.97) | 0.02 | 1.03 (1.02,1.04) | <0.001 | 1.04 (1.02,1.05) | <0.001 |
| Hospital level (reference = Regional trauma centers) | ||||||||||||
| Regional emergency centers | 0.51 (0.06,4.23) | 0.531 | 0.91 (0.1,8.21) | 0.936 | 1.19 (0.62,2.3) | 0.605 | 1.19 (0.6,2.38) | 0.621 | 1.62 (1.11,2.36) | 0.013 | 1.3 (0.86,1.94) | 0.21 |
| Local emergency centers/institutes | 0.49 (0.14,1.75) | 0.273 | 0.61 (0.16,2.35) | 0.474 | 1.19 (0.77,1.83) | 0.428 | 0.92 (0.58,1.46) | 0.721 | 1.31 (0.98,1.77) | 0.071 | 0.94 (0.67,1.32) | 0.728 |
| Mechanism (reference = motor vehicle collisions) | ||||||||||||
| Falls and slippages | 24,817,221.73 (0,∞) | 0.991 | 1.16 (0.77,1.76) | 0.485 | 1.79 (1.38,2.32) | <0.001 | 2.08 (1.38,3.14) | <0.001 | ||||
| Blunt injury | 13,608,211.79 (0,∞) | 0.991 | 0.4 (0.1,1.69) | 0.215 | 0.95 (0.46,1.93) | 0.879 | ||||||
| Penetrative injury | 64,430,717.0 (0,∞) | 0.99 | 0.79 (0.24,2.64) | 0.705 | 1.77 (0.54,5.81) | 0.35 | ||||||
| Machine | 1 (0,∞) | 1 | 0 (0,∞) | 0.976 | 0.17 (0.02,1.23) | 0.079 | ||||||
| Time from 119 call time to ER visit | 1 (0.99,1.01) | 0.86 | 0.97 (0.95,0.99) | 0.001 | 0.97 (0.96,0.99) | 0.005 | 0.99 (0.98,0.99) | 0.002 | 0.98 (0.97,0.99) | 0.003 | ||
| Number of surgeries performed | 0.72 (0.09,5.62) | 0.753 | 0.65 (0.43,0.99) | 0.047 | 0.72 (0.46,1.12) | 0.145 | 0.54 (0.41,0.7) | <0.001 | 0.52 (0.39,0.69) | <0.001 | ||
| Number of angio-embolizations performed | 0 (0,∞) | 0.992 | 3.63 (1.44,9.14) | 0.006 | 4.61 (1.61,13.23) | 0.004 | 1.01 (0.64,1.58) | 0.978 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, H.; Baik, S.M.; Cho, H.; Kim, M.; Lee, J.-M. Challenges in Saving Trauma Patients in Seoul Based on the 2016–2020 Community-Based Severe Trauma Survey. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051471
Park H, Baik SM, Cho H, Kim M, Lee J-M. Challenges in Saving Trauma Patients in Seoul Based on the 2016–2020 Community-Based Severe Trauma Survey. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(5):1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051471
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Hoonsung, Seung Min Baik, Hangjoo Cho, Maru Kim, and Jae-Myeong Lee. 2025. "Challenges in Saving Trauma Patients in Seoul Based on the 2016–2020 Community-Based Severe Trauma Survey" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 5: 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051471
APA StylePark, H., Baik, S. M., Cho, H., Kim, M., & Lee, J.-M. (2025). Challenges in Saving Trauma Patients in Seoul Based on the 2016–2020 Community-Based Severe Trauma Survey. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(5), 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051471






