Comparison of Brucellosis and Rickettsiosis in Children: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Diagnosis of Brucellosis
2.4. Diagnosis of Rickettsiosis
2.5. Variables and Data Collection
2.6. Quantitative Variables and Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Parameters
3.2. Seasonality
3.3. Clinical Parameters
3.4. Laboratory Features
3.5. Outcomes
3.6. Multivariate Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chow, A.; Robinson, J.L. Fever of unknown origin in children: A systematic review. World J. Pediatr. 2011, 7, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epidemiological Situation of Rickettsioses in EU/EFTA Countries. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/epidemiological-situation-rickettsioses-euefta-countries (accessed on 4 December 2024).
- Dean, A.S.; Crump, L.; Greter, H.; Schelling, E.; Zinsstag, J. Global burden of human brucellosis: A systematic review of disease frequency. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saydam, F.N.; Erdem, H.; Ankarali, H.; El-Arab Ramadan, M.E.; El-Sayed, N.M.; Civljak, R.; Pshenichnaya, N.; Moroti, R.V.; Mahmuodabad, F.M.; Maduka, A.V.; et al. Vector-borne and zoonotic infections and their relationships with regional and socioeconomic statuses: An ID-IRI survey in 24 countries of Europe, Africa and Asia. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 44, 102174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickettsial Diseases | CDC Yellow Book 2024. Available online: https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/yellowbook/2024/infections-diseases/rickettsial-diseases?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 26 January 2025).
- Fruchtman, Y.; Segev, R.W.; Golan, A.A.; Dalem, Y.; Tailakh, M.A.; Novak, V.; Peled, N.; Craiu, M.; Leibovitz, E. Epidemiological, diagnostic, clinical, and therapeutic aspects of Brucella bacteremia in children in southern Israel: A 7-year retrospective study (2005–2011). Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015, 15, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagupsky, P.; Morat, P.; Colmenero, J.D. Laboratory Diagnosis of Human Brucellosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakir, R. Brucellosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 420, 117280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Shimol, S.; Farahvar, S.; Fruchtman, Y.; Justman, N. Factors Associated with Single and Recurrent Bacteremia in Childhood Brucellosis. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2020, 9, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merhej, V.; Angelakis, E.; Socolovschi, C.; Raoult, D. Genotyping, evolution and epidemiological findings of Rickettsia species. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 25, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, D.; Beth-Din, A.; Cohen, R.; Lazar, S.; Glinert, I.; Zayyad, H.; Atiya-Nasagi, Y. New Spotted Fever Group Rickettsia Isolate, Identified by Sequence Analysis of Conserved Genomic Regions. Pathogens 2020, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, R.; Finn, T.; Babushkin, F.; Paran, Y.; Ami, R.B.; Atamna, A.; Reisfeld, S.; Weber, G.; Petersiel, N.; Zayyad, H.; et al. Spotted Fever Group Rickettsioses in Israel, 2010–2019. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 2117–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalev, H.; Raissa, R.; Evgenia, Z.; Yagupsky, P. Murine typhus is a common cause of febrile illness in Bedouin children in Israel. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 38, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peniche Lara, G.; Dzul Rosado, K.R.; Zavala Velásquez, J.E.; Zavala-Castro, J. Murine Typhus: Clinical and epidemiological aspects. Colomb. Méd. CM 2012, 43, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spernovasilis, N.; Markaki, I.; Papadakis, M.; Mazonakis, N.; Ierodiakonou, D. Mediterranean Spotted Fever: Current Knowledge and Recent Advances. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 6, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guirao-Arrabal, E.; Muñoz-Medina, L.; Anguita-Santos, F.; Vinuesa-García, D.; Hernández-Quero, J. Empirical treatment with doxycycline of fever of intermediate duration. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariza, J.; Gudiol, F.; Pallares, R.; Viladrich, P.F.; Rufi, G.; Corredoira, J.; Miravitlles, M.R. Treatment of human brucellosis with doxycycline plus rifampin or doxycycline plus streptomycin. A randomized, double-blind study. Ann. Intern. Med. 1992, 117, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solera, J.; Espinosa, A.; Martínez-Alfaro, E.; Sánchez, L.; Geijo, P.; Navarro, E.; Escribano, J.; Fernández, J.A. Treatment of human brucellosis with doxycycline and gentamicin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Koumi, M.A.; Afify, M.; Al-Zahrani, S.H. A Prospective Study of Brucellosis in Children: Relative Frequency of Pancytopenia. Iran. J. Pediatr. 2014, 24, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Fan, Z.; Gao, R.; Li, X.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Z. Research progress on complications of Brucellosis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1136674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, M.P.; Mulder, M.; Gilman, R.H.; Smits, H.L. Human brucellosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2007, 7, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakir, R.A.; Al-din, A.S.N.; Araj, G.F.; Lulu, A.R.; Mousa, A.R.; Saadah, M.A. Clinical categories of neurobrucellosis. A report on 19 cases. Brain 1987, 110 Pt 1, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, R.; Muthukumar, V.; Premji, S.; Khan, R.; Schmidt, R.M. Murine Typhus-Induced Myocarditis. Am. J. Med. 2022, 135, e397–e398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, E.J. An overview of human brucellosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1995, 21, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, R.; Casanova, A.; Ariza, J.; Moriyón, I. The Rose Bengal Test in human brucellosis: A neglected test for the diagnosis of a neglected disease. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, C.Y.; Chung, I.H.; Robinson, L.K.; Austin, A.L.; Dasch, G.A.; Massunga, R.F. Assessment of Real-Time PCR Assay for Detection of Rickettsia spp. and Rickettsia rickettsii in Banked Clinical Samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santibáñez, S.; Portillo, A.; Santibáñez, P.; Palomar, A.M.; Oteo, J.A. Usefulness of rickettsial PCR assays for the molecular diagnosis of human rickettsioses. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2013, 31, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aita, T.; Sando, E.; Katoh, S.; Hamaguchi, S.; Fujita, H.; Kurita, N. Serological cross-reactivity between spotted fever and typhus groups of rickettsia infection in Japan. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 130, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolaños-Rivero, M.; Santana-Rodriguez, É.; Ángel-Moreno, A.; Hernández-Cabrera, M.; Limiñana-Canal, J.M.; Carranza-Rodríguez, C.; Martín-Sánchez, A.-M.; Pérez-Arellano, J.-L. Seroprevalence of Rickettsia typhi and Rickettsia conorii infections in the Canary Islands (Spain). Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 15, e481–e485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantsø, B.; Svendsen, C.B.; Jørgensen, C.S.; Krogfelt, K.A. Evaluation of serological tests for the diagnosis of rickettsiosis in Denmark. J. Microbiol. Methods 2009, 76, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; Cohen, P.; West, S.G.; Aiken, L.S. Applied Multiple Regression/Correlation Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 3rd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–704. Available online: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/mono/10.4324/9780203774441/applied-multiple-regression-correlation-analysis-behavioral-sciences-jacob-cohen-patricia-cohen-stephen-west-leona-aiken (accessed on 4 December 2024).
- Mann, H.B.; Whitney, D.R. On a Test of Whether one of Two Random Variables is Stochastically Larger than the Other. Ann. Math. Statist. 1947, 18, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardenstein, S.; Gibbs, R.E.; Yagel, Y.; Motro, Y.; Moran-Gilad, J. Brucellosis Outbreak Traced to Commercially Sold Camel Milk through Whole-Genome Sequencing, Israel. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcell, H.G.; Garcia, E.G.; Pueyo, P.V.; Martín, I.R.; Arias, A.V.; Alfonso Serrano, R.N. Outbreaks of brucellosis related to the consumption of unpasteurized camel milk. J. Infect. Public Health 2016, 9, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappas, G.; Papadimitriou, P.; Akritidis, N.; Christou, L.; Tsianos, E.V. The new global map of human brucellosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, K.A.; Parvez, A.; Fahmy, N.A.; Abdel Hady, B.H.; Kumar, S.; Ganguly, A.; Atiya, A.; Elhassan, G.O.; Alfadly, S.O.; Parkkila, S.; et al. Brucellosis: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment—A comprehensive review. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 2295398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharabi, S.; Sagi, O.; Ben-Shimol, S. Serologic Diagnosis of Acute Rickettsiosis in Children in Southern Israel. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2021, 40, E521–E523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilnejad-Ganji, S.M.; Esmaeilnejad-Ganji, S.M.R. Osteoarticular manifestations of human brucellosis: A review. World J. Orthop. 2019, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzein, F.E.; Sherbeeni, N. Brucella Septic Arthritis: Case Reports and Review of the Literature. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2016, 2016, 4687840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premaratna, R. Rickettsial illnesses, a leading cause of acute febrile illness. Clin. Med. 2022, 22, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Ismail, N.; Walker, D.H. Rickettsiae. In Medical Microbiology, 4th ed.; University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996; pp. 1121–1145. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK7624/ (accessed on 21 September 2024).
- Crosby, E.; Llosa, L.; Quesada, M.M.; Carrillo, P.C.; Gotuzzo, E. Hematologic Changes in Brucellosis. J. Infect. Dis. 1984, 150, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.F.; Du, J.; Mi, X.M.; Lu, Q.B.; Bai, J.Y.; Cui, N.; Yang, Z.-D.; Wang, Z.-B.; Zhang, X.-A.; Zhang, P.-H.; et al. Rickettsia typhi infection in severe fever with thrombocytopenia patients, China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouallem, M.; Friedman, E.; Pauzner, R.; Schwartz, E.; Rubinstein, E. Rickettsiosis-associated hyponatremia. Infection 1987, 15, 315–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paddock, C.D.; Guerra, M.A.; Childs, J.E.; Swerdlow, D.L. Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (Rickettsia rickettsii). In Principles and Practice of Pediatric Infectious Disease: 3rd ed.; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023; pp. 915–919. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430881/ (accessed on 21 September 2024).
- Herberg, J.; Pahari, A.; Walters, S.; Levin, M. Infectious Diseases and the Kidney. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2009, 1235–1273. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, M.F.H.; Ahmed, A.O.E.; Habib, M.B.; Abdalla, M.; Almohtasib, Y.S.; Mohamed, H.F.H.; Mohamed, Z.A.S.; Abdalla, L.; Saleh, A.O. The prevalence of the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH) in brucellosis patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 74, 103340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinikina, Y.; Tsoy, U.; Dyachkov, A.; Grozov, R.; Mushkin, A.; Zorin, V.; Nikitina, I.; Grineva, E. Presentation of severe brucellosis in 5-year-old boy—Challenges and results. BMC Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, I.F.; Lin, J.N.; Tsai, C.T.; Wu, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Lai, C.H. Serum C-reactive protein and procalcitonin values in acute Q fever, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.C.; Bricker, B. Brucella. In Medical Microbiology, 4th ed.; University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996; pp. 259–269. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK8572/ (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- Alavi, S.M.; Alavi, L. Treatment of brucellosis: A systematic review of studies in recent twenty years. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 4, 636. [Google Scholar]

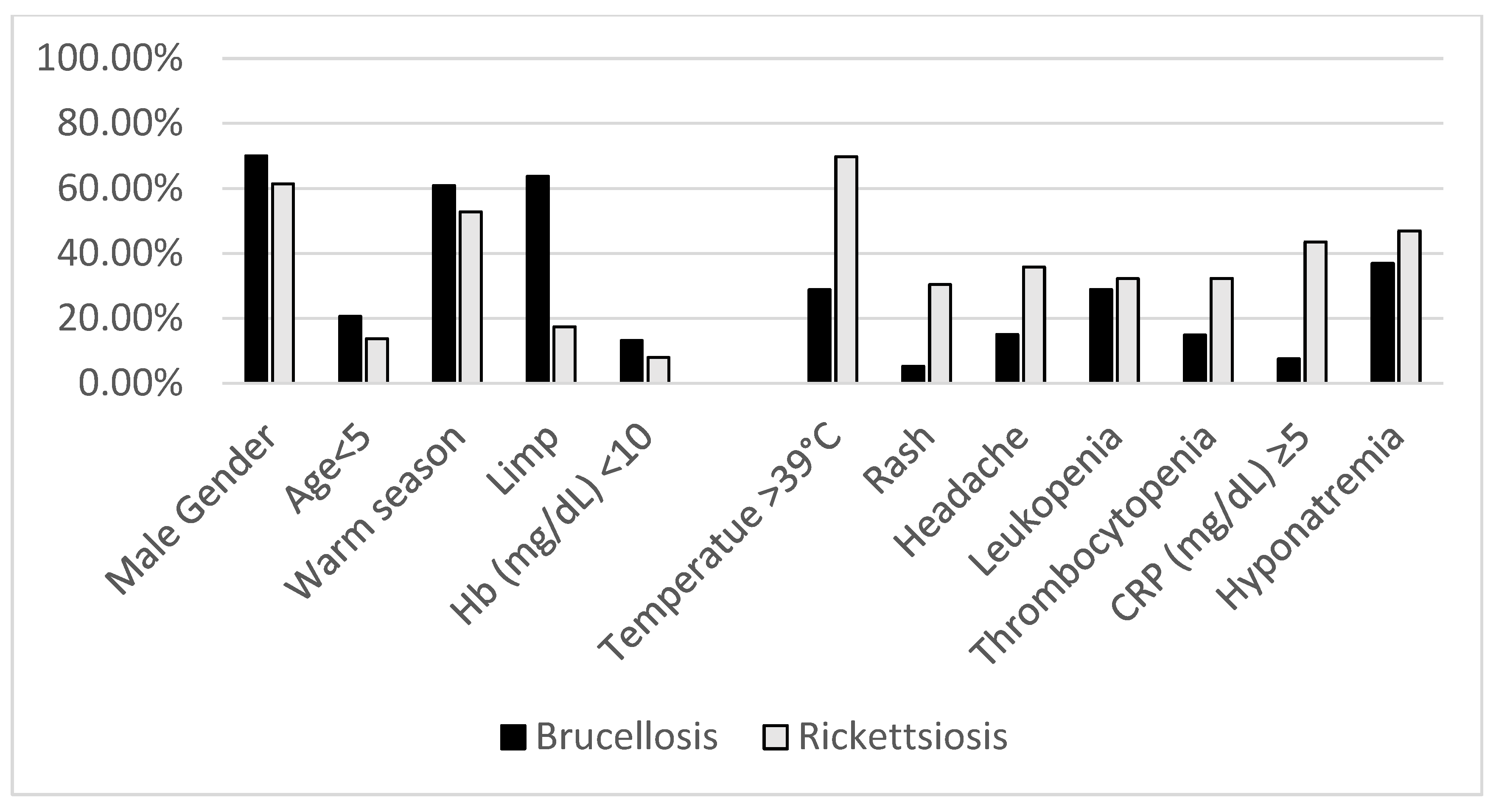
| Brucellosis N = 440 | Rickettsiosis N = 335 | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | Jewish (N, %) | 2 (0.5%) | 31 (9.3%) | <0.001 |
| Bedouin (N, %) | 438 (99.5%) | 304 (90.7%) | <0.001 | |
| Gender—male (N, %) | 308 (70.0%) | 206 (61.4%) | 0.01 | |
| Gender—female (N, %) | 132 (30.0%) | 129 (38.6%) | 0.01 | |
| Age (years); mean ± SD | 9.9 ± 4.9 | 10.1 ± 5.0 | <0.001 | |
| Age (years) < 5; (N, %) | 91 (20.6%) | 46 (13.7%) | 0.01 | |
| Seasonality | Warm season (March–August) (N, %) | 268 (60.9%) | 177 (52.8%) | 0.03 |
| Cold season (September–February) (N, %) | 172 (39.1%) | 156 (47.2%) | 0.03 | |
| Clinical parameters | Temperature at ER; mean ± SD | 38.3 ± 1.16 | 39.4 ± 0.96 | <0.001 |
| Temperature ≥39.0; (N, %) | 127 (28.8%) | 234 (69.8%) | <0.001 | |
| Rash; (N, %) | 23/440 (5.2%) | 102 (30.4%) | <0.001 | |
| Limp; (N, %) | 250/392 (63.7%) | 58/334 (17.4%) | <0.001 | |
| Headache; (N, %) | 66/440 (15.0%) | 120/335 (35.8%) | <0.001 | |
| Laboratory features | Hb (mg/dL); mean ± SD | 11.44 ± 1.47 | 12.25 ± 1.63 | <0.001 |
| Hb (mg/dL) < 10; (N, %) | 57/434 (13.1%) | 26/331 (7.9%) | 0.025 | |
| WBC (×1000/mm3); mean ± SD | 8.29 ± 28.6 | 7.42 ± 4.44 | 0.58 | |
| WBC (×1000/mm3) < 5; (N, %) | 127/440 (28.9%) | 108/335 (32.2%) | 0.34 | |
| Platelets (×1000/mm3); mean ± SD | 254.9 ± 109.9 | 210.4 ± 107.9 | <0.001 | |
| Platelets (×1000/mm3) < 150; (N, %) | 64/433 (14.8%) | 108/334 (32.3%) | <0.001 | |
| ALT (U/L); mean ± SD | 41.35 ± 46.18 | 45.51 ± 155.44 | 0.63 | |
| ALT (U/L) ≥ 45; (N, %) | 89/369 (24.1%) | 76/309 (24.6%) | 0.93 | |
| AST (U/L); mean ± SD | 56.66 ± 42.29 | 70.20 ± 282.71 | 0.37 | |
| AST (U/L) ≥ 45; (N, %) | 201/367 (54.8%) | 129/297 (43.4%) | 0.004 | |
| CRP (mg/dL); mean ± SD | 1.74 ± 2.12 | 6.49 ± 7.68 | <0.001 | |
| CRP (mg/dL) ≥ 5; (N, %) | 12/159 (7.5%) | 124/285 (43.5%) | <0.001 | |
| Sodium (mEq/L); mean ± SD | 135.43 ± 2.90 | 134.48 ± 3.37 | <0.001 | |
| Sodium (mEq/L) < 135; (N, %) | 147/398 (36.9%) | 153/326 (46.9%) | 0.008 | |
| Clinical outcomes | Hospitalization duration (days); Mean ± SD | 6.15 ± 3.83 | 4.18 ± 2.58 | <0.001 |
| Number of antimicrobial agents used; mean ± SD | 1.89 ± 0.85 | 0.53 ± 0.86 | <0.001 | |
| Doxycycline used; (N, %) | 278 (63.1%) | 164 (48.9%) | <0.001 | |
| Gentamicin used; (N, %) | 407 (92.5%) | 17 (5.1%) | <0.001 | |
| Co-trimoxazole used; (N, %) | 130 (29.5%) | 0 (0%) | <0.001 | |
| Antimicrobial treatment duration (days); mean ± SD | 38.52 ± 11.7 | 3.56 ± 3.98 | <0.001 | |
| Mortality; mean ± SD | 2 (0.5%) | 0 (0%) | 0.50 |
| Factors | Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Intervals | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factors Associated with Diagnosis of Brucellosis | Limp | 7.27 | 5.15–10.38 | <0.001 |
| Hb (mg/dL) < 10 | 2.01 | 1.14–3.64 | 0.018 | |
| Age (years) < 5 | 1.95 | 1.25–3.07 | 0.003 | |
| Warm season (March–August) | 1.84 | 1.31–2.59 | <0.001 | |
| Gender—male | 1.57 | 1.10–2.25 | 0.012 | |
| Factors Associated with Diagnosis of Rickettsiosis | Rash | 9.06 | 3.91–24.9 | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/dL) ≥ 5 | 4.03 | 1.86–9.81 | <0.001 | |
| Headache | 3.01 | 1.75–5.30 | <0.001 | |
| Platelets (×1000/mm3) < 150 | 2.61 | 1.23–6.06 | 0.017 | |
| WBC (×1000/mm3) < 5 | 1.88 | 1.19–2.98 | 0.006 | |
| Temperature ≥ 39.0 | 1.66 | 1.03–2.68 | <0.001 | |
| Sodium (mEq/L) < 135 | 0.79 | 0.48–1.28 | 0.33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lendner, I.; Shmueli, M.; Elamour, S.; Ling, G.; Ben-Shimol, S. Comparison of Brucellosis and Rickettsiosis in Children: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051465
Lendner I, Shmueli M, Elamour S, Ling G, Ben-Shimol S. Comparison of Brucellosis and Rickettsiosis in Children: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(5):1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051465
Chicago/Turabian StyleLendner, Idan, Moshe Shmueli, Siham Elamour, Galina Ling, and Shalom Ben-Shimol. 2025. "Comparison of Brucellosis and Rickettsiosis in Children: A Retrospective Cohort Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 5: 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051465
APA StyleLendner, I., Shmueli, M., Elamour, S., Ling, G., & Ben-Shimol, S. (2025). Comparison of Brucellosis and Rickettsiosis in Children: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(5), 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051465







