Physeal-Sparing Soft Tissue Realignment in Pediatric Patellofemoral Instability Patients: A Review of Treatment Options and Outcomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
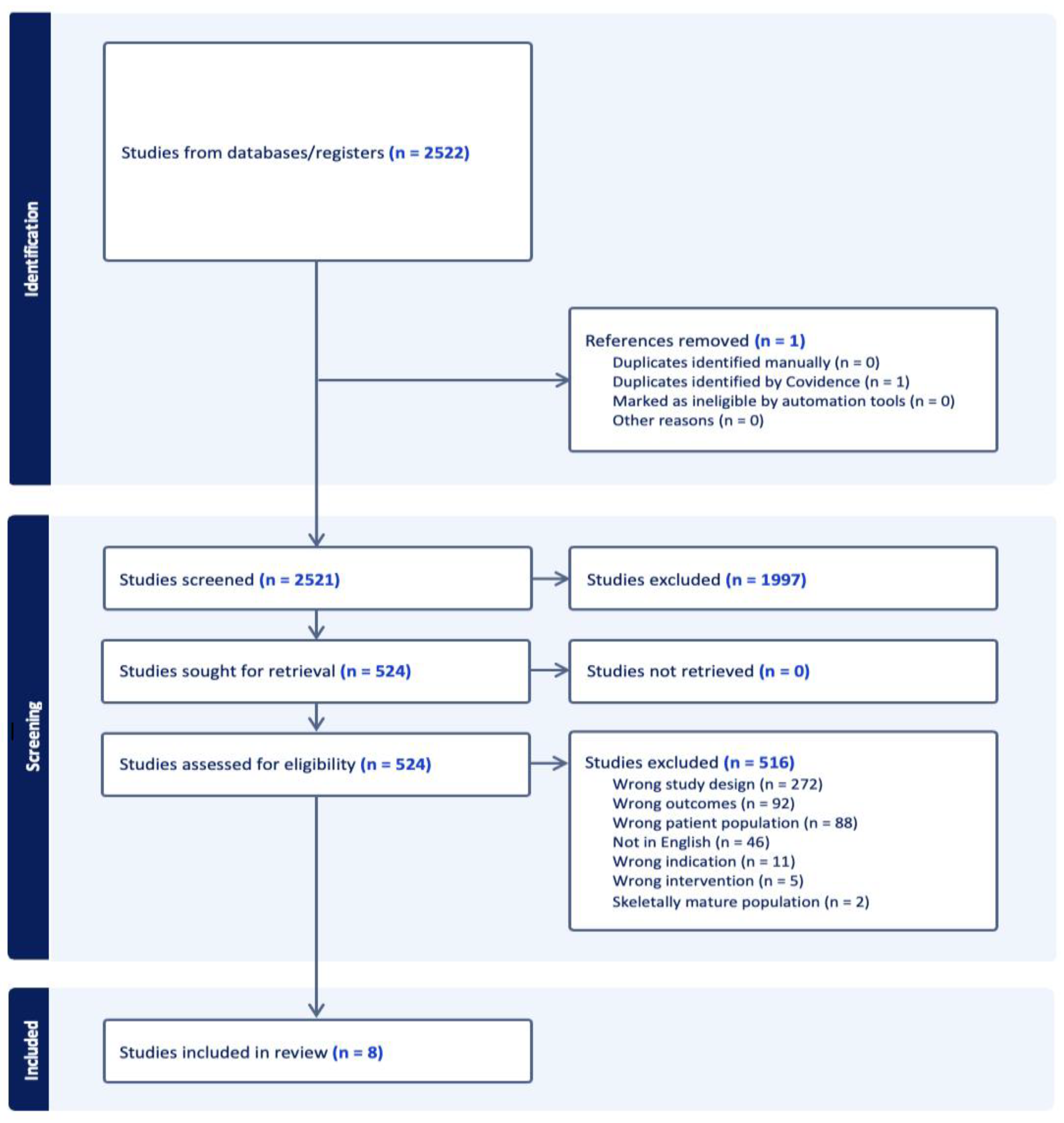
2.1. Literature Search and Screening
2.2. Appraisal of Research Quality and Risk of Bias
3. Results
3.1. Quality Assessment
3.2. Study and Cohort Characteristics
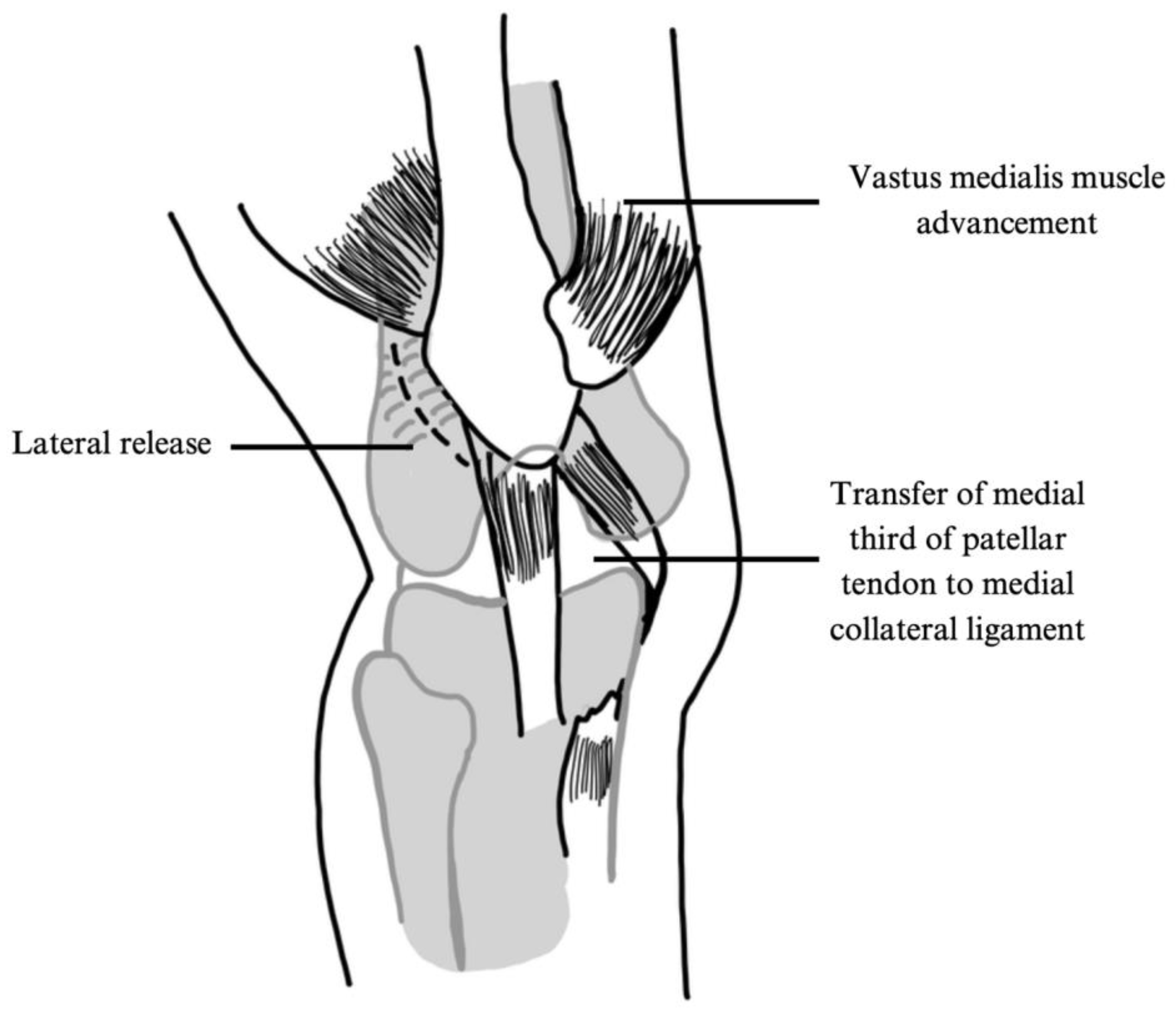
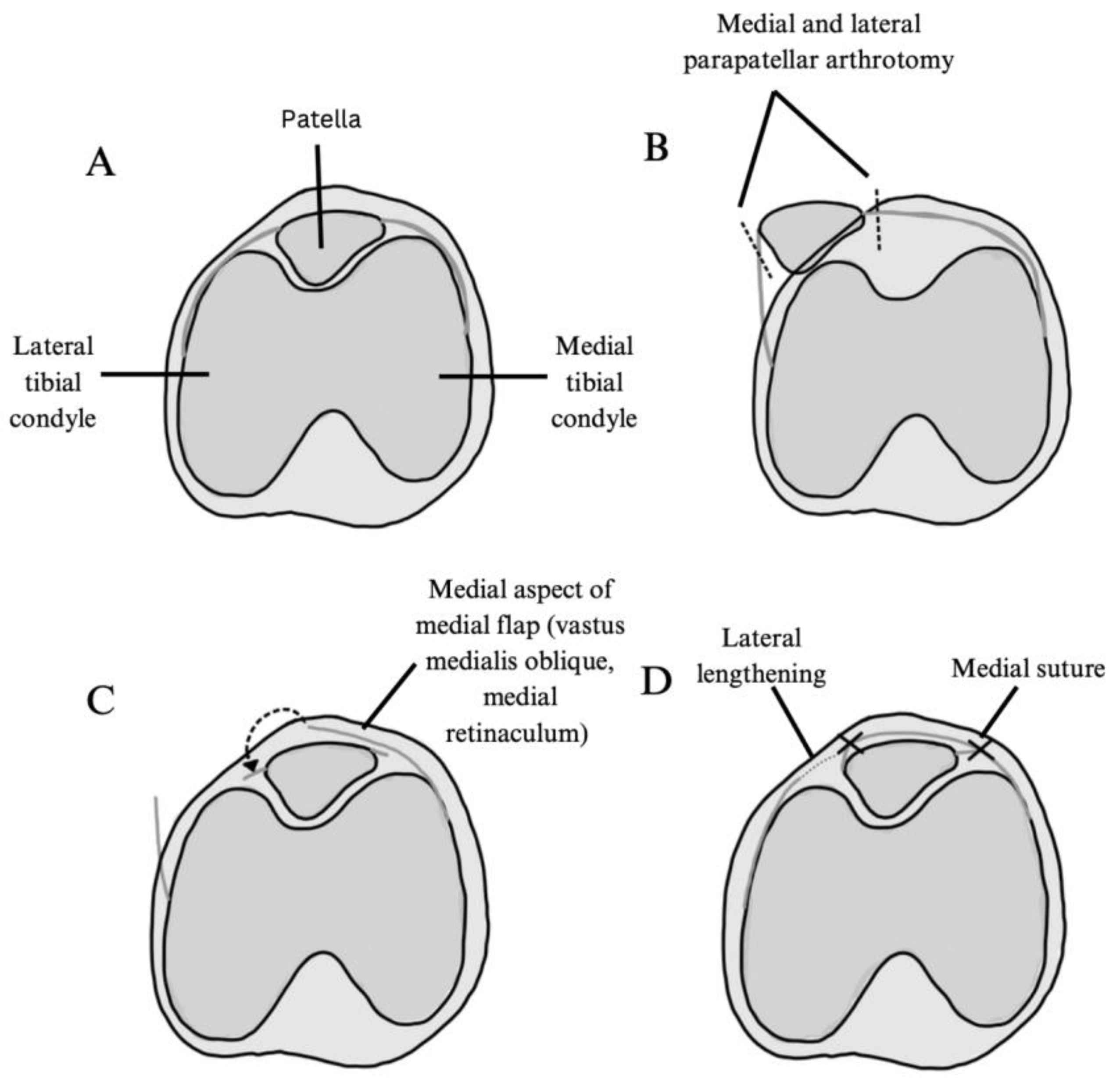
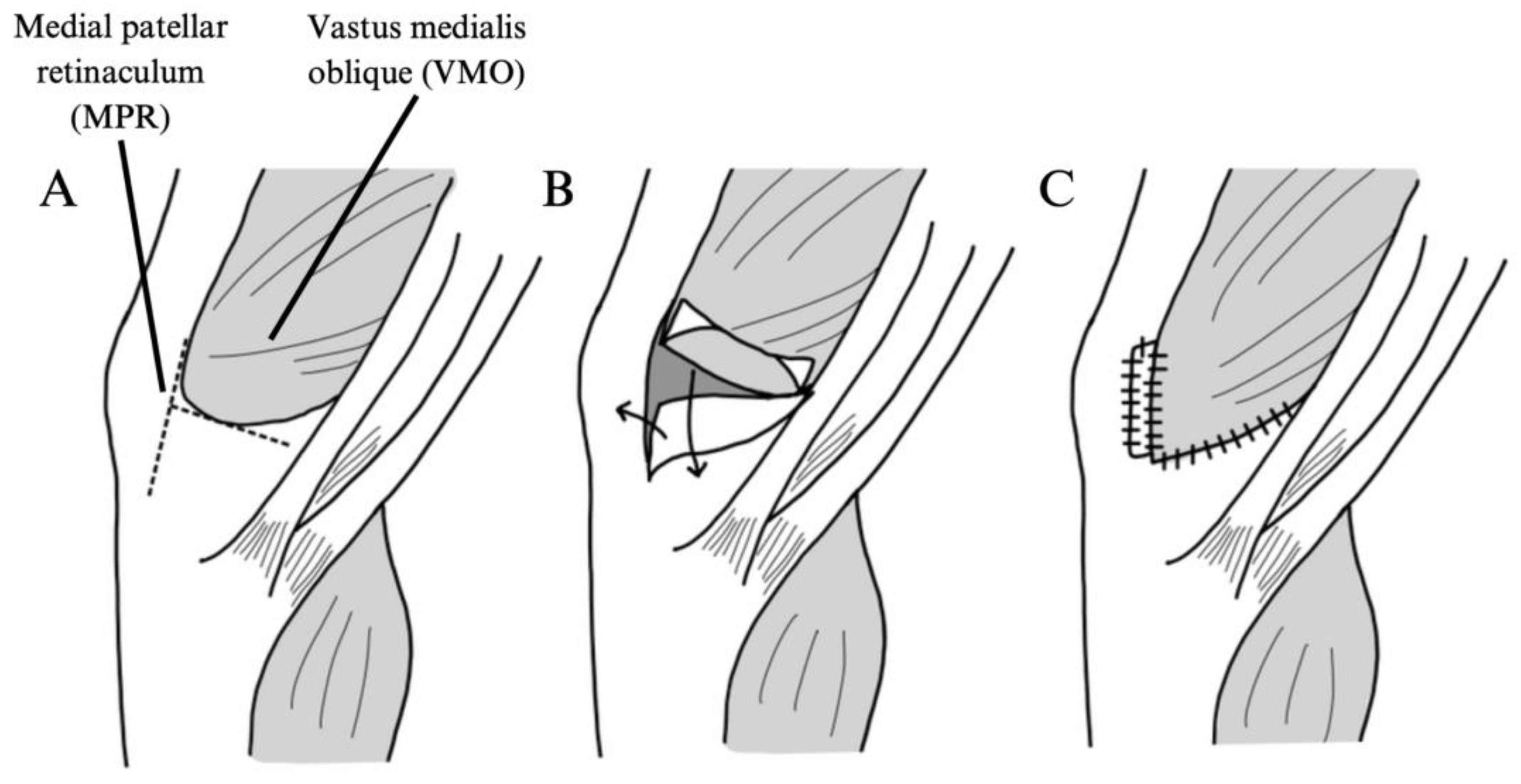
3.3. Surgical Techniques and Patient Cohort
3.4. Patient Reported Outcomes
3.5. Return to Sport/Return to Activities of Daily Living
3.6. Complications and Other Notable Findings
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MPFL | Medial patellofemoral ligament |
| PFI | Patellofemoral instability |
| MINORS | Methodological Index for Nonrandomized Studies |
| IKDC | International Knee Documentation Committee Subjective Knee Form |
| ADL | Activities of daily living |
| AKPS | Anterior knee pain scale |
| HSS-Pedi FABS | The Hospital for Special Surgery Pediatric Functional Activity Brief Scale |
| KOOS | Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score |
| Pre-Op | Preoperative |
Appendix A
| Set # | Search Strategy | Results |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Pediatrics | “Adolescent”[Mesh] OR “Child”[Mesh] OR “Child, Preschool”[Mesh] OR “Hospitals, Pediatric”[Mesh] OR “Infant”[Mesh] OR “Infant, Newborn”[Mesh] OR “Neonatology”[Mesh] OR “Minors”[Mesh] OR “Pediatrics”[Mesh] OR “Pediatric Anesthesia”[Mesh] OR “Pediatric Emergency Medicine”[Mesh] OR “Perinatology”[Mesh] OR “Puberty”[Mesh] OR adolescent[tiab] OR adolescents[tiab] OR adolescence[tiab] OR baby[tiab] OR babies[tiab] OR boy[tiab] OR boys[tiab] OR boyhood[tiab] OR child[tiab] OR childhood[tiab] OR children[tiab] OR “emerging adult”[tiab] OR “emerging adults”[tiab] OR girl[tiab] OR girls[tiab] OR girlhood[tiab] OR infant[tiab] OR infants[tiab] OR infancy[tiab] OR juvenile[tiab] OR juveniles[tiab] OR kid[tiab] OR kids[tiab] OR minors[tiab] OR newborn[tiab] OR newborns[tiab] OR neonatal[tiab] OR neonate[tiab] OR neonates[tiab] OR neonatology[tiab] OR neonatologist[tiab] OR neonatologists[tiab] OR preterm[tiab] OR prematurity[tiab] OR preadolescent[tiab] OR preadolescents[tiab] OR preadolescence[tiab] OR puberty[tiab] OR pubescent[tiab] OR pubescence[tiab] OR prepubescent[tiab] OR prepubescence[tiab] OR pediatric[tiab] OR pediatrics[tiab] OR paediatric[tiab] OR paediatrics[tiab] OR PICU[tiab] OR Pediatrician[tiab] OR pediatricians[tiab] OR paediatrician[tiab] OR paediatricians[tiab] OR pediatric[tiab] OR pediatrics[tiab] OR paediatric[tiab] OR paediatrics[tiab] OR stepchild[tiab] OR stepchildren[tiab] OR schoolchild[tiab] OR schoolgirl[tiab] OR schoolgirls[tiab] OR schoolboy[tiab] OR schoolboys[tiab] OR “school age”[tiab] OR “school aged”[tiab] OR toddler[tiab] OR toddlers[tiab] OR teen[tiab] OR teens[tiab] OR teenager[tiab] OR teenagers[tiab] OR teenaged[tiab] OR teenage[tiab] OR youth[tiab] OR youths[tiab] OR youngster[tiab] OR youngsters[tiab] OR “young person”[tiab] OR “young persons”[tiab] OR “young people”[tiab] | 5,024,019 |
| 2. Patella | “Patellofemoral Joint”[Mesh] OR “Patella”[Mesh] OR Patell*[tiab] | 31,417 |
| 3. Instability | “Joint Instability”[Mesh] OR “Joint Dislocations”[Mesh] OR “Patellar Dislocation”[Mesh] OR sublux*[tiab] OR disloca*[tiab] OR instabil*[tiab] OR unstabl*[tiab] | 334,717 |
| 4. COMBINE | #1 AND #2 AND #3 | 2522 |
References
- Tan, S.H.S.; Sin, Q.S.; Tan, L.Y.H.; Lim, A.K.S.; Hui, J.H. Combination of tibial tubercle transfer, medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction, trochleoplasty and lateral release for patellofemoral instability provides good middle- to long-term outcomes in adolescents. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2024, 34, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abouelsoud, M.M.; Abdelhady, A.; Elshazly, O. Anatomic physeal-sparing technique for medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction in skeletally immature patients with ligamentous laxity. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2015, 25, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alm, L.; Krause, M.; Mull, C.; Frosch, K.H.; Akoto, R. Modified adductor sling technique: A surgical therapy for patellar instability in skeletally immature patients. Knee 2017, 24, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Bastrom, T.P.; Dennis, M.M.; Pennock, A.T.; Edmonds, E.W. Adolescent Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction: A Comparison of the Use of Autograft Versus Allograft Hamstring. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2018, 6, 2325967118774272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremond, N.; Prima, R.; Rabattu, P.Y.; Accadbled, F.; Chotel, F.; Konkel, M.; Eid, A.; Philippe, C.; Godinho, A.; Turati, M.; et al. Isolated MPFL reconstruction with soft tissue femoral fixation technique in 54 skeletally immature patients: Clinical outcomes at 2 years follow-up. A French multicenter retrospective study. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2023, 109, 103530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husen, M.; Milbrandt, T.A.; Shah, V.; Krych, A.J.; Stuart, M.J.; Saris, D.B.F. Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction Using Allografts in Skeletally Immature Patients. Am. J. Sports Med. 2023, 51, 1513–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xiong, Y.; Li, J. A Combined Surgical Approach for Recurrent Patellar Dislocation in Adolescents With Patella Alta and Increased Tibial Tuberosity-Trochlear Groove Distance: Improved Clinical Outcomes but Decreased Posterior Tibial Slopes in Skeletally Immature Patients at Minimum 4-Year Follow-Up. Arthroscopy 2024, 40, 1529–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gornick, B.R.; Kwan, K.Z.; Schlechter, J.A. Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Augmentation Repair for Primary Patellar Dislocation With Concomitant Chondral or Osteochondral Injury in Children and Adolescents: Outcomes at Minimum 2-Year Follow-up. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2024, 12, 23259671241242010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, J.S.; Daigneault, J.P.; Sethi, P.; Polzhofer, G.K. Treatment of recurrent patellar instability with a modification of the Roux-Goldthwait technique. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2006, 26, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regalado, G.; Lintula, H.; Kokki, H.; Kröger, H.; Väätäinen, U.; Eskelinen, M. Six-year outcome after non-surgical versus surgical treatment of acute primary patellar dislocation in adolescents: A prospective randomized trial. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2016, 24, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, G.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Ma, L.; Dong, J. Medial patella retinaculum plasty for treatment of habitual patellar dislocation in adolescents. Int. Orthop. 2012, 36, 1819–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zein, A.M.N.; Allam, A.F.A.; Hassan, A.Z.M.; Soliman, A.M.; Mohamed, M.M.A. Outcomes of an All-Soft Tissue Fixation Technique for Reconstruction of the Medial Patellofemoral Complex Using Double-Bundle Quadriceps Tendon Autograft for Recurrent Patellar Dislocation in Skeletally Immature Patients. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2024, 12, 23259671241259051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelitz, M.; Dreyhaupt, J.; Reichel, H.; Woelfle, J.; Lippacher, S. Anatomic reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament in children and adolescents with open growth plates: Surgical technique and clinical outcome. Am. J. Sports Med. 2013, 41, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Örs, Ç.; Çaylak, R.; Karataş, Ö.; Sarpel, Y. Anatomical medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction improves sport participation and activity levels in adolescents with recurrent patellar dislocation. Jt. Dis. Relat. Surg. 2024, 35, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueth, M.J.; Koehl, P.; Schuh, A.; Goyal, T.; Wagner, D. Return to sports and short-term follow-up of 101 cases of medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction using gracilis tendon autograft in children and adolescents. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2023, 143, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, C.B.G.; Hinckel, B.B.; Ribeiro, G.F.; Giglio, P.N.; Santos, T.P.; Bonadio, M.B.; Arendt, E.; Gobbi, R.G. Medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction in skeletally immature patients without correction of bony risk factors leads to acceptable outcomes but higher failure rates. J. ISAKOS 2023, 8, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, M.; Enderlein, D.; Nielsen, T.; Christiansen, S.E.; Faunø, P. Clinical outcome after reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament in paediatric patients with recurrent patella instability. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2016, 24, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, E.; Criseo, N.; Annibaldi, A.; Carrozzo, A.; Pagnotta, S.M.; Cantagalli, M.R.; Orlandi, P.; Daggett, M. Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction Using Gracilis Tendon Graft and “All Suture” Knotless Anchors for Patellar Fixation. Arthrosc. Tech. 2023, 12, e2329–e2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, L.S.; Vidal, A.F. Traumatic patellar dislocation in children and adolescents: Treatment update and literature review. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2004, 16, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, F.; Ji, G.; Liu, F.; Fan, C.; Yang, G.; Lu, J. Combined medial and lateral patellar retinaculum plasty for skeletally immature patients with patellar dislocation and low-grade trochlear dysplasia. Knee 2020, 27, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucirek, N.K.; Lansdown, D.A. Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Repair: Still a Relevant Treatment for Patellar Instability? Oper. Tech. Sports Med. 2023, 31, 151033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagelada, F.; Rahbek, O.; Sahirad, C.; Ramachandran, M. Results of operative 4-in-1 patella realignment in children with recurrent patella instability. J. Orthop. 2018, 15, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, S.N.; Lopreiato, N.; Veerkamp, M. 4-in-1 Quadricepsplasty for Habitual and Fixed Lateral Patellar Dislocation in Children. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2023, 43, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelitz, M.; Dornacher, D.; Dreyhaupt, J.; Reichel, H.; Lippacher, S. The relation of the distal femoral physis and the medial patellofemoral ligament. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2011, 19, 2067–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shea, K.G.; Styhl, A.C.; Jacobs, J.C.; Ganley, T.J.; Milewski, M.D.; Cannamela, P.C.; Anderson, A.F.; Polousky, J.D. The Relationship of the Femoral Physis and the Medial Patellofemoral Ligament in Children:A Cadaveric Study. Am. J. Sports Med. 2016, 44, 2833–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slim, K.; Nini, E.; Forestier, D.; Kwiatkowski, F.; Panis, Y.; Chipponi, J. Methodological index for non-randomized studies (minors): Development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J. Surg. 2003, 73, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulisa, A.G.; Falciglia, F.; Giordano, M.; Savignoni, P.; Guzzanti, V. Galeazzi’s modified technique for recurrent patella dislocation in skeletally immature patients. J. Orthop. Sci. 2012, 17, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danino, B.; Deliberato, D.; Abousamra, O.; Singh, S.; Klingele, K. Four-in-one Extensor Realignment for the Treatment of Obligatory or Fixed, Lateral Patellar Instability in Skeletally Immature Knee. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2020, 40, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grannatt, K.; Heyworth, B.E.; Ogunwole, O.; Micheli, L.J.; Kocher, M.S. Galeazzi semitendinosus tenodesis for patellofemoral instability in skeletally immature patients. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2012, 32, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, F.; Ronga, M.; Longo, U.G.; Testa, V.; Capasso, G.; Maffulli, N. The 3-in-1 procedure for recurrent dislocation of the patella in skeletally immature children and adolescents. Am. J. Sports Med. 2009, 37, 1814–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trisolino, G.; Depaoli, A.; Gallone, G.; Ramella, M.; Olivotto, E.; Zarantonello, P.; Stallone, S.; Persiani, V.; Casadei, G.; Rocca, G. A 20-Year Retrospective Study of Children and Adolescents Treated by the Three-in-One Procedure for Patellar Realignment. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nietosvaara, Y.; Paukku, R.; Palmu, S.; Donell, S.T. Acute patellar dislocation in children and adolescents. Surgical technique. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2009, 91 (Suppl. S2), 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, M.; Falciglia, F.; Aulisa, A.G.; Guzzanti, V. Patellar dislocation in skeletally immature patients: Semitendinosous and gracilis augmentation for combined medial patellofemoral and medial patellotibial ligament reconstruction. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2012, 20, 1594–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlichte, L.M.; Sidharthan, S.; Green, D.W.; Parikh, S.N. Pediatric Management of Recurrent Patellar Instability. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rev. 2019, 27, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinterakis, G.; Vlastos, I.; Gianzina, E.; Dimitriadis, S.; Mastrantonakis, K.; Chronopoulos, E.; Yiannakopoulos, C.K. MPFL Reconstruction in Skeletally Immature Patients: Comparison Between Anatomic and Non-Anatomic Femoral Fixation-Systematic Review. Children 2024, 11, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobson, T.E.; Tomasevich, K.M.; Quinlan, N.J.; Mortensen, A.J.; Aoki, S.K. Tape Augmentation Does Not Affect Mid-Term Outcomes of Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction in Skeletally Mature Adolescent Patients. Arthrosc. Sports Med. Rehabil. 2022, 4, e359–e370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, N.J.; Tomasevich, K.M.; Mortensen, A.J.; Hobson, T.E.; Adeyemi, T.; Metz, A.K.; Aoki, S.K. Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction in the Pediatric Population: Skeletal Immaturity Does Not Affect Functional Outcomes but Demonstrates Increased Rate of Subsequent Knee Injury. Arthrosc. Sports Med. Rehabil. 2022, 4, e1589–e1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

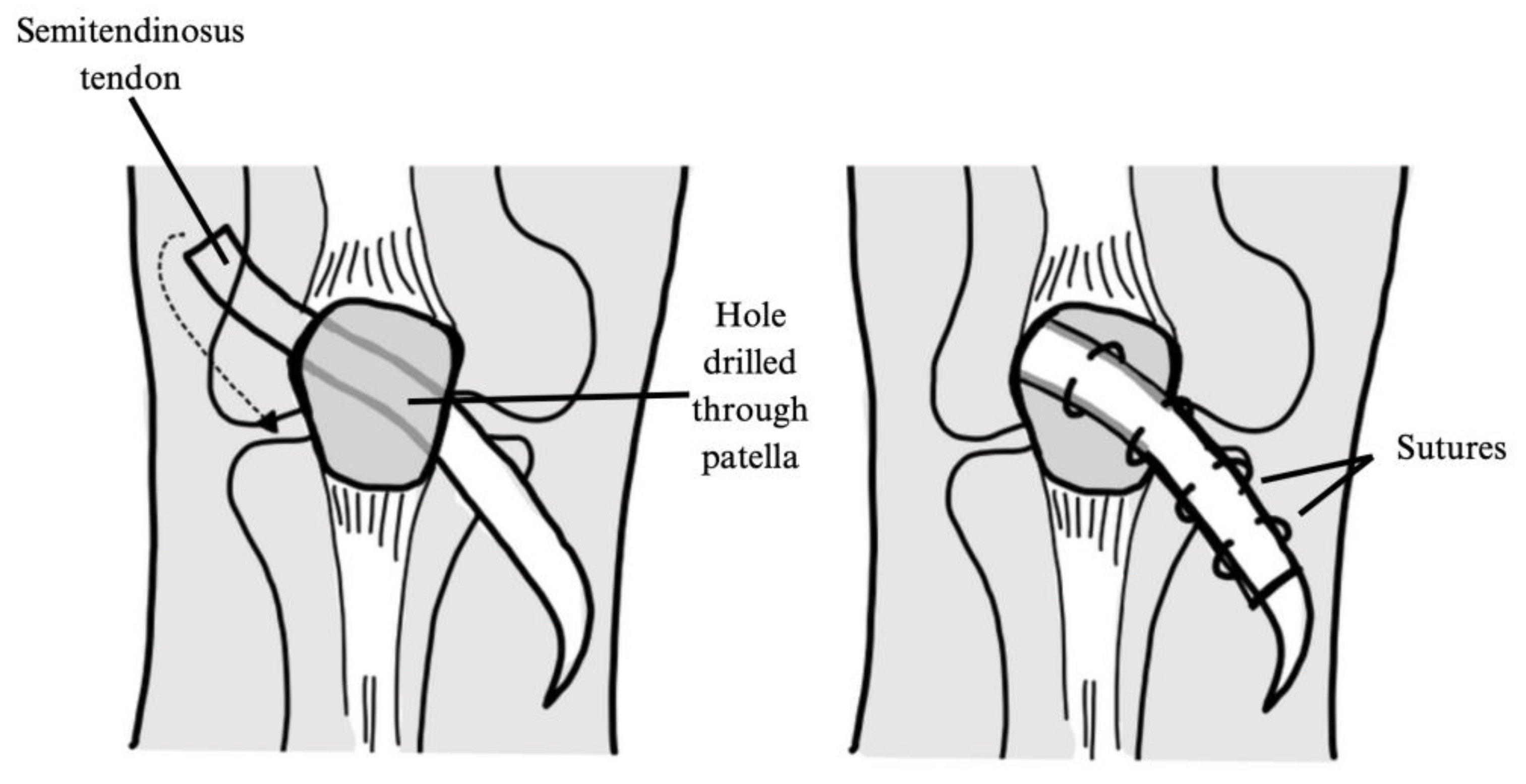
| Author, Year | Title | Risk of Bias Assessment (MINORS Score) |
|---|---|---|
| Aulisa, 2012 [27] | Galeazzi’s modified technique for recurrent patella dislocation in skeletally immature patients | 13 |
| Danino, 2020 [28] | Four-in-one Extensor Realignment for the Treatment of Obligatory or Fixed, Lateral Patellar Instability in Skeletally Immature Knee | 11 |
| Grannatt, 2012 [29] | Galeazzi semitendinosus tenodesis for patellofemoral instability in skeletally immature patients | 11 |
| Li, 2020 [20] | Combined medial and lateral patellar retinaculum plasty for skeletally immature patients with patellar dislocation and low-grade trochlear dysplasia | 11 |
| Malagelada, 2018 [22] | Results of operative 4-in-1 patella realignment in children with recurrent patella instability | 12 |
| Oliva, 2009 [30] | The 3-in-1 procedure for recurrent dislocation of the patella in skeletally immature children and adolescents | 14 |
| Parikh, 2023 [23] | 4-in-1 Quadricepsplasty for Habitual and Fixed Lateral Patellar Dislocation in Children | 10 |
| Trisolino, 2023 [31] | A 20-Year Retrospective Study of Children and Adolescents Treated by the Three-in-One Procedure for Patellar Realignment | 10 |
| Author | Study Design | Number of Subjects (n) | Number of Knees | Age, in Years (Mean ± SD, Range) | Female (n) | Follow-Up in Months (Mean ± SD, Range) | First Time or Recurrent Dislocation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aulisa, 2012 [27] | Prospective | 14 | 14 | 11.1 (9.2–13.1) | 10 | 52.8 (49.2–69.6) | Recurrent |
| Danino, 2020 [28] | Retrospective | 34 | 46 | 10.3 ± 2.4 (6–13) | 25 | 51.6 ± 31.5 (12–146) | Recurrent |
| Grannatt 2012 [29] | Retrospective | 28 | 34 | 11.1 (4.5–15.8) | 19 | 70 (27–217) | Recurrent |
| Li, 2020 [20] | Retrospective | 19 | 19 | 12.4 (8–15) | 7 | 35.4 (24–48) | Both |
| Malagelada, 2018 [22] | Prospective | 12 | 16 | 12.6 (9–16) | 8 | 65 (36–98) | Recurrent |
| Oliva, 2009 [30] | Prospective | 25 | 25 | 13.6 ± 3.8 | 7 | 45.6 (30–72) | Recurrent |
| Parikh, 2023 [23] | Retrospective | 12 | 12 | 9 ± 3.8 (5–15) | 7 | 39.3 | Recurrent |
| Trisolino, 2023 [31] | Retrospective | 126 | 168 | 11.5 ± 3.7 (4.1–17.6) | 80 | 63.6 ± 40.8 (18–146.4) | Recurrent |
| Author | Kujala (Mean ± SD, Range) | IKDC (Mean ± SD, Range) | Other | Complications | Return to Sports/Activities of Daily Living (ADLs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aulisa, 2012 [27] | Insall: Excellent: 9/14 knees (62.5%) Good: 5/14 knees (37.5%) Poor: 0/14 knees | Transient saphenous aerve deficit: 4/14 patients (28.8%) | |||
| Danino, 2020 [28] | Follow-up 93.0 ± 5.2 (83–100) | Recurrent instability: 6/34 patients (17.7%) Additional surgical procedure for instability: 5/34 (14.7%) patients Recurrent dislocation: 2/34 (5.9%) patients Additional surgical procedure for dislocation: 2/3 (5.9%) patients Subluxation: 3/34 (8.8%) patients Additional other surgical procedure: 3/34 (8.8%) patients Superficial wound infection: 2/34 (5.9%) patients | ADLs: 16/16 patients full function Return to Sport: 20/22 knees (91%) | ||
| Grannatt, 2012 [29] | Follow-up 79.7 | Follow-up 63.6 | Marx Activity Score: follow-up 8.0 | Recurrent instability: 28/34 knees (82.4%) Subsequent surgery for recurrent instability: 12/34 knees (35.3) Superficial wound infection: 1/28 patients (3.6%) Mild wound dehiscence: 1/28 patients (3.6%) | |
| Li, 2020 [20] | Pre-op 57.6 ± 4.2 Follow-up 86.9 ± 8.1 (90–99) p < 0.05 | Tegner: pre-op 2.6 ± 1.0 Follow-up 5.0 ± 1.3 p < 0.05 | Knee pain: 3/19 patients (15.8%) Lateral patellar shift greater than 1.5cm: 2/19 patients (10.5%) Loss of flexion < 10°: 2/19 patients (10.5%) | ADLS: 19/19 patients full function | |
| Malagelada, 2018 [22] | Follow-up 83.4 ± 11.5 | Follow-up 79.5 ± 12.6 | Minor patellar maltracking treated with therapy: 3/12 patients (25%) Pain: 2/12 patients (16.7%) Keloid scar formation: 1/12 patients (8.3%) Superficial wound infection treated with antibiotics: 1/12 patients (8.3%) Recurrent Dislocation: 0 patients | Return to sport: 10/12 patients (83.3%) | |
| Oliva, 2009 [30] | Pre-op 54.4 Follow-up 93.8 p < 0.02 | Insall Salvati: Pre-op 1.0 Follow-up 1.0 p = ns Cincinnati: Pre-op 51.7 ± 12.6 Follow-up 94.3 ± 10.8 p < 0.02 | Traumatic dislocation: 1/25 patients (4%) Subsequent surgery for dislocation: 1/25 patients (4%) Lost to follow-up: 1/25 patients (4%) | Return to sport: Higher than preoperatively: 2/24 patients (8.3%) Same as preoperatively: 9/24 patients 37.5%) Lower than preoperatively: 9/24 patients (37.5%) Did not return: 4/24 patients (16.7%) (due to knee in all 4 patients) | |
| Parikh, 2023 [23] | Follow-up 90 ± 16.5 | Follow-up 88.1 ± 13.8 | Banff Patellar Instability: Follow-up 78.2 ± 23.1 KOOS: Follow-up 93.9 ± 12.9 HSS-Pedi FABS Activity Score: Follow-up 15.6 ± 7.5 | Recurrent instability: 3/12 patients (25%) Postoperative arthrofibrosis requiring manipulation under anesthesia: 1/12 patient (8.3%) Superficial wound infection treated with local wound care: 1/12 patients (8.3%) | |
| Trisolino, 2023 [31] | Follow-up 86.4 ± 16.3 (range 28–100) | Lost to follow-up: 20/168 knees (11.9%) in 14/126 patients (11.1%) Recurrent dislocation: 19/168 knees (11.3%) Additional surgical procedure for dislocation: 14/168 knees (8.3%) Additional staged surgical procedure: 22/168 knees (13.1%) in 18/126 patients (14.3%) Avascular necrosis of the patella: 1/126 patients (0.8%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zirbes, C.F.; Henriquez, A.; Amanah, A.; Therien, A.D.; Perez-Espina, S.; Dorrestein, E.; Zheng, D.; Lilly, J.; Luo, E.J.; Fox, M.A.; et al. Physeal-Sparing Soft Tissue Realignment in Pediatric Patellofemoral Instability Patients: A Review of Treatment Options and Outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041116
Zirbes CF, Henriquez A, Amanah A, Therien AD, Perez-Espina S, Dorrestein E, Zheng D, Lilly J, Luo EJ, Fox MA, et al. Physeal-Sparing Soft Tissue Realignment in Pediatric Patellofemoral Instability Patients: A Review of Treatment Options and Outcomes. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(4):1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041116
Chicago/Turabian StyleZirbes, Christian F., Alyssa Henriquez, Alaowei Amanah, Aaron D. Therien, Sebastian Perez-Espina, Emilie Dorrestein, Diana Zheng, Jason Lilly, Emily J. Luo, Michael A. Fox, and et al. 2025. "Physeal-Sparing Soft Tissue Realignment in Pediatric Patellofemoral Instability Patients: A Review of Treatment Options and Outcomes" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 4: 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041116
APA StyleZirbes, C. F., Henriquez, A., Amanah, A., Therien, A. D., Perez-Espina, S., Dorrestein, E., Zheng, D., Lilly, J., Luo, E. J., Fox, M. A., & Lau, B. C. (2025). Physeal-Sparing Soft Tissue Realignment in Pediatric Patellofemoral Instability Patients: A Review of Treatment Options and Outcomes. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(4), 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041116






