Prognostic Models for Disease Progression and Outcomes in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Critical Appraisal
2.5. Meta-Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Overall Mortality
3.2. Exacerbations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADO | Age, Dyspnea, and airflow Obstruction |
| B-AE-D | Body mass index, Acute Exacerbations, Dyspnea |
| BODE | Body mass index, airflow Obstruction, Dyspnea, and Exercise |
| BODEX | Body mass index, airflow Obstruction, Dyspnea, and EXacerbations |
| CHARMS | CHecklist for critical Appraisal and data extraction for systematic Reviews of prediction Modelling Studies |
| CODEX | Comorbidity, airflow Obstruction, Dyspnea, and EXacerbations |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| COTE | COmorbidity TEst |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| DOSE | Dyspnea, airflow Obstruction, Smoking, Exacerbation |
| FEV1 | Forced Expiratory Volume in the first second |
| GOLD | Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease |
| HPI | History of present illness |
| ICS | Inhaled corticosteroids |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| LABA | Long-acting beta-agonist |
| LAMA | Long-acting muscarinic antagonist |
| ML | Machine learning |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| PROBAST | Prediction model Risk Of Bias Assessment Tool |
| ROB | Risk of bias |
References
- Agustí, A.; Celli, B.R.; Criner, G.J.; Halpin, D.; Anzueto, A.; Barnes, P.; Bourbeau, J.; Han, M.K.; Martinez, F.J.; Montes de Oca, M.; et al. Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease 2023 Report: GOLD Executive Summary. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, 819–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boers, E.; Barrett, M.; Su, J.G.; Benjafield, A.V.; Sinha, S.; Kaye, L.; Zar, H.J.; Vuong, V.; Tellez, D.; Gondalia, R.; et al. Global Burden of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Through 2050. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2346598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbert, R.J.; Natoli, J.L.; Gano, A.; Badamgarav, E.; Buist, A.S.; Mannino, D.M. Global Burden of COPD: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 28, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershon, A.S.; Dolmage, T.E.; Stephenson, A.; Jackson, B. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Socio-economic Status: A Systematic Review. COPD J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2012, 9, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Burden of 288 Causes of Death and Life Expectancy Decomposition in 204 Countries and Territories and 811 Subnational Locations, 1990–2021: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2024, 403, 2100–2132. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Kuhn, M.; Prettner, K.; Yu, F.; Yang, T.; Bärnighausen, T.; Bloom, D.E.; Wang, C. The Global Economic Burden of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease for 204 Countries and Territories in 2020-50: A Health-Augmented Macroeconomic Modelling Study. Lancet Glob. Health 2023, 11, e1183–e1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, L.M.; Hurd, S.S. Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD: 2003 Update. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 22, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization—The Top 10 Causes of Death. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- Raherison, C.; Girodet, P.-O. Epidemiology of COPD. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2009, 18, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.C.; Wrobel, J.P. Epidemiology and Clinical Impact of Major Comorbidities in Patients with COPD. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2014, 9, 871–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellou, V.; Belbasis, L.; Konstantinidis, A.K.; Tzoulaki, I.; Evangelou, E. Prognostic Models for Outcome Prediction in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Systematic Review and Critical Appraisal. BMJ 2019, 367, l5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.-J.E.; Moore, E.; Ali, I.; Smeeth, L.; Stone, P.; Quint, J.K. Prognostic Variables and Scores Identifying the End of Life in COPD: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2017, 12, 2239–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, B.; Gaveikaite, V.; Bianchi, C.; Puhan, M.A. Prediction Models for Exacerbations in Patients with COPD. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 160061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, F.; Xin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Prognostic risk prediction model for patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (AECOPD): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir. Res. 2024, 25, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corlateanu, A.; Plahotniuc, A.; Corlateanu, O.; Botnaru, V.; Bikov, A.; Mathioudakis, A.G.; Covantev, S.; Siafakas, N. Multidimensional Indices in the Assessment of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Respir. Med. 2021, 185, 106519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moons, K.G.M.; de Groot, J.A.H.; Bouwmeester, W.; Vergouwe, Y.; Mallett, S.; Altman, D.G.; Reitsma, J.B.; Collins, G.S. Critical Appraisal and Data Extraction for Systematic Reviews of Prediction Modelling Studies: The CHARMS Checklist. PLoS Med. 2014, 11, e1001744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, R.F.; Moons, K.G.M.; Riley, R.D.; Whiting, P.F.; Westwood, M.; Collins, G.S.; Reitsma, J.B.; Kleijnen, J.; Mallett, S.; PROBAST Group. PROBAST: A Tool to Assess the Risk of Bias and Applicability of Prediction Model Studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 170, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohl, C.; McIntosh, E.J.; Unger, S.; Haddaway, N.R.; Kecke, S.; Schiemann, J.; Wilhelm, R. Online Tools Supporting the Conduct and Reporting of Systematic Reviews and Systematic Maps: A Case Study on CADIMA and Review of Existing Tools. Environ. Evid. 2018, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cassai, A.; Boscolo, A.; Zarantonello, F.; Pettenuzzo, T.; Sella, N.; Geraldini, F.; Munari, M.; Navalesi, P. Enhancing Study Quality Assessment: An in-Depth Review of Risk of Bias Tools for Meta-Analysis—A Comprehensive Guide for Anesthesiologists. J. Anesth. Analg. Crit. Care 2023, 3, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celli, B.R.; Locantore, N.; Yates, J.; Tal-Singer, R.; Miller, B.E.; Bakke, P.; Calverley, P.; Coxson, H.; Crim, C.; Edwards, L.D.; et al. Inflammatory Biomarkers Improve Clinical Prediction of Mortality in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgür, E.S.; Nayci, S.A.; Özge, C.; Taşdelen, B. An Integrated Index Combined by Dynamic Hyperinflation and Exercise Capacity in the Prediction of Morbidity and Mortality in COPD. Respir. Care 2012, 57, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puhan, M.A.; Hansel, N.N.; Sobradillo, P.; Enright, P.; Lange, P.; Hickson, D.; Menezes, A.M.; ter Riet, G.; Held, U.; Domingo-Salvany, A.; et al. Large-scale international validation of the ADO index in subjects with COPD: An individual subject data analysis of 10 cohorts. BMJ Open 2012, 2, e002152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divo, M.; Cote, C.; de Torres, J.P.; Casanova, C.; Marin, J.M.; Pinto-Plata, V.; Zulueta, J.; Cabrera, C.; Zagaceta, J.; Hunninghake, G.; et al. Comorbidities and Risk of Mortality in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.H.; Mapel, D.W.; Bruse, S.; Petersen, H.; Nyunoya, T. Development of a Modified BODE Index as a Mortality Risk Measure among Older Adults with and without Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 178, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almagro, P.; Soriano, J.B.; Cabrera, F.J.; Boixeda, R.; Alonso-Ortiz, M.B.; Barreiro, B.; Diez-Manglano, J.; Murio, C.; Heredia, J.L. Working Group on COPD, Spanish Society of Internal Medicine. Short- and Medium-Term Prognosis in Patients Hospitalized for COPD Exacerbation: The CODEX Index. Chest 2014, 145, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, L.M.A.; Leimer, I.; Metzdorf, N.; Becker, K.; Rutten-van Mölken, M.P.M.H. Does the 2013 GOLD Classification Improve the Ability to Predict Lung Function Decline, Exacerbations and Mortality: A Post-Hoc Analysis of the 4-Year UPLIFT Trial. BMC Pulm. Med. 2014, 14, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montserrat-Capdevila, J.; Godoy, P.; Marsal, J.R.; Barbé-Illa, F. Risk factors for mortality in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Aten. Primaria 2015, 47, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolz, D.; Kostikas, K.; Blasi, F.; Boersma, W.; Milenkovic, B.; Lacoma, A.; Louis, R.; Aerts, J.G.; Welte, T.; Torres, A.; et al. Adrenomedullin Refines Mortality Prediction by the BODE Index in COPD: The “BODE-A” Index. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolz, D.; Meyer, A.; Rakic, J.; Boeck, L.; Scherr, A.; Tamm, M. Mortality Risk Prediction in COPD by a Prognostic Biomarker Panel. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 1557–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskela, J.; Kilpeläinen, M.; Kupiainen, H.; Mazur, W.; Sintonen, H.; Boezen, M.; Lindqvist, A.; Postma, D.; Laitinen, T. Co-morbidities are the key nominators of the health related quality of life in mild and moderate COPD. BMC Pulm. Med. 2014, 14, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grolimund, E.; Kutz, A.; Marlowe, R.J.; Vögeli, A.; Alan, M.; Christ-Crain, M.; Thomann, R.; Falconnier, C.; Hoess, C.; Henzen, C.; et al. Long-Term Prognosis in COPD Exacerbation: Role of Biomarkers, Clinical Variables and Exacerbation Type. COPD J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2015, 12, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.P.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Chong, P.; Chin, S.; Wong, X.Y.; Ong, V.; Chan, Y.H.; Lim, T.K.; Phua, J. Prognostication in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Using the BOS Index. Chest 2015, 148, 683A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horita, N.; Koblizek, V.; Plutinsky, M.; Novotna, B.; Hejduk, K.; Kaneko, T. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Prognostic Score: A New Index. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky Olomouc 2016, 160, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeck, L.; Soriano, J.B.; Brusse-Keizer, M.; Blasi, F.; Kostikas, K.; Boersma, W.; Milenkovic, B.; Louis, R.; Lacoma, A.; Djamin, R.; et al. Prognostic Assessment in COPD without Lung Function: The B-AE-D Indices. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 1635–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanasse, A.; Courteau, J.; Couillard, S.; Beauchesne, M.-F.; Larivée, P. Predicting One-Year Mortality After a “First” Hospitalization for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: An Eight-Variable Assessment Score Tool. COPD J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2017, 14, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.P.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Chong, P.L.P.; Chin, S.; Wong, X.Y.; Ong, V.; Chan, Y.H.; Lim, T.K.; Phua, J. Prognostic Utility of the 2011 GOLD Classification and Other Multidimensional Tools in Asian COPD Patients: A Prospective Cohort Study. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2016, 11, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, D.R.; Flynn, R.; Zhang, J.; Trucco, E.; Quint, J.K.; Zutis, K. External Validation of ADO, DOSE, COTE and CODEX at Predicting Death in Primary Care Patients with COPD Using Standard and Machine Learning Approaches. Respir. Med. 2018, 138, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gedebjerg, A.; Szépligeti, S.K.; Wackerhausen, L.-M.H.; Horváth-Puhó, E.; Dahl, R.; Hansen, J.G.; Sørensen, H.T.; Nørgaard, M.; Lange, P.; Thomsen, R.W. Prediction of Mortality in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease with the New Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease 2017 Classification: A Cohort Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almagro, P.; Martínez-Camblor, P.; Miravitlles, M.; Rodríguez-Carballeira, M.; Navarro, A.; Lamprecht, B.; Ramirez-Garcia Luna, A.S.; Kaiser, B.; Alfageme, I.; Casanova, C.; et al. External Validation and Recalculation of the CODEX Index in COPD Patients. A 3CIAplus Cohort Study. COPD J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2019, 16, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, C.I.; Ricciardi, F.; Smeeth, L.; Stone, P.; Quint, J.K. P119 Predicting One-Year Mortality in COPD Using Prognostic Predictors Routinely Measured in Primary Care. Thorax 2018, 73, A166–A167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, C.; Castro-Acosta, A.; Alvarez-Martínez, C.J.; Capelastegui, A.; López-Campos, J.L.; Pozo-Rodriguez, F. Predictors of One-Year Mortality after Hospitalization for an Exacerbation of COPD. BMC Pulm. Med. 2018, 18, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloom, C.I.; Ricciardi, F.; Smeeth, L.; Stone, P.; Quint, J.K. Predicting COPD 1-Year Mortality Using Prognostic Predictors Routinely Measured in Primary Care. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramburu, A.; Arostegui, I.; Moraza, J.; Barrio, I.; Aburto, M.; García-Loizaga, A.; Uranga, A.; Zabala, T.; Quintana, J.M.; Esteban, C. COPD Classification Models and Mortality Prediction Capacity. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2019, 14, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, M.; Regan, E.A.; Hunninghake, G.M.; Vestbo, J.; Make, B.J.; Tal-Singer, R.; Han, M.K.; Silverman, E.K.; Cho, M.H.; Hobbs, B.D. Improved COPD Mortality Prediction Using Machine Learning in the COPDGene and ECLIPSE Studies. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, A3996. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-García, S.; Represas-Represas, C.; Ruano-Raviña, A.; Botana-Rial, M.; Martínez-Reglero, C.; Fernández Villar, A. Dependence IN Performing Activities as a Predictor of Mortality Following Hospitalization for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Exacerbation. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2020, 56, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.-K.; Tung, Y.-C. Validated the Power of Terminal Status Criteria in the Prediction of 1-Year Mortality in Patiens with COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Z.-W.; Chen, Y.-A.; Dong, Y.-H. Comparative Performance of Comorbidity Measures in Predicting Health Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2020, 15, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, J.A.; Barker, R.E.; Kon, S.S.C.; Jones, S.E.; Banya, W.; Nolan, C.M.; Patel, S.; Polgar, O.; Haselden, B.M.; Polkey, M.I.; et al. Gait Speed and Adverse Outcomes Following Hospitalised Exacerbation of COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 58, 2004047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Cho, Y.H.; Lee, S.M.; Hwang, J.; Lee, J.S.; Oh, Y.-M.; Lee, S.-D.; Loh, L.-C.; Ong, C.-K.; Seo, J.B.; et al. Deep Radiomics-Based Survival Prediction in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shen, N.; Wang, Q.; Chai, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, D.; et al. Nomograms for Predicting Coexisting Cardiovascular Disease and Prognosis in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Study Based on NHANES Data. Can. Respir. J. 2022, 2022, 5618376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusuaa, C.; van der Leest, C.; Helfrich, G.; Heller-Baan, R.; van Loenhout, C.; Herbrink, J.W.; Nieboer, D.; van der Rijt, C.C.; van der Heide, A. The Development of the ADO-SQ Model to Predict 1-Year Mortality in Patients with COPD. Palliat. Med. 2022, 36, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijnant, S.R.A.; Benz, E.; Luik, A.I.; Rivadeneira, F.; Voortman, T.; Brusselle, G.G.; Lahousse, L. Frailty Transitions in Older Persons with Lung Function Impairment: A Population-Based Study. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci 2023, 78, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlyarov, S. The Role of Multidimensional Indices for Mortality Prediction in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, P.C.; Stanbrook, M.B.; Anderson, G.M.; Newman, A.; Gershon, A.S. Comparative Ability of Comorbidity Classification Methods for Administrative Data to Predict Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Ann. Epidemiol. 2012, 22, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, P.M.; Williamson, P.A.; Singanayagam, A.; Akram, A.; Schembri, S.; Chalmers, J.D. P136 Multidimensional Prognostic Index for Exacerbations of COPD. Thorax 2013, 68, A137–A138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.P.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Chong, P.L.P.; Chin, S.; Wong, X.Y.; Ong, V.; Chan, Y.H.; Lim, T.K.; Phua, J. Role of BMI, Airflow Obstruction, St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire and Age Index in Prognostication of Asian COPD. Respirology 2017, 22, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusse-Keizer, M.; Klatte, M.; Zuur-Telgen, M.; Koehorst-Ter Huurne, K.; van der Palen, J.; VanderValk, P. Comparing the 2007 and 2011 GOLD Classifications as Predictors of All-Cause Mortality and Morbidity in COPD. COPD J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2017, 14, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vela, E.; Tényi, Á.; Cano, I.; Monterde, D.; Cleries, M.; Garcia-Altes, A.; Hernandez, C.; Escarrabill, J.; Roca, J. Population-based analysis of patients with COPD in Catalonia: A cohort study with implications for clinical management. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e017283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-Y.; Huang, C.-K.; Wu, C.-L.; Peng, H.-C.; Yu, C.-J.; Chien, J.-Y. Prognostic Value of the Post-Exercise Heart Rate Recovery and BHDE-Index in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. BMC Pulm. Med. 2023, 23, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-Z.; Ou, C.-Y.; Hsu, C.-H.; Hsiue, T.-R. Validation of the GOLD 2013 Classification in Predicting Exacerbations and Mortality in Taiwanese Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2015, 114, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-Z.; Ou, C.-Y.; Yu, C.-H.; Yang, S.-C.; Chang, H.-Y.; Hsiue, T.-R. Comparison of Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 2013 Classification and Body Mass Index, Airflow Obstruction, Dyspnea, and Exacerbations Index in Predicting Mortality and Exacerbations in Elderly Adults with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2015, 63, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.-Z.; Hsiue, T.-R.; Tsai, S.-H.; Huang, T.-H.; Liao, X.-M.; Chen, C.-Z. Validation of the GOLD 2017 and New 16 Subgroups (1A–4D) Classifications in Predicting Exacerbation and Mortality in COPD Patients. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2018, 13, 3425–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criner, R.N.; Labaki, W.W.; Regan, E.A.; Bon, J.M.; Soler, X.; Bhatt, S.P.; Murray, S.; Hokanson, J.E.; Silverman, E.K.; Crapo, J.D.; et al. Mortality and Exacerbations by Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease Groups ABCD: 2011 Versus 2017 in the COPDGene® Cohort. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2019, 6, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agusti, A.; Edwards, L.D.; Celli, B.; Macnee, W.; Calverley, P.M.A.; Müllerova, H.; Lomas, D.A.; Wouters, E.; Bakke, P.; Rennard, S.; et al. Characteristics, Stability and Outcomes of the 2011 GOLD COPD Groups in the ECLIPSE Cohort. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 42, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, R.H.; Nag, A.; Mapel, D.W.; Lee, T.A.; Rosiello, R.; Schatz, M.; Vekeman, F.; Gauthier-Loiselle, M.; Merrigan, P.; Duh, M. Risk Assessment of First Severe COPD Exacerbation Using Predictive Models Based on Health Claims Data. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, A2867. [Google Scholar]
- Montserrat-Capdevila, J.; Godoy, P.; Marsal, J.R.; Barbé, F. Predictive Model of Hospital Admission for COPD Exacerbation. Respir. Care 2015, 60, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.C.; Price, D.; Chavannes, N.H.; Lee, A.J.; Hyland, M.E.; Ställberg, B.; Lisspers, K.; Sundh, J.; van der Molen, T.; Tsiligianni, I.; et al. Multi-Component Assessment of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: An Evaluation of the ADO and DOSE Indices and the Global Obstructive Lung Disease Categories in International Primary Care Data Sets. NPJ Prim. Care Respir. Med. 2016, 26, 16010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, R.H.; Nag, A.; Mapel, D.W.; Lee, T.A.; Rosiello, R.; Schatz, M.; Vekeman, F.; Gauthier-Loiselle, M.; Merrigan, J.F.P.; Duh, M.S. Claims-Based Risk Model for First Severe COPD Exacerbation. Am. J. Manag. Care 2018, 24, e45–e53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Annavarapu, S.; Goldfarb, S.; Gelb, M.; Moretz, C.; Renda, A.; Kaila, S. Development and Validation of a Predictive Model to Identify Patients at Risk of Severe COPD Exacerbations Using Administrative Claims Data. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2018, 13, 2121–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yii, A.C.A.; Loh, C.; Tiew, P.; Xu, H.; Taha, A.A.M.; Koh, J.; Tan, J.; Lapperre, T.S.; Anzueto, A.; Tee, A.K.H. A Clinical Prediction Model for Hospitalized COPD Exacerbations Based on “Treatable Traits”. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2019, 14, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutsen, M.R.C.; Keene, S.J.; Nakken, D.J.A.J.N.; Groenen, M.T.; van Kuijk, S.M.J.; Franssen, F.M.E.; Wouters, E.F.M.; Spruit, M.A. Physical, Psychological, and Social Factors Associated with Exacerbation-Related Hospitalization in Patients with COPD. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adibi, A.; Sin, D.D.; Safari, A.; Johnson, K.M.; Aaron, S.D.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Sadatsafavi, M. The Acute COPD Exacerbation Prediction Tool (ACCEPT): A Modelling Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, W.; Xu, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y. A Nomogram for Predicting Severe Exacerbations in Stable COPD Patients. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2020, 15, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-K.; Lan, C.-C.; Tzeng, I.-S.; Wu, C.-W. The COPD-Readmission (CORE) Score: A Novel Prediction Model for One-Year Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Readmissions. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2021, 120, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, N.A.; Giezendanner, S.; Urwyler, P.; Bridevaux, P.-O.; Chhajed, P.N.; Garnier, C.V.; Geiser, T.; Zell-Weger, L.J.; Kohler, M.; Maier, S.; et al. Nomogram for Patients with Exacerbation in the General Practitioners Based Swiss Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Cohort. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 58, PA1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, M.F.A.; Hoffman, E.A.; Comellas, A.P.; Guo, J.; Fortis, S.; Bodduluri, S.; Abtin, F.; Barr, R.G.; Bhatt, S.P.; Christensen, G.E.; et al. CT Texture Features Predict Severe COPD Exacerbations in SPIROMICS. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, A1122. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, S.; Arjomandi, M.; Tong, Y.; Liao, Z.C.; Luo, G. Developing a Machine Learning Model to Predict Severe Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Exacerbations: Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2022, 24, e28953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebner, S.T.; Henny, S.; Giezendanner, S.; Brack, T.; Brutsche, M.; Chhajed, P.; Clarenbach, C.; Dieterle, T.; Egli, A.; Frey, M.; et al. Prediction of Acute COPD Exacerbation in the Swiss Multicenter COPD Cohort Study (TOPDOCS) by Clinical Parameters, Medication Use, and Immunological Biomarkers. Respiration 2022, 101, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Sun, W.; Zhao, H.; Wang, X.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, X.; Mao, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, M.; Sheng, Z.; et al. Characteristics of 12-Month Readmission for Hospitalized Patients with COPD: A Propensity Score Matched Analysis of Prospective Multicenter Study. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2022, 17, 2329–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makimoto, K.; Koo, M.; Hogg, J.C.; Bourbeau, J.; Tan, W.; Kirby, M. Texture-Based Computed Tomography Radiomics with Machine Learning Improves Predicting Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Outcomes. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, A6543. [Google Scholar]
- Safari, A.; Adibi, A.; Sin, D.D.; Lee, T.Y.; Ho, J.K.; Sadatsafavi, M. ACCEPT 2·0: Recalibrating and Externally Validating the Acute COPD Exacerbation Prediction Tool (ACCEPT). eClinicalMedicine 2022, 51, 101574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertens, L.C.M.; Reitsma, J.B.; Moons, K.G.M.; van Mourik, Y.; Lammers, J.W.J.; Broekhuizen, B.D.L.; Hoes, A.W.; Rutten, F.H. Development and Validation of a Model to Predict the Risk of Exacerbations in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2013, 8, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, M.; Ingebrigtsen, T.S.; Marott, J.L.; Dahl, M.; Lange, P.; Vestbo, J.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Inflammatory Biomarkers and Exacerbations in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. JAMA 2013, 309, 2353–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montserrat-Capdevila, J.; Godoy, P.; Marsal, J.R.; Barbé, F.; Galván, L. Risk of Exacerbation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Primary Care Retrospective Cohort Study. BMC Fam. Pract. 2015, 16, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, C.; Zeng, Y.; Zhou, A.; Duan, J.; Cheng, W.; Sun, T.; Li, X.; Ma, L.; Liu, Q.; et al. Modified and Simplified Clinically Important Deterioration: Multidimensional Indices of Short-Term Disease Trajectory to Predict Future Exacerbations in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2020, 14, 1753466620977376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Hurst, J.R.; Martinez, F.J.; Rabe, K.F.; Bafadhel, M.; Jenkins, M.; Salazar, D.; Dorinsky, P.; Darken, P. Predictive Modeling of COPD Exacerbation Rates Using Baseline Risk Factors. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2022, 16, 17534666221107314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalakuhan, B.; Kiljanek, L.; Parvathaneni, A.; Hester, M.; Cheriyath, P.; Fischman, D. A Prediction Model for COPD Readmissions: Catching up, Catching Our Breath, and Improving a National Problem. J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect. 2012, 2, 9915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motegi, T.; Jones, R.C.; Ishii, T.; Hattori, K.; Kusunoki, Y.; Furutate, R.; Yamada, K.; Gemma, A.; Kida, K. A Comparison of Three Multidimensional Indices of COPD Severity as Predictors of Future Exacerbations. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2013, 8, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batzlaff, C.M.; Karpman, C.; Afessa, B.; Benzo, R.P. Predicting 1-Year Mortality Rate for Patients Admitted with an Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease to an Intensive Care Unit: An Opportunity for Palliative Care. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2014, 89, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahanovich, A.; Kadushkin, A. Laboratory and Clinical Parameters in Predicting Risk of Future Exacerbations in Both Non-Smoking and Smoking COPD Patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, P3987. Available online: https://publications.ersnet.org/content/erj/44/suppl58/p3987 (accessed on 2 December 2025).
- Suzuki, M.; Makita, H.; Östling, J.; Thomsen, L.H.; Konno, S.; Nagai, K.; Shimizu, K.; Pedersen, J.H.; Ashraf, H.; Bruijnzeel, P.L.B.; et al. Lower Leptin/Adiponectin Ratio and Risk of Rapid Lung Function Decline in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2014, 11, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miravitlles, M.; García-Sidro, P.; Fernández-Nistal, A.; Buendía, M.J.; Espinosa de Los Monteros, M.J.; Esquinas, C.; Molina, J. The Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Assessment Test Improves the Predictive Value of Previous Exacerbations for Poor Outcomes in COPD. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2015, 10, 2571–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadushkin, A.; Tahanovich, A. Mathematical Model to Predict the Risk of Future Exacerbations in Non-Smoking Patients with COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, PA4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundh, J.; Ekström, M. Risk Factors for Developing Hypoxic Respiratory Failure in COPD. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2017, 12, 2095–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keene, S.; Jordan, R.; Vries, F.D.; Sitch, A.; Adab, P.; Franssen, F. External Validation of Two Prognostic Scores Predicting Exacerbations in ECLIPSE COPD Patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, C.K.; Kim, J.W.; Yoo, K.H.; Jung, K.-S. Prediction Model of COPD Acute Exacerbation with Big Data by Machine Learning Methods. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, J.; Dutta, J.; Guo, N.; Hu, C.; Zhou, D.; Sitek, A.; Li, Q. Classification of Exacerbation Frequency in the COPDGene Cohort Using Deep Learning with Deep Belief Networks. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Chen, S. Prediction of Readmission in Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease within One Year after Treatment and Discharge. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, S.; Lowe, D.; Taylor, A.; Mcginness, P.; Carlin, C. Predicting 12-Month Mortality in a Scottish COPD Cohort. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 58, PA3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Xu, J.; Wang, F.; Chen, H.; Tang, J.; Chen, D.; Li, Q.; Jian, W.; Tang, G.; Zheng, J.; et al. Development of a Radiomics Model for Predicting COPD Exacerbations Based on Complementary Visual Information. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, A2296. [Google Scholar]
- Esther, C.R.; O’Neal, W.K.; Anderson, W.H.; Kesimer, M.; Ceppe, A.; Doerschuk, C.M.; Alexis, N.E.; Hastie, A.T.; Barr, R.G.; Bowler, R.P.; et al. Identification of Sputum Biomarkers Predictive of Pulmonary Exacerbations in COPD. Chest 2022, 161, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Dai, H.; Zhu, H.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Yang, Z.; Chu, S.; Xi, Q. Identification of Frequent Acute Exacerbations Phenotype in COPD Patients Based on Imaging and Clinical Characteristics. Respir. Med. 2023, 209, 107150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Lu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, F.; Tan, H.; Wang, X.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, N.; Chen, J. MRI-Assessed Diaphragmatic Function Can Predict Frequent Acute Exacerbation of COPD: A Prospective Observational Study Based on Telehealth-Based Monitoring System. BMC Pulm. Med. 2022, 22, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boueiz, A.; Xu, Z.; Chang, Y.; Masoomi, A.; Gregory, A.; Lutz, S.M.; Qiao, D.; Crapo, J.D.; Dy, J.G.; Silverman, E.K.; et al. Machine Learning Prediction of Progression in Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 Second in the COPDGene® Study. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2022, 9, 349–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.K.; Safari, A.; Adibi, A.; Sin, D.D.; Johnson, K.; Sadatsafavi, M.; IMPACT Study. Generalizability of Risk Stratification Algorithms for Exacerbations in COPD. Chest 2023, 163, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valera-Novella, E.; Bernabeu-Mora, R.; Montilla-Herrador, J.; Escolar-Reina, P.; García-Vidal, J.A.; Medina-Mirapeix, F. Development of the ESEx Index: A Tool for Predicting Risk of Recurrent Severe COPD Exacerbations. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2023, 14, 20406223231155115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Calster, B.; McLernon, D.J.; van Smeden, M.; Wynants, L.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Topic Group. ‘Evaluating diagnostic tests and prediction models’ of the STRATOS initiative. Calibration: The Achilles heel of predictive analytics. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puhan, M.A.; Garcia-Aymerich, J.; Frey, M.; ter Riet, G.; Antó, J.M.; Agustí, A.G.; Gómez, F.P.; Rodríguez-Roisín, R.; Moons, K.G.; Kessels, A.G.; et al. Expansion of the prognostic assessment of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: The updated BODE index and the ADO index. Lancet 2009, 374, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celli, B.R.; Cote, C.G.; Marin, J.M.; Casanova, C.; Montes de Oca, M.; Mendez, R.A.; Pinto Plata, V.; Cabral, H.J. The body-mass index, airflow obstruction, dyspnea, and exercise capacity index in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler-Cataluña, J.J.; Martínez-García, M.A.; Sánchez, L.S.; Tordera, M.P.; Sánchez, P.R. Severe exacerbations and BODE index: Two independent risk factors for death in male COPD patients. Respir Med. 2009, 103, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.C.; Donaldson, G.C.; Chavannes, N.H.; Kida, K.; Dickson-Spillmann, M.; Harding, S.; Wedzicha, J.A.; Price, D.; Hyland, M.E. Derivation and validation of a composite index of severity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: The DOSE Index. Am. J. Respir Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 1189–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vestbo, J.; Hurd, S.S.; Agustí, A.G.; Jones, P.W.; Vogelmeier, C.; Anzueto, A.; Barnes, P.J.; Fabbri, L.M.; Martinez, F.J.; Nishimura, M.; et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. Am. J. Respir Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


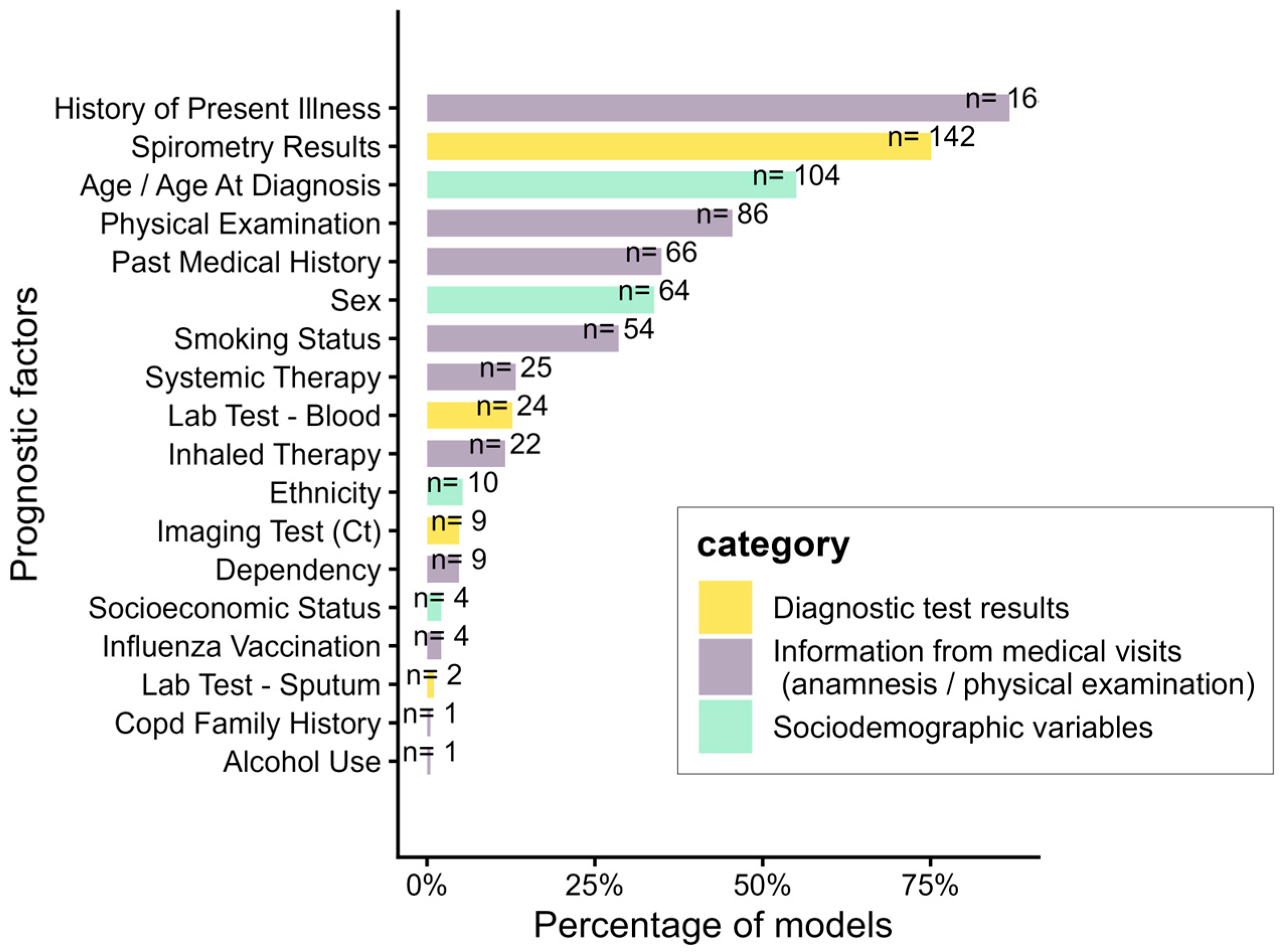


| Variable | Min | Q1 | Median | Q3 | Max | N (%) of Cohorts with Reported Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age (years) | 58.80 | 65.50 | 68.00 | 71.00 | 76.30 | 69 (71.8%) |
| % male | 9.55 | 56.08 | 70.40 | 88.38 | 100.00 | 70 (72.9%) |
| Mean body mass index (kg/m2) | 21.65 | 23.61 | 25.70 | 26.95 | 29.03 | 51 (53.1%) |
| Smoking habit | ||||||
| % current smokers (vs. ex/never) | 0.00 | 25.00 | 32.00 | 39.00 | 73.00 | 49 (51%) |
| Mean smoking pack-years | 18.82 | 40.68 | 46.40 | 51.84 | 75.60 | 30 (31.2%) |
| Disease severity | ||||||
| Mean FEV1% predicted | 27.00 | 47.41 | 49.14 | 59.90 | 77.10 | 44 (54.2%) |
| % GOLD Stage I | 0.00 | 2.45 | 8.80 | 17.00 | 50.80 | 27 (28.1%) |
| % GOLD Stage II | 32.00 | 37.52 | 42.90 | 50.20 | 72.60 | 26 (27.1%) |
| % GOLD Stage III | 6.40 | 24.18 | 32.75 | 38.60 | 45.00 | 26 (27.1%) |
| % GOLD Stage IV | 0.00 | 5.825 | 11.75 | 17.00 | 22.03 | 26 (27.1%) |
| Treatment | ||||||
| % treated with LAMA | 4.50 | 33.60 | 46.00 | 56.40 | 81.10 | 17 (17.7%) |
| % treated with LABA | 33.50 | 48.30 | 56.20 | 68.05 | 80.60 | 19 (19.8%) |
| % treated with ICS | 22.57 | 47.62 | 58.69 | 68.78 | 87.70 | 22 (22.9%) |
| Time (Years) | Model Type | N of Models | Min | Q1 | Median | Q3 | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (A) Outcome: overall mortality (n = 85) | |||||||
| 1 | Logistic regression | 14 | 0.655 | 0.723 | 0.782 | 0.814 | 0.832 |
| 1 | Cox regression | 27 | 0.413 | 0.652 | 0.709 | 0.760 | 0.926 |
| 1 | Machine learning | 3 | 0.651 | 0.652 | 0.654 | 0.685 | 0.716 |
| 2–3 | Logistic regression | 14 | 0.657 | 0.670 | 0.723 | 0.739 | 0.789 |
| 2–3 | Cox regression | 25 | 0.600 | 0.670 | 0.709 | 0.771 | 0.801 |
| 2–3 | Machine learning | 2 | 0.650 | 0.653 | 0.654 | 0.655 | 0.657 |
| 4–5 | Logistic regression | 11 | 0.620 | 0.642 | 0.678 | 0.695 | 0.761 |
| 4–5 | Cox regression | 8 | 0.590 | 0.692 | 0.720 | 0.845 | 0.920 |
| 4–5 | Machine learning | 0 | - | - | - | - | - |
| (B) Outcome: severe exacerbations (n = 38) | |||||||
| 1 | Logistic regression | 12 | 0.703 | 0.723 | 0.774 | 0.794 | 0.861 |
| 1 | Cox regression | 4 | 0.690 | 0.728 | 0.740 | 0.753 | 0.790 |
| 1 | Machine learning | 3 | 0.580 | 0.688 | 0.796 | 0.831 | 0.866 |
| 2–3 | Logistic regression | 2 | 0.720 | 0.735 | 0.750 | 0.765 | 0.780 |
| 2–3 | Cox regression | 3 | 0.694 | 0.694 | 0.694 | 0.707 | 0.720 |
| 2–3 | Machine learning | 0 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 4–5 | Logistic regression | 1 | 0.710 | 0.710 | 0.710 | 0.710 | 0.710 |
| 4–5 | Cox regression | 4 | 0.690 | 0.690 | 0.695 | 0.710 | 0.740 |
| 4–5 | Machine learning | 0 | - | - | - | - | - |
| (C) Outcome: moderate or severe exacerbations (n = 16) | |||||||
| 1 | Logistic regression | 4 | 0.730 | 0.748 | 0.772 | 0.790 | 0.790 |
| 1 | Cox regression | 0 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1 | Machine learning | 0 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2–3 | Logistic regression | 3 | 0.660 | 0.675 | 0.690 | 0.735 | 0.780 |
| 2–3 | Cox regression | 1 | 0.591 | 0.591 | 0.591 | 0.591 | 0.591 |
| 2–3 | Machine learning | 0 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 4–5 | Logistic regression | 0 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 4–5 | Cox regression | 1 | 0.730 | 0.730 | 0.730 | 0.730 | 0.730 |
| 4–5 | Machine learning | 0 | - | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Testa, D.; Magnoni, P.; Fanizza, C.; Bussa, M.; Zanfino, A.; Khaleghi Hashemian, D.; Rebora, P.; Bisceglia, L.; Russo, A.G., on behalf of the PROPHET-I Study Group. Prognostic Models for Disease Progression and Outcomes in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8725. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248725
Testa D, Magnoni P, Fanizza C, Bussa M, Zanfino A, Khaleghi Hashemian D, Rebora P, Bisceglia L, Russo AG on behalf of the PROPHET-I Study Group. Prognostic Models for Disease Progression and Outcomes in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(24):8725. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248725
Chicago/Turabian StyleTesta, Deborah, Pietro Magnoni, Caterina Fanizza, Martino Bussa, Adele Zanfino, Dariush Khaleghi Hashemian, Paola Rebora, Lucia Bisceglia, and Antonio Giampiero Russo on behalf of the PROPHET-I Study Group. 2025. "Prognostic Models for Disease Progression and Outcomes in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 24: 8725. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248725
APA StyleTesta, D., Magnoni, P., Fanizza, C., Bussa, M., Zanfino, A., Khaleghi Hashemian, D., Rebora, P., Bisceglia, L., & Russo, A. G., on behalf of the PROPHET-I Study Group. (2025). Prognostic Models for Disease Progression and Outcomes in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(24), 8725. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248725







