Harmonisation of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Results Obtained with Different Direct Methods: A Study Based on an External Quality Assessment Program
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Scheme Organisation
2.2. Analysis of the Results
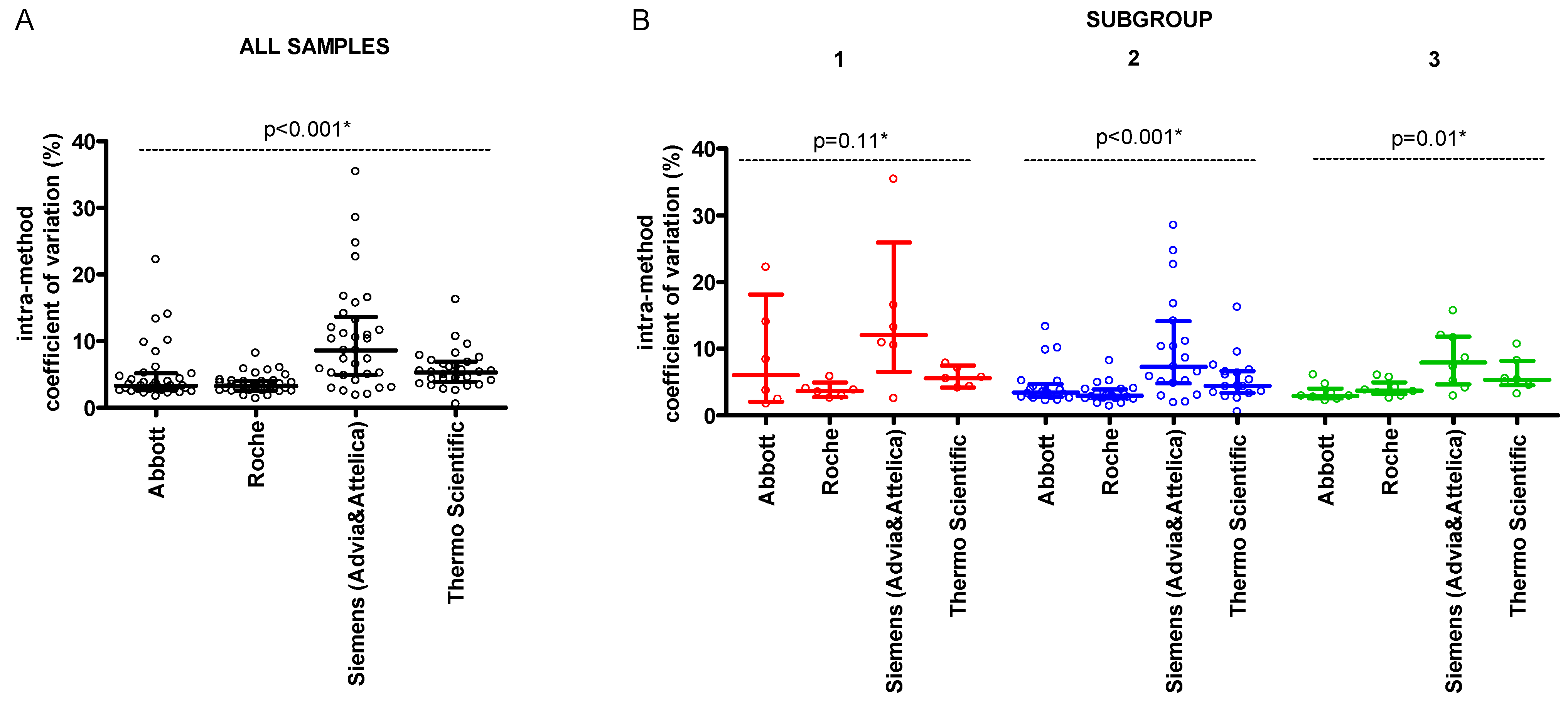
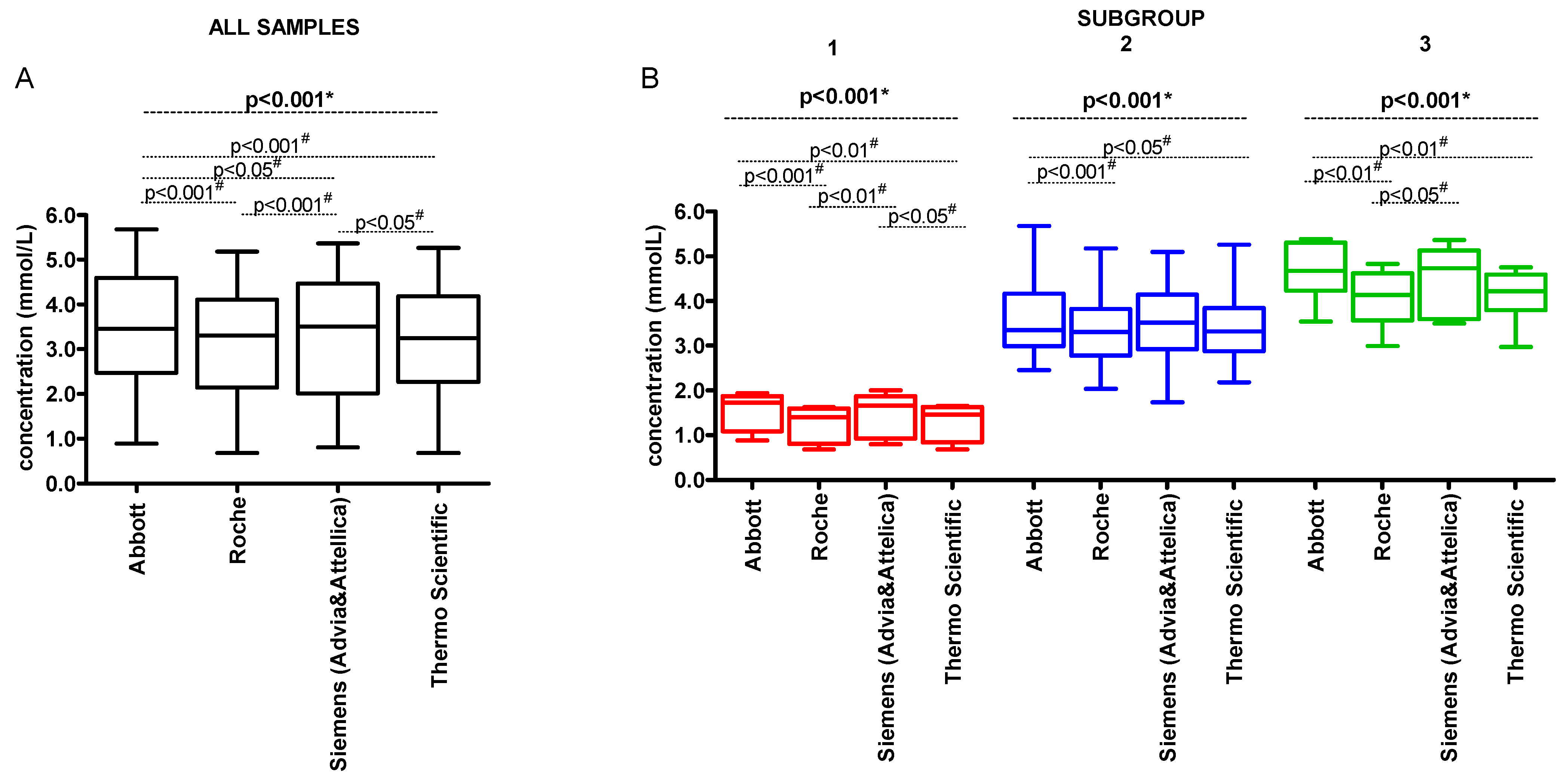
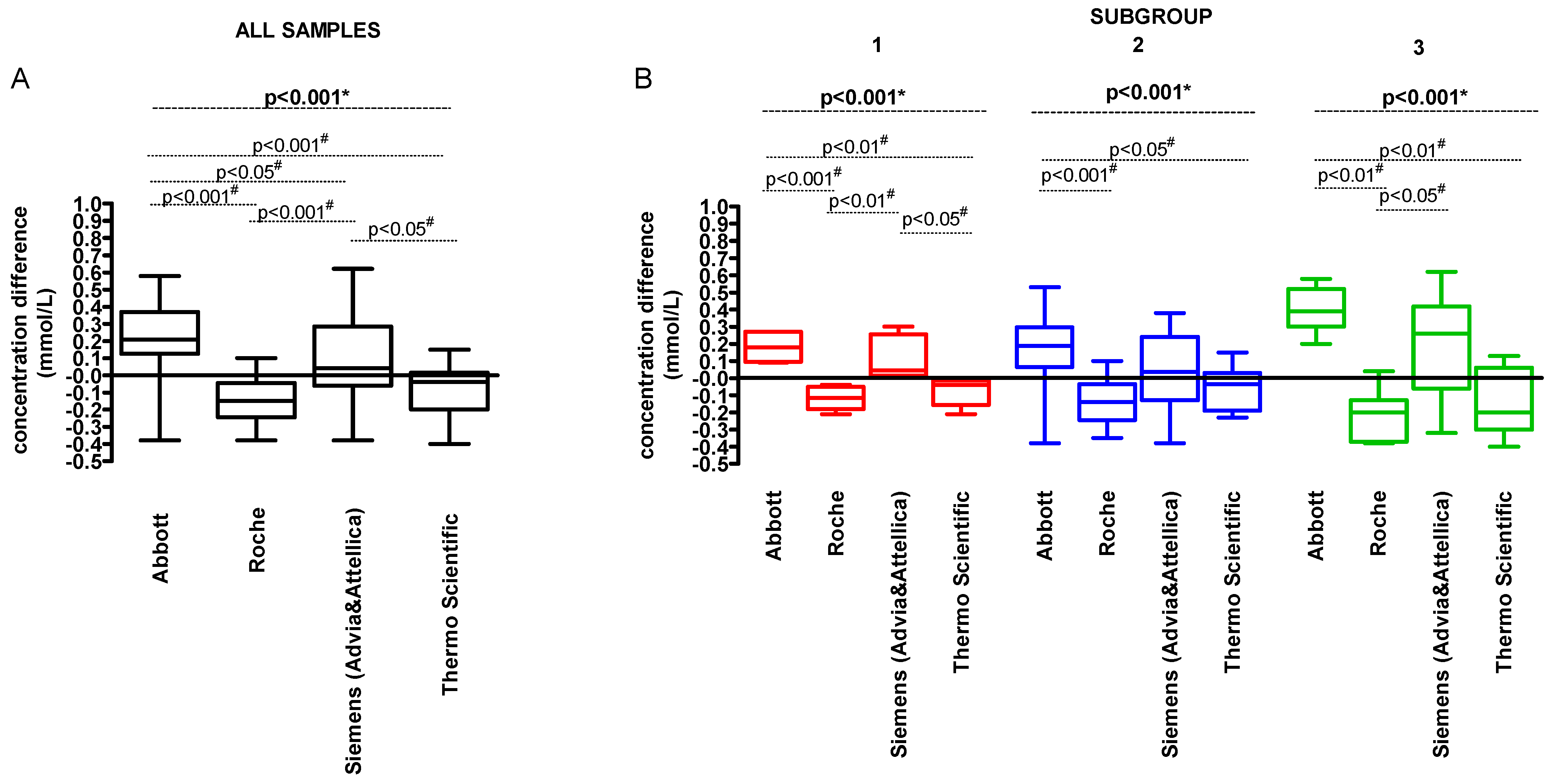
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CV | Coefficient of variation |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| HDL-C | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| EQA | External quality assessment |
| IDL | Intermediate-density lipoprotein |
| LDL-C | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| VLDL | Very-low-density lipoprotein |
| Q | Quartile |
References
- Mach, F.; Baigent, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Koskina, K.C.; Casula, M.; Badimon, L.; Chapman, M.J.; De Backer, G.G.; Delgado, V.; Ference, B.A.; et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidaemias: Lipid Modification to Reduce Cardiovascular Risk. Atherosclerosis 2019, 290, 140–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ćwiklińska, A.; Wieczorek, E.; Gliwińska, A.; Marcinkowska, M.; Czaplińska, M.; Mickiewicz, A.; Kuchta, A.; Kortas-Stempak, B.; Gruchała, M.; Dȩbska-Ślizień, A.; et al. Non-HDL-C/TG Ratio Indicates Significant Underestimation of Calculated Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (LDL-C) Better than TG Level: A Study on the Reliability of Mathematical Formulas Used for LDL-C Estimation. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2021, 59, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narasimhan, M.; Cao, J.; Meeusen, J.W.; Remaley, A.T.; Martin, S.S.; Muthukumar, A. Fatigued with Friedewald: Why Isn’t Everyone Onboard yet with the New LDL-C Equations? Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2025, 12, 1534460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solnica, B.; Sygitowicz, G.; Sitkiewicz, D.; Jóźwiak, J.; Kasperczyk, S.; Broncel, M.; Wolska, A.; Odrowąż-Sypniewska, G.; Banach, M. 2024 Guidelines of the Polish Society of Laboratory Diagnostics and the Polish Lipid Association on Laboratory Diagnostics of Lipid Metabolism Disorders. Arch. Med. Sci. 2024, 20, 357–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauck, M.; Warnick, G.R.; Rifai, N. Methods for Measurement of LDL-Cholesterol: A Critical Assessment of Direct Measurement by Homogeneous Assays versus Calculation. Clin. Chem. 2002, 48, 236–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, W.G.; Myers, G.L.; Sakurabayashi, I.; Bachmann, L.M.; Caudill, S.P.; Dziekonski, A.; Edwards, S.; Kimberly, M.M.; Korzun, W.J.; Leary, E.T.; et al. Seven Direct Methods for Measuring HDL and LDL Cholesterol Compared with Ultracentrifugation Reference Measurement Procedures. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaninotto, M.; Graziani, M.S.; Plebani, M. The Harmonization Issue in Laboratory Medicine: The Commitment of CCLM. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2023, 61, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 17043; Conformity Assessment—General Requirements for the Competence of Proficiency Testing Providers. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- Otokozawa, S.; Ai, M.; Asztalos, B.F.; White, C.C.; Demissie-Banjaw, S.; Cupples, L.A.; Nakajima, K.; Wilson, P.W.F.; Schaefer, E.J. Direct Assessment of Plasma Low Density Lipoprotein and High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels and Coronary Heart Disease: Results from the Framingham Offspring Study. Atherosclerosis 2010, 213, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, S.; Kawase, R.; Nakaoka, H.; Nakatani, K.; Inagaki, M.; Yuasa-Kawase, M.; Tsubakio-Yamamoto, K.; Sandoval, J.C.; Masuda, D.; Ohama, T.; et al. Differential Reactivities of Four Homogeneous Assays for LDL-Cholesterol in Serum to Intermediate-Density Lipoproteins and Small Dense LDL: Comparisons with the Friedewald Equation. Clin. Chim. Acta 2009, 410, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushima, K.; Sugiuchi, H.; Anraku, K.; Nishimura, H.; Manabe, M.; Ikeda, K.; Ando, Y.; Kondo, Y.; Ishitsuka, Y.; Irikura, M.; et al. Differences in Reaction Specificity toward Lipoprotein X and Abnormal LDL among 6 Homogeneous Assays for LDL-Cholesterol. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 439, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, M.; Matsunaga, A.; Harada, S.; Zhang, B.; Kawachi, E.; Tadera, M.; Saku, K. Comparison of Two Homogeneous LDL-Cholesterol Assays Using Fresh Hypertriglyceridemic Serum and Quantitative Ultracentrifugation Fractions. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2019, 26, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miida, T.; Nishimura, K.; Okamura, T.; Hirayama, S.; Ohmura, H.; Yoshida, H.; Miyashita, Y.; Ai, M.; Tanaka, A.; Sumino, H.; et al. A Multicenter Study on the Precision and Accuracy of Homogeneous Assays for LDL-Cholesterol: Comparison with a Beta-Quantification Method Using Fresh Serum Obtained from Non-Diseased and Diseased Subjects. Atherosclerosis 2012, 225, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timón-Zapata, J.; Laserna-Mendieta, E.J.; Sáenz-Mateos, L.F.; Ruiz-Trujillo, L.; Arpa-Fernández, A.; Palomino-Muñoz, T.J.; Loeches-Jiménez, M.P.; Gómez-Serranillos, M. A Multicentre Analysis of Four Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Direct Assays in Samples with Extreme High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Concentrations. Clin. Chim. Acta 2014, 430, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langlois, M.R.; Descamps, O.S.; van der Laarse, A.; Weykamp, C.; Baum, H.; Pulkki, K.; von Eckardstein, A.; De Bacquer, D.; Borén, J.; Wiklund, O.; et al. Clinical Impact of Direct HDLc and LDLc Method Bias in Hypertriglyceridemia. A Simulation Study of the EAS-EFLM Collaborative Project Group. Atherosclerosis 2014, 233, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Lang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Tao, C.; Gan, W. Challenges in LDL-C Measurement in Lipemic Specimens: A Comparative Evaluation of Four Homogeneous Assays. Clin. Chim. Acta 2026, 579, 120607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.S.; Jang, H.; Rim, J.H.; Cho, J.; Seo, J.D.; Yun, Y.M.; Park, Y.M.; Kwon, G.C.; Cho, C.I.; Lee, S.G.; et al. Influence of remnant cholesterol on direct LDL and HDL cholesterol measurement accuracy. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2025; Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchta, C.; Marrington, R.; De la Salle, B.; Albarède, S.; Albe, X.; Badrick, T.; Berghäll, H.; Bullock, D.; Cobbaert, C.M.; Coucke, W.; et al. Behind the Scenes of EQA—Characteristics, Capabilities, Benefits and Assets of External Quality Assessment (EQA) Part III—EQA Samples. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2025, 63, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, G.R.D. The Role of EQA in Harmonization in Laboratory Medicine—A Global Effort. Biochem. Med. 2017, 27, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badrick, T.; Miller, W.G.; Panteghini, M.; Delatour, V.; Berghall, H.; MacKenzie, F.; Jones, G. Interpreting EQA-Understanding Why Commutability of Materials Matters. Clin. Chem. 2022, 68, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
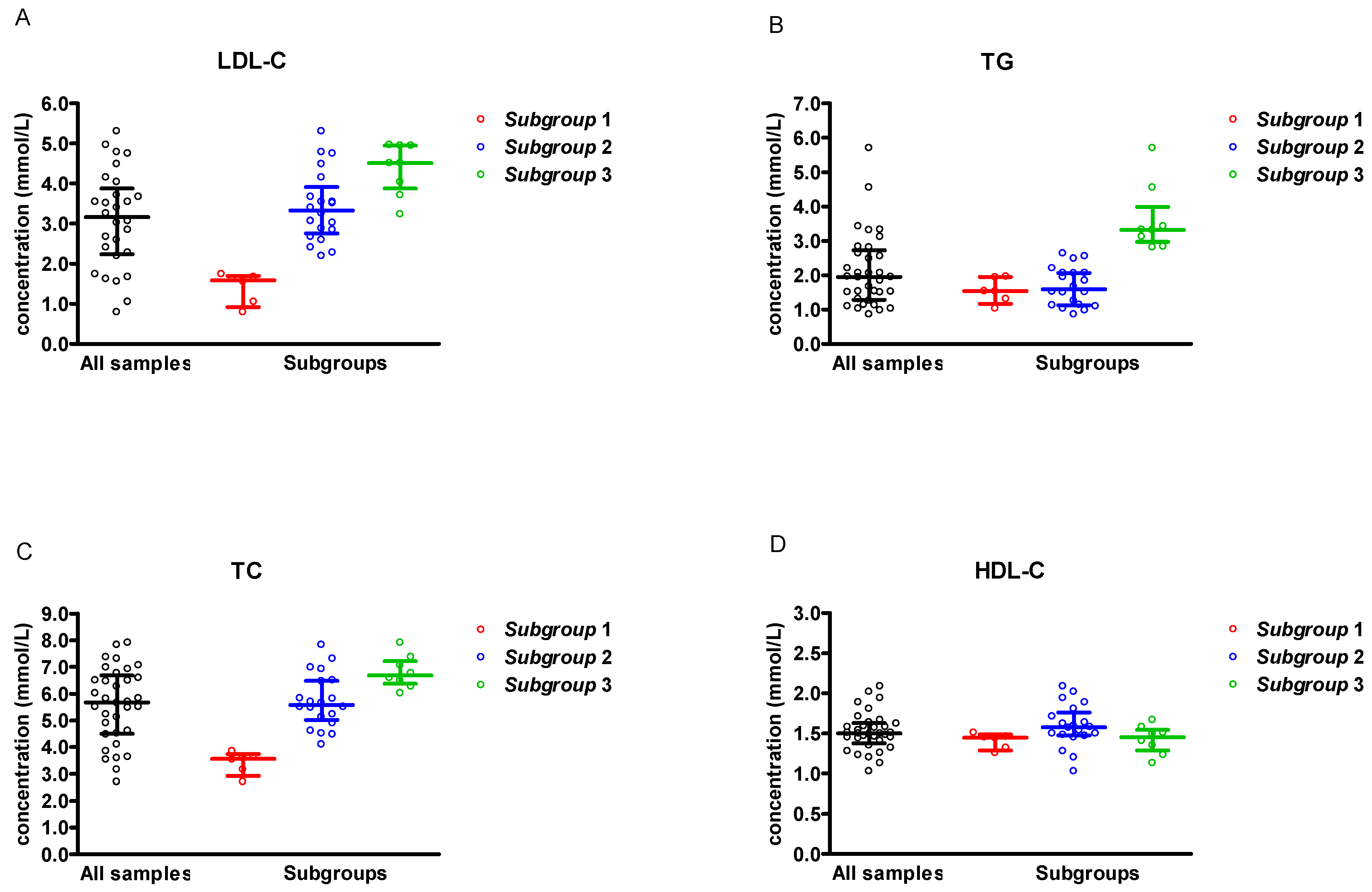

| Parameter | Concentration (mmol/L) | |
|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD (Minimum–Maximum) | ||
| All serum samples (n = 34) | LDL-C | 3.29 ± 1.22 (0.79–5.31) |
| TG | 2.12 ± 1.07 (0.86–5.70) | |
| TC | 5.57 ± 1.39 (2.70–7.91) | |
| HDL-C | 1.52 ± 0.24 (1.03–2.09) | |
| Subgroup 1 (n = 6) | LDL-C | 1.41 ± 0.39 (0.79–1.74) |
| TG | 1.55 ± 0.36 (1.03–1.96) | |
| TC | 3.41 ± 0.41 (2.70–3.85) | |
| HDL-C | 1.41 ± 0.10 (1.26–1.51) | |
| Subgroup 2 (n = 20) | LDL-C | 3.42 ± 0.89 (2.19–5.31) |
| TG | 1.68 ± 0.56 (0.86–2.64) | |
| TC | 5.72 ± 1.01 (4.10–7.83) | |
| HDL-C | 1.60 ± 0.27 (1.03–2.09) | |
| Subgroup 3 (n = 8) | LDL-C | 4.36 ± 0.65 (3.23–4.97) |
| TG | 3.63 ± 1.00 (2.81–5.70) | |
| TC | 6.81 ± 0.62 (6.02–7.91) | |
| HDL-C | 1.42 ± 0.18 (1.13–1.67) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ćwiklińska, A.; Fijałkowska, A. Harmonisation of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Results Obtained with Different Direct Methods: A Study Based on an External Quality Assessment Program. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8706. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248706
Ćwiklińska A, Fijałkowska A. Harmonisation of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Results Obtained with Different Direct Methods: A Study Based on an External Quality Assessment Program. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(24):8706. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248706
Chicago/Turabian StyleĆwiklińska, Agnieszka, and Aleksandra Fijałkowska. 2025. "Harmonisation of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Results Obtained with Different Direct Methods: A Study Based on an External Quality Assessment Program" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 24: 8706. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248706
APA StyleĆwiklińska, A., & Fijałkowska, A. (2025). Harmonisation of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Results Obtained with Different Direct Methods: A Study Based on an External Quality Assessment Program. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(24), 8706. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248706






