Basic Optics Underlying Current Intraocular Lenses
Abstract
1. Introduction
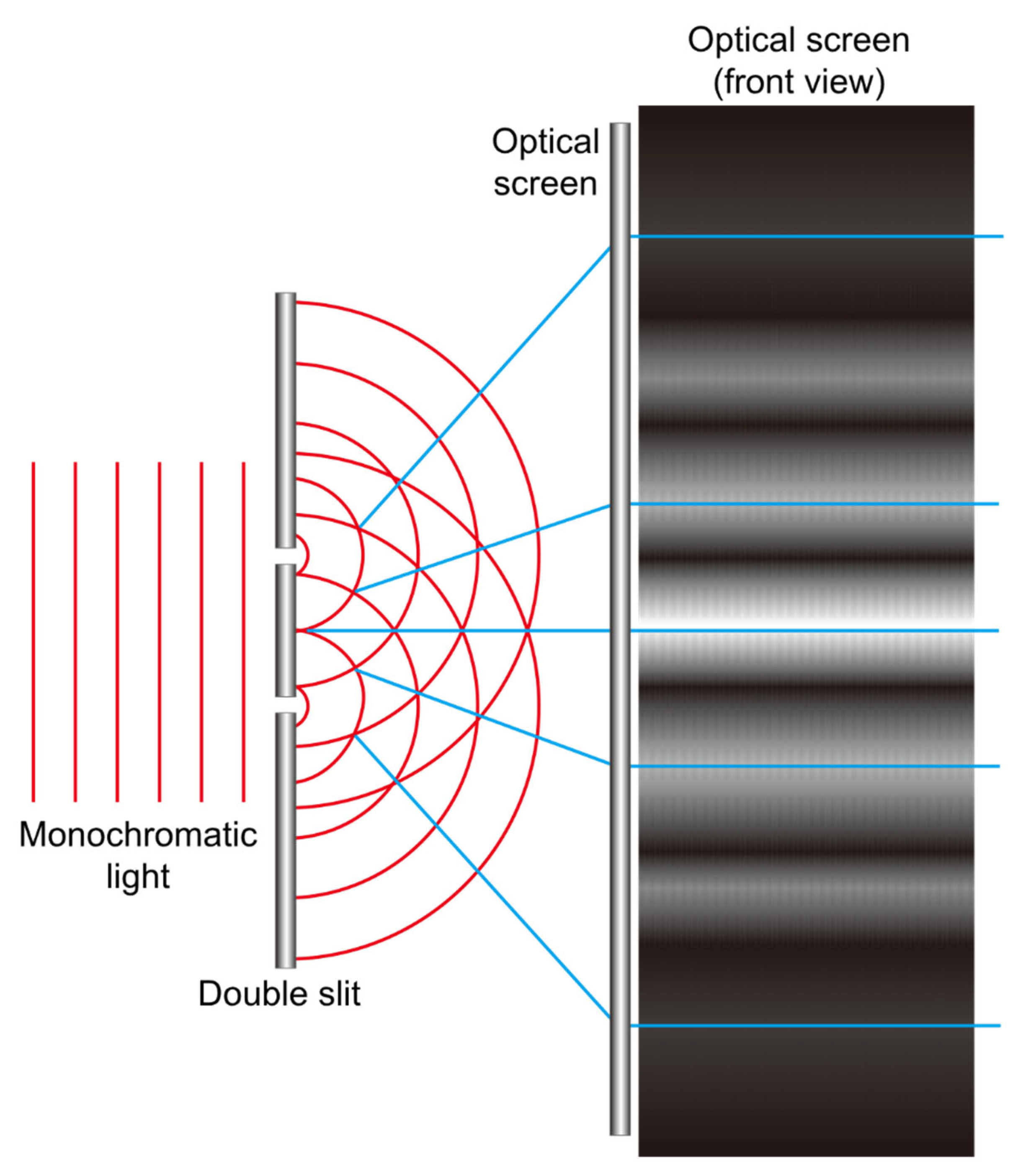
2. Understanding Light
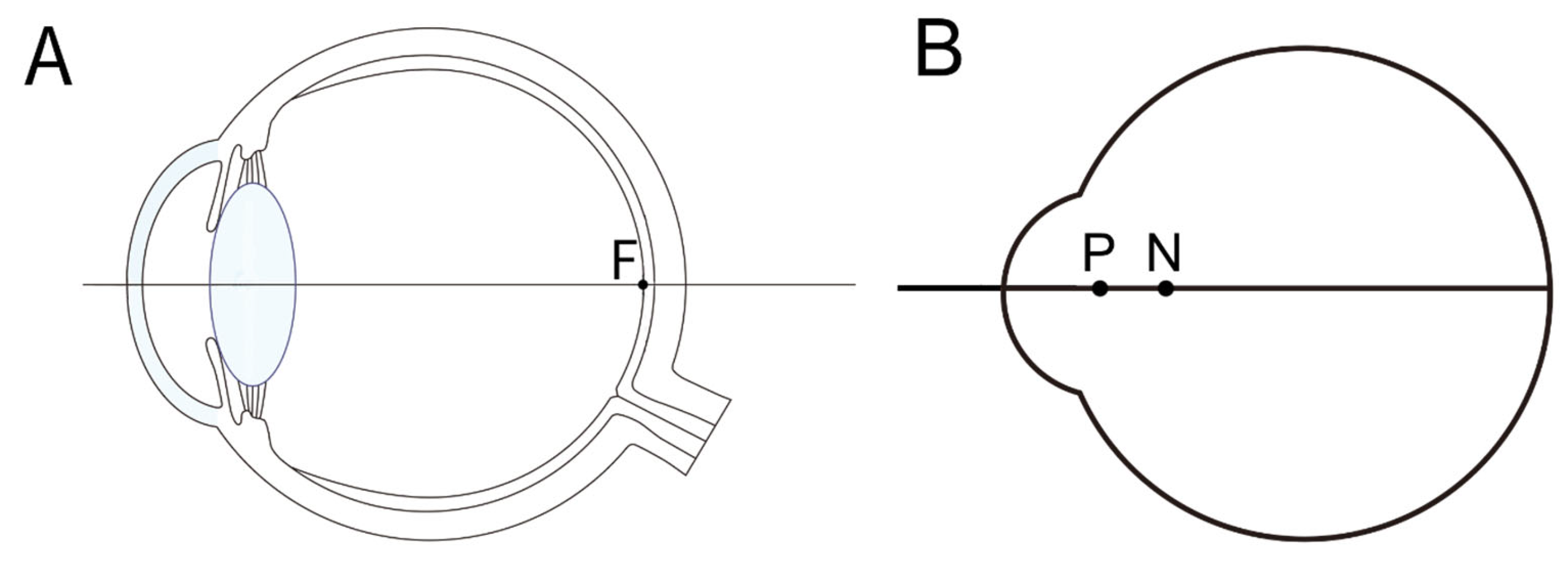
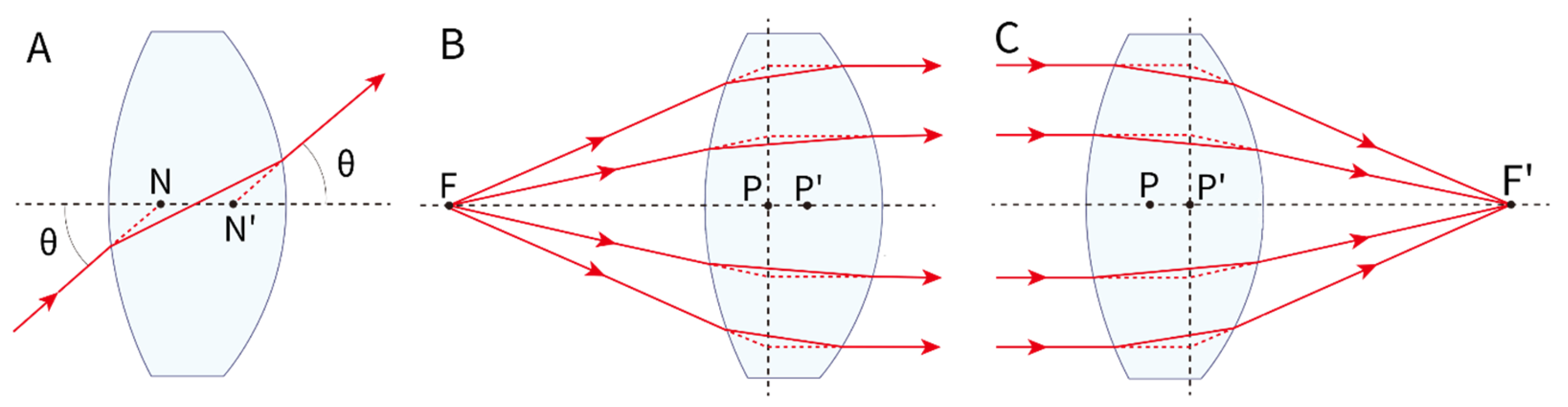
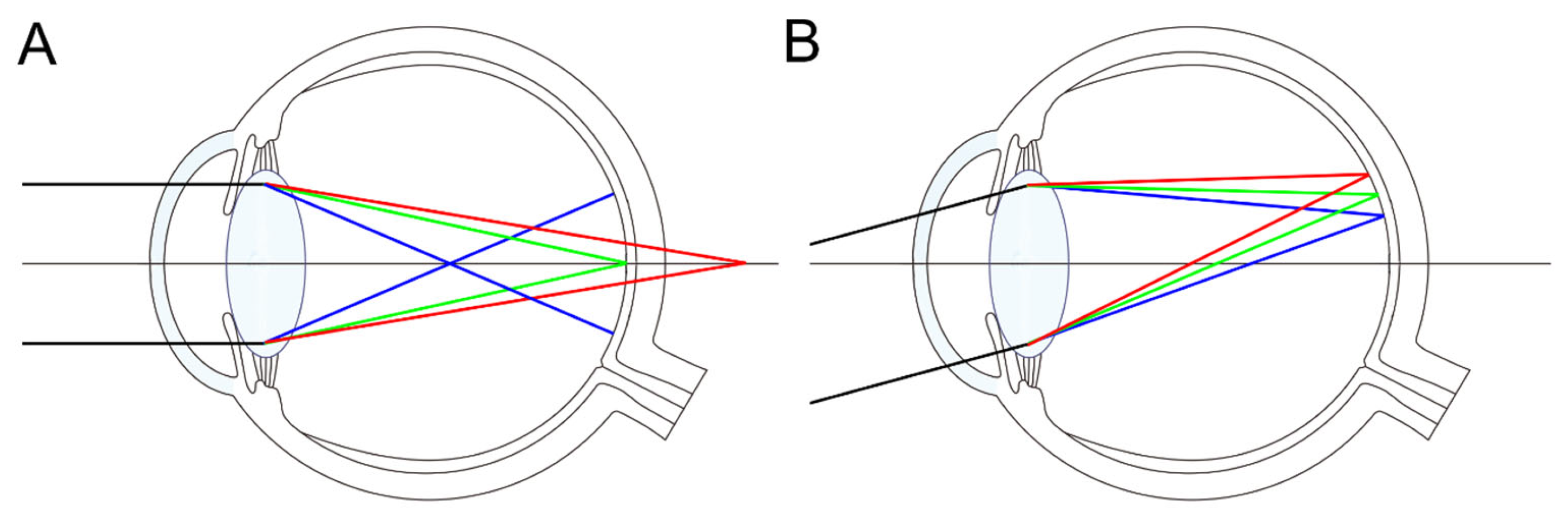
3. Gaussian Approximation
4. Chromatic Aberration
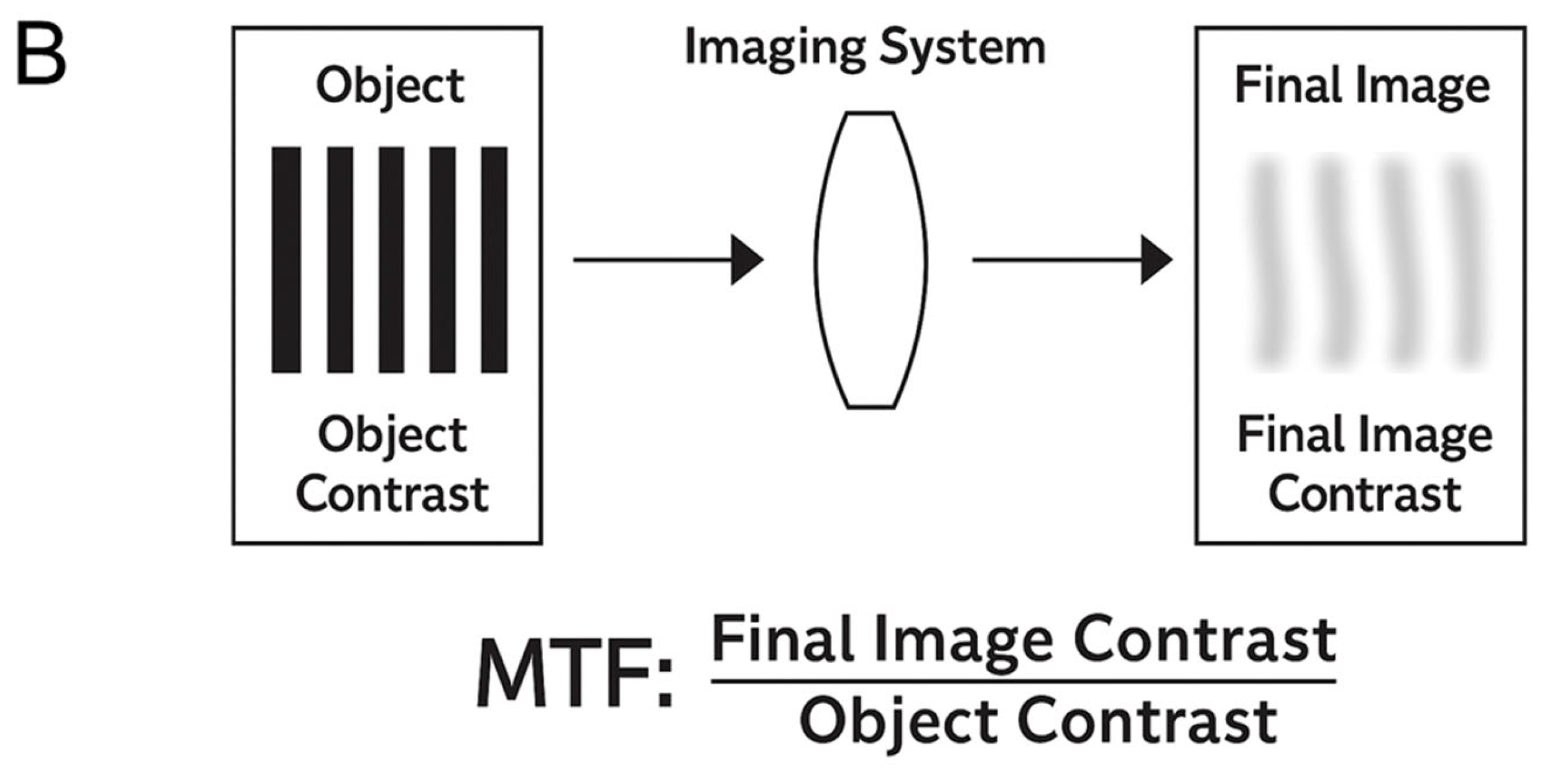
5. Optical System Evaluation
6. Spherical Aberration
7. Diffractive Optics for IOLs
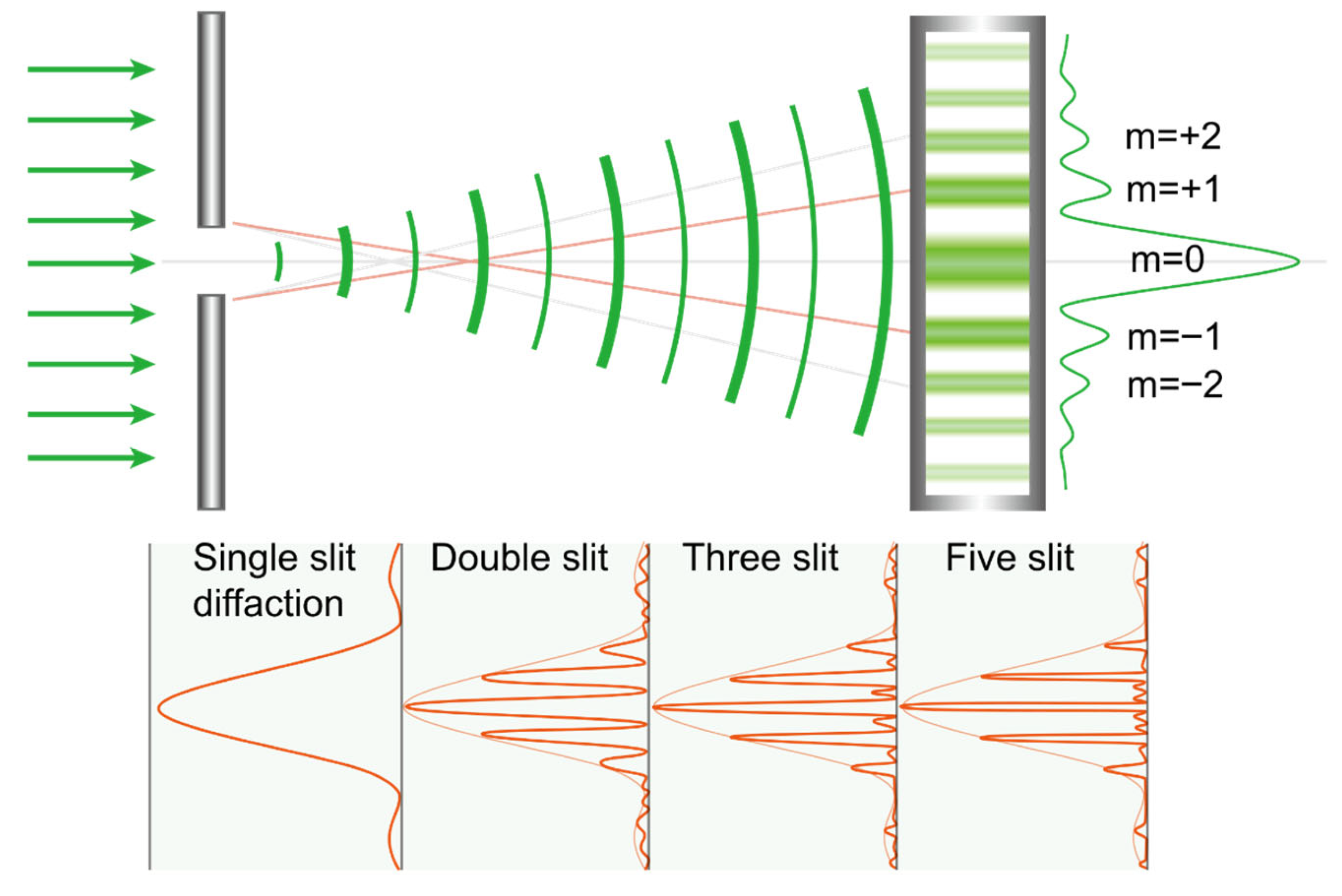
7.1. Diffractive Phenomenon
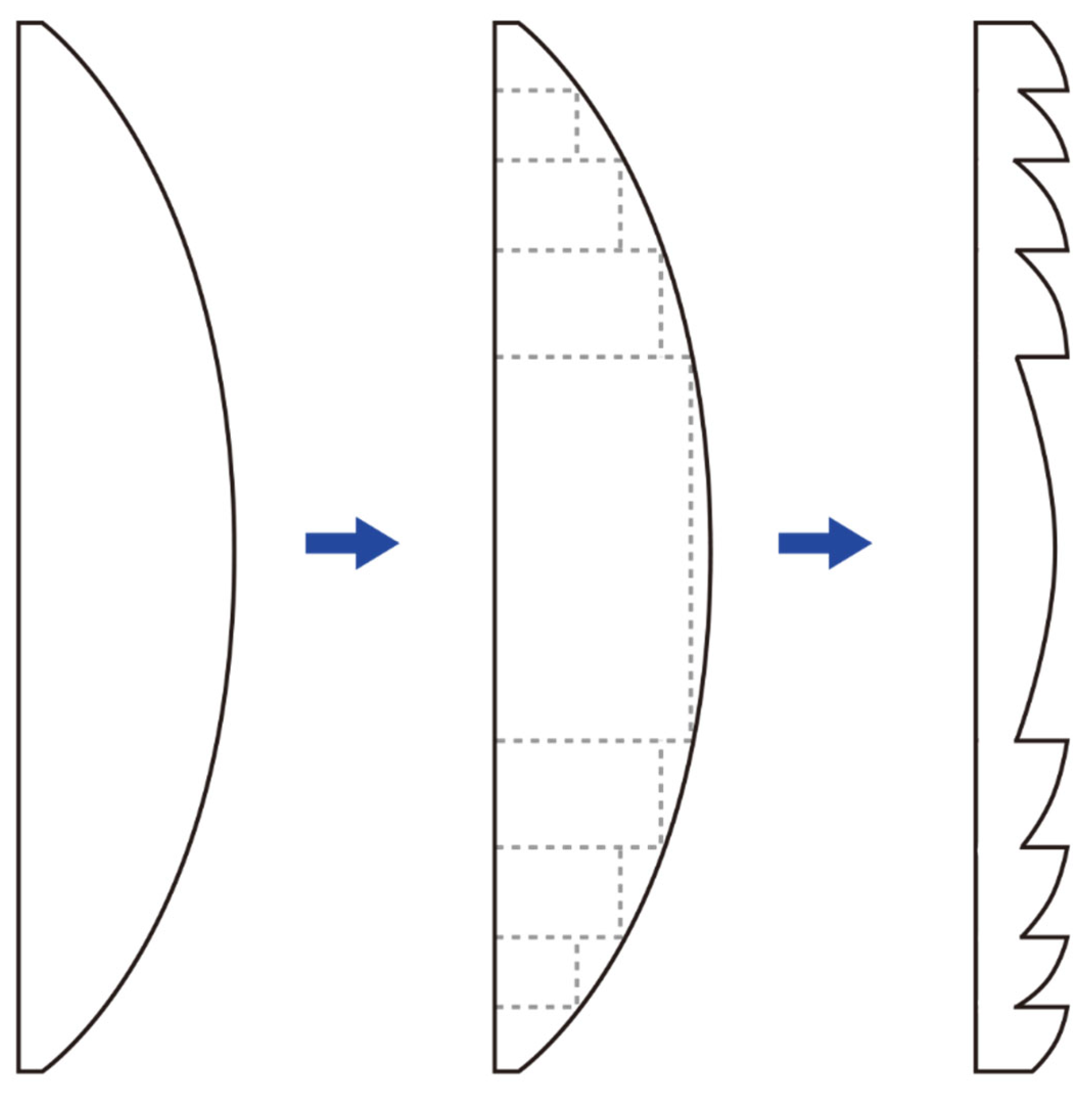
7.2. Fresnel Lenses
7.3. Distribution of Light in Diffraction
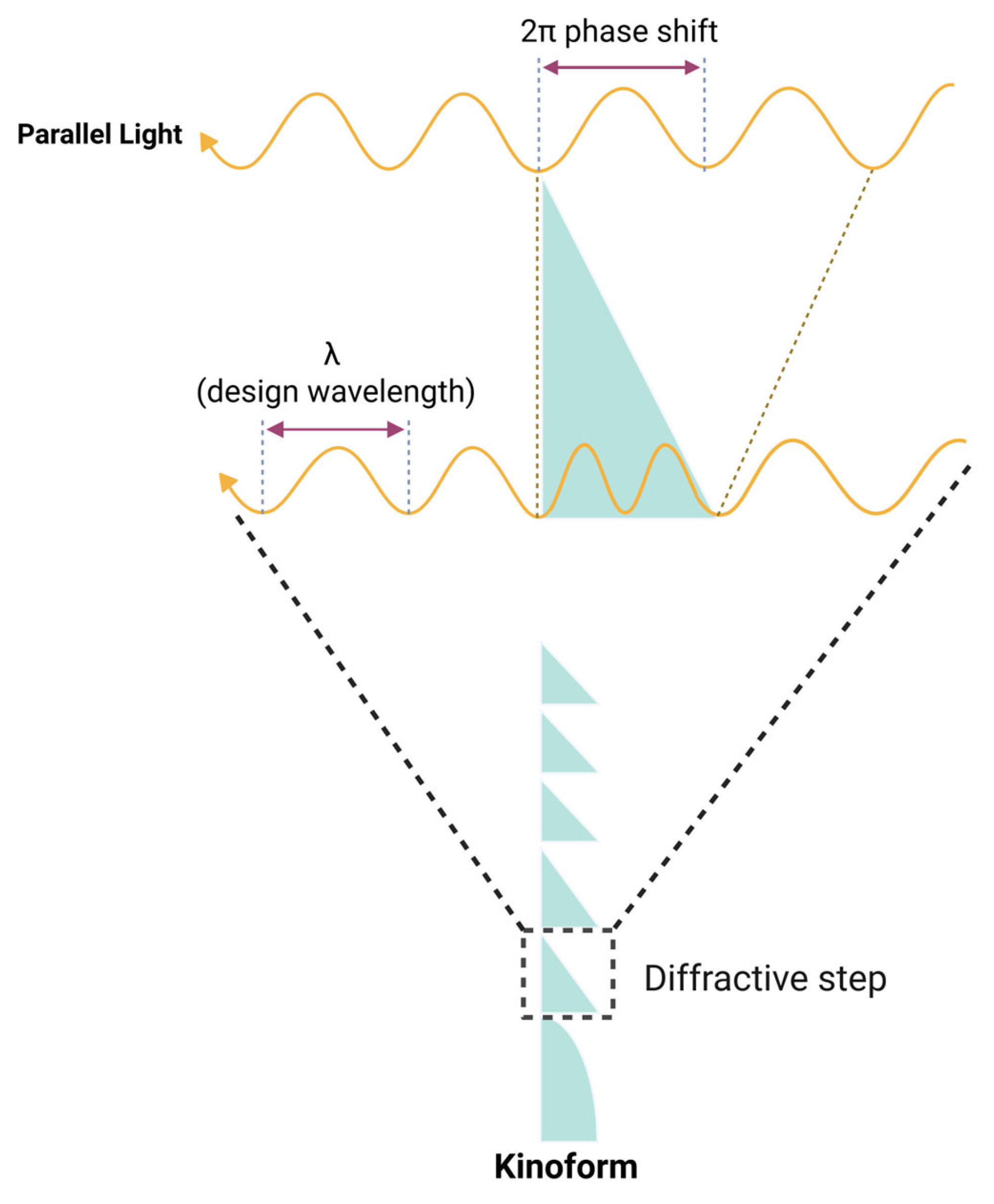
7.4. Diffractive Optic Element
7.5. From Fresnel Lenses to Monofocal Diffractive Lenses
7.6. From Monofocal to Multifocal Diffractive Lenses
7.7. Higher Order Diffractive Lenses: Chromatic Aberration Compensation
8. The Importance of Cornea Optical Characteristics
9. Pros and Cons for Multifocal or EDOF IOLs
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CI | Confidence interval |
| EDOF | Extended depth of focus |
| IOL | Intraocular lens |
| LCA | Longitudinal chromatic aberration |
| MTF | Modulation transfer function |
| OPD | Optical pathway difference |
| PSF | Point spread function |
| RR | Relative ratio |
| TCA | Transverse chromatic aberration |
References
- Bradley, A.; Xu, R.; Wang, H.; Jaskulski, M.; Hong, X.; Brink, N.; Van Noy, S. The Impact of IOL Abbe Number on Polychromatic Image Quality of Pseudophakic Eyes. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2020, 14, 2271–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, M.J.; Gatinel, D.; Faria-Ribeiro, M.; Wei, X.; Yoon, G.; Liang, J.; Artal, P.; Marcos, S. Design Concepts for Advanced-Technology Intraocular Lenses [Invited]. Biomed. Opt. Express 2024, 16, 334–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langenbucher, A.; Hoffmann, P.; Cayless, A.; Gatinel, D.; Debellemanière, G.; Wendelstein, J.; Szentmáry, N. Considerations of a Thick Lens Formula for Intraocular Lens Power Calculation. Z. Med. Phys. 2024, 34, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, M.J. Pre-Clinical Estimation of the Intraocular Lens A-Constant, and Its Relationship to Power, Shape Factor, and Asphericity. Appl. Opt. 2021, 60, 5662–5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, T. Calculation of Intraocular Lens Power: A Review. Acta Ophthalmol. Scand. 2007, 85, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norrby, S. Sources of Error in Intraocular Lens Power Calculation. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2008, 34, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatinel, D.; Debellemaniere, G.; Saad, A.; Rampat, R. Theoretical Relationship Among Effective Lens Position, Predicted Refraction, and Corneal and Intraocular Lens Power in a Pseudophakic Eye Model. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2022, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, S.; Langenbucher, A. Relationship between Effective Lens Position and Axial Position of a Thick Intraocular Lens. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatinel, D.; Debellemanière, G.; Saad, A.; Dubois, M.; Rampat, R. Determining the Theoretical Effective Lens Position of Thick Intraocular Lenses for Machine Learning-Based IOL Power Calculation and Simulation. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatinel, D.; Debellemanière, G.; Saad, A.; Rampat, R.; Malet, J. Theoretical Impact of Intraocular Lens Design Variations on the Accuracy of IOL Power Calculations. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, M.J. Nodal Points and the Eye. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 2797–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibos, L.N.; Applegate, R.A.; Schwiegerling, J.T.; Webb, R.; VSIA Standards Taskforce Members. Vision science and its applications Standards for Reporting the Optical Aberrations of Eyes. J. Refract. Surg. 2002, 18, S652–S660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atchison, D.A.; Thibos, L.N. Optical Models of the Human Eye. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2016, 99, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, S.; Sabesan, R.; Tiruveedhula, P.; Privitera, C.; Unsbo, P.; Lundström, L.; Roorda, A. Transverse Chromatic Aberration across the Visual Field of the Human Eye. J. Vis. 2016, 16, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibos, L.N.; Bradley, A.; Still, D.L.; Zhang, X.; Howarth, P.A. Theory and Measurement of Ocular Chromatic Aberration. Vis. Vision. Res. 1990, 30, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, S.P.; Lyu, J.; Ng, C.J.; Yoon, G. Visual Axis and Stiles–Crawford Effect Peak Show a Positional Correlation in Normal Eyes: A Cohort Study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2022, 63, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsner, R.; Gerlach, M.; Bohn, S.; Sievers, J.; Stolz, H.; Guthoff, R.F.; Stachs, O.; Sperlich, K. Assessment of Diffractive Intraocular Lenses Using Near-Infrared Light: A Critical Evaluation. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2025, 14, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchison, D.A.; Smith, G. Chromatic Dispersions of the Ocular Media of Human Eyes. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 2005, 22, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedi-Garcia, C.; Vinas, M.; Dorronsoro, C.; Burns, S.A.; Peli, E.; Marcos, S. Vision Is Protected against Blue Defocus. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Artal, P.; Gutierrez, D.; Williams, D.R. Neural Compensation for the Best Aberration Correction. J. Vis. 2007, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artal, P.; Chen, L.; Fernández, E.J.; Singer, B.; Manzanera, S.; Williams, D.R. Neural Compensation for the Eye’s Optical Aberrations. J. Vis. 2004, 4, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Mainster, M.A. The Effect of Chromatic Dispersion on Pseudophakic Optical Performance. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 91, 1225–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokushita, Y.; Furuya, S.; Nobe, S.; Nakabayashi, K.; Samitsu, S.; Mori, H. Preparation of Highly Transparent Poly(Meth)Acrylates with Enhanced Refractive Indices by Radical (Co)Polymerization of Seleno(Meth)Acrylates. Polymer 2021, 237, 124346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvá, L.; García, S.; García-Delpech, S.; Martínez-Espert, A.; Montagud-Martínez, D.; Ferrando, V. Comparison of the Polychromatic Image Quality of Two Refractive-Segmented and Two Diffractive Multifocal Intraocular Lenses. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahram, M.; Milanfar, P. Imaging below the Diffraction Limit: A Statistical Analysis. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Williams, D.R.; Miller, D.T. Supernormal Vision and High-Resolution Retinal Imaging through Adaptive Optics. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A JOSAA 1997, 14, 2884–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.-S.; Łabuz, G.; Khoramnia, R.; Yildirim, T.M.; Auffarth, G.U. Laboratory Analysis and Ray Visualization of Diffractive Optics with Enhanced Intermediate Vision. BMC Ophthalmol. 2021, 21, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Huang, Y. Laboratory Evaluation of Halos and Through-Focus Performance of Three Different Multifocal Intraocular Lenses. J. Refract. Surg. 2022, 38, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.C.; Na, K.-S.; Kim, H.S.; Hwang, H.S. How Does the World Appear to Patients with Multifocal Intraocular Lenses?: A Mobile Model Eye Experiment. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020, 20, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.S.; Tandogan, T.; Liebing, S.; Merz, P.; Choi, C.Y.; Khoramnia, R.; Auffarth, G.U. In Vitro Optical Quality Measurements of Three Intraocular Lens Models Having Identical Platform. BMC Ophthalmol. 2017, 17, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppig, T.; Scholz, K.; Langenbucher, A. Assessing the Optical Performance of Multifocal (Diffractive) Intraocular Lenses. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2008, 28, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkmenoglu, M.; Sengul, O.; Yalcıner, L. MTF Measurements for the Imaging System Quality Analysis. Gazi Univ. J. Sci. 2012, 25, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Alarcon, A.; Canovas, C.; Rosen, R.; Weeber, H.; Tsai, L.; Hileman, K.; Piers, P. Preclinical Metrics to Predict Through-Focus Visual Acuity for Pseudophakic Patients. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 1877–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, F.; Valentino, M.; Rigato, F.; Millán, M.S. Optical Design and Performance of a Trifocal Sinusoidal Diffractive Intraocular Lens. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 3338–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łabuz, G.; Yan, W.; Baur, I.D.; Khoramnia, R.; Auffarth, G.U. Comparison of Five Presbyopia-Correcting Intraocular Lenses: Optical-Bench Assessment with Visual-Quality Simulation. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holladay, J.T.; Piers, P.A.; Koranyi, G.; van der Mooren, M.; Norrby, N.E.S. A New Intraocular Lens Design to Reduce Spherical Aberration of Pseudophakic Eyes. J. Refract. Surg. 2002, 18, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sayyari, T.M.; Fawzy, S.M.; Al-Saleh, A.A. Corneal Spherical Aberration and Its Impact on Choosing an Intraocular Lens for Cataract Surgery. Saudi J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 28, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasser, A.; Campbell, M.C. Presbyopia and the Optical Changes in the Human Crystalline Lens with Age. Vis. Vision. Res. 1998, 38, 209–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medical Advisory Secretariat. Intraocular Lenses for the Treatment of Age-Related Cataracts: An Evidence-Based Analysis. Ont. Health Technol. Assess. Ser. 2009, 9, 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, F.; Iskander, D.R.; Collins, M. Depth of Focus and Visual Acuity with Primary and Secondary Spherical Aberration. Vis. Vision. Res. 2011, 51, 1648–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikš, A.; Pokorný, P. Spherical Aberration of an Optical System and Its Influence on Depth of Focus. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 5099–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshirfar, M. Spherical Aberration of Intraocular Lenses. J. Ophthalmic Vis. Res. 2010, 5, 215–216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Zhao, T.-Y.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Wang, W. Tilt and Decentration with Various Intraocular Lenses: A Narrative Review. World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10, 3639–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Gracia, J.; Varea, A.; Ares, J.; Vallés, J.A.; Remón, L. Evaluation of the Optical Performance for Aspheric Intraocular Lenses in Relation with Tilt and Decenter Errors. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Bradley, A.; Thibos, L.N. Impact of Primary Spherical Aberration, Spatial Frequency and Stiles Crawford Apodization on Wavefront Determined Refractive Error: A Computational Study. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2013, 33, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mencucci, R.; Morelli, A.; Cennamo, M.; Roszkowska, A.M.; Favuzza, E. Enhanced Monofocal Intraocular Lenses: A Retrospective, Comparative Study between Three Different Models. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benard, Y.; Lopez-Gil, N.; Legras, R. Optimizing the Subjective Depth-of-Focus with Combinations of Fourth- and Sixth-Order Spherical Aberration. Vis. Vision. Res. 2011, 51, 2471–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, S.P.; Jung, H.; Li, K.Y.; Yoon, G. Comparison of Modal and Zonal Wavefront Measurements of Refractive Extended Depth of Focus Intraocular Lenses. Biomed. Opt. Express BOE 2024, 15, 1618–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, R.; Borkenstein, A.F. Optical Bench Evaluation of the Latest Refractive Enhanced Depth of Focus Intraocular Lens. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2024, 18, 1921–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liang, C.; Xu, Y.; Wu, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, A.; Tan, X.; Luo, L. Effect of Crystalline Lens Decentration and Tilt on Visual Performance in Eyes Implanted with Bifocal or Extended Depth of Focus Intraocular Lenses. BMC Ophthalmol. 2025, 25, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, R.; Luedtke, H.; Borkenstein, A.F. Effect of Decentration and Tilt on Four Novel Extended Range of Vision Intraocular Lenses Regarding Far Distance. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 33, 11206721221128864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, J.; Bang, S.P.; Yoon, G. Refractive Extended Depth-of-Focus Lens Design Based on Periodic Power Profile for Presbyopia Correction. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2024, 44, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, S.P.; Sabesan, R.; Yoon, G. Effects of Long-Term Neural Adaptation to Habitual Sspherical Aberration on through-Focus Visual Acuity in Adults. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, S.P.; Aaker, J.D.; Sabesan, R.; Yoon, G. Improvement of Neural Contrast Sensitivity after Long-Term Adaptation in Pseudophakic Eyes. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 4528–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, R.; Wang, Z. Design and Experimental Study on Fresnel Lens of the Combination of Equal-Width and Equal-Height of Grooves. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 69, 012177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampat, R.; Gatinel, D. Multifocal and Extended Depth-of-Focus Intraocular Lenses in 2020. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, e164–e185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A. Multifocal Diffractive Lens Design in Ophthalmology. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, 9807–9823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, E.; Senel, E.C.; Holmström, S.T.S.; Piñero, D.P. Comparison of the Optical Behaviour of Five Different Multifocal Diffractive Intraocular Lenses in a Model Eye. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatinel, D. Docteur Damien Gatinel—Ophtalmologie. Available online: https://www.gatinel.com/2019/11/topography-and-longitudinal-chromatic-aberration-characterizations-of-refractive-diffractive-multifocal-intraocular-lenses-loicq-j-willet-n-gatinel-d-jcrs-2019/ (accessed on 21 November 2025).
- Mendroch, D.; Altmeyer, S.; Oberheide, U. Characterization of Diffractive Bifocal Intraocular Lenses. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepose, J.S.; Wang, D.; Altmann, G.E. Comparison of Through-Focus Image Quality Across Five Presbyopia-Correcting Intraocular Lenses (An American Ophthalmological Society Thesis). Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 2011, 109, 221–231. [Google Scholar]
- Vila-Andrés, R.; Martínez-Espert, A.; Furlan, W.D.; Esteve-Taboada, J.J.; Micó, V. Non-Contact Lensless Holographic Reconstruction of Diffractive Intraocular Lenses Profiles. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonov, A.I.; Greisukh, G.I.; Ezhov, E.G.; Ryzhova, E.A. Mathematical Tool for Calculating the Microstructure of a Harmonic Kinoform Lens. Optoelectron. Instrument. Proc. 2019, 55, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, H. Modified Phase Function Model for Kinoform Lenses. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, 4055–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sales, T.R.; Morris, G.M. Diffractive-Refractive Behavior of Kinoform Lenses. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buralli, D.A.; Morris, G.M.; Rogers, J.R. Optical Performance of Holographic Kinoforms. Appl. Opt. 1989, 28, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrazek Hafez, T.; Helaly, H.A. Spectacle Independence And Patient Satisfaction With Pseudophakic Mini-Monovision Using Aberration-Free Intraocular Lens. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2019, 13, 2111–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid-Costa, D.; Ruiz-Alcocer, J.; Ferrer-Blasco, T.; García-Lázaro, S.; Montés-Micó, R. In Vitro Optical Performance of a New Aberration-Free Intraocular Lens. Eye 2014, 28, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, M.S.; Vega, F. Extended Depth of Focus Intraocular Lens: Chromatic Performance. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 4294–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, M.S.; Vega, F. Through-Focus Energy Efficiency and Longitudinal Chromatic Aberration of Three Presbyopia-Correcting Intraocular Lenses. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łabuz, G.; Yan, W.; Baur, I.D.; Khoramnia, R.; Auffarth, G.U. Chromatic Aberration and Spectral Dependency of Extended-Range-of-Vision Intraocular Lens Technology. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łabuz, G.; Papadatou, E.; Khoramnia, R.; Auffarth, G.U. Longitudinal Chromatic Aberration and Polychromatic Image Quality Metrics of Intraocular Lenses. J. Refract. Surg. 2018, 34, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artal, P.; Manzanera, S.; Piers, P.; Weeber, H. Visual Effect of the Combined Correction of Spherical and Longitudinal Chromatic Aberrations. Opt. Express OE 2010, 18, 1637–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nankivil, D.; Cottaris, N.P.; Brainard, D.H. Theoretical Impact of Chromatic Aberration Correction on Visual Acuity. Biomed. Opt. Express BOE 2024, 15, 3265–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łabuz, G.; Khoramnia, R.; Yan, W.; van den Berg, T.J.T.P.; Auffarth, G.U.; Naujokaitis, T.; Tandogan, T. Characterizing Glare Effects Associated with Diffractive Optics in Presbyopia-Correcting Intraocular Lenses. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2024, 50, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loicq, J.; Willet, N.; Gatinel, D. Topography and Longitudinal Chromatic Aberration Characterizations of Refractive–Diffractive Multifocal Intraocular Lenses. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2019, 45, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcon Smart Educator. Available online: https://smarteducator.myalcon.com/ (accessed on 9 May 2025).
- Millan, M.S.; Clavé, L.; Torrents, A.; Armengol, J.; Vega, F. Spatio-Chromatic Vision with Multifocal Diffractive Intraocular Lens. Eye Vis 2023, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, S.; Amano, Y.; Yamagami, S.; Miyai, T.; Miyata, K.; Samejima, T.; Oshika, T. Age-Related Changes in Corneal and Ocular Higher-Order Wavefront Aberrations. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2004, 137, 988–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Chen, X.; Ortega-Usobiaga, J.; Zheng, H.; Luo, W.; Tu, B.; Wang, Y. Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Corneal Higher-Order Aberrations in Patients with Cataract. BMC Ophthalmol. 2023, 23, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Kawahara, S.; Manabe, S.; Hirata, A. Changes in Irregular Corneal Astigmatism With Age in Eyes With and Without Cataract Surgery. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 7988–7998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellucci, R.; Cargnoni, M.; Bellucci, C. Clinical and Aberrometric Evaluation of a New Extended Depth-of-Focus Intraocular Lens Based on Spherical Aberration. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2019, 45, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Choi, Y.; Nam, D.; Choi, S.-H. Importance of Corneal Spherical Aberration in Pupil Area for Multifocal Intraocular Lens Selection: A Case Report. BMC Ophthalmol. 2025, 25, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, S.R.; Evans, J.R.; Kirthi, V.; Ziaei, M.; Leyland, M. Multifocal versus Monofocal Intraocular Lenses after Cataract Extraction. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 12, CD003169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




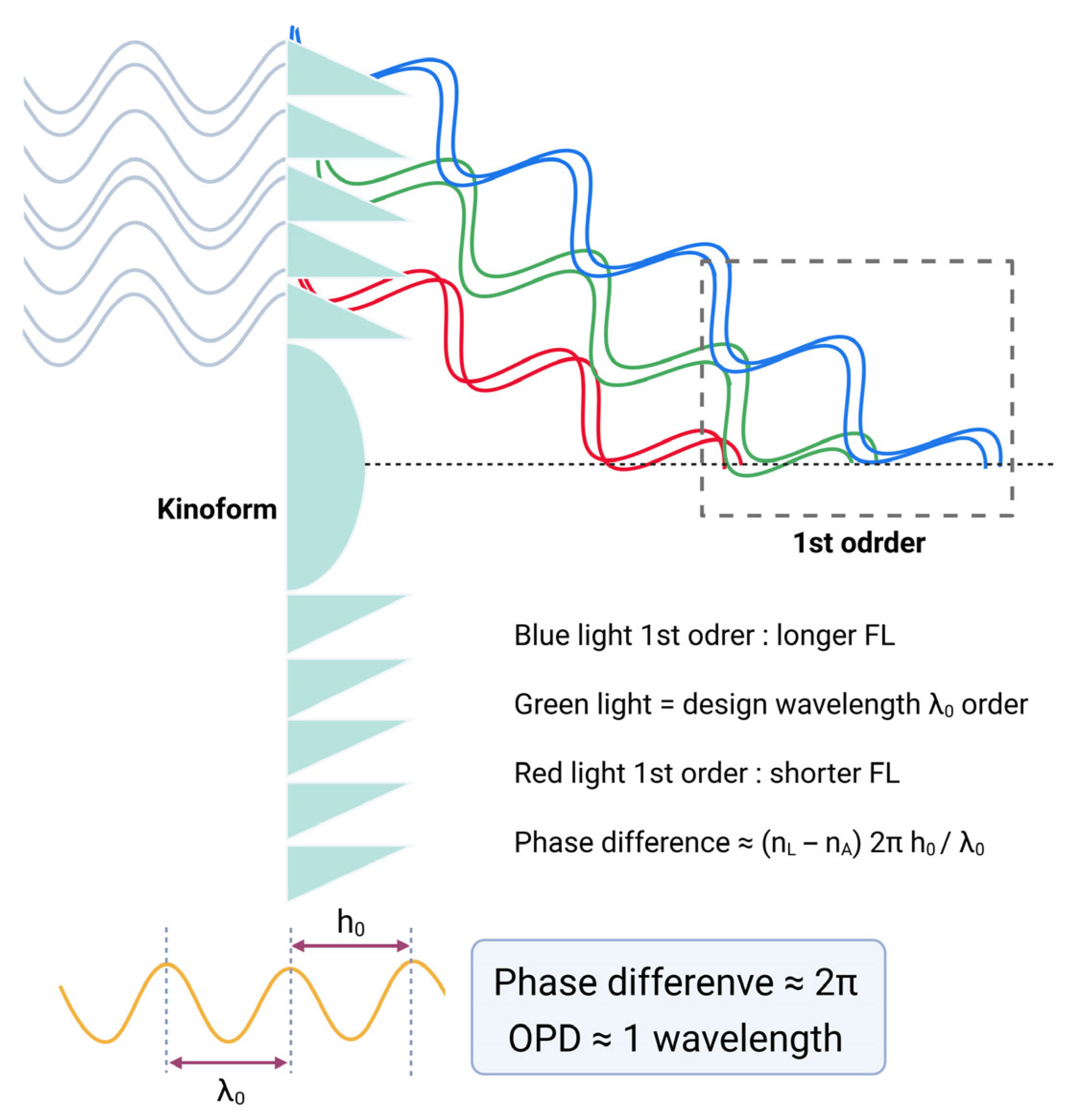
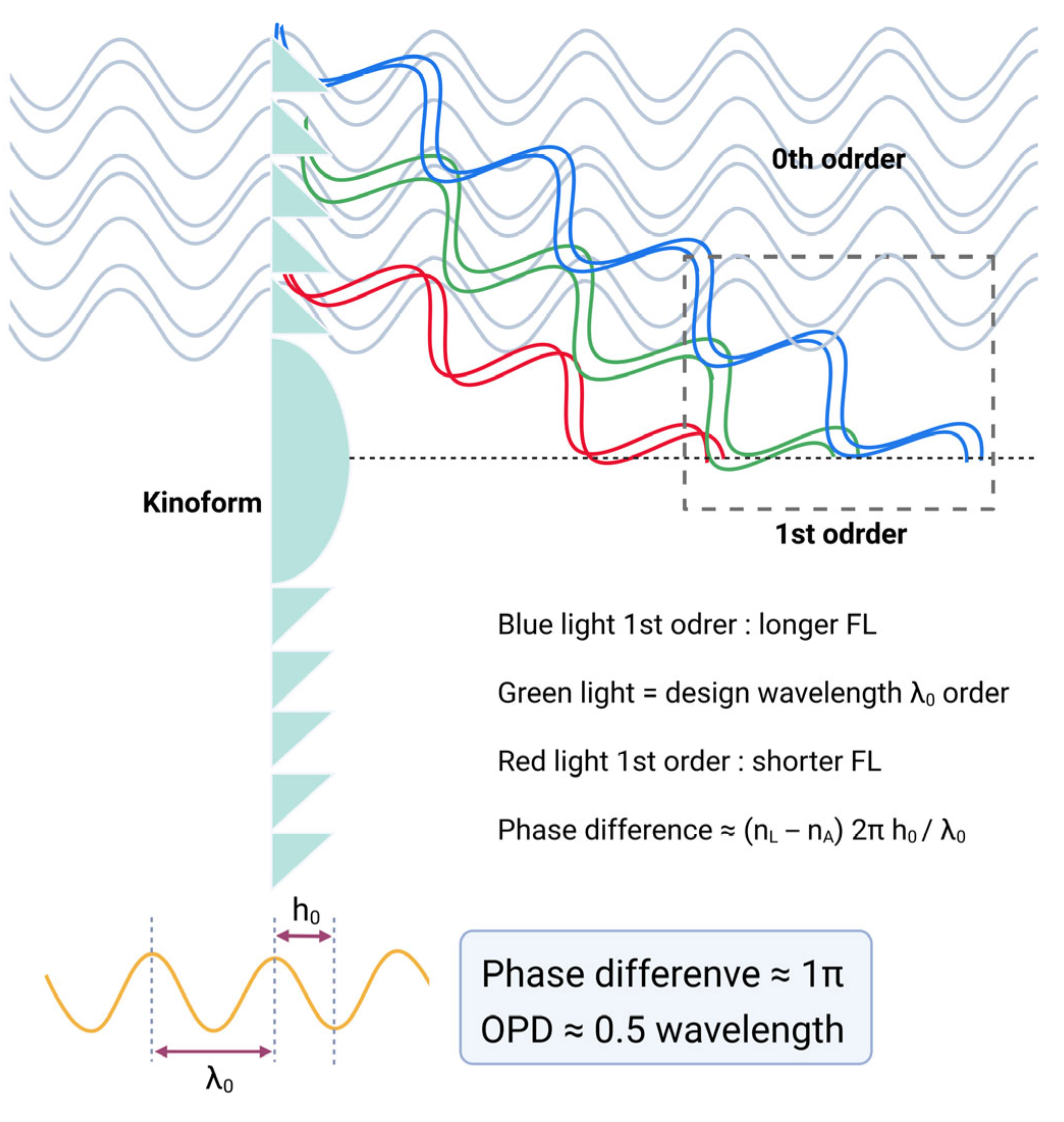
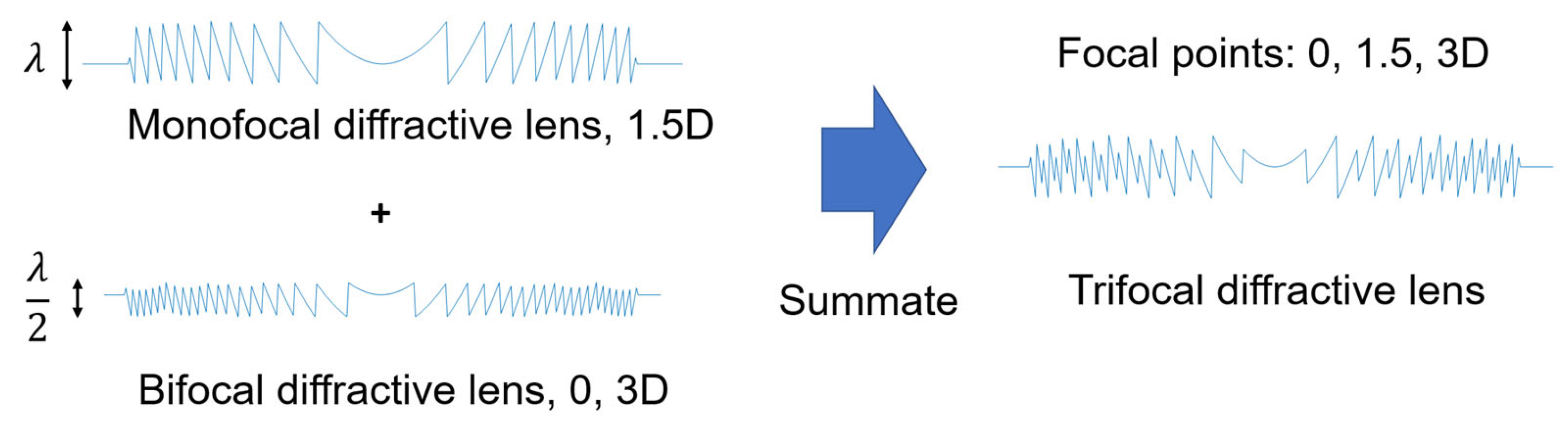

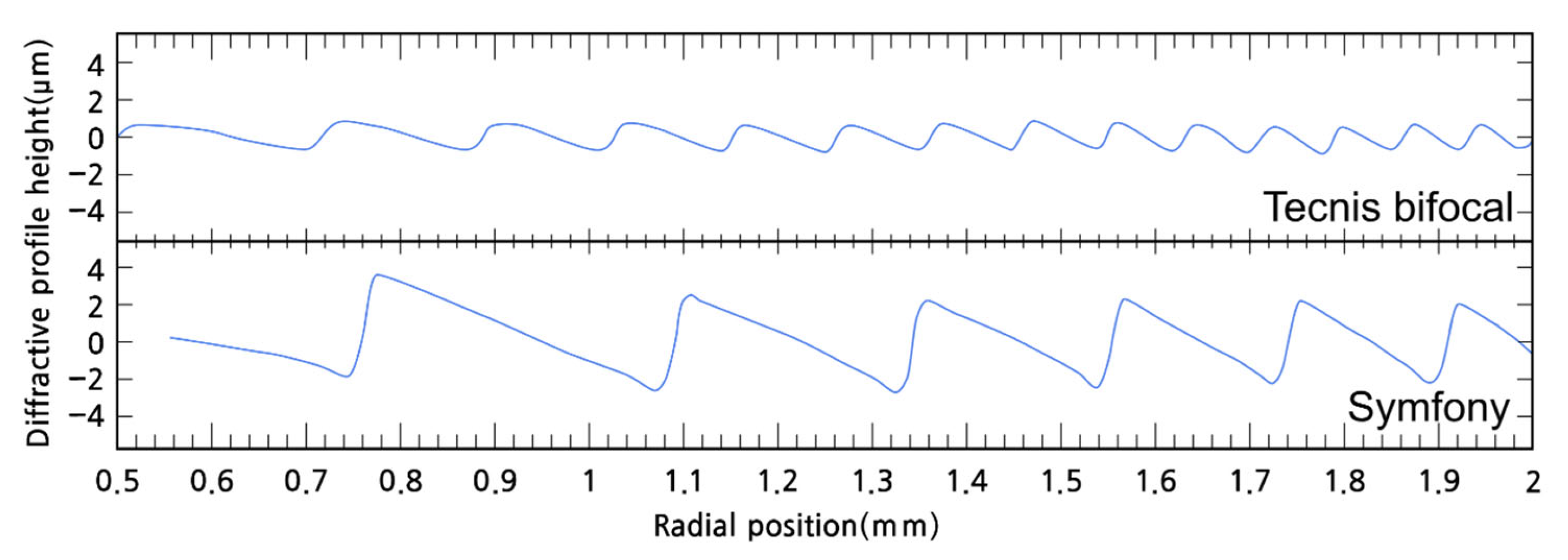
| Echelette/Ring | Step Height (µm) | Outer Diameter (mm) | OPD (λ0 Units) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Design | Experimental (±0.2) | Design | Experimental (±0.1) | Design | |
| 1 | 6.2 | NA | 1.60 | 1.57 | 1.5 |
| 2 | 6.2 | 6.3 | 2.20 | 2.21 | 1.5 |
| 3 | 6.2 | 6.2 | 2.75 | 2.72 | 1.5 |
| 4 | 5.6 | 5.5 | 3.17 | 3.14 | 1.366 |
| 5 | 5.6 | 5.7 | 3.55 | 3.53 | 1.366 |
| 6 | 5.6 | 5.8 | 3.88 | 3.86 | 1.366 |
| 7 | 5.6 | NA | 4.20 | 4.19 | 1.366 |
| 8 | 5.6 | NA | 4.48 | 4.46 | 1.366 |
| 9 | 5.6 | NA | 4.76 | 4.74 | 1.366 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Son, Y.; Bang, S.P.; Park, C.Y. Basic Optics Underlying Current Intraocular Lenses. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8608. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238608
Son Y, Bang SP, Park CY. Basic Optics Underlying Current Intraocular Lenses. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(23):8608. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238608
Chicago/Turabian StyleSon, Yengwoo, Seung Pil Bang, and Choul Yong Park. 2025. "Basic Optics Underlying Current Intraocular Lenses" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 23: 8608. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238608
APA StyleSon, Y., Bang, S. P., & Park, C. Y. (2025). Basic Optics Underlying Current Intraocular Lenses. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(23), 8608. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238608






