From Clinic to Reality: Integrating Sound Field Testing and Hearing Quality Measures in Cochlear Implant Users
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
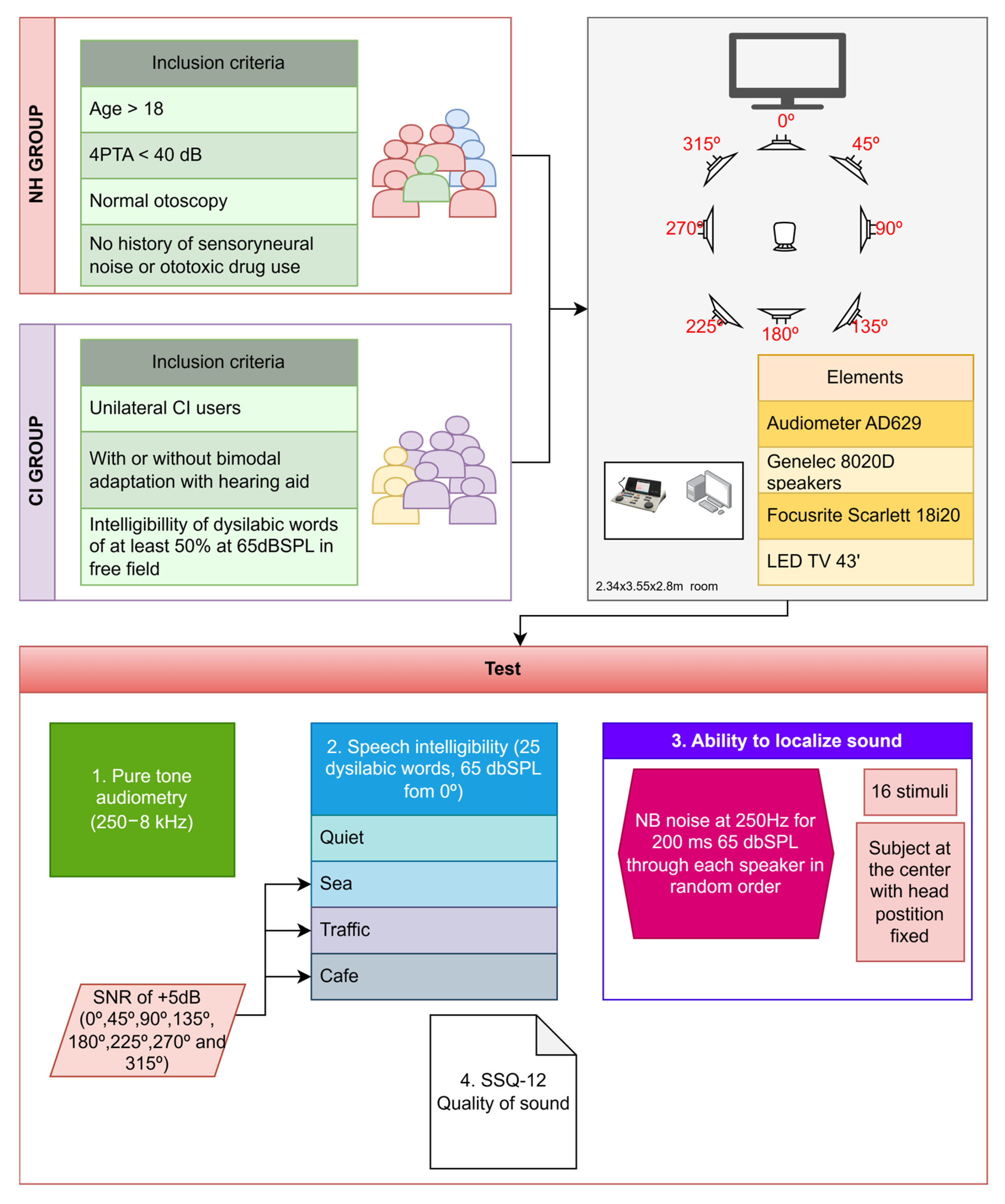
2.1. Design and Participants
2.2. Test Material
2.3. Data and Outcome Measures
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
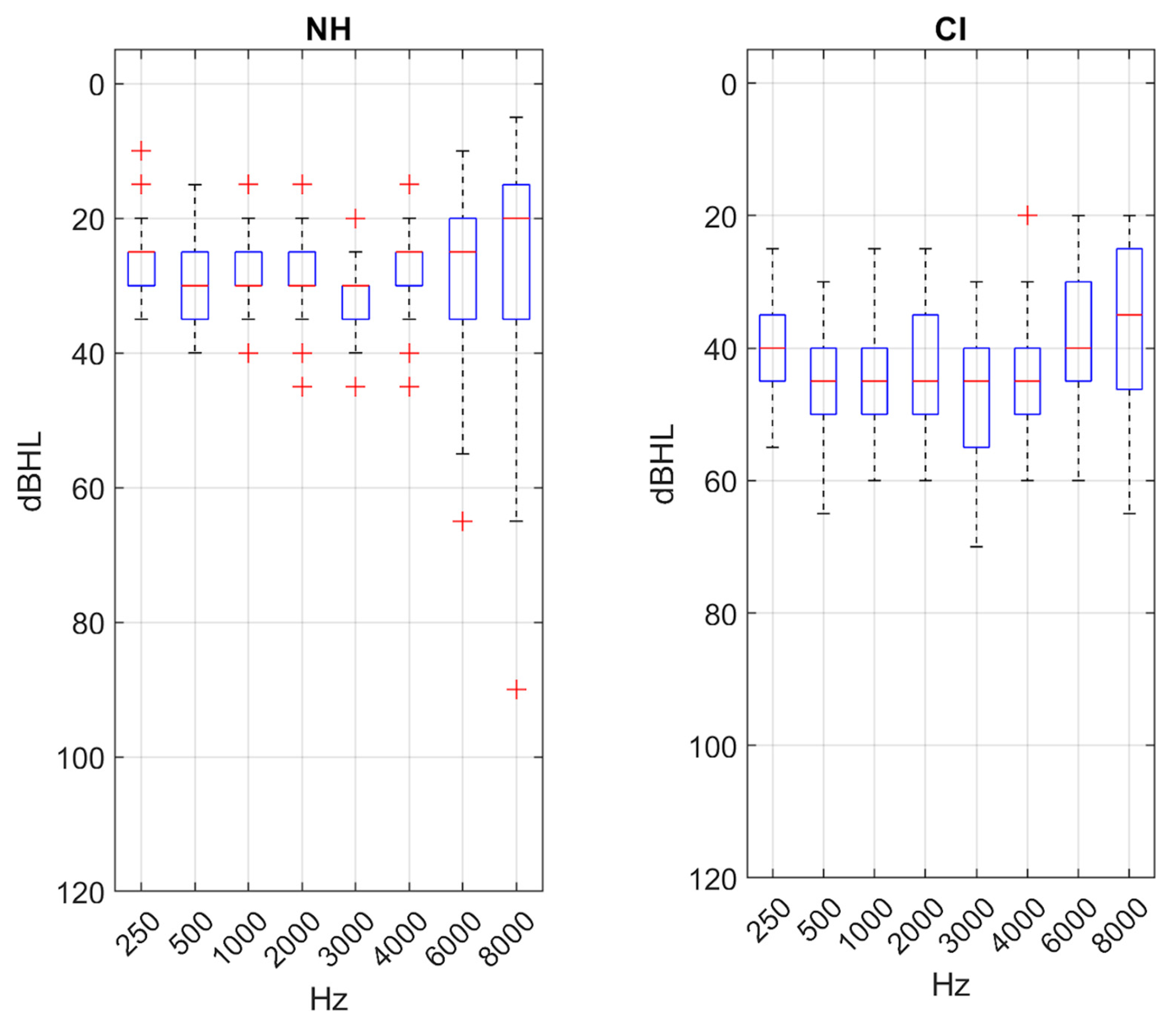
3.1. Descriptive Analysis
3.2. Correlation Analysis
3.3. Regression Analysis
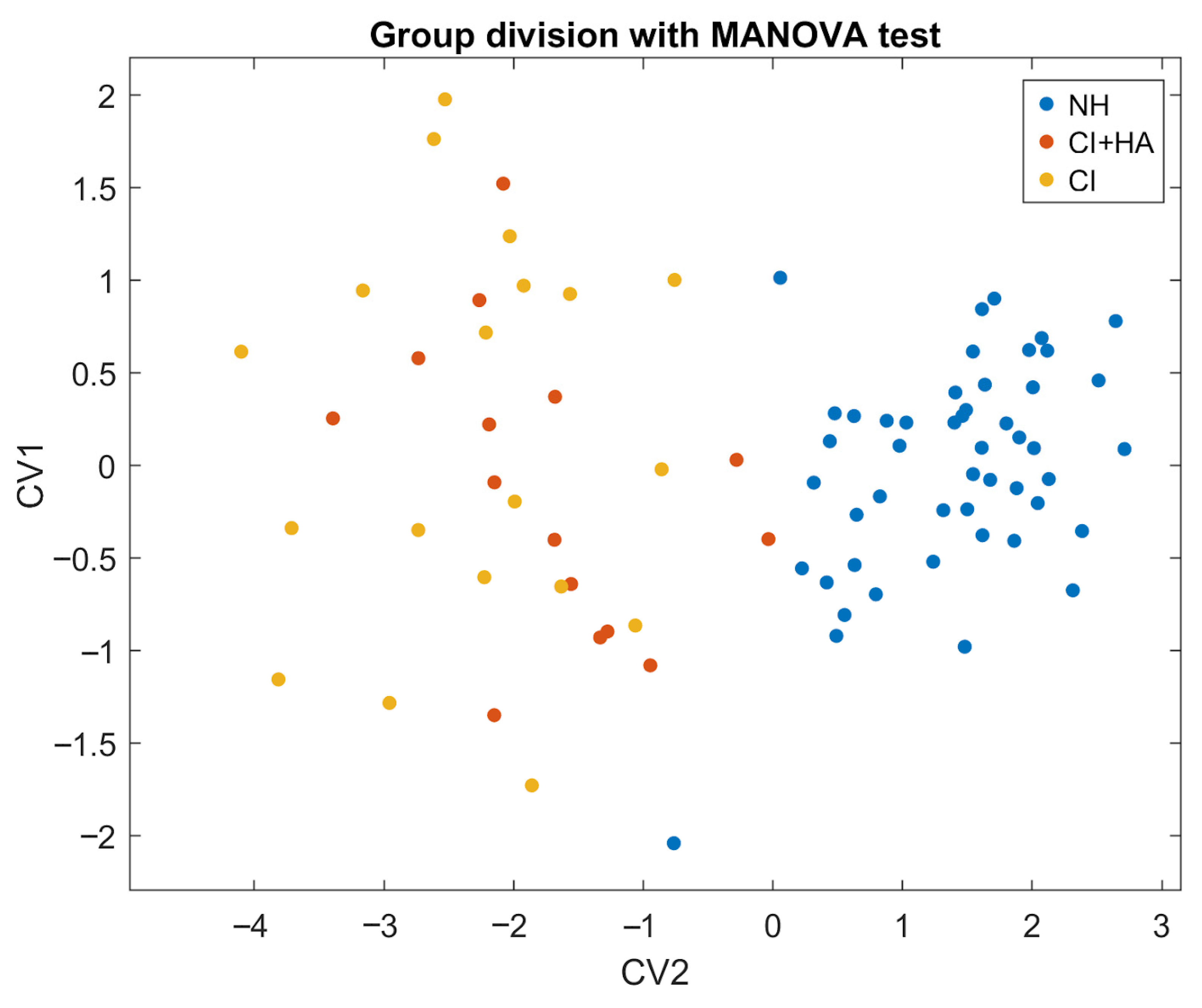
3.4. MANOVA Analysis
3.5. SSQ-12: Subdomain Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Differences in Hearing Performance Across Groups
4.1.1. Speech Recognition
4.1.2. Sound Localization
4.2. Subjective Auditory Perception and Correlation with Objective Measures
4.3. Influence of Age
4.4. Multivariate Analysis and Predictors of Performance
4.5. Clinical Implications
4.6. Limitations and Implications for Future Research
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CI | Cochlear Implant |
| NH | Normal Hearing |
| PTA | Pure-Tone Average |
| WRS | Word Recognition Score |
| SSQ-12 | Speech, Spatial. and Qualities of Hearing Scale |
| HA | Hearing Aid |
| ASHA | American Speech Language Hearing Association |
| Hz | Hertz |
| kHz | Kilohertz |
| dB | Decibel |
| SPL | Sound Pressure Leve |
| SNR | Signal to Noise Ratio |
| NB | Narrow Band |
| SE | Standard Error |
| CV | Canonical Variable |
| ITD | Interaural Time Difference |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
References
- Vigliano, M.; Huarte, A.; Borro, D.; Lasarte, U.; Manrique Rodriguez, M.J. Realistic Environment Audiometric Booth: Development and Clinical Validation. Audiol. Neurotol. 2021, 26, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorländer, M. Sound Fields in Complex Listening Environments. Trends Amplif. 2011, 15, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joly, C.-A.; Reynard, P.; Mezzi, K.; Bakhos, D.; Bergeron, F.; Bonnard, D.; Borel, S.; Bouccara, D.; Coez, A.; Dejean, F.; et al. Guidelines of the French Society of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery (SFORL) and the French Society of Audiology (SFA) for Speech-in-Noise Testing in Adults. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2022, 139, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Prell, C.G.; Clavier, O.H.; Bao, J. Noise-Induced Hearing Disorders: Clinical and Investigational Tools. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2023, 153, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinn, S.K.; Le Prell, C.G. Evaluation of Hidden Hearing Loss in Normal-Hearing Firearm Users. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1005148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, M.N. The Limitations of Pure-Tone Audiometry (as the Gold Standard Test of Hearing) That Are Worthy of Consideration. Indian J. Otol. 2021, 27, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlSamhori, J.F.; AlSamhori, A.R.F.; Amourah, R.M.; AlQadi, Y.; Koro, Z.W.; Haddad, T.R.A.; AlSamhori, A.F.; Kakish, D.; Kawwa, M.J.; Zuriekat, M.; et al. Artificial Intelligence for Hearing Loss Prevention, Diagnosis, and Management. J. Med. Surg. Public Health 2024, 3, 100133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crum, R.; Chowsilpa, S.; Kaski, D.; Giunti, P.; Bamiou, D.-E.; Koohi, N. Hearing Rehabilitation of Adults with Auditory Processing Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Current Evidence-Based Interventions. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1406916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, G.V.M.; Ribas, A.; Calleros, J. Sound Localization Test in Presence of Noise (Sound Localization Test) in Adults without Hearing Alteration. Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 23, E276–E280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Lutman, M.E.; Wang, S.; Bleeck, S. Relationship between Speech Recognition in Noise and Sparseness. Int. J. Audiol. 2012, 51, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ai, Y.; Han, Y.; Fan, Z.; Shi, P.; Wang, H. Extended High-Frequency Audiometry in Healthy Adults with Different Age Groups. J. Otolaryngol.—Head Neck Surg. 2021, 50, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, N.; Westermann, A.; Marschall, M.; May, T.; Dau, T.; Buchholz, J. Guided Ecological Momentary Assessment in Real and Virtual Sound Environments. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2021, 150, 2695–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suatbayeva, R.; Toguzbayeva, D.; Taukeleva, S.; Mukanova, Z.; Sadykov, M. Speech Perception and Parameters of Speech Audiometry after Hearing aid: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Electron. J. Gen. Med. 2024, 21, em563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenoy, S.; Bhatt, K.; Yazdani, Y.; Rahimian, H.; Djalilian, H.R.; Abouzari, M. A Systematic Review: State of the Science on Diagnostics of Hidden Hearing Loss. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Álvarez, M.; Johannesen, P.T.; Coelho-de-Sousa, S.L.; Klump, G.M.; Lopez-Poveda, E.A. The Relative Contribution of Cochlear Synaptopathy and Reduced Inhibition to Age-Related Hearing Impairment for People with Normal Audiograms. Trends Hear. 2023, 27, 23312165231213191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohrman, D.C.; Wan, G.; Cassinotti, L.; Corfas, G. Hidden Hearing Loss: A Disorder with Multiple Etiologies and Mechanisms. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2020, 10, a035493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrama, J.T.; Beach, E.F.; Yeend, I.; Sharma, M.; Van Dun, B.; Dillon, H. Effects of Lifetime Noise Exposure on the Middle-Age Human Auditory Brainstem Response, Tinnitus and Speech-in-Noise Intelligibility. Hear. Res. 2018, 365, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Tripathy, R.; Saxena, U. Critical Appraisal of Speech in Noise Tests: A Systematic Review and Survey. Int. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2016, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshahrani, N.A.; AlSufyani, N.H.; Aldawish, R.A.; Alrashdi, A.K.; Moafa, R.H.; Alqahtani, M.A.N.; Aljabri, A.M.; Alawad, F.H.; Alarfaj, A.A. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Comparing the Effect of Unilateral versus Bilateral Cochlear Implant in Hearing Impairment. J. Adv. Trends Med. Res. 2024, 1, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellis, T.J.; Ross, J. Performance of Normal Adults and Children on Central Auditory Diagnostic Tests and Their Corresponding Visual Analogs. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2011, 22, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigras, C.; Duda, V.; Hébert, S. Sensory and Affective Dimensions in Loudness Perception: Insights from Young Adults. Hear. Res. 2024, 454, 109147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucker, J.R. Auditory Processing Testing: In the Booth versus Outside the Booth. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2017, 28, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behar, A. Audiometric Tests without Booths. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morvan, P.; Buisson-Savin, J.; Boiteux, C.; Bailly-Masson, E.; Buhl, M.; Thai-Van, H. Factors in the Effective Use of Hearing Aids among Subjects with Age-Related Hearing Loss: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatehouse, S.; Noble, W. The Speech, Spatial and Qualities of Hearing Scale (SSQ). Int. J. Audiol. 2004, 43, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañete, O.M.; Marfull, D.; Torrente, M.C.; Purdy, S.C. The Spanish 12-Item Version of the Speech, Spatial and Qualities of Hearing Scale (Sp-SSQ-12): Adaptation, Reliability, and Discriminant Validity for People with and without Hearing Loss. Disabil. Rehabil. 2022, 44, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huarte, A. The Castilian Spanish Hearing in Noise Test. Int. J. Audiol. 2008, 47, 369–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecklenburg, D.J.; Graham, P.L.; James, C.J. Relationships Between Speech, Spatial and Qualities of Hearing Short Form SSQ-12 Item Scores and Their Use in Guiding Rehabilitation for Cochlear Implant Recipients. Trends Hear. 2024, 28, 23312165231224643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, W.; Jensen, N.S.; Naylor, G.; Bhullar, N.; Akeroyd, M.A. A Short Form of the Speech, Spatial and Qualities of Hearing Scale Suitable for Clinical Use: The SSQ-12. Int. J. Audiol. 2013, 52, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Xiang, Y.; Xu, H.; Yin, Q.; Li, J.; Zou, Y. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Extended High-Frequency Audiometry in Tinnitus Patients. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 12129–12139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Beek, F.B.; Briaire, J.J.; Frijns, J.H.M. Population-Based Prediction of Fitting Levels for Individual Cochlear Implant Recipients. Audiol. Neurotol. 2015, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorini, E.; Van Dijk, B.; Philips, B.; Mylanus, E.; Huinck, W. The Relation between Cochlear Implant Programming Levels and Speech Perception Performance in Post-Lingually Deafened Adults: A Data-Driven Approach. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2024, 281, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capach, N.H.; Zigdon, N.; Payne, T.A.; Neukam, J.D.; Choi, Y.; Park, H.J.; Shapiro, W.H.; Svirsky, M.A. Cochlear Implants and the Aided Audiogram: A Retrospective Study Comparing Performance Across Device Manufacturers. Audiol. Res. 2025, 15, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangaraj, M.; Arunachalam, R.; Gore, M.; Uppunda, A.K. Effect of Minimum and Maximum Electrical Stimulation Levels on Sound Field Thresholds, and Speech Perception in Children Using the Advanced Bionics Cochlear Implant. J. Otol. 2025, 20, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeuws, M.; Pascoal, D.; Bermejo, I.; Artaso, M.; De Ceulaer, G.; Govaerts, P.J. Computer-Assisted CI Fitting: Is the Learning Capacity of the Intelligent Agent FOX Beneficial for Speech Understanding? Cochlear Implant. Int. 2017, 18, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Cárdenas, M.R.; Aguiar, V.M. Cuaderno de Logoaudiometría; Red de Bibliotecas Universitarias: Madrid, Spain, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Vaerenberg, B.; Govaerts, P.J.; De Ceulaer, G.; Daemers, K.; Schauwers, K. Experiences of the Use of FOX, an Intelligent Agent, for Programming Cochlear Implant Sound Processors in New Users. Int. J. Audiol. 2011, 50, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risoud, M.; Hanson, J.-N.; Gauvrit, F.; Renard, C.; Bonne, N.-X.; Vincent, C. Azimuthal Sound Source Localization of Various Sound Stimuli under Different Conditions. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2020, 137, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahveninen, J.; Kopčo, N.; Jääskeläinen, I.P. Psychophysics and Neuronal Bases of Sound Localization in Humans. Hear. Res. 2014, 307, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obuchi, C.; Kaga, K. Development of a Questionnaire to Assess Listening Difficulties in Adults with Auditory Processing Disorder. Hear. Balance Commun. 2020, 18, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamiou, D.-E.; Iliadou, V.V.; Zanchetta, S.; Spyridakou, C. What Can We Learn about Auditory Processing from Adult Hearing Questionnaires? J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2015, 26, 824–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea Pérez, F.; Hartley, D.E.H.; Kitterick, P.T.; Zekveld, A.A.; Naylor, G.; Wiggins, I.M. Listening Efficiency in Adult Cochlear-Implant Users Compared with Normally-Hearing Controls at Ecologically Relevant Signal-to-Noise Ratios. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1214485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, P.; Alain, C.; Chen, J.; Le, T.; Lin, V.; Dimitrijevic, A. Effects of Age on the Neural Correlates of Auditory Working Memory in Cochlear Implant Users. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0325930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, L.; Lee, J.; Han, J.-H.; Jeon, H.; Hong, S.-K.; Lee, H.-J. Feasibility of Virtual Reality-Based Auditory Localization Training with Binaurally Recorded Auditory Stimuli for Patients with Single-Sided Deafness. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2023, 16, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philips, C.; Jacquemin, L.; Lammers, M.J.; Wouters, K.; Moyaert, J.; Vanderveken, O.; Van Rompaey, V. Impact of Hearing Impairment and Cochlear Implantation on Productivity and Social Well-Being in a Professionally Active but Severely Hearing-Impaired Group: Protocol of the ‘Hear Again, Work Again’ Longitudinal Prospective Cohort Study. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e064514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federici, A.; Fantoni, M.; Pavani, F.; Handjaras, G.; Bednaya, E.; Martinelli, A.; Berto, M.; Trabalzini, F.; Ricciardi, E.; Nava, E.; et al. Resilience and Vulnerability of Neural Speech Tracking after Hearing Restoration. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalarikkal, G.; Jain, C. A Systematic Review of Psychoacoustic Abilities in Post-Lingually Hearing-Impaired Cochlear Implant Users. Egypt. J. Otolaryngol. 2025, 41, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, J.J.; Kuhlmey, M.; Alexiades, G.; Hoffman, R.; Kim, A.H. Comparison of Speech Performance in Bimodal versus Bilateral Cochlear Implant Users. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, E1322–E1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.R.; Burg, E.; Suveg, L.; Litovsky, R.Y. Review of Binaural Processing with Asymmetrical Hearing Outcomes in Patients with Bilateral Cochlear Implants. Trends Hear. 2024, 28, 23312165241229880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieper, S.H.; Hamze, N.; Brill, S.; Hochmuth, S.; Exter, M.; Polak, M.; Radeloff, A.; Buschermöhle, M.; Dietz, M. Considerations for Fitting Cochlear Implants Bimodally and to the Single-Sided Deaf. Trends Hear. 2022, 26, 23312165221108259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlyon, R.P.; Deeks, J.M.; Delgutte, B.; Chung, Y.; Vollmer, M.; Ohl, F.W.; Kral, A.; Tillein, J.; Litovsky, R.Y.; Schnupp, J.; et al. Limitations on Temporal Processing by Cochlear Implant Users: A Compilation of Viewpoints. Trends Hear. 2025, 29, 23312165251317006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podury, A.; Jiam, N.T.; Kim, M.; Donnenfield, J.I.; Dhand, A. Hearing and Sociality: The Implications of Hearing Loss on Social Life. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1245434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ávila-Cascajares, F.; Waleczek, C.; Kerres, S.; Suchan, B.; Völter, C. Cross-Modal Plasticity in Postlingual Hearing Loss Predicts Speech Perception Outcomes After Cochlear Implantation. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arras, T.; Boudewyns, A.; Dhooge, I.; Zarowski, A.; Philips, B.; Desloovere, C.; Wouters, J.; Van Wieringen, A. Duration of Cochlear Implant Use in Children with Prelingual Single-Sided Deafness Is a Predictor of Word Perception in the CI Ear. Hear. Res. 2024, 450, 109076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grégoire, A.M.; Dricot, L.; Huart, C.; Decat, M.; Deggouj, N.; Kupers, R. Preoperative MRI, Audiovisual Speech Perception, and Mood Are Associated with Cochlear Implant Outcomes in Adults with Postlingual Deafness. Hear. Res. 2025, 461, 109272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleich, M.; Galvin, J.J.; Micaletti, F.; Bakhos, D. Longitudinal Study of Hearing Preservation and Electrocochleography after Cochlear Implantation in Adults. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2025, 91, 101584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haumann, S.; Lenarz, T.; Büchner, A. Speech Perception with Cochlear Implants as Measured Using a Roving-Level Adaptive Test Method. ORL 2010, 72, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gifford, R.H.; Grantham, D.W.; Sheffield, S.W.; Davis, T.J.; Dwyer, R.; Dorman, M.F. Localization and Interaural Time Difference (ITD) Thresholds for Cochlear Implant Recipients with Preserved Acoustic Hearing in the Implanted Ear. Hear. Res. 2014, 312, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, M.B.; Ward, K.M.; Gianakas, S.P.; Smith, M.L.; Blevins, N.H.; Swanson, A.P. Speech-in-Noise Assessment in the Routine Audiologic Test Battery: Relationship to Perceived Auditory Disability. Ear Hear. 2024, 45, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Valiente, A.; Roldán Fidalgo, A.; Villarreal, I.M.; García Berrocal, J.R. Audiometría con Extensión en Altas Frecuencias (9.000–20.000 Hz): Utilidad en el Diagnóstico Audiológico. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp. 2016, 67, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafieibavani, E.; Goudey, B.; Kiral, I.; Zhong, P.; Jimeno-Yepes, A.; Swan, A.; Gambhir, M.; Buechner, A.; Kludt, E.; Eikelboom, R.H.; et al. Predictive Models for Cochlear Implant Outcomes: Performance, Generalizability, and the Impact of Cohort Size. Trends Hear. 2021, 25, 23312165211066174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt, P.; Müller, V.; Meister, H.; Weglage, A.; Lang-Roth, R.; Walger, M.; Sandmann, P. Age Effects on Cognitive Functions and Speech-in-Noise Processing: An Event-Related Potential Study with Cochlear-Implant Users and Normal-Hearing Listeners. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1005859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langerak, N.C.; Stronks, H.C.; Briaire, J.J.; Frijns, J.H.M. The Benefit of Bimodal Hearing and Beamforming for Cochlear Implant Users. Audiol. Neurotol. 2024, 29, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, N.J.; Dillon, M.T.; Buss, E.; Rooth, M.A.; King, E.R.; Bucker, A.L.; McCarthy, S.A.; Deres, E.J.; O’Connell, B.P.; Pillsbury, H.C.; et al. Subjective Benefits of Bimodal Listening in Cochlear Implant Recipients with Asymmetric Hearing Loss. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2020, 162, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.D. Hidden Cochlear Impairments. J. Otol. 2018, 13, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitterick, P.T.; O’Donoghue, G.M.; Edmondson-Jones, M.; Marshall, A.; Jeffs, E.; Craddock, L.; Riley, A.; Green, K.; O’Driscoll, M.; Jiang, D.; et al. Comparison of the Benefits of Cochlear Implantation versus Contra-Lateral Routing of Signal Hearing Aids in Adult Patients with Single-Sided Deafness: Study Protocol for a Prospective within-Subject Longitudinal Trial. BMC Ear Nose Throat Disord. 2014, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sladen, D.P.; Carlson, M.L.; Dowling, B.P.; Olund, A.P.; DeJong, M.D.; Breneman, A.; Hollander, S.; Beatty, C.W.; Neff, B.A.; Driscoll, C.L. Cochlear Implantation in Adults with Asymmetric Hearing Loss: Speech Recognition in Quiet and in Noise, and Health Related Quality of Life. Otol. Neurotol. 2018, 39, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, L.K.; Finley, C.C.; Firszt, J.B.; Holden, T.A.; Brenner, C.; Potts, L.G.; Gotter, B.D.; Vanderhoof, S.S.; Mispagel, K.; Heydebrand, G.; et al. Factors Affecting Open-Set Word Recognition in Adults with Cochlear Implants. Ear Hear. 2013, 34, 342–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermiglio, A.J.; Velappan, K.; Heeke, P.; Bulla, E.; Fang, X.; Bonilla, E.; Garner, E.; Skinner, J. The Relationship between Speech Recognition in Noise and Non-Speech Recognition in Noise Test Performances: Implications for Central Auditory Processing Disorders Testing. J. Commun. Disord. 2019, 77, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Fried, J.; Nguyen, S.A.; Schvartz-Leyzac, K.C.; Camposeo, E.L.; Meyer, T.A.; Dubno, J.R.; McRackan, T.R. Longitudinal Speech Recognition Changes After Cochlear Implant: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 2023, 133, 1014–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| NH (n = 50) | CI (n = 34) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.69 | ||
| Women | 33 (66.0%) | 21 (61.8%) | |
| Men | 17 (34.0%) | 13 (38.2%) | |
| age ± SE | 46.2 ± 15.6 [20–73] | 56.6 ± 15.9 [26–79] | 0.348 |
| Implanted ear | - | - | |
| Right | 17 (50%) | ||
| Left | 17 (50%) | ||
| Full electrode insertion | - | 27 (79.4%) | - |
| Type of insertion | - | - | |
| Round window | 22 (64.7%) | ||
| Cochleostomy | 11 (32.4%) | ||
| Type of implant | - | ||
| Straight | 30 (88.2%) | ||
| Perimodiolar | 4 (11.8%) | ||
| Bimodal fitting | 15 (44.1%) | - | |
| PTA (dBHL) | 28.5 ± 5.1 [15–40] | 44.3 ± 7.7 [25–61.3] | <0.01 |
| Pre-CI PTA (dBHL) | |||
| Ipsilateral | 91.5 ± 22.7 [53–120] | ||
| Contralateral | 96.0 ± 22.8 [72–120] | ||
| WRS (%) in quiet | 99.2 ± 2.0 [90–100] | 83.4 ± 10.7 [65–100] | <0.01 |
| WRS (%) in noise (sea) | 88.3 ± 8.5 [68–100] | 53.2 ± 21.4 [0–90] | <0.01 ε |
| WRS (%) in noise (traffic) | 84.1 ± 11.3 [52–100] | 36.1 ± 23.2 [0–80] | <0.01 ε |
| WRS (%) in noise (cafeteria) | 73.9 ± 16.6 [48–100] | 16.2 ± 18.1 [0–70] | <0.01 |
| Sound localization (%) | 56.9 ± 22.7 [6.3–100] | 18.7 ± 11.8 [0–43.8] | <0.01 |
| SSQ-12 | 7.3 ± 1.2 [2.3–9.1] | 4.5 ± 1.8 [1.1–7.6] | <0.01 |
| Age | PTA | WRS Quiet | WRS Sea | WRS Traffic | WRS Cafe | Sound Localization | SSQ-12 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1 | 0.748 *** | 0.309 * | −0.189 *** | −0.448 *** | −0.611 *** | −0.039 | −0.460 *** |
| PTA | 0.748 *** | 1 | 0.108 | −0.321 * | −0.475 *** | −0.667 *** | −0.213 | −0.334 ** |
| WRS quiet | 0.309 * | 0.108 | 1 | 0.038 | −0.038 | −0.141 | 0.201 | −0.106 |
| WRS sea | −0.189 | −0.321 * | 0.038 | 1 | 0.700 *** | 0.485 *** | −0.270 * | 0.007 |
| WRS traffic | −0.448 *** | −0.475 *** | −0.038 | 0.700 *** | 1 | 0.704 *** | −0.173 | 0.281 * |
| WRS cafe | −0.611 *** | −0.667 *** | −0.141 | 0.485 *** | 0.704 *** | 1 | 0.011 | 0.301 * |
| Sound localization | −0.039 | −0.213 | 0.201 | −0.270* | −0.173 | 0.011 | 1 | 0.061 |
| SSQ-12 | −0.460 *** | −0.334 * | −0.106 | 0.007 | 0.218 * | 0.301 * | 0.061 | 1 |
| Age | PTA | WRS Quiet | WRS Sea | WRS Traffic | WRS Cafe | Sound Localization | SSQ-12 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1 | 0.224 | −0.182 | −0.056 | −0.140 | −0.219 | −0.252 | −0.206 |
| PTA | 0.224 | 1 | −0.391 * | −0.436 ** | −0.545 *** | −0.573 *** | −0.175 | −0.135 |
| WRS quiet | −0.182 | −0.391 * | 1 | 0.463 ** | 0.322 | 0.129 | 0.047 | −0.184 |
| WRS sea | −0.056 | −0.436 ** | 0.463 ** | 1 | 0.795 *** | 0.577 *** | 0.387 * | −0.166 |
| WRS traffic | −0.140 | −0.545 *** | 0.322 | 0.795 *** | 1 | 0.801 *** | 0.261 | −0.127 |
| WRS cafe | −0.219 | −0.573 *** | 0.129 | 0.577 *** | 0.801 *** | 1 | 0.238 | −0.023 |
| Sound localization | −0.252 | −0.175 | 0.047 | 0.387 * | 0.261 | 0.238 | 1 | 0.017 |
| SSQ-12 | −0.206 | −0.135 | −0.184 | −0.166 | −0.127 | −0.023 | 0.017 | 1 |
| Adjusted b (mean ± SE) | 95% CI | p-Value | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSQ-12 | 0.224 | |||
| WRS (noise—cafe) | 0.040 ± 0.011 | [0.019, 0.064] | <0.001 | |
| WRS (quiet) | 0.204 | |||
| Age | 0.083 ± 0.024 | [0.035, 0.130] | 0.001 | |
| PTA | −0.166 ± 0.073 | [−0.313, −0.019] | 0.027 | |
| WRS (noise—cafe) | 0.411 | |||
| Age | −0.358 ± 0.167 | [−0.692, −0.023] | 0.037 | |
| PTA | −1.176 ± 0.510 | [−2.202, −0.149] | 0.026 | |
| Localization | - | - | - | 0 |
| Adjusted b (mean ± SE) | 95% CI | p-Value | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSQ-12 | - | - | - | 0 |
| WRS quiet | 0.5102 | |||
| PTA4_pre_CONTRA | −0.399 ± 0.0799 | [−0.564, −0.234] | <0.001 | |
| WRS cafe | 0.402 | |||
| PTA | −1.503 ± 0.3241 | [−2.1634, −0.8431] | <0.001 | |
| Localization | - | - | - | 0 |
| Wilks’ Lambda | χ2 (dof) | Rao’s F (dof) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canonical Dimension 1 | 0.153 | 148 (10) | 223 (2.81) | >0.001 |
| Canonical Dimension 2 | 0.91631 | 7 (4) | 3.7 (2.81) | 0.14 |
| Speech SSQ 12 | Spatial SSQ 12 | Qualities SSQ 12 | SSQ-12_Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTA | −0.755 *** | 0.852 *** | −0.477 *** | −0.638 *** |
| Localization | 0.576 *** | 0.526 *** | 0.297 * | 0.536 *** |
| WRS Quiet | 0.548 *** | 0.539 *** | 0.319 * | 0.514 *** |
| WRS Sea | 0.556 *** | 0.518 *** | 0.345 ** | 0.504 *** |
| WRS Traffic | 0.711 *** | 0.707 *** | 0.457 *** | 0.642 *** |
| WRS Cafeteria | 0.721 *** | 0.713 *** | 0.504 *** | 0.664 *** |
| Age | −0.508 *** | −0.572 *** | −0.363 ** | −0.448 *** |
| Speech SSQ 12 | 1 | 0.852 *** | 0.759 *** | 0.965 *** |
| Spatial SSQ 12 | 0.852 *** | 1 | 0.657 *** | 0.905 *** |
| Qualities SSQ 12 | 0.759 *** | 0.657 *** | 1 | 0.853 *** |
| SSQ-12_Total | 0.965 *** | 0.905 *** | 0.853 *** | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Álvarez-Cendrero, M.; Lazo-Maestre, M.; Sánchez-Gómez, S.; Callejón-Leblic, M.A. From Clinic to Reality: Integrating Sound Field Testing and Hearing Quality Measures in Cochlear Implant Users. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8430. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238430
Álvarez-Cendrero M, Lazo-Maestre M, Sánchez-Gómez S, Callejón-Leblic MA. From Clinic to Reality: Integrating Sound Field Testing and Hearing Quality Measures in Cochlear Implant Users. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(23):8430. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238430
Chicago/Turabian StyleÁlvarez-Cendrero, Marta, Manuel Lazo-Maestre, Serafín Sánchez-Gómez, and María A. Callejón-Leblic. 2025. "From Clinic to Reality: Integrating Sound Field Testing and Hearing Quality Measures in Cochlear Implant Users" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 23: 8430. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238430
APA StyleÁlvarez-Cendrero, M., Lazo-Maestre, M., Sánchez-Gómez, S., & Callejón-Leblic, M. A. (2025). From Clinic to Reality: Integrating Sound Field Testing and Hearing Quality Measures in Cochlear Implant Users. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(23), 8430. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238430








