From Resuscitation to Rehabilitation: The Post-Intensive Care Syndrome Continuum in Sepsis Care
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
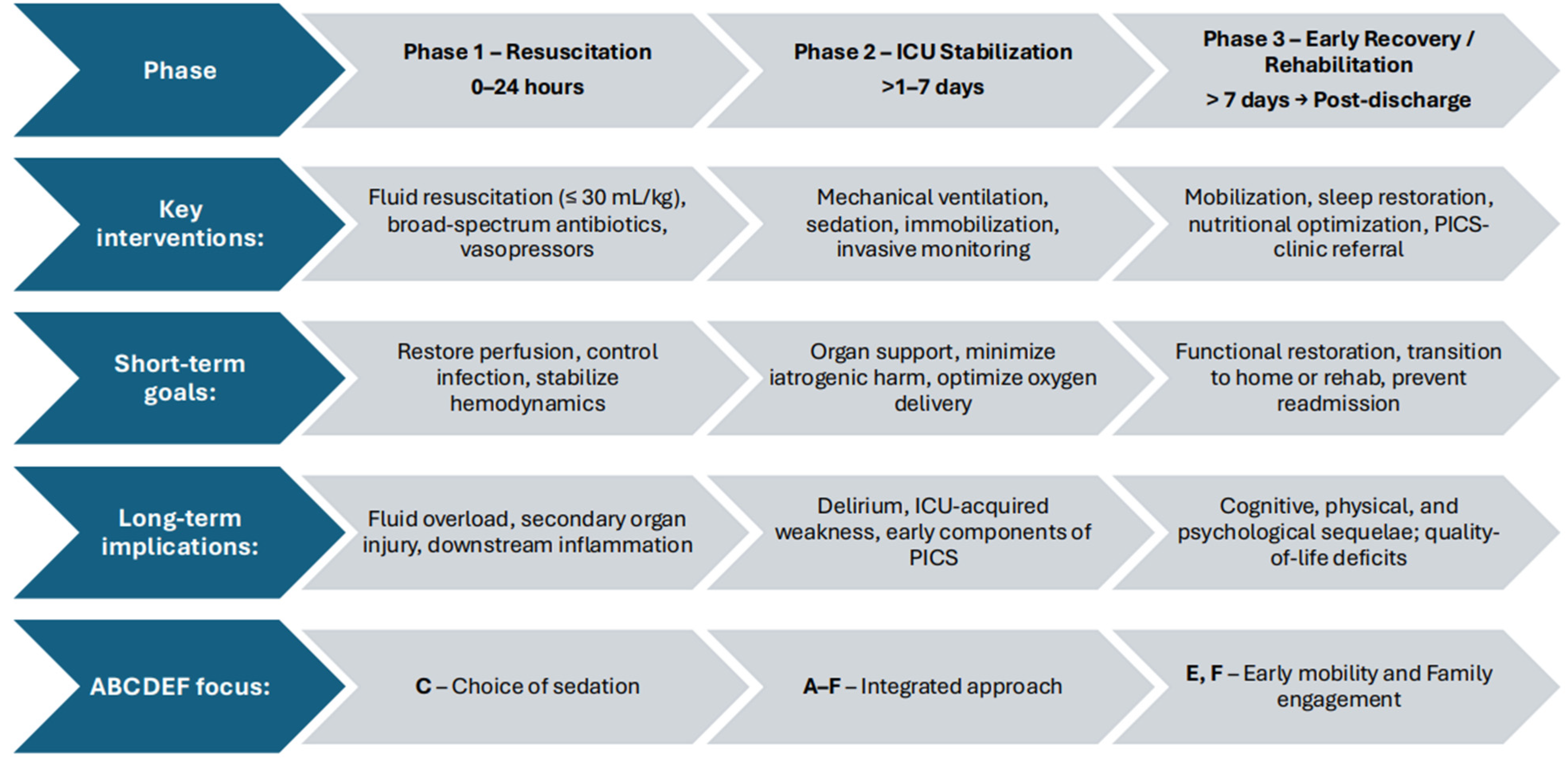
2.1. The Recovery Trajectory: From Resuscitation to Rehabilitation
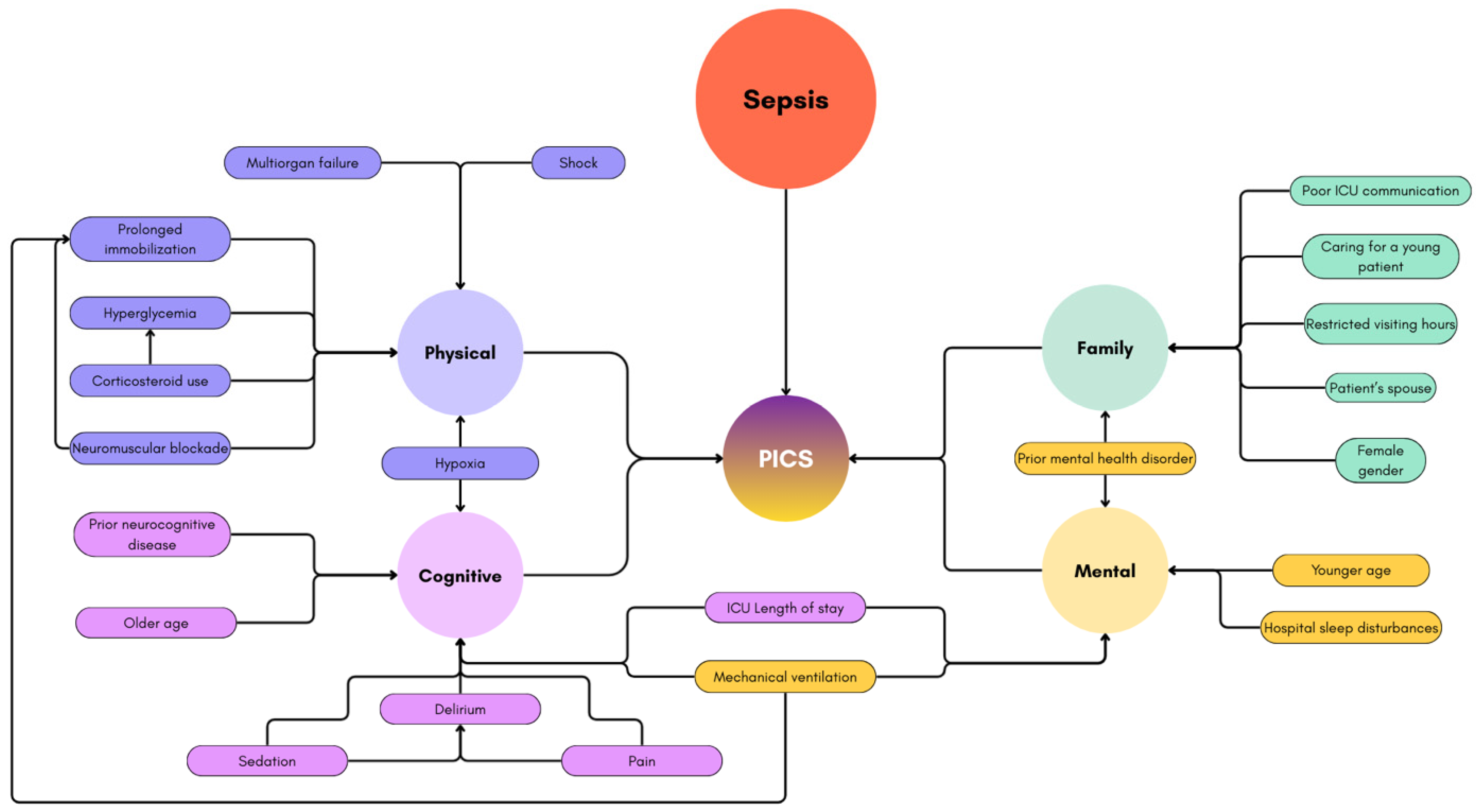
2.2. Post-Intensive Care Syndrome (PICS)
2.3. PICS-Cognitive Dysfunction
2.4. PICS-Physical Impairment
2.5. PICS-Psychological Disorders
2.6. PICS-Family and Financial Impact
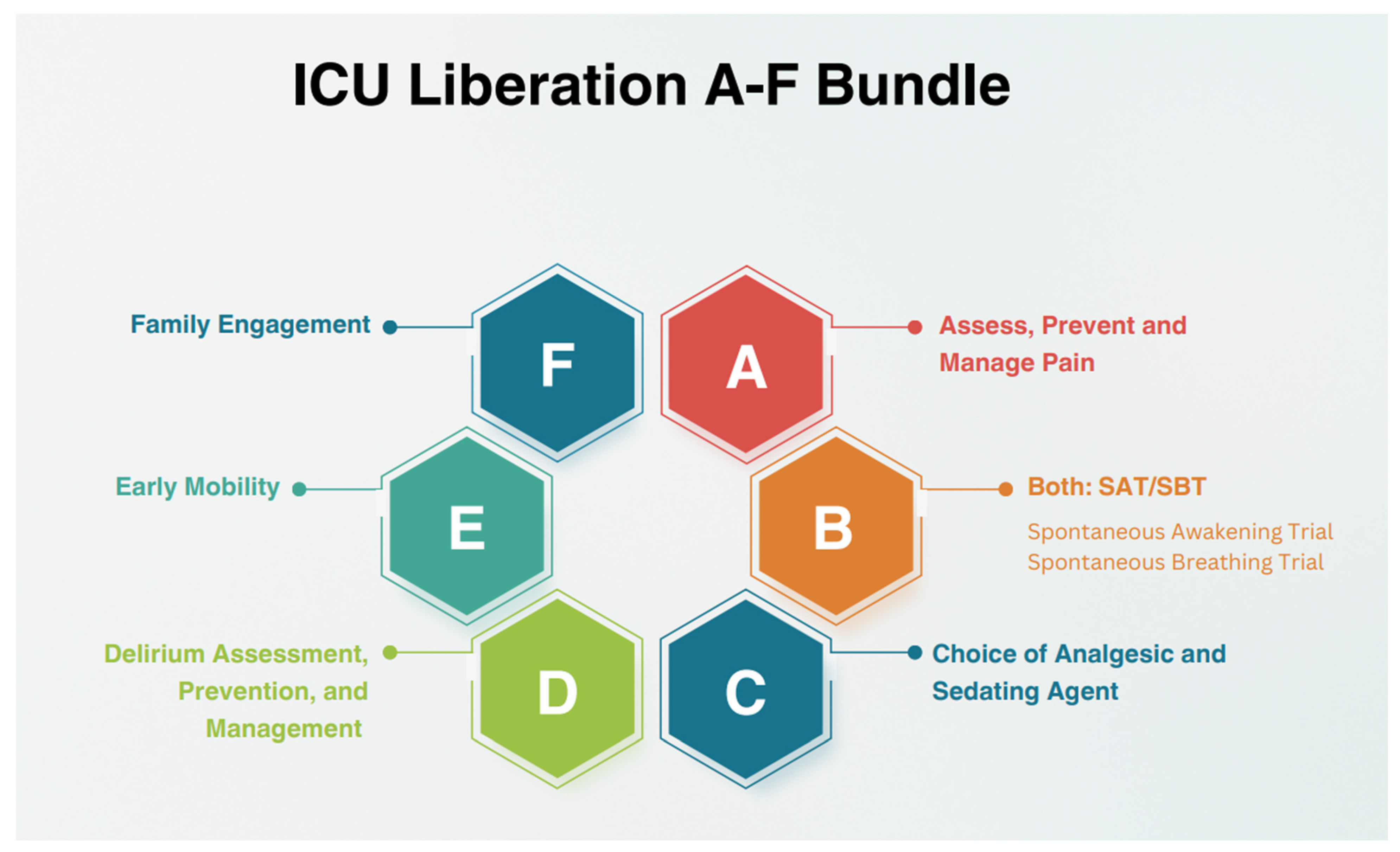
2.7. Intervention and Prevention Using the A2F Bundle
2.7.1. Assess, Prevent, and Treat Pain
2.7.2. Both Spontaneous Awakening Trials (SAT) and Spontaneous Breathing Trials (SBT)
2.7.3. Choice of Analgesia and Sedation
2.7.4. Delirium: Assess, Prevent, and Manage
2.7.5. Early Mobility and Exercise
2.7.6. Family Engagement and Empowerment
2.8. Rehabilitation and Future Directions
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, Y.; Jaschinski, U.; Wittebole, X.; Szakmany, T.; Lipman, J.; Ñamendys-Silva, S.A.; Hernandez, G.; Leone, M.; Bauer, M.; Vincent, J.L. Sepsis in Intensive Care Unit Patients: Worldwide Data from the Intensive Care over Nations Audit. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018, 5, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, J.L.; Sakr, Y.; Sprung, C.L.; Ranieri, V.M.; Reinhart, K.; Gerlach, H.; Moreno, R.; Carlet, J.; Le Gall, J.R.; Payen, D.; et al. Sepsis in European intensive care units: Results of the SOAP study. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaukonen, K.M.; Bailey, M.; Suzuki, S.; Pilcher, D.; Bellomo, R. Mortality related to severe sepsis and septic shock among critically ill patients in Australia and New Zealand, 2000–2012. JAMA 2014, 311, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshar, M.; Arain, E.; Ye, C.; Emily, G.; Xie, M.; Lee, J.; Churpek, M.M.; Durazo-Arvizu, R.; Markossian, T.; Joyce, C. Patient Outcomes and Cost-Effectiveness of a Sepsis Care Quality Improvement Program in a Health System. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bone, R.C.; Balk, R.A.; Cerra, F.B.; Dellinger, R.P.; Fein, A.M.; Knaus, W.A.; Schein, R.M.; Sibbald, W.J. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. Chest 1992, 101, 1644–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.M.; Fink, M.P.; Marshall, J.C.; Abraham, E.; Angus, D.; Cook, D.; Cohen, J.; Opal, S.M.; Vincent, J.L.; Ramsay, G.; et al. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference. Intensive Care Med. 2003, 29, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, D.M.; Davidson, J.; Cohen, H.; Hopkins, R.O.; Weinert, C.; Wunsch, H.; Zawistowski, C.; Bemis-Dougherty, A.; Berney, S.C.; Bienvenu, O.J.; et al. Improving long-term outcomes after discharge from intensive care unit: Report from a stakeholders’ conference. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayenew, T.; Gete, M.; Gedfew, M.; Getie, A.; Afenigus, A.D.; Edmealem, A.; Amha, H.; Alem, G.; Tiruneh, B.G.; Messelu, M.A.; et al. Prevalence of Post-intensive care syndrome among intensive care unit-survivors and its association with intensive care unit length of stay: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0323311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Watanabe, S.; Nakamura, K.; Nakano, H.; Motoki, M.; Kamijo, H.; Ayaka, M.; Ishii, K.; Morita, Y.; Hongo, T.; et al. One-year outcomes in sepsis: A prospective multicenter cohort study in Japan. J. Intensive Care 2025, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudd, K.E.; Johnson, S.C.; Kristina, E.; Shackelford, K.A.; Tsoi, D.; Kievlan, D.R.; Colombara, D.V.; Ikuta, K.S.; Kissoon, N.; Finfer, S.; et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Via, L.; Sangiorgio, G.; Stefani, S.; Marino, A.; Nunnari, G.; Cocuzza, S.; La Mantia, I.; Cacopardo, B.; Stracquadanio, S.; Spampinato, S.; et al. The Global Burden of Sepsis and Septic Shock. Epidemiologia 2024, 5, 456–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, V.; Escobar, G.J.; Greene, J.D.; Soule, J.; Whippy, A.; Angus, D.C.; Iwashyna, T.J. Hospital Deaths in Patients with Sepsis From 2 Independent Cohorts. JAMA 2014, 312, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar-Hari, M.; Harrison, D.A.; Rowan, K.M. Differences in Impact of Definitional Elements on Mortality Precludes International Comparisons of Sepsis Epidemiology—A Cohort Study Illustrating the Need for Standardized Reporting. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 44, 2223–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, F.R.; Cavalcanti, A.B.; Bozza, F.A.; Ferreira, E.M.; Carrara, F.S.A.; Sousa, J.L.; Caixeta, N.; Salomao, R.; Angus, D.C.; Azevedo, L.C.P.; et al. The epidemiology of sepsis in Brazilian intensive care units (the Sepsis PREvalence Assessment Database, SPREAD): An observational study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 1180–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divatia, J.V.; Amin, P.R.; Ramakrishnan, N.; Kapadia, F.N.; Todi, S.; Sahu, S.; Govil, D.; Chawla, R.; Kulkarni, A.P.; Samavedam, S.; et al. Intensive Care in India: The Indian Intensive Care Case Mix and Practice Patterns Study. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 20, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, L.; Rhodes, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Antonelli, M.; Coopersmith, C.M.; French, C.; Machado, F.R.; Mcintyre, L.; Ostermann, M.; Prescott, H.C.; et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 1181–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Roberts, D.; Wood, K.E.; Light, B.; Parrillo, J.E.; Sharma, S.; Suppes, R.; Feinstein, D.; Zanotti, S.; Taiberg, L.; et al. Duration of hypotension before initiation of effective antimicrobial therapy is the critical determinant of survival in human septic shock. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.; Östholm-Balkhed, Å.; Fredrikson, M.; Holmbom, M.; Hällgren, A.; Berg, S.; Hanberger, H. Delay of appropriate antibiotic treatment is associated with high mortality in patients with community-onset sepsis in a Swedish setting. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 38, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messmer, A.S.; Zingg, C.; Müller, M.; Gerber, J.L.; Schefold, J.C.; Pfortmueller, C.A. Fluid Overload and Mortality in Adult Critical Care Patients—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, 1862–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrier, R.W. Fluid administration in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zampieri, F.G.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Semler, M.W. Fluid Therapy for Critically Ill Adults with Sepsis: A Review. JAMA 2023, 329, 1967–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehlenbach, W.J.; Hough, C.L.; Crane, P.K.; Haneuse, S.J.P.A.; Carson, S.S.; Curtis, J.R.; Larson, E.B. Association Between Acute Care and Critical Illness Hospitalization and Cognitive Function in Older Adults. JAMA 2010, 303, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jesus Pereira, I.; Santos, M.; Sganzerla, D.; Robinson, C.C.; Souza, D.d.; Kochhann, R.; Falavigna, M.; Azevedo, L.; Bozza, F.; Sharshar, T.; et al. Long term cognitive dysfunction among critical care survivors: Associated factors and quality of life—A multicenter cohort study. Ann. Intensive Care 2024, 14, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasker, R.C.; Menon, D.K. Critical Care and the Brain. JAMA 2016, 315, 749–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herridge, M.S.; Azoulay, É. Outcomes after Critical Illness. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, J.P.; Hall, J.B. ICU-Acquired Weakness and Recovery from Critical Illness. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1626–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocheteau, P.; Chatre, L.; Briand, D.; Mebarki, M.; Jouvion, G.; Bardon, J.; Crochemore, C.; Serrani, P.; Lecci, P.P.; Latil, M.; et al. Sepsis induces long-term metabolic and mitochondrial muscle stem cell dysfunction amenable by mesenchymal stem cell therapy. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, L.A.; Supinski, G.S. Sepsis-induced myopathy. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37 (Suppl. S10), S354–S367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beumeler, L.F.E.; van Wieren, A.; Buter, H.; van Zutphen, T.; Bruins, N.A.; de Jager, C.M.; Koopmans, M.; Navis, G.J.; Boerma, E.C. Patient-reported physical functioning is limited in almost half of critical illness survivors 1-year after ICU-admission: A retrospective single-centre study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, L.; Subair, M.N.; Munjal, J.; Singh, B.; Bansal, V.; Gupta, V.; Jain, R. Beyond survival: Understanding post-intensive care syndrome. Acute Crit. Care 2024, 39, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, M.T.; Knauert, M.P.; Pisani, M.A. Sleep Disturbance After hospitalization and critical illness: A systematic review. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2017, 14, 1457–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jonghe, B.; Lacherade, J.C.; Sharshar, T.; Outin, H. Intensive care unit-acquired weakness: Risk factors and prevention. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37 (Suppl. S10), S309–S315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischmann-Struzek, C.; Born, S.; Kesselmeier, M.; Ely, E.W.; Töpfer, K.; Romeike, H.; Bauer, M.; Bercker, S.; Bodechtel, U.; Fiedler, S.; et al. Functional dependence following intensive care unit-treated sepsis: Three-year follow-up results from the prospective Mid-German Sepsis Cohort (MSC). Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2024, 46, 101066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Costa, L.H.A.; Santos-Junior, N.N.; Catalão, C.H.R.; Rocha, M.J.A. Microglial Activation Modulates Neuroendocrine Secretion During Experimental Sepsis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 2133–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanczkowski, W.; Sue, M.; Zacharowski, K.; Reincke, M.; Bornstein, S.R. The role of adrenal gland microenvironment in the HPA axis function and dysfunction during sepsis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 408, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berghe, G.; Téblick, A.; Langouche, L.; Gunst, J. The hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis in sepsis- and hyperinflammation-induced critical illness: Gaps in current knowledge and future translational research directions. EBioMedicine 2022, 84, 104284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, H.C.; Angus, D.C. Enhancing Recovery from Sepsis: A Review. JAMA 2018, 319, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwitzer, E.; Jensen, K.S.; Brinkman, L.; DeFrancia, L.; VanVleet, J.; Baqi, E.; Aysola, R.; Qadir, N. Survival ≠ Recovery. A Narrative Review of Post-Intensive Care Syndrome. CHEST Crit. Care 2023, 1, 100003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatch, R.; Young, D.; Barber, V.; Griffiths, J.; Harrison, D.A.; Watkinson, P. Anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder after critical illness: A UK-wide prospective cohort study. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, M.E.; Christie, J.D.; Lanken, P.N.; Biester, R.C.; Thompson, B.T.; Bellamy, S.L.; Localio, A.R.; Demissie, E.; Hopkins, R.O.; Angus, D.C.; et al. The adult respiratory distress syndrome cognitive outcomes study: Long-term neuropsychological function in survivors of acute lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sell, S.; Fleischmann-Struzek, C.; Spoden, M.; Rosendahl, J. Mental health in the first year after ICU-treated sepsis: Analysis of administrative diagnoses in German health claims data. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2025, 93, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, S.M.; Qureshi, D.; Sood, M.M.; Pugliese, M.; Talarico, R.; Myran, D.T.; Herridge, M.S.; Needham, D.M.; Rochwerg, B.; Cook, D.J.; et al. Suicide and self-harm in adult survivors of critical illness: Population-based cohort study. BMJ 2021, 373, n973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, R.O.; Key, C.W.; Suchyta, M.R.; Weaver, L.K.; Orme, J.F., Jr. Risk factors for depression and anxiety in survivors of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2010, 32, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abri, M.A. Sleep deprivation and depression: A bi-directional association. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 2015, 15, e4–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, J.E.; Jones, C.; Bienvenu, O.J. Family response to critical illness: Postintensive care syndrome-family. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrinec, A.B.; Martin, B.R. Post-intensive care syndrome symptoms and health related quality of life in family decision makers of critically ill patients. Palliat. Support. Care 2018, 16, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Tate, J.A.; Donahoe, M.P.; Ren, D.; Hoffman, L.A.; Chasens, E.R. Sleep in family caregivers of ICU survivors for two months post-ICU discharge. Intensive Crit. Care Nurs. 2016, 37, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirasaki, K.; Hifumi, T.; Isokawa, S.; Hashiuchi, S.; Tanaka, S.; Yanagisawa, Y.; Takahashi, O.; Otani, N. Postintensive Care Syndrome-Family Assoiiated with COVID-19 Infection. Crit. Care Explor. 2022, 4, e0725. [Google Scholar]
- Pochard, F.; Azoulay, E.; Chevret, S.; Lemaire, F.; Hubert, P.; Canoui, P.; Grassin, M.; Zittoun, R.; le Gall, J.R.; Dhainaut, J.F.; et al. Symptoms of anxiety and depression in family members of intensive care unit patients: Ethical hypothesis regarding decision making capacity. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 29, 1893–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, J.; Hatch, R.A.; Bishop, J.; Morgan, K.; Jenkinson, C.; Cuthbertson, B.H.; Brett, S.J. An exploration of social and economic outcome and asscoiated health-related quality of life after critical illness in general intensive care unit survivors: A 12-month follow-up study. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveria, C.; Saka, M.; Bone, L.; Jacobs, R. The Role of Mental Health on Workplace Productivity: A critical review of the literature. Appl. Health Econ. Health Policy 2023, 21, 167–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, A.; Ely, E.W.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Patel, M.B. The ABCDEF Bundle in Critical Care. Crit. Care Clin. 2017, 33, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, J.; Fraser, G.L.; Puntillo, K.; Ely, E.W.; Gélinas, C.; Dasta, J.F.; Davidson, J.E.; Devlin, J.W.; Kress, J.P.; Joffe, A.M.; et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of pain, agitation, and delirium in adult patients in the intensive care unit. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 41, 263–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, J.; Downs, B.; Ferrell, K.; Talebian, M.; Robinson, S.; Kolodisner, L.; Kendall, H.; Holdych, J. Improving Outcomes in Mechanically Ventilated Adult ICU Patients Following Implementation of the ICU Liberation (ABCDEF) Bundle Across a Large Healthcare System. Crit. Care Explor. 2024, 6, e1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payen, J.F.; Chanques, G.; Mantz, J.; Hercule, C.; Auriant, I.; Leguillou, J.L.; Binhas, M.; Genty, C.; Rolland, C.; Bosson, J.L. Current practices in sedation and analgesia for mechanically ventilated critically ill patients: A prospective multicenter patient-based study. Anesthesiology 2007, 106, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puntillo, K.A.; Max, A.; Timsit, J.F.; Vignoud, L.; Chanques, G.; Robleda, G.; Roche-Campo, F.; Mancebo, J.; Divatia, J.V.; Soares, M.; et al. Determinants of procedural pain intensity in the intensive care unit. The Europain® study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erstad, B.L.; Puntillo, K.; Gilbert, H.C.; Grap, M.J.; Li, D.; Medina, J.; Mularski, R.A.; Pasero, C.; Varkey, B.; Sessler, C.N. Pain management principles in the critically ill. Chest. 2009, 135, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martyn, J.A.J.; Mao, J.; Bittner, E.A. Opioid Tolerance in Critical Illness. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, N.; Bazo-Alvarez, J.C.; Koopmans, M.; West, E.; Sampson, E.L. Understanding the association between pain and delirium in older hospital inpatients: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing 2024, 53, afae073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumbach, P.; Götz, T.; Günther, A.; Weiss, T.; Meissner, W. Prevalence and Characteristics of Chronic Intensive Care–Related Pain: The Role of Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 44, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freundlich, R.E.; Li, G.; Leis, A.; Engoren, M. Factors Associated with Initiation of Mechanical Ventilation in Patients With Sepsis: Retrospective Observational Study. Am. J. Crit. Care 2023, 32, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Oh, D.K.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, M.H.; Lim, C.M.; Korean Sepsis Alliance (KSA) Investigators. Impact of the timing of invasive mechanical ventilation in patients with sepsis: A multicenter cohort study. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehabi, Y.; Bellomo, R.; Reade, M.C.; Bailey, M.; Bass, F.; Howe, B.; McArthur, C.; Seppelt, I.M.; Webb, S.; Weisbrodt, L.; et al. Early intensive care sedation predicts long-term mortality in ventilated critically ill patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, L.M.; Azevedo, L.C.; Park, M.; Schettino, G.; Nassar, A.P.; Réa-Neto, A.; Tannous, L.; Souza-Dantas, V.C.; Torelly, A.; Lisboa, T.; et al. Early sedation and clinical outcomes of mechanically ventilated patients: A prospective multicenter cohort study. Crit. Care 2014, 18, R156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzer, F.; Weiss, B.; Kumpf, O.; Treskatsch, S.; Spies, C.; Wernecke, K.D.; Krannich, A.; Kastrup, M. Early deep sedation is associated with decreased in-hospital and two-year follow-up survival. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, J.P.; Pohlman, A.S.; O’Connor, M.F.; Hall, J.B. Daily interruption of sedative infusions in critically ill patients undergoing mechanical ventilation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandharipande, P.; Banerjee, A.; McGrane, S.; Ely, E.W. Liberation and animation for ventilated ICU patients: The ABCDE bundle for the back-end of critical care. Crit. Care 2010, 14, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ely, E.W.; Baker, A.M.; Dunagan, D.P.; Burke, H.L.; Smith, A.C.; Kelly, P.T.; Johnson, M.M.; Browder, R.W.; Bowton, D.L.; Haponik, E.F. Effect on the duration of mechanical ventilation of identifying patients capable of breathing spontaneously. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 335, 1864–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, T.D.; Kress, J.P.; Fuchs, B.D.; Thomason, J.W.; Schweickert, W.D.; Pun, B.T.; Taichman, D.B.; Dunn, J.G.; Pohlman, A.S.; Kinniry, P.A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of a paired sedation and ventilator weaning protocol for mechanically ventilated patients in intensive care (Awakening and Breathing Controlled trial): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2008, 371, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Fang, D.; Hu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, J.; Wu, G. The impact of sedation and analgesia scores on prognosis in critically ill sepsis patients with sepsis-associated encephalopathy: A retrospective analysis. Front. Neurol. 2025, 16, 1622964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ely, E.W.; Truman, B.; Shintani, A.; Thomason, J.W.; Wheeler, A.P.; Gordon, S.; Francis, J.; Speroff, T.; Gautam, S.; Margolin, R.; et al. Monitoring sedation status over time in ICU patients: Reliability and validity of the Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale (RASS). JAMA 2003, 289, 2983–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devlin, J.W.; Skrobik, Y.; Gélinas, C.; Needham, D.M.; Slooter, A.J.C.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Watson, P.L.; Weinhouse, G.L.; Nunnally, M.E.; Rochwerg, B.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Pain, Agitation/Sedation, Delirium, Immobility, and Sleep Disruption in Adult Patients in the ICU. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, e825–e873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandharipande, P.P.; Pun, B.T.; Herr, D.L.; Maze, M.; Girard, T.D.; Miller, R.R.; Shintani, A.K.; Thompson, J.L.; Jackson, J.C.; Deppen, S.A.; et al. Effect of Sedation with Dexmedetomidine vs Lorazepam on Acute Brain Dysfunction in Mechanically Ventilated Patients: The MENDS Randomized Controlled Trial. JAMA 2007, 298, 2644–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandharipande, P.; Shintani, A.; Peterson, J.; Pun, B.T.; Wilkinson, G.R.; Dittus, R.S.; Bernard, G.R.; Ely, E.W. Lorazepam is an independent risk factor for transitioning to delirium in intensive care unit patients. Anesthesiology 2006, 104, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, C.W.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Koestner, T.; Hudson, L.D.; Thompson, J.L.; Shintani, A.K.; Ely, E.W.; Girard, T.D. Diurnal sedative changes during intensive care: Impact on liberation from mechanical ventilation and delirium. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 2788–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.G.; Mailloux, P.T.; Devlin, J.W. Dexmedetomidine or Propofol for Sedation in Mechanically Ventilated Adults with Sepsis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1424–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tang, Y.; Bai, Z.; Liang, X.; Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Cheng, H.; Lyu, J.; Wang, Y. Assessing the Risk of Delirium and Death in Sepsis Using the Braden Score: A Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Nurs. 2025, 34, 2779–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, P.; Klein, K.U.; Falkenberg, L.; Berres, M.; Closhen, D.; Werhahn, K.J.; David, M.; Werner, C.; Engelhard, K. Impaired cerebrovascular autoregulation in patients with severe sepsis and sepsis-associated delirium. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusmao-Flores, D.; Salluh, J.I.; Chalhub, R.A.; Quarantini, L.C. The Confusion Assessment Method for the Intensive Care Unit (CAM-ICU) and Intensive Care Delirium Screening Checklist (ICDSC) for the diagnosis of delirium: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical studies. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pun, B.T.; Ely, E.W. The importance of diagnosing and managing ICU delirium. Chest 2007, 132, 624–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcantonio, E.R.; Goldman, L.; Mangione, C.M.; Ludwig, L.E.; Muraca, B.; Haslauer, C.M.; Donaldson, M.C.; Whittemore, A.D.; Sugarbaker, D.J.; Poss, R.; et al. A clinical prediction rule for delirium after elective noncardiac surgery. JAMA 1994, 271, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandharipande, T.D.; Girard, J.C.; Jackson, A.; Morandi, A.; Thompson, J.L.; Pun, B.T.; Brummel, N.E.; Hughes, C.G.; Vasilevskis, E.E.; Shintani, A.K.; et al. Long-Term Cognitive Impairment after Critical Illness. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, T.D.; Exline, M.C.; Carson, S.S. Haloperidol and Ziprasidone for Treatment of Delirium in Critical Illness. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2506–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen-Ranberg, N.C.; Poulsen, L.M.; Perner, A.; Hästbacka, J.; Morgan, M.; Citerio, G.; Collet, M.O.; Weber, S.O.; Andreasen, A.S.; Bestle, M.; et al. Haloperidol vs. placebo for the treatment of delirium in ICU patients: A pre-planned, secondary Bayesian analysis of the AID-ICU trial. Intensive Care Med. 2023, 49, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakhary, T.; Ahmed, I.; Luttfi, I.; Montasser, M. Quetiapine Versus Haloperidol in the Management of Hyperactive Delirium: Randomized Controlled Trial. Neurocrit. Care 2024, 41, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reade, M.C.; Eastwood, G.M.; Bellomo, R.; Bailey, M.; Bersten, A.; Cheung, B.; Davies, A.; Delaney, A.; Ghosh, A.; van Haren, F.; et al. Effect of Dexmedetomidine Added to Standard Care on Ventilator-Free Time in Patients with Agitated Delirium: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 315, 1460–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herridge, M.S.; Cheung, A.M.; Tansey, C.M.; Matte-Martyn, A.; Diaz-Granados, N.; Al-Saidi, F.; Cooper, A.B.; Guest, C.B.; Mazer, C.D.; Mehta, S.; et al. One-year outcomes in survivors of the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herridge, M.S.; Tansey, C.M.; Matte, A.; Tomlinson, G.; Diaz-Granados, N.; Cooper, A.; Guest, C.B.; Mazer, C.D.; Mehta, S.; Stewart, T.E.; et al. Functional disability 5 years after acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacanella, E.; Perez-Castejon, J.M.; Nicolas, J.M.; Masanés, F.; Navarro, M.; Castro, P.; López-Soto, A. Functional status and quality of life 12 months after discharge from a medical ICU in healthy elderly patients: A prospective observational study. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammeyer, J.; Dickinson, S.; Packard, D.; Baldwin, N.; Ricklemann, C. Building a protocol to guide mobility in the ICU. Crit. Care Nurs. Q. 2013, 36, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R.; Maley, K. Mobilization of intensive care cardiac surgery patients on mechanical circulatory support. Crit. Care Nurs. Q. 2013, 36, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweickert, W.D.; Pohlman, M.C.; Pohlman, A.S.; Nigos, C.; Pawlik, A.J.; Esbrook, C.L.; Spears, L.; Miller, M.; Franczyk, M.; Deprizio, D.; et al. Early physical and occupational therapy in mechanically ventilated, critically ill patients: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2009, 373, 1874–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, M.; Nordon-Craft, A.; Malone, D.; Van Pelt, D.; Frankel, S.K.; Warner, M.L.; Kriekels, W.; McNulty, M.; Fairclough, D.L.; Schenkman, M. A Randomized Trial of an Intensive Physical Therapy Program for Acute Respiratory Failure Patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 193, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, Y.; Taniuchi, K.; Karasawa, T.; Matsui, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Ikegami, S.; Imamura, H.; Horiuchi, H. The Impact of Early Mobilization on the Incidence of Intensive Care Unit-Acquired Weakness in Patients with Sepsis in the Critical Care-The Shinshu Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study (EROSCCS Study). J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eakin, M.N.; Ugbah, L.; Arnautovic, T.; Parker, A.M.; Needham, D.M. Implementing and sustaining an early rehabilitation program in a medical intensive care unit: A qualitative analysis. J. Crit. Care 2015, 30, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naef, R.; Von Felten, S.; Ernst, J. Factors influencing post-ICU psychological distress in family members of critically ill patients: A linear mixed-effects model. Biopsychosoc. Med. 2021, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Tsubaki, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Yagome, S.; Sakaguchi, Y. Effect size estimates of risk factors for post-intensive care syndrome-family: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart Lung 2023, 59, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.B.; Angus, D.C.; Sields, A.M.; Buddadhumaruk, P.; Pidro, C.; Paner, C.; Chaitin, E.; Chang, C.H.; Pike, F.; Weissfeld, L.; et al. A Randomized Trial of a Family-Support Intervention in Intensive Crae Units. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2365–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, M.A.; Schleien, C.L.; Morris, M.C. Parental presence on pediatric intensive care unit rounds. J. Pediatr. 2009, 155, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickelson, R.S.; Piras, S.E.; Brown, L.; Carlile, C.; Drumright, K.S.; Boehm, L. The use and usefulness of ICU diaries to support family members of critically ill patients. J. Crit. Care 2021, 61, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, W.G.; Arnold, R.M.; Angus, D.; Bryce, C.L. Passive decision making preference is associated with anxiety and depression in relatives of patients in the intensive care unit. Crit. Care 2009, 24, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, D.; Snthilkumar, V.R.; Ramakrishan, N.; Ramakrishnan, N.; Vignesh, C. Decision making preferences and levels of anxiety and depression in family members admitted to the ICU. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2025, 29, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davidson, J.E.; Aslakson, R.A.; Long, A.C.; Puntillo, K.A.; Kross, E.K.; Hart, J.; Cox, C.E.; Wunsch, H.; Wickline, M.A.; Nunnally, M.E.; et al. Guidelines for Family-Centered Care in the Neonatal, Pediatric, and Adult ICU. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 45, 103–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pun, B.T.; Balas, M.C.; Barnes-Daly, M.A.; Thompson, J.L.; Aldrich, J.M.; Barr, J.; Byrum, D.; Carson, S.S.; Devlin, J.W.; Engel, H.J.; et al. Caring for Critically Ill Patients with the ABCDEF Bundle: Results of the ICU Liberation Collaborative in Over 15,000 Adults. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldmann, C.S. Intensive after care after intensive care. Curr. Anaesth. Crit. Care 1998, 9, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevin, C.M.; Bloom, S.L.; Jackson, J.C.; Wang, L.; Ely, E.W.; Stollings, J.L. Comprehensive care of ICU survivors: Development and implementation of an ICU recovery center. J. Crit. Care 2018, 46, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, N.; Liu, K.; Hatakeyama, J.; Kawauchi, A.; Yoshida, M.; Sumita, H.; Miyamoto, K.; Nakamura, K. Post-intensive care syndrome follow-up system after hospital discharge: A narrative review. J. Intensive Care 2024, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, M.E.; Still, M.; Anderson, B.J.; Bienvenu, O.J.; Brodsky, M.B.; Brummel, N.; Butcher, B.; Clay, A.S.; Felt, H.; Ferrante, L.E.; et al. Society of Critical Care Medicine’s International Consensus Conference on Prediction and Identification of Long-Term Impairments After Critical Illness. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, 1670–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, S.L.; Stollings, J.L.; Kirkpatrick, O.; Wang, L.; Byrne, D.W.; Sevin, C.M.; Semler, M.W. Randomized Clinical Trial of an ICU Recovery Pilot Program for Survivors of Critical Illness. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, B.A.; Perkins, A.J.; Khan, S.H.; Unverzagt, F.W.; Lasiter, S.; Gao, S.; Wang, S.; Zarzaur, B.L.; Rahman, O.; Eltarras, A.; et al. Mobile Critical Care Recovery Program for Survivors of Acute Respiratory Failure: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2353158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, K.P.; Boustany, H.; Cassity, E.P.; Soper, M.K.; Kalema, A.G.; Kolpek, J.H.; Montgomery-Yates, A.A. ICU Recovery Clinic Attendance, Attrition, and Patient Outcomes: The Impact of Severity of Illness, Gender, and Rurality. Crit. Care Explor. 2020, 2, e0206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezz Al-Regal, A.R.; Ramzy, E.A.; Atia, A.A.A.; Emara, M.M. Dexmedetomidine for Reducing Mortality in Patients with Septic Shock: A Randomized Controlled Trial (DecatSepsis). Chest 2024, 166, 1394–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioccari, L.; Luethi, N.; Bailey, M.; Shehabi, Y.; Howe, B.; Messmer, A.S.; Proimos, H.K.; Peck, L.; Young, H.; Eastwood, G.M.; et al. The effect of dexmedetomidine on vasopressor requirements in patients with septic shock: A subgroup analysis of the Sedation Practice in Intensive Care Evaluation [SPICE III] Trial. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Assess, Prevent, and Treat Pain | Both SAT and SBT | Choice of Analgesia and Sedation | Delirium: Assess, Prevent, and Manage | Early Mobility and Exercise | Family Engagement and Empowerment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assessment Tools | Numerical Rating Scale (NRS); Behavioral Pain Scale (BPS); Critical-Care Pain Observation Tool (CPOT) | SAT and SBT Screening Protocols | Richmond Agitation–Sedation Scale (RASS); Riker Sedation–Agitation Scale | Confusion Assessment Method for the ICU (CAM-ICU); Intensive Care Delirium Screening Checklist (ICDSC) | Physical/occupational therapy screening tools; functional strength scales | Family satisfaction/engagement surveys; documentation of participation in rounds |
| Intervention | Routine pain assessment; pre-procedure analgesia; multimodal analgesia favoring non-opioid and non-pharmacologic adjuncts | Paired SAT and SBT | Light sedation targeting RASS 0 to –1; preference for non-benzodiazepine agents (propofol, dexmedetomidine) | Daily screening; minimize benzodiazepines; maintain sleep–wake cycles; early mobility | Progressive mobility within 72 h of stability; multidisciplinary rehab team | Structured family meetings, ICU diaries, open visitation, inclusion on rounds |
| Short term Benefits | Reduced agitation, stress response, and physiologic instability | Shorter ventilation duration and ICU stay; decreased delirium | Less delirium, shorter ventilation and ICU stay | Reduced delirium duration, fewer days of coma | Reduced delirium, shorter ventilation and LOS | Improved communication, shorter LOS, lower family anxiety/depression |
| Long term Benefits | Lower risk of anxiety, depression, and chronic pain syndromes | Lower mortality, improved functional recovery, reduced PICS risk | Improved cognition and reduced long-term neurocognitive impairment | Improved cognitive outcomes, reduced long-term neuropsychiatric morbidity | Improved functional independence and quality of life; reduced PICS-related weakness | Reduced PICS-F burden, enhanced caregiver recovery, better long-term adherence to care goals |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sherman, M.; Lim, P.; Cheema, T.; DiSilvio, B.; Tiberio, P. From Resuscitation to Rehabilitation: The Post-Intensive Care Syndrome Continuum in Sepsis Care. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8374. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238374
Sherman M, Lim P, Cheema T, DiSilvio B, Tiberio P. From Resuscitation to Rehabilitation: The Post-Intensive Care Syndrome Continuum in Sepsis Care. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(23):8374. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238374
Chicago/Turabian StyleSherman, Matthew, Perry Lim, Tariq Cheema, Briana DiSilvio, and Perry Tiberio. 2025. "From Resuscitation to Rehabilitation: The Post-Intensive Care Syndrome Continuum in Sepsis Care" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 23: 8374. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238374
APA StyleSherman, M., Lim, P., Cheema, T., DiSilvio, B., & Tiberio, P. (2025). From Resuscitation to Rehabilitation: The Post-Intensive Care Syndrome Continuum in Sepsis Care. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(23), 8374. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238374








